PSYC*4750 (Motivation & Emotion Lecture 1)
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Human Behavior is
motivated by physical,
psychological, and social needs
seek outcomes that we need/want
Human Behavior
Human behavior results form a willingness
/urge/drive to expend effort (work) to obtain such
outcomes.
Prioritization is to
satisfy motivational states, priority must be given to some thoughts
and actions over others.
When prioritizing food, how is emotion/evaluation involved
1: nice or nasty?
2: approach or avoid?
When prioritizing food, how is attention involved?
1: Is it task relevant?
2: Does it facilitate or suppress the prioritization
Motivation is that which
gives energy and direction to behavior.
1: Arousal / Urge / Drive
2: Goals / Intentions / Plans of action
3: Seeking / Avoiding
These are all involved in
Motivation
Emotion is a process which evaluates the
significance of events with respect to important goals.
Emotion is a means of
communicating with others
In the emotional theory, the answer to the question of “Is emotion expression”{ is that
Emotion has evolved to transmit social / biologically-relevant
signals
In the emotional theory, the answer to the question of “Is emotion an action tendency” was found by Dewey in 1895 and is that
-emotions are states of readiness to act in
certain ways
- approach, avoidance, domination, submission
In the emotional theory, the answer to the question of “Is emotion a bodily reaction”, the answer was found by James–Lange (1884/1885) and states that it is a
Physiological response that precedes emotion:
Bodily reactions elicit emotions in consciousness
and are consequently primary to other
emotional components
James Lange on “Is emotion a bodily reaction”
Who said “My theory... is that the bodily changes follow
directly the perception of the exciting fact, and
that our feeling of the same changes as they
occur IS the emotion” in regards to emotion being a bodily response
William James, 1884
In emotion theory, Cannon–Bard (1927/1928) believed that with emotions
bodily reactions do not cause the emotion elicitation,
because they lack specificity
similar bodily reactions accompany very
different emotions, as well as other
non-emotional states.
Cannon–Bard (1927/1928) on emotions and bodily reactions
Discrete emotions are when
Each emotion has its own ‘essence’
Corresponds to a unique combination of
subjective experience, physiology, and
behaviour.
Discrete emotions
Discrete emotions should be universal because they are
1: Both experienced and recognized across
cultures, backgrounds etc.
2: Homologous in other animals
Discrete emotions should be measurable via
behavior
(e.g., facial movements) and physiology
What is included in the basic emotions?
1: Fear
2: Anger
3: Disgust
4: Sadness
5: Joy
6: Interest
What are the two themes of the basic emotions
Negative emotions & Positive Emotions
What are the negative emotions on the basic emotions
Threat & Harm
What are the positive emotions in the basic emotions
Motive Involvement and satisfaction
What are the Self-Conscious Emotions
1: Shame
2: Guilt
3: Embarrassment
4: Triumph
5: Pride
What are the Cognitively Complex
Emotions
1: Envy
2: Guilt
3: Disappointment
4: Regret
5: Schadenfreude
6: Empathy
7: Compassion
What is the problems with emotion and emotional facial expression charts?
- Not as universal, specific, or consistent as it
should be.
- Lots of variability.
The response to variation is to create
more fine grained typologies, in an attempt to bring nature under control and make it easier to identify emotions essence
But their is another approach to emotion, one that accounts for all the empirical evidence (Bothe the evidence that supports the classical view and that which does not) this is an
essence - free view that considers typological thinking as a lot of misplaced creativity and effort (construction approach to emotion)
Dimensional/Constructionist views are that an emotion is not
an entity with firm boundaries but a category of instances that vary highly depending on the specific situation
An instance of an emotion category emerges
as the brain makes meaning of incoming
sensory inputs from the body and the world.
This is talking about the Dimensional/Constructionist views
In Dimensional/Constructionist views, emotions emerge as you make sense of
the
complex dynamics within your nervous
system, which is constantly in dynamic
interaction with the surrounding context,
including with other people / emotional
beings.
What is the categorical theory?
It involves basic emotions

What is the Dimensional view
It involves Arousal & Valence
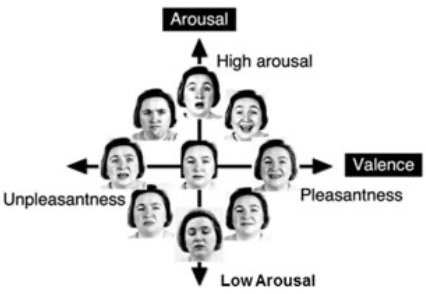
In Dimensional/Constructionist views, All emotions emerge from shared causal
mechanisms– a few common dimensions include Valence which is
1: Pleasure/Displeasure
2: Positive / Negative
In Dimensional/Constructionist views, All emotions emerge from shared causal
mechanisms– a few common dimensions include Intensity which is
1: Activation / Excitement / Arousal / Tension
2: Engagement / Disengagement
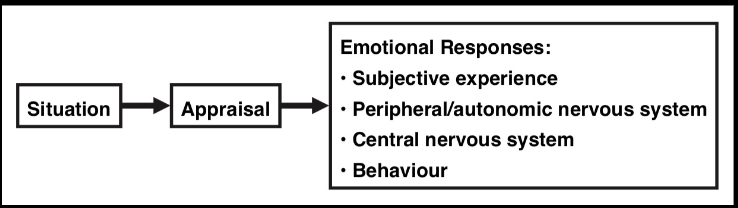
In Appraisal theories, an emotional response begins with
appraisal
of the personal significance of an event
What is the sequence of events for the appraisal theory
Core affect is a state of
pleasure or displeasure with some degree of arousal
barring injury, core affect is grounded in the
Somatovisceral, kinesthetic, proprioceptive, and neurochemical fluctuations that take place within the core of the body
Somatovisceral is
the complex, bidirectional communication between the body's musculoskeletal system, skin and the internal organs, often involving nerve signals that link these systems to influence bodily functions, sensations, and emotions
With Somatovisceral, the Soma is the
body's musculoskeletal system and skin
With Somatovisceral, the viscera is the
Internal Organs
often involving nerve signals that link these systems to influence bodily functions, sensations, and emotions, such as pain, stress responses, and emotional development.
It describes how signals from the body's outer parts (skin, muscles, joints) affect internal organs (viscera), and vice versa, forming crucial pathways for perception and regulation.
This is talking about the Somatovisceral,
The hypothesized neural reference space for core effect include brain areas like
1: Visceromotor
2: Sensory Integration Networks in the OFC
3: The Anterior Insuli
4: The Amygdala
5: Sungenual and Pregenual parts of the ACC
6: Hypothalamus
7: Ventral Striatum
8: Midbraim
9: Brainstem
What are the different categories of emotions
1: Feelings
2: Sense of Purpose
3: Bodily arousal
4: Social Expression
What is the feelings part of emotion
• Subjective Experience
• Phenomenological Awareness
• Cognition
What is the Sense of Purpose part of emotion
• Goal-Directed Motivational State
• Functional Aspect
What is the Bodily Arousal Part of emotion
• Physiological Activation
• Bodily Preparation for Action
• Motor Responses
What is the Social Expressive part of emotion
• Social Communication
• Facial Expression
• Vocal Expression
1. Communicate our feelings to others.
2. Influence how others interact with us.
4. Create, maintain, and dissolve relationships.
3. Invite and facilitate social interaction.
This is talking about the social functions of emotion
Positive affect and Negative affect are
independent ways of feeling
In Everyday moods, positive effects include
• Pleasurable engagement
• Reward-driven, appetitive
motivational system
• Approach behavior
• Dopaminergic pathways
In Everyday moods, Negative effects include
• Unpleasant engagement
• Punishment-driven, aversive
motivational system
• Withdrawal behavior
• Serotonergic and noradrenergic
pathways