AP Bio Semester 1 (Units 1-5)
1/352
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
353 Terms
open system
exchanges material with surroundings
closed system
encloses material/ energy in a system
First law of Thermodynamics
energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred or transformed
anabolic reaction
take small particles to build up bigger particles

catabolic reaction
take large particles and break down to smaller particles

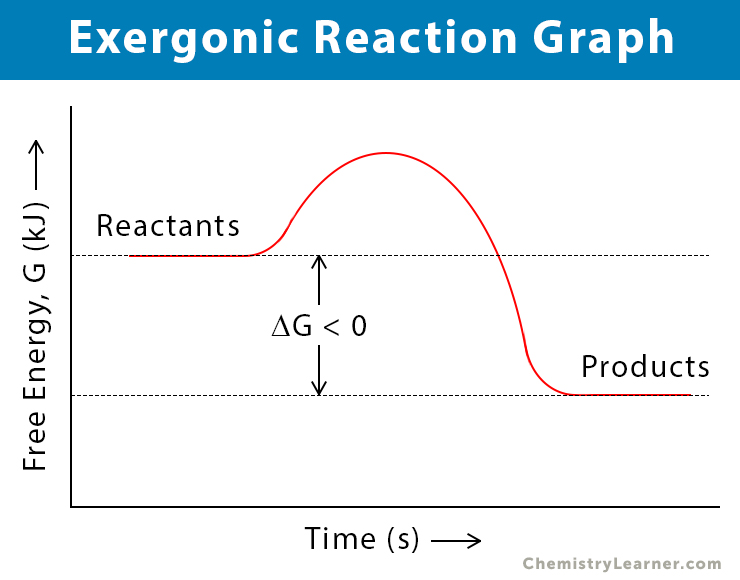
exergonic reaction
spontaneous, releasing energy, -ΔG
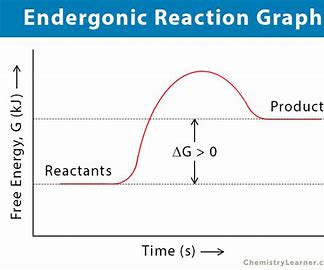
endergonic reaction
nonspontaneous, requires energy, +ΔG
induced-fit
enzymes conform to substrate to break it down
enzymes
proteins (tertiary structure) that catalyze reactions by lowering activation energy, speeding up a reaction
Formula for Photosynthesis
6CO2+6H2O —light—> C6H12O6+6O2
Enzyme amino acid property interactions
side chains determine interactions between active site and substrate, usually weak interactions to bind temporarily. Ex. large/small, acidic/basic, hydrophobic/hydrophilic, negative/positive charge
activation energy
energy required to start a reaction
active site
where substrate binds with enzyme temporarily, has a specific shape that calls for specific substrate- lock and key

allosteric inhibitor
binds to enzymes allosteric site (not the same as active site), causing the enzyme to change shape and inhibit its ability to work, same as noncompetitive inhibition
catalyst
reactant that speeds up a reaction by providing alternate pathway that has a lower activation energy; not used up in reaction (can be reused). Ex. enzymes
competitive inhibition
when an inhibitor binds to active site of enzyme, blocking other substrates from entering therefore ceasing the work of that enzyme
denaturation
when an enzyme shape (breaks weak bonds) is altered due to extreme pH or temperature changes
enzyme-substrate complex
the temporary molecule that forms when an enzyme binds with substrate
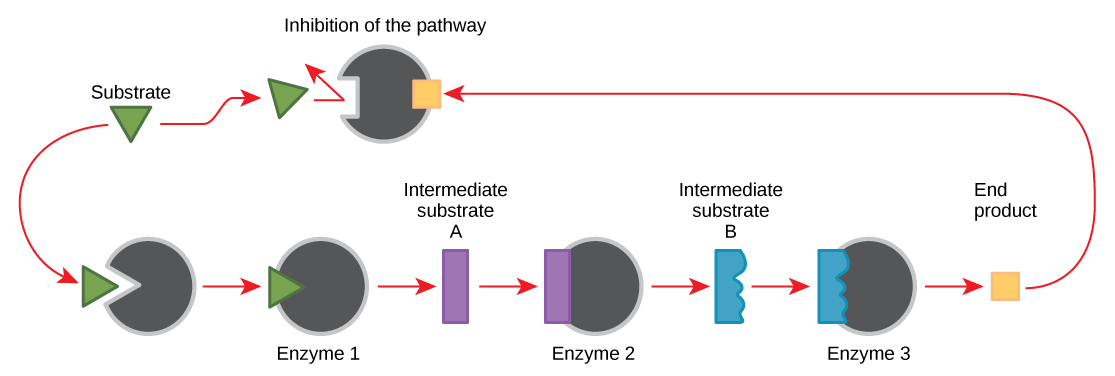
feedback inhibition
cellular control mechanism where an enzyme is inhibited by the end product of a biochemical pathway; regulates how much product is made. Negative feedback is the stopping of a process, positive is the activation of a process
globular protein
protein that is spherical or ball-like, tertiary structure; enzymes are mainly globular
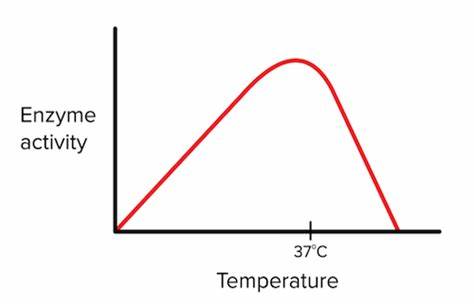
low temp to high temp vs enzyme activity
More collisions tend to happen as temperatures increase due to increase in kinetic energy, so enzymatic activity also would increase. However, too high of a temp causes denaturation. Optimal temperatures is when enzyme activity is highest without becoming denatured.
noncompetitive inhibition
when an inhibitor binds to allosteric site, conforming shape of enzyme and inhibits its ability to work
facultative anaerobes
organisms that can make enough ATP to survive using fermentation or respiration, ex. muscle cells
obligate anaerobes
organisms that carry out only fermentation of anaerobic respiration; cannot survive in presence of oxygen
fermentation vs. cellular respiration
fermentation: final electron acceptor is an organic molecule, 2 net ATP produced (from glycolysis), substrate-level phosphorylation
both: glycolysis, NAD+ accepts electrons
cellular respiration: final electron acceptor is oxygen, NAD+ is regenerated through electron-transport chain, ~32 net ATP produced, substrate-level and oxidative phosphorylation
substrate-level phosphorylation
when an organic molecule combines with ADP in an enzyme, and the ADP takes an inorganic phosphate group from molecule to combine and make ATP or GTP; used in glycolysis and Kreb cycle
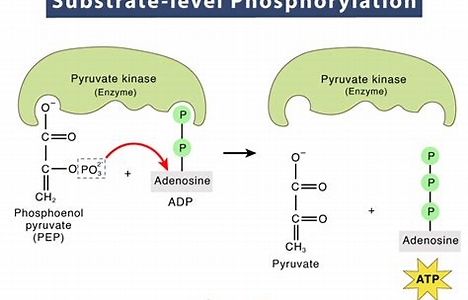
oxidative phosphorylation
last step of cellular respiration, when ATP synthase synthesizes ATP from an inorganic phosphate and ADP; reaction is driven by protons cycling through electrochemical gradient that then combine with the negatively charged ½ O₂ to make H₂O
electron transport chain
collection of molecules (mostly proteins called cytochromes) in inner membrane of mitochondria; transport electrons to matrix through series of electron carriers that alternate form oxidized and reduced states to move down the “waterslide”; electrons at end of chain combine with ½ O₂ to produce negative charge on molecule
cytochromes
electron carrier protein that functions in ETC; last cytochrome is very electronegative and passes electrons to oxygen
chemiosmosis
process in which energy is stored on the form of H+ ion gradient across the membrane to do cellular work; protons are taken from NADH and FADH₂ and pumped across the mitochondrial membrane by transport proteins to the intermembrane space by using energy from ETC, developing a electrochemical gradient (more positive charge on intermembrane side); once across, the protons drive the production of ATP by traveling through ATPase
energy flow for cellular respiration
glucose → NADH → ETC → chemiosmosis → ATP
spontaneous reaction
reaction that requires no input of energy; downhill reaction
Stages of Cellular Respiration
Glycolysis
Pyruvate oxidation and Kreb Cycle
oxidative phosphorylation: ETC and chemiosmosis
summary of glycolysis
Happens in ALL cells; occurs in cytosol; requires 2 ATP and a 6-carbon glucose to commence; ATP undergoes ATP hydrolysis to make ADP, releasing energy to break down glucose by donating a phosphate group- this happens for both ATP, producing 2 3-carbon sugars; NAD+ is reduced to NADH by picking up 2 electrons and proton from sugar; by substrate level phosphorylation, the sugar combines with 2 ADP to create 2 ATP and a pyruvate; since there are 2 ATP, this happens for both and 4 total ATP and 2 pyruvate are made
acetyl CoA
produced when pyruvate molecule is transported to mitochondria through transport protein and releases a CO₂, NAD+ is reduced to NADH, and Coenzyme A forms a temporary bond to replace the CO₂
Summary of Kreb cycle
occurs in mitochondrial matrix; aerobic process- requires oxygen; 2 acetyl CoA are required to start reaction; CoA breaks off to form 2-carbon molecule that oxaloacetate combines with to make citrate (6-carbon molecule); a CO₂ breaks off as byproduct, NAD+ reduces to NADH by harnessing energy in reaction of breaking bond; another CO₂ leaves and powers ADP to make ATP through substrate-level phosphorylation and NAD+ reduces to NADH resulting in 4-carbon molecule; molecule is continuously broken down, and FAD is reduced to FADH₂; finally, NAD+ is reduced to NADH and resulting molecule is oxaloacetate which is recycled in the process; reaction happens twice to account for 2 acetyl CoA, producing total of 2 ATP, 6NADH, 2FADH₂ and 4CO₂
compartmentalization
separates materials for specialized functions
oxidative phosphorylation summary
occurs in mitochondrial matrix but requires a few steps before it can occur; first NADH/FADH₂ are broken down into 3 parts: 2 electrons, H+ ion, and NAD+/FAD (recycled); electrons are pumped across innermembrane through trasport protein and enter the ETC where they are pumped back across and attaches to oxygen. Since H+ are electronegative, they follow electrons across and create an electrochemical gradient that is necessary to do work (chemiosmosis); H+ ions are then used to power ATPase and get pumped back into the matrix, meanwhile, oxidative phosphorylation occurs and ATP is made from ADP and inorganic phosphate; H+ travels to negatively charged oxygen to make H₂O; products are 26-32 ATP, 1 H₂O, NAD+
paracrine signaling
cells communicate with other local cells in vicinity
growth factors
local regulation in animals that simulate target cells to grow and divide and simultaneously receive and report
synaptic signaling
in animal nervous system; electric signal along nerve cell triggers secretion of chemical signal carrying neurotransmitters eventually triggering response in target cell
hormones
both plants and animals use this for long-distance signaling (also called endocrine signaling)
types of local cell communication/signaling
cell-cell: gap junctions (animal cells) and plasmodesmata (plant cells)
paracrine, synaptic
Stages of cell signaling
reception, transduction and response
reception
target cells detection of signaling molecule from outside cell; signaling molecule (ligand) binds to receptor
transduction
step or series of steps that converts signal to bring cellular response
signal transduction pathway
sequence of changes in series of different molecules (relay molecules)
response
cellular activity that is triggered
ligand
molecule that specifically bonds to another molecule; usually changes shape of receptor, initiating interactions
G-protein coupled receptor (GPCR)
cell-surface transmembrane receptor that works with help of G-protein
G-protein
protein that binds to energy rich GTP
ligand-gated ion channel
membrane receptor with a region that can act as a “gate” for ions opening or closing due to induced fit
intracellular proteins
in cytoplasm on nucleosol target cells and must pass through plasma membrane. ex steroids
transcription factors
control what genes are transcribed into mRNA in particular cell and time
protein kinase
enzyme that transfers phosphate groups from ATP to a protein; compose most of relay molecules on signal transduction pathway
phosphorylation cascade
pathway of signal transduction pathway containing protein kinases where signals are transmitted by
protein phosphatases
enzymes that can rapidly remove phosphate groups from proteins- dephosphorylation; make protein kinases available for use
second messengers
small; nonprotein, water soluble molecules or ions that can spread throughout through diffusion
cyclic AMP (cAMP)
epinephrine binds to G-protein activating enzyme that converts ATP to cAMP; important in mitosis-
cell division
reproduction of cells; allows multicellular eukaryotes to develop from single cell and replace dead cells
cell cycle
life of a cell from the time it first formed during division of parent cell until own division into two daughter cells
genome
cells genetic information
chromosomes
structures of packaged DNA; structure maintained by proteins called histones; nuclei in humans contain 46 chromosomes
chromatin
entire complex of DNA and proteins of chromosomes
somatic cells
body cells except reproductive
gamete cells
reproductive cells; XX-female, XY-male
sister chromatids
2 in duplicated chromosomes; joined copies of original chromosome; cohesions connect chromatids along length by protein complexes- sister chromatid cohesion
centromere
region made up of repetitive sequences in the chromosomal DNA where chromatid is attached most closely to sister chromatid; mediated by proteins
mitosis
division of genetic material in nucleus into 2 genetically identical diploid cells; 5 phases
cytokinesis
follows mitosis; division of cytoplasm; cleavage starts process; outside, contractile ring of actin microfilaments interact wit myosin and contract, pinching cell into 2 cells
miotic phase (M phase)
part of cell cycle that includes mitosis and cytokinesis and usually shortest part of the cycle
Interphase
longer stage that alternates with M phase; divided into G1 phase, s phase and G2 phase
5 stages of mitosis
prophase, prometaphase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
prophase
chromatin fibers tightly coil; nucleoli disappear; each duplicated chromosome appears as 2 sister chromatids joined at centromeres, mitotic spindle begins to form centrosomes and microtubules; centrosomes move away from one another by lengthening microtubules
nucleoli
large structures in nucleus that are involved in synthesis of rRNA and ribosomes; disappear in prophase and reappear in telophase
prometaphase
nuclear envelope fragments; microtubules invade nuclear area; chromosomes become more condensed; kinetochores forms at each centromere of chromatid; microtubules attach to kinetochores; non-kinetochore microtubules lengthen cell with interactions
metaphase
longest stage; centrosomes at opposite ends of poles; chromosomes arrive at metaphase plate; kinetochores are attached to kinetochore microtubules of opposite plates.
anaphase
shortest stage; cohesion proteins are cleaves\d and each chromatid becomes independent chromosome; 2 new daughter chromosomes begin moving toward opposite ends as kinetochore microtubules shorten; cell elongates as non-kinetochore microtubules cohesion; both ends have equivalent and complete chromosomes
telophase
2 daughter cells in nuclei form in cell; nuclear envelopes arise from fragments of parent cells; nucleoli reappear; chromosomes become less condensed; microtubules are depolymerized
cleavage furrow
shallow groove in cell surface near old metaphase plate; oustide
cell plate
in plant cells, vesicles from Golgi move along microtubules to center where they release cell wall material so that cell plate enlarges until it fuses with plasma membrane
binary fission
prokaryotic reproduction in which cell grows to double its size and divides into two cells; DNA replicates and splits to opposite sides then cell divides.
growth factor
protein released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide
meiosis I and meiosis II
2 consecutive cell divisions resulting in 4 daughter cells with one set of parent cell chromosomes
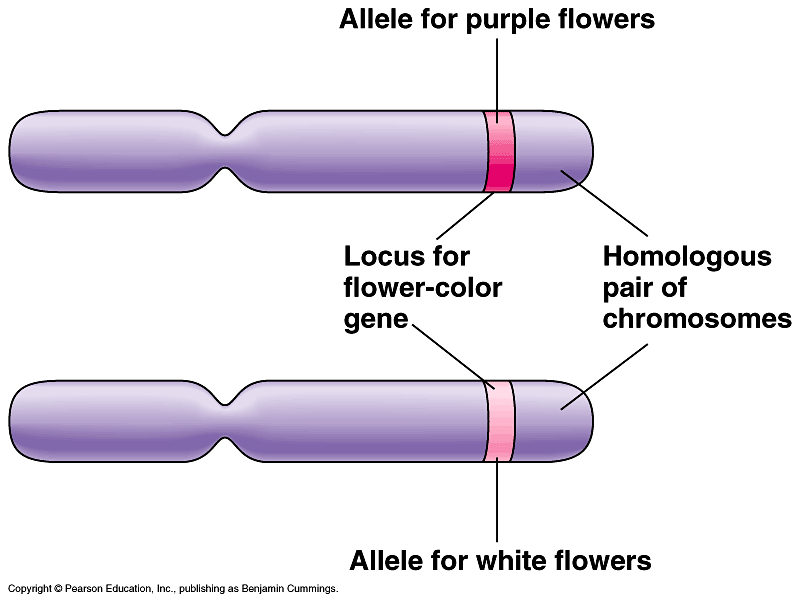
allele
different version of gene at corresponding loci; variations in gene nucleotide sequence
prophase 1
2 members of homologous chromosomes associate along length; synapsis and crossing over occurs, and duplicated homologs pair up and crossover
metaphase 1
pairs of homologous chromosomes align at metaphase plate
chiasma
location where crossing over and swapping of genes occur; holds together homologous chromosomes into a tetrad
recombinant chromosomes
individual chromosomes that carry genes from different parents; increases genetic variability; result of crossing over
independent assortment chromosomes
at metaphase 1, homologous pairs are situated at metaphase plate and each pair may randomly orient with either maternal or paternal homolog closer to given pole
character
heritable feature that varies among individuals
trait
each varient for a character
true breeding
breeding over many generations of self-pollination
hybridization
mating, or crossing of 2 true-breeding varieties
P generation
true-breeding parents, parental generation
F1 generation
hybrid offspring- first filial generation
F2 generation
allowing F1 hybrids to self-pollinate produces this -second filial generation
law of segregation
2 alleles for heritable character segregate during gamete formation and end up in different gametes
phenotype
appearance or observable trait and physiological
genotype
genetic makeup