Anatomy and Physiology Lab 3: Tissues
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
50 Terms
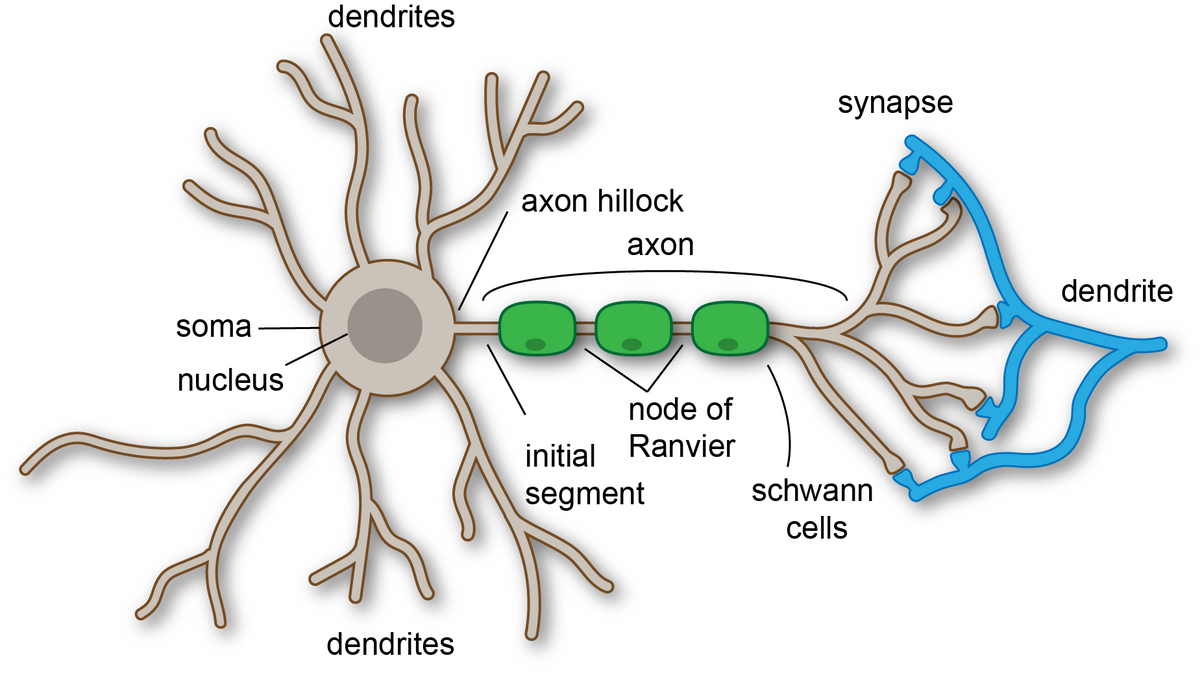
What is a neuron’s function?
to transmit electrical impulses to communicate information throughout the body
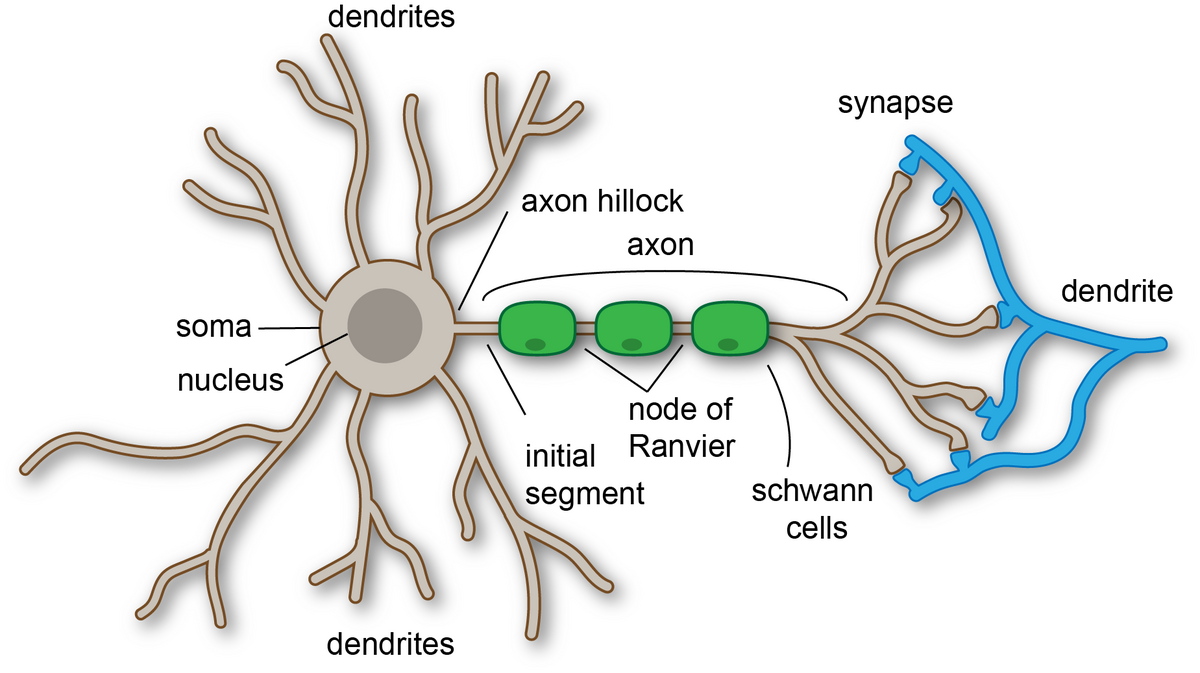
What is the function of dendrites?
to receive electrical impulses from neighboring neurons
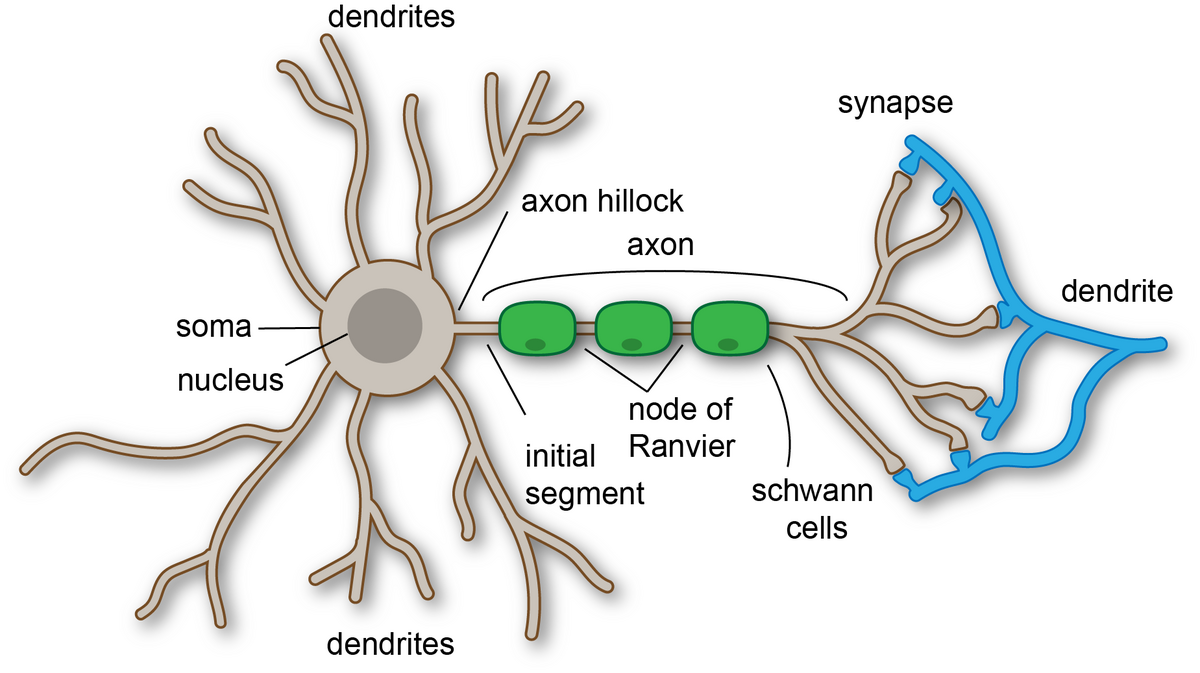
What is the function of the cell body (neurons)?
houses the nucleus and processes electrical signals taken in from the dendrites
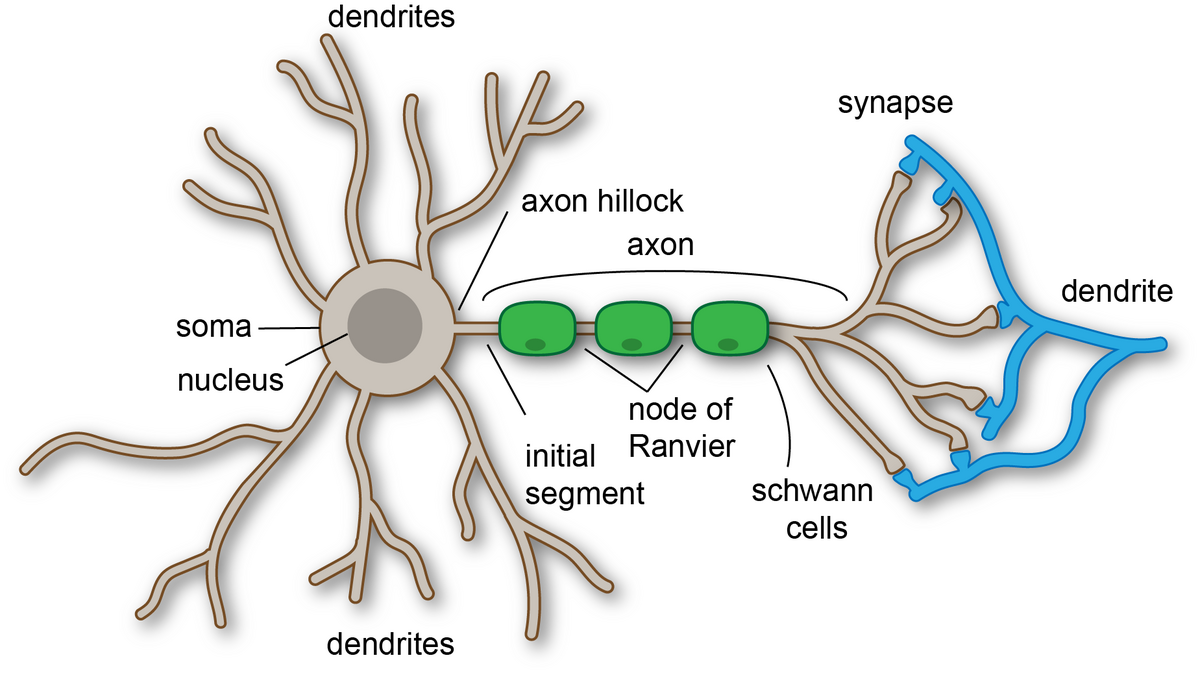
What is the function of an axon hillock?
processes incoming signals from neighboring neurons
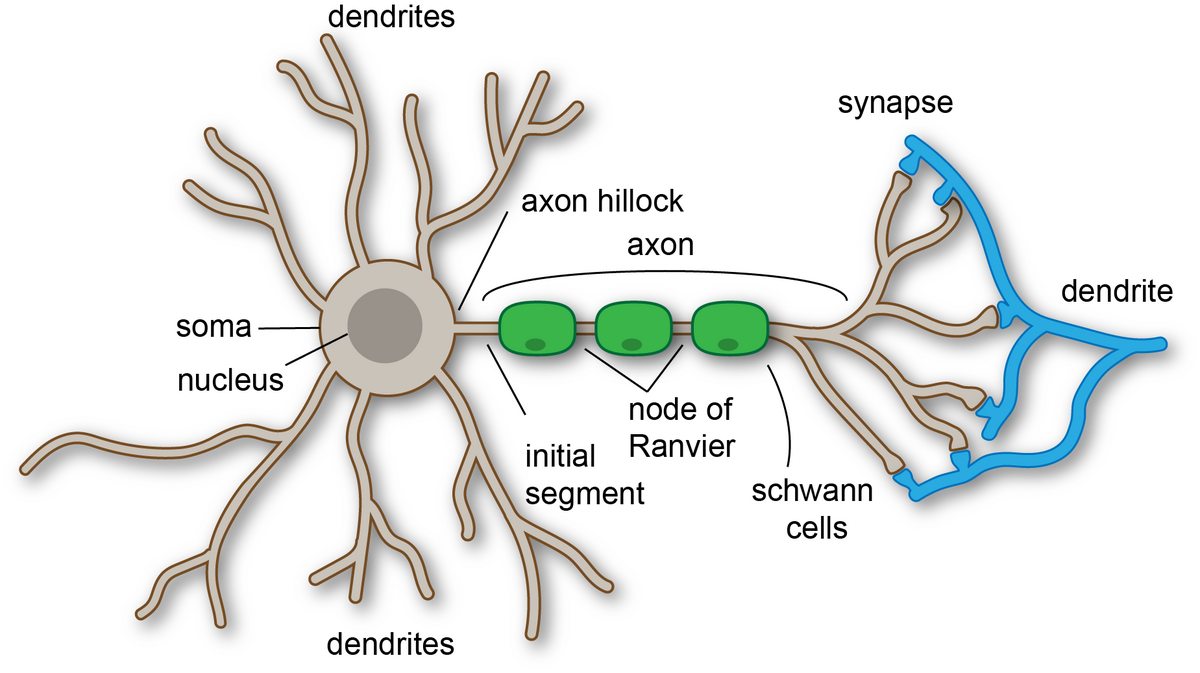
What is the function of an axon?
transmits electrical impulses to other the axon terminals which will then move to other neurons. Signals can also move to muscles or glands.
What is the function of an axon?
What are glial cells and what are their function?
glial cells make up nervous tissue and support, protect, and nourish neurons
Are skeletal muscles voluntary or involuntary?
voluntary
Are cardiac muscles voluntary or involuntary?
involuntary
Are smooth muscles voluntary or involuntary?
involuntary
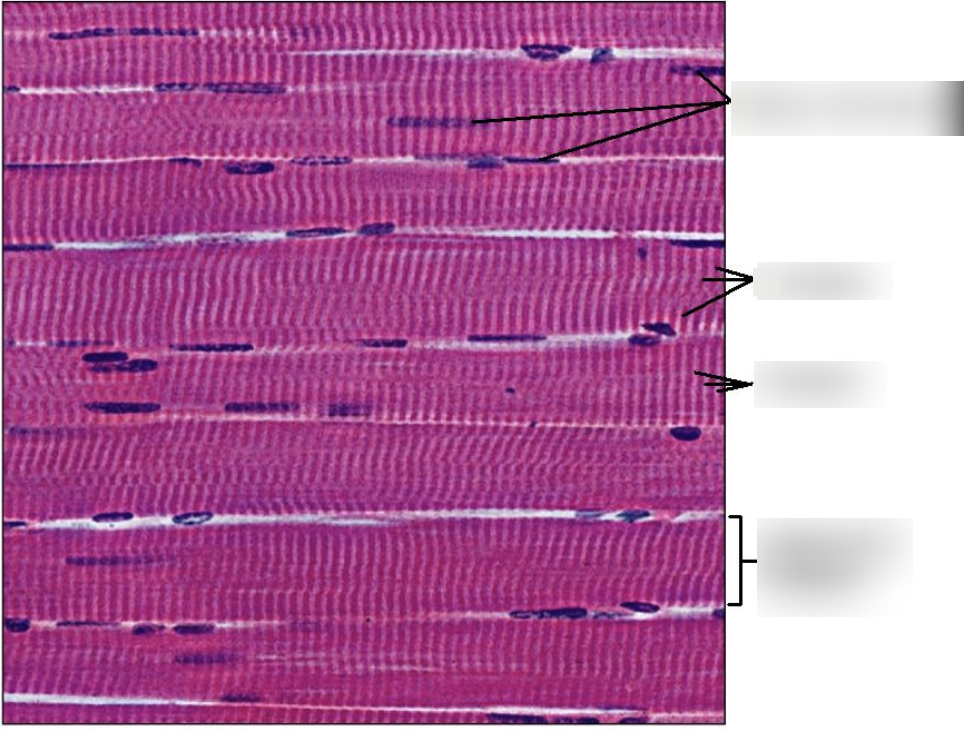
distinctive features of skeletal muscles?
striations (banded pattern)
multiple nuclei
highly organized bundles
have sarcomeres (A band, Z line, I band, etc)
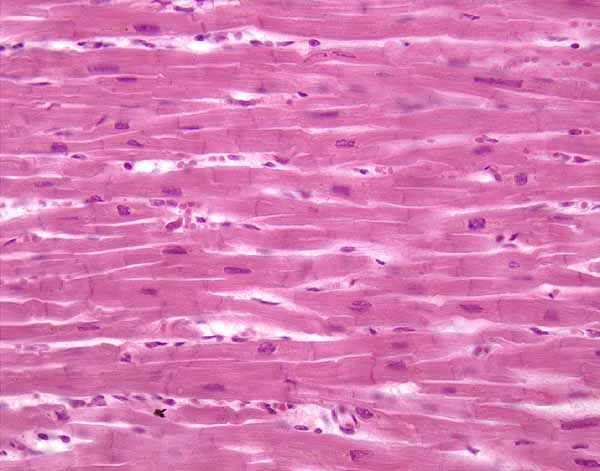
Distinctive features of cardiac muscles?
short, branching appearance
electrical junctions (intercalated discs)
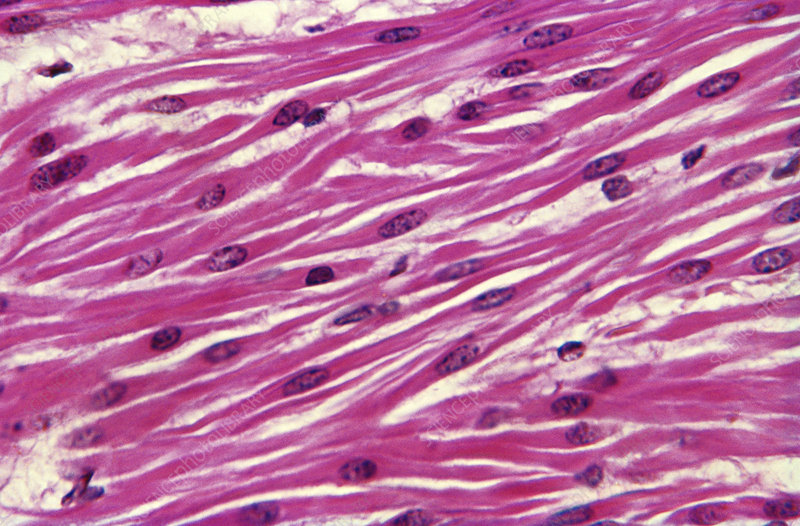
Distinctive features of smooth muscle cells?
short spindle-shaped cells
no striations
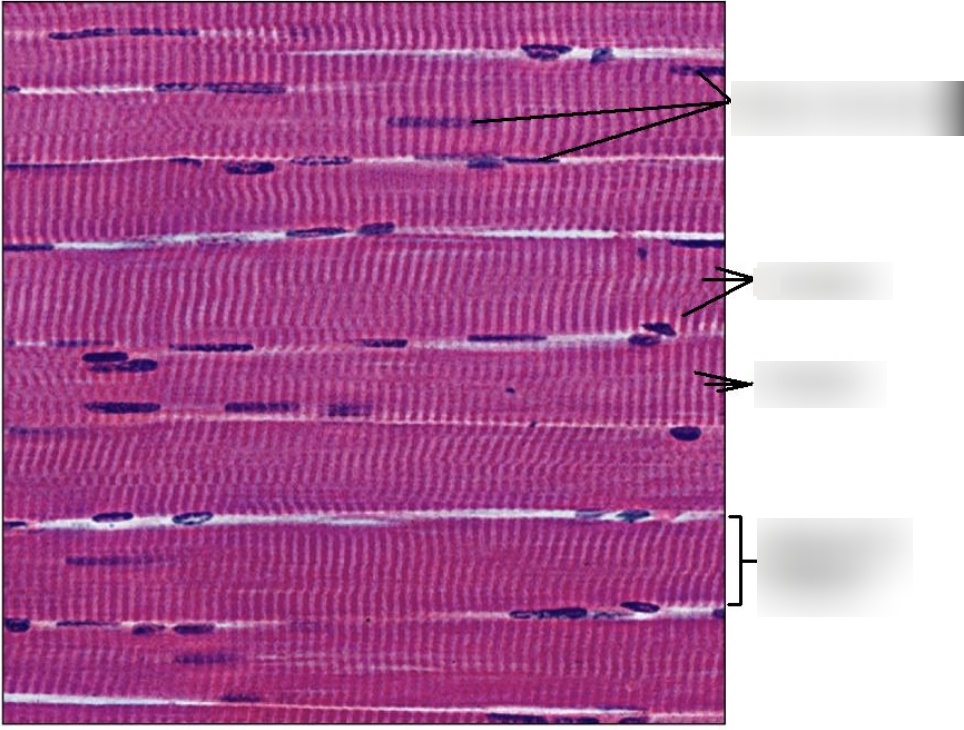
location and function of skeletal muscle cells?
location: all over the body (attacked to bone by tendons)
function: movement and stabilization of joints
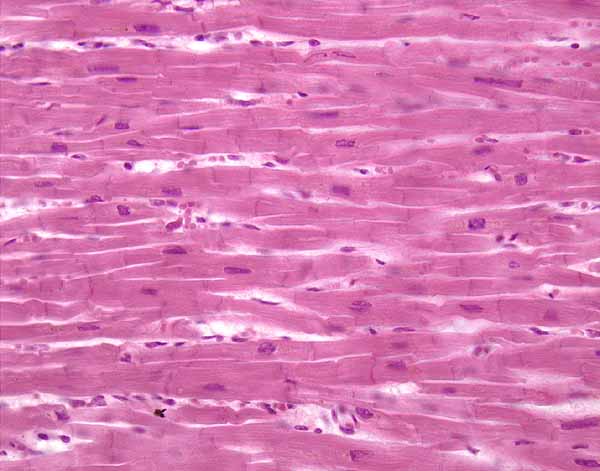
location and function of cardiac muscle cells?
location: heart
function: coordinated contraction of the heart (made possible through the intercalated discks)
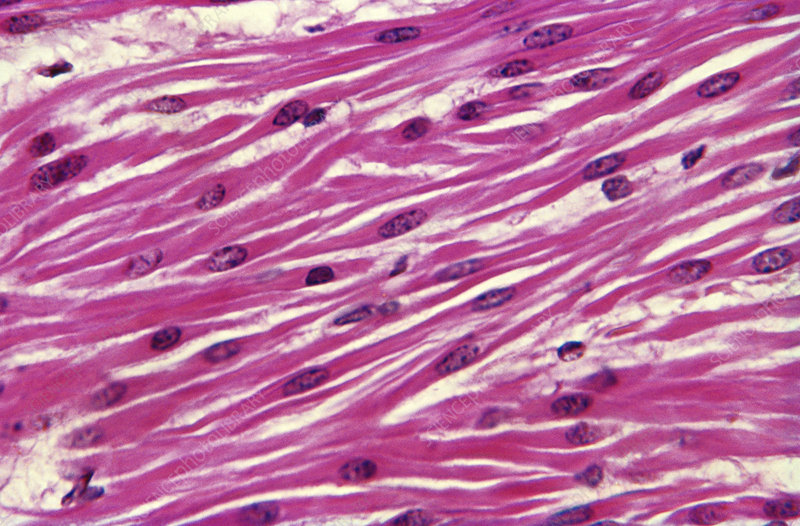
location and function of smooth muscle cells?
location: walls of hallow organs (GI system, tubes of arteries, + more)
function: strong, slow, sustained, synchronous contractions (moves food thru GI track, maintains BP)
What is the function of connective tissues?
binds, supports, and protects other tissues and organs
What are the types of connective tissues?
connective tissue proper
supporting connective tissue
fluid connective tissue
What are the types of connective tissue proper?
loose (areolar, adipose, and reticular)
dense (regular, irregular, elastic)
What are the types of supporting connective tissues?
cartilage
bone
What are the types of bone/
spongy and compact
What are the types of cartilage?
Hyaline
Fibrocartilage
Elastic
What is fluid connective tissue?
blood
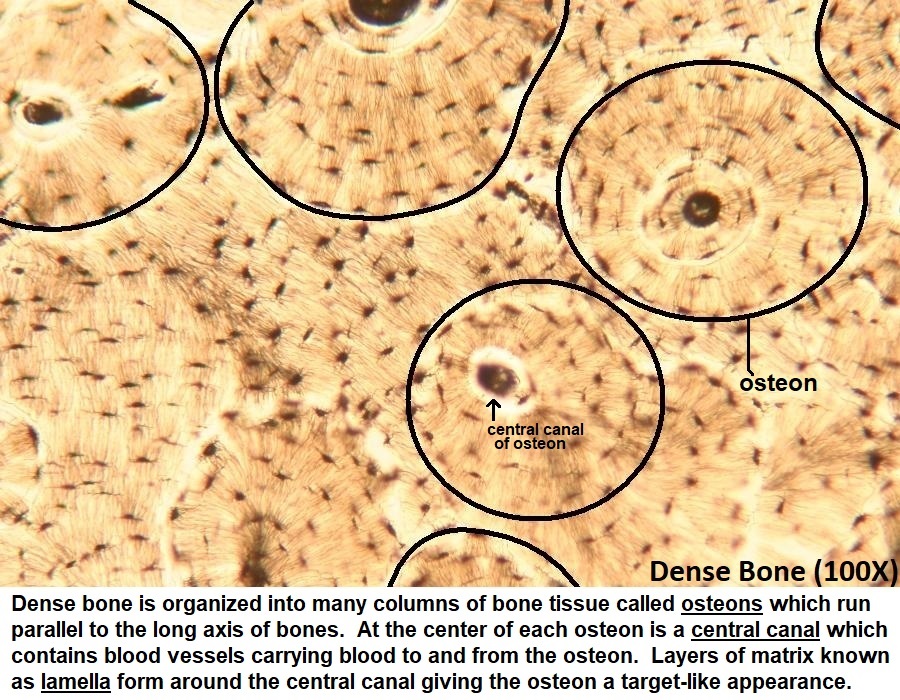
What is the location and function of compact bone?
location: in the superficial layers of bones
Function: supports body, protects organs, and calcium storage
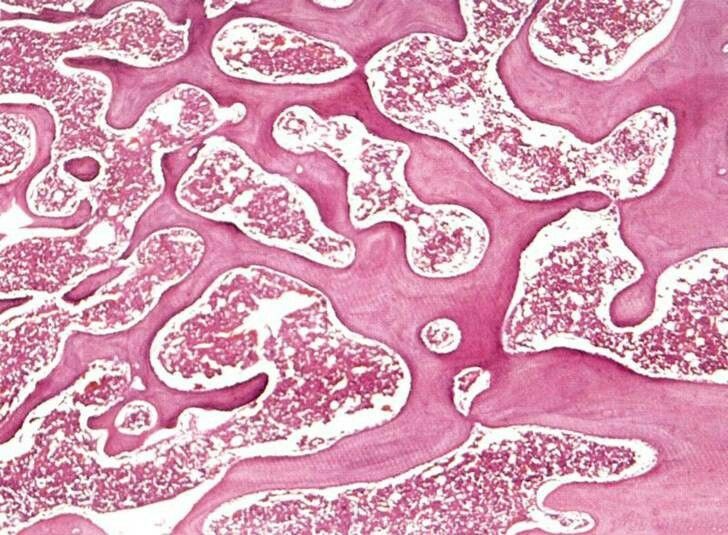
What is the location and function of spongy bone?
location: in the deeper layers of bones (generally on the ends of the bones)
function: producing RBC, WBC, and platelates
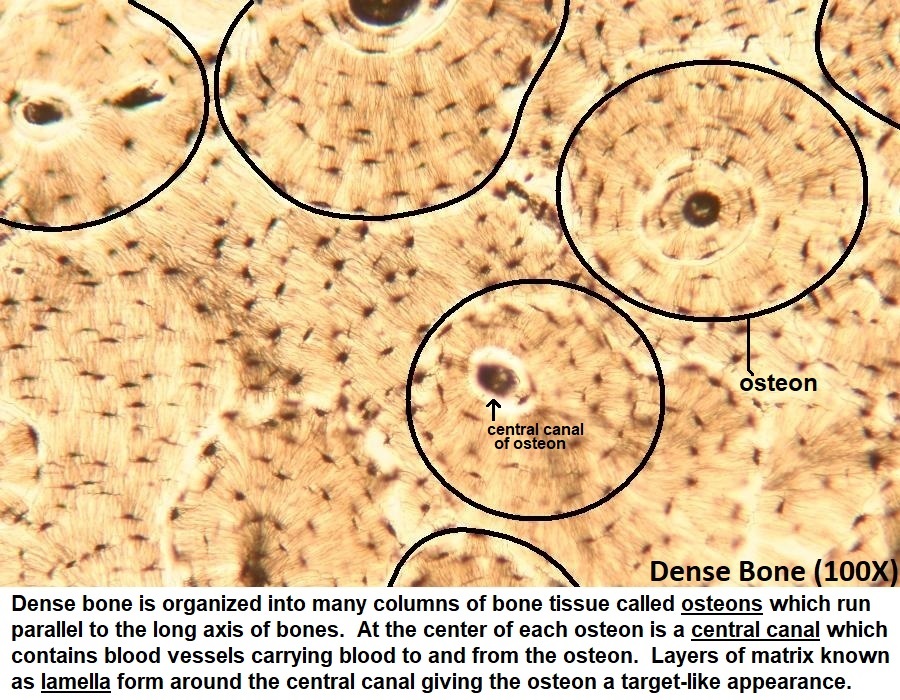
distinctive features of compact bone?
round cell shape that looks like a transverse cut of a tree trunk
osteon (structural unit; see above)
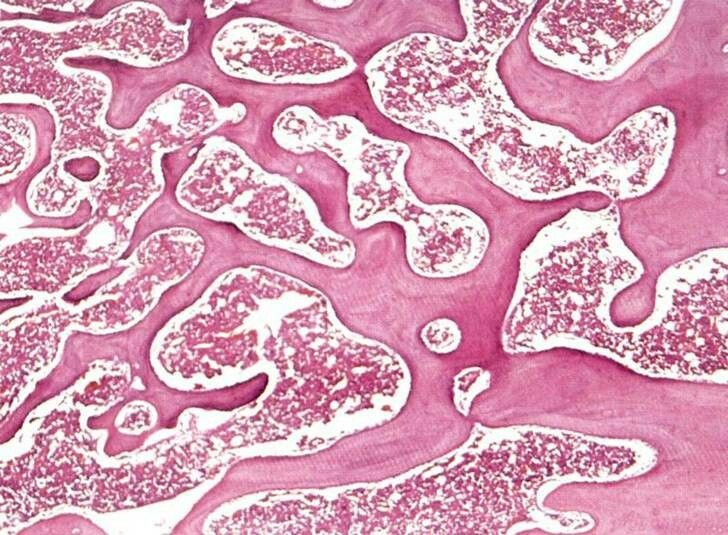
distinctive features of spongy bone?
no osteons
looks like a dried sponge (ish)
have marrow cavities (inbetween the blobs)
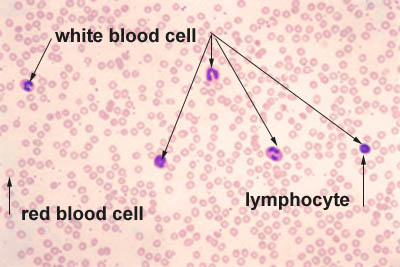
What is the function of erythrocytes (RBC)
transporting oxygen
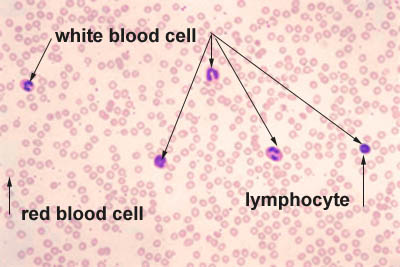
What is the function of leukocytes (WBC)?
fighting infections
(there are diff types of WBC that all have different functions; this is determined by the shape of the nucleus)
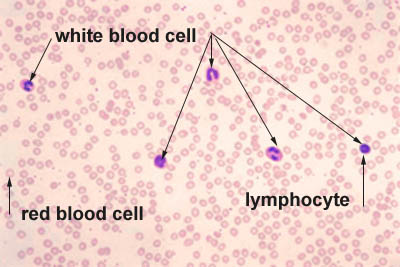
What is the function of thrombocytes (platelets)?
blood clotting
What is loose connective tissue and where is it found?
what? It’s a loose network of cells and fibers that provide cushion to all kinds of organs and tissues (fewer fibers, more ground substance)
where? all over the body
What is dense connective tissue and where is it found?
what? made of collagen fibers and fibroblasts (more fibers, less ground substance)
where? in ligaments and tendons
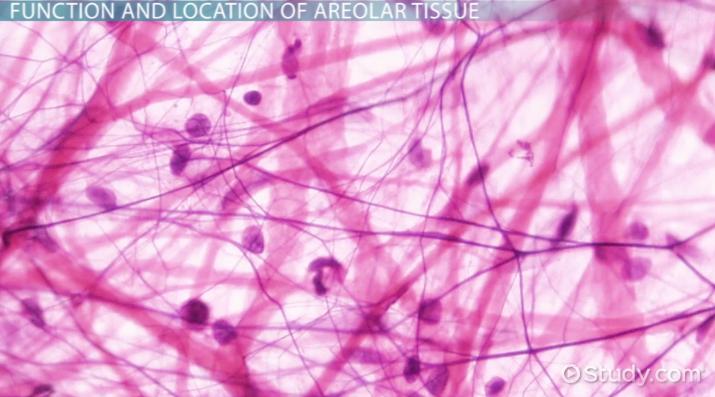
Location and function of areolar connective tissue (loose)
Location: dermis
Function: binds, protects, provides strength and elasticity to organs
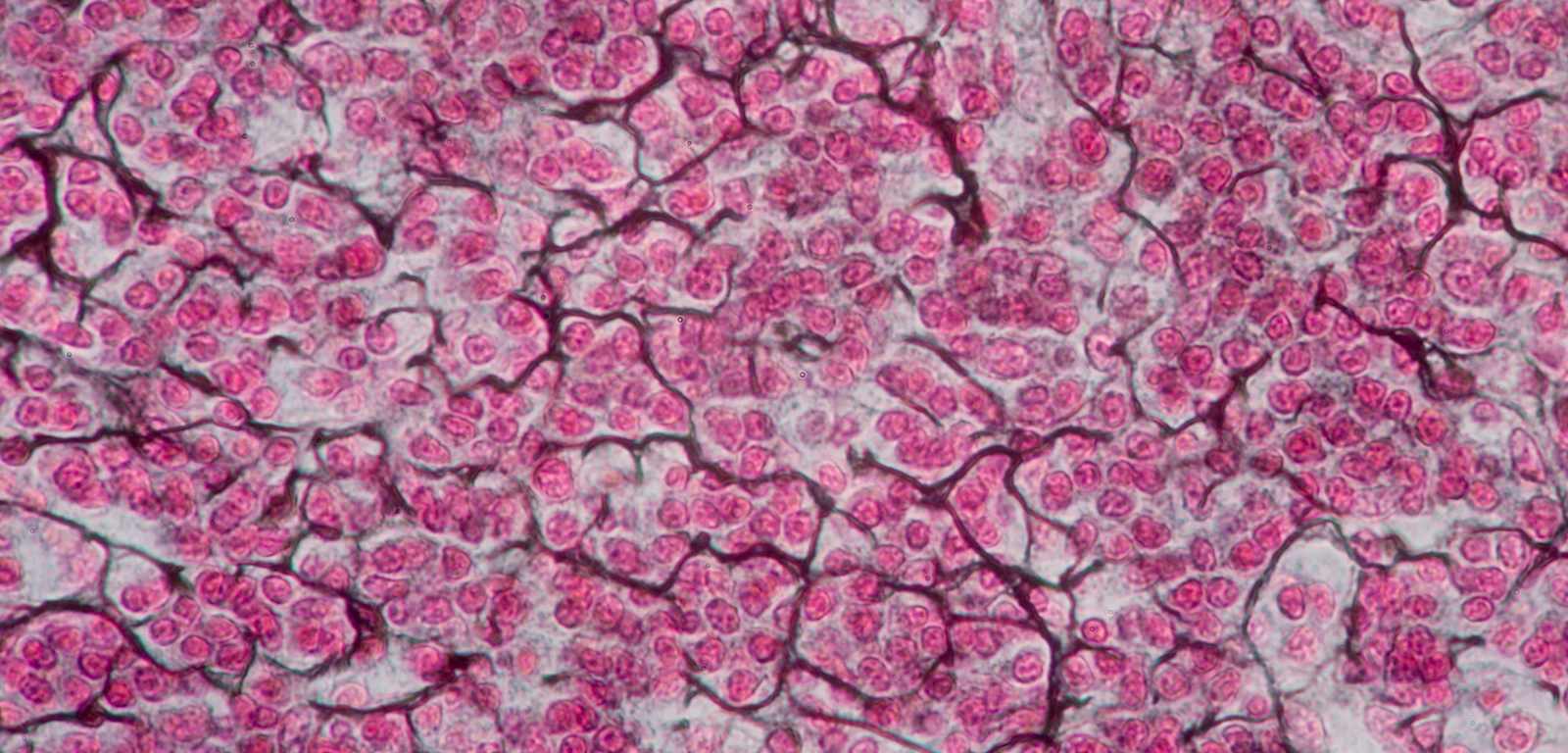
Location and function of reticular connective tissue (loose)
Location: lymph nodes
Function: structural framework (still elastic, but def denser than areolar tissue)
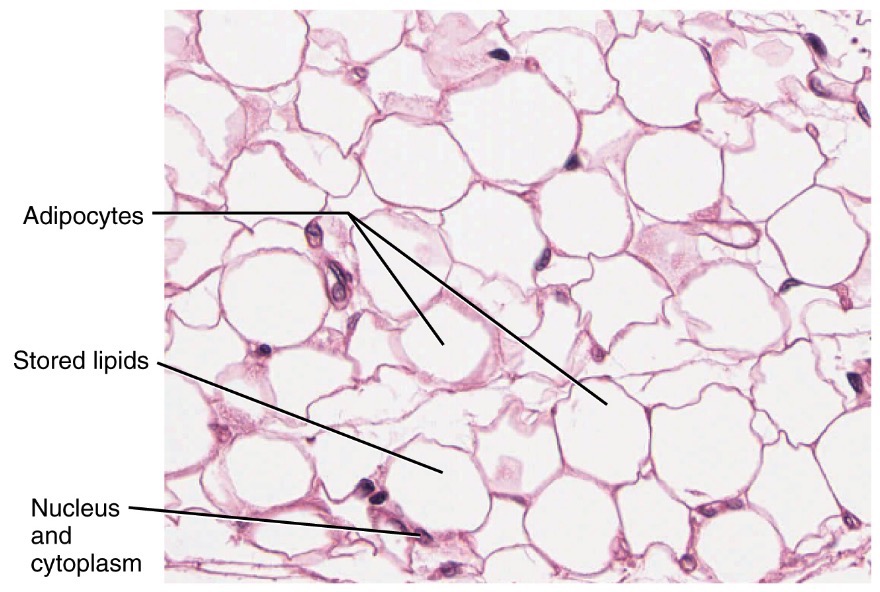
Location and function of adipose connective tissue (loose)
Location: hypodermis (deeper than epidermis and dermis); found in fat cells
Function: energy storage, provides energy, cushions, and insulates
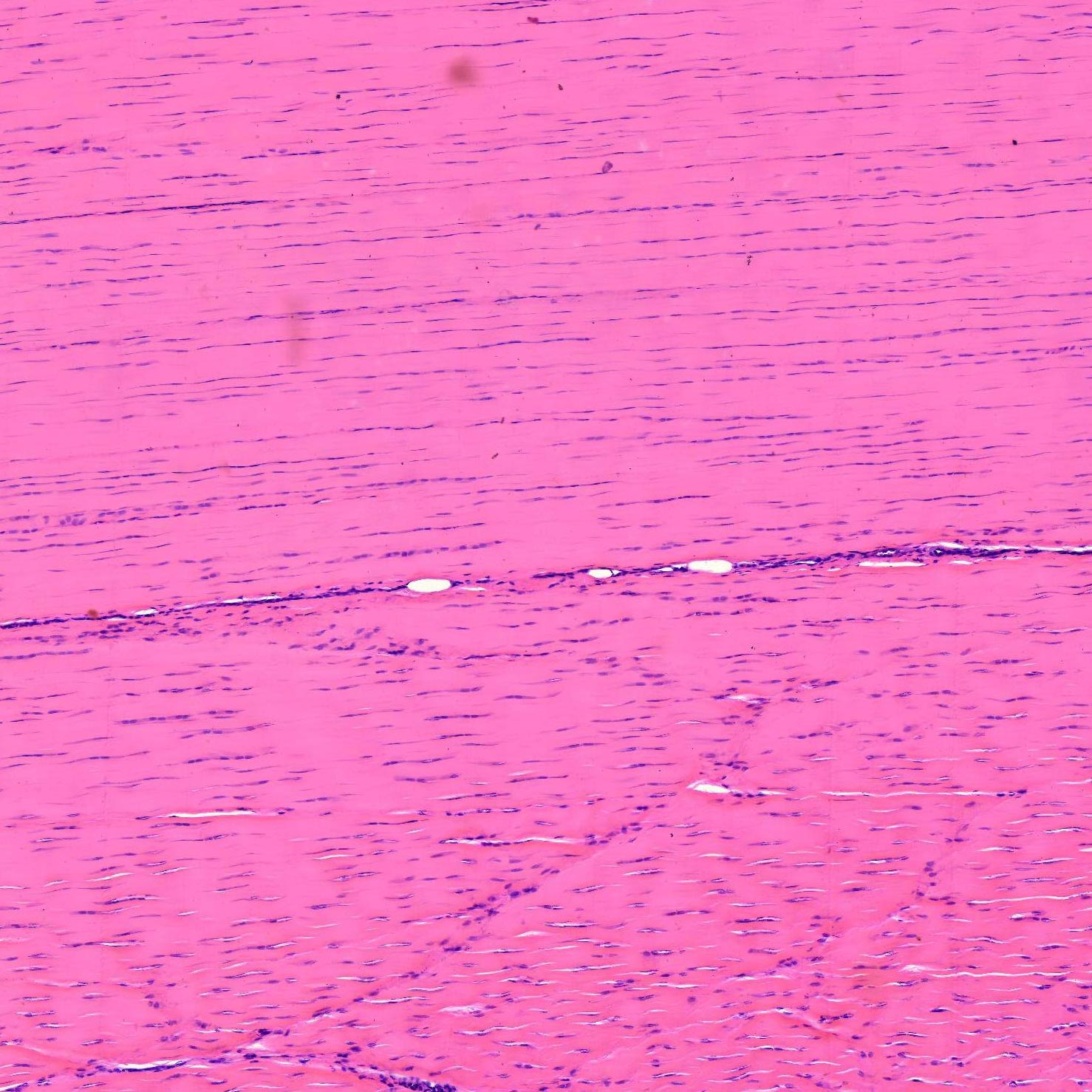

Location and function of dense regular connective tissue
Location: tendons and ligaments
Function: to resist stress (in one direction)
Location and function of dense irregular connective tissue
Location: dermis (deepest layer of skin)
Function: resisting stress in multiple directions
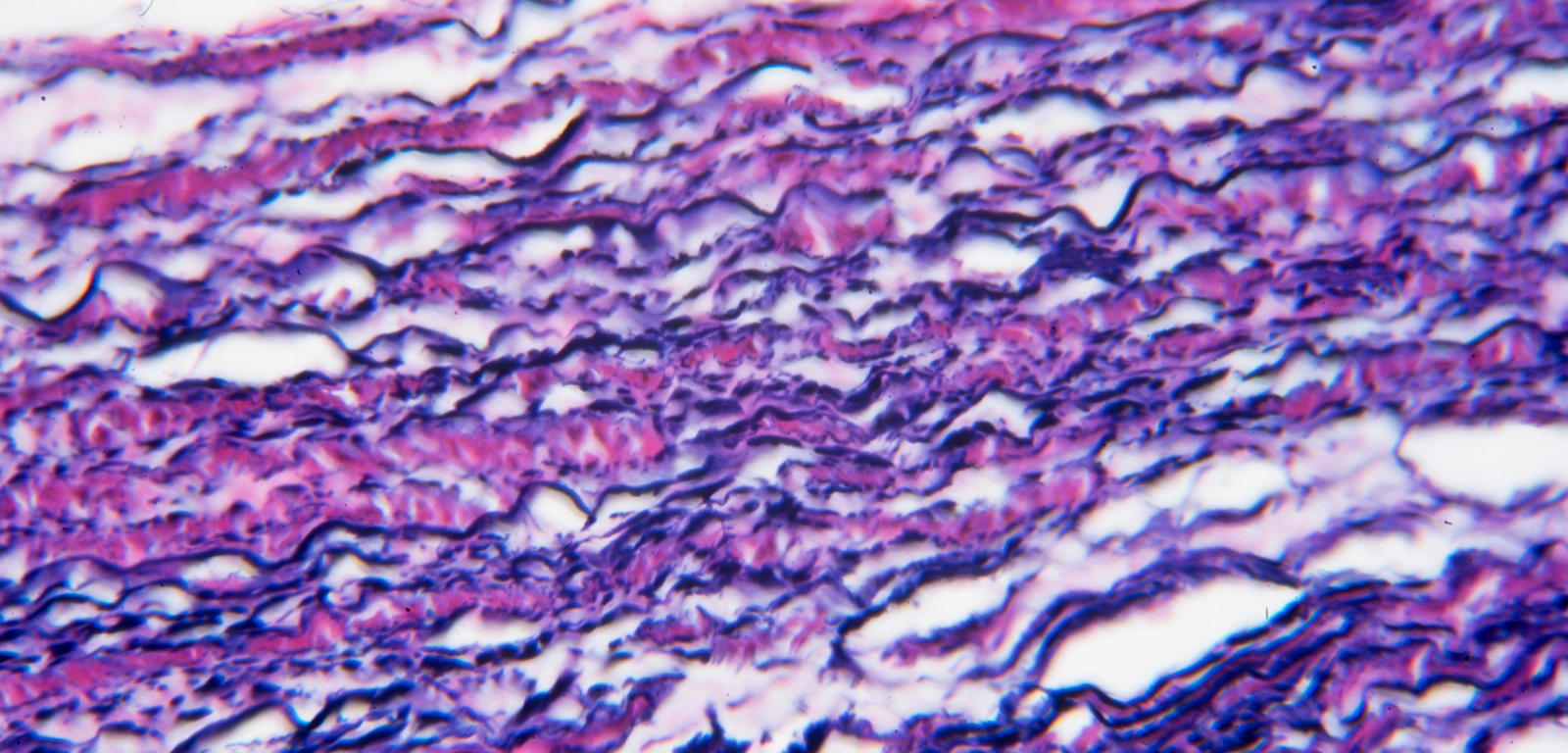
Location and function of elastic connective tissue
Location: aorta, trachea
Function: stretching (not too taut though, because then it risks breaking)
What is the location and function of hyaline cartilage?
location: smooth surface of joints, model for bone growth in growing infants
function: covers the long end of bones, costal cartilage, larynx, and trachea
What is the location and function of fibrocartilage?
location: intervertebral discs
function: resists compression, absorbs shock
What is the location and function of elastic cartilage?
location: epiglottis
function: keeps structure, but allows for flexibility
What does “simple” mean in terms of epithelial cells?
ONE layer of cells
What does “stratified” mean in terms of epithelial cells?
multiple layers of cells
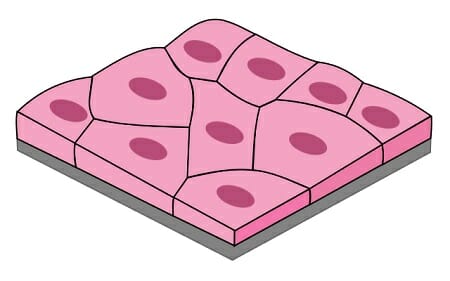
Location and function of simple squamous epithelial cells
location: blood vessels
function: diffusion, filtration
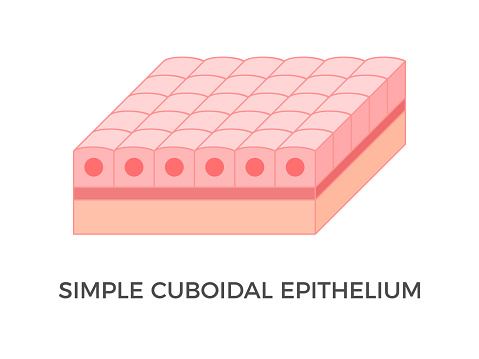
Location and function of simple cuboidal epithelial cells
location: kidney tubules
function: absorption, secretion

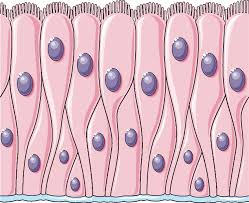
location and function of simple columnar epithelial cells
location: digestive tract
function: absorption, secretion (have microvilli to help move food along tract)
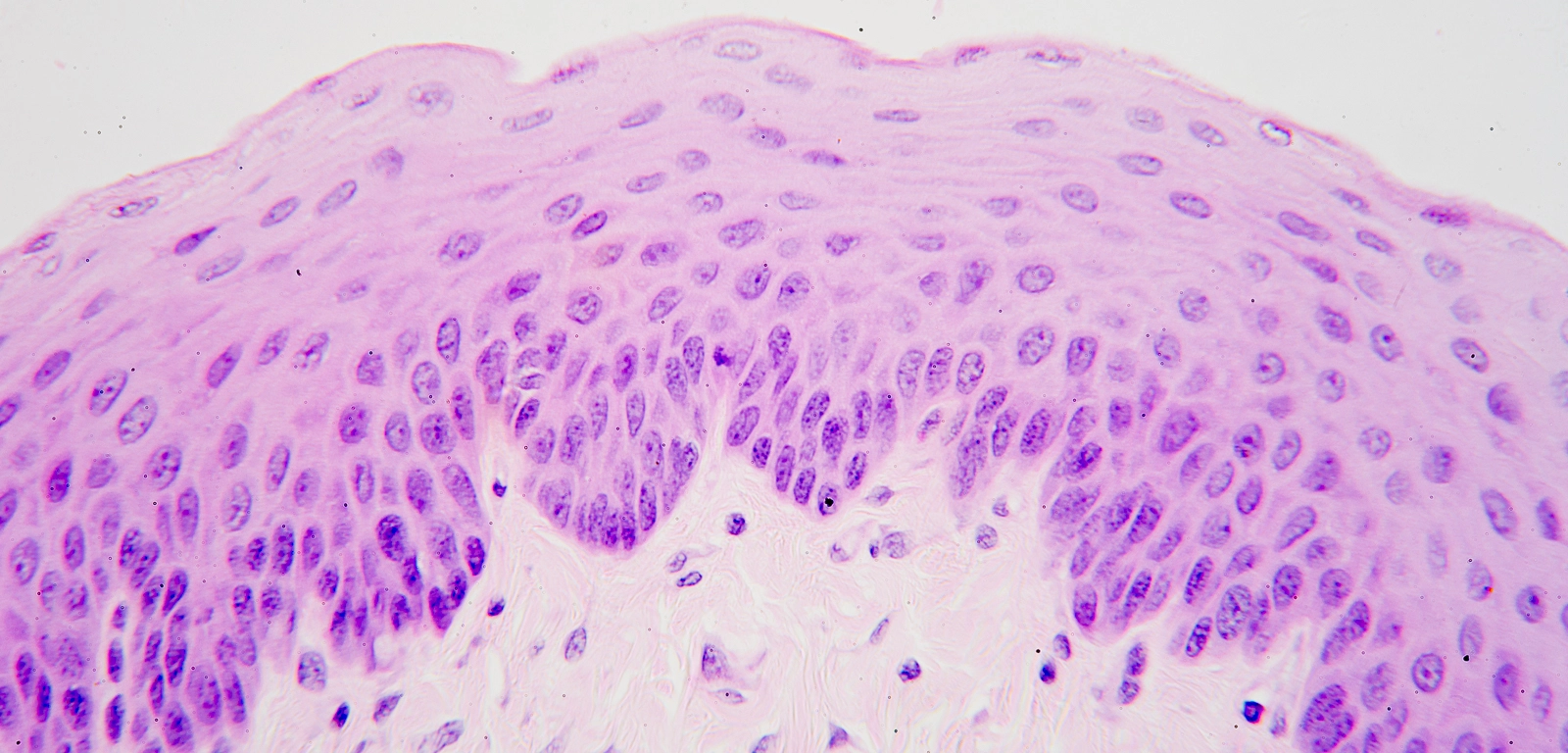
Location and function of stratified squamous, non keratinized epithelial cells
Location: oral cavity, esophagus
Function: protection
living cells all the way through every layer of epithelial tissue (keratinized means there are dead cells)
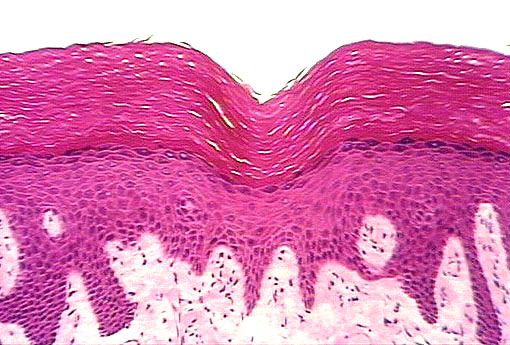
Location and function of stratified squamous, keratinized epithelial cells
location: epidermis of the skin
function: more protection than non-keratinized because the dead cells create a layer of insulation between the living cells and the environment
Location and function of pseudostratified columnar epithelial cells
location: trachea
function: protection (have cilia)
all cells touch the basal layer, but not all reach the apical surface
location and function of transitional epithelial cells?
location: ureter, bladder, urethra
function: to stretch as more pee is stored in the organ. The cells start out as several layers of cuboidal, but with more pee, the cells stretch and flatten.