Demand and supply
1/26
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
27 Terms
Demand
The willingness and ability of a consumer to buy certain goods or services at different price levels during a specific time period
Law of demand
If price increase demand decreases and if price decreases demand increases ceteris paribus
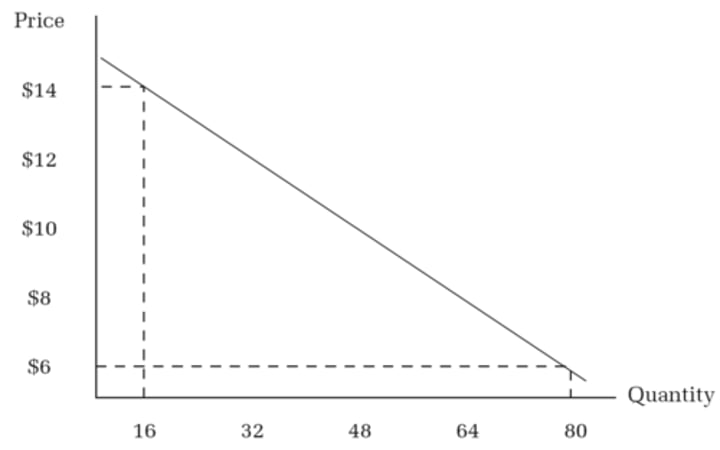
Demand curve
A graphic representation of a demand schedule (Always downward)
Demand schedule
A table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity demanded
Ceteris Paribus
When all other factors affecting it other than price and quantity demanded are constant (like weather)
Contraction of demand
If the price increases and the quantity demanded decreases
Extension of demand
If the price decreases and the quantity demanded increases
Individual demand
Demand of one person for a product
Market demand
The sum of all the individual demands for a product at every price
Shifts in the demand (excluding price)
Changes in a consumer's income, changes in taxes on incomes, the prices and availability of other goods and services, changes in the tastes/habits/fashion, population change, and other factors (weather regulations natural disasters)
Disposable income
The income left for a consumer to spend after paying taxes
Complement goods
Goods that are needed to use other goods like petrol and cars
Joint demand
The demand for goods are directly proportional (for complement goods)
Substitute goods
Goods that can replace other goods like coffee and tea
Normal goods
As the income increases the demand increases
Inferior goods
As the income increases the demand decreases
Supply
The willingness and the ability of the producer to produce goods or services
Quantity supplied
The quantity of goods or services producers are willing and able to produce
Supply schedule
A table that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied
Supply curve
A diagram showing the quantity of goods produced at a price (always upward from origin)
Law of supply
As the price increases the quantity supplied increases and vice versa ceteris paribus
Market supply
The sum of multiple firm's individual quantity supplied
Quantity extension
When the price increases the quantity supplied increases
Quantity contraction
When the price decreases the quantity supplied decreases
Shifts in the supply curve (Excluding price)
Changes in the costs of the factors of production, changes in the price and profitability of other goods and services, technological advancements, business optimism, and global factors (wars and pandemics)
Market equilibrium
When the quantity supplied is equal to the quantity demanded (E)
Market price
Whatever the consumers have demanded and the producers are able and willing to produce it and the consumer buy everything at that price