Ideal Gas Heat Capacity
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
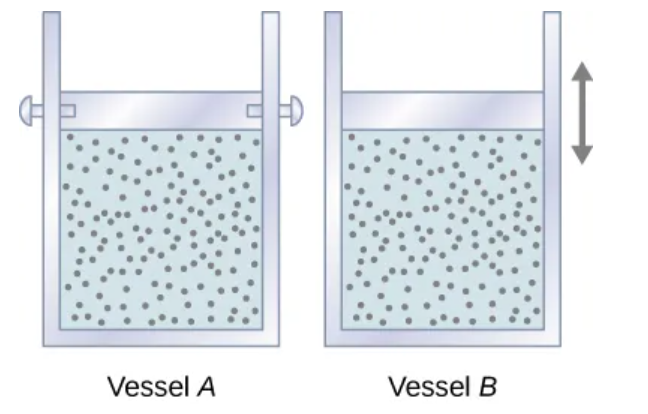
Two vessels are identical except that the piston at the top A is fixed, whereas that at top of B is free to move against a constant external pressure p.
Cv
Molar Heat capacity measured while volume remains constant
Meaning gas does not work
All the added heat increases internal energy
Cp
Molar Heat capacity measured at constant pressure
The gas expands and does work
So extra heat is required compared to Cv
Isochoric Process
A thermodynamic process where volume stays fixed, so no work (W = 0) is done. Heat is added directly increases internal energy.
Isobaric Process
A process where pressure stays constant.
Added heat goes partly into work pdV
And partly into raising internal energy,
dW = pdV = nRdT
Mathematical Representation of the work at a constant pressure (when a gas expands)
dQ = n(C_V)dT
Mathematical representation of the heat at a constant volume. (Because dW = 0, all heat increases internal energy)
dQ = n(C_p)dT
Mathematical representation of the heat at a constant pressure.
temperature
Internal energy of an ideal gas depends only on the ___________
dEint = n(C_V)dT
Mathematical representation of the Internal energy inside an ideal gas for any temperature change.
Mayer’s Relation
Derived from applying the first law to Isochoric and isobaric heating of an ideal gas.
Cp = Cv + R
Mayer’s Relation
Because at constant pressure, the gas must do expansion work, so it needs extra heat compared to constant volume.
Why Cp is greater?
Degrees of Freedom
Independent ways a molecule can store energy
C_V = (d/2)R
Formula that provides the relationship between the Degrees of Freedom and Heat Capacity
Cv = (3/2)R
Cv formula applicable for monoatomic gases like Helium, Neon, and Argon gas
Cp = (5/2)R
Cp formula applicable for monoatomic gases like Helium, Neon, and Argon gas
Cv = (5/2)R
Cv formula applicable for diatomic gases Oxygen and Nitrogen gases at room temperature.
Cp = (7/2)R
Cp formula applicable for diatomic gases Oxygen and Nitrogen gases at room temperature.
Cv = 3R
Cv formula for polyatomic gas as vibrational modes add extra energy storage.
Cp = 4R
Cp formula for polyatomic gas as vibrational modes add extra energy storage.
Cp - Cv = R
Universal Difference of Heat Capacities for all dilute gases regardless of molecular type.
Because vibrational mode contribute even at room temperature.
Why does real gases have slightly higher heat capacities?
Vessel A Behavior
No volume change → no work → all added heat raises internal energy
dEint = dQ
Vessel B Behavior
Gas expands → Work done → Heat splits into:
Raising internal energy
Doing pdV work
dQ = dEint + pdV
pdV = nRdT
pdV for constant pressure gas
(Cv)ndT = (Cpn - Rn)dT
Internal energy path independence which is a must match for both isobaric and Isochoric paths because internal energy is a state function.