CompTIA A+ Core 1: Part 2:
1/150
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
151 Terms
Define: Thermal Load
Heat from different components inside the computer
Define: Passive Cooling
Type of cooling that doesn’t rely on moving parts or power
Define: Heat Sink
Finned metal device that radiates heat away from the processor
Define: Thermal Paste
Compound that ensures heat transfer by eliminating air gaps
Passive cooling requires:
No power to operate and is silent when operating
Define: Active Cooling
Uses a fan to cool down the heat from the device
Define: Closed Loop System
Cooling of a single component
Define: Open Loop System
Liquid cooling-based system of different components
Define: Liquid Cooling
High performance systems
Define: Alternating current (AC)
Cycled between positives and negatives repeatedly
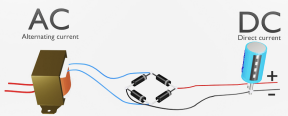
The main purpose of power supply is to:
Deliver DC to all components inside the PC when receiving an AC power supply
Define: Modular PSU / Modular Power Supply Unit
Allows to unhook the connectors and detach from the unit
Frees up space inside of the computer
Define: Main Board / Motherboard Adapter
Provides power to the motherboard
How many pins does ATX Standard use?
20-pin connector
How many pins does ATX 12V use?
24-pin connector
Define: 20+4 Pin
Two connectors are coupled together before plugging into a 24-pin connector
What kind of pin connectors does a Processor Power/ CPU Power have?
Has a four, six, or eight-pin connector
What are Molex Connector’s used for?
Used for IDE and PATA hard disks, CDs, and DVD drives
Define: Y Connector
One connector that can support multiple devices
US-based power supply:
120V AC (Low Line Power)
Europe and Asia power supply:
230V AC (High Line Power)
Most power supplies will support:
Multi-voltage outputs
Define: Voltage Sensing / Dual Voltage Power Supplies
Detects the outlet and converts it into the voltage of DC
Define: Rail
Wire that provides current at a particular voltage
12 VDC Rail
Cable or wire that provides 12 VDC
Most used voltage in the PC
Define: Wattage Rating
Power supply’s output capacity or capability
The devices inside a computer require power from a power supply
What are the formulas used to convert Amperage to Wattage?
A x V (amps x volts = watts)
I x V (amps x volts = watts)
A and I are both symbols for amps.
What should we do if a power supply has increments of 50 or 100 Watts?
Buy a power supply that is bigger than calculated
How much power is being drawn out of a wall outlet?
A 500-watt power supply that is 70% efficient will draw 714 watts
A 500-watt power supply that is 80% efficient will draw 625 watts
Power supplies are:
Not 100% efficient
Define: Random Access Memory (RAM)
Used to load applications and files into a non-persistent and fast storage area
Define: Cache
High-speed memory
Define: Storage
Mass storage device that holds more data but is slower than a cache
Define: Mass Storage Devices
Permanent storage area
Define: Random Access Memory (RAM) / System Memory
Temporary storage area/non-persistent storage
Define: Disk Cache
Pulls the files from the disc into memory and replaces the old file
Define: Mechanical system
Uses an electronic system that can access the RAM with instant speed
Define: Addressing Memory
Processor reaching the files inside RAM
How many bits are in a Single Channel Memory Controller?
32 or 64 bits
How many bits are in a x86?
32-bit
How many bits are in a x64?
64-bit
An x86 or 32-bit processor can address a maximum of how much RAM?
4 GB of RAM
An x64 or 64-bit processor can access:
More than 4 GB of RAM (8, 16, 32, or 64 GB)
Define: Single Bank
Can put any size of module in any slot
What kind of pin connector does a Dual Inline Memory Module (DIMM) have?
240 or 184-pin connector
Dual Data Rate (DDR) is the:
Most common type of memory
PC133: 133 MHz
Define: Throughput
Calculated based on the bus speed and the width of the data bus
Define: Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
Oldest type of memory that requires frequent refreshing
Storage cell is dynamic
Define: Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM)
First memory module that operates at the same speed as the motherboard bus (168-pin connector)
PC66: 66 MHz bus
PC133: 133 MHz bus
PC266: 266 MHz bus
Define: Double Data Rate Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR SDRAM)
Doubles the transfer speed of an SRAM module (184-pin connector)
Define: Double Data Rate 2 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR2 SDRAM)
Higher latency and has faster access to the external bus (240-pin connector)
PC2-4200: 4200 MB/s or 4.2 GB/s
Define: Double Data Rate 3 Synchronous Dynamic Random-Access Memory (DDR3 SDRAM)
Runs at a lower voltage and at a higher speed than DDR2 (240 keyed pin connector)
PC3-10600: 10600 MB/s or 10.6 GB/s
DDR3 throughput is 6.4 to 17 GB/s with a maximum module size of 8GB per memory module
What is a Small Outline Dual In-line Memory Module (SODIMM) classified as?
DDR3, DDR4, or DDR5
Define: Multi-Channel Memory
Uses two different memory modules to increase the performance and throughput
Single-channel Memory: ____-bit data bus
64-bit data bus
Dual-channel Memory: ____-bit data bus
128-bit data bus
Interleaving
Provides increased performance
In multi-channel configurations:
Use the same model, speed, and throughput of memory
Define: Single-Channel
Uses one memory module on one bus (64-bit data bus)
Define: Dual-Channel
Requires two memory modules and two memory slots on the motherboard (128-bit data bus)
Define: Triple-Channel
Uses three memory modules and three memory slots (192-bit data bus)
Define: Quad-Channel
Uses four memory modules and four memory slots (256-bit data bus)
Multiple modules give:
Faster speeds and add memory for storage
Define: Non-Parity Memory
Standard memory that does not check for errors and allows data to be put in or taken out
Define: Parity Memory
Performs basic error checking and ensures the memory contents are reliable
A parity check does basic calculation
Every bit has an associated parity bit
Bits can only be a zero or one
Define: Error Correcting Code (ECC)
Detects and corrects an error
Define: Buffered / Registered Memory
Additional hardware (register) between memory and CPU
The system requires buffering or registering the data to reduce the electrical load
Motherboard supports:
ECC modules
DDR5 has:
An internal error checking for its modules
Can still be sold as ECC or non-ECC modules
Define: Virtual Memory/Page File
Space on a hard drive that is allocated by the OS and pretends to be memory
Check the available memory and the free memory
Define: Page File or Swap Space
A file that is hidden on a storage device and pretend as system memory
Define: Basic Input/Output System (BIOS)
Program that a CPU uses to start the computer system/Program a computer’s microprocessor uses to start and boot after being turned on
Serves as a method of configuring the motherboard using a textbased interface
Define: Firmware
Software on a chip and contains BIOS program code in the flash memory of a motherboard
Define: Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
Supports 64-bit processors and provides a GUI
BIOS is an example of firmware:
Power-on self-test
Hardware configuration
Boot order setup
Define: Read-Only Memory (ROM)
Type of chip embedded in the motherboard and can be upgraded through flashing
The new CMOS uses an:
Internal lithium-ion battery that can last up to 10 years
Define: Power-On Self-Test (POST)
Diagnostic testing sequence to check the computer’s basic input/output system
Variable beeps are used to:
Tell what is wrong with the system
ie: Keyboard is not detected = Two short beeps and one long beep
The BIOS has a:
Low-level OS which allows to take input and give output to the basic components
To configure the settings inside CMOS, enter the BIOS configuration environment
F2-DEL-ESC-F1-F10-F12

BIOS relied on a:
Text-based menu system and a keyboard as its system of input
Define: Unified Extensible Firmware Interface (UEFI)
Updated form of BIOS that allows keyboard and mouse as input and provides a GUI
● Supports 64-bit systems
● Supports larger HDDs and SSDs (9.4 zettabytes ~ 9.4 x 10^21 bytes)
● Supports the new GUID Partition Table (GPT) format
● Faster boot-up system
● Uses a larger ROM size
Disable booting from an optical drive or USB drive
Configure the system to boot from the installed hard drive using the installed OS
Boot the OS using PXE as the primary option
Define: Flashing
Performed during upgrades, security fixes, or feature improvements
Steps for Flashing:
1.) Back up the configuration and information
2.) Use a USB flash drive to flash the firmware
3.) The BIOS or UEFI will copy the firmware to the system and overwrite the old code
BIOS and UEFI are used during:
Loading and booting up the OS
Computers that rely on BIOS use:
MBR to hold the boot information
Computers that rely on UEFI use:
GPT to hold the boot information
Define: Supervisor/Administrator/Setup Password
Used to protect access to the BIOS or UEFI configuration program and prevents access from unauthorized users
Define: User/System Password
Used to lock access to the computer
Define: Storage/Hard Drive Password
Password that locks access to a hard drive connected to the system and requires the end user’s password
Define: Secure Boot
Enabled in the UEFI interface and settings and is not supported by BIOS
Define: Root kit
A special type of malware
Modern systems are configured to:
Enable or disable the USB ports on the motherboard
Disable the ability of USB to read and write from mass storage devices by:
Set passwords
Enable secure boot
Restrict or disable USB ports
Define: Hardware RoT
The foundation of all secure operations of a computing system
Define: Hardware Root of Trust (RoT)
Cryptographic module embedded in a computer system that endorses trusted execution and attests to boot settings and metrics
A hardware RoT is used to:
Scan the boot metrics in the OS files to verify signatures and then use them to sign the report
Define: Trusted Platform Module (TPM)
Specification for hardware-based storage of digital certificates, keys, hashed passwords, and other user and platform identification information
● Is a hardware RoT
● Secured boot-up
● Provides encryption
Can be managed in Windows via tpm.msc console or through group policy
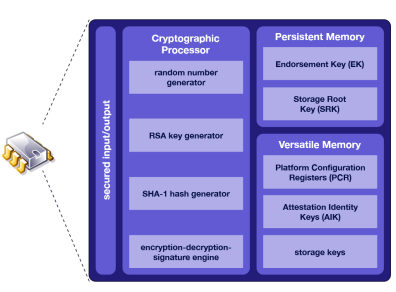
Define: Hardware Security Module (HSM)
Appliance for generating and storing cryptographic keys that is less susceptible to tampering and insider threats
BIOS and UEFI can configure fans, the modes being:
Quiet mode, Balanced mode, and Cool mode