BIO 233 Exam 7 (Set #1) Lab practical terms
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
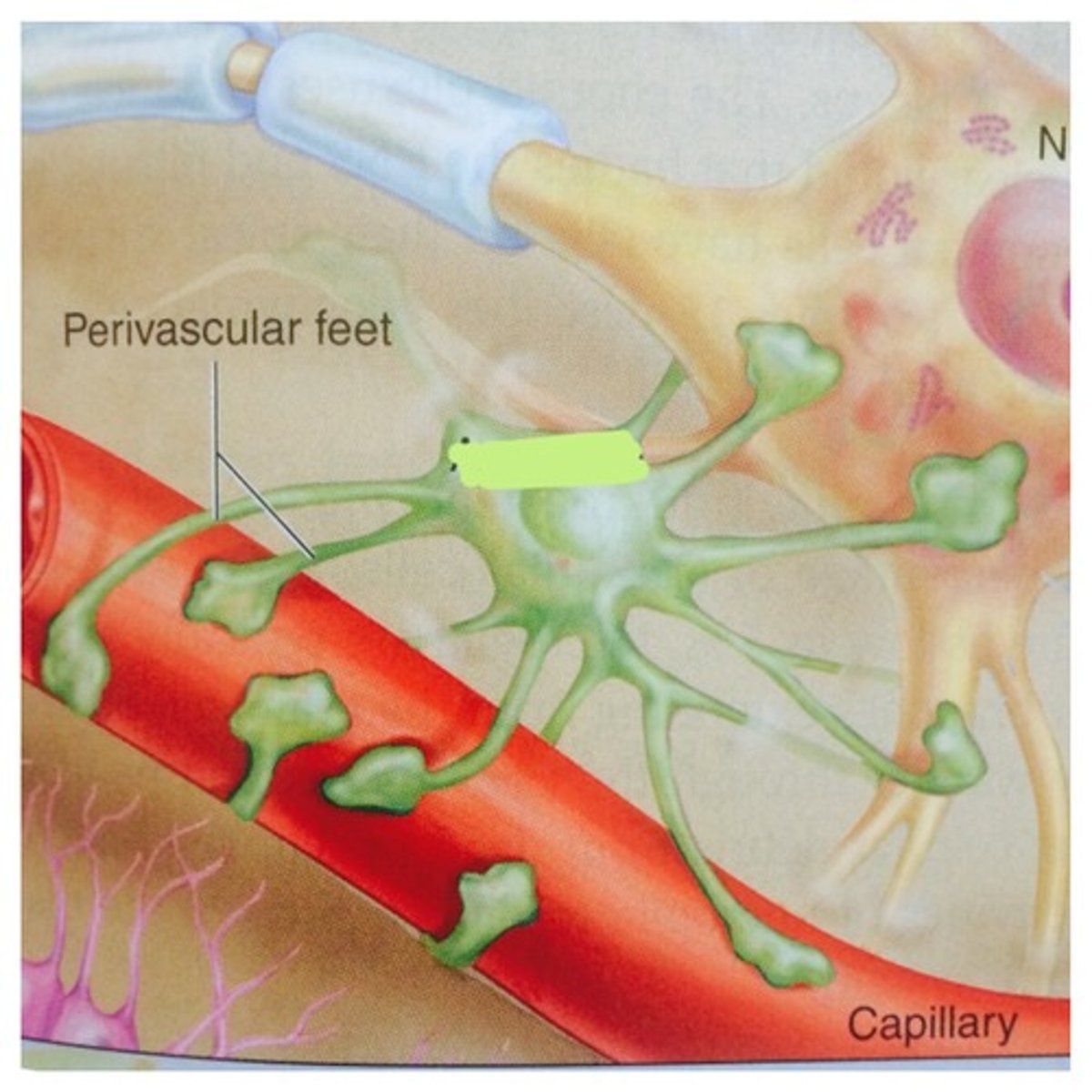
astrocyte
Star -shaped cell, supports neurons in CNS, helps create BBB (blood-brain barrier) by wrapping feet around capillaries
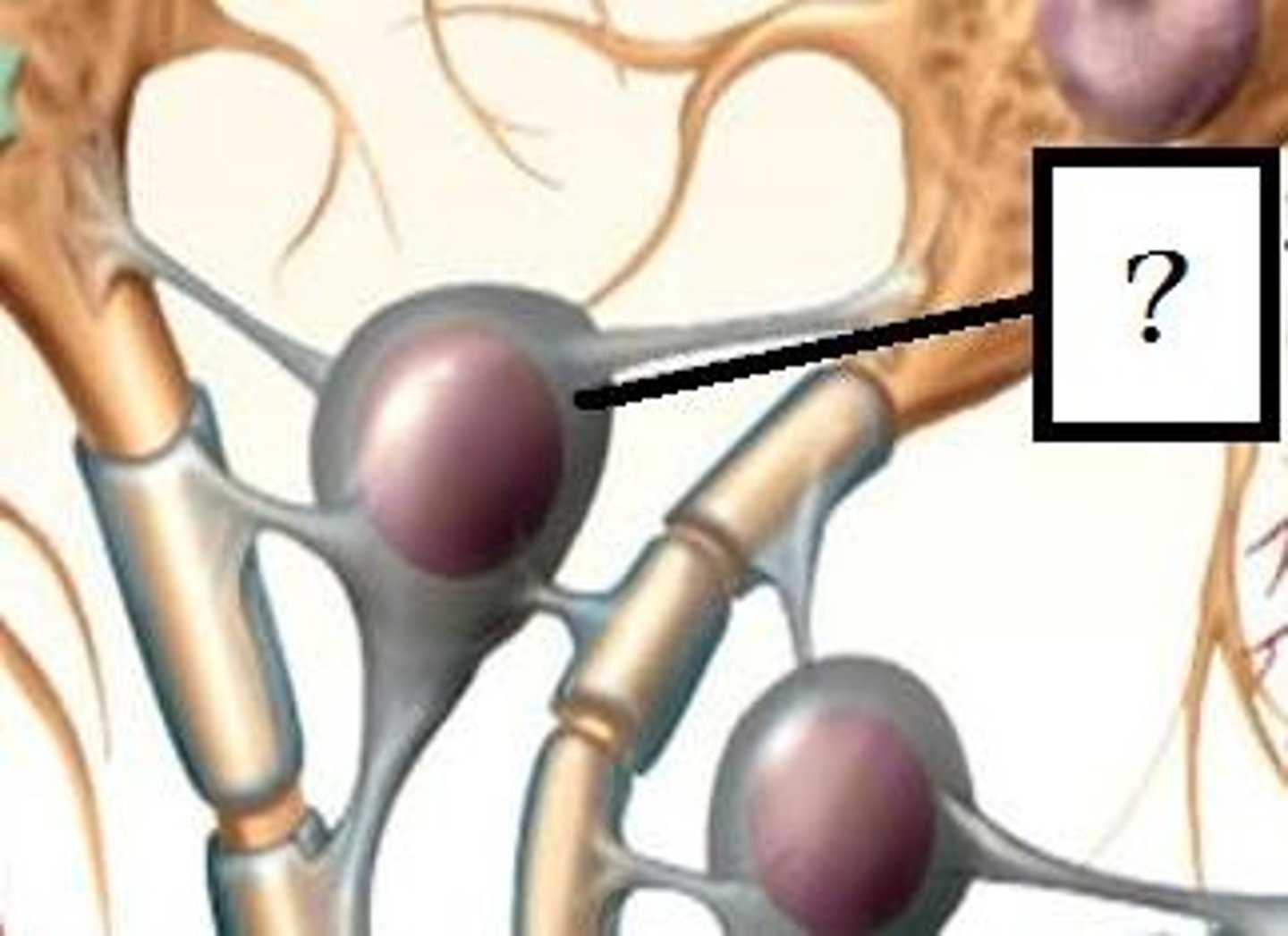
oligodendrocyte
a type of glial cell that forms myelin in the central nervous system
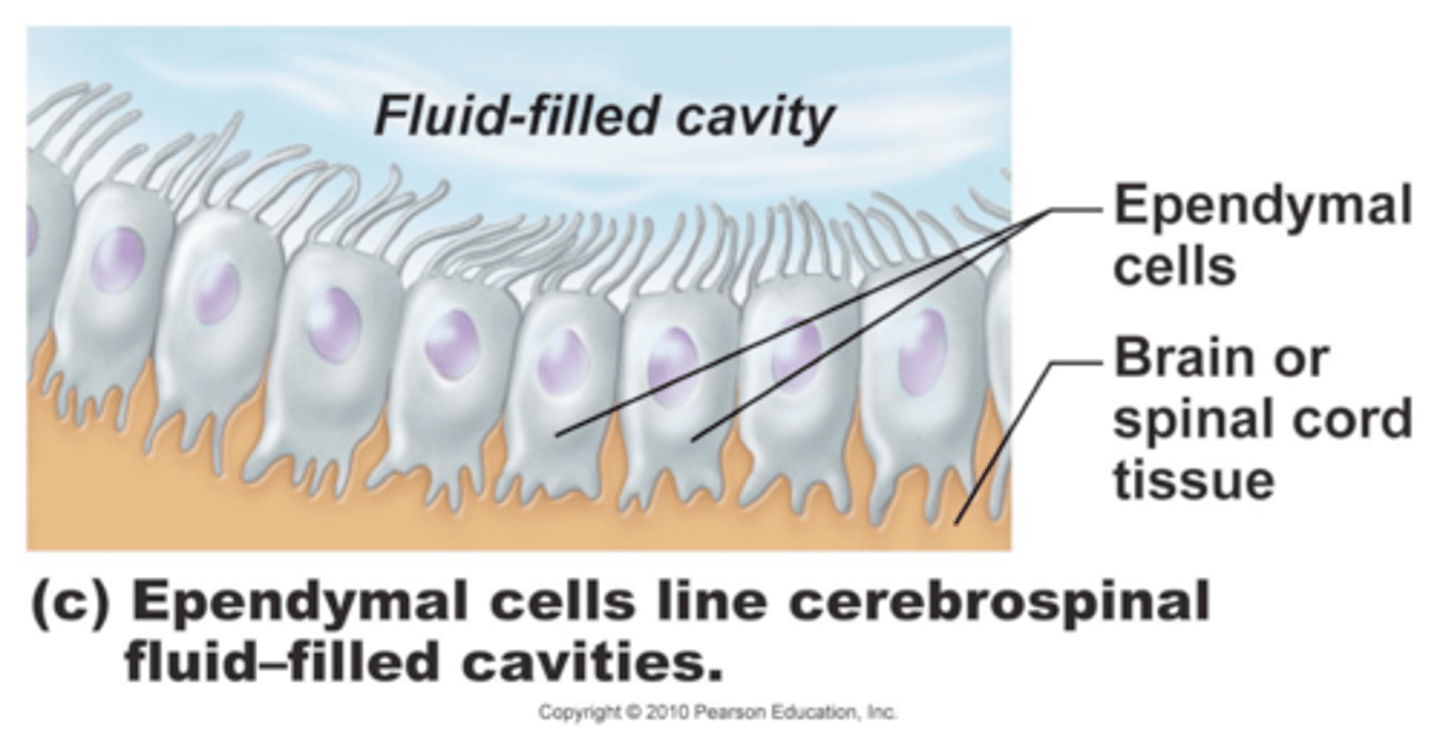
ependymal cells
line cavities of the brain and spinal cord, circulate cerebrospinal fluid
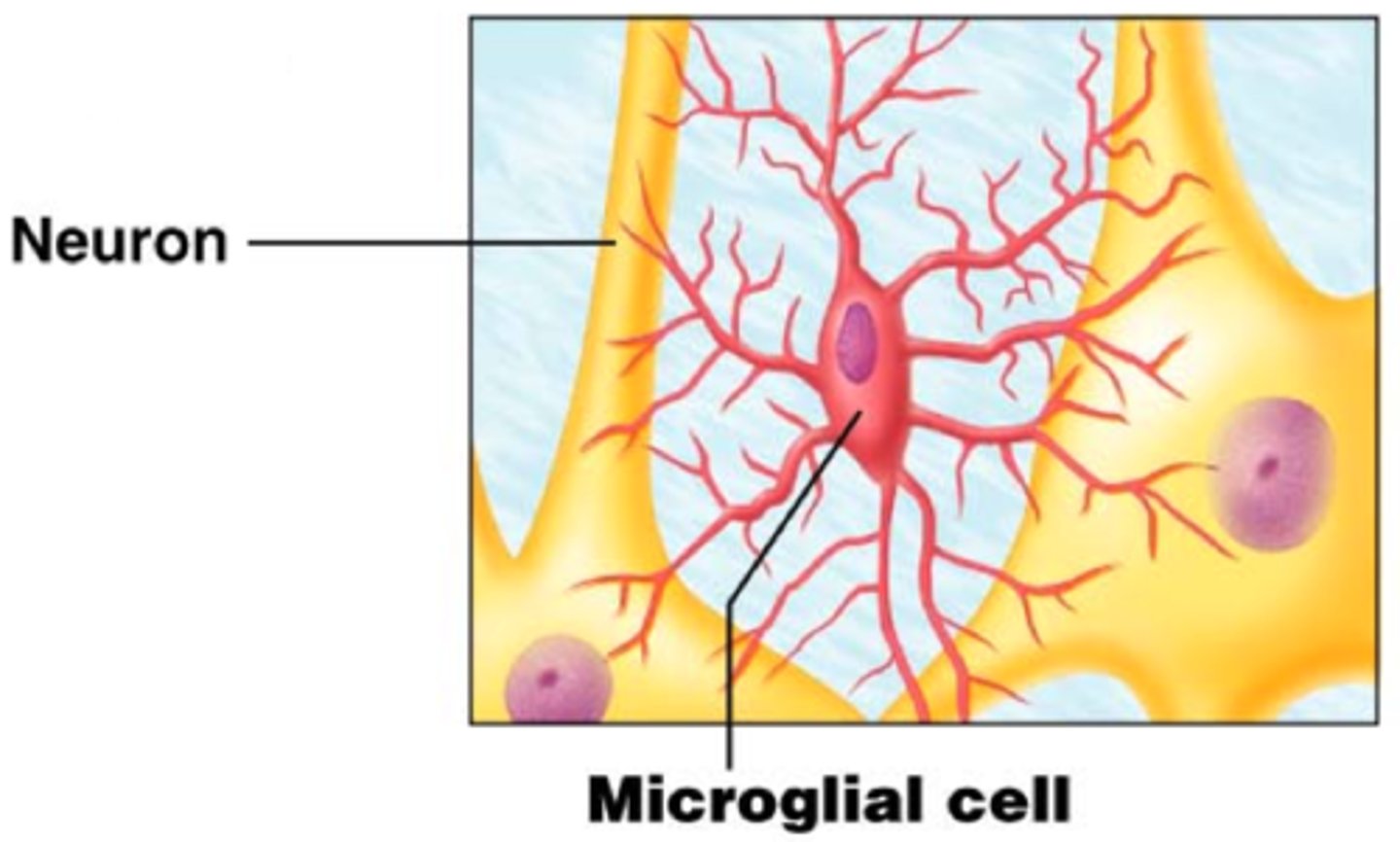
Microglia
Act as phagocytes, eating damaged cells and bacteria, act as the brain's immune system
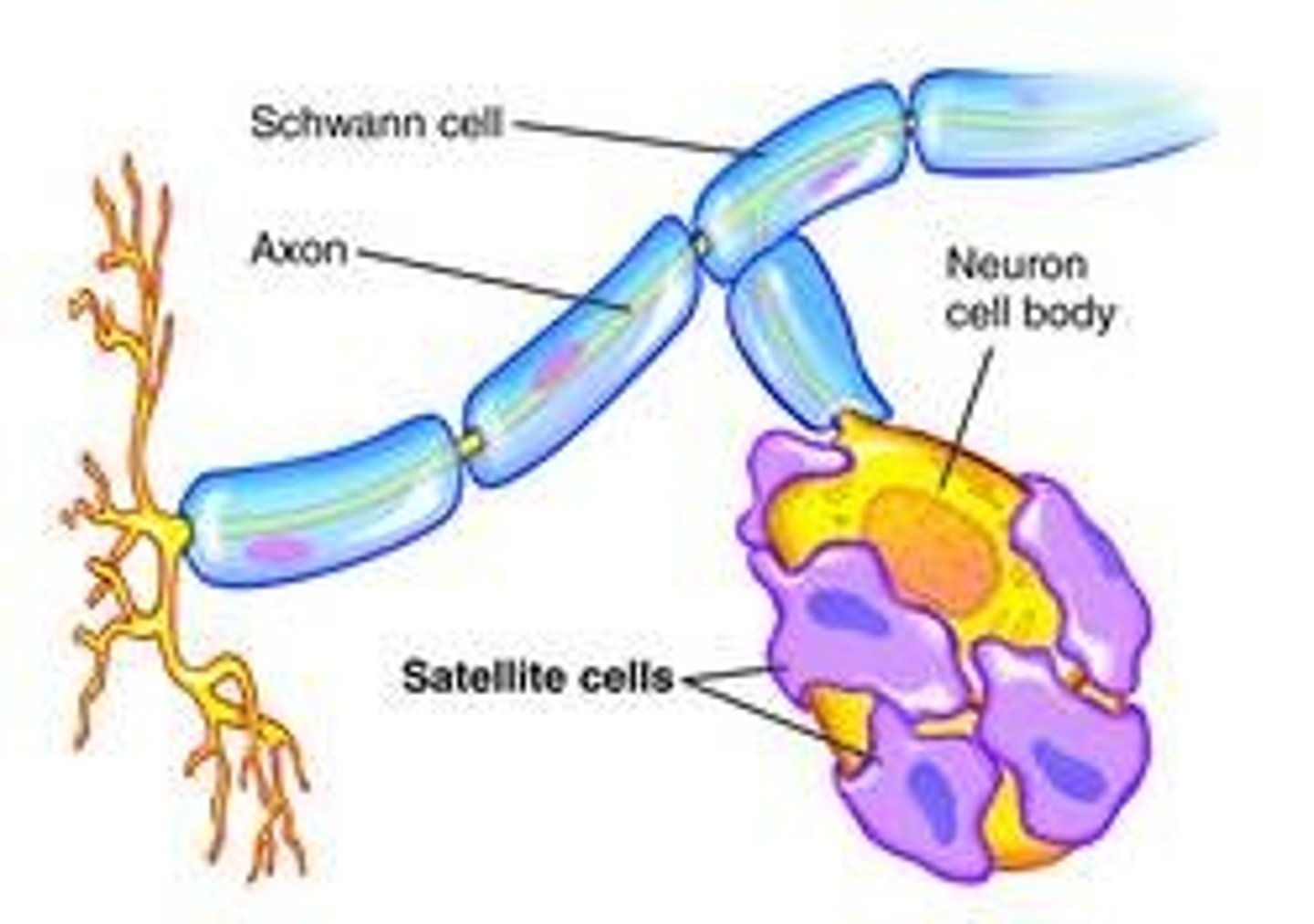
sattelite cells
neuroglia in the PNS that are located around cell bodies--help support nerve cells
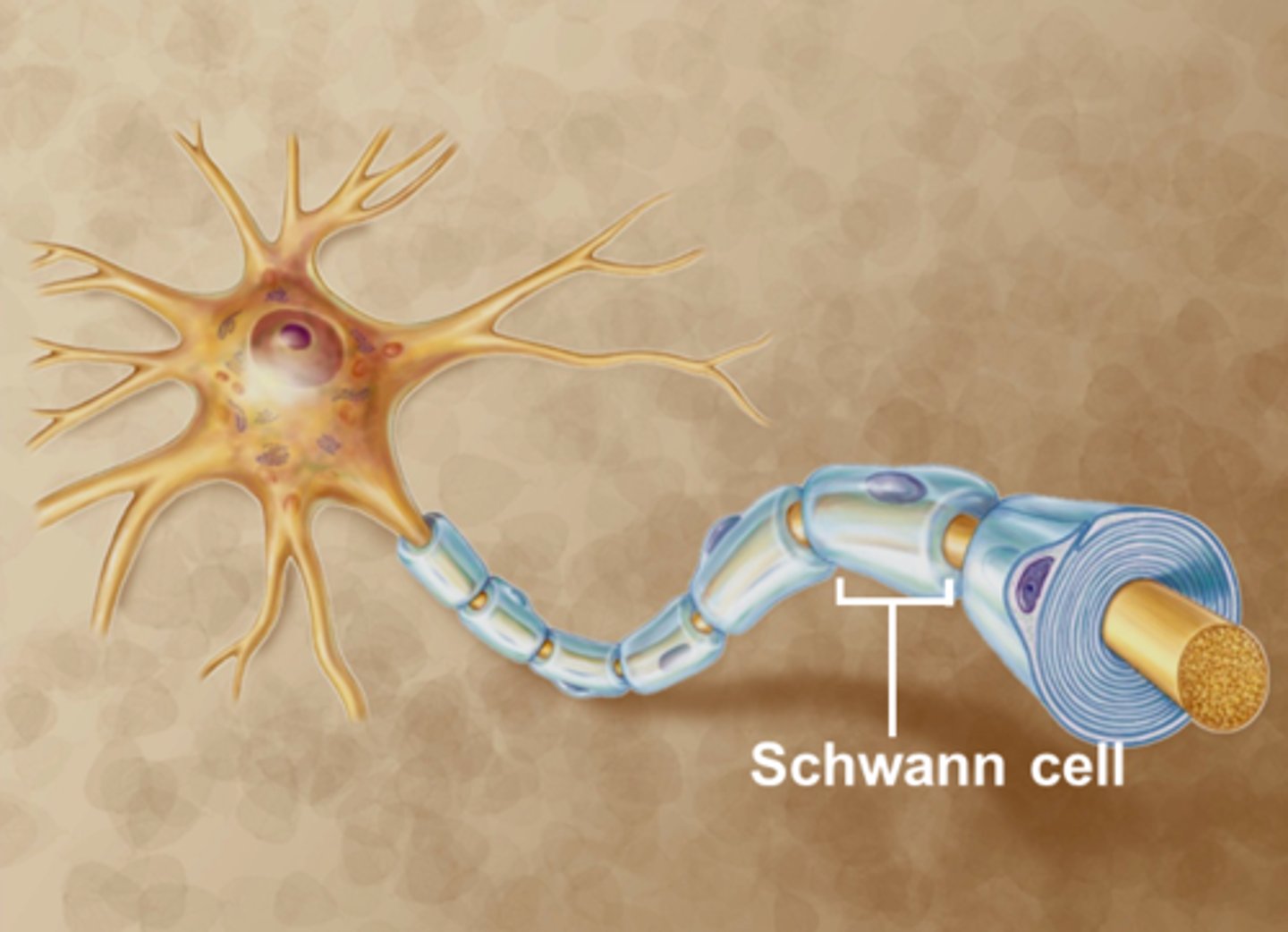
Schwann cells
produce myelin in PNS
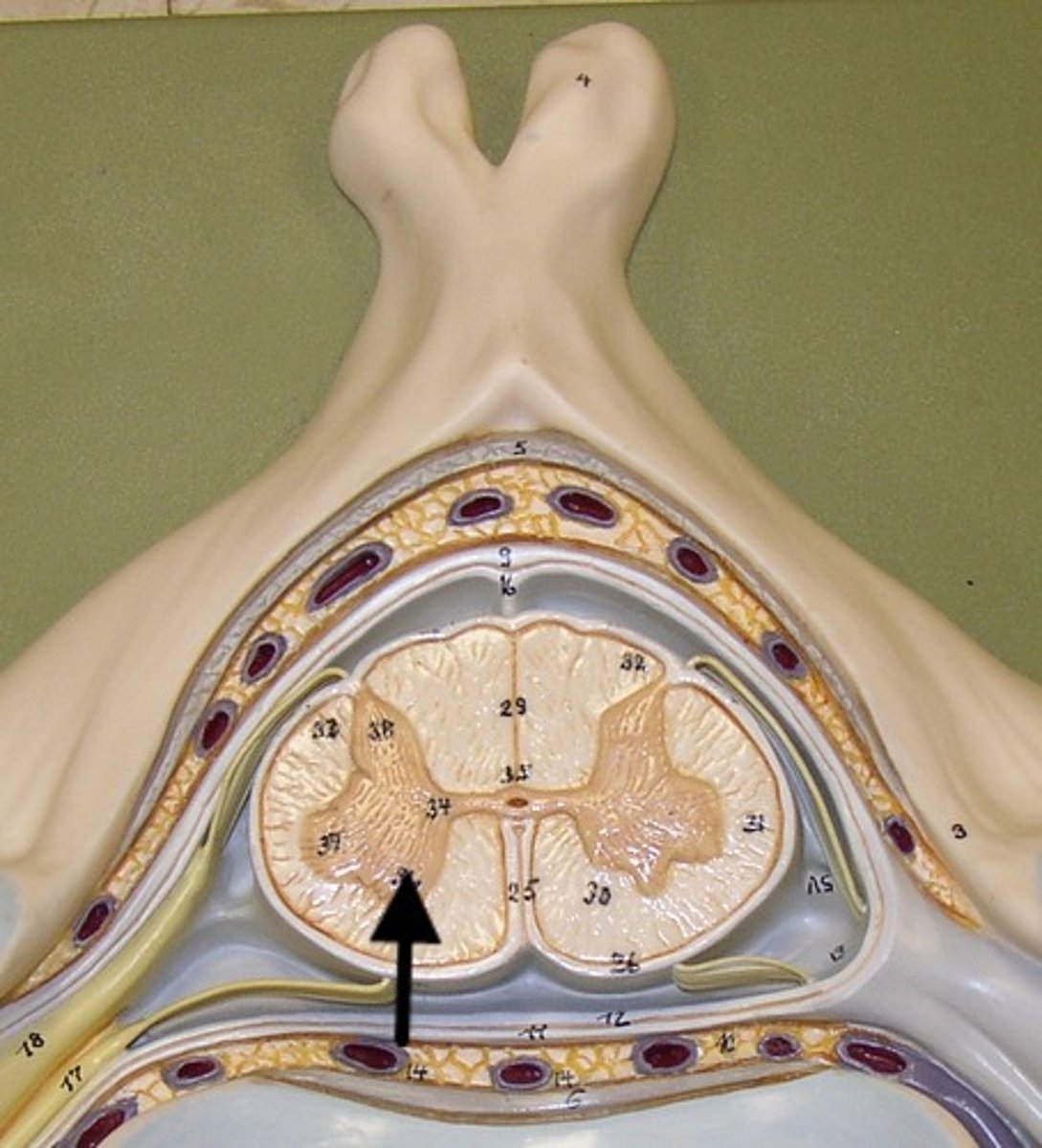
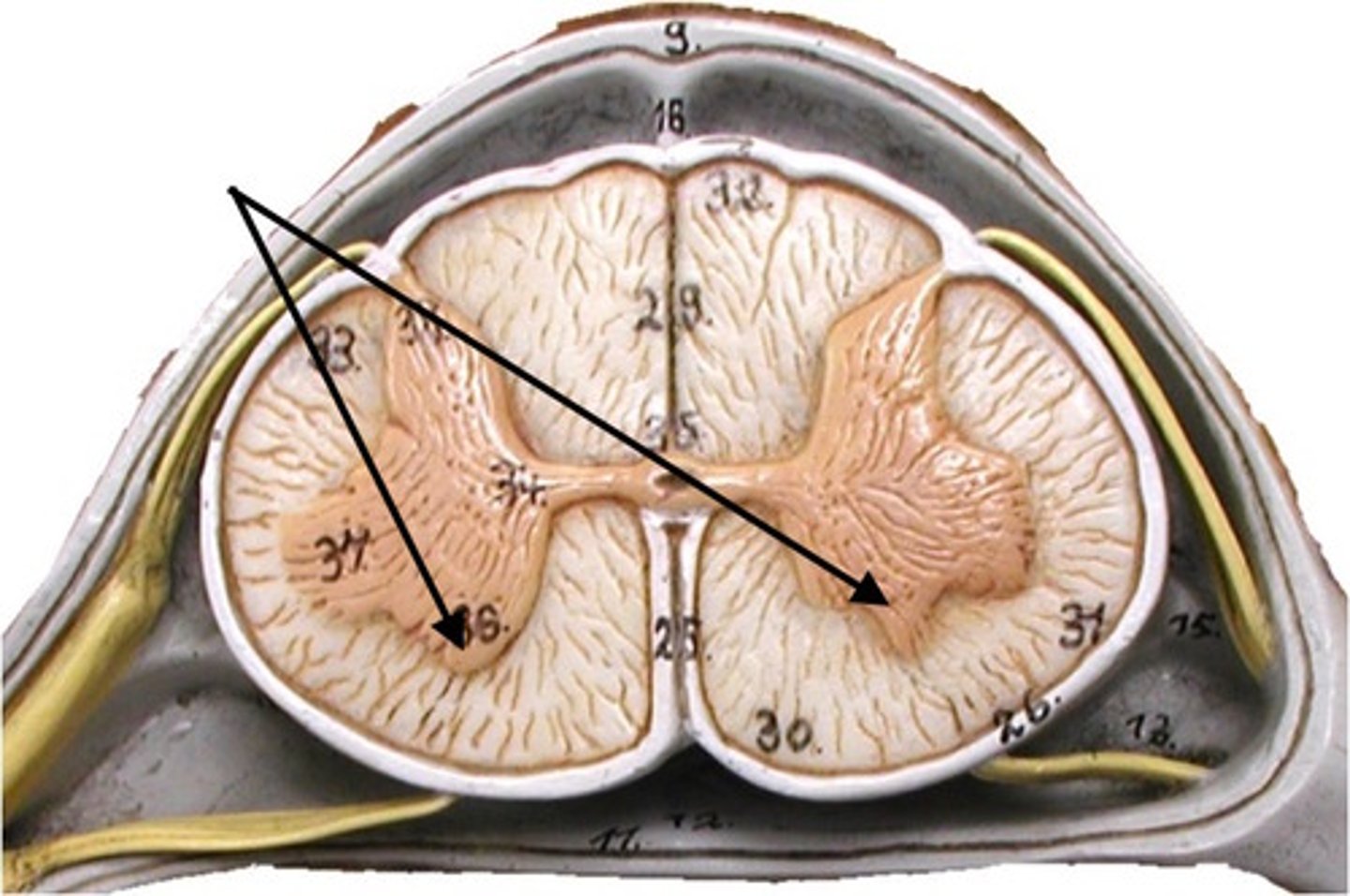
Anterior gray horn
contains somatic motor neuron cell bodies
Lateral gray horn
(Only need to ID) {FYI -- located only in thoracic and lumbar segments, contains visceral motor nuclei}
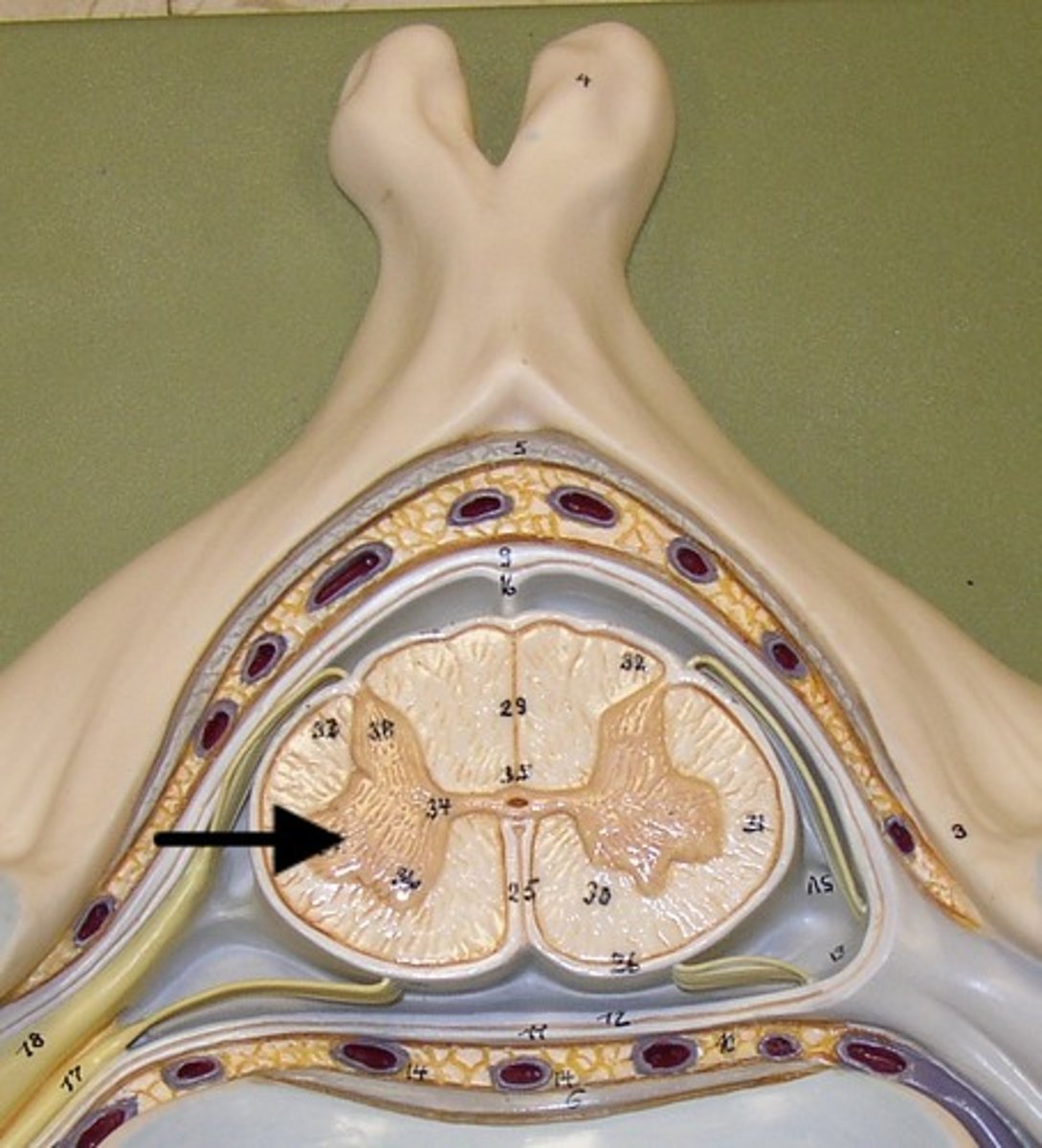
ventral gray horn
contains motor nuclei to skeletal muscles
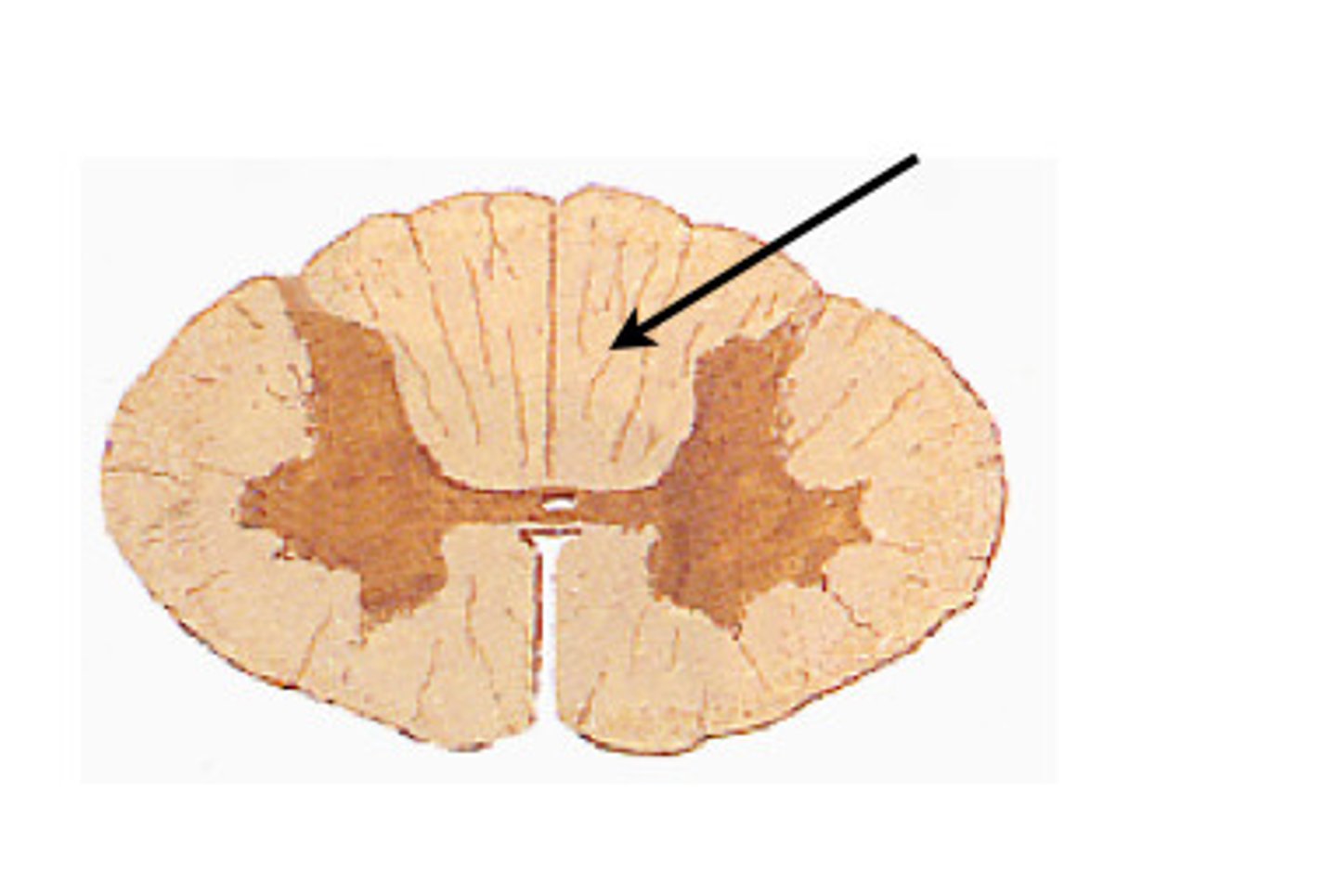
posterior white columns
lie between posterior gray horns and posterior median sulcus
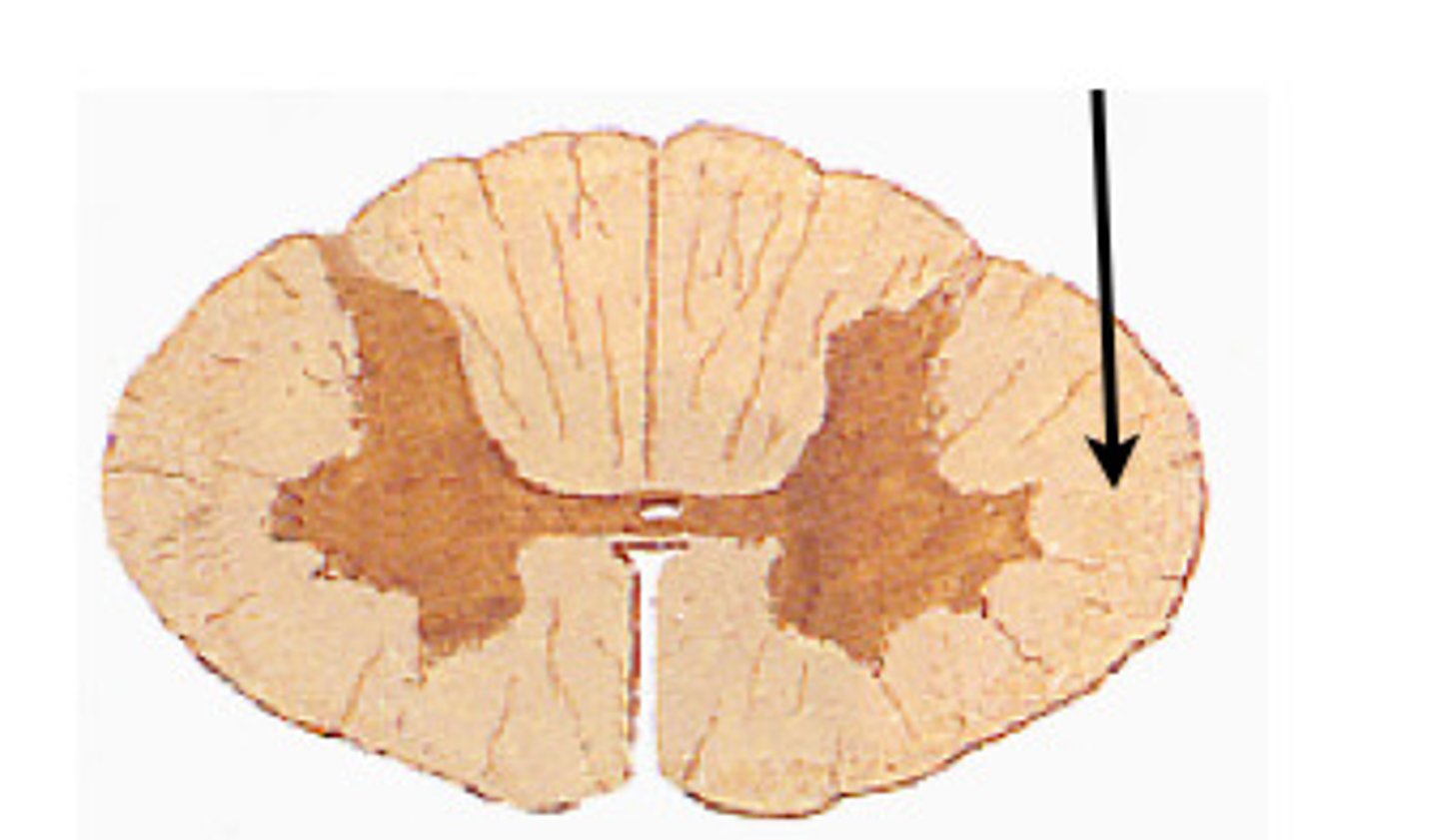
lateral white columns
located on each side of spinal cord between anterior and posterior columns
anterior white columns
between anterior horns and anterior median fissure
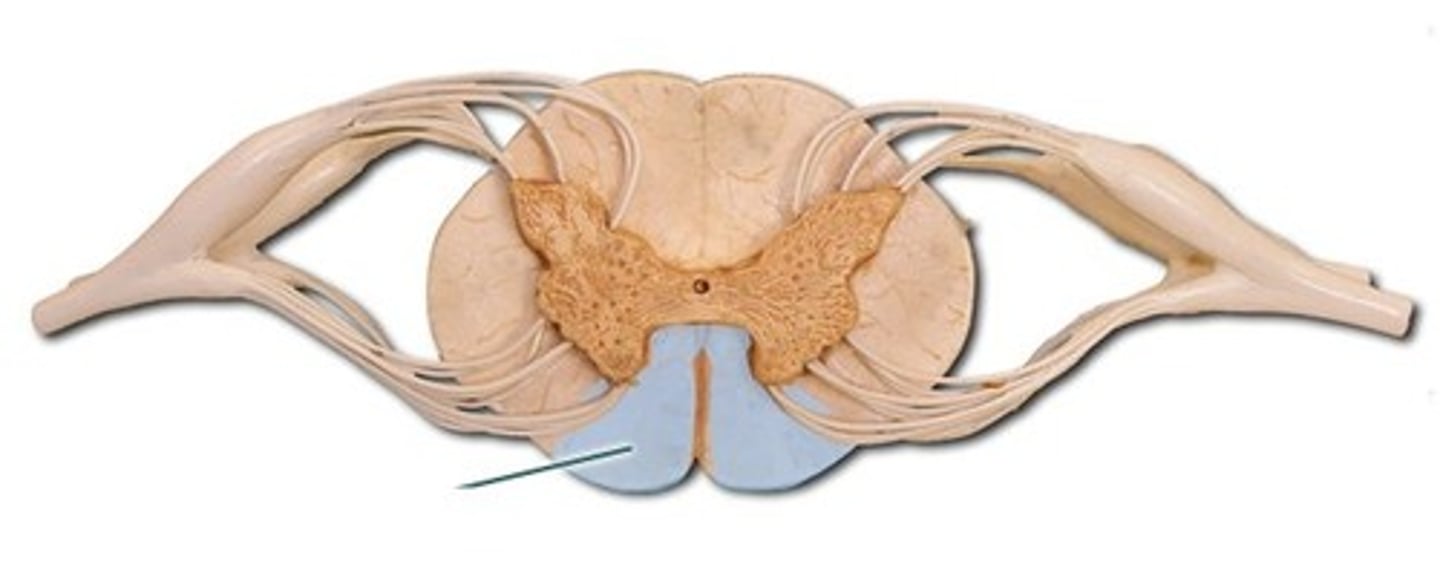
anterior median fissure
wide, deep crease along the ventral surface of the spinal cord
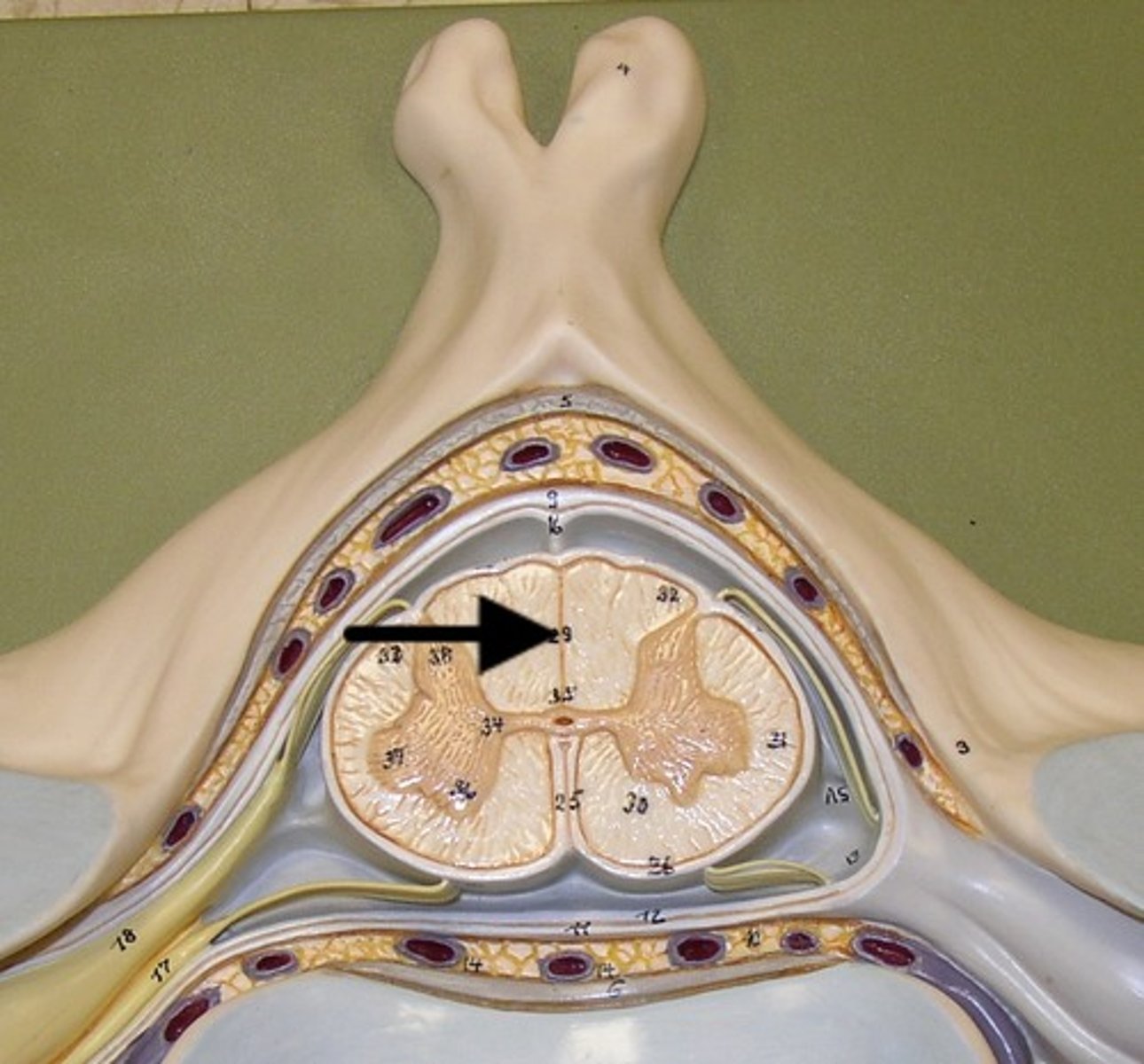
posterior median sulcus
a longitudinal shallow groove on the posterior side of the spinal cord
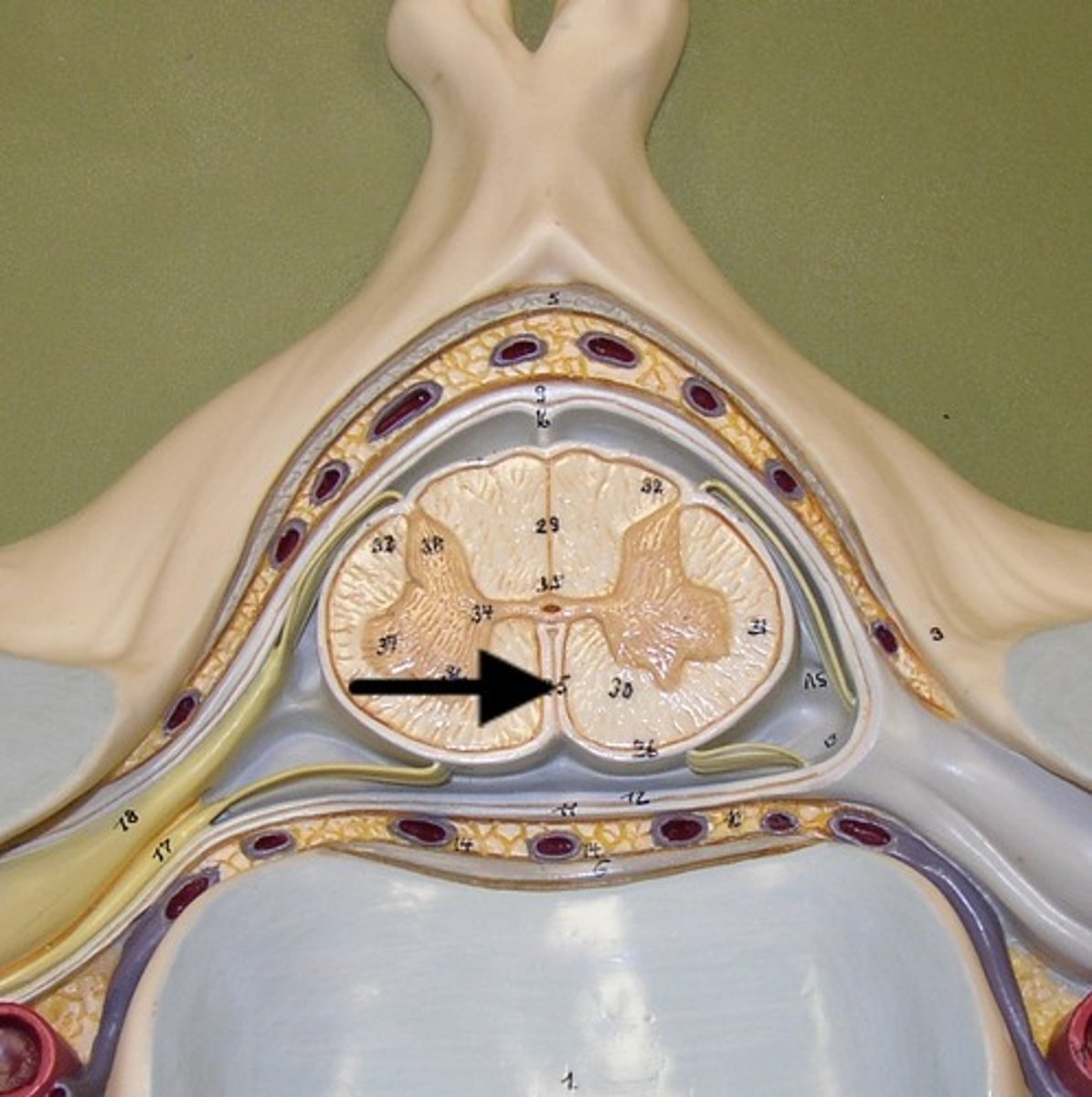
central canal of spinal cord
center of spinal cord which contains cerebrospinal fluid
What is the white matter of the spinal cord made of?
myelinated axons
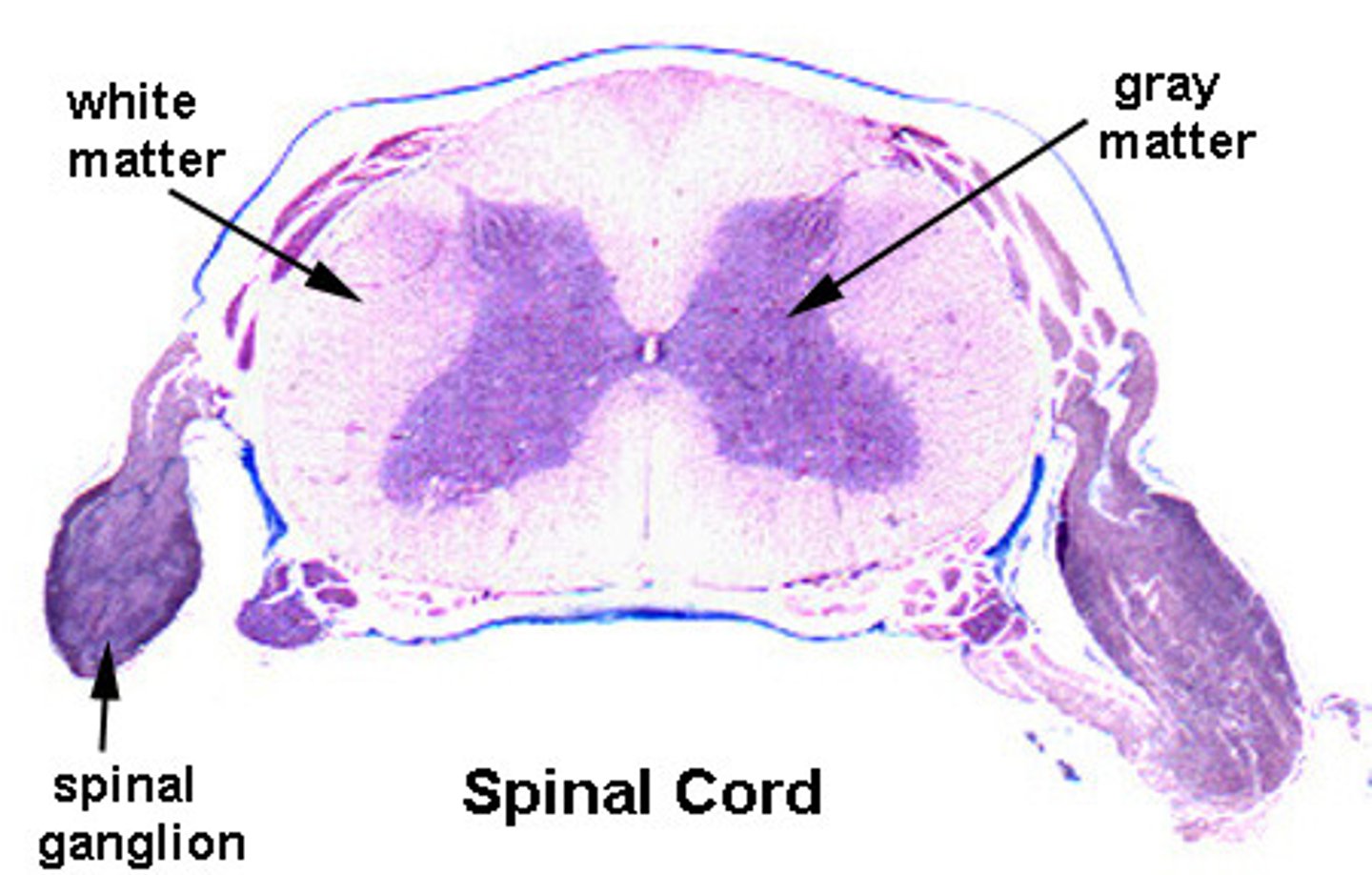
What is the gray matter of the spinal cord made of?
cell bodies
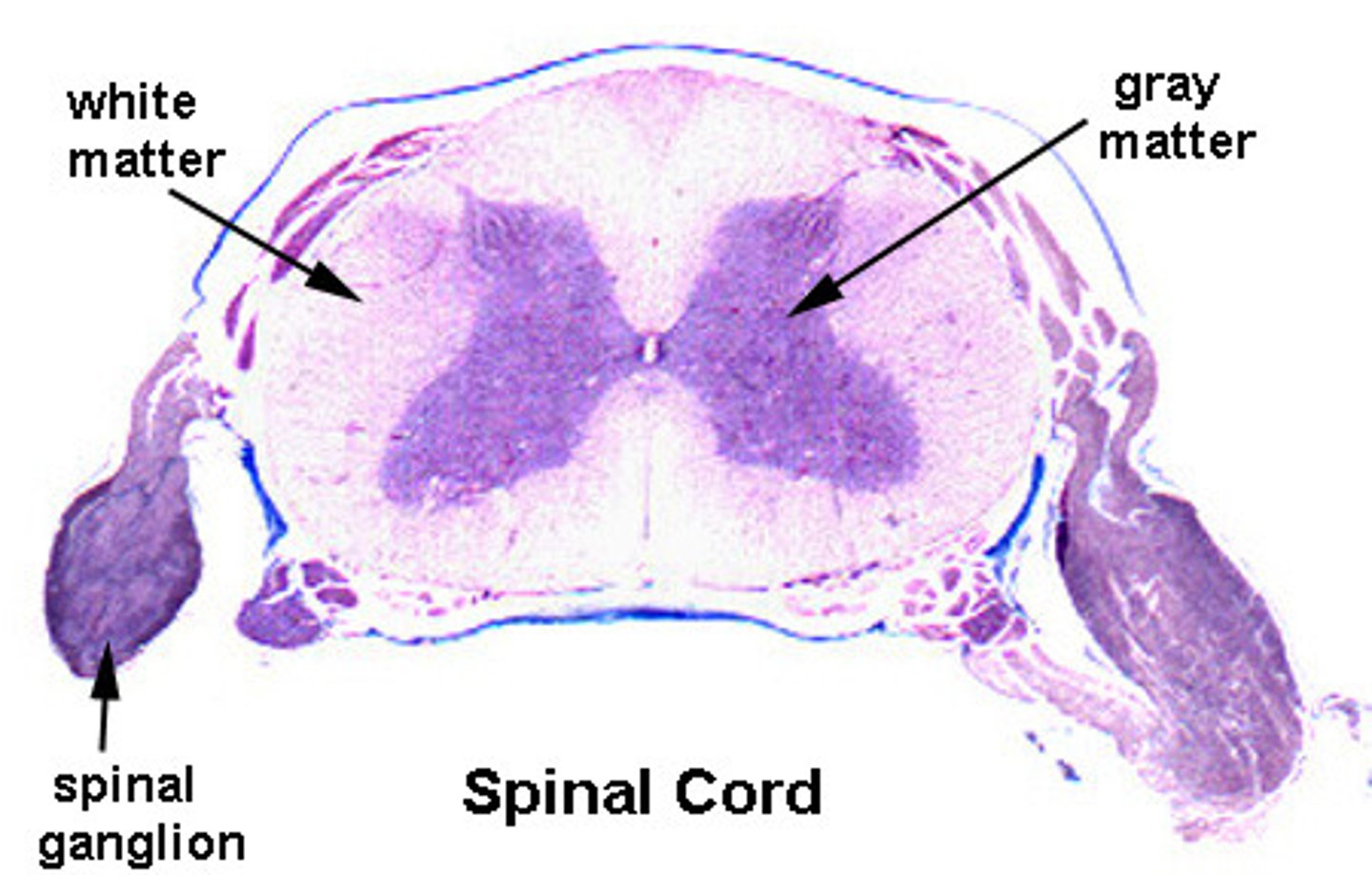
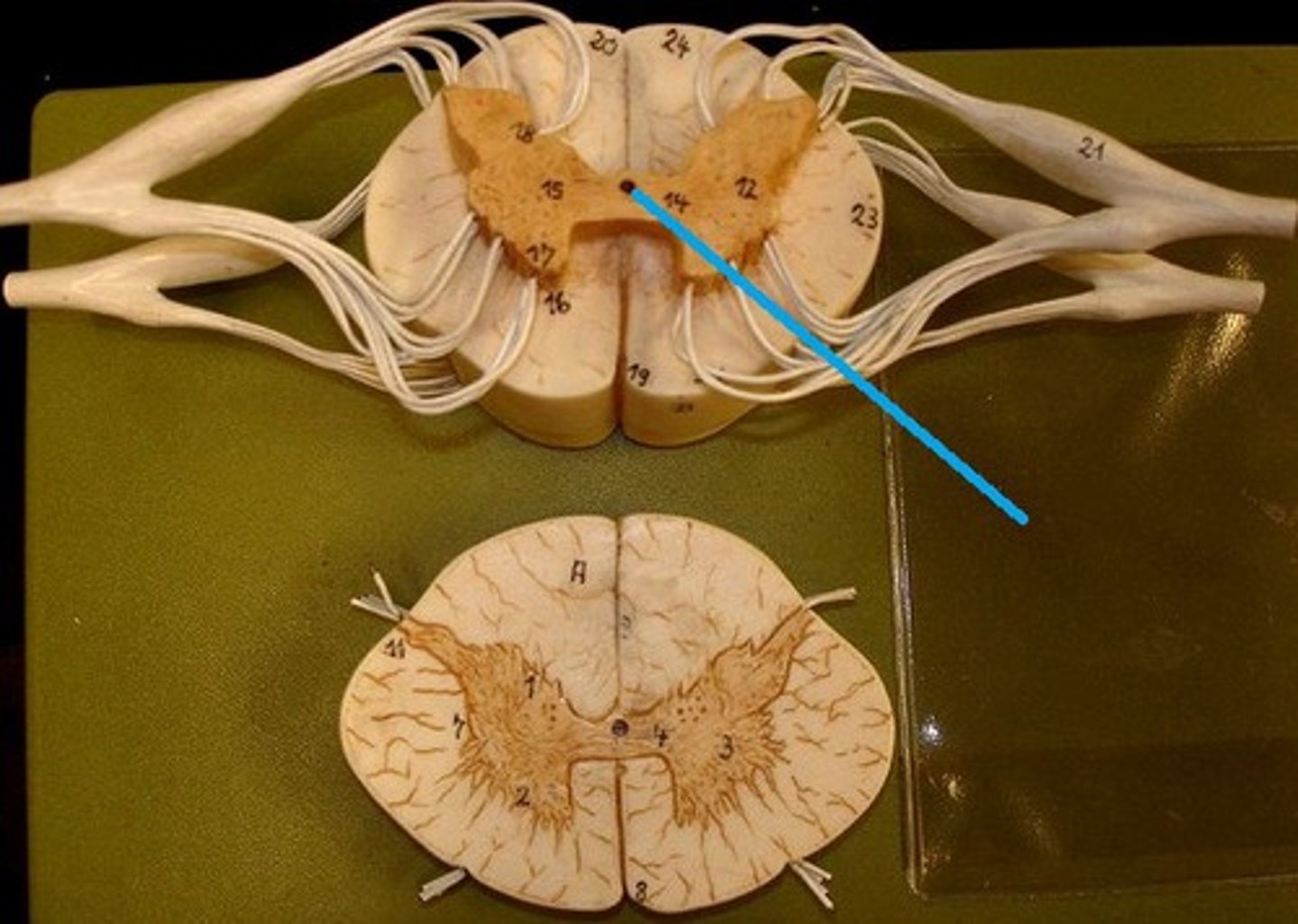
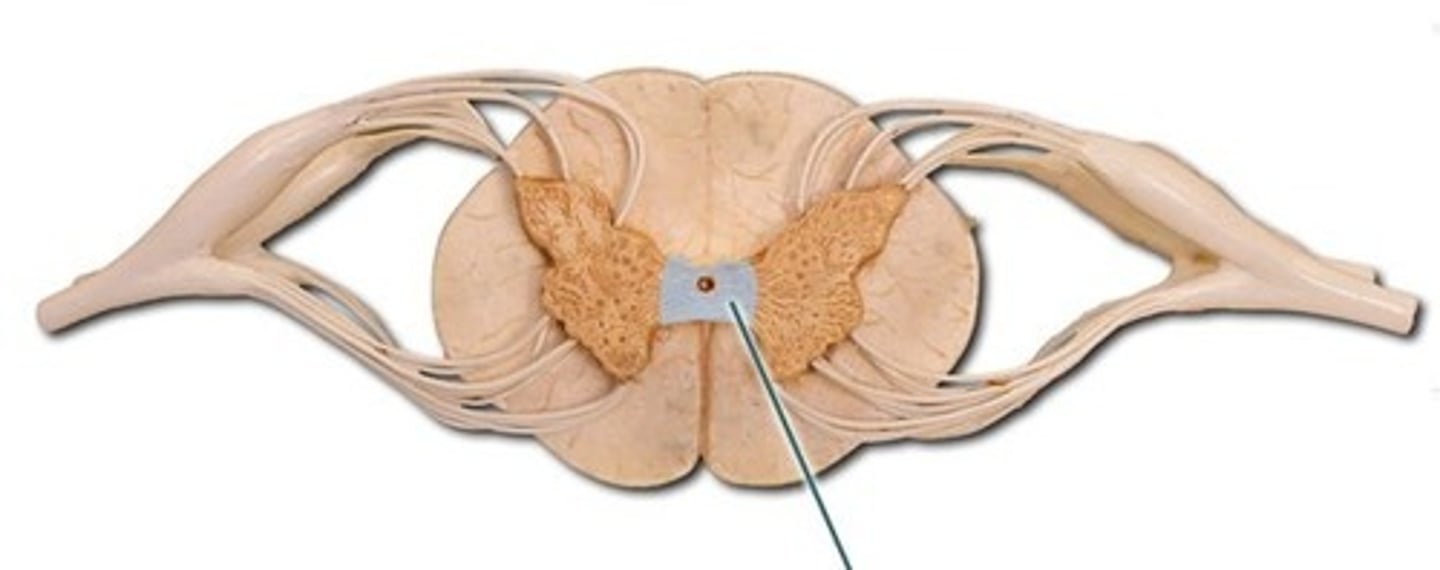
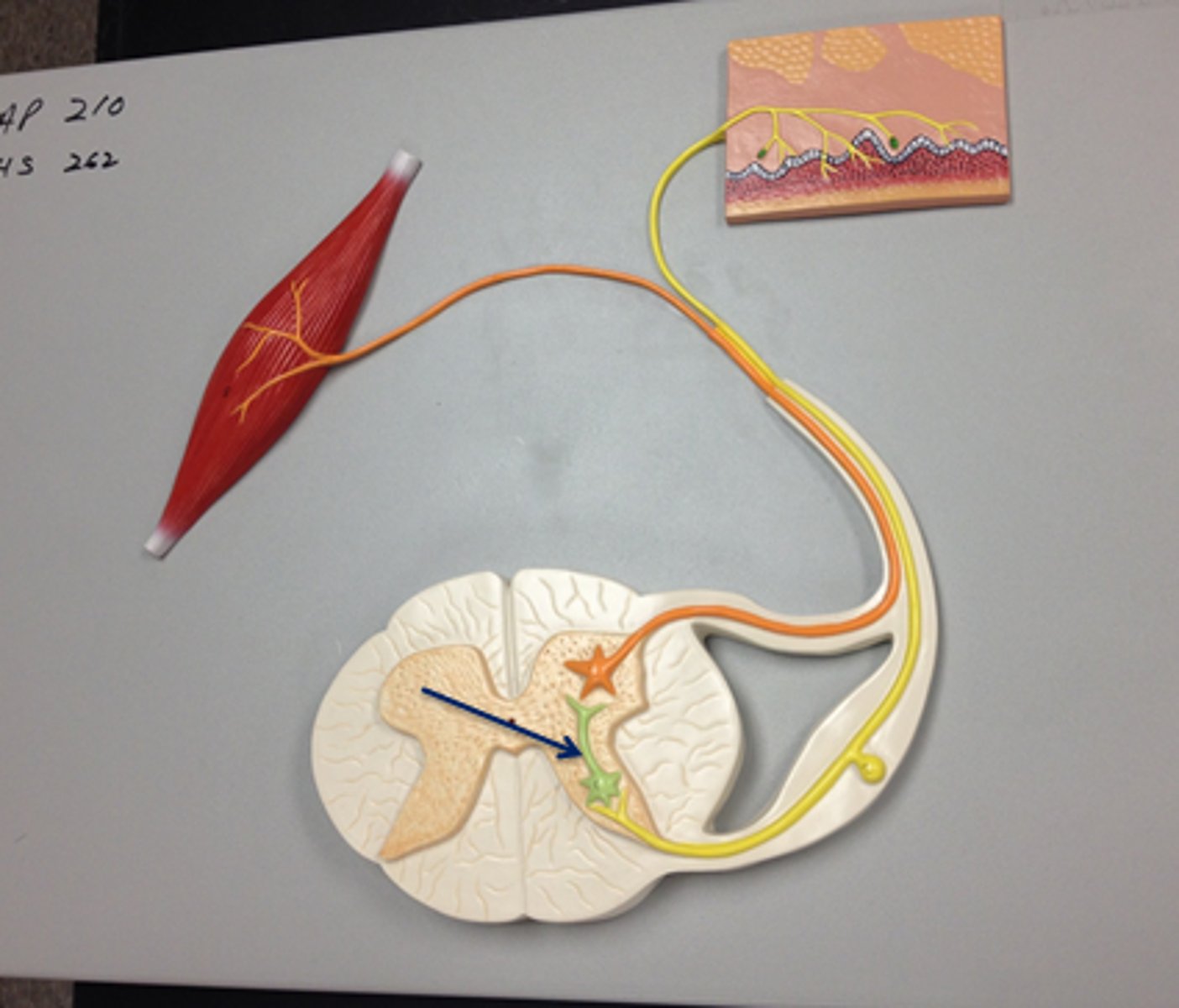
Gray Commissure Function
connect horns
surrounds central canal - where CSF flows
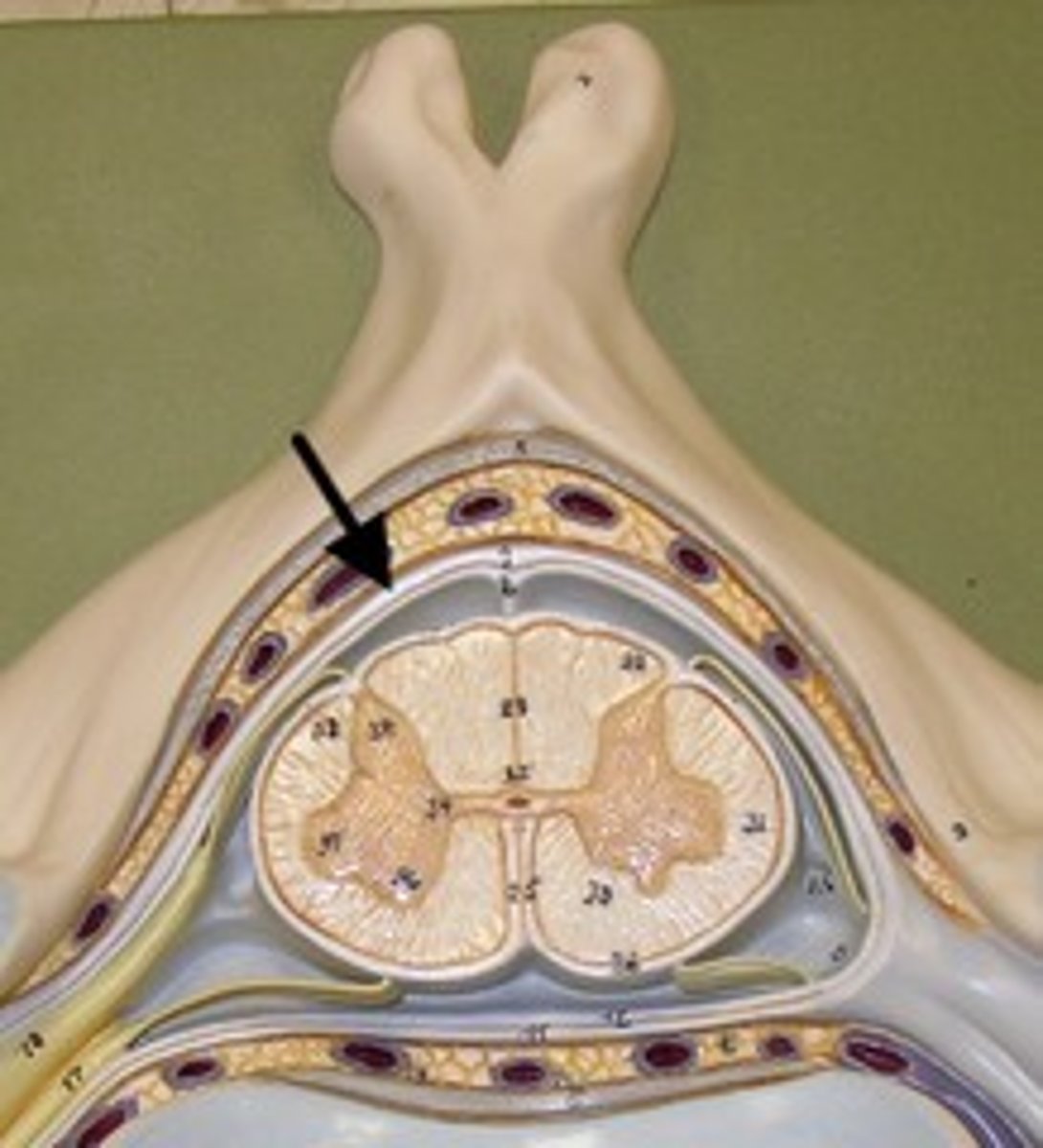
dura mater of spinal cord
The outermost and toughest layer menix covering the spinal cord.
arachnoid mater of spinal cord
middle layer of the meninges (shown here just beneath the dura--they are tightly adhered in the model)
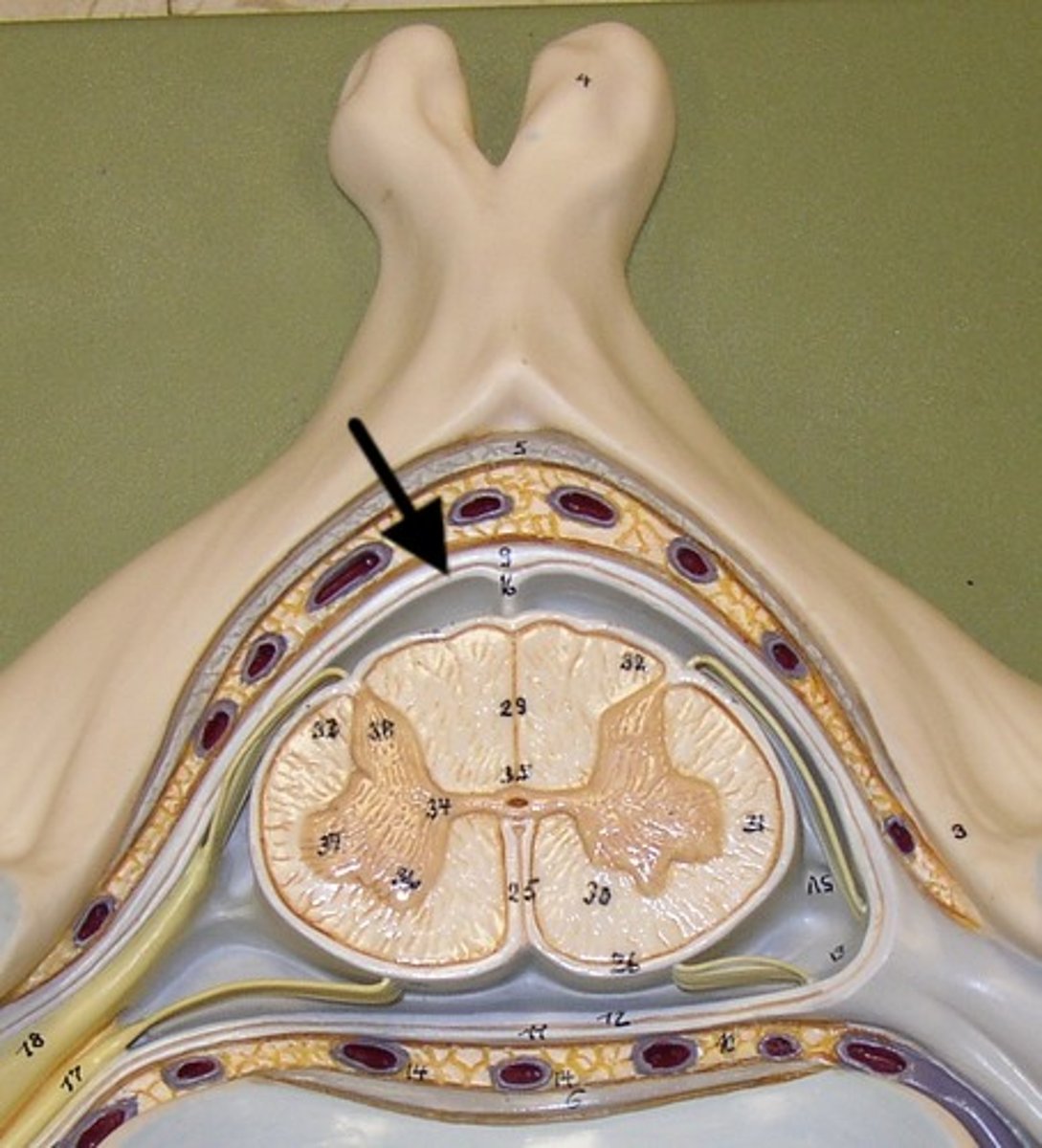
pia mater
Innermost layer of the meninges
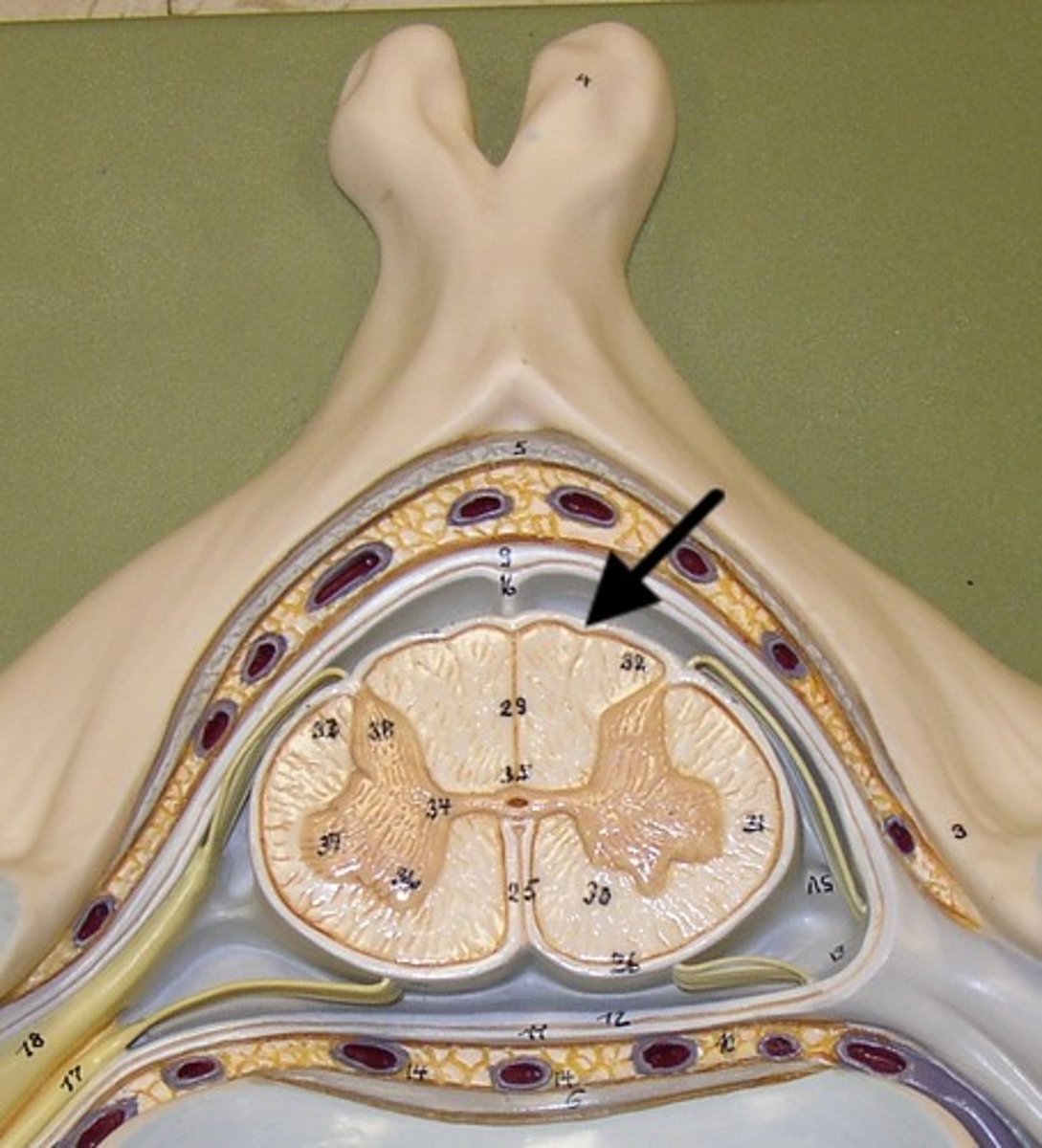
epidural space
space between the dura mater and the wall of the vertebral canal
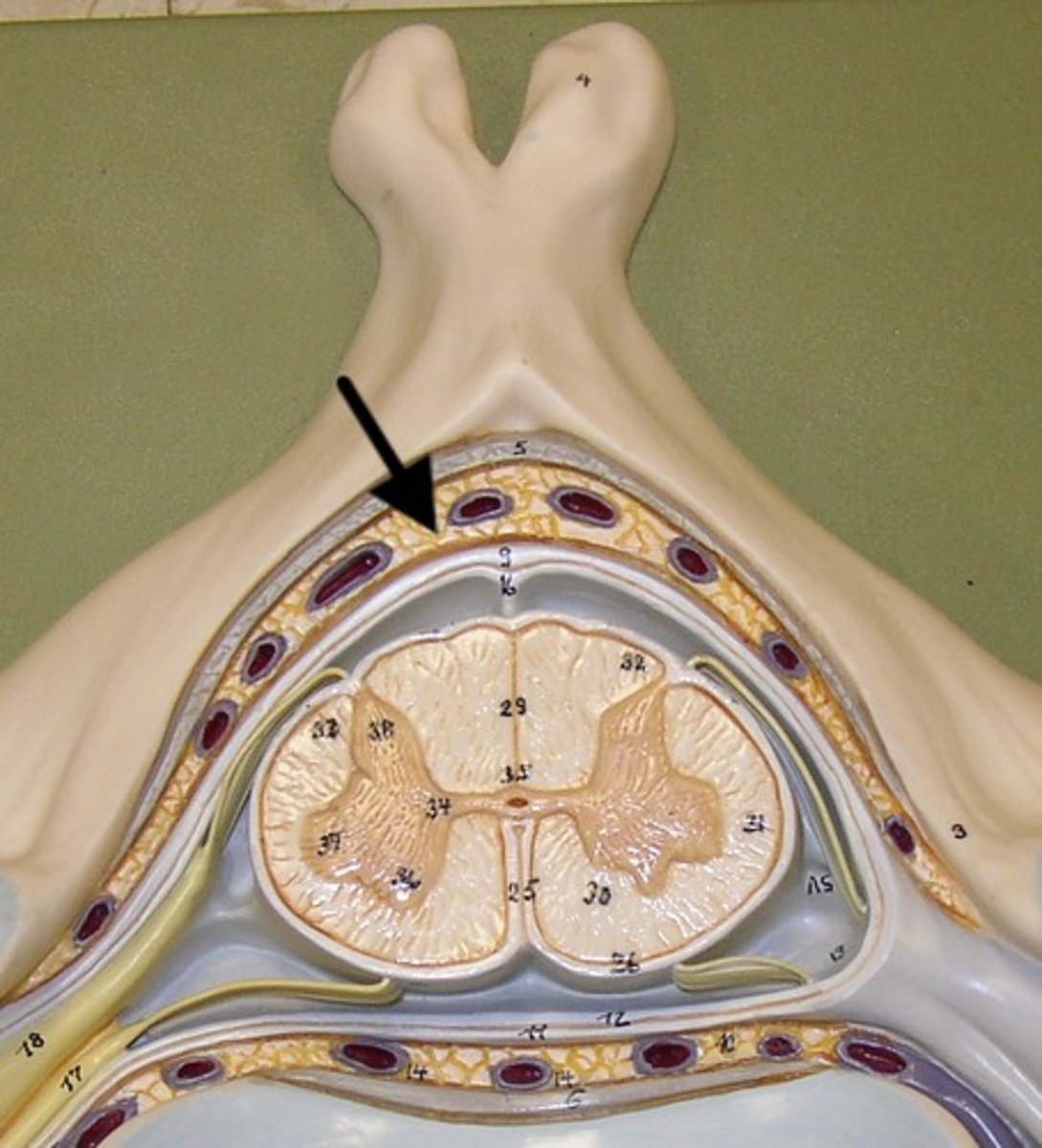
subarachnoid space
a space in the meninges beneath the arachnoid membrane and above the pia mater that contains the cerebrospinal fluid
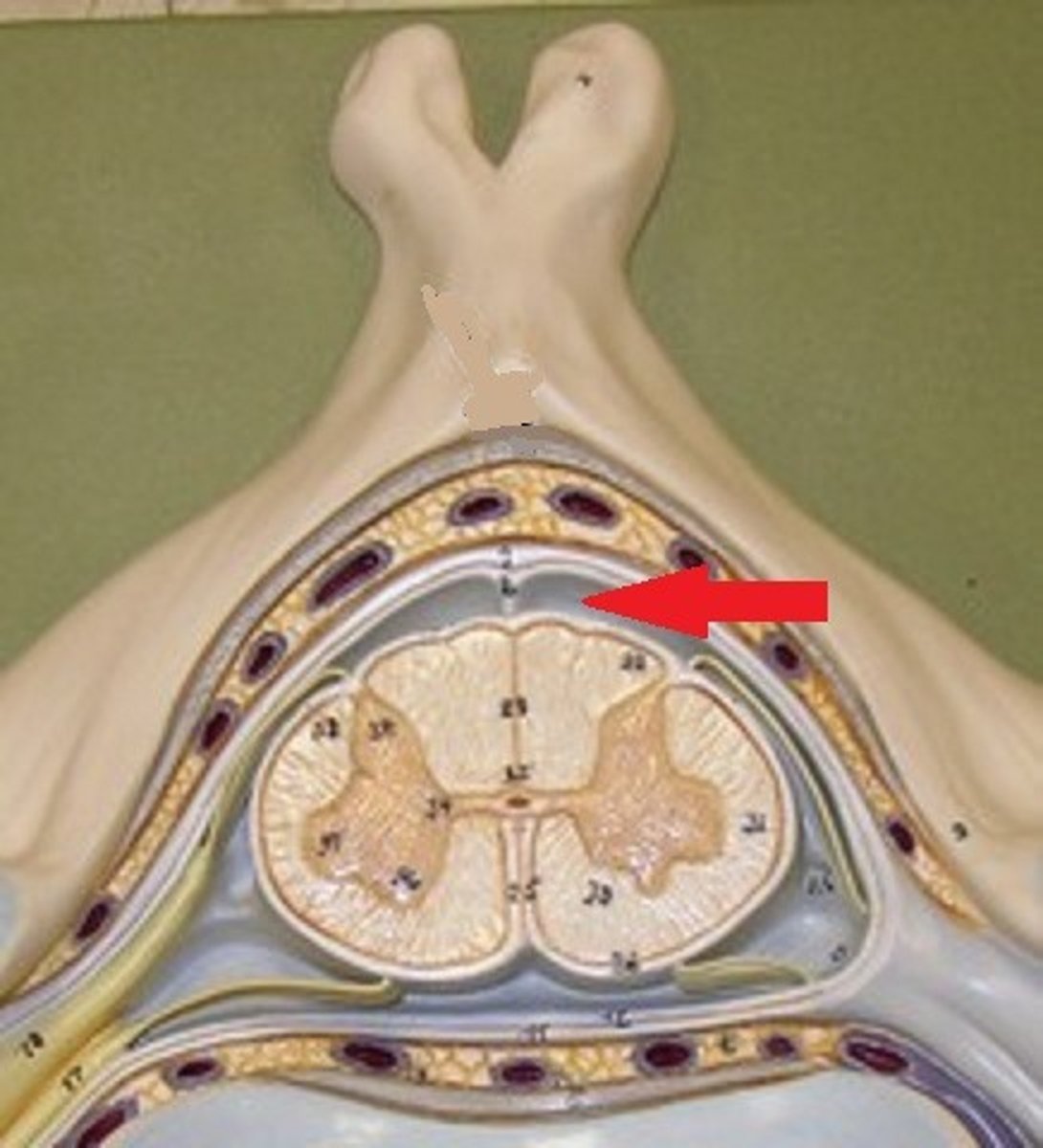
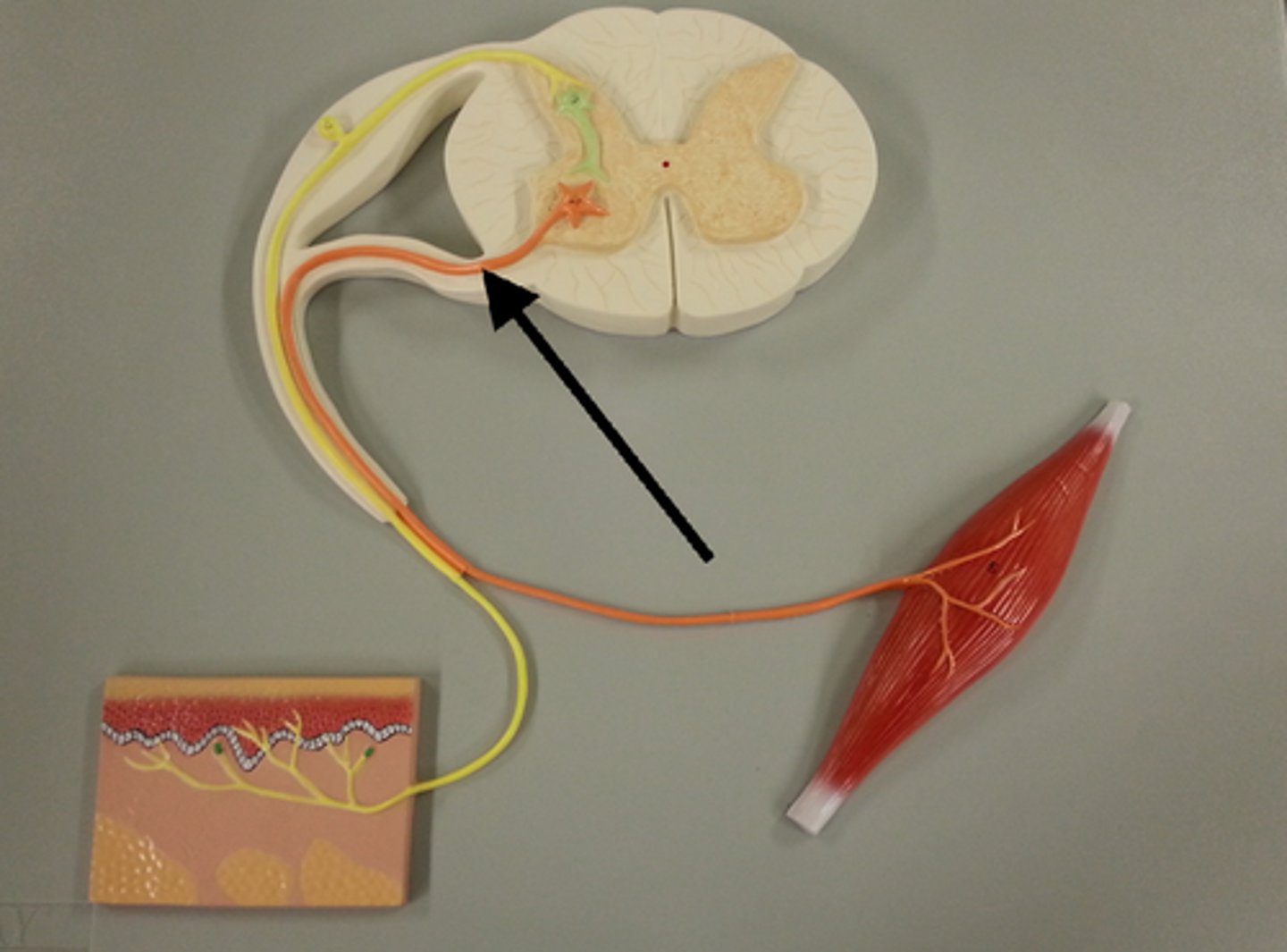
ventral root of spinal nerve
Contains axons of efferent motor neurons
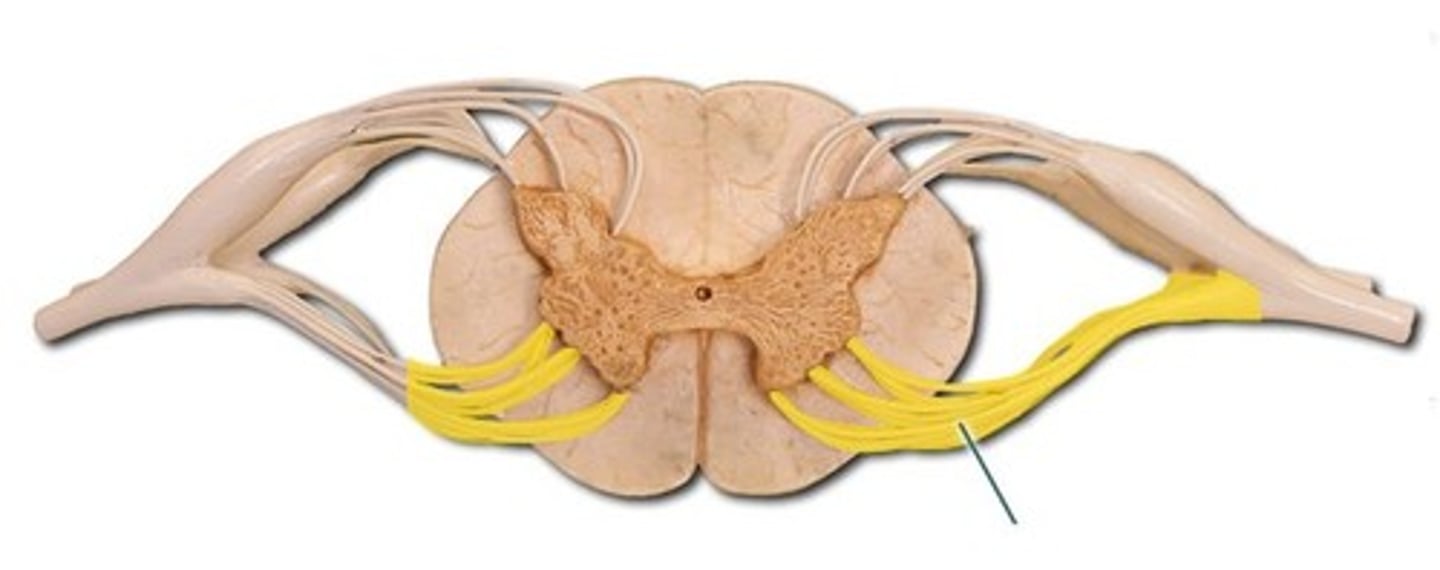
dorsal root of spinal nerve
Contains axons of afferent sensory neurons
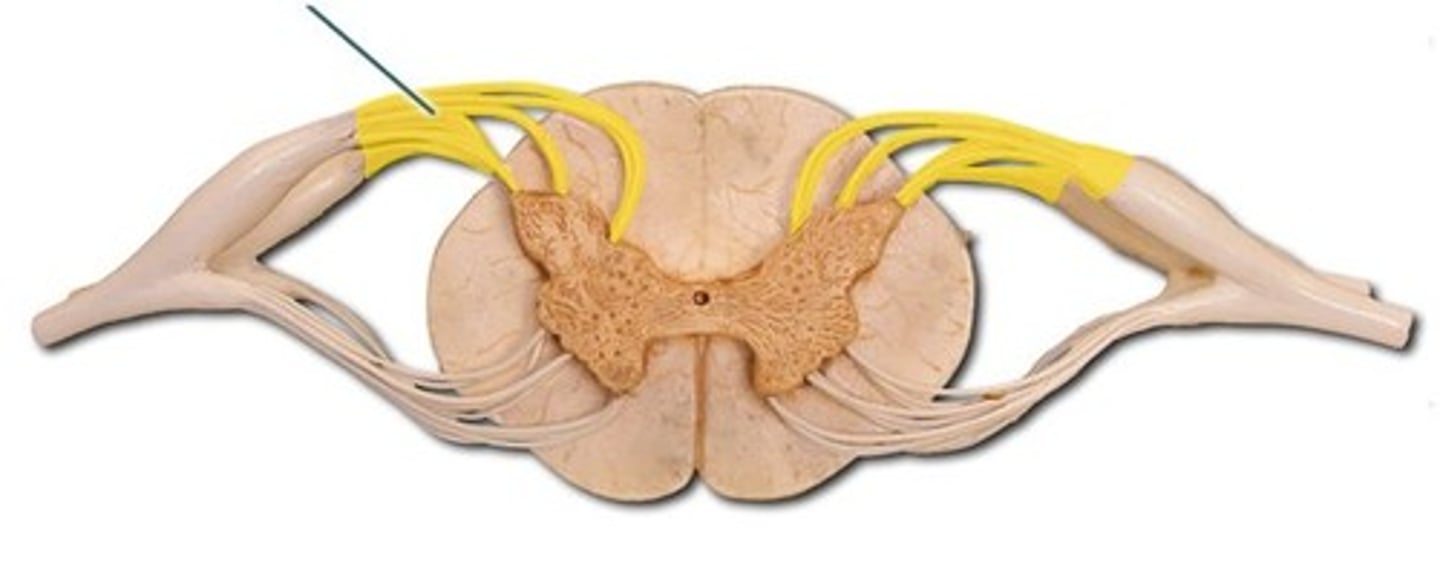
dorsal root ganglia
contain cell bodies of sensory neurons
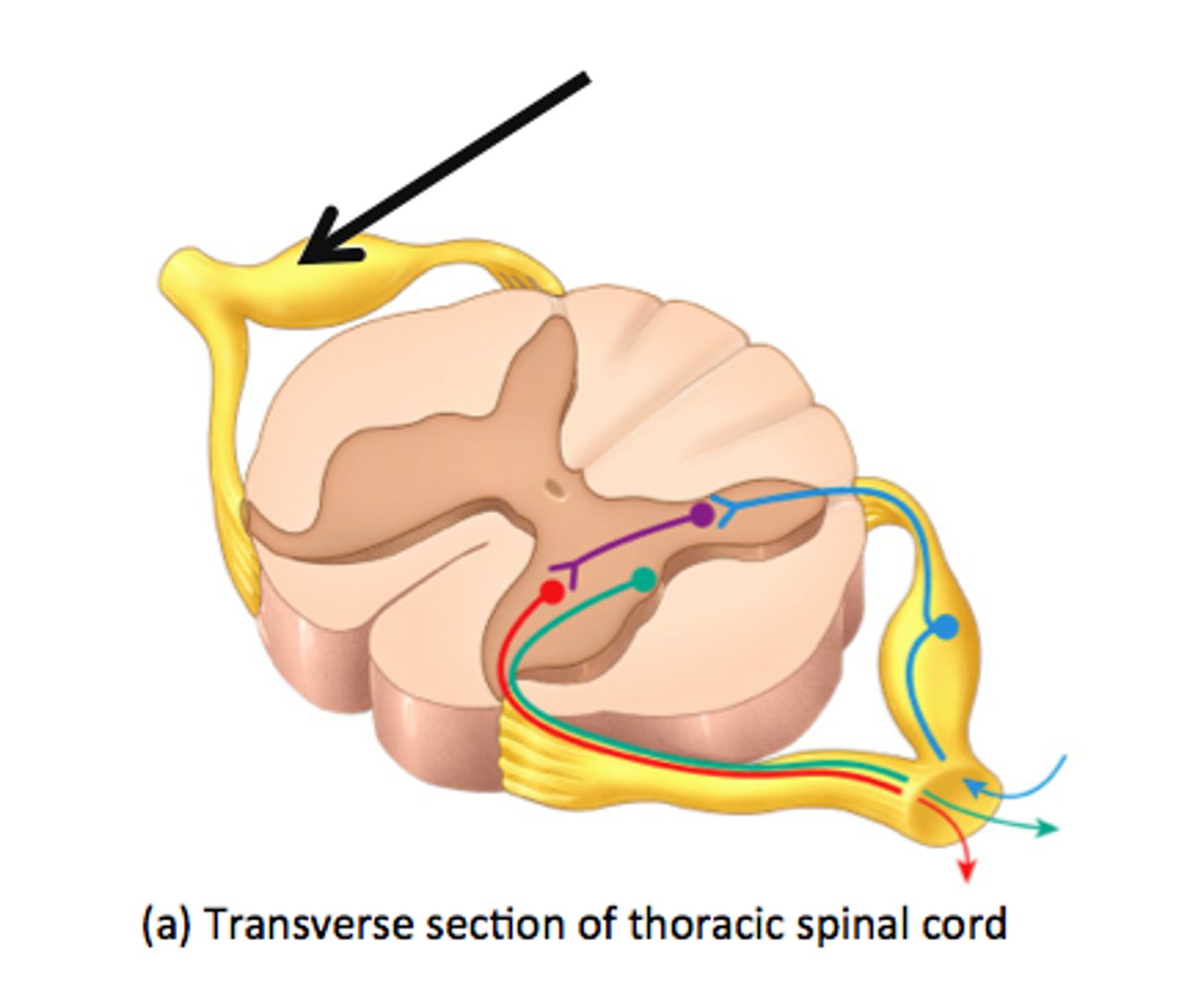
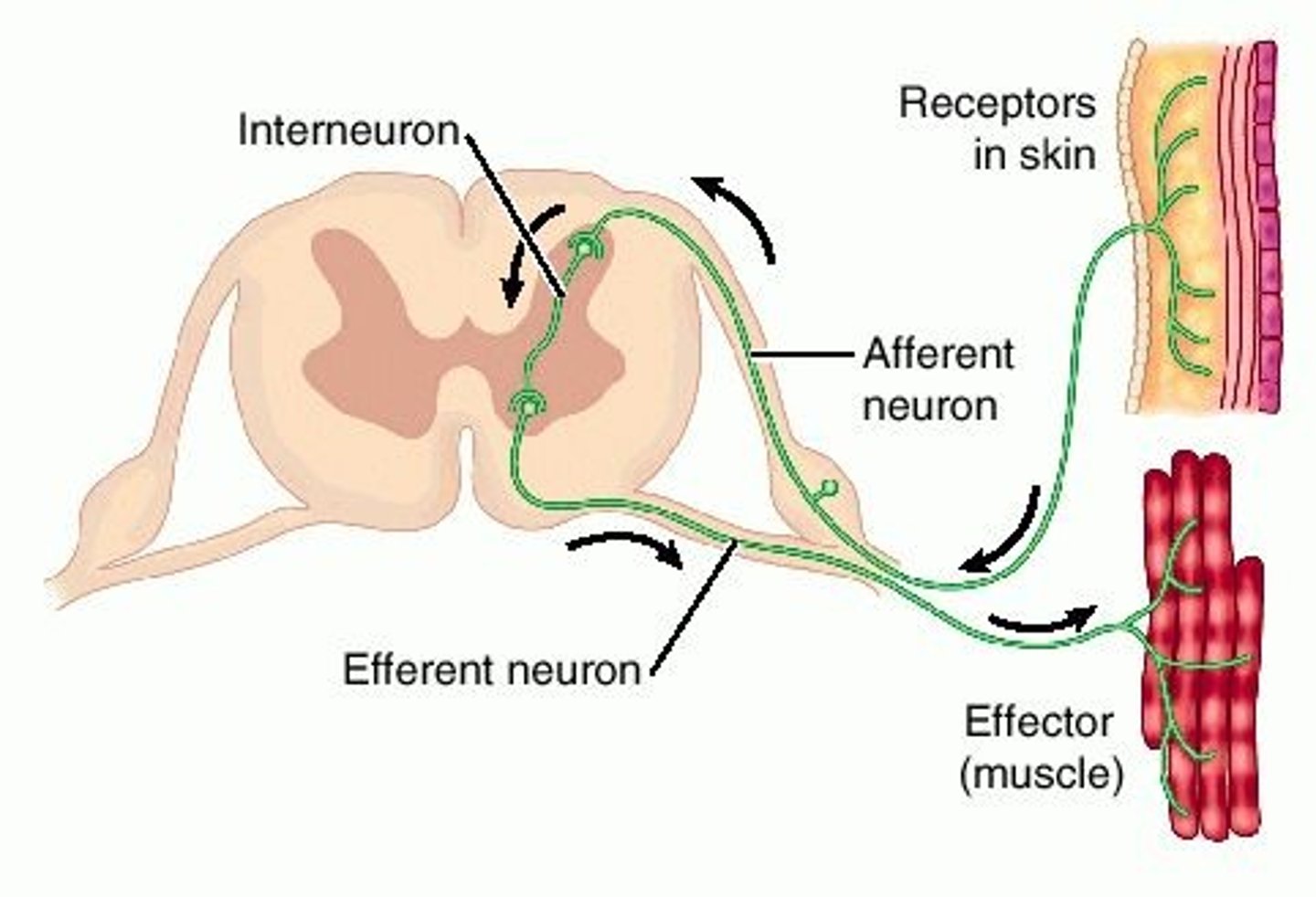
receptor in reflex arc
sensory organ containing sensory receptors (such as receptors in skin, ear, etc)
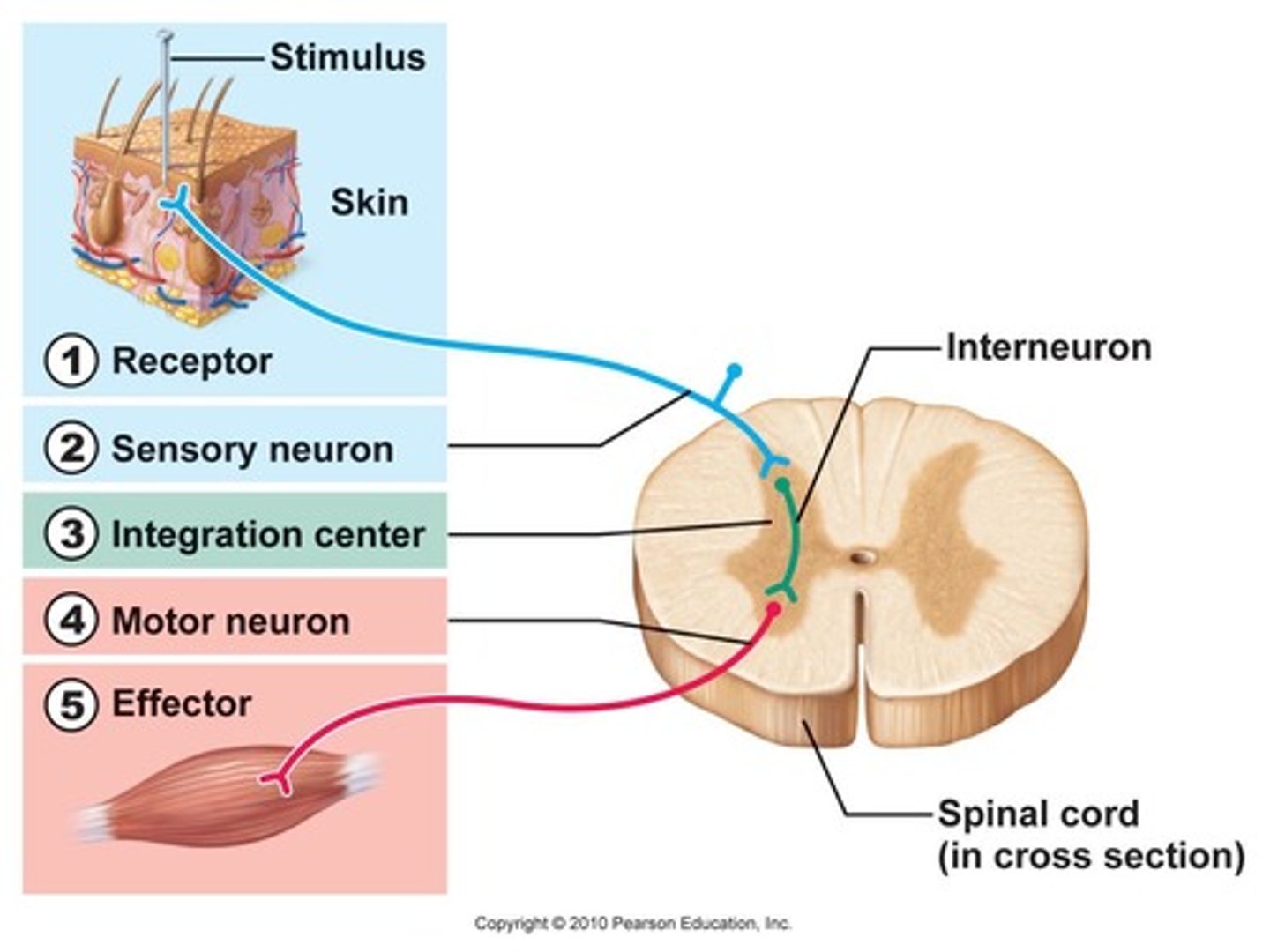
effector in reflex arc
muscle or gland that responds to the efferent impulse
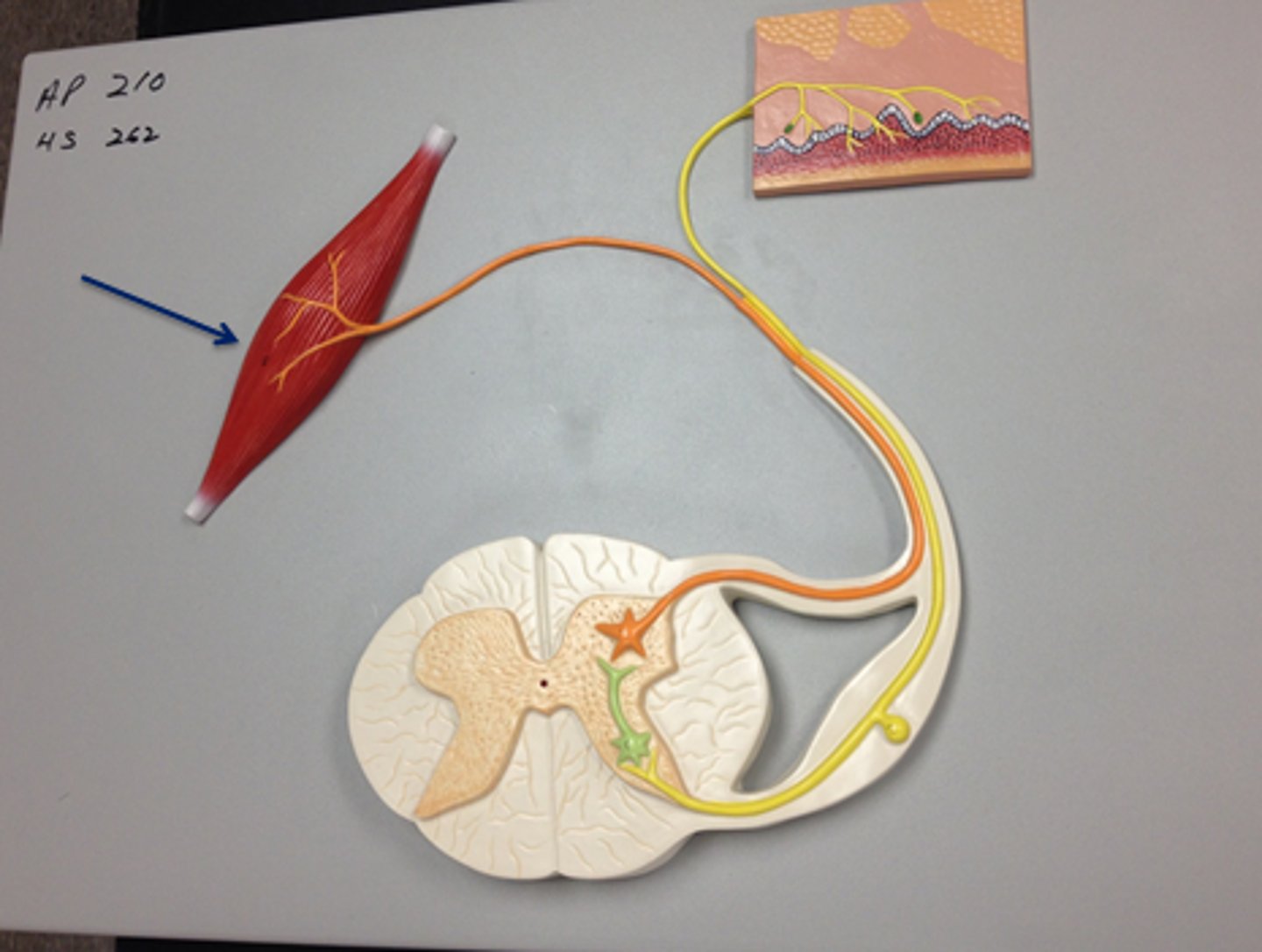
Interneuron (reflex arc)
relays and (sometimes) processes sensory information
motor neuron of reflex arc
axon conducts impulses from integrating center to effector
Where is cell body of efferent motor neuron in a reflex arc?
Ventral gray horn
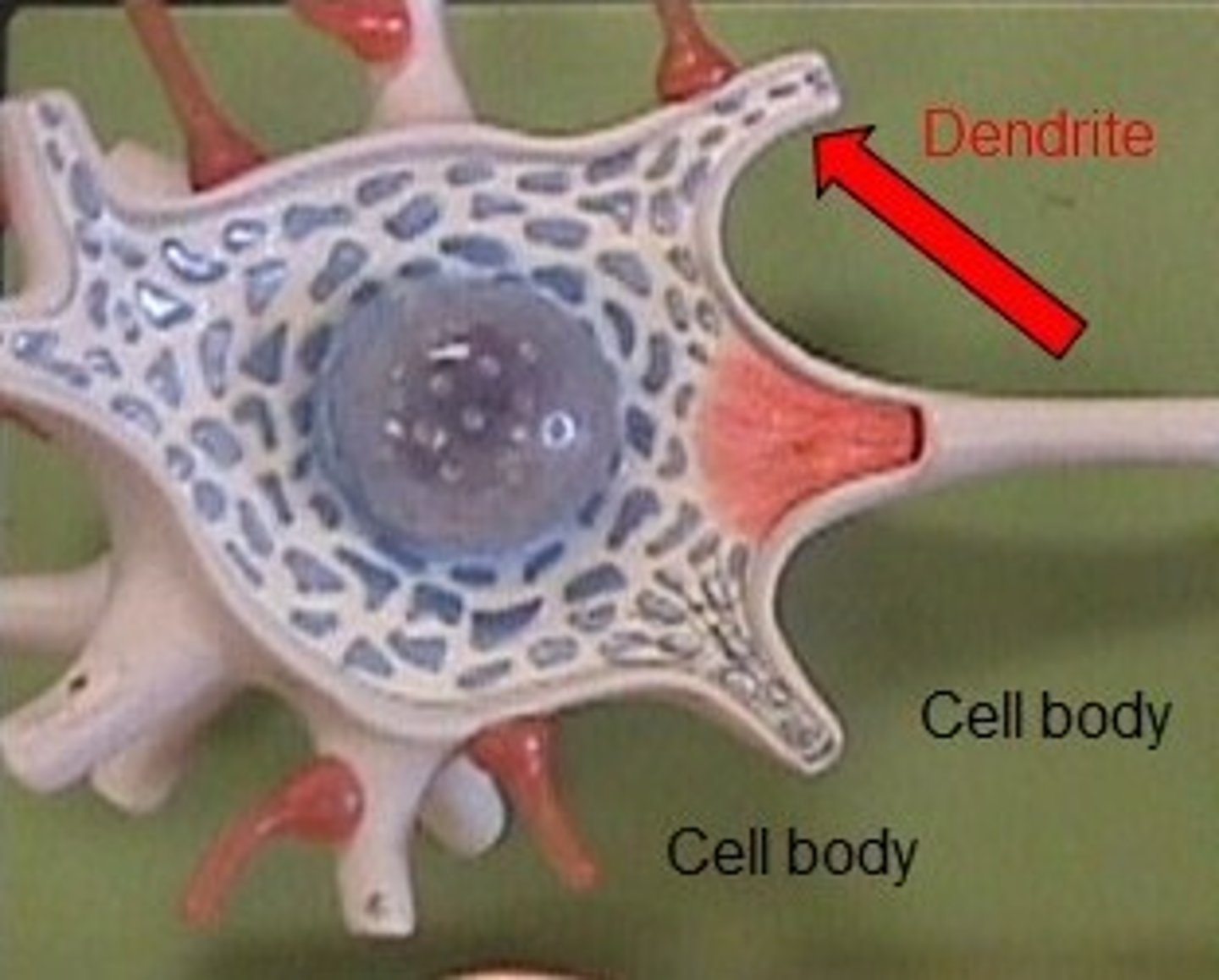
dendrite
Branchlike parts of a neuron that are specialized to receive information.
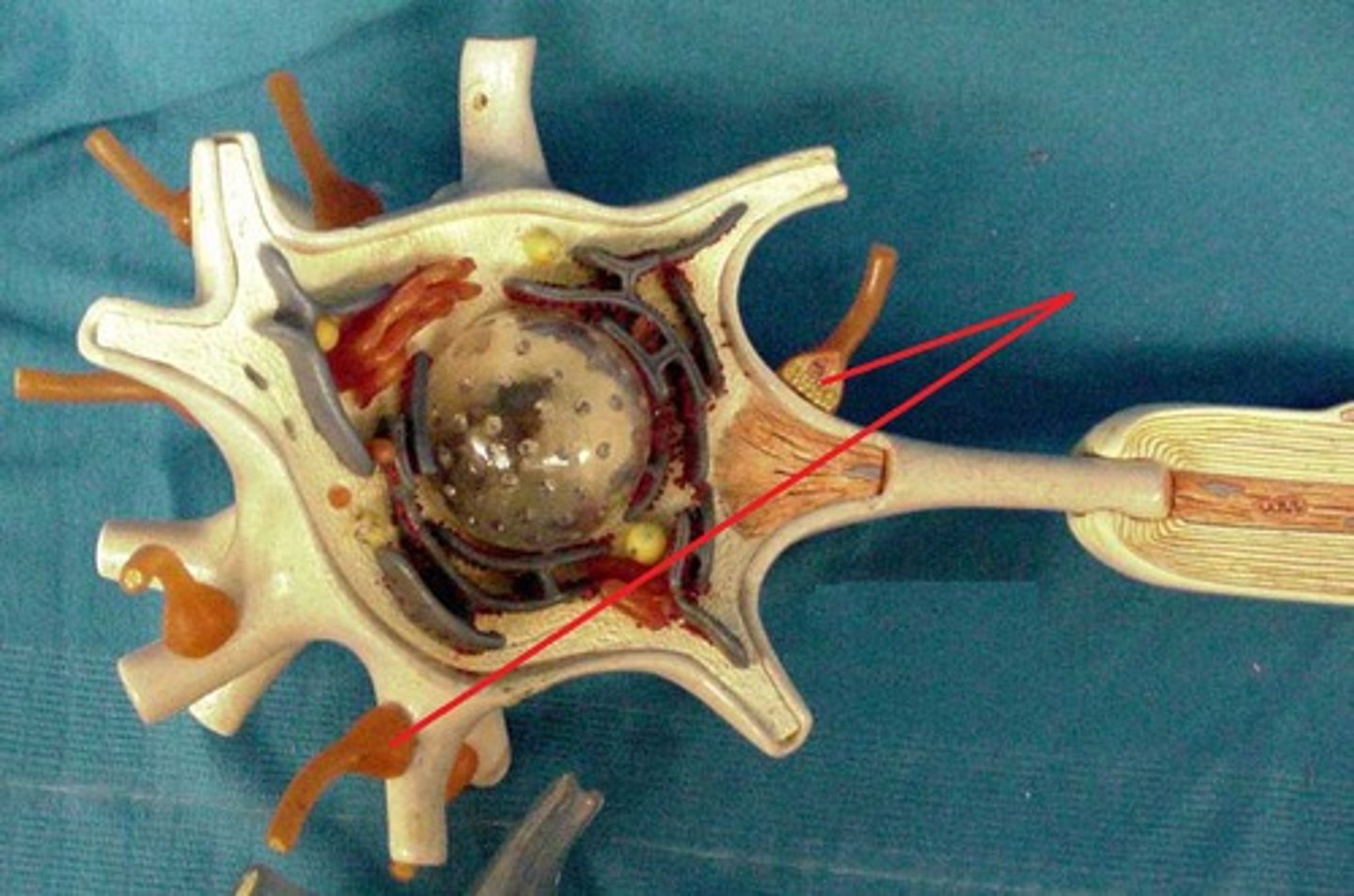
terminal boutons (axon terminals)
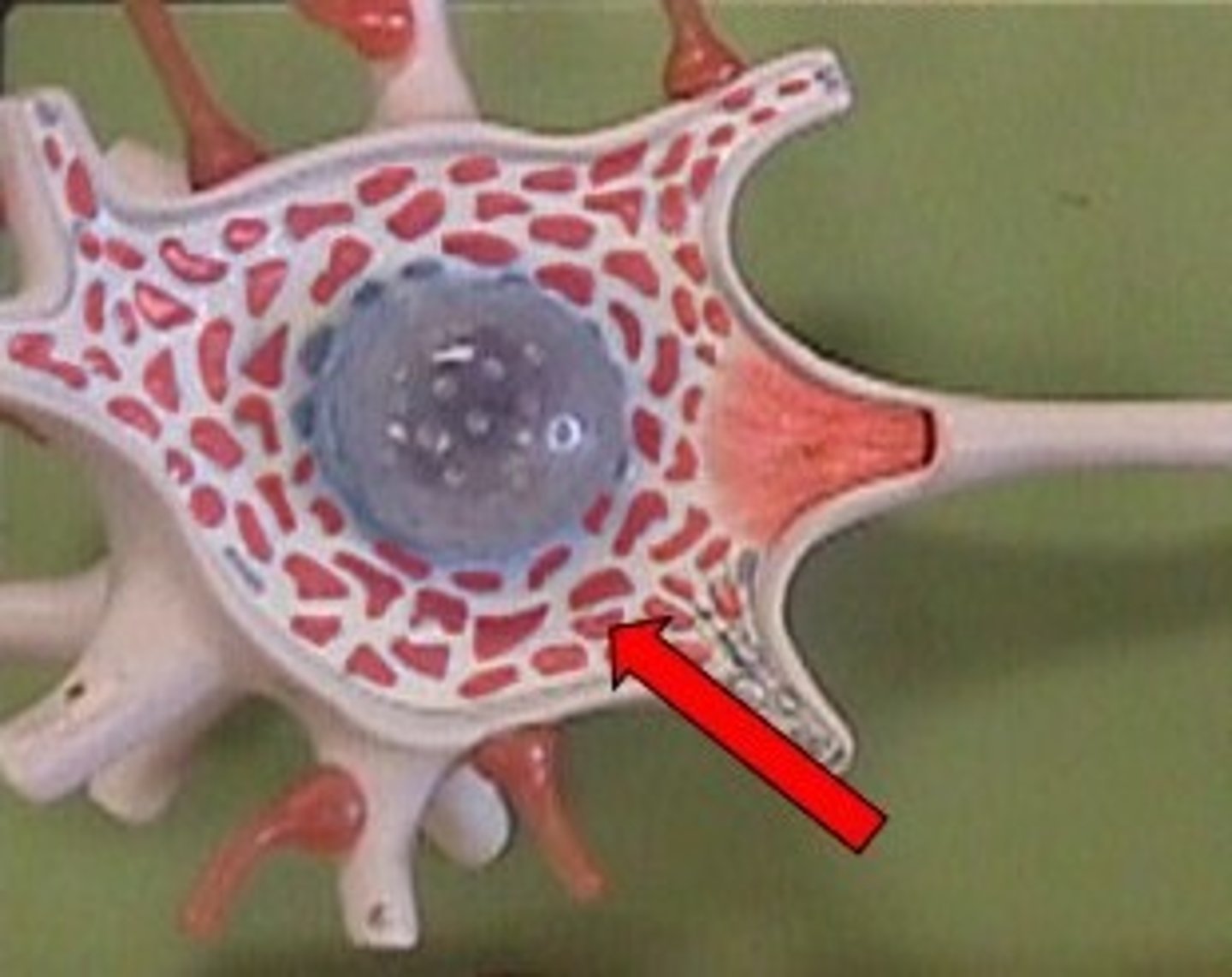
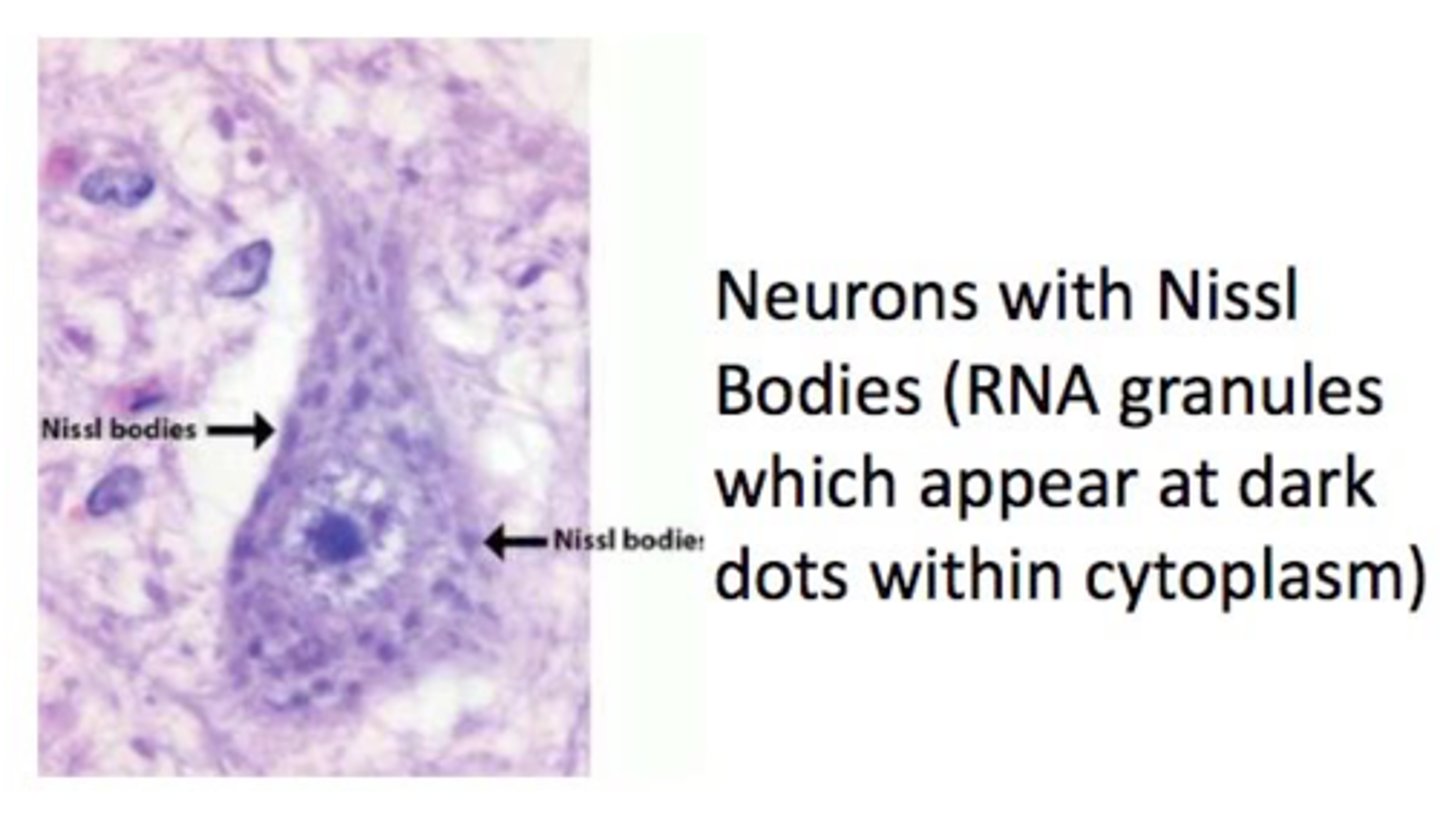
Nissl bodies
Rough endoplasmic reticulum in neuron
What are Nissl bodies made of?
Rough ER
axon hillock
Cone shaped region of an axon where it joins the cell body - summation occurs here
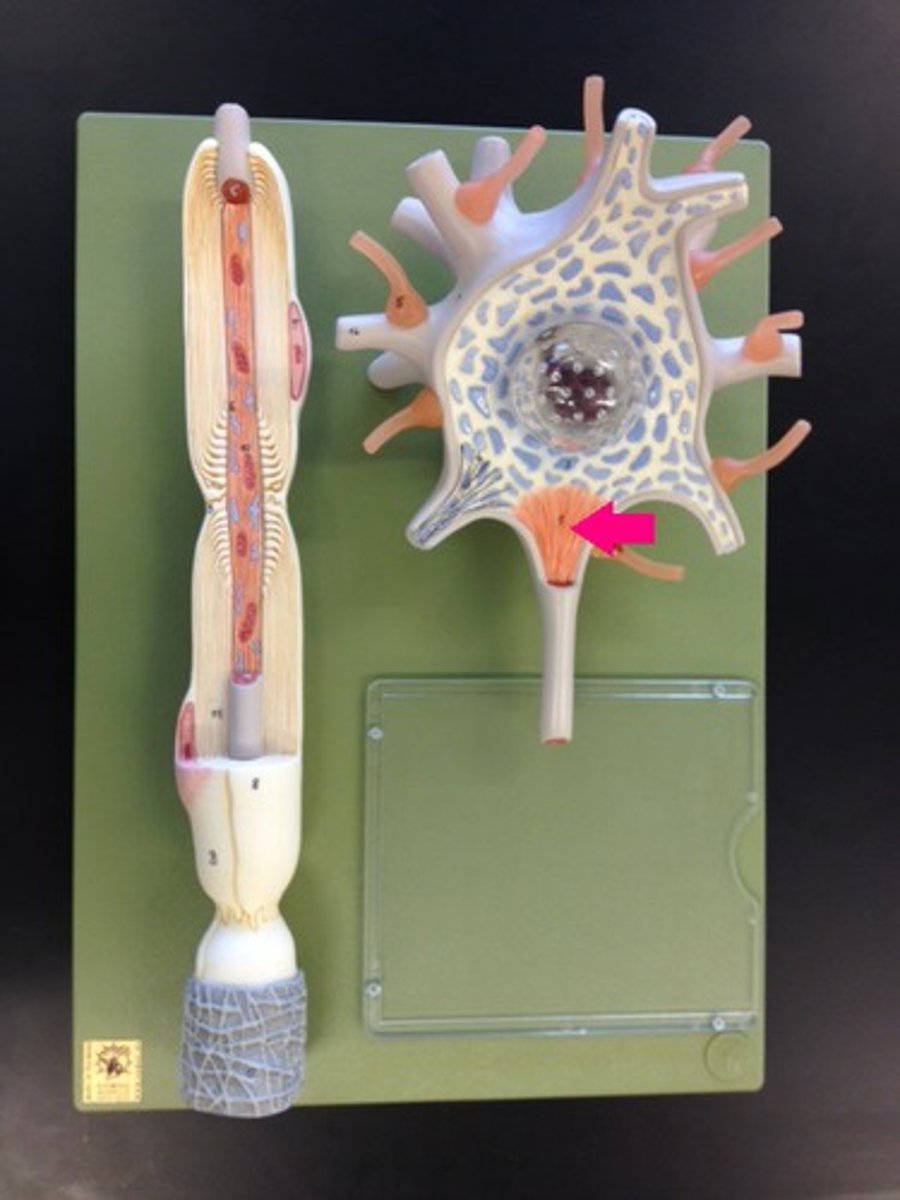
node of ranvier
a gap in the myelin sheath of a nerve, between adjacent Schwann cells.
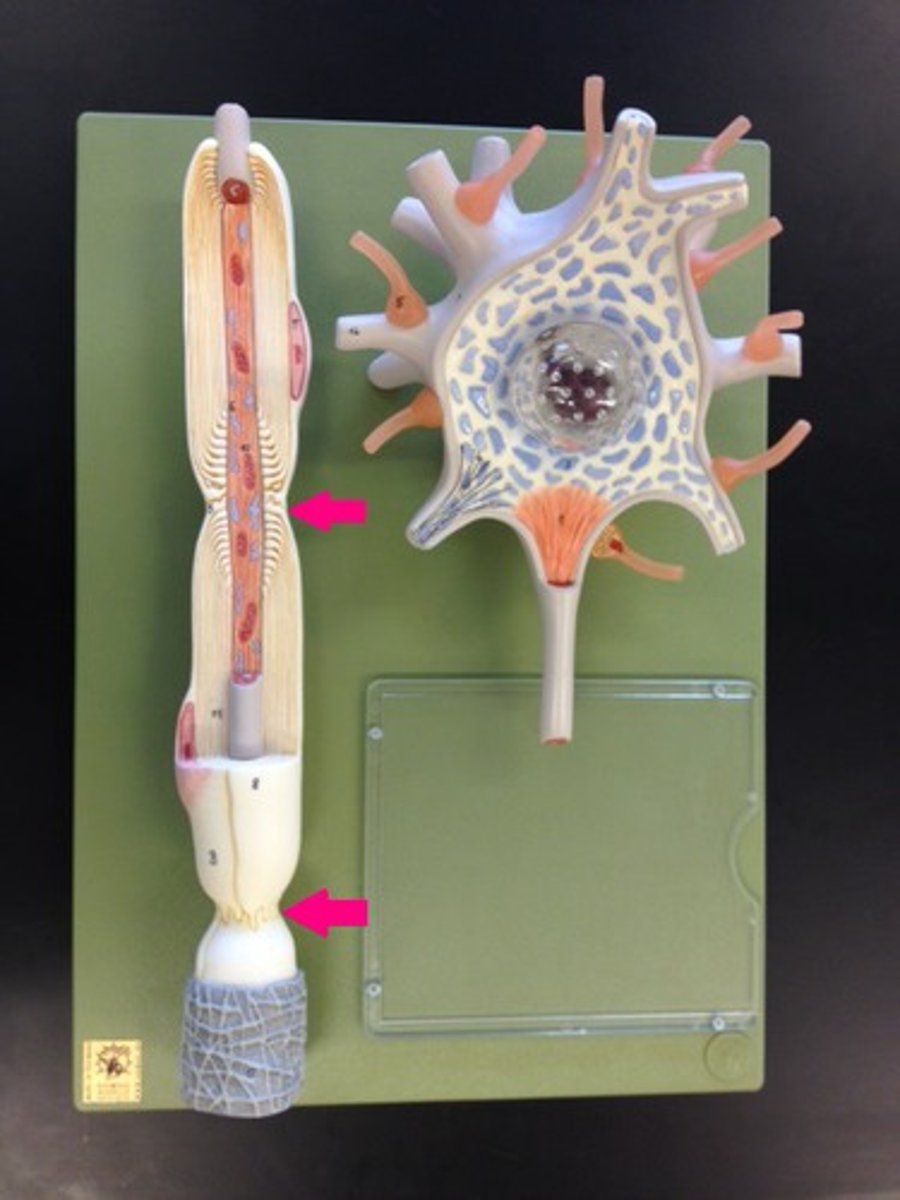
nucleus of schwann cell
neurolemma of schwann cell
schwann cell
Creates myelin sheaths in peripheral nervous system
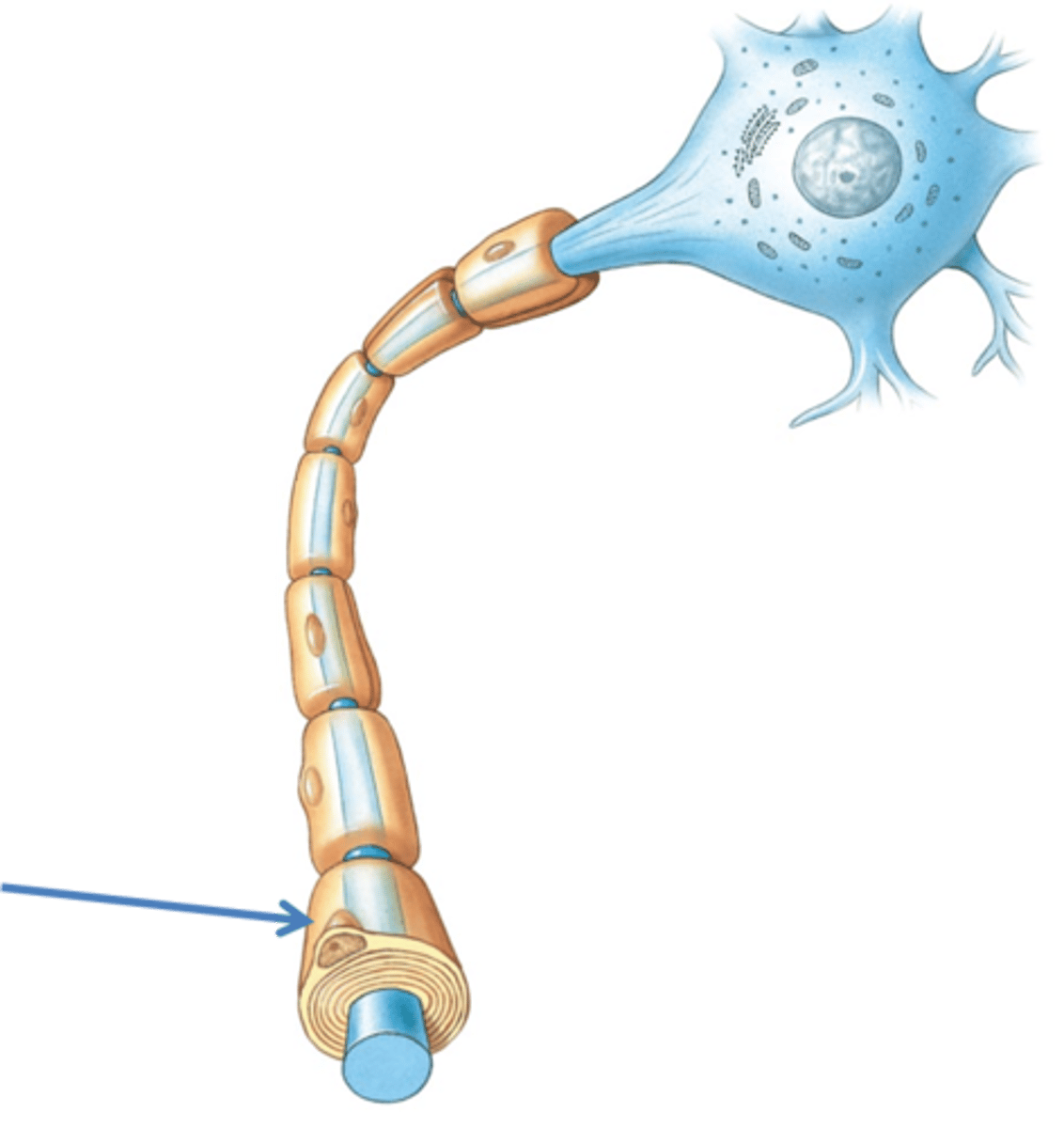
myelin sheath
covers the axon of most neurons and helps insulate and increase speed of impulses
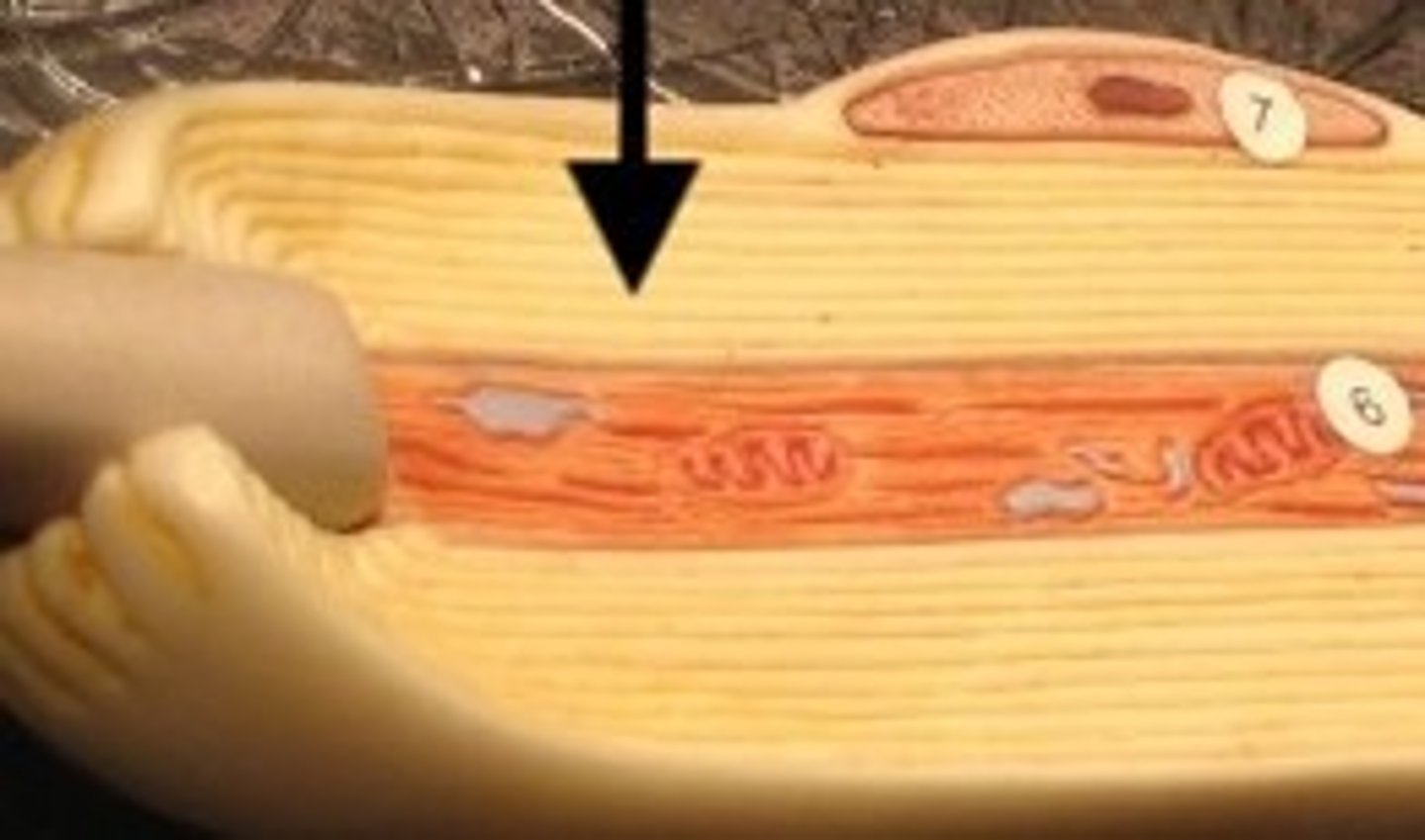
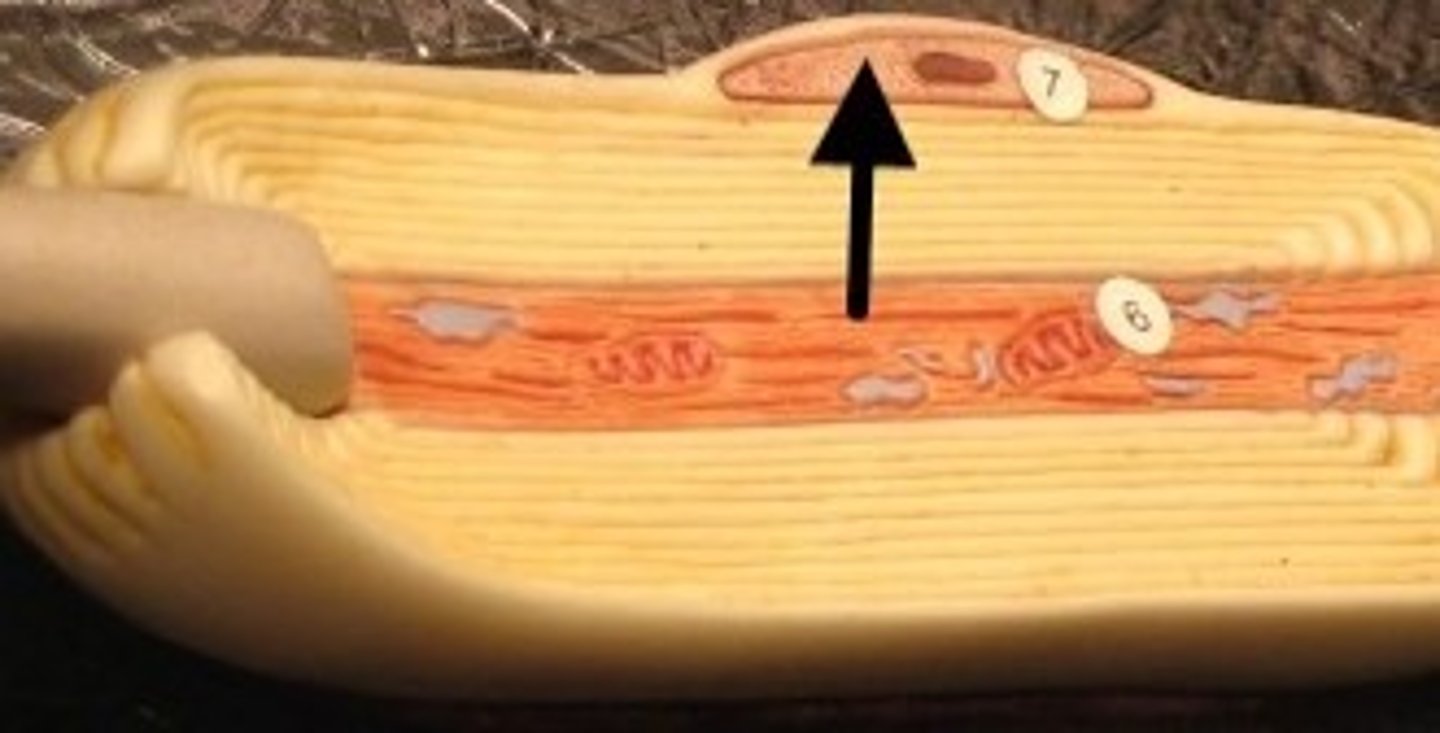
endoneurium
surrounds each nerve cell
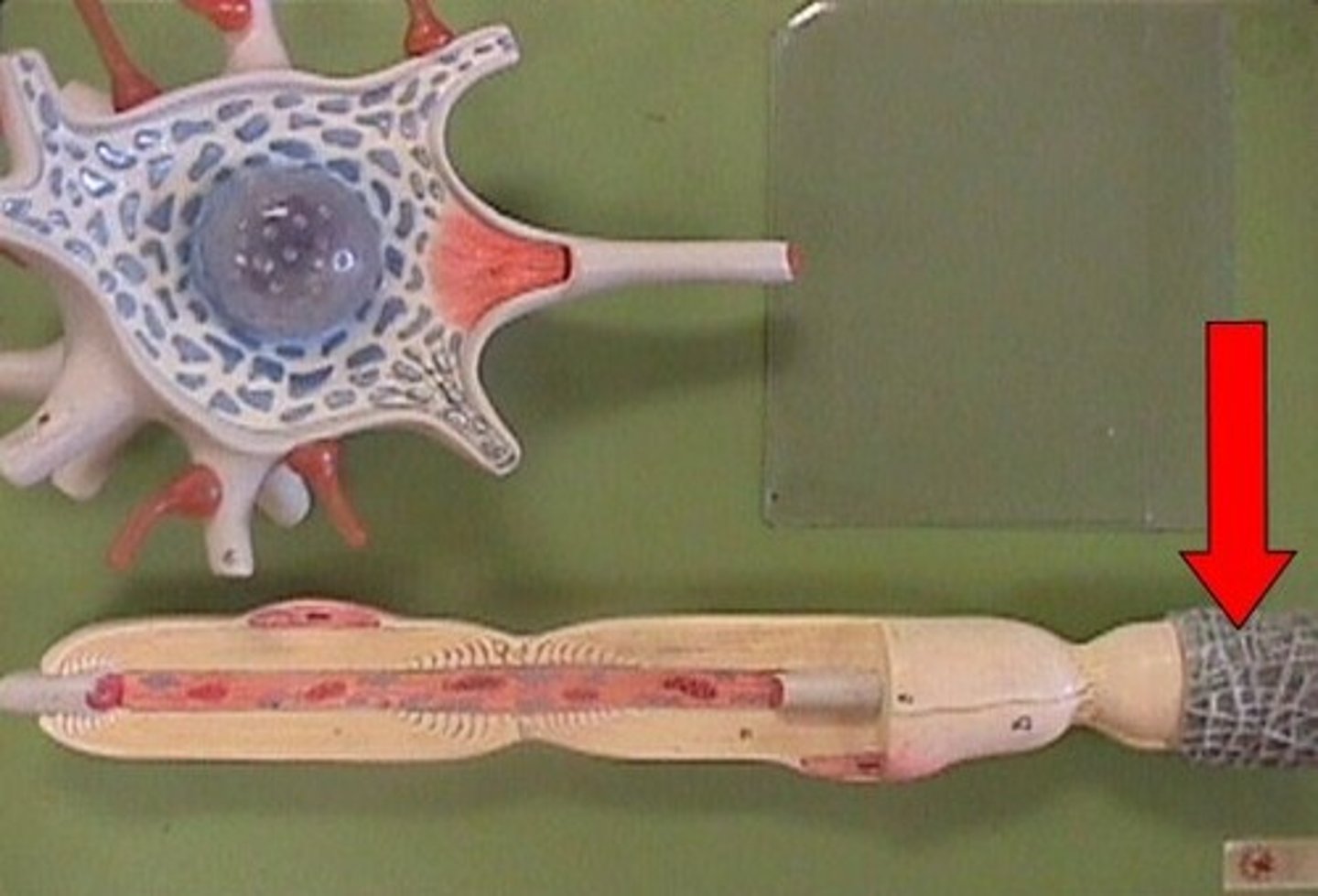
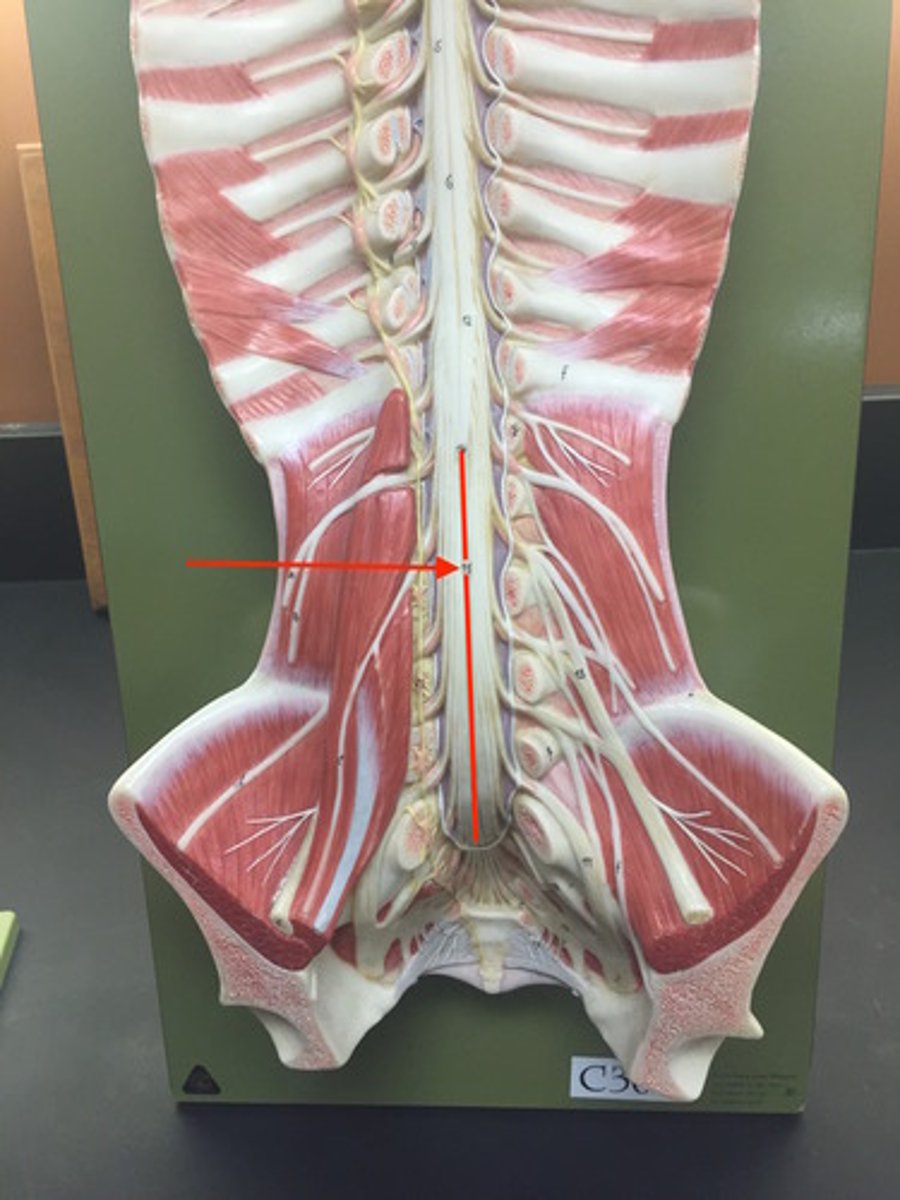
cervical plexus
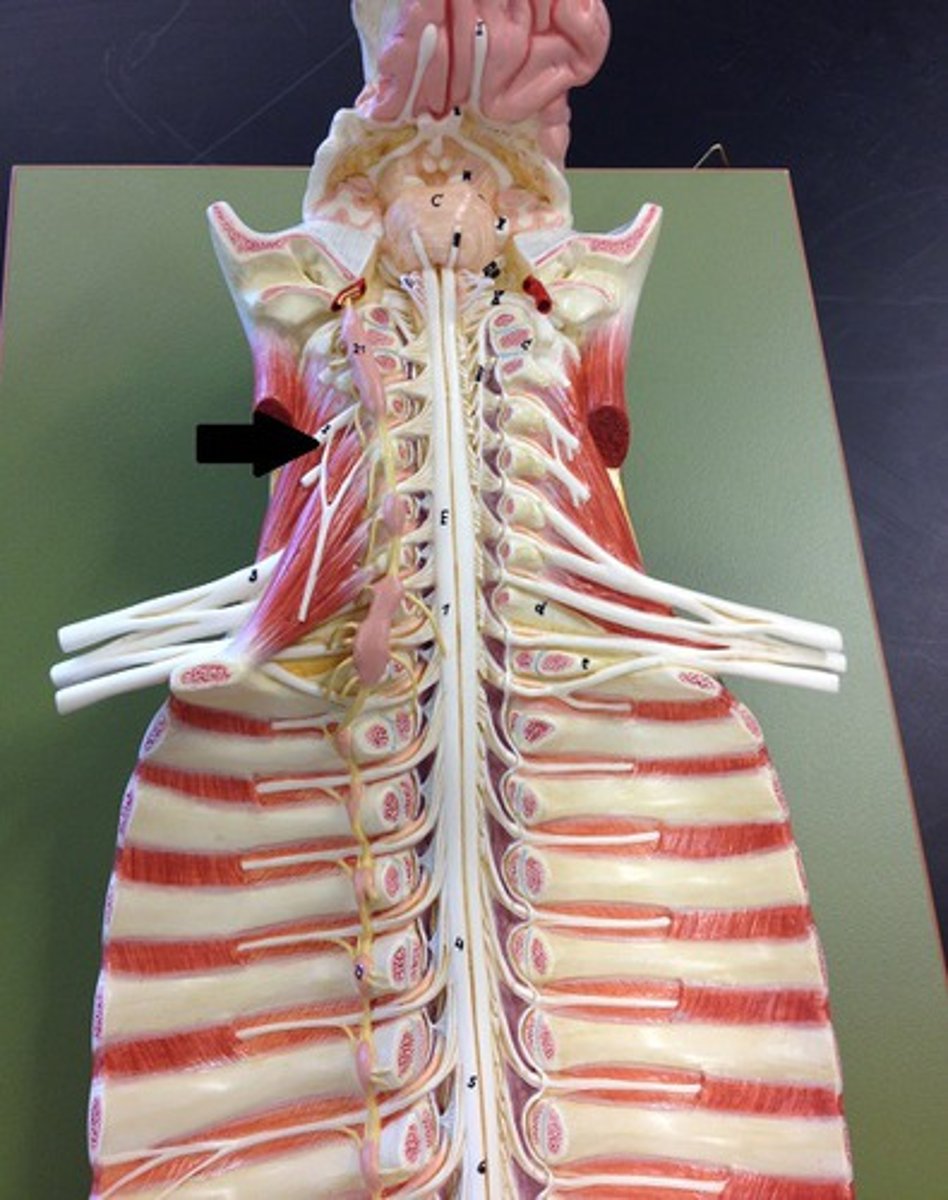
cervical enlargement
nerves of shoulders and upper limbs
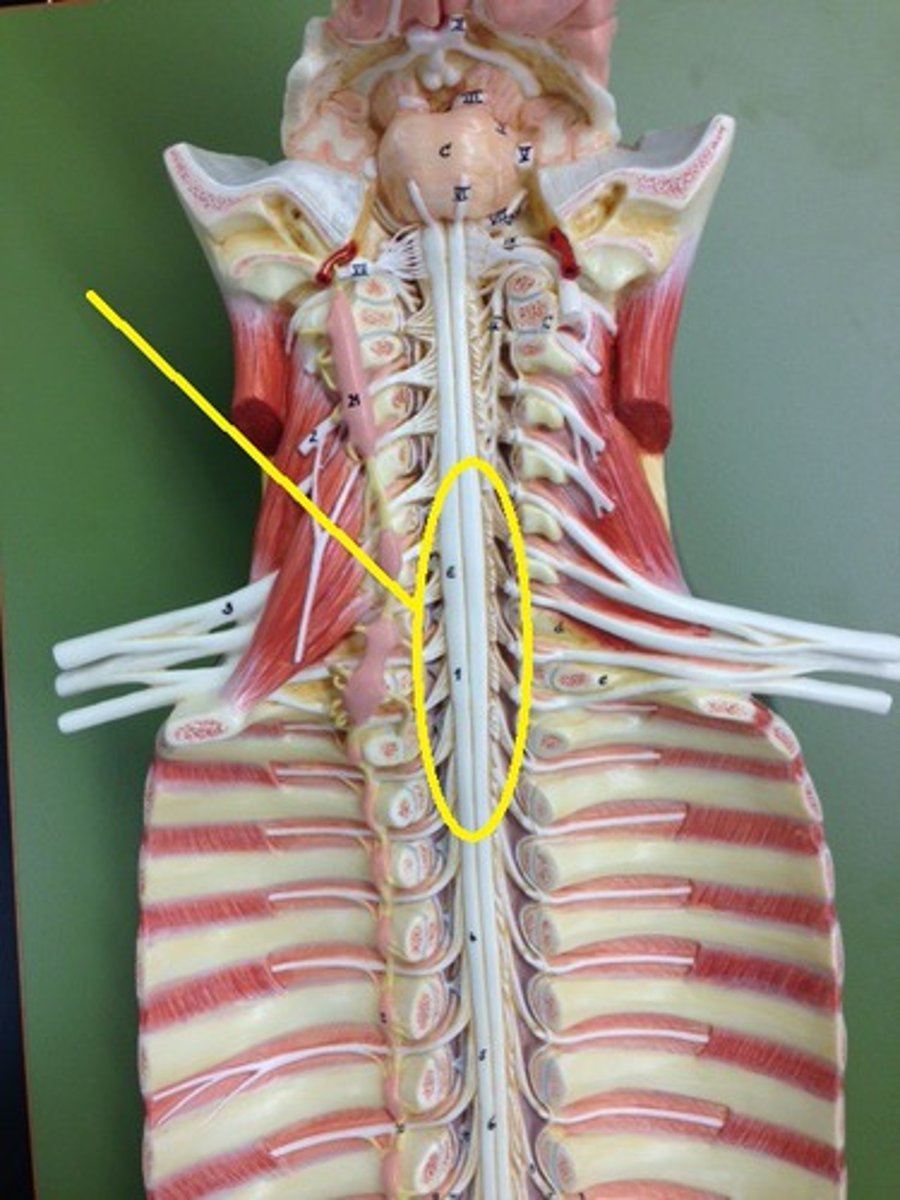
lumbar enlargement
nerves of pelvis and lower limbs
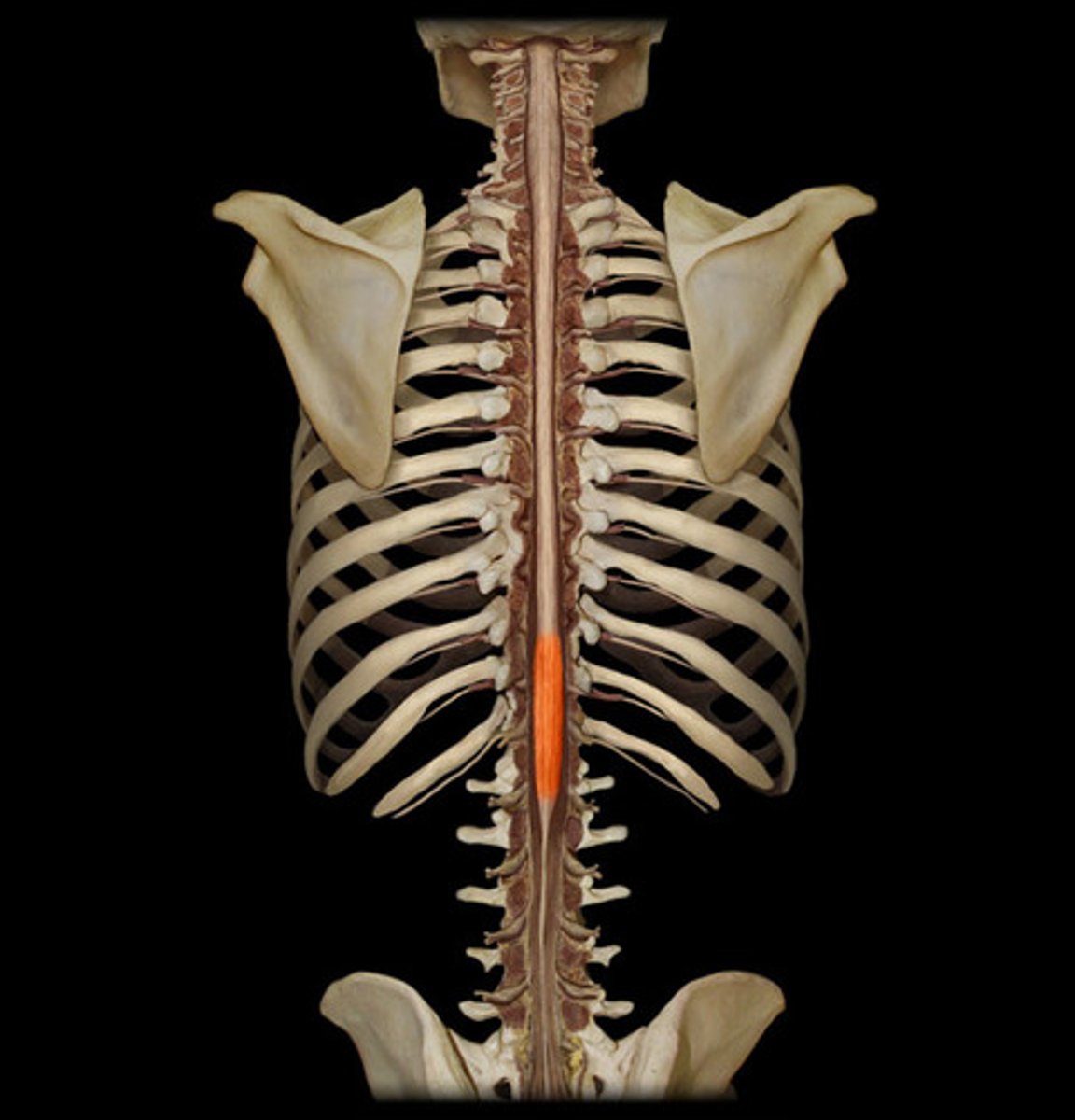
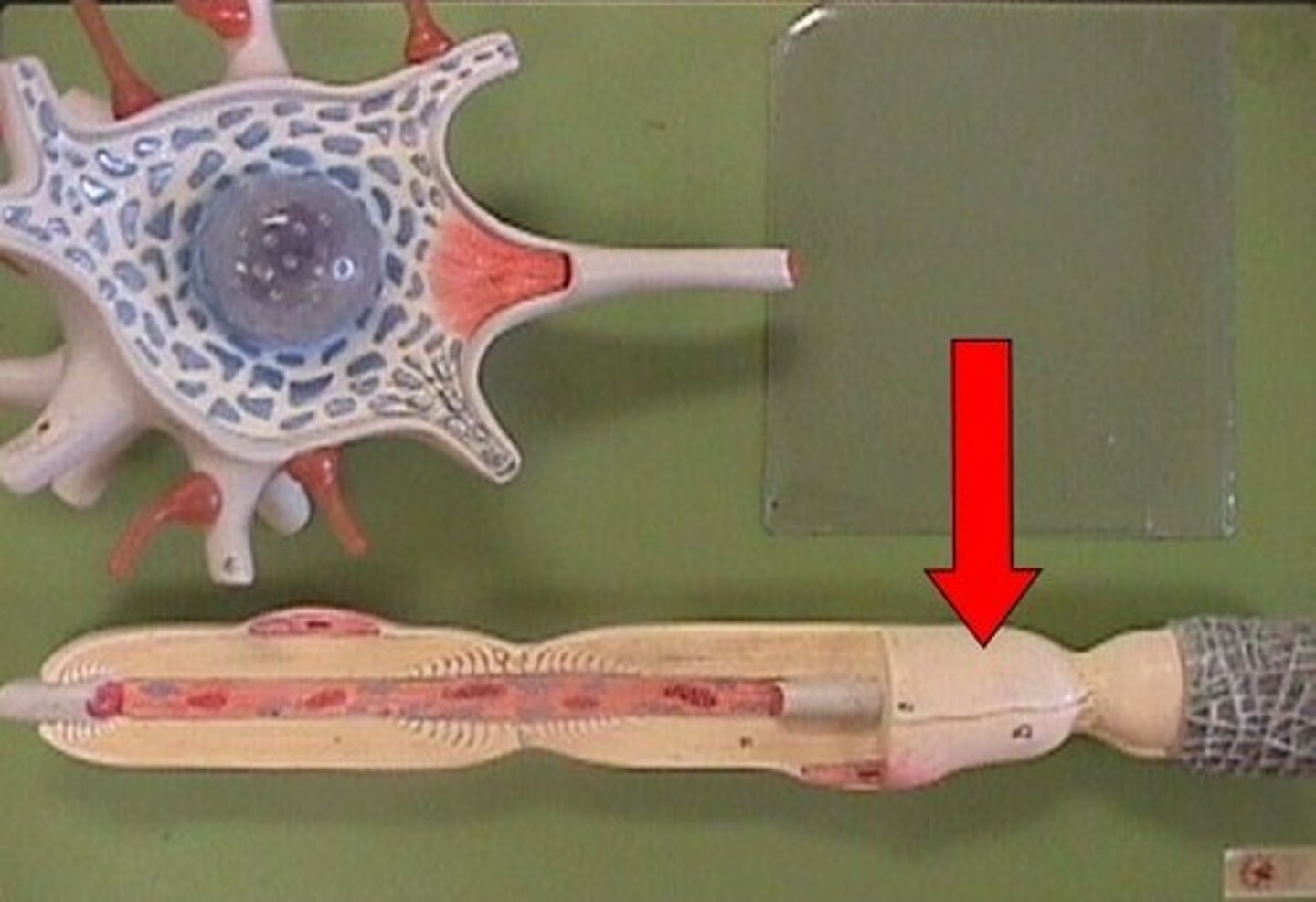
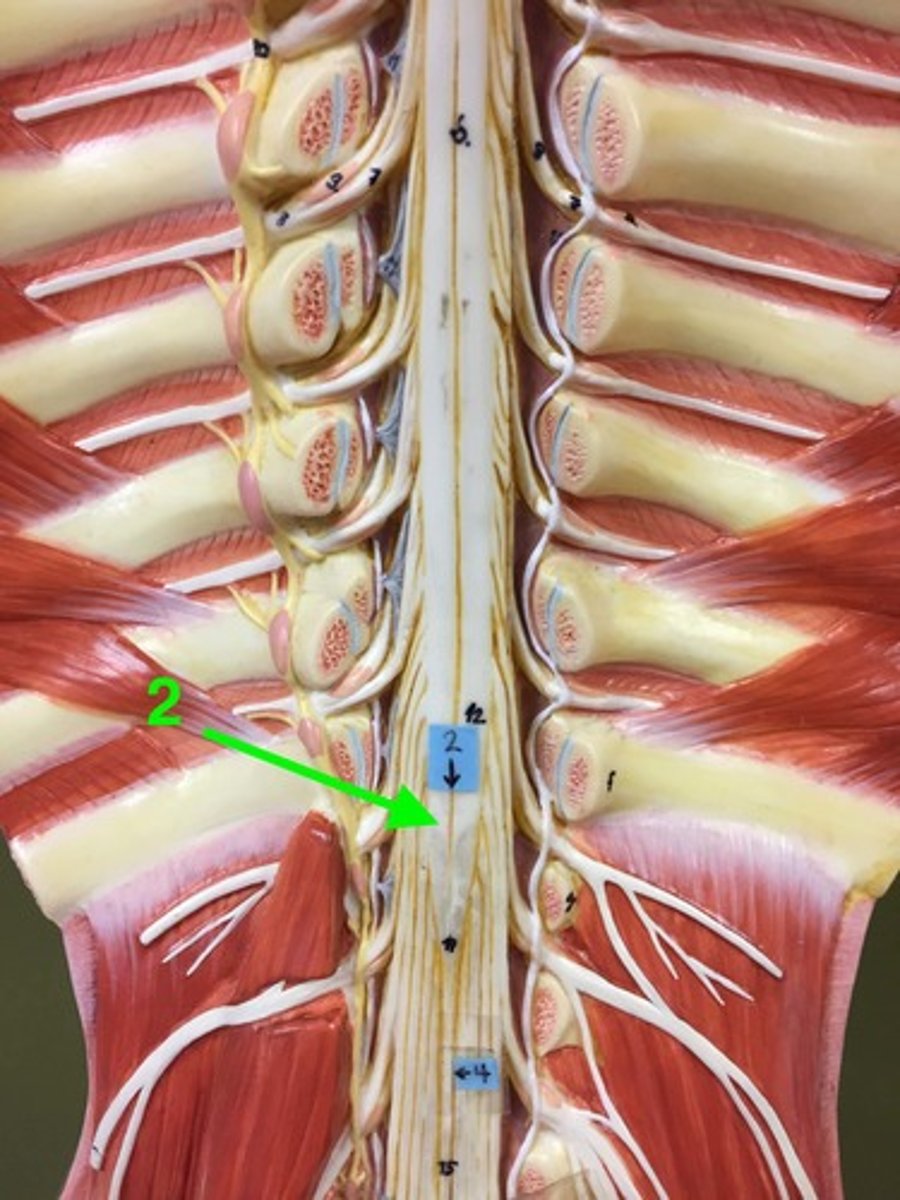
conus medullaris
end of spinal cord
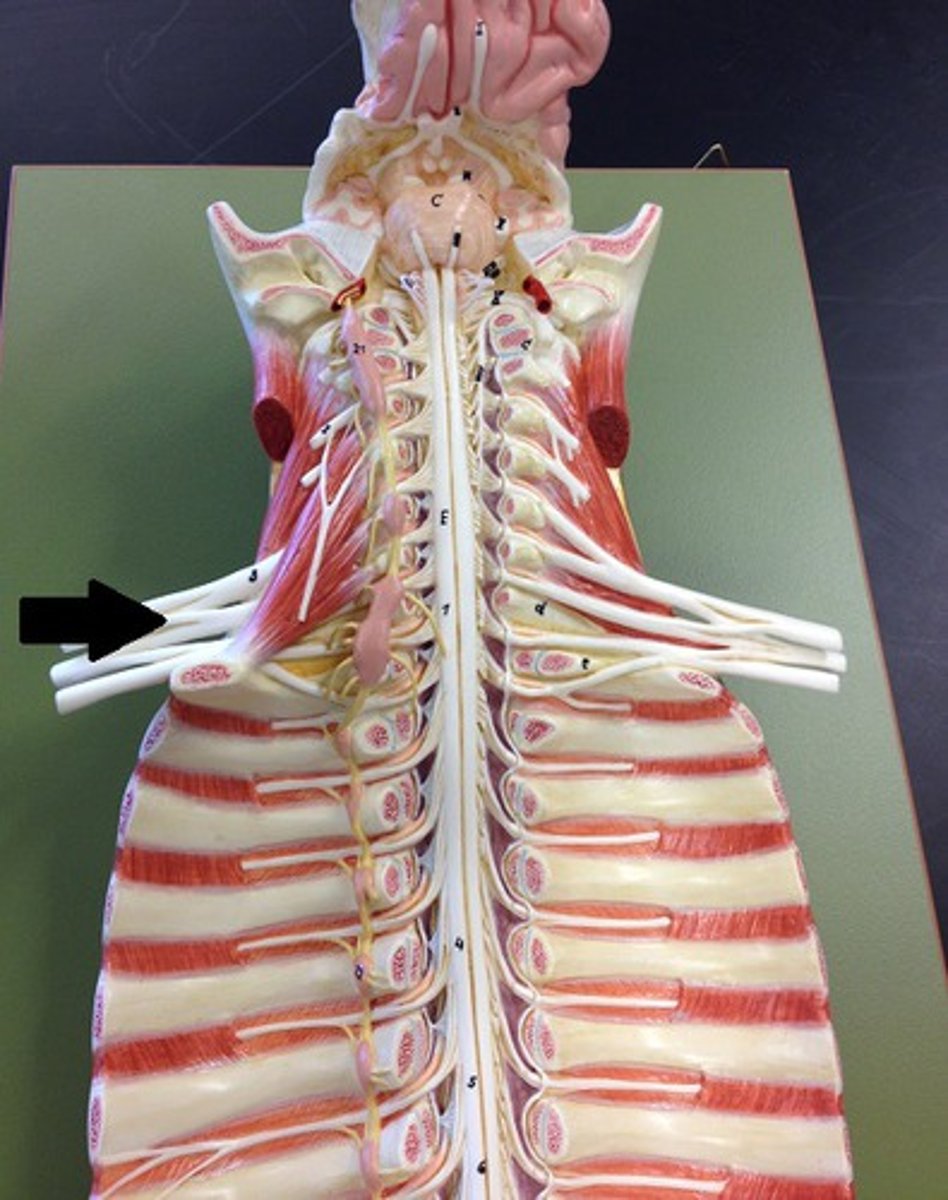
brachial plexus
network of interlacing nerves found in the upper arm area
lumbar plexus
femoral nerve
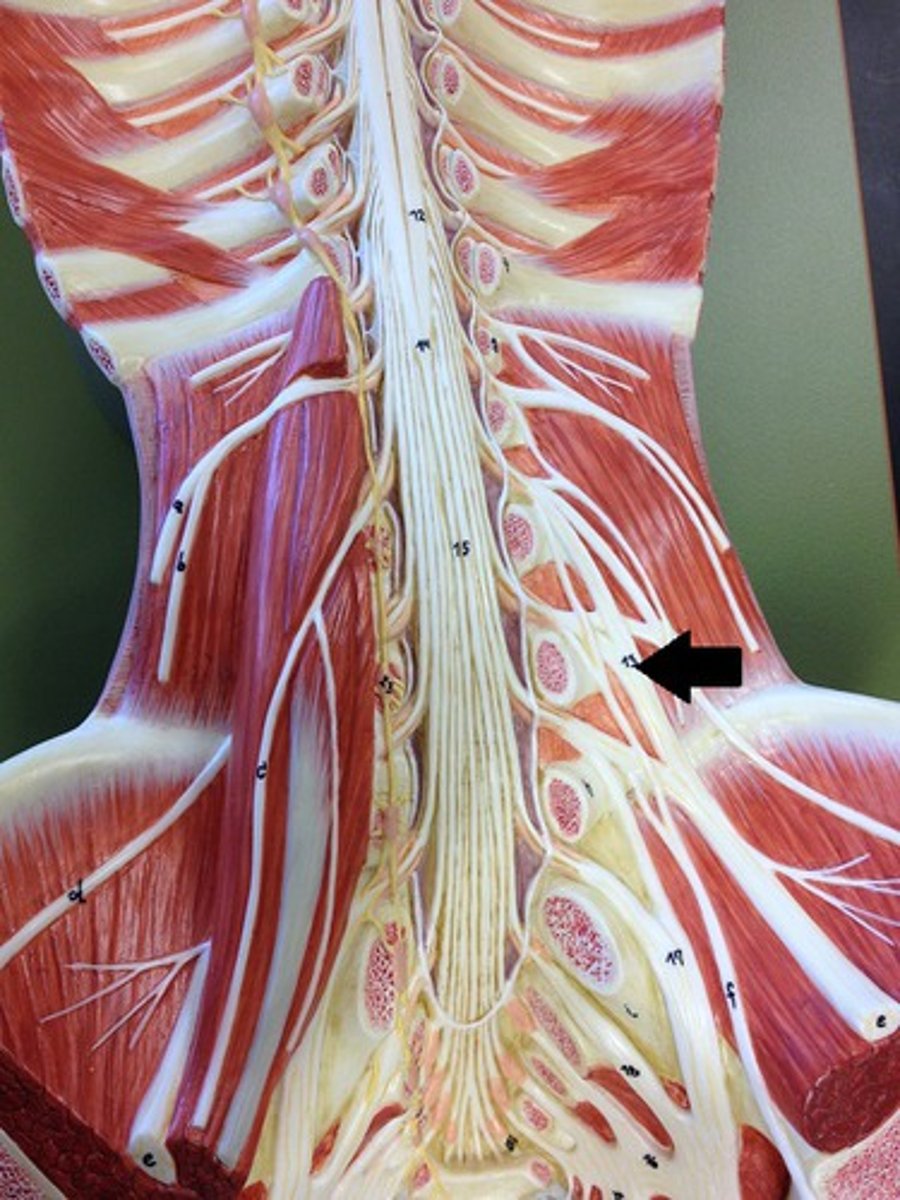
saccral plexus
formed L4 - S4; consists of sciatic nerve
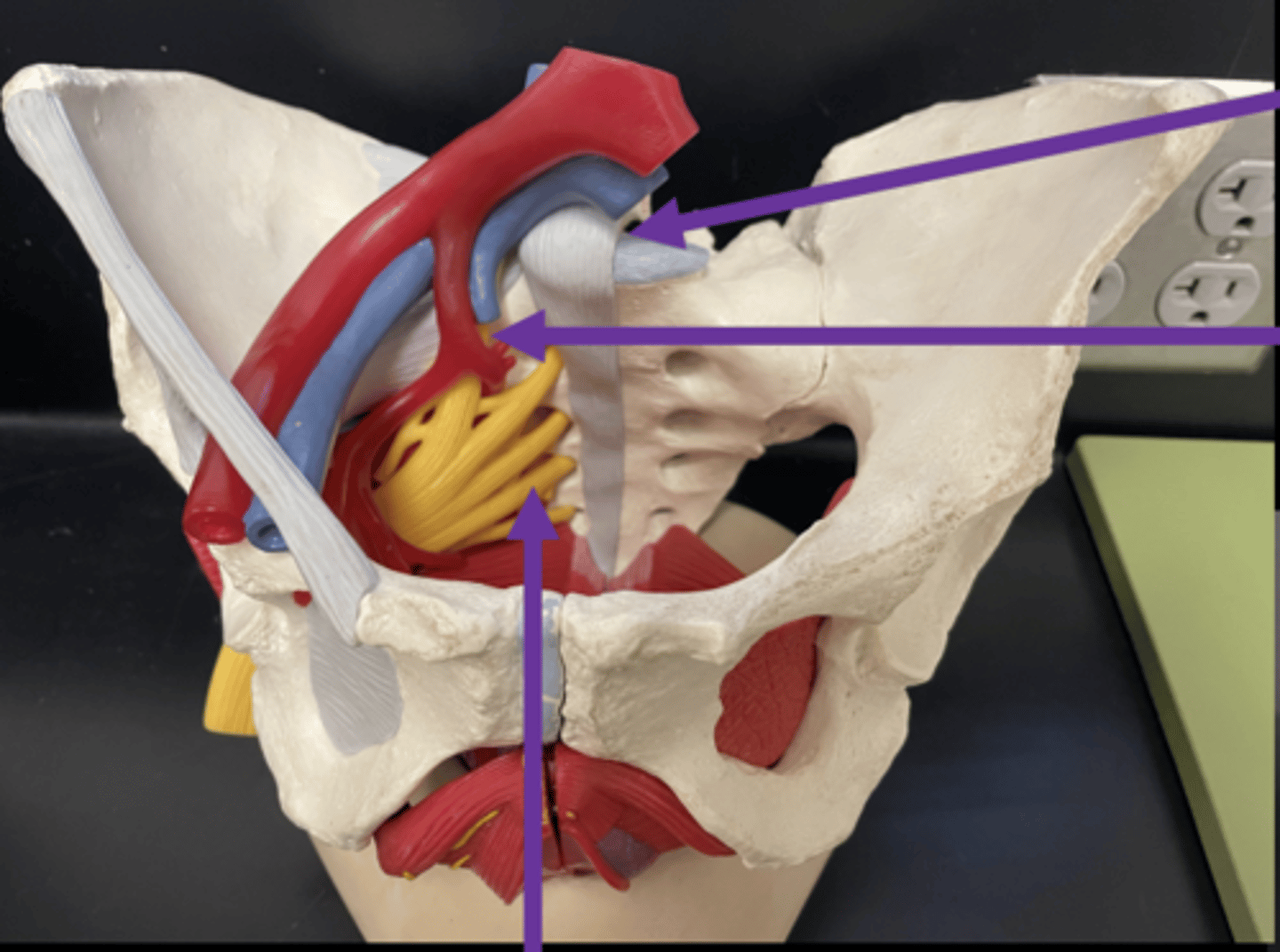
cauda equina
collection of spinal nerves below the end of the spinal cord
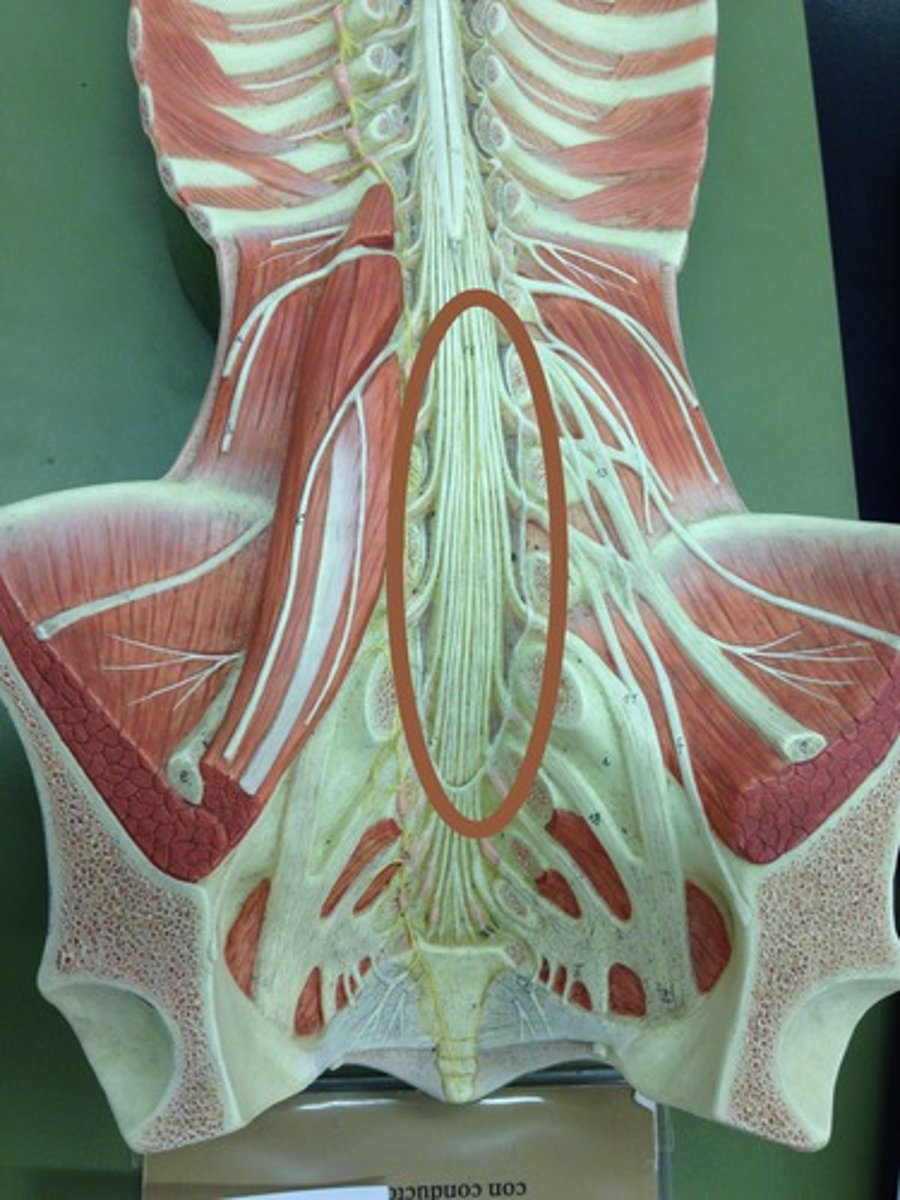
filum terminale
anchors spinal cord to coccyx