7.3
5.0(1)
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/26
Study Analytics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
1
New cards
Ribosomes are made of…
\-Protein (stability)
\-ribosomal RNA (for catalytic activity)
\-ribosomal RNA (for catalytic activity)
2
New cards
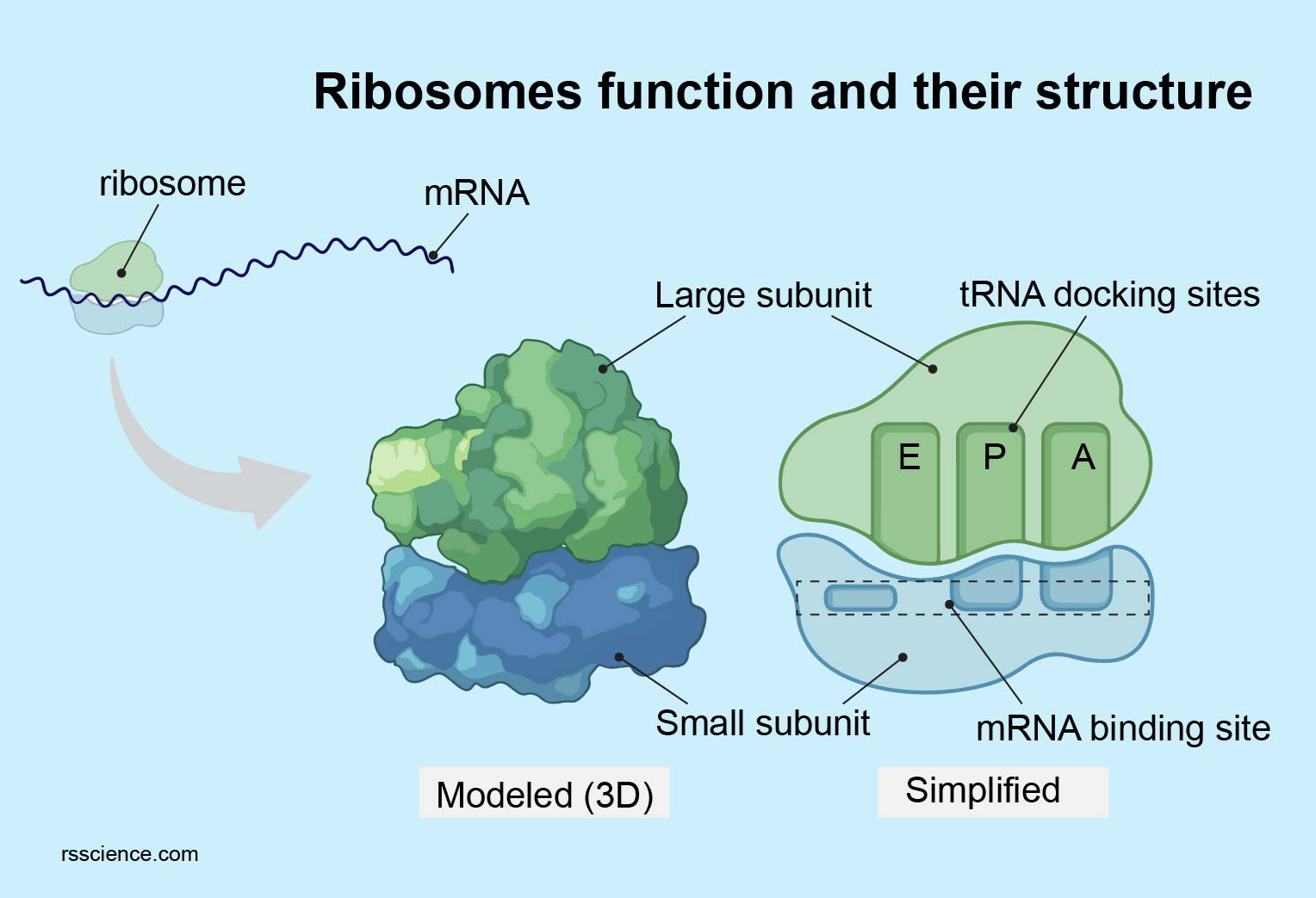
Subunits of RNA
\-small→ mRNA binding site
\-large→ 3 binding sites: A, P and E sites
\-large→ 3 binding sites: A, P and E sites
3
New cards
RIbosomes are found…
\-freely floating in the cytosol
\-bound to the rough ER (eukaryotes)
\-bound to the rough ER (eukaryotes)
4
New cards
Ribosomes sizes
70S→ prokaryotes
80S→eukaryotes
80S→eukaryotes
5
New cards
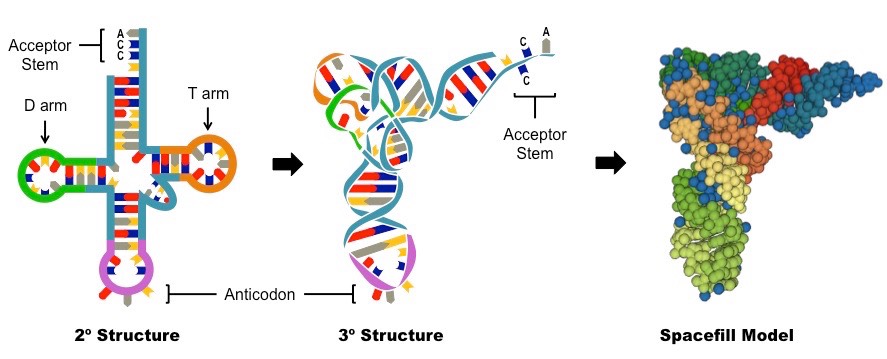
Acceptor stem
Carries an amino acid
6
New cards
Anticodon
On the opposite side of the acceptor stem
\-Complementary to the mRNA codon for a particular amino acid
\-Complementary to the mRNA codon for a particular amino acid
7
New cards
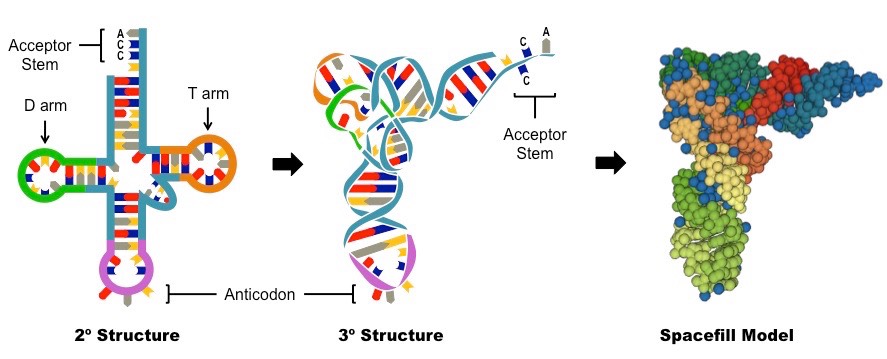
Bonds that hold together the clover shape
Hydrogen bons
8
New cards
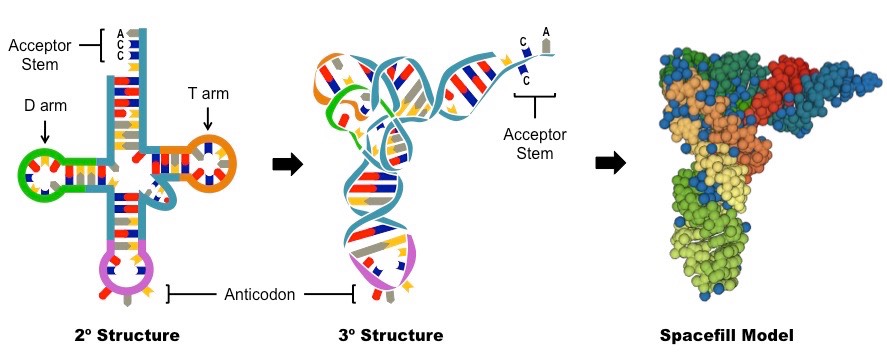
T arm
Associates with the ribosome (via the E, P and A binding sites)
9
New cards
D arm
associates with the tRNA activating enzyme
10
New cards
Binding of an amino acid to the tRNA acceptor stem
\-enzyme binds ATP to the amino acid, forming an amino acid-AMP complex
\-The amino acid is coupled to tRNA and then AMP
\-The amino acid is coupled to tRNA and then AMP
11
New cards
Steps of translation
\-initiation
\-elongation
\-translocation
(-termination)
\-elongation
\-translocation
(-termination)
12
New cards
Large subunit binding sites in order
E P A, synthesis happends from A to E (starts from P)
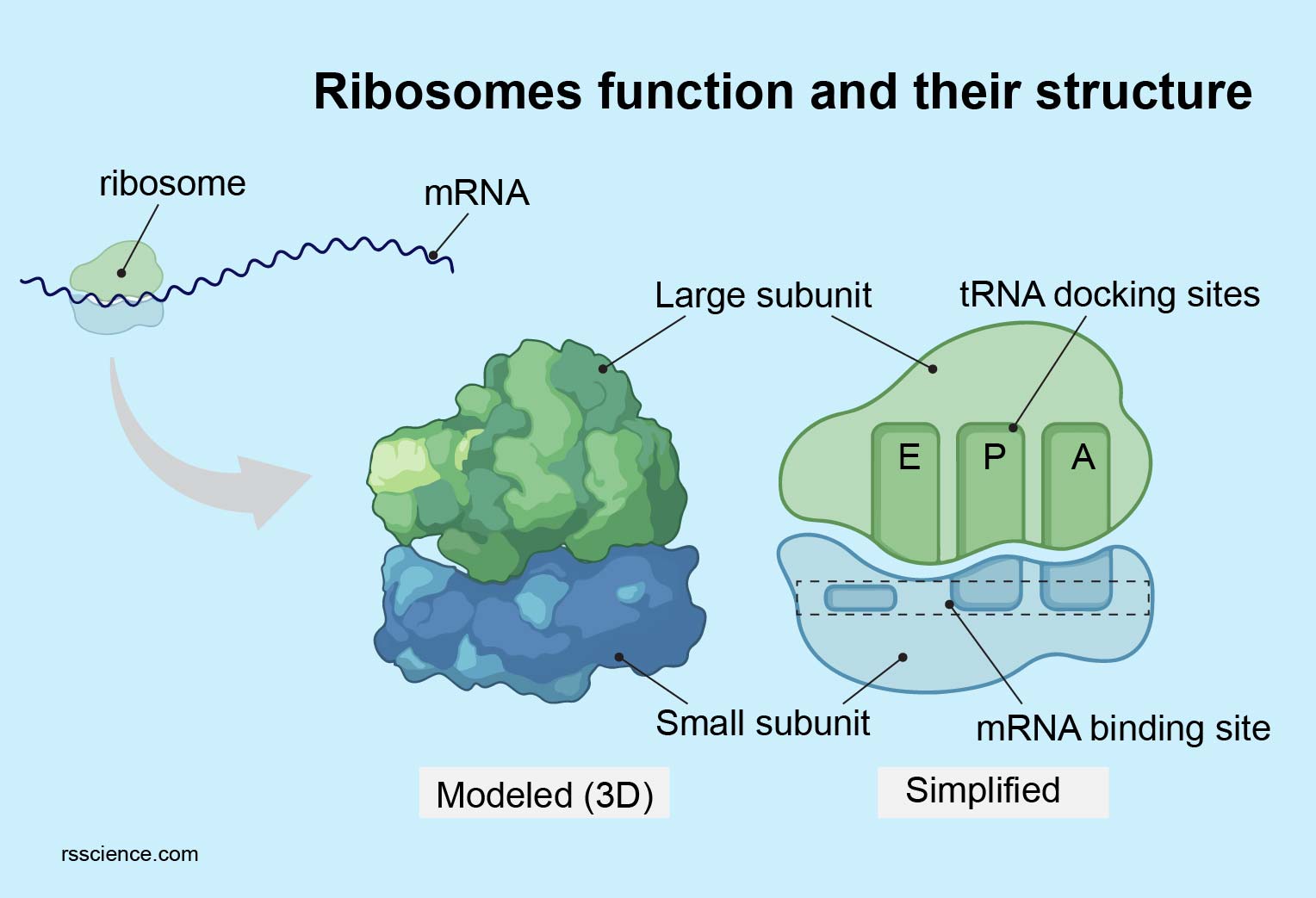
13
New cards
Initiation
\-the small ribosomal subunit bind to the 5’ end of the mRNA and moves along it reaches a start codon (AUG)
\-appropiate tRNA molecule bind to the codon through the anticodon in the P side and forms a complex with the small subunit
\-appropiate tRNA molecule bind to the codon through the anticodon in the P side and forms a complex with the small subunit
14
New cards
Elognation
\-Second tRNA molecule pairs with the next codon in the ribosomal A site
\-A peptide bond is formed between the amino acids (covalent and condensation)
\-the tRNA on the P side deattaches from the amino acid
\-A peptide bond is formed between the amino acids (covalent and condensation)
\-the tRNA on the P side deattaches from the amino acid
15
New cards
Translocation
\-the ribosome moves from a 5’ to 3’ memory
\-The deacylated tRNA moves to the E site and is released
\-Another tRNA molecule attaches to the next codon in A site and the process is repeated
\-The deacylated tRNA moves to the E site and is released
\-Another tRNA molecule attaches to the next codon in A site and the process is repeated
16
New cards
Termination
\-Until a stop codon is reached process continues
\-The stop codon binds to a **release factor** that signals for the translation to stop
\-The polypeptide is released and the ribosome disassembles back into its two independent subunits
\-The stop codon binds to a **release factor** that signals for the translation to stop
\-The polypeptide is released and the ribosome disassembles back into its two independent subunits
17
New cards
What happens after transcription in eukaryotes?
\-mRNA is transported from the nucleus via **nuclear pores** prior to translation by the ribosome
\-this requires modification to form mature mRNA
\-this requires modification to form mature mRNA
18
New cards
What happens after after transcription in prokaryotes?
\-Since they don’t have a nucleus transcription and translation do not need to be seperated
\-Ribosomes may begin translating the mRNA molecule while it is still being transcribed from the DNA template
\-This is possible because both transcription and translation occur in a 5’ → 3’ direction
\-Ribosomes may begin translating the mRNA molecule while it is still being transcribed from the DNA template
\-This is possible because both transcription and translation occur in a 5’ → 3’ direction
19
New cards
Polysome (polyribosome) definition
\-a group of two or more ribosomes translating an mRNA sequence simultaneously
\-will appear as beads on a string (bead→ ribosome, string→ mRNA strand)
\-will appear as beads on a string (bead→ ribosome, string→ mRNA strand)
20
New cards
Proteins synthesised in free ribosomes
\-intercellular use within the cytosol
21
New cards
Proteins synthesised in bound ribosomes
\-made for secretion, membrane fixation or use in lysosomes
\-ribosome becomes bound to the ER
\-ribosome becomes bound to the ER
22
New cards
Primary Structure
\-the sequence of amino acids
\-formed by **covalent bonds** between amine and carboxyl groups
\-formed by **covalent bonds** between amine and carboxyl groups
23
New cards
Secondary Structure
\-α-helices (spiral)
\-β-pleated sheets (folded)
\-**hydrogen bonding** between amine and carboxyl groups of non-adjacent amino acids
\-provides mechanical stability
\-Sequences that do not form either an alpha helix or beta-pleated sheet will exist as a random coil
\-β-pleated sheets (folded)
\-**hydrogen bonding** between amine and carboxyl groups of non-adjacent amino acids
\-provides mechanical stability
\-Sequences that do not form either an alpha helix or beta-pleated sheet will exist as a random coil
24
New cards
Tertiary Structure
\-caused by interactions between R groups
\-includes hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions
\-Relative amino acid positions are important
\-includes hydrogen bonds, ionic bonds and hydrophobic interactions
\-Relative amino acid positions are important
25
New cards
Quaternary Structure
\-multiple polypeptides or prosthetic groups may interact to form a single protein
\-Quaternary structures may be held together by a variety of bonds
\-Quaternary structures may be held together by a variety of bonds
26
New cards
A prosthetic group
\-an inorganic compound involved in protein structure or function (e.g. the **heme group** in haemoglobin)
\-A protein containing a prosthetic group is called a **conjugated protein**
\-A protein containing a prosthetic group is called a **conjugated protein**
27
New cards
The start codon
AUG- methionine