Organic Chemistry I - Functional Groups & pKas
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
49 Terms
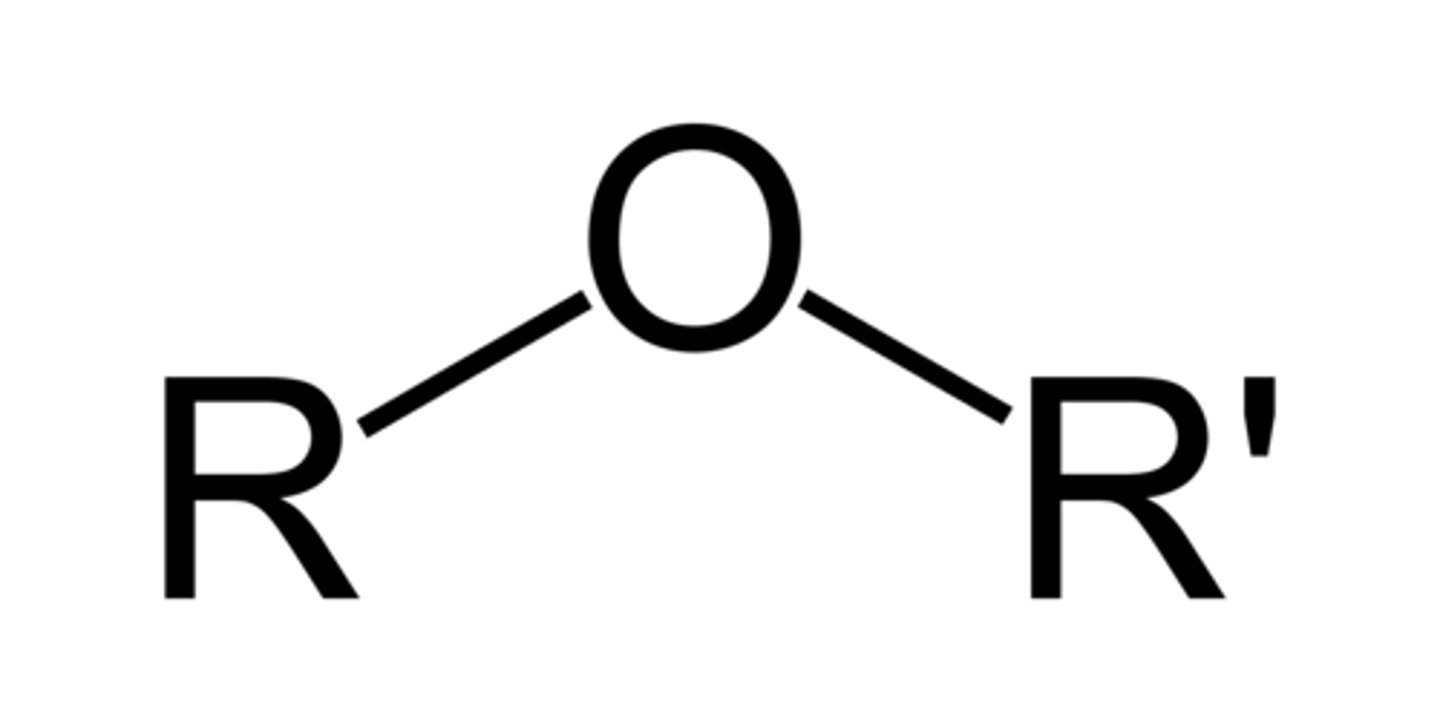
ether
R-O-R
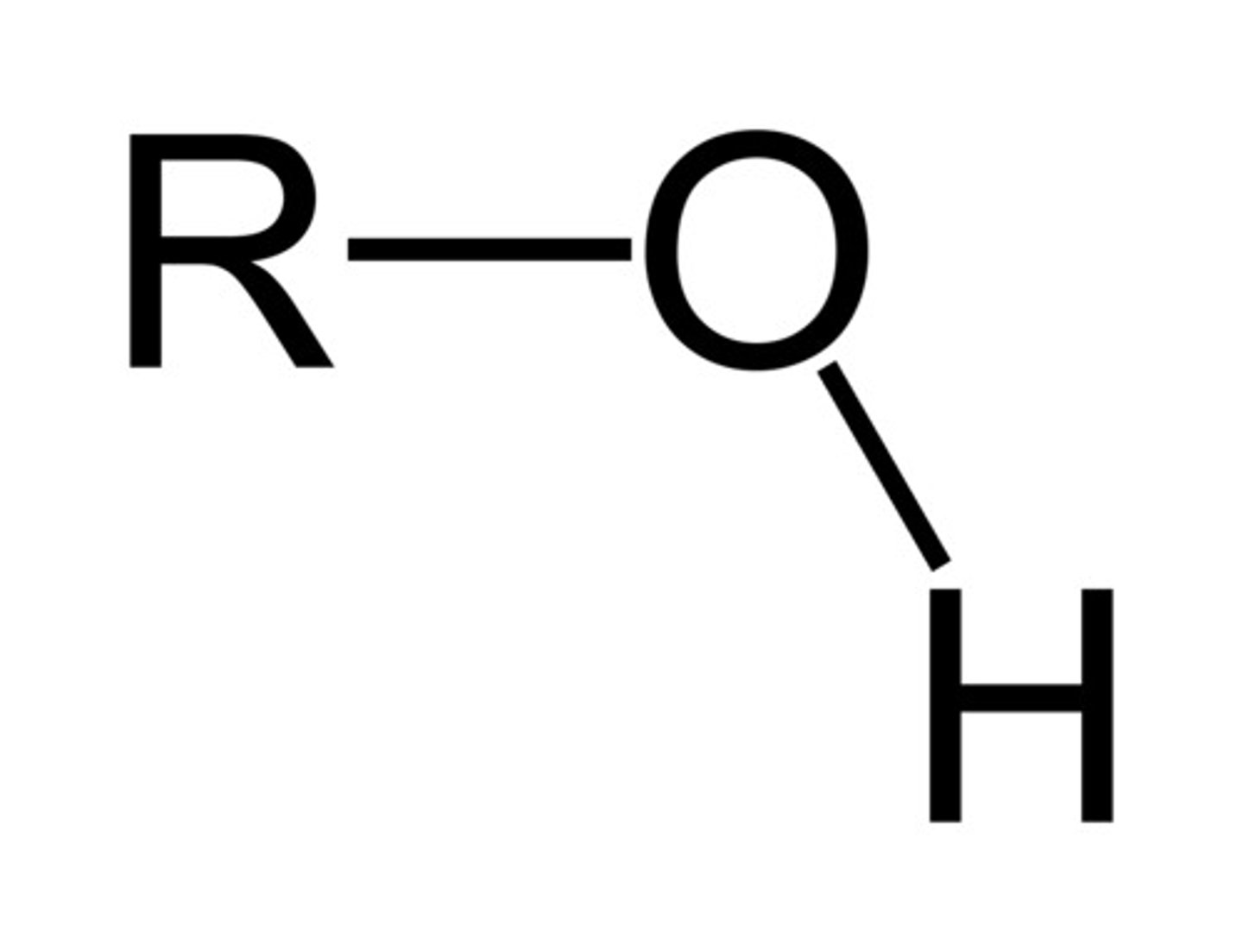
Alcohol
R-OH
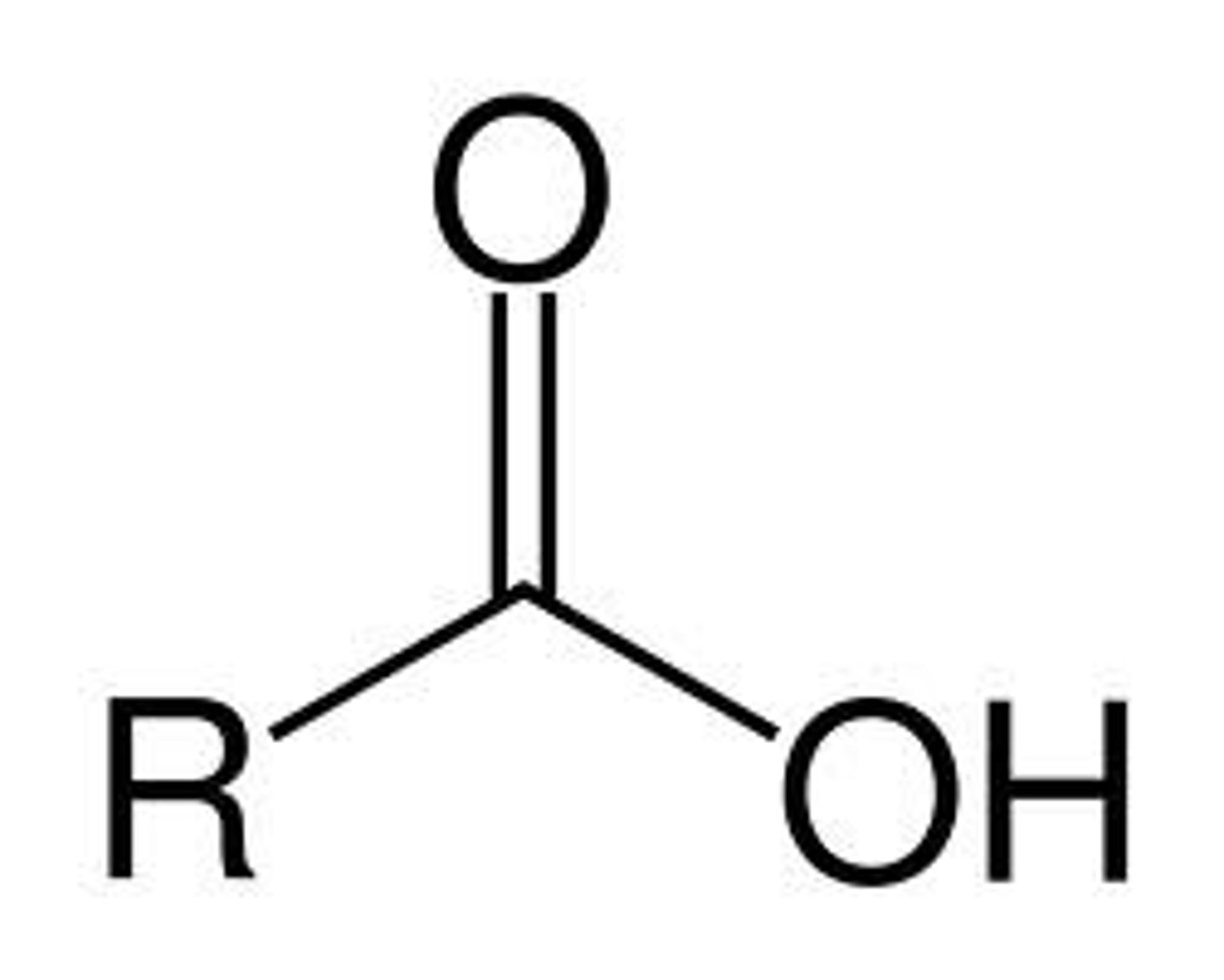
Carboxylic Acid
COOH
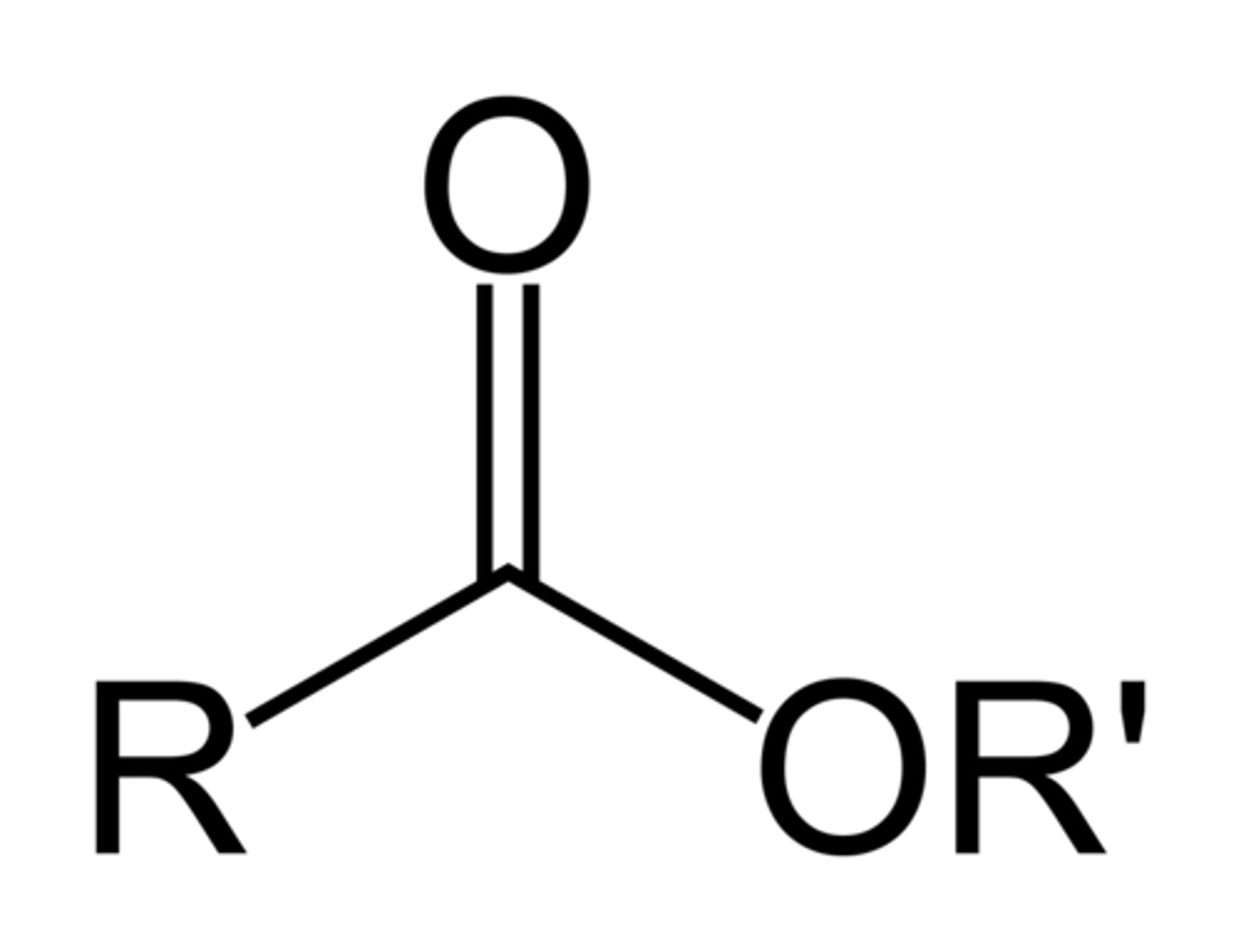
Ester
COOR
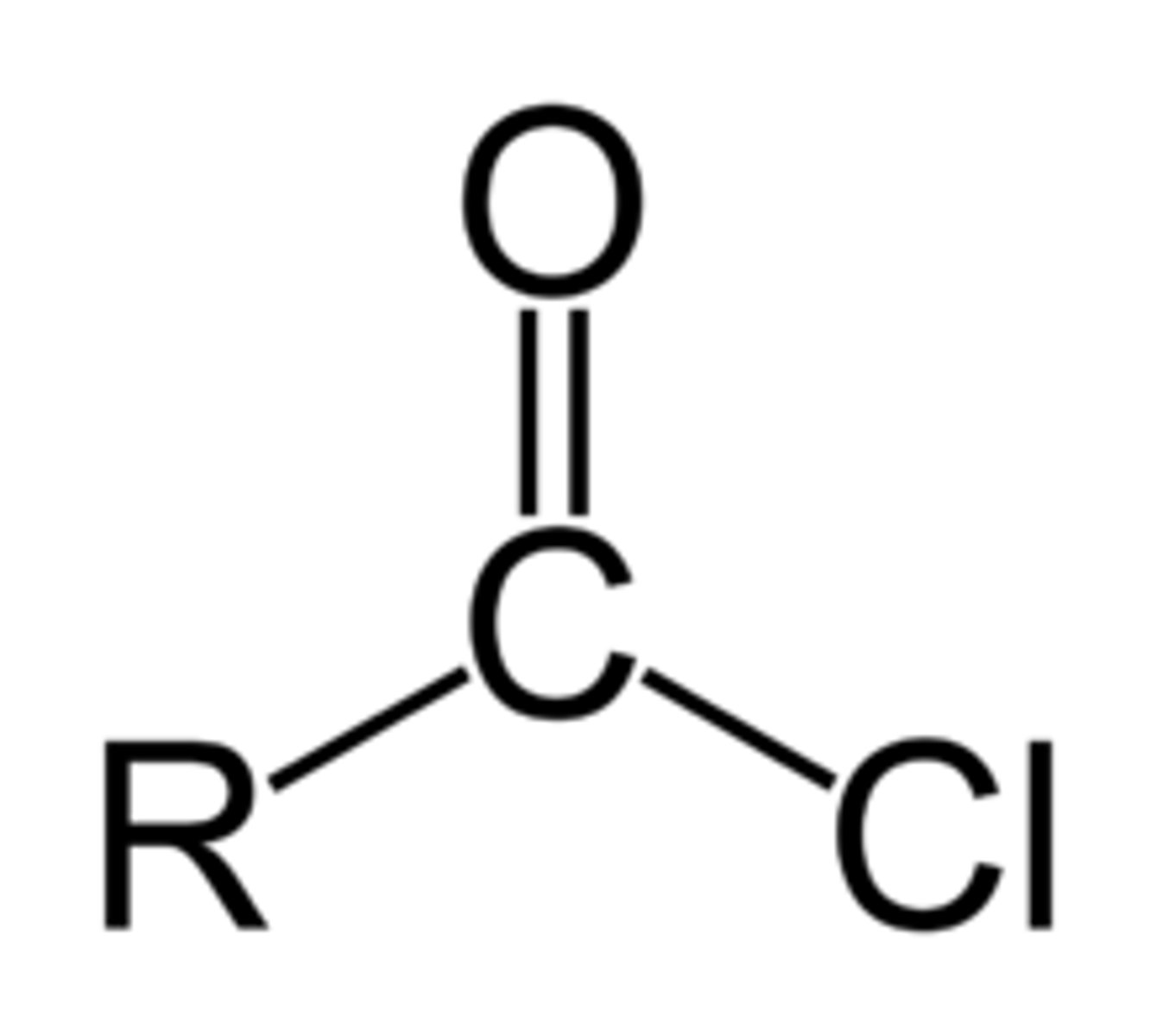
Acid Chlorine
-COCl
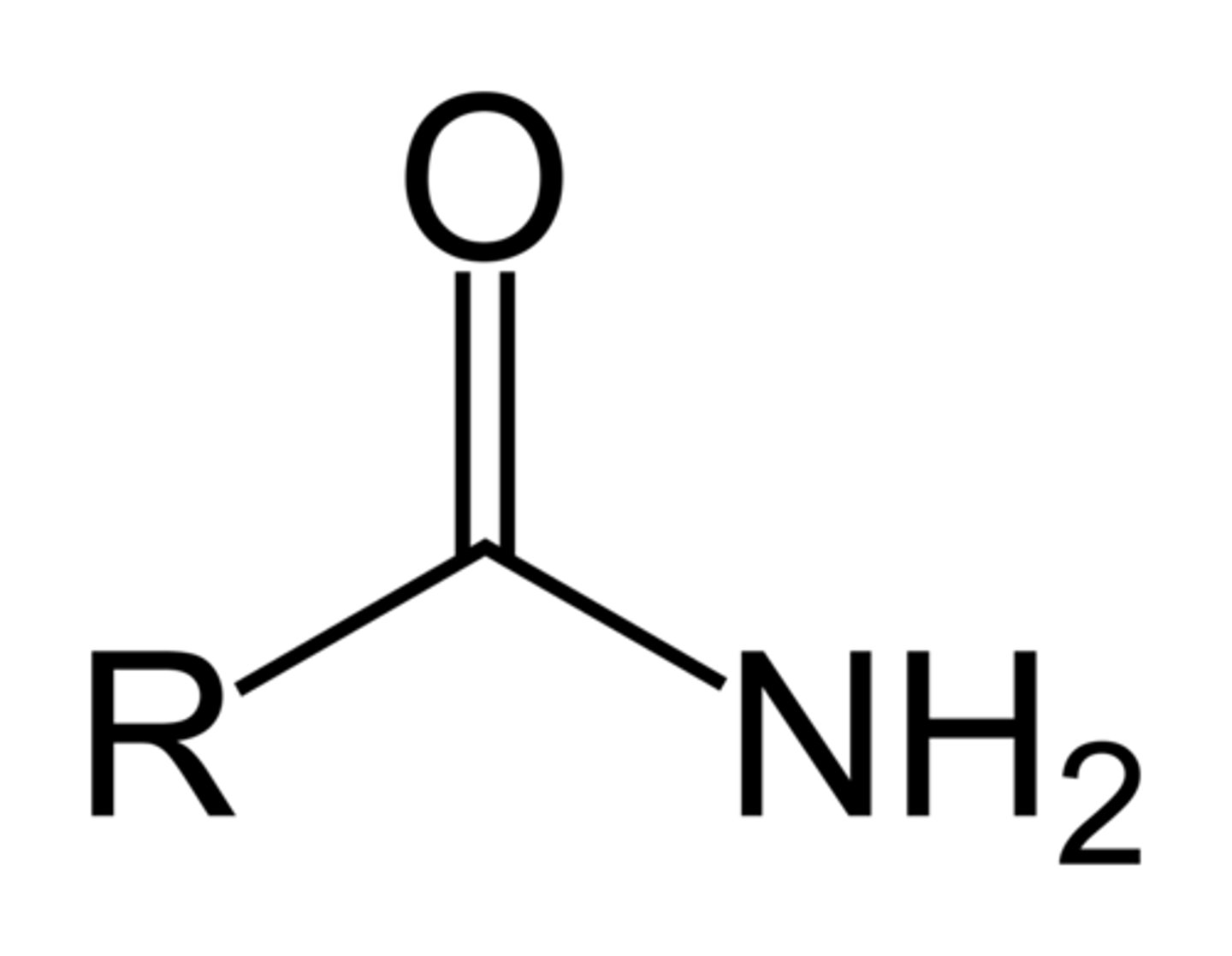
Amide
CONH2; Amine plus a keytone
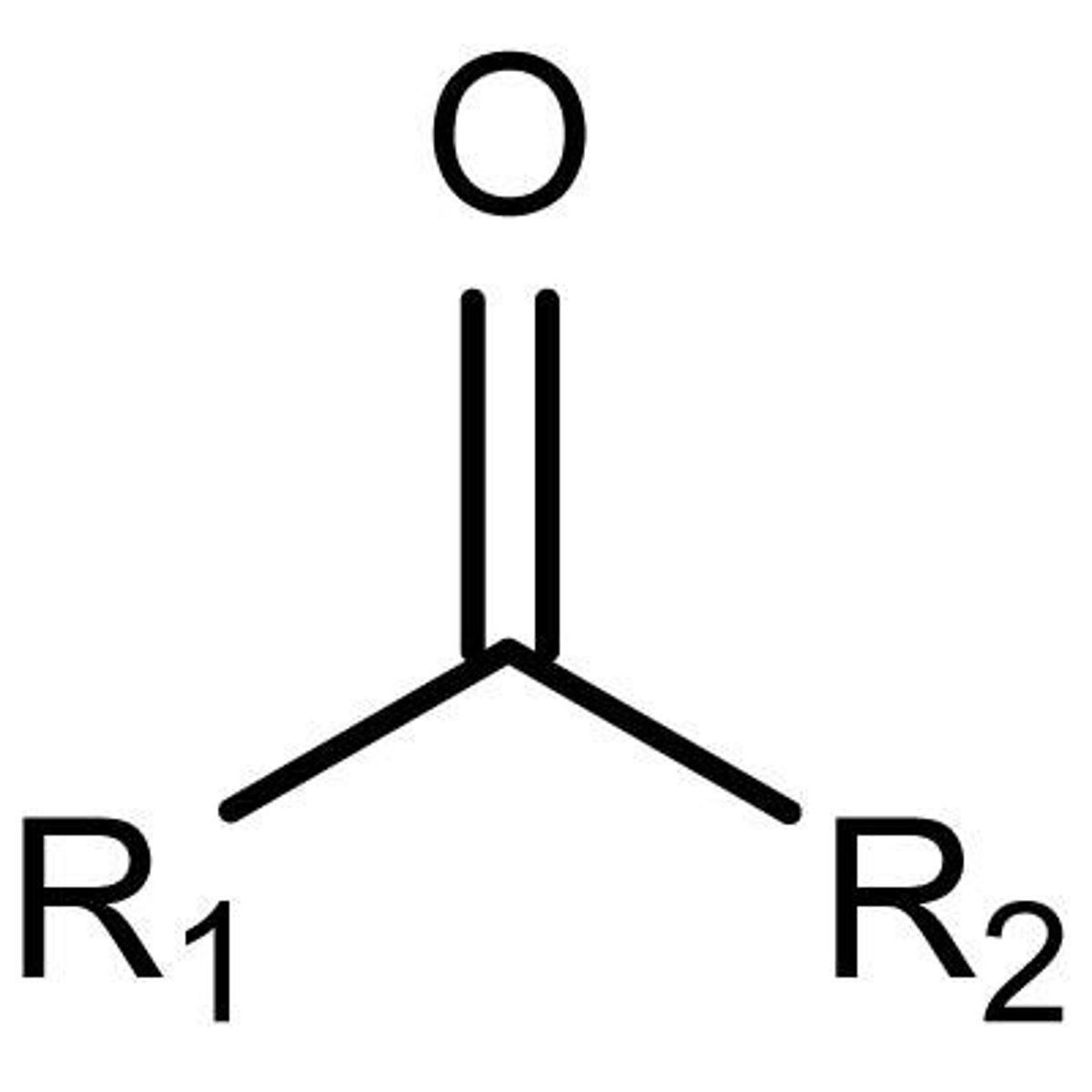
Keytone
C=O
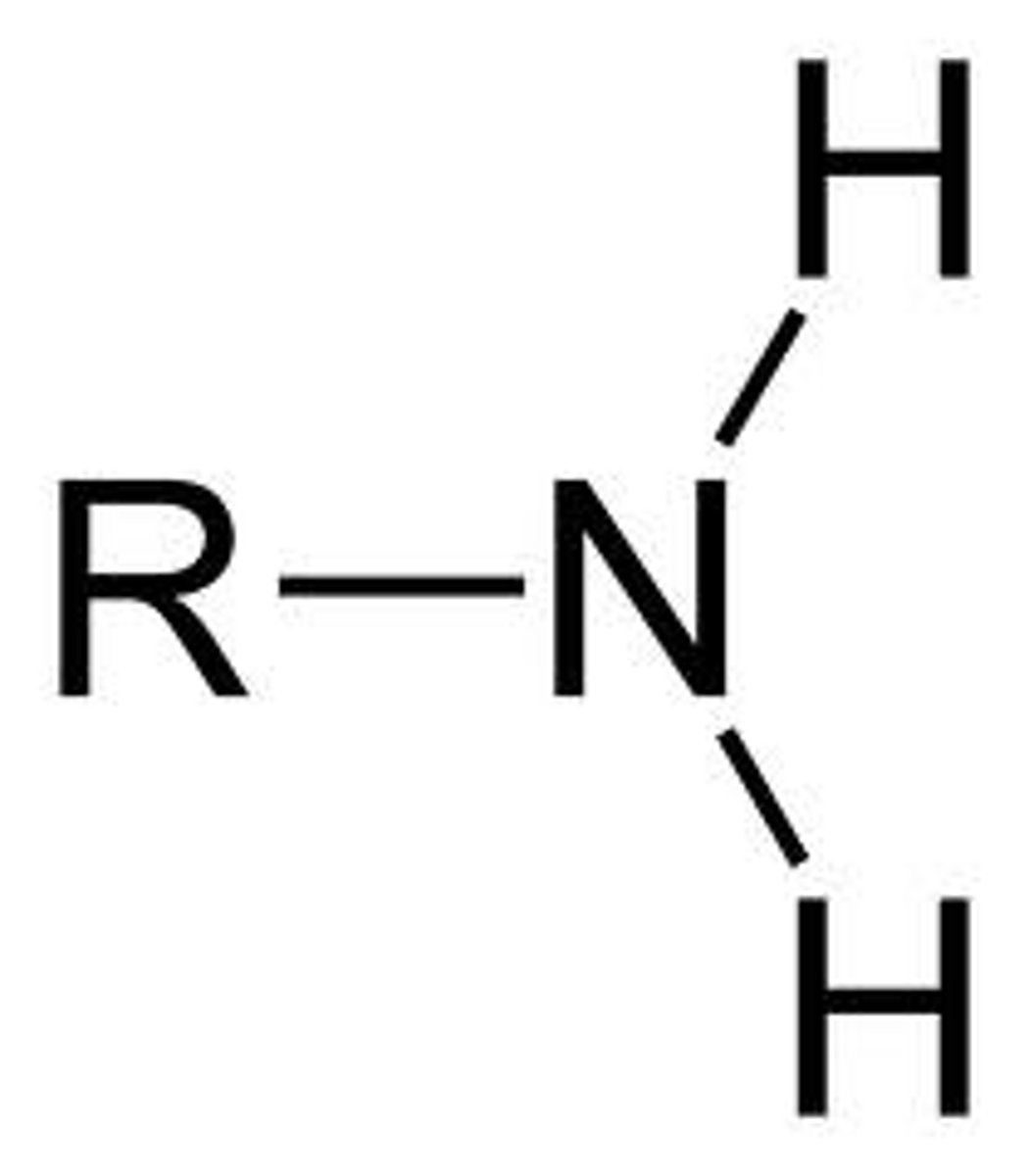
Amine
NH2
Sulfide
R-S-R
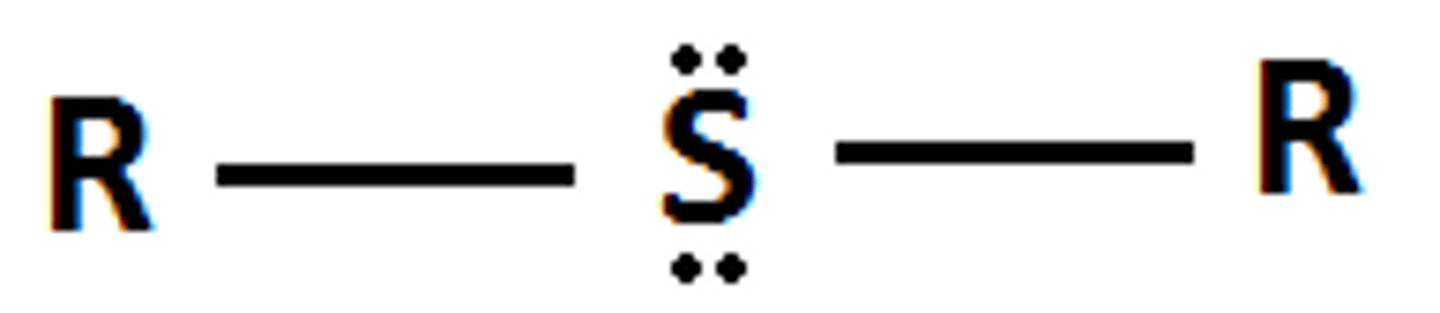
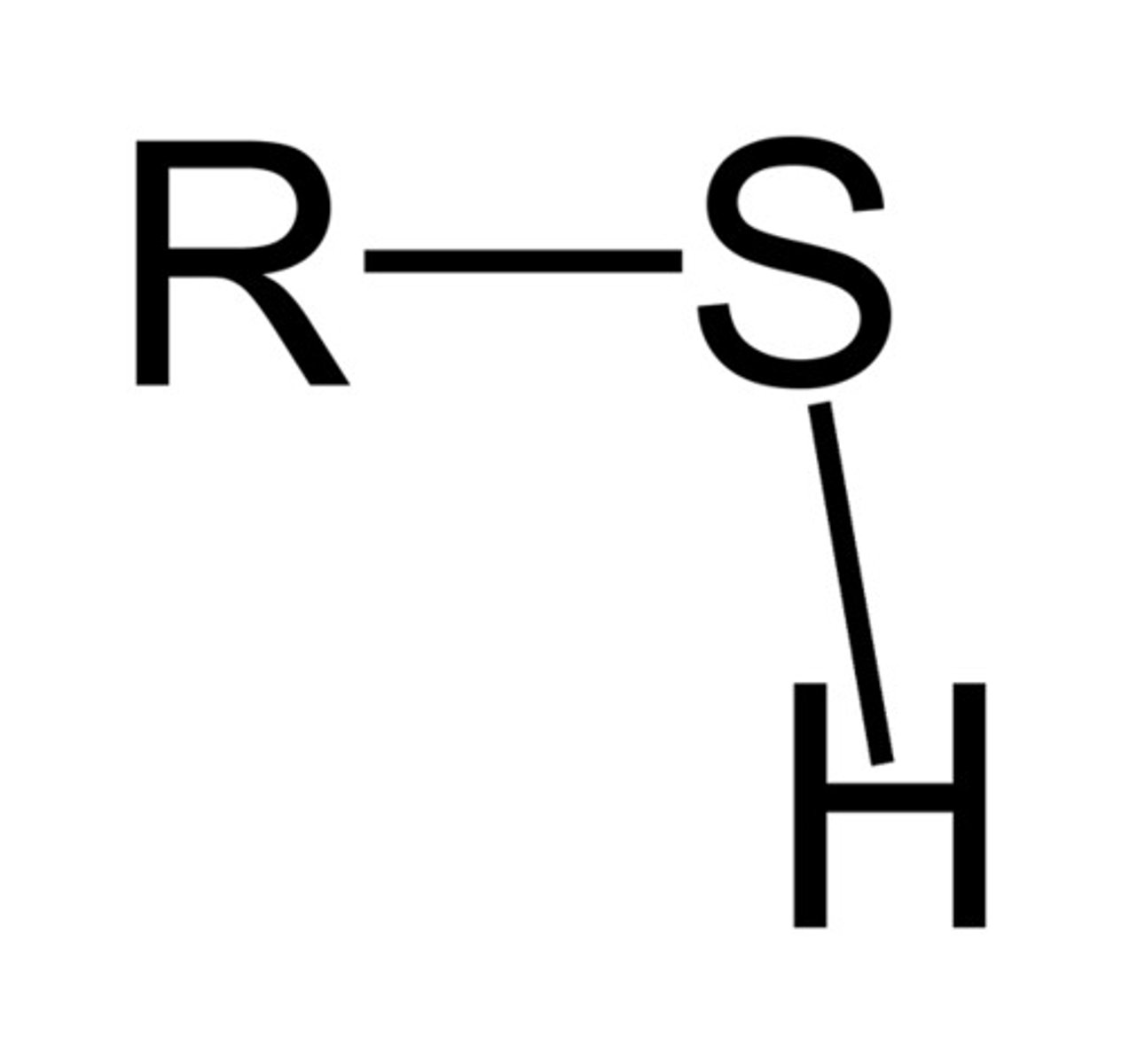
Thiol
R-SH
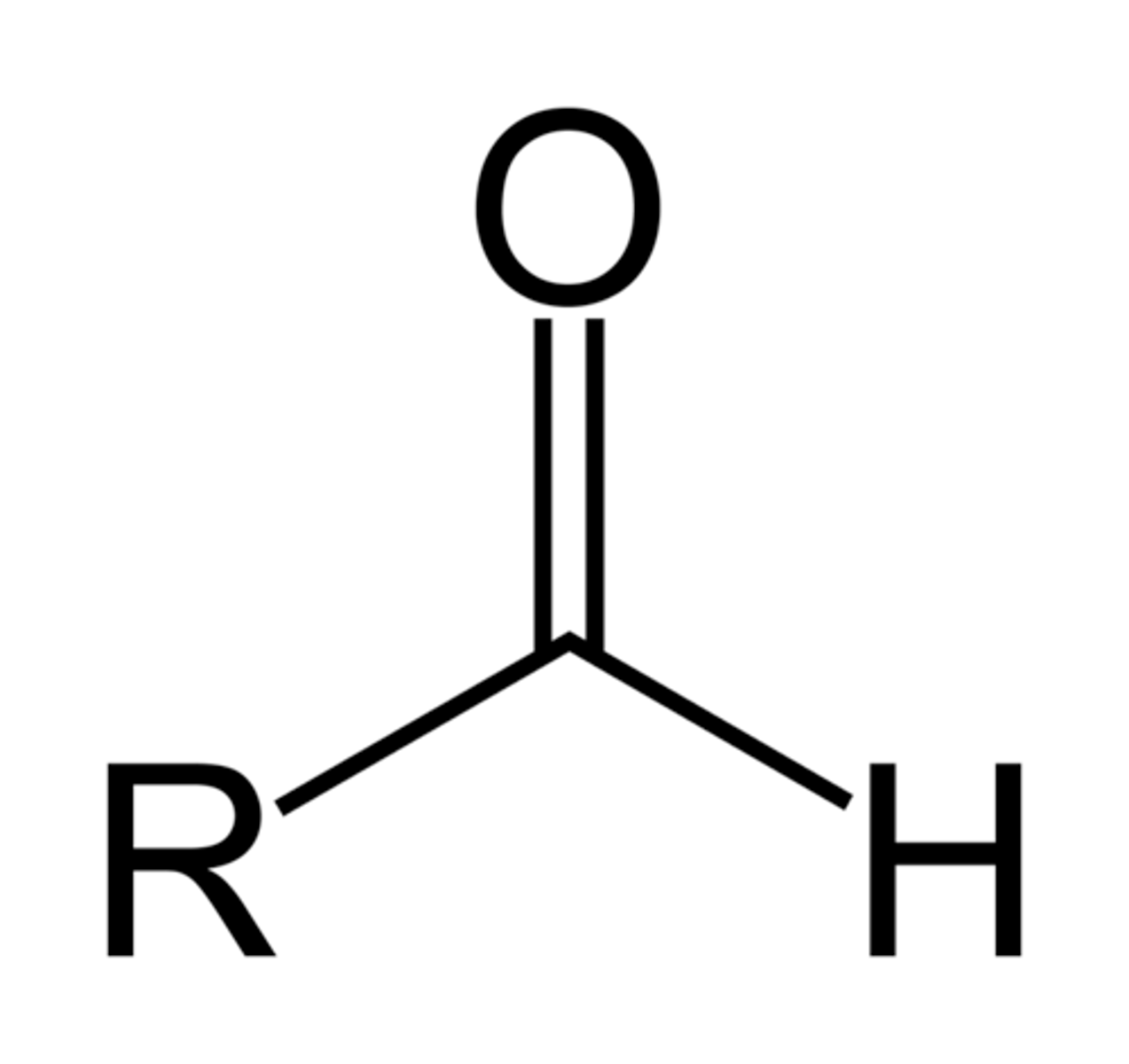
Aldehyde
CHO
alkane
Single bonded carbons
alkene
double bonded carbons
alkyne
triple bonded carbons
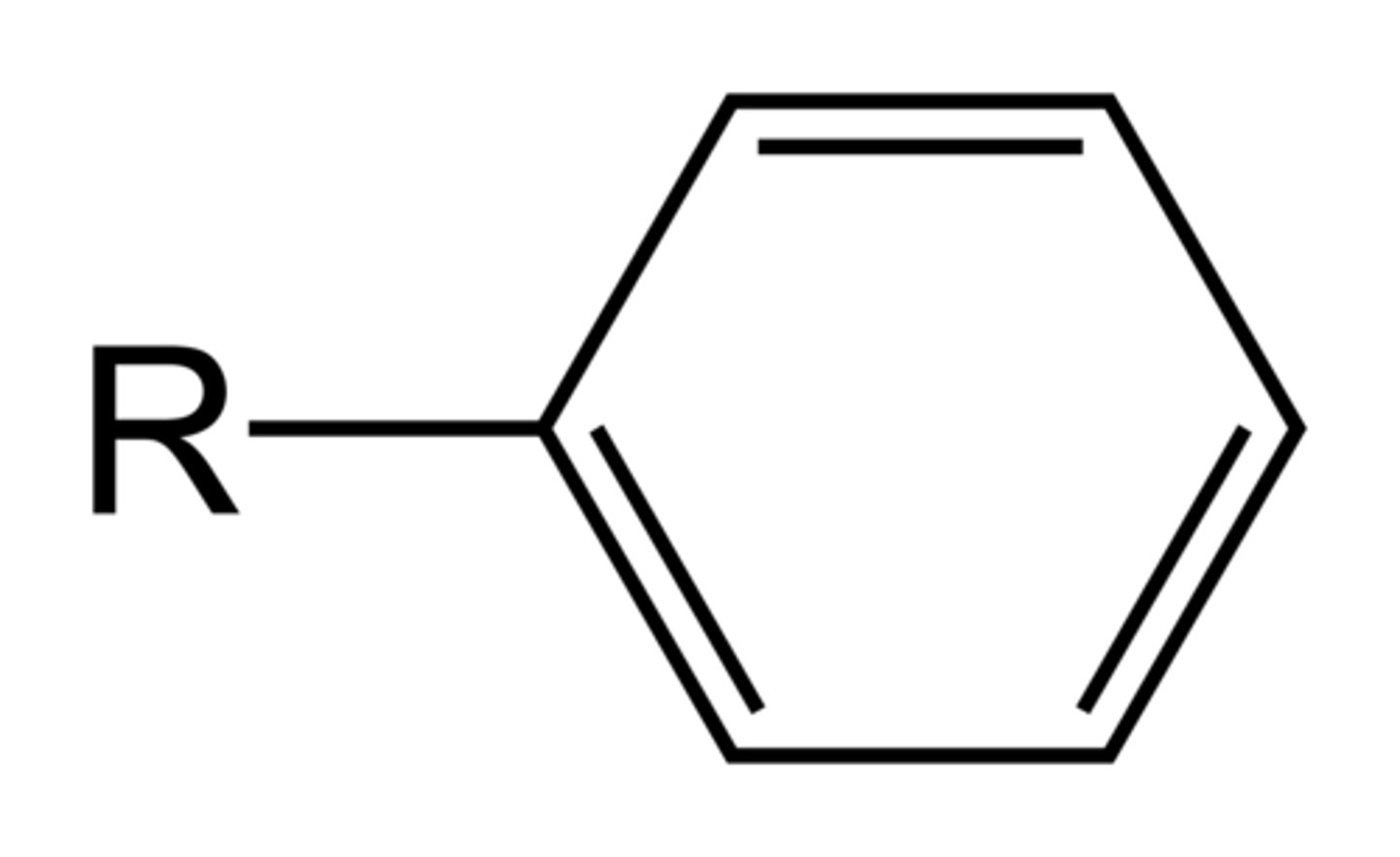
benzene ring (phenyl)
6-member ring with alternating double bonds.
Alkyl Halide
R-X (X being a halogen)
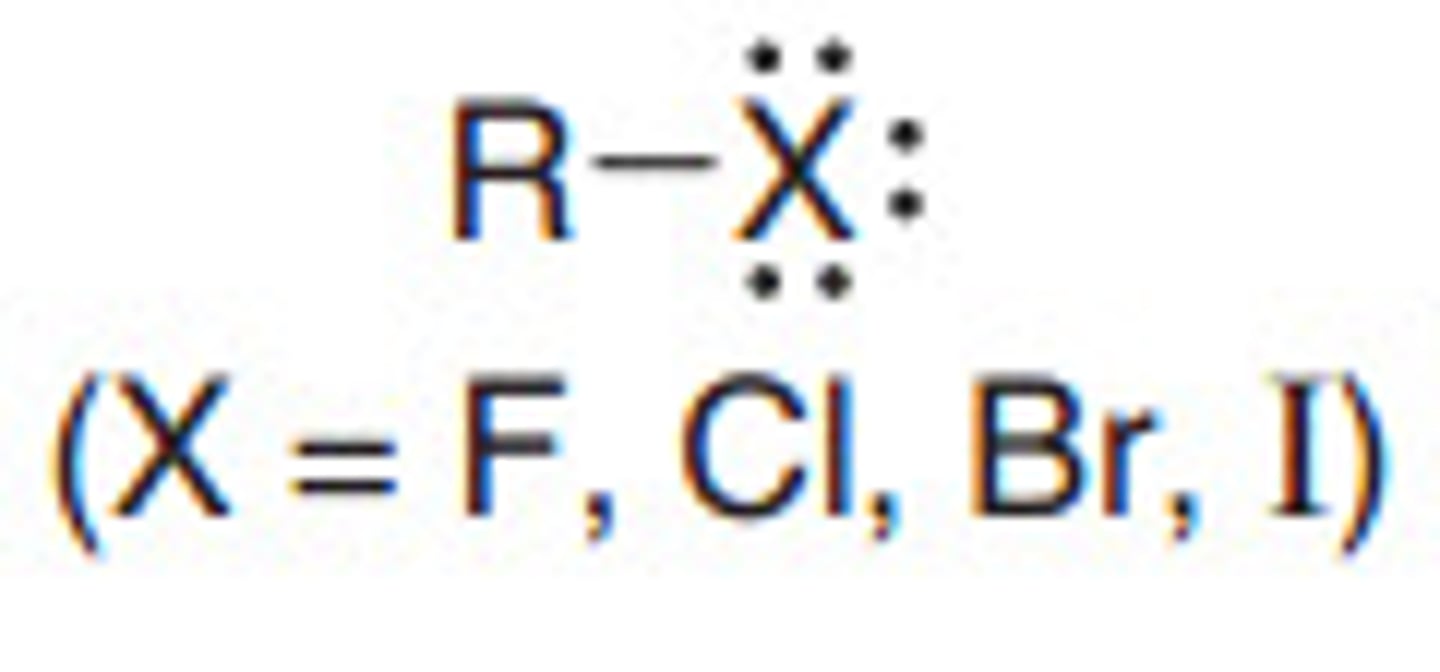
HCl pka
-7
TsOH, H2SO4 pka
-3
H3O+ pka
-2
H2O, alcohol pka
16
COOH (carboxylic acid) pKa
5
H2S pka
7
NH4 pka
9
Phenol (benzene + alcohol) pKa
10
aldehyde pKa
17
keytone pka
20
alkyne pKa
25
H2, NaH pKa
35
NH3 pka
38
alkene pka
44
Ch4, Me pka
50
ARIO
mnemonic for memorizing factors that affect the acidity of an acid. (Atom, Resonance, Induction, Orbital)
A in Ario
Atom; What atom is the acidic H attached to?
(i.e. atoms further down the periodic table will be more acidic)
R in Ario
Resonance; Is the conjugate base (deprotonated version) resonance stabilized?
I in Ario
Induction; Are there inductive effects from other atoms?
O in Ario
Orbital; how much s-character does the atom attached to the H have?
(i.e. HC-CH will have more s character than Me-Me)
ARIO is only useful when discussing _________ charges.
negative
Phenyl vs. Phenol
Phenyl is the functional group (a 6-member aromatic ring); phenol is the name for the full structure of a phenyl combined with an alcohol.
Meth- prefix
1 carbon
Eth- prefix
2 carbons
Tert-butyl
-C(CH3)3; a four carbon branch -- with three being methyls.
prop- prefix
3 carbons
but- prefix
4 carbons
pent- prefix
5 carbons
hex- prefix
6 carbons
hept- prefix
7 carbons
oct- prefix
8 carbons
non- prefix
9 carbons
dec- prefix
10 carbons