Valencia College: Paramedic Program P2 - Cardiac A&P/Electrophysiology Test Study Guide
1/49
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
50 Terms
Tricuspid Valve
lies between right atrium and right ventricle; closed during systole to prevent backflow
Mitral (Bicuspid) Valve
lies between left atrium and left ventricle; closed during systole to prevent backflow
Pulmonic Valve
lies between right ventricle and pulmonic artery; closed during diastole to prevent backflow of blood from vessels into the ventricles
Aortic Valve
lies between left ventricle and aorta; closed during diastole to prevent backflow of blood from vessels into the ventricles
What is happening during the diastole phase of the cardiac cycle?
period of relaxation during which the chambers are filling
The area where the heart and great vessels reside
mediastinum
Mechanical phases of the cardiac cycle:
1. Diastole
2. Depolarization
3. Systole
4. Repolarization
3 components that create BP:
1. Stroke Volume(Cardiac Output)
2. Heart Rate(Cardiac Output)
3. Peripheral Vascular Resistance
What happens on phase 1 of cardiac cycle?
K+ channels open and K+ leaves the cell; CA2+ channels open and CA2+ rushes in (plateau); cellular contraction happens
What is the inner most layer of the heart?
endocardium
SA node Intrinsic rate:
60-100 bpm
AV Intrinsic rate:
40-60 bpm
Purkinjes Intrinsic rate:
20-40 bpm
Negative ECG waves have what deflection?
wave of depolarization moving towards a negative electrode; negative deflection
What is role of the myocardium?
Middle layer; thick, muscular layer that is responsible for pumping action
What electrolyte is prevalent in phase 1 and 2 of the cardiac cycle?
Calcium (Ca++)
Resting Potential
The difference in electric charge between the inside and outside of a neuron's cell membrane; -90mV
How many ECG leads are required to detect a life threatening dysrhythmia?
1
The epicardium is contagious with what structure?
serous pericardium
What nerve is associated with the parasympathetic system and what effect does it have on the heart?
Vagus nerve (Cranial X); innervates heart at SA and AV nodes causing a drop in heart rate
What ECG wave represents the depolarization of the atrium?
P wave
What role does BNP play play in congestive heart failure?
a hormone that is secreted by the ventricles to counteract the RAAS system, which is released during CHF, by stimulating loss of water, sodium, and vasodilation
What is considered the pacemaker of the heart?
SA Node
What does ejection fraction represent?
the amount of blood your heart pumps each time it beats
How does preload effect BP?
it is the amount of blood that is returned to the heart from the venous side during diastole so it determines how much blood gets back into the heart
What is an ECG monitor capable of doing?
can provide information about rate and rhythm, the orientation of the heart, in the chest, conduction disturbances, the electrical effects of medications and electrolytes, the mass of cardiac muscle, and the presence of ischemic damage
How does the myocardium receives its blood?
Coronary Arteries
What happens during phase 0 of the cardiac cycle?
K+ leaks out, threshold potential (-70mV) is reached, fast Na+ channels open and drives membrane positive; cell depolarization occurs
Compare the right ventricle and left ventricle:
Right Side - low pressure system; smaller; pumps deoxygenated venous blood to the lungs
Left Side - high pressure system; bigger; pumps oxygenated arterial blood to systemic circulation
Anatomical location landmark of Heart: Apex
5-6th rib above diaphragm
Anatomical location landmark of Heart: Base
2nd rib
How are positive waveforms represented on ECG?
wave of depolarization moving towards the positive electrode; positive deflection
What is the prevalent electrolyte in phase 3 and what role does it play?
Potassium (K+); K+ leaves the cells and the cell becomes negative; Repolarization occurs
What is the typical stroke volume of the left ventricle?
about 70mL
How is Time measured on ECG paper?
on the horizontal axis; each small box = 0.04 secs(40ms) and each large box(5 small boxes) = 0.20 secs(200ms)
How is Amplitude(Voltage) measured on ECG paper?
on the vertical axis; 10mm = 1mV
The absolute refractory period is represented by what 2 EKG landmarks?
from the onset of QRS complex to the peak of the T wave
What is the function of the atrium?
Atrial kick
300 Rule
count the number of large boxes between 2 consecutive waveforms (R-R interval and P-P interval) and divide into 300(must be regular); 1 box = 300, 2 boxes = 150, 3 boxes = 100, 4 boxes = 75, 5 boxes = 60, 6 boxes = 50
Trace the path of electrical depolarization in the pathway:
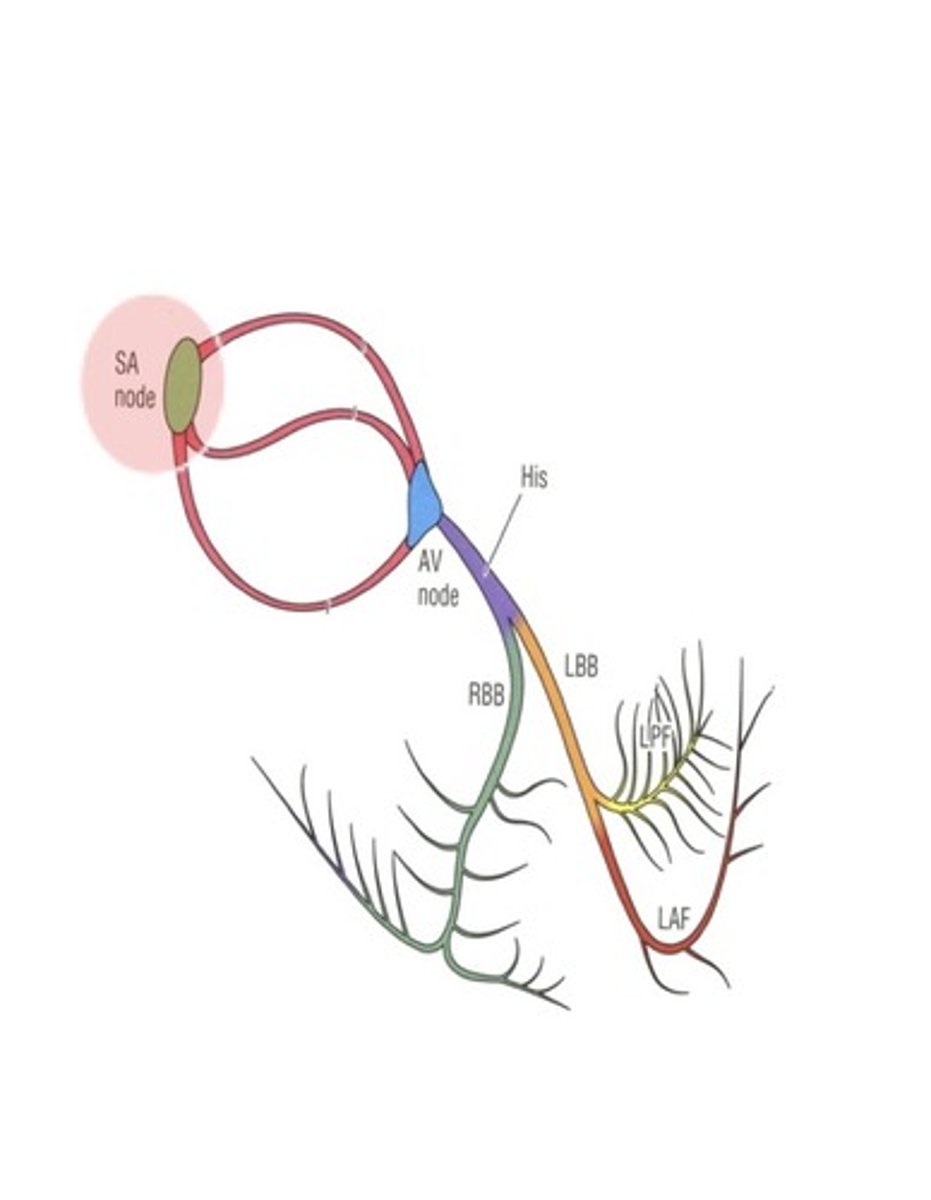
What does T wave represent?
ventricular repolarization
Starling's Law
the more a myocardial muscle is stretched, the greater the force of contraction (and stroke volume); influenced by preload and afterload
Afterload
the pressure/resistance against which the ventricles must pump to eject blood; increased afterload usually means an increase in the work of the heart
Anatomic Location of Lead V1
right side of sternum, 4th intercostal space
Anatomic Location of Lead V2
left side of sternum, 4th intercostal space
Anatomic Location of Lead V3
midway between V2 and V4
Anatomic Location of Lead V4
left midclavicular line, 5th intercostal
Anatomic Location of Lead V5
left anterior axillary line, same level as V4
Anatomic Location of Lead V6
left midaxillary line, same level as V4
End Diastolic Volume
the volume of blood in the left ventricle at the end of ventricular filling (diastole)