Hole's Human Anatomy & Physiology Chapter 7 and 8: Bones and Joints
1/71
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
72 Terms
long bones
have long longitudinal axes and expanded ends
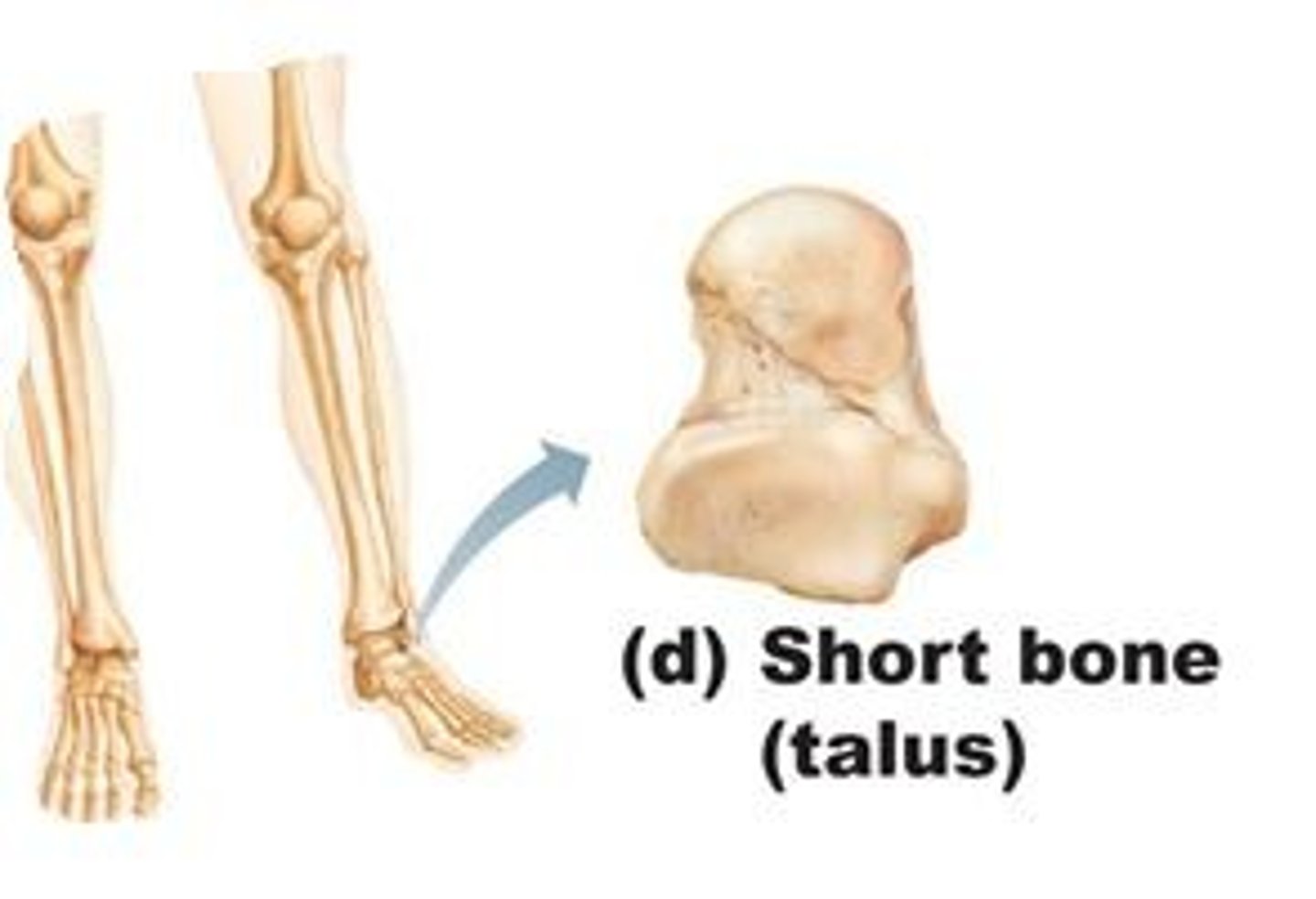
short bones
are cube-like, with roughly equal lengths and widths.
seasmoid or round bone
small and nodular and are embedded within tendons adjacent to a joint
flat bone
plate-like structures with broad surfaces
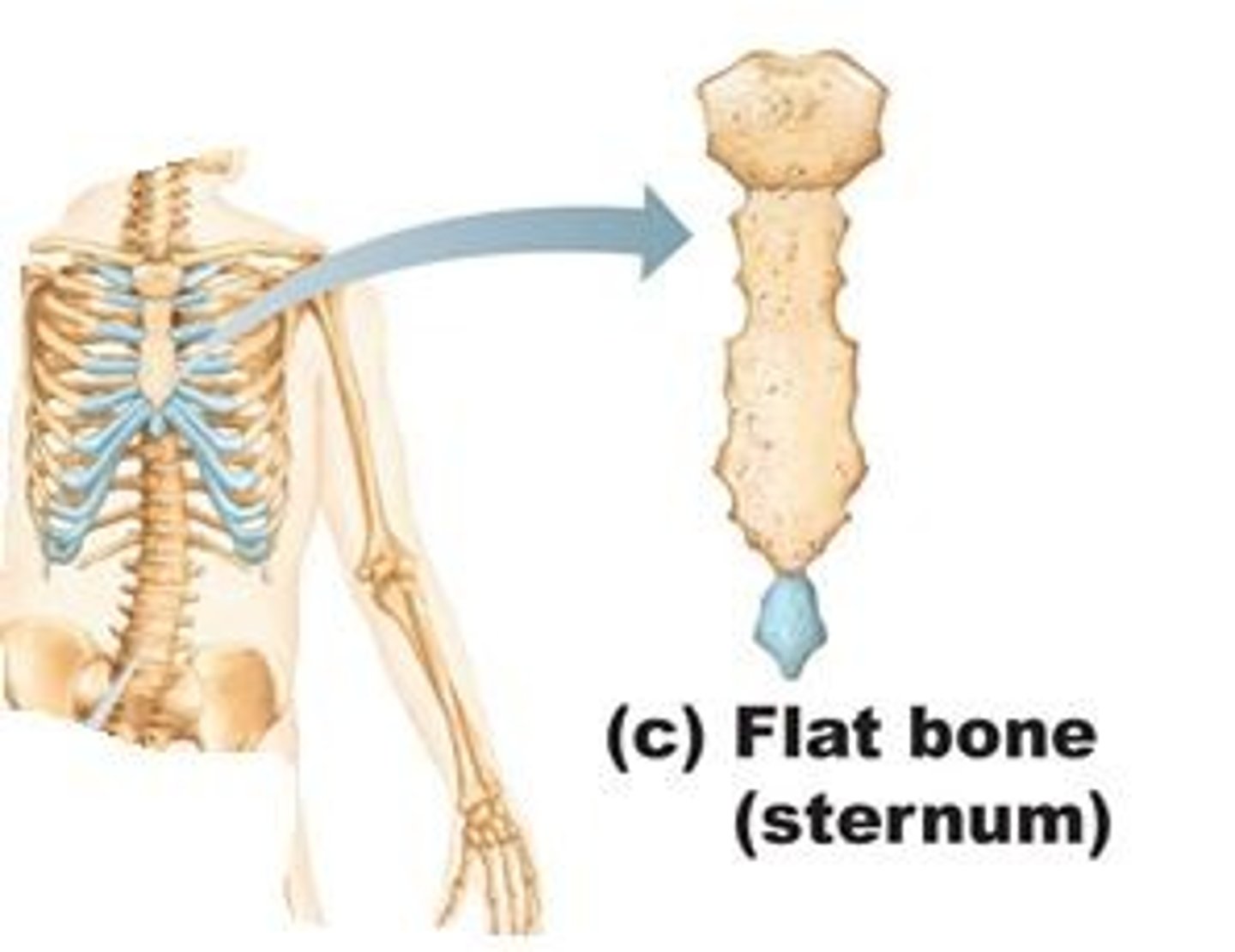
irregular bones
have a variety of shapes, and most are connected to several other bones
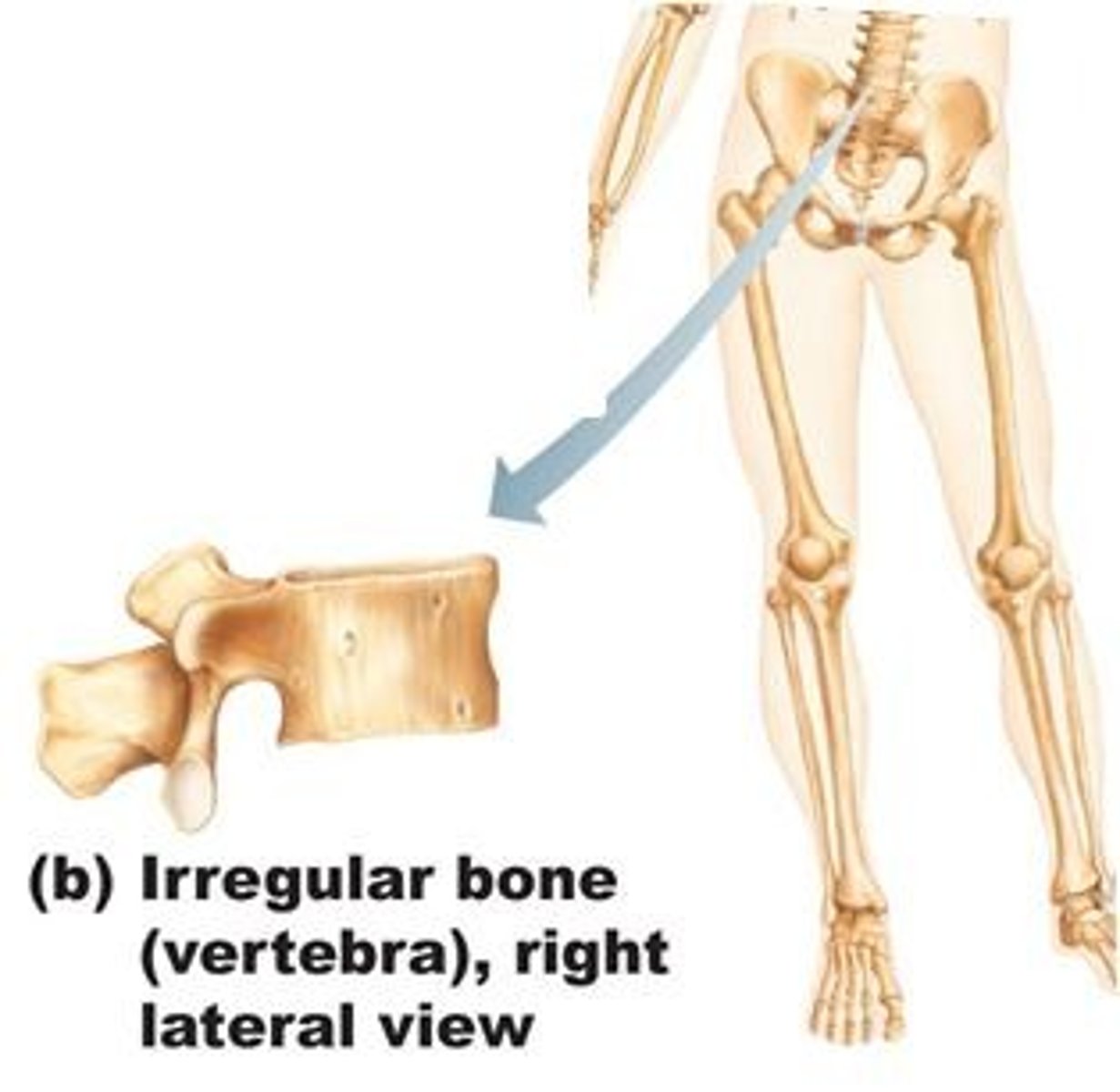
long bones
what type of bones are the forearm and thigh bones?
short bones
what type of bones are the bones of the wrist, and ankle?
sesamoid bone or round bone
what type of bone is the kneecap?
flat bone
what type of bone are the scapulae, ribs, and some bones of the skull?
irregular bones
what types of bones are the vertebrae and many of the facial bones?
intermembraous ossification
the process of replacing connective tissue to form an intermembranous bone
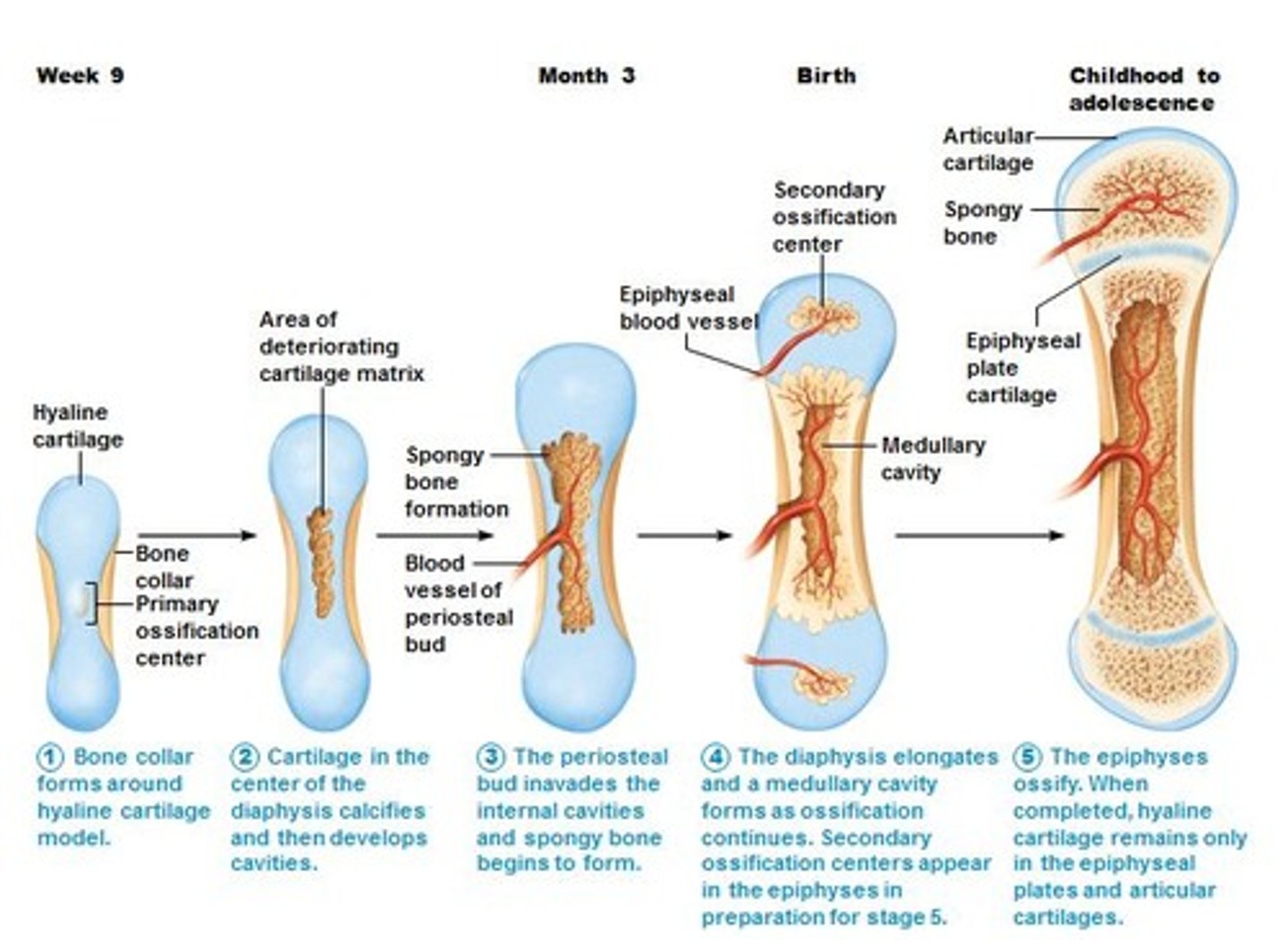
endochondral bones
most bones of the skeleton are these types of bones. bone that begins as hyaline cartilage that is subsequently replaced by bone tissue
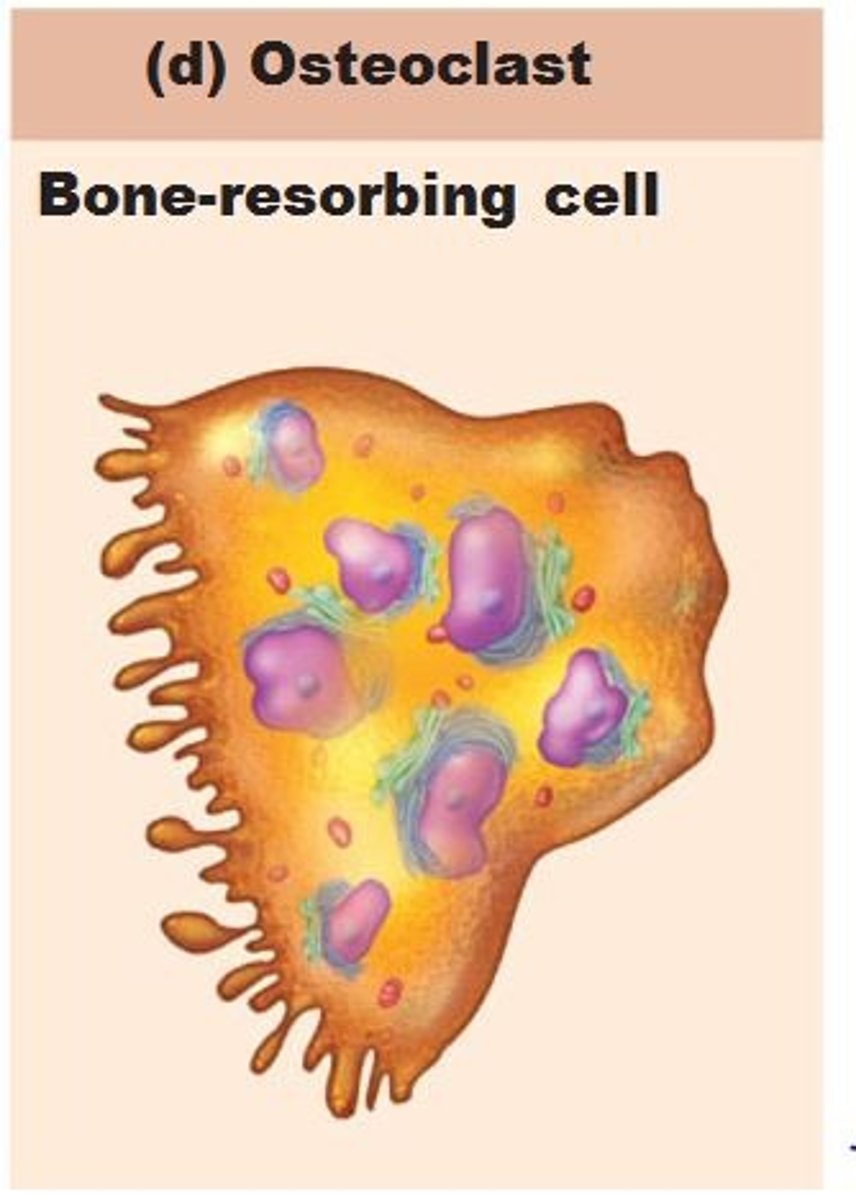
osteoclast
cell that breaks down bone
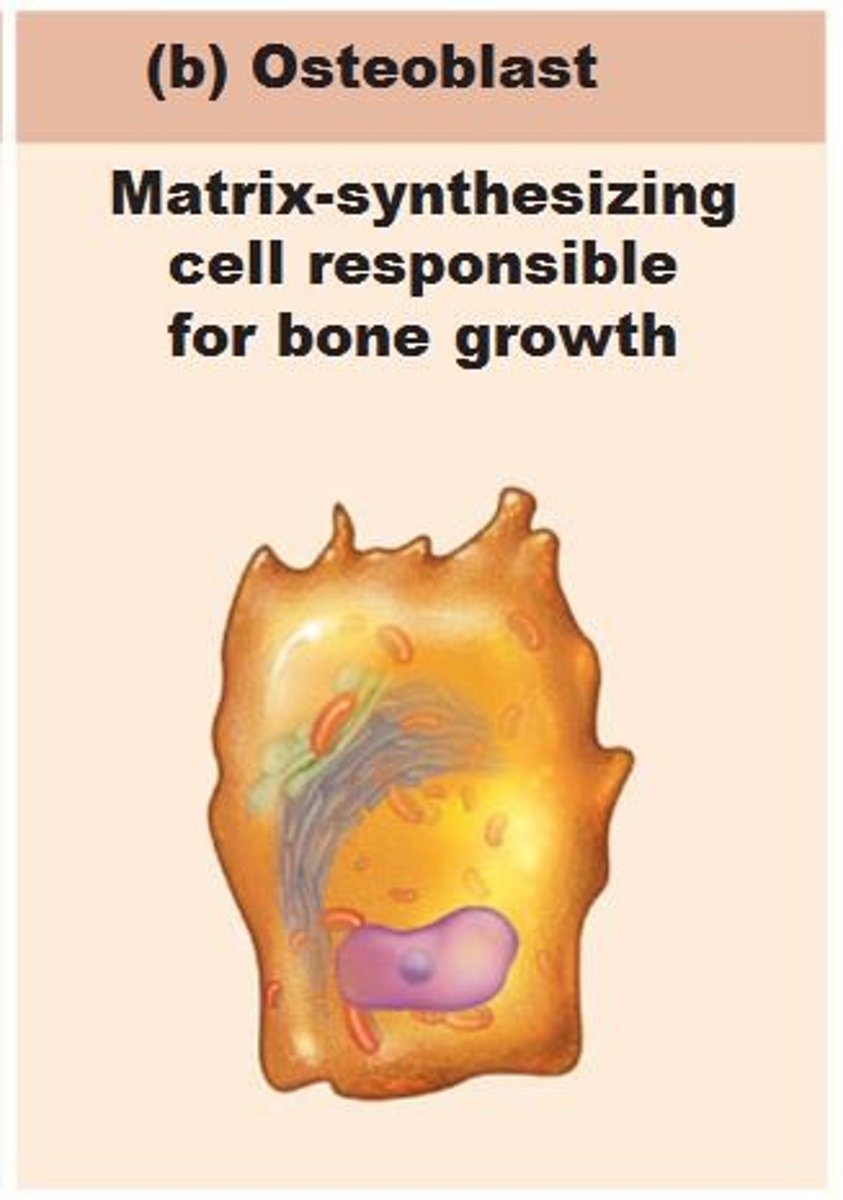
osteoblast
bone making cell
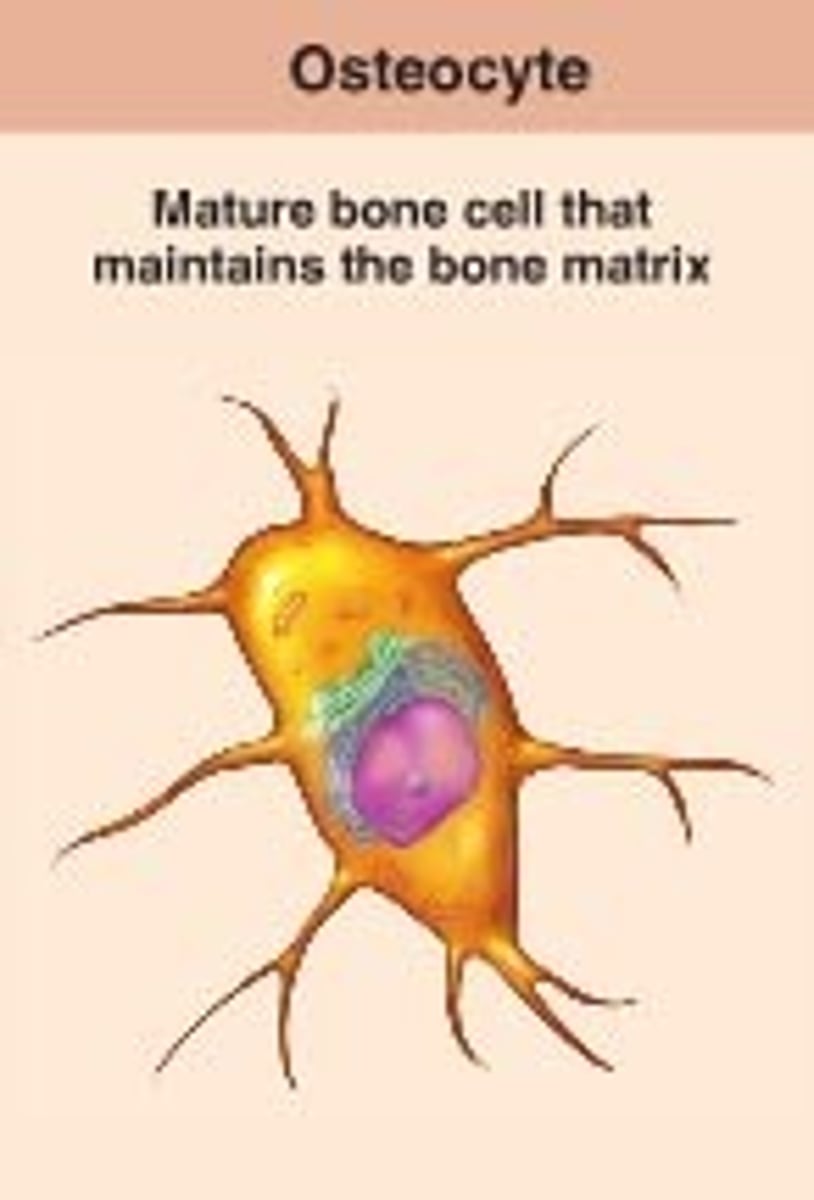
osteocyte
mature bone cell
major functions of bones
support, protection, and movement, blood cell formation, inorganic salt storage
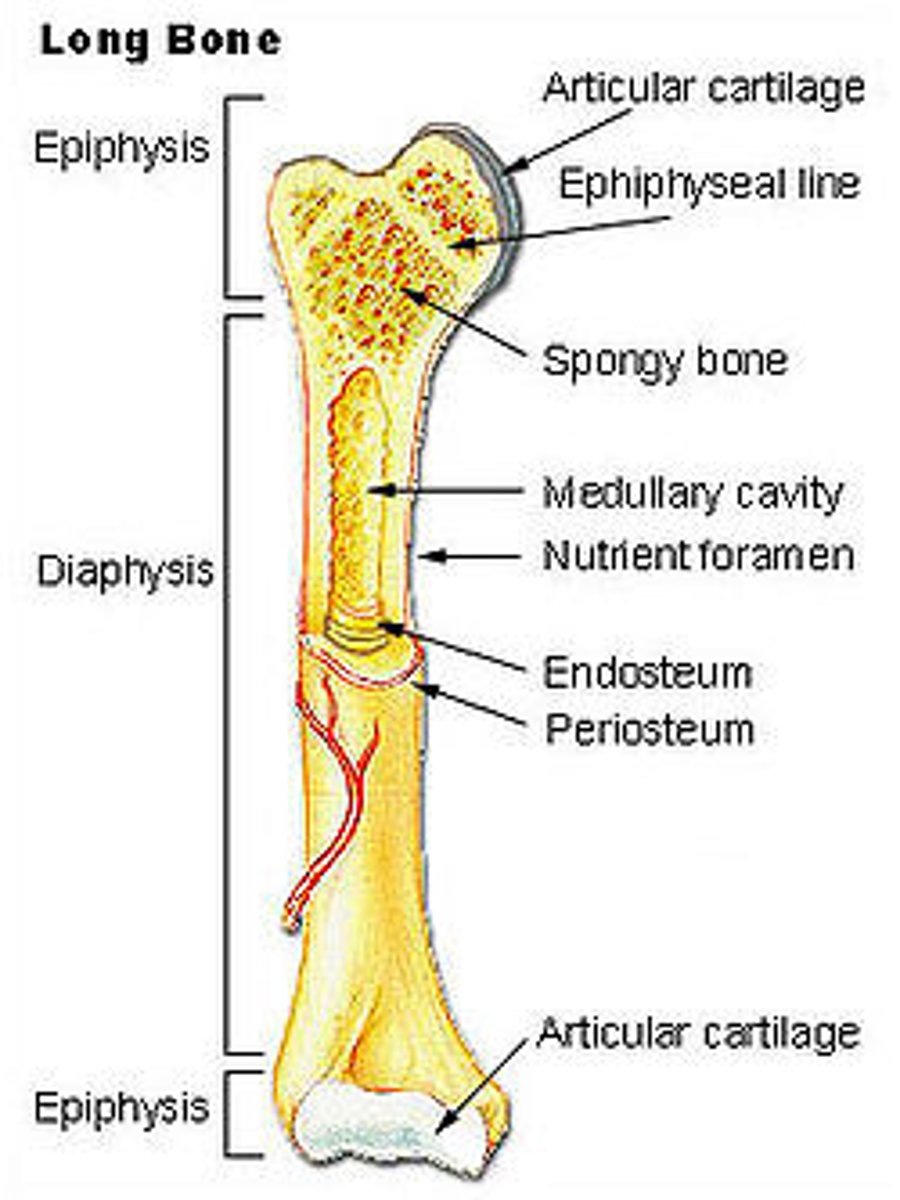
epiphysis
either end of a long bone
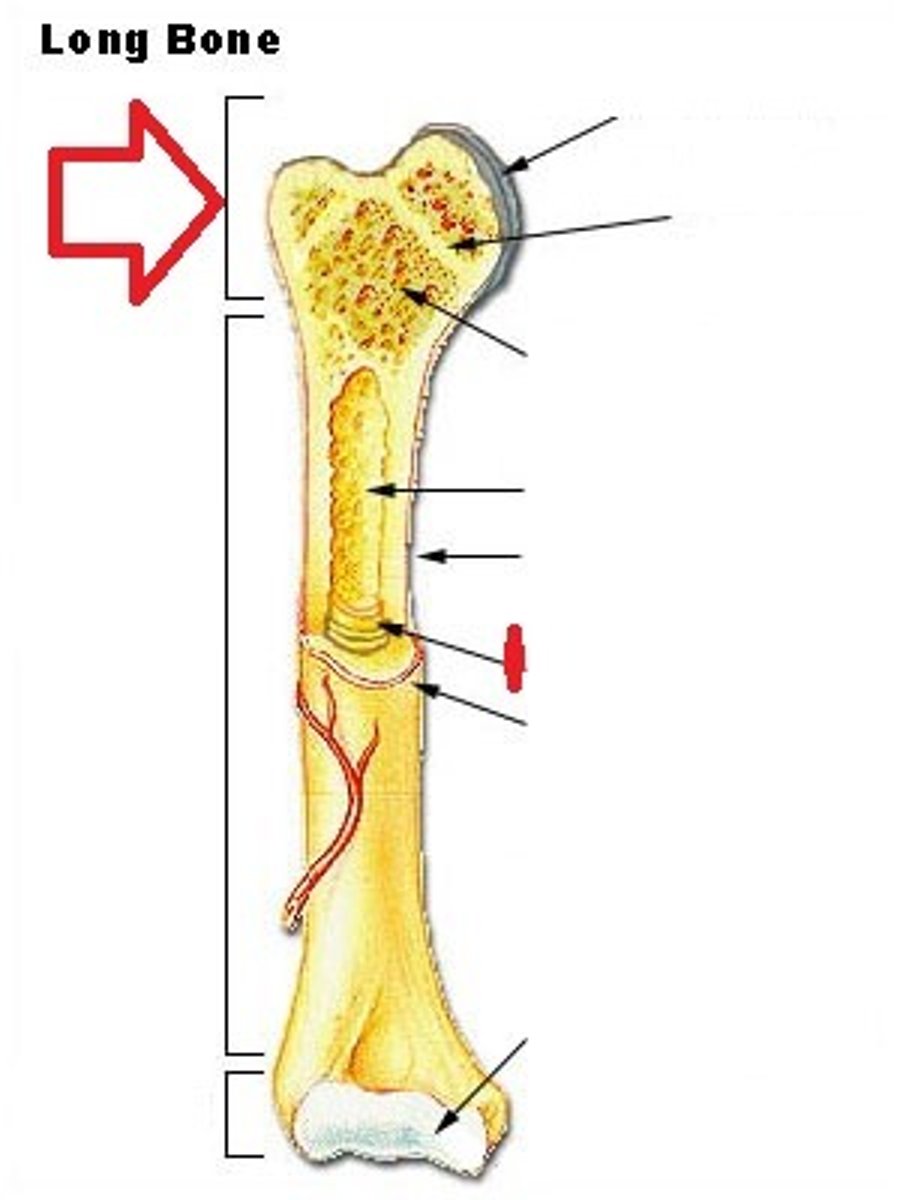
articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage that covers the ends of bones in synoival joints
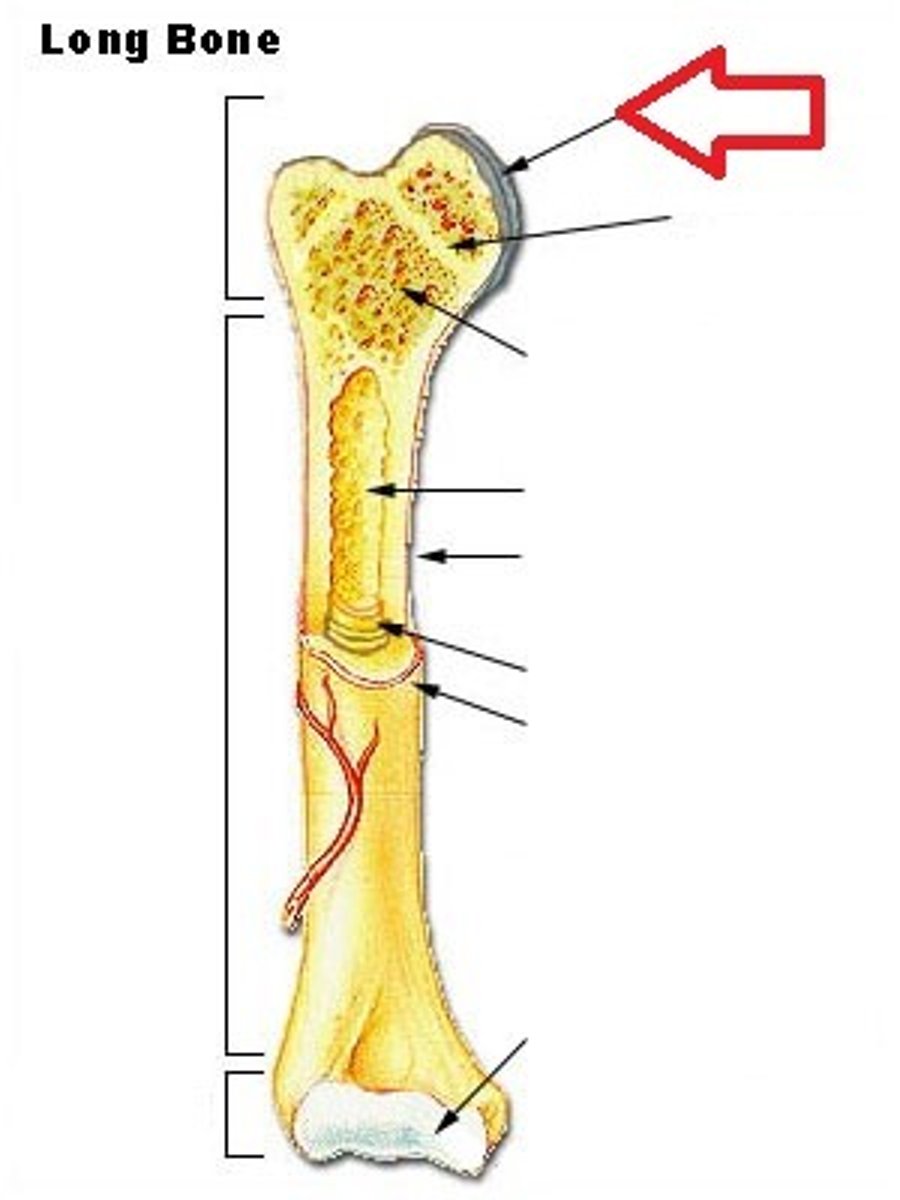
periosteum
dense connective tissue covering the surface of a bone
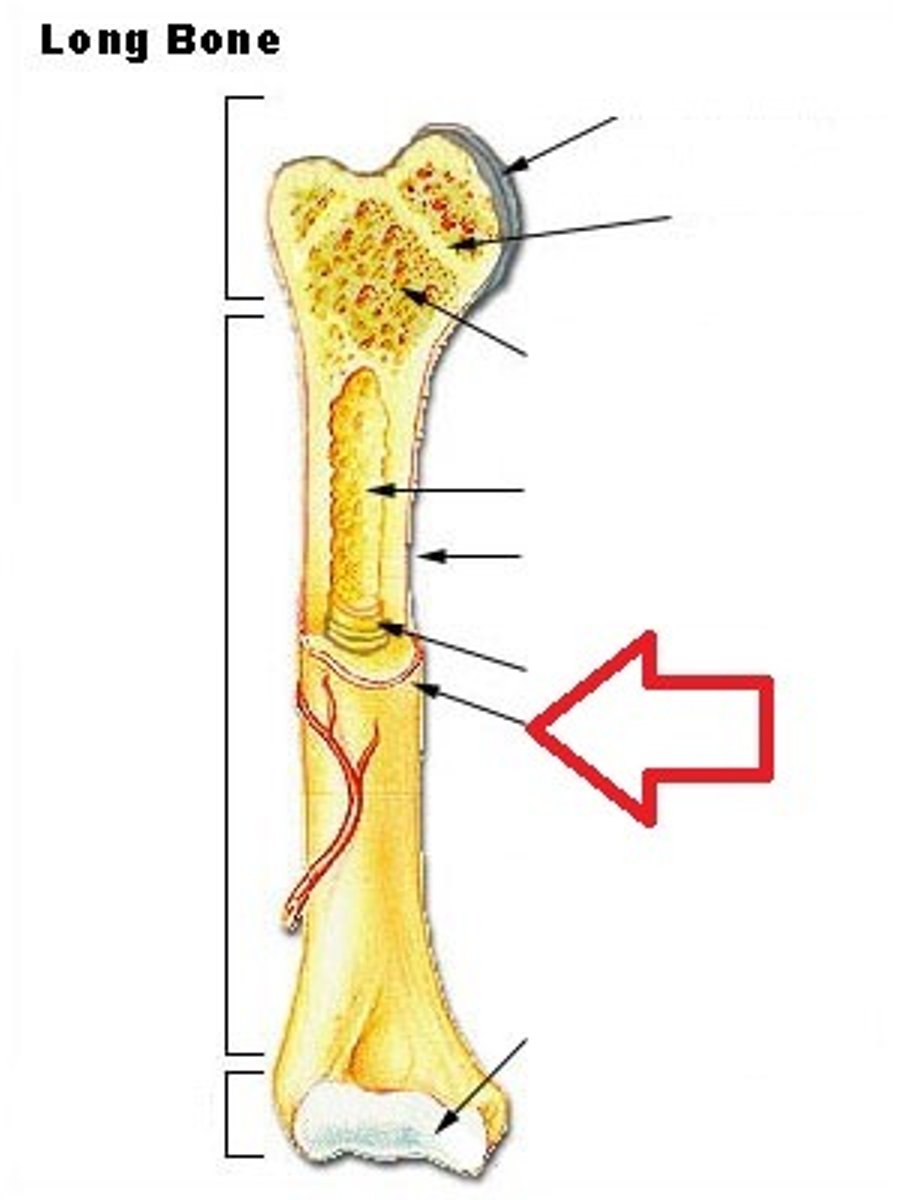
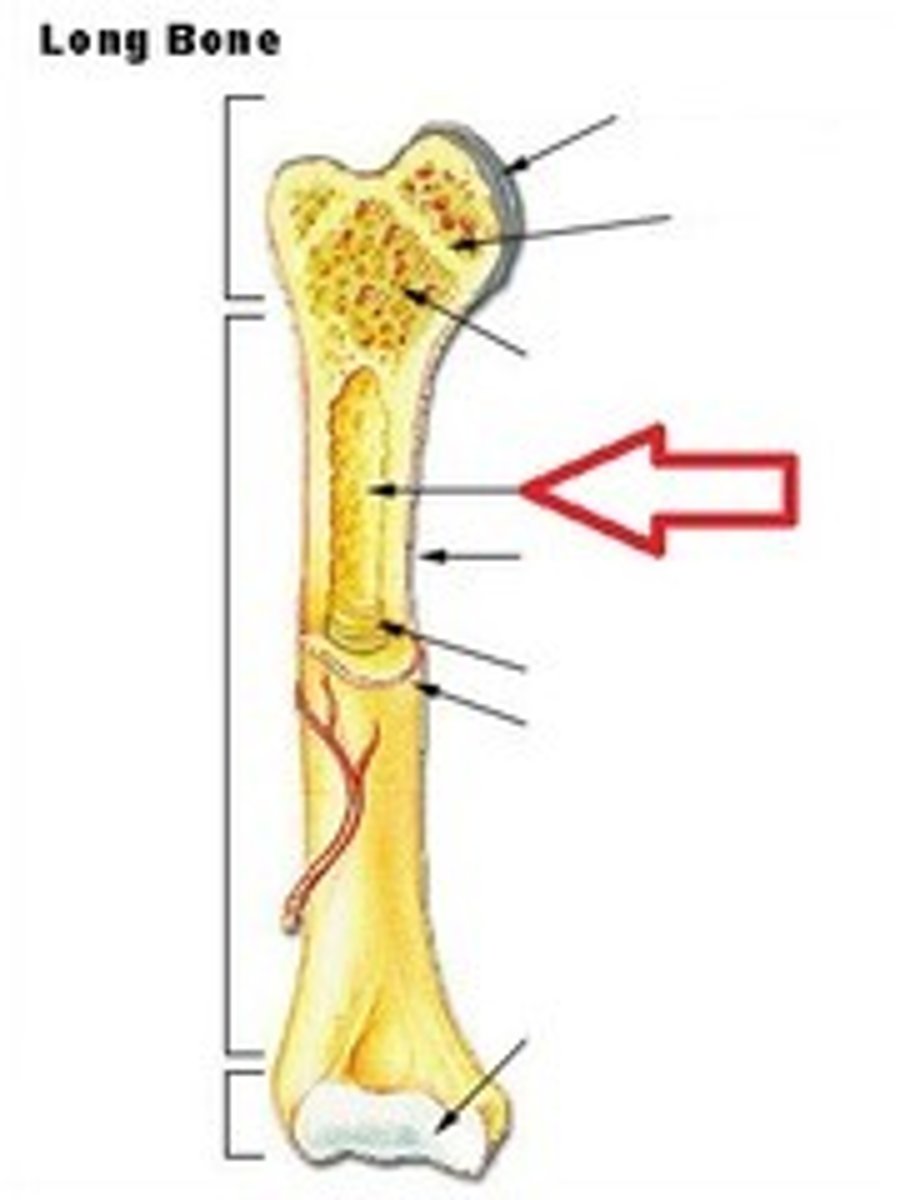
medullary cavity
cavity containing marrow in the diaphysis of a long bone
endosteum
tissue lining the the meduallary cavity in a bone
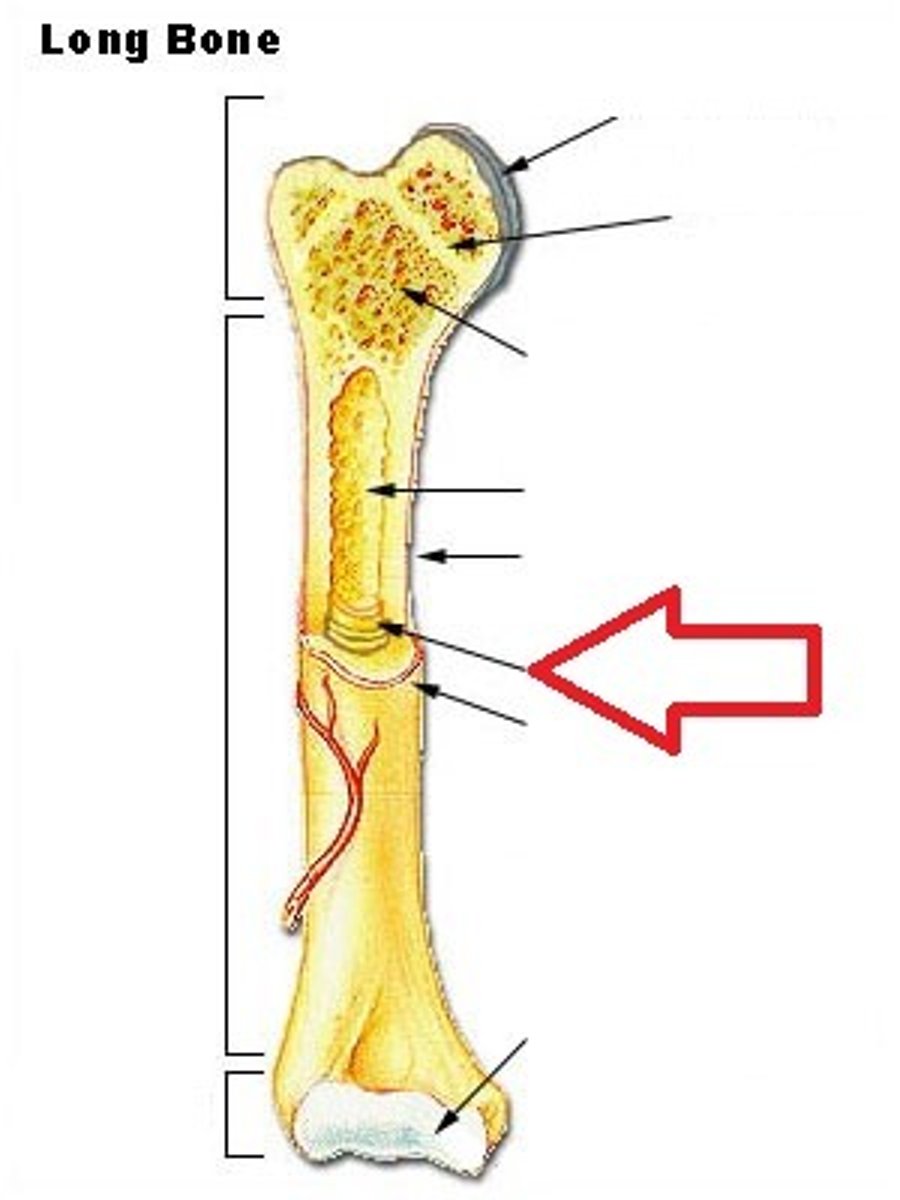
diaphysis
shaft of a long bone
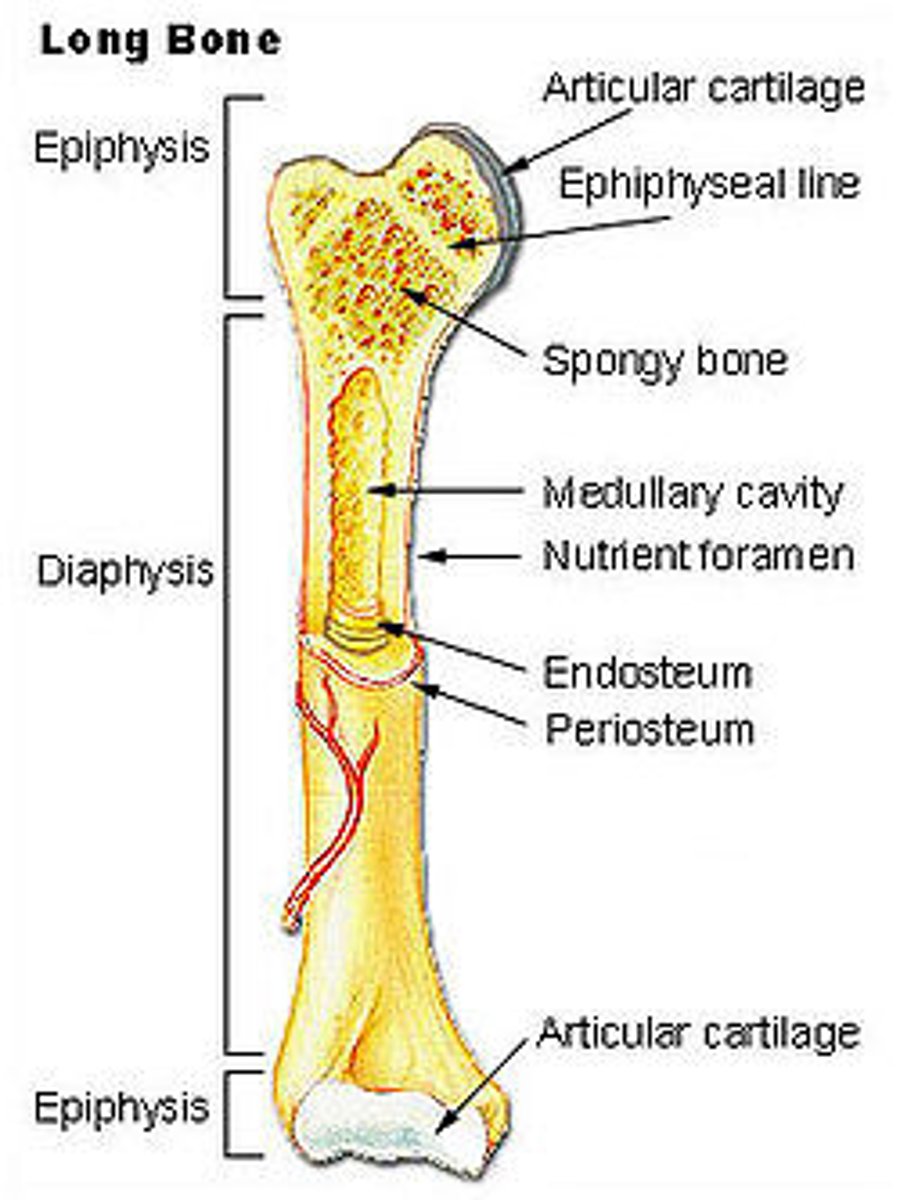
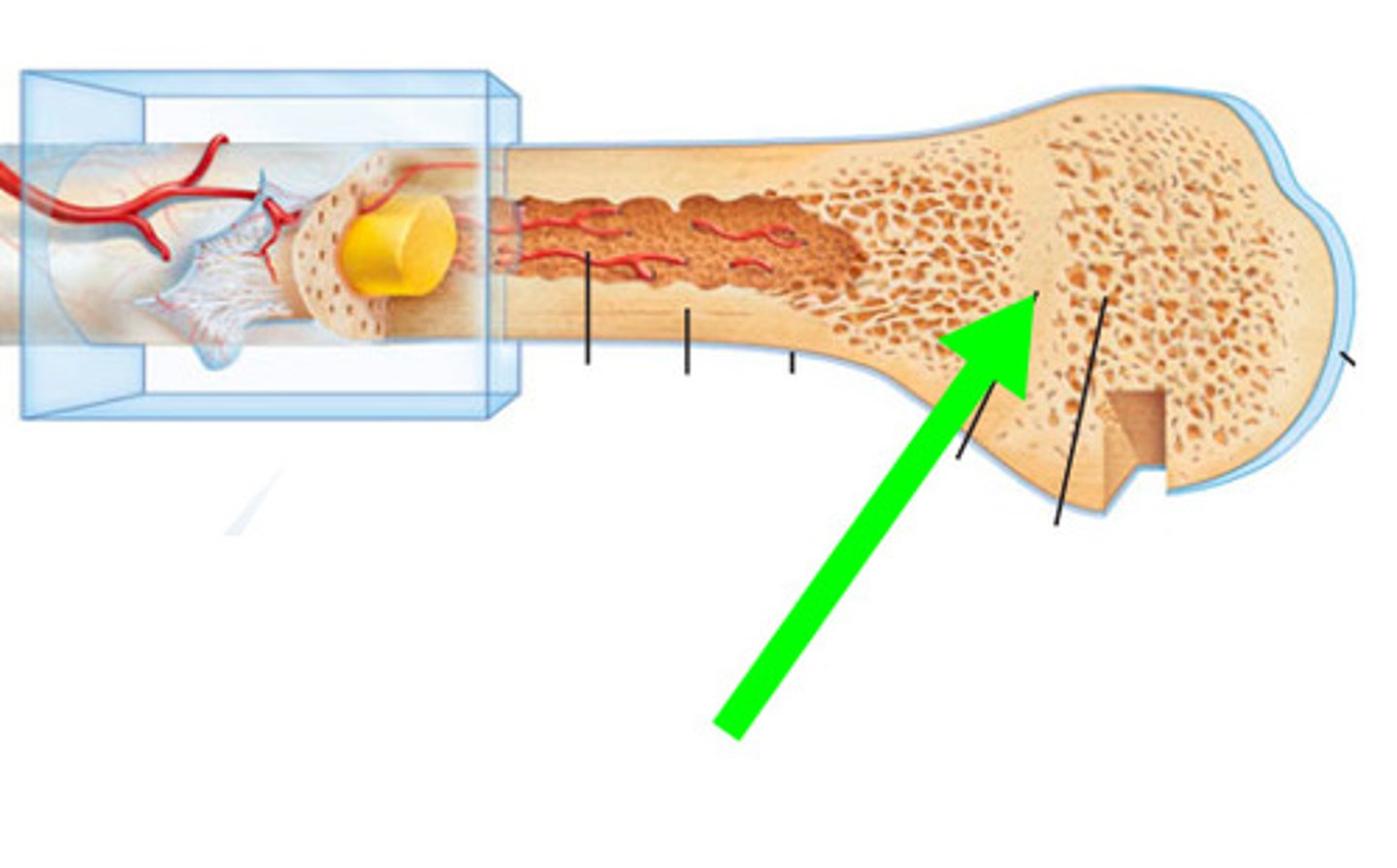
epipheseal plate
growth plate; band of hyaline cartilage located in the epiphysis
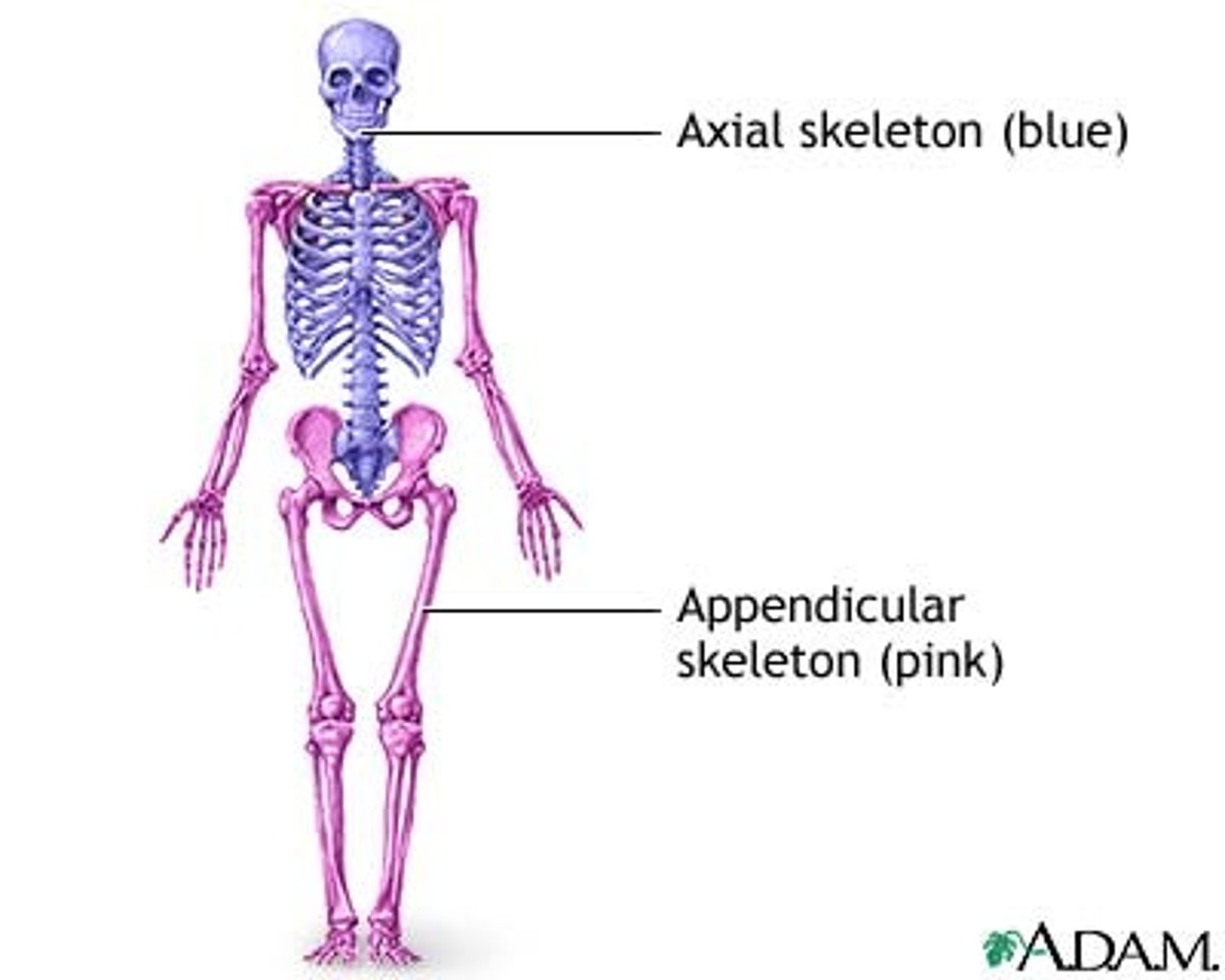
axial skeleton
consists of the bones of the head, neck and trunk
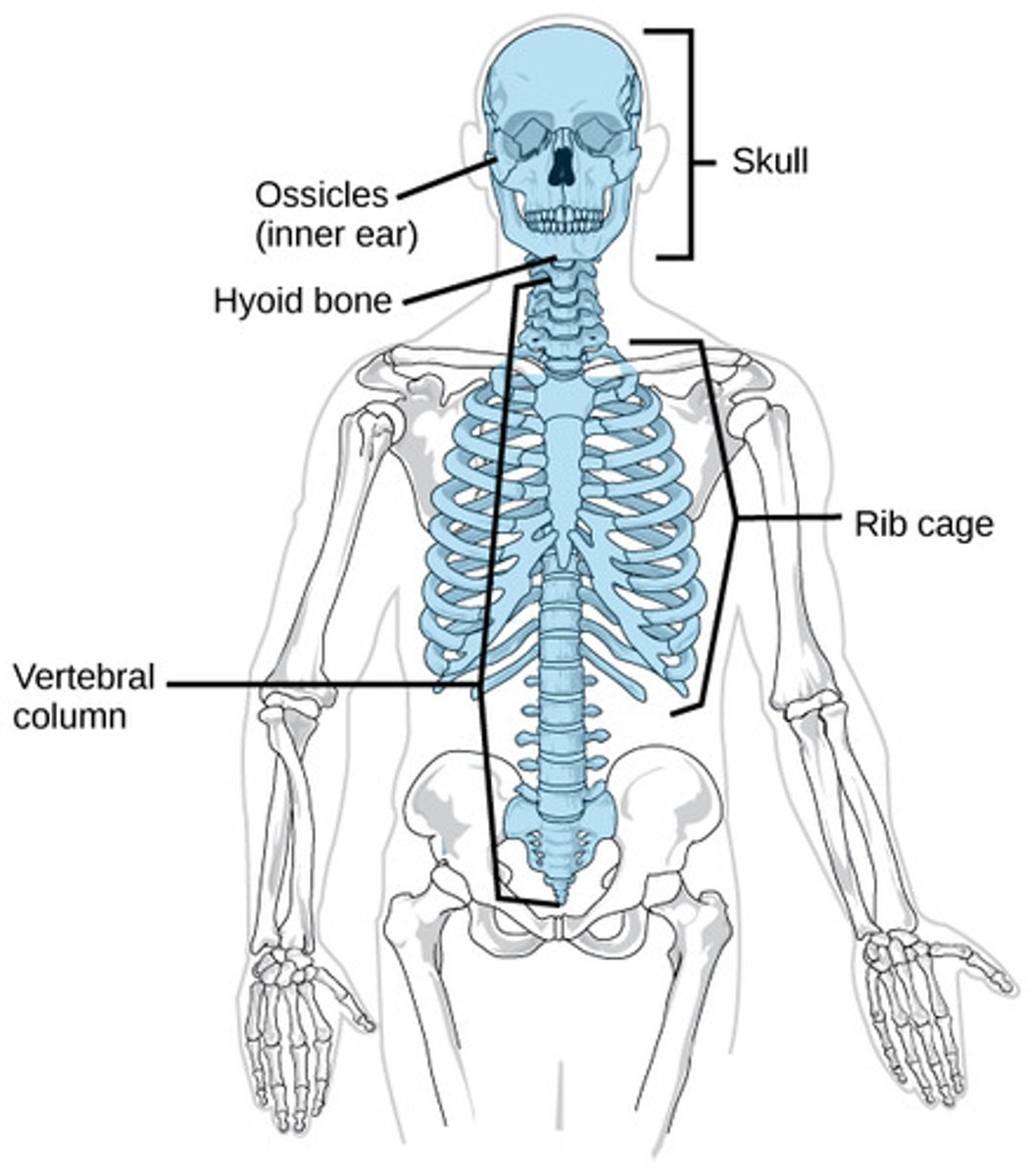
appendicular skeleton
consists of the bones of the upper and lower limbs as well as the pectoral and pelvic girdles
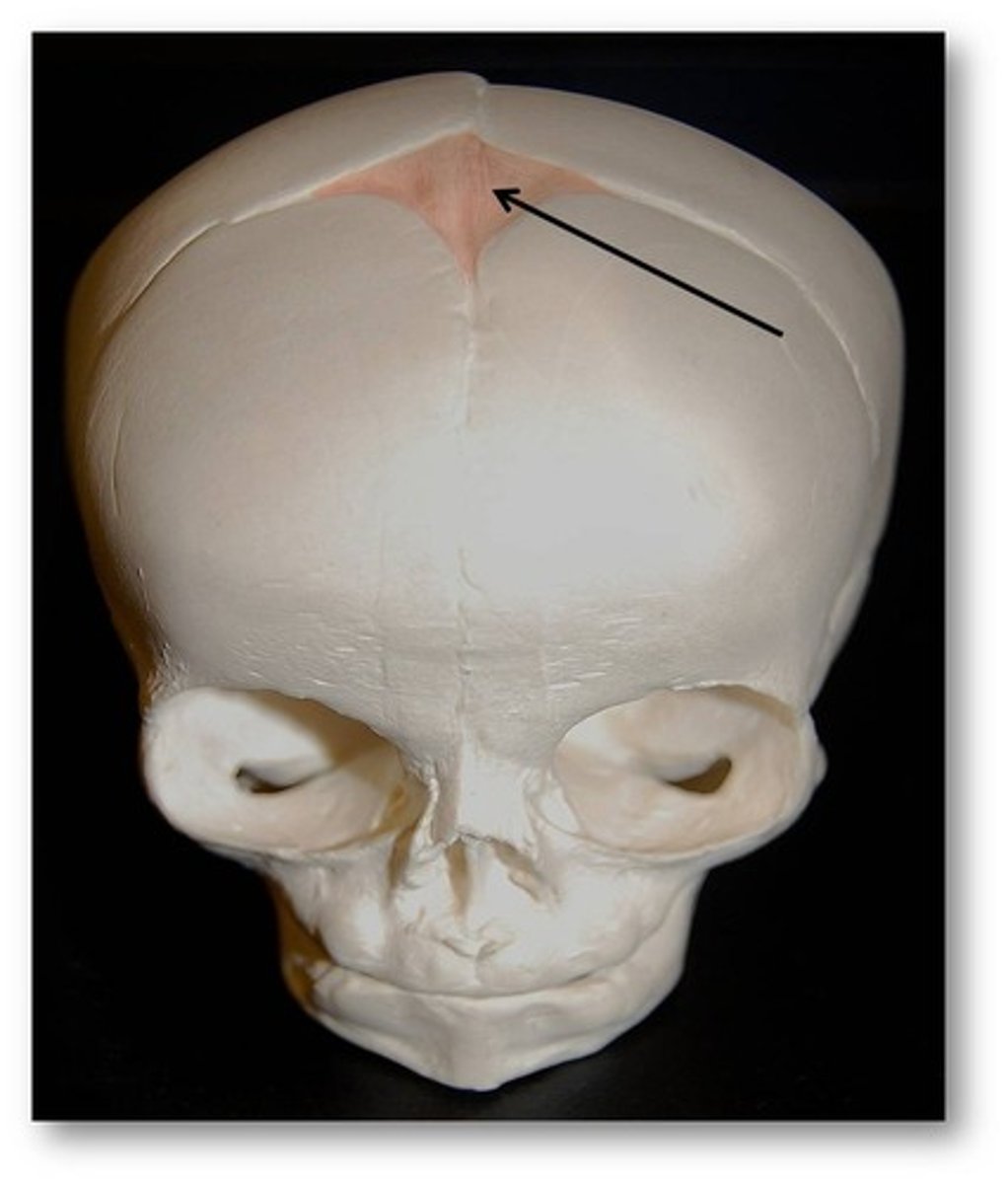
fontanels
"soft spots"; found in the skulls of infants
Joints
also known as articulations; functional junction between 2 bones
Structural classifications (joints)
- fibrous joints
- cartilaginous joints
- synovial joints
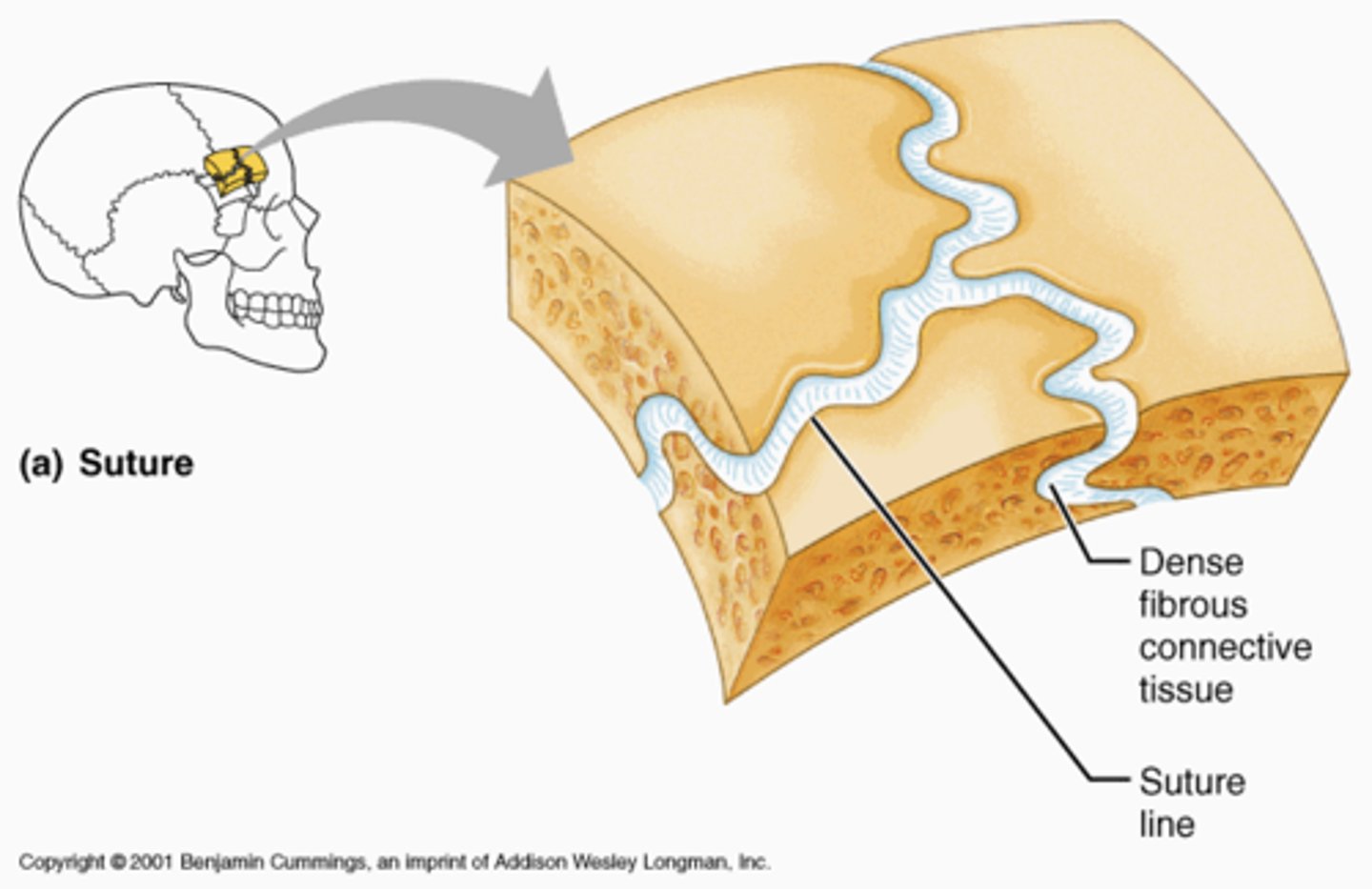
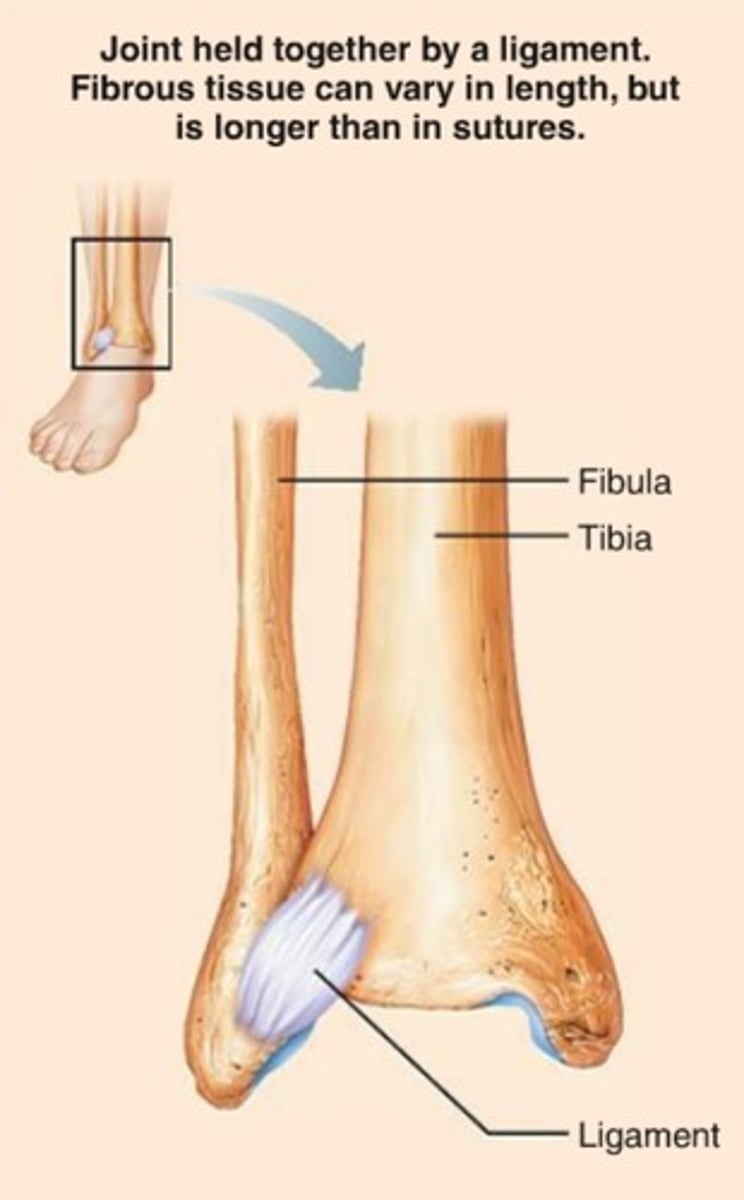
Fibrous joints
held together by dense connective tissue
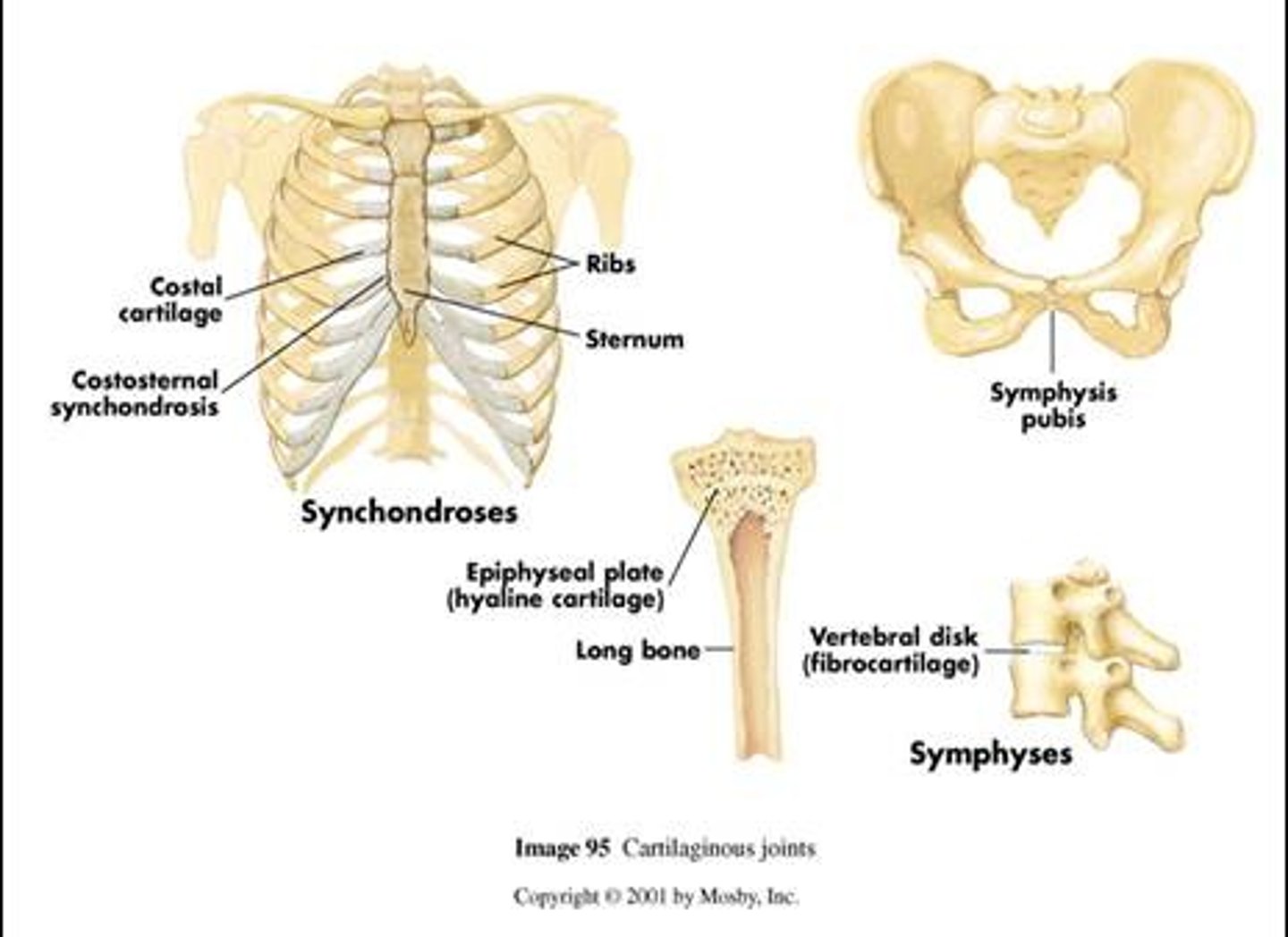
Cartilaginous joints
hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage connect bones
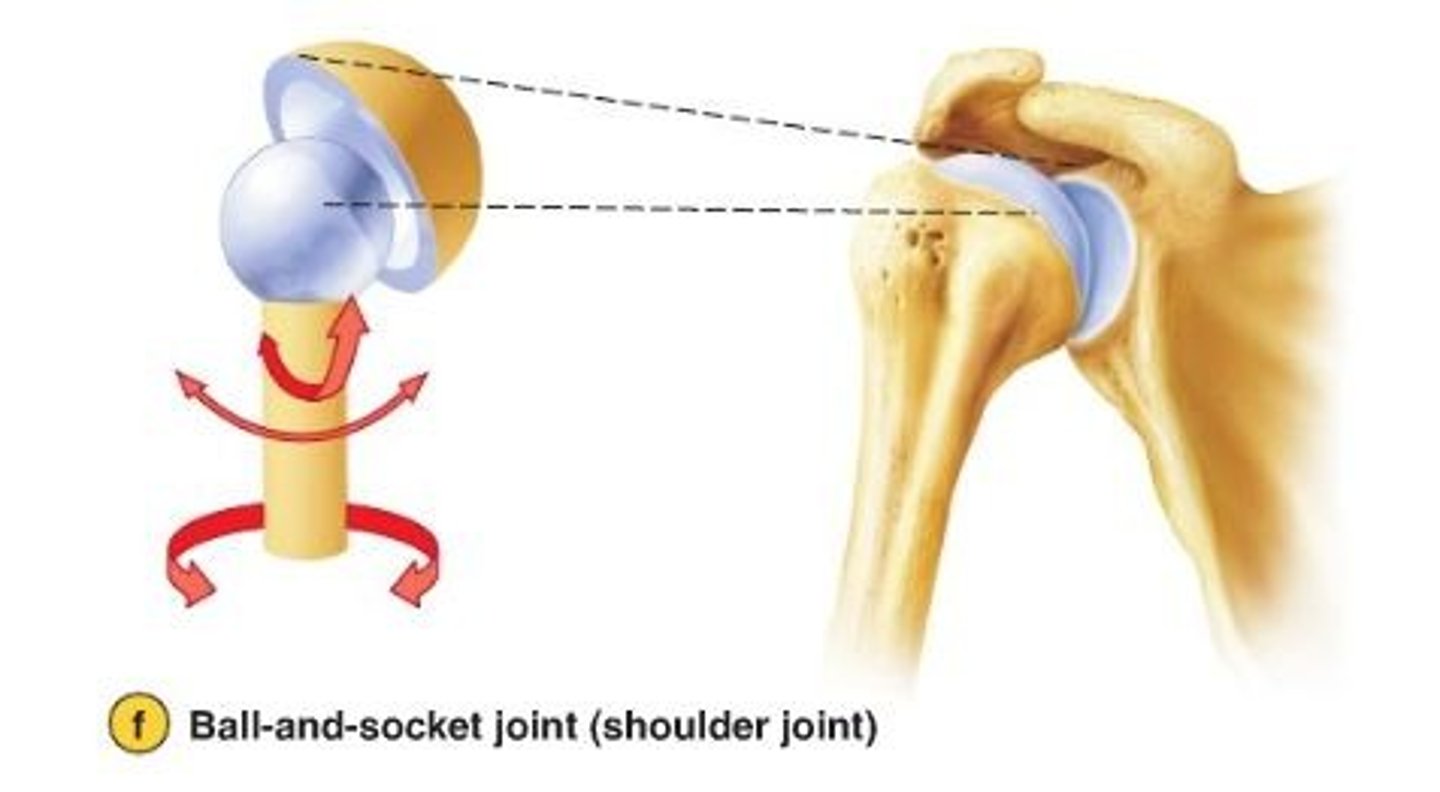
Synovial joints
allow free movement
Functional classifications (joints)
- synarthrotic joints
- amphiarthrotic joints
- diarthrotic joints
Synarthrotic joints
considered immovable
Amphiarthrotic joints
slightly movable
Diarthrotic joints
freely movable
Types of Fibrous joints (3)
- syndesmosis
- suture
- gomphosis
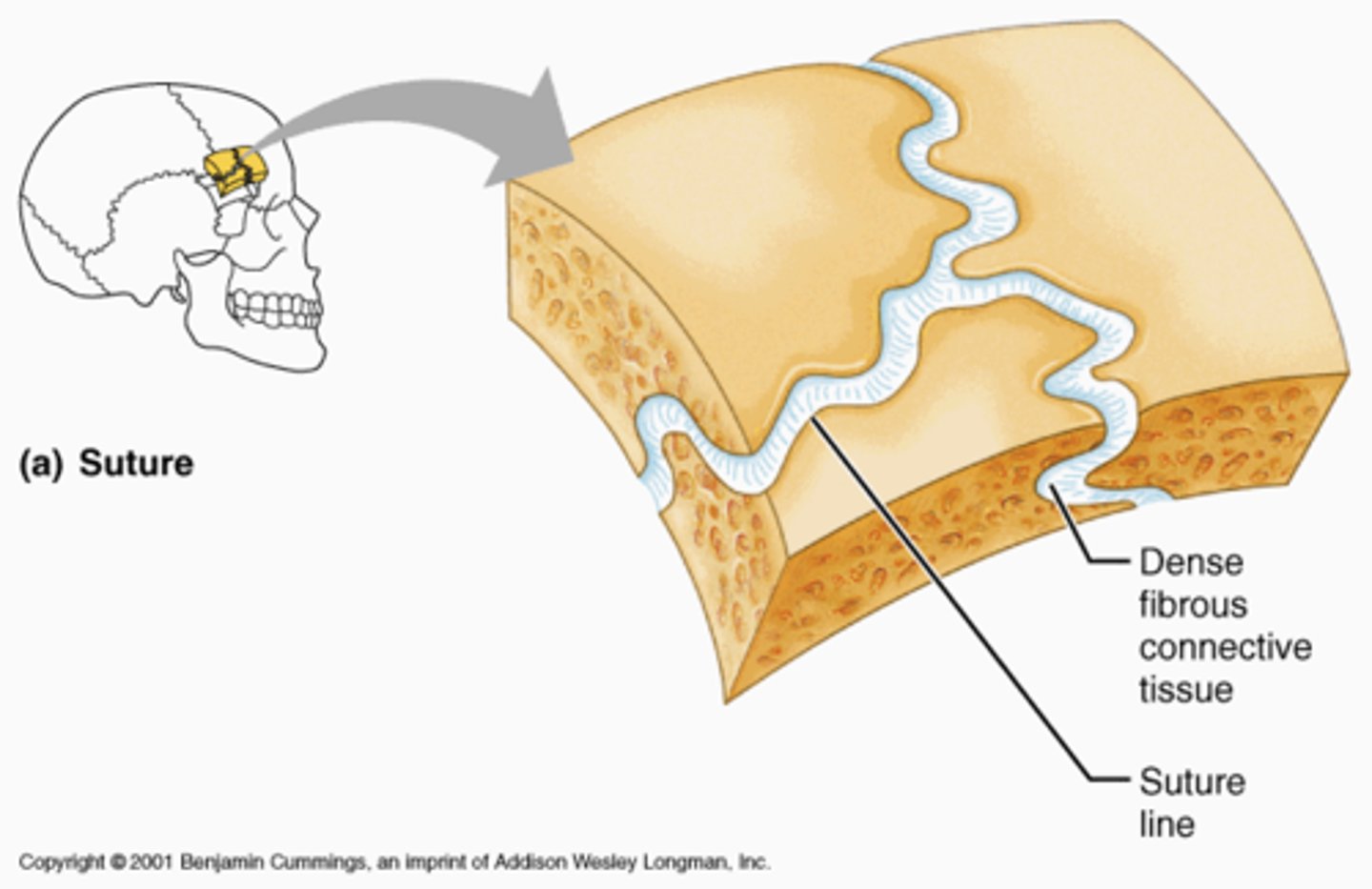
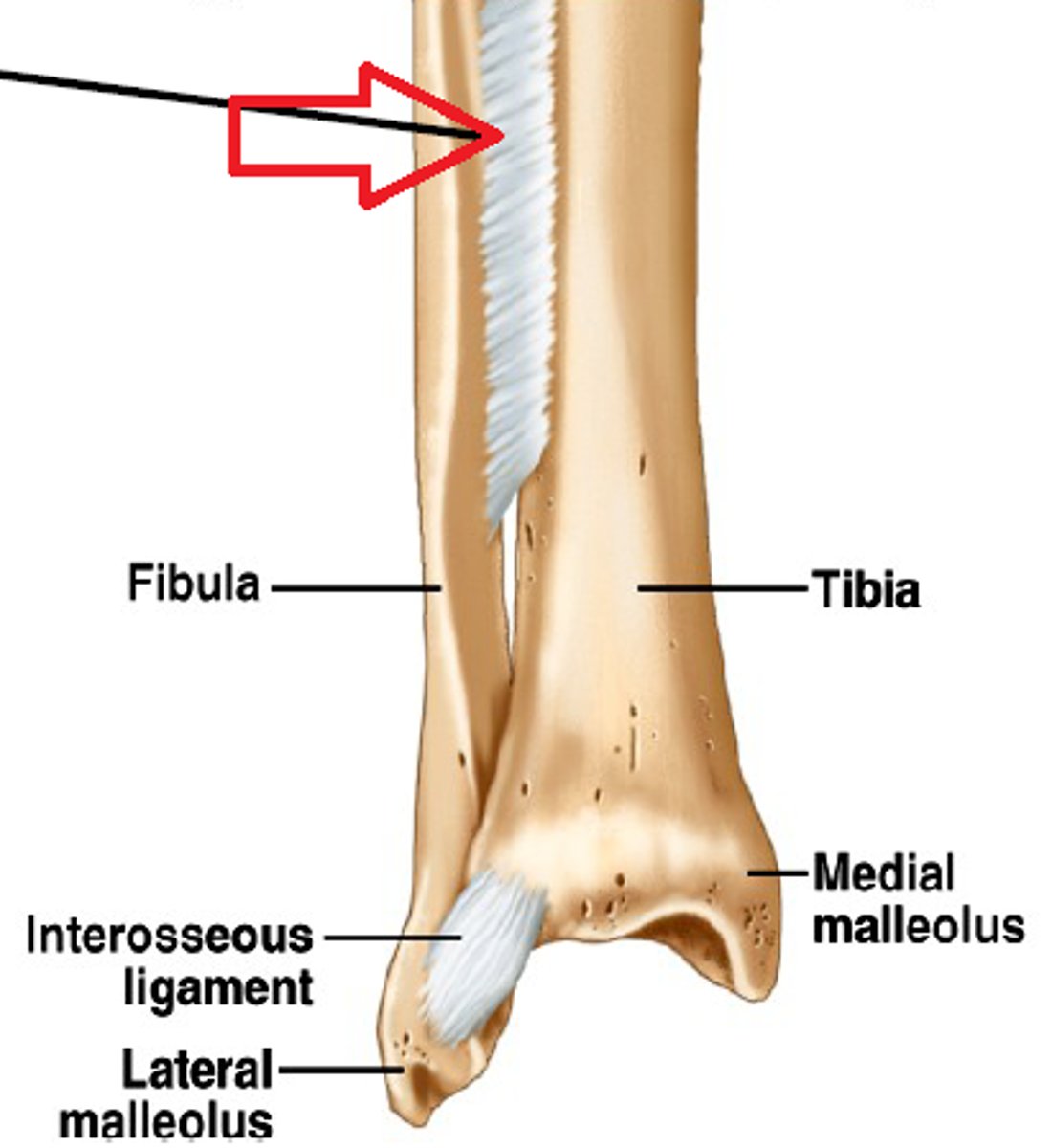
Syndesmosis
a sheet or bundle of fibrous tissue connecting bones
- lies between tibia and fibula (interosseous membrane)
- amphiarthrotic - slightly moveable
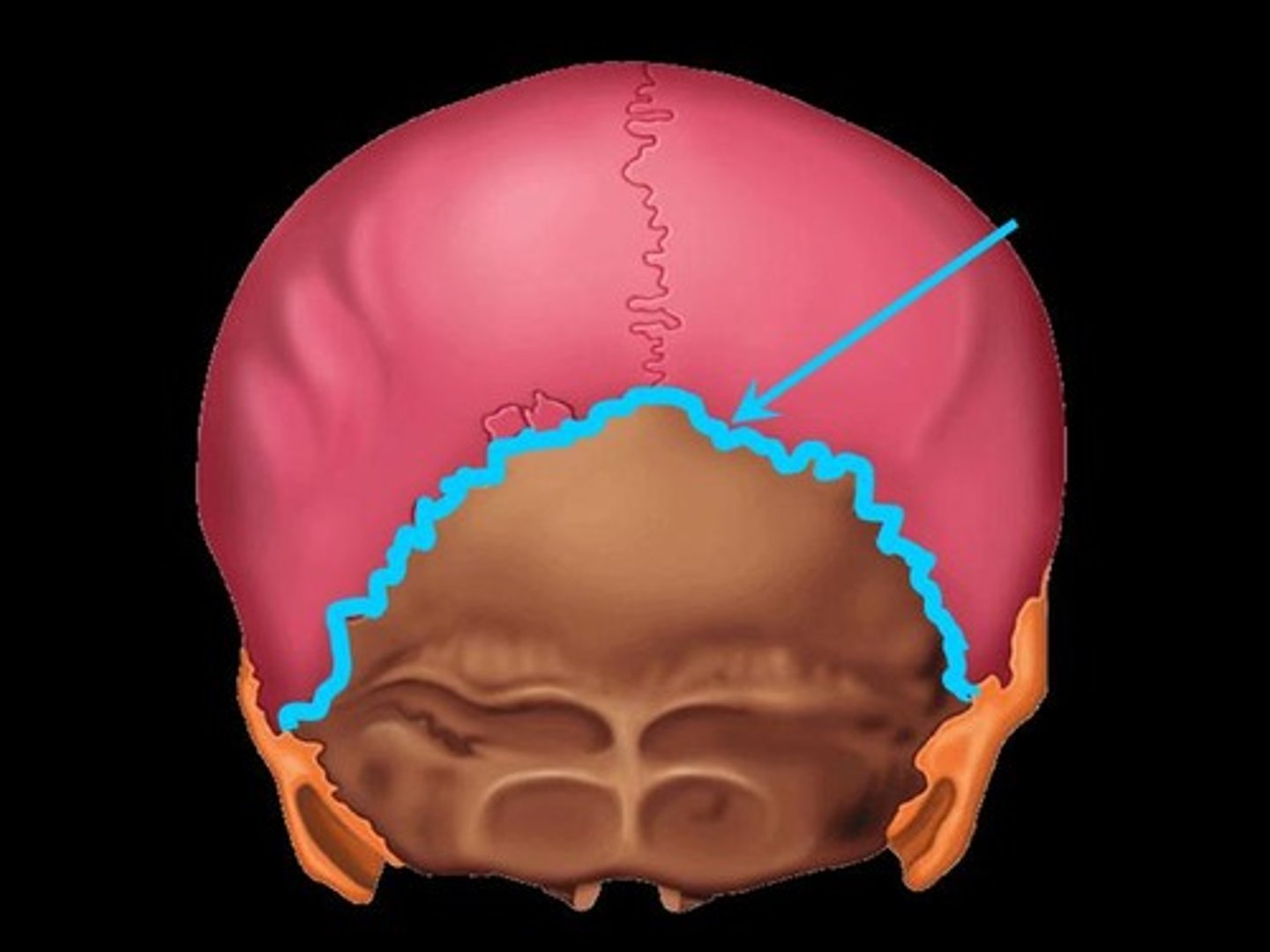
Suture
between flat bones (of skull)
- teeth-like projections
- thin layer of connective tissue connects bone
- synarthritic - immovable
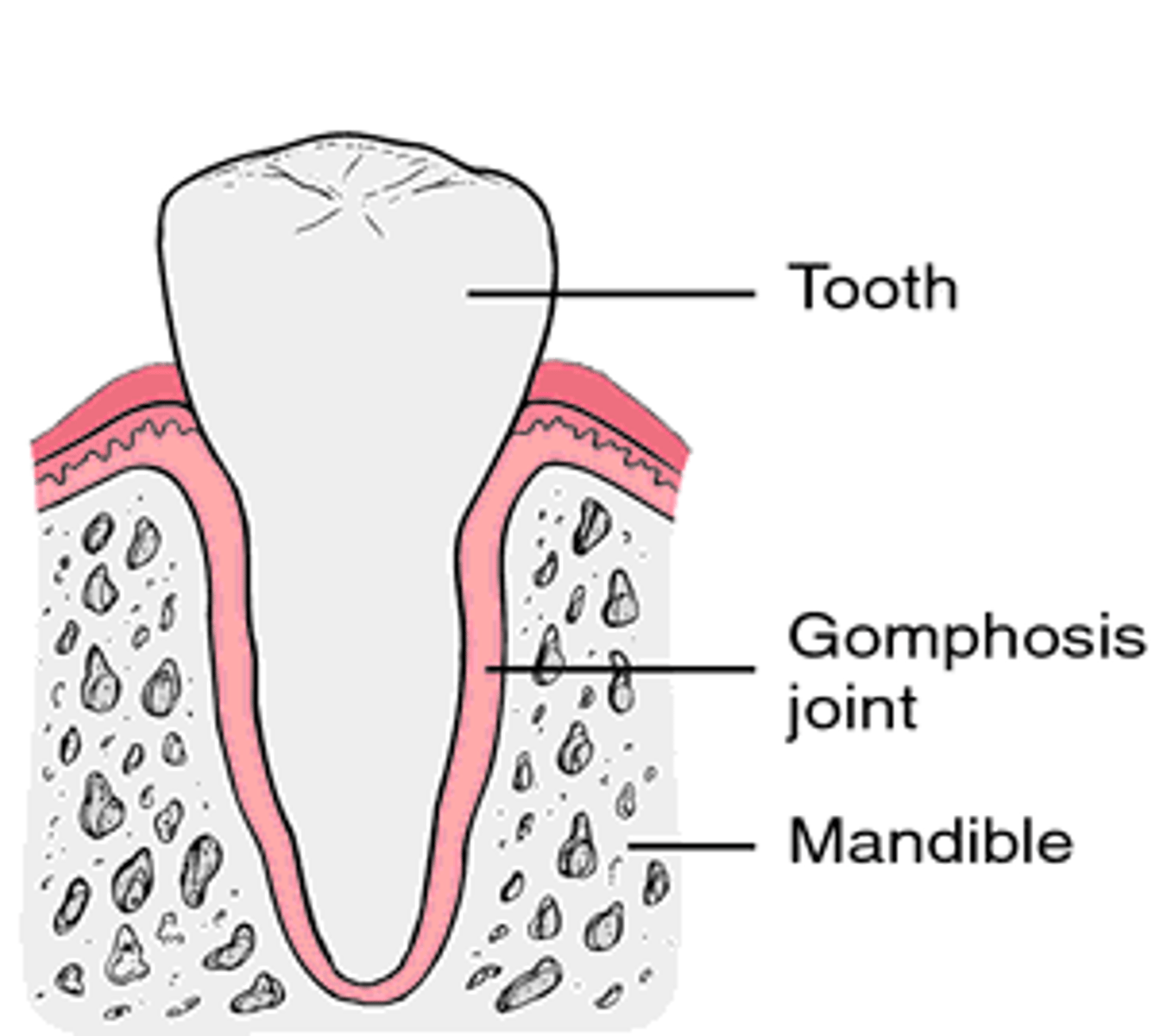
Gomphosis
- cone-shaped bony process in a socket
- tooth in jawbone
- synarthritic - immovable
Types of cartilaginous joints (2)
- synchondrosis
- symphysis
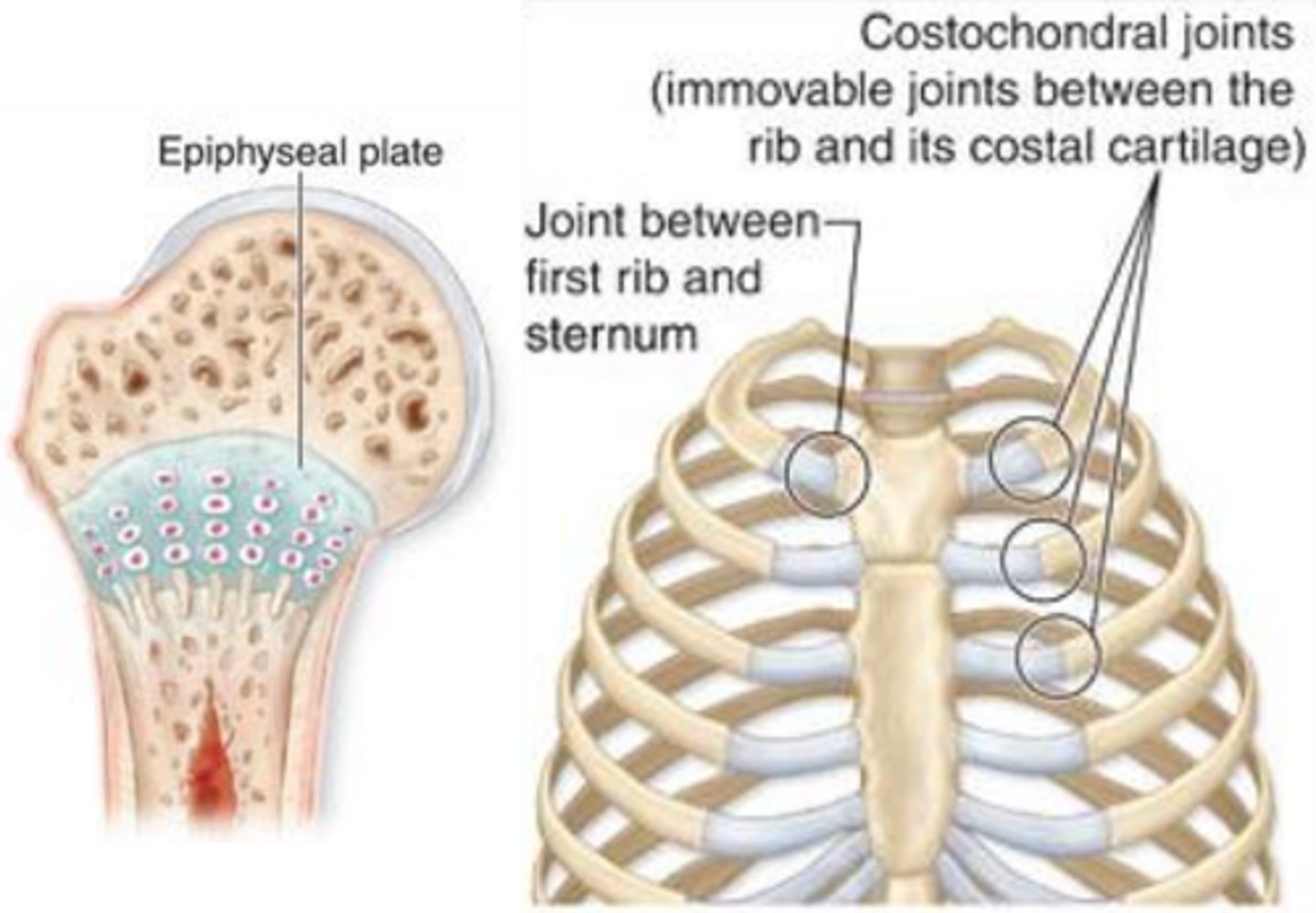
Synchondrosis
bands of hyaline cartilage unite bones
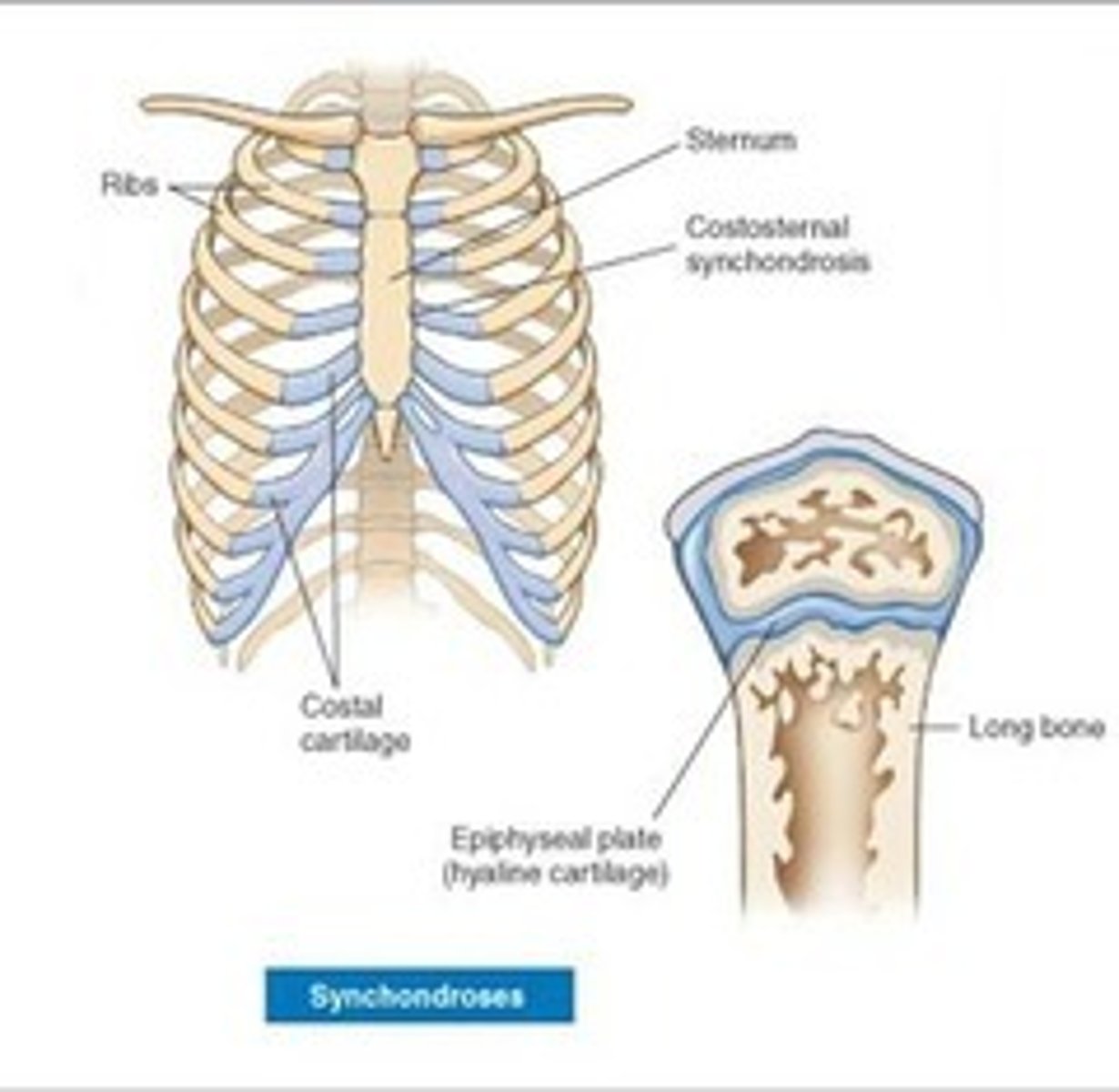
Examples of synchondrosis
- epiphyseal plate (temporary)
- between manubrium and the first rib (coastal cartilages)
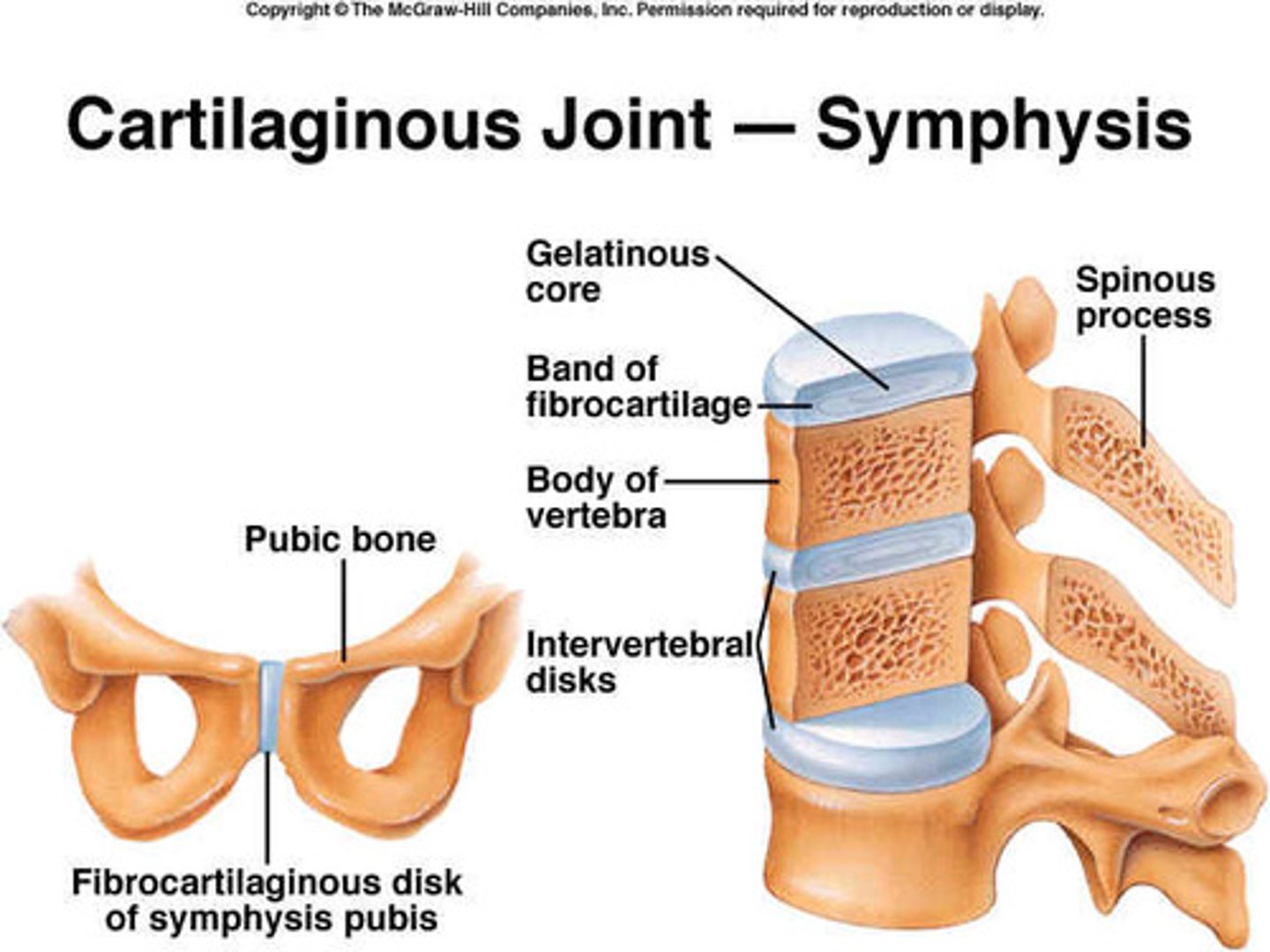
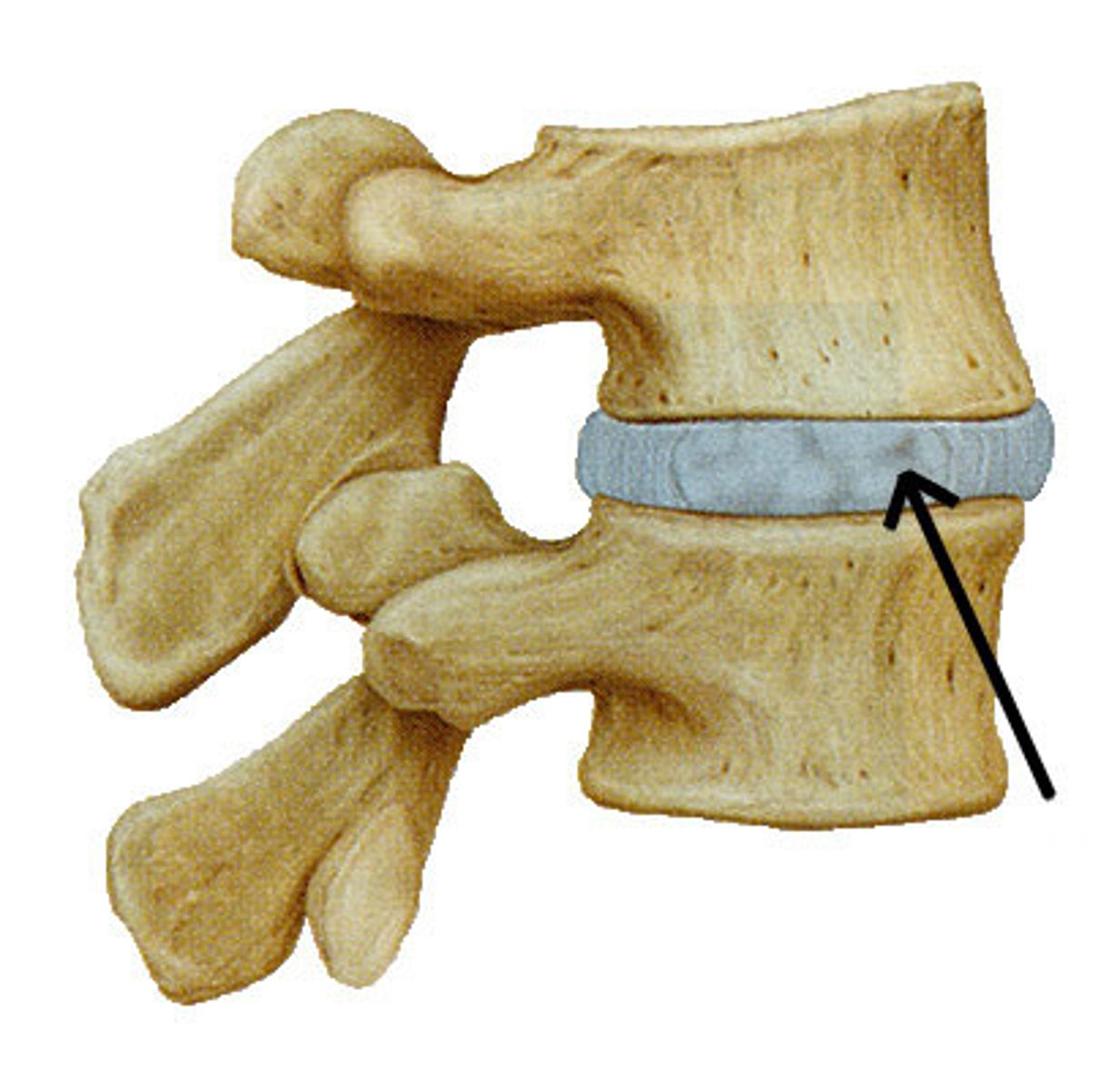
Symphysis
pad of fibrocartilage between bones
- amphiarthrotic - slighly moveable
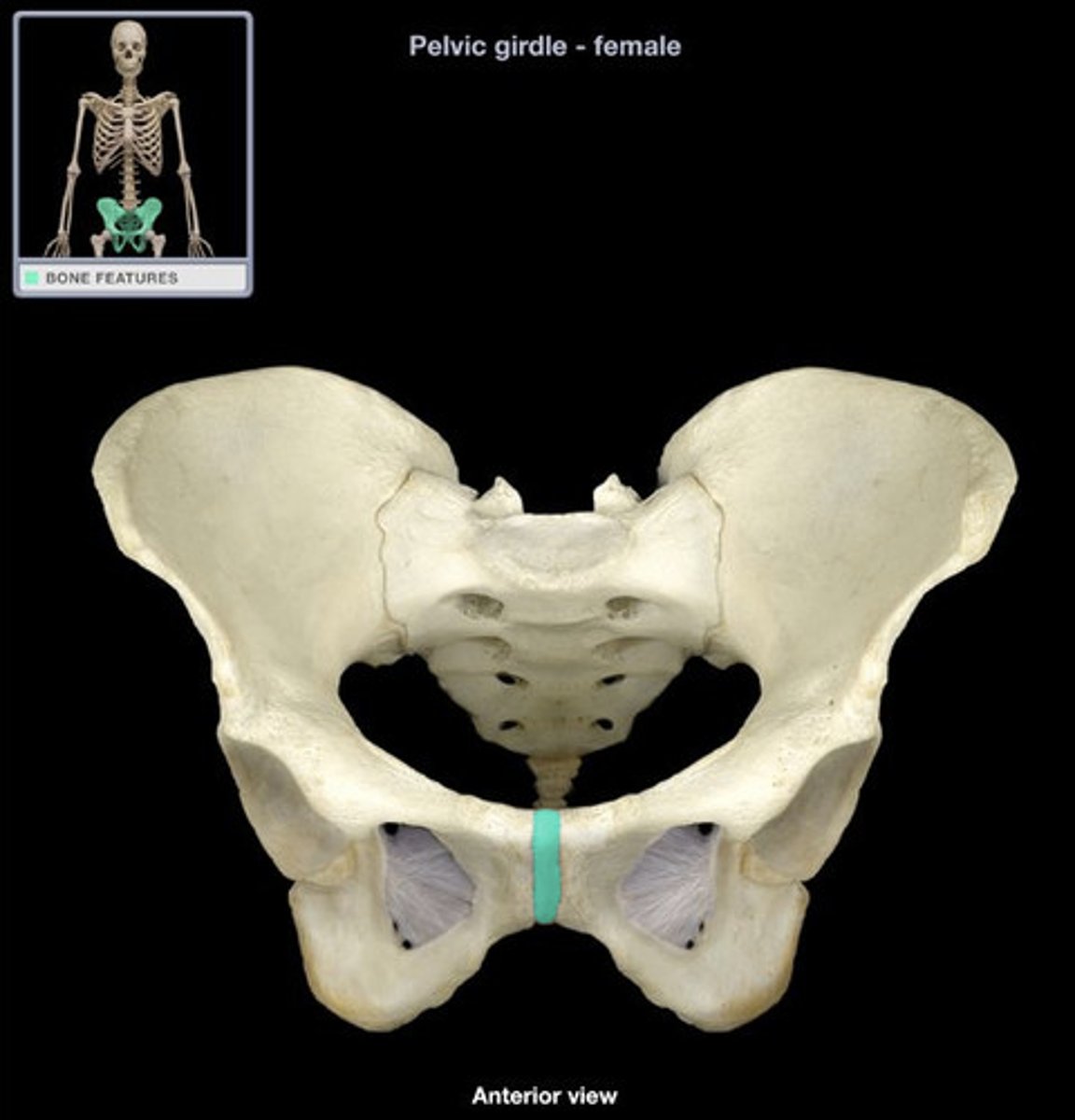
Examples of symphysis
- pubic symphysis
- joint between bodies of adjacent vertebrae
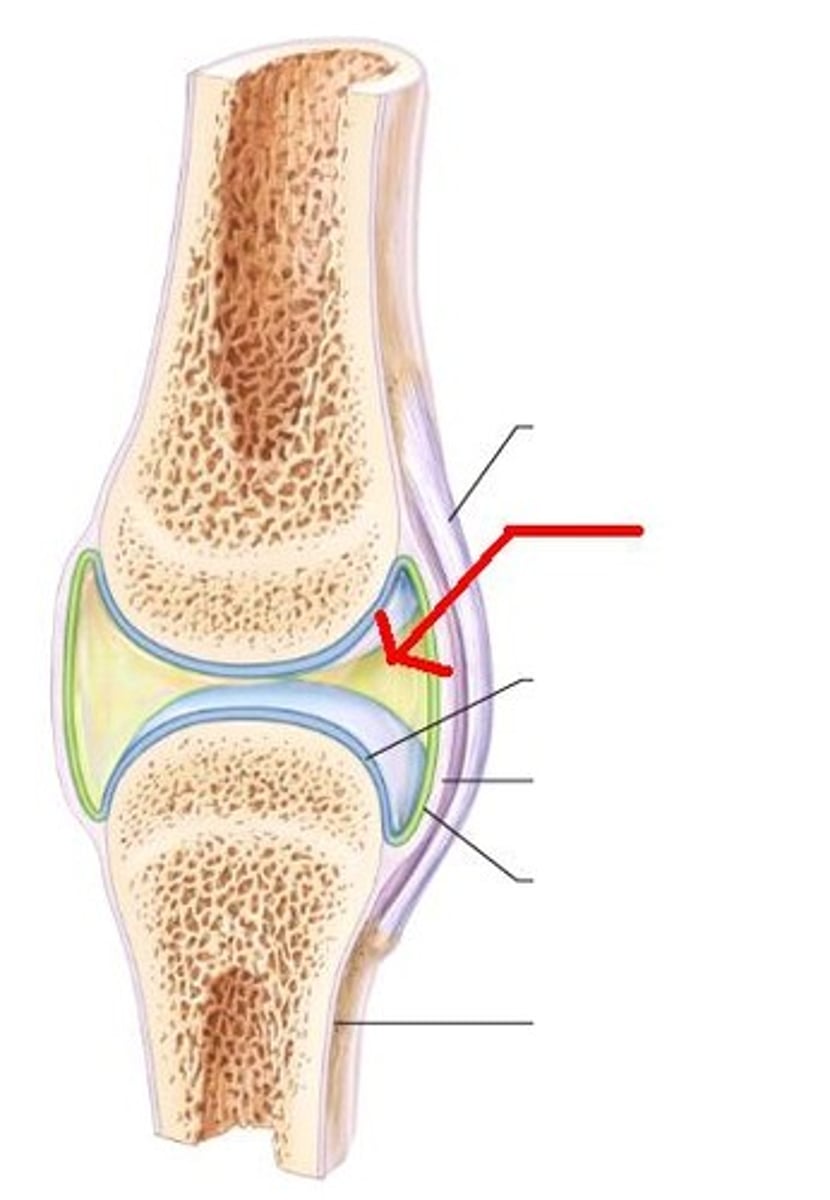
Synovial joint
- most common joint
- all are diarthritic - freely moving
Joint capsule
holds together the bones of a synovial joint
- two distinct layers
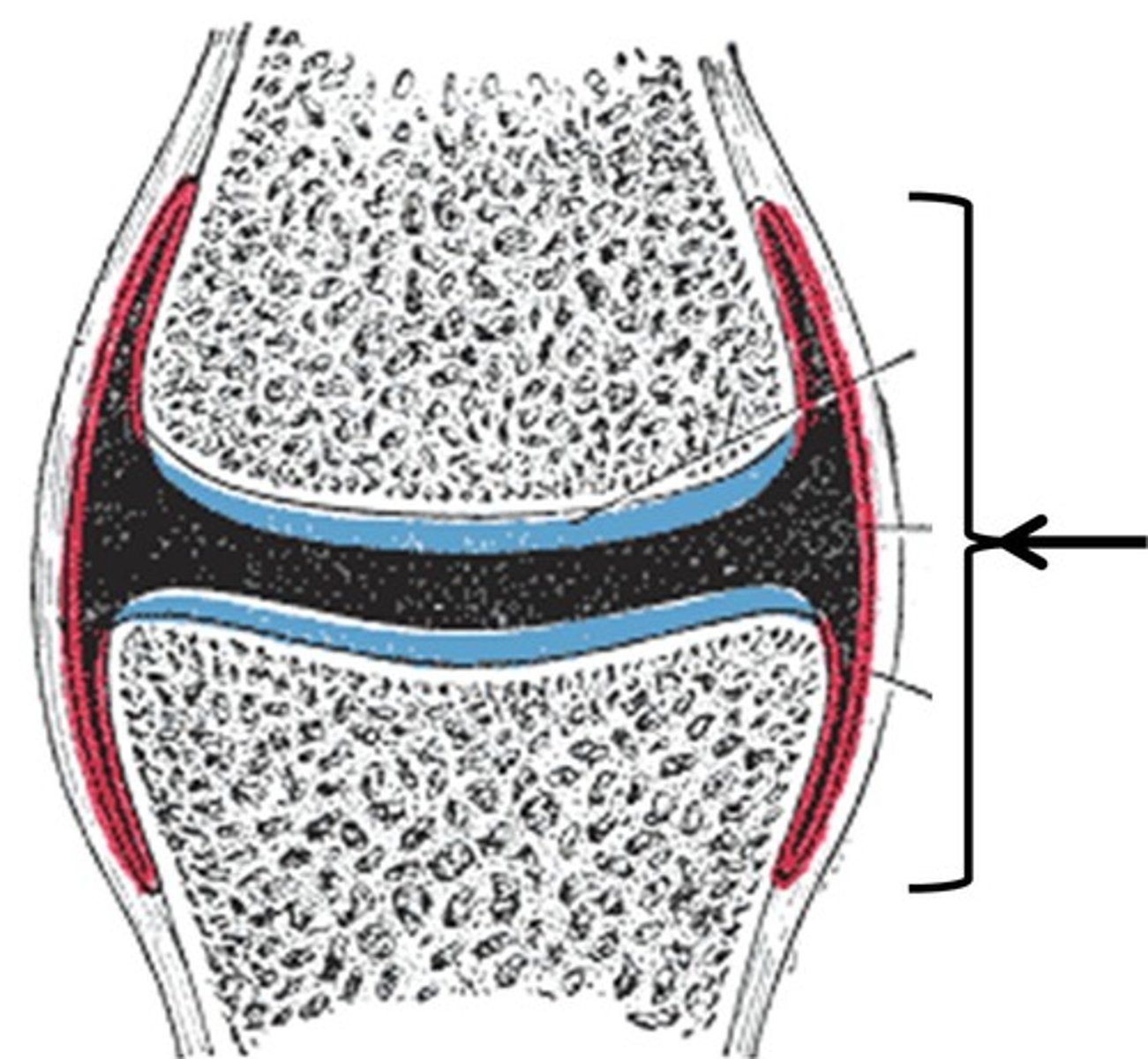
Synovial membrane
secretes synovial fluid
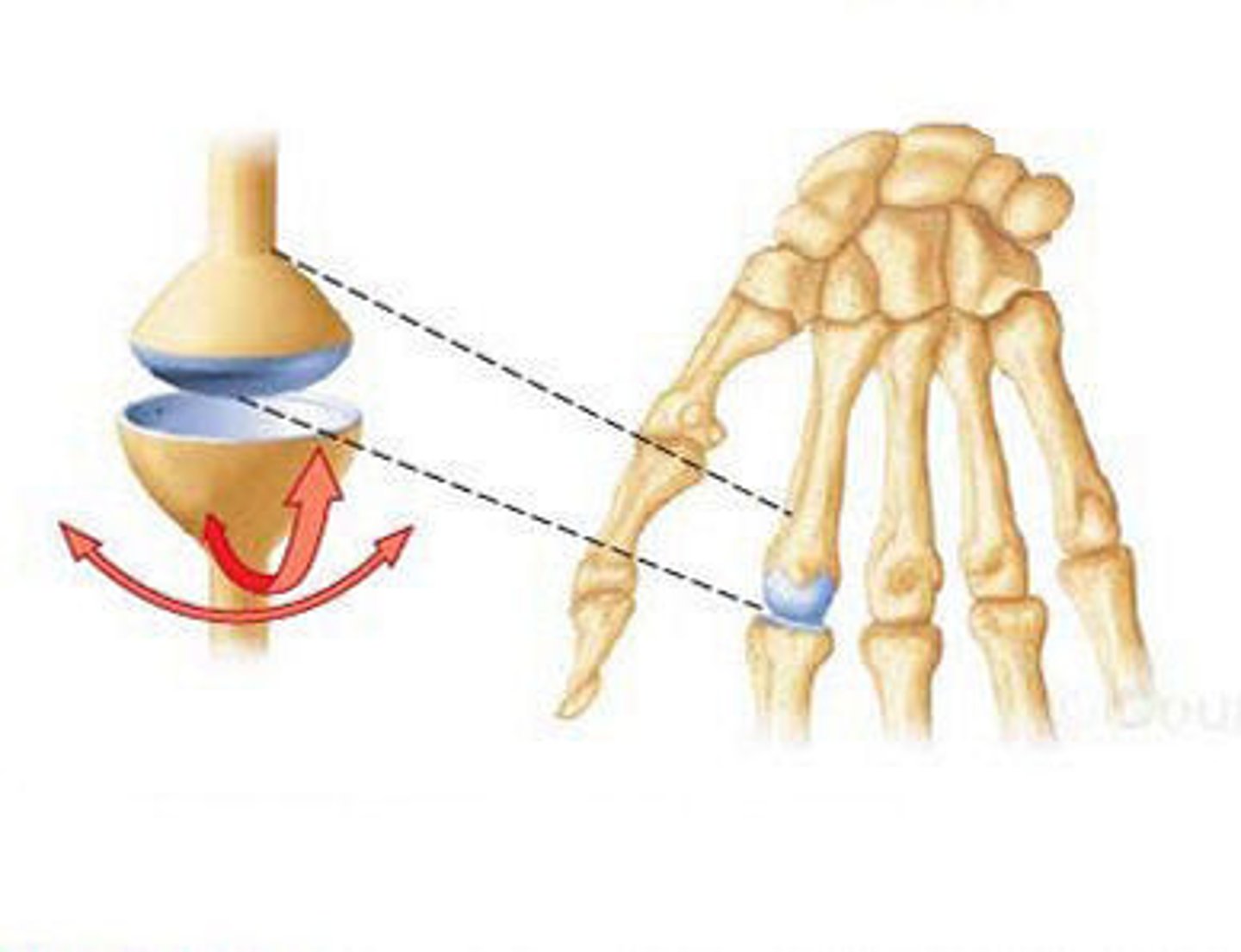
Types of synovial joints (6)
- ball and socket
- condyloid/ellipsoidal joint
- plane/gliding joint
- hinge joint
- pivot joint
- saddle joint
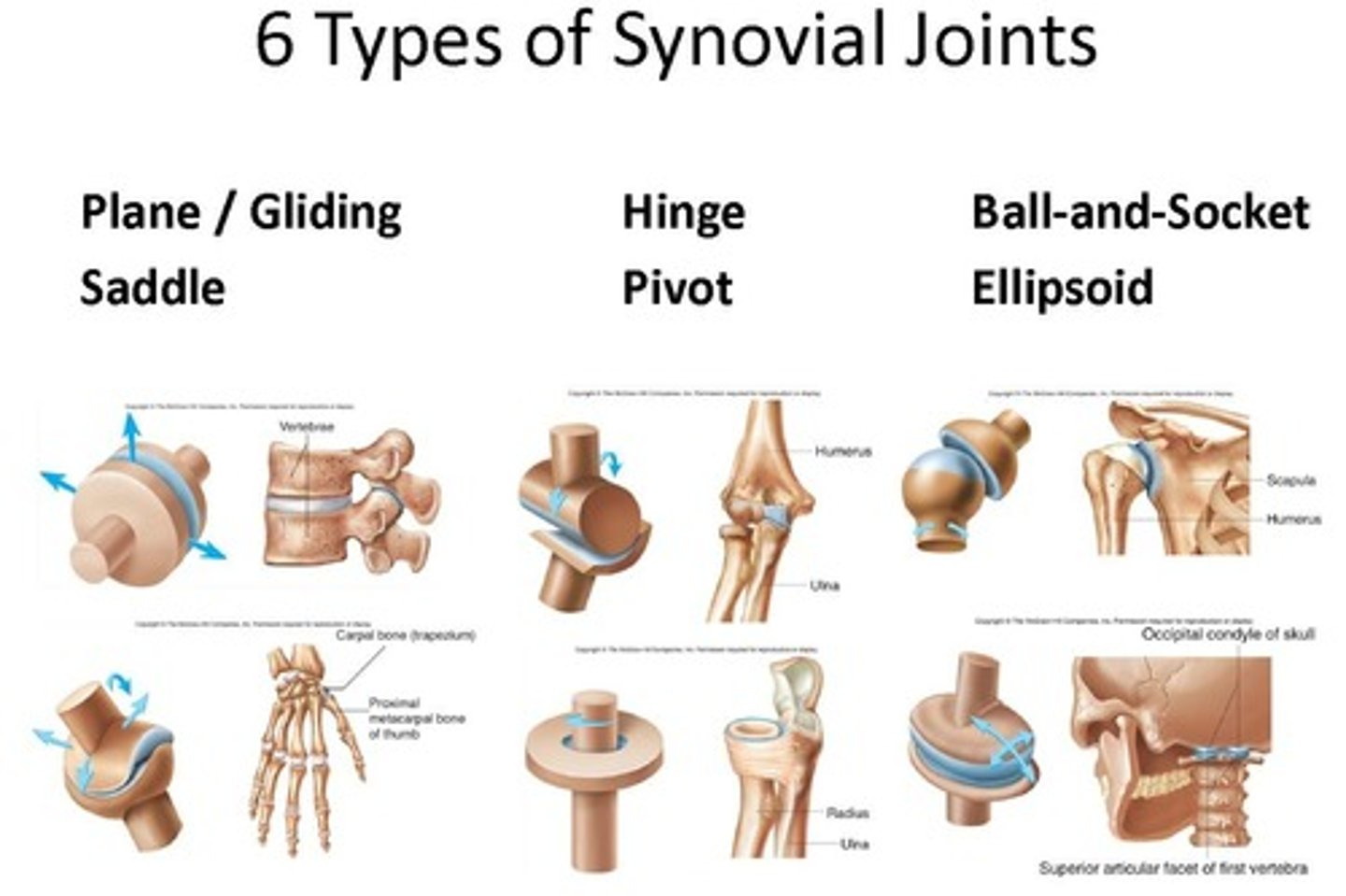
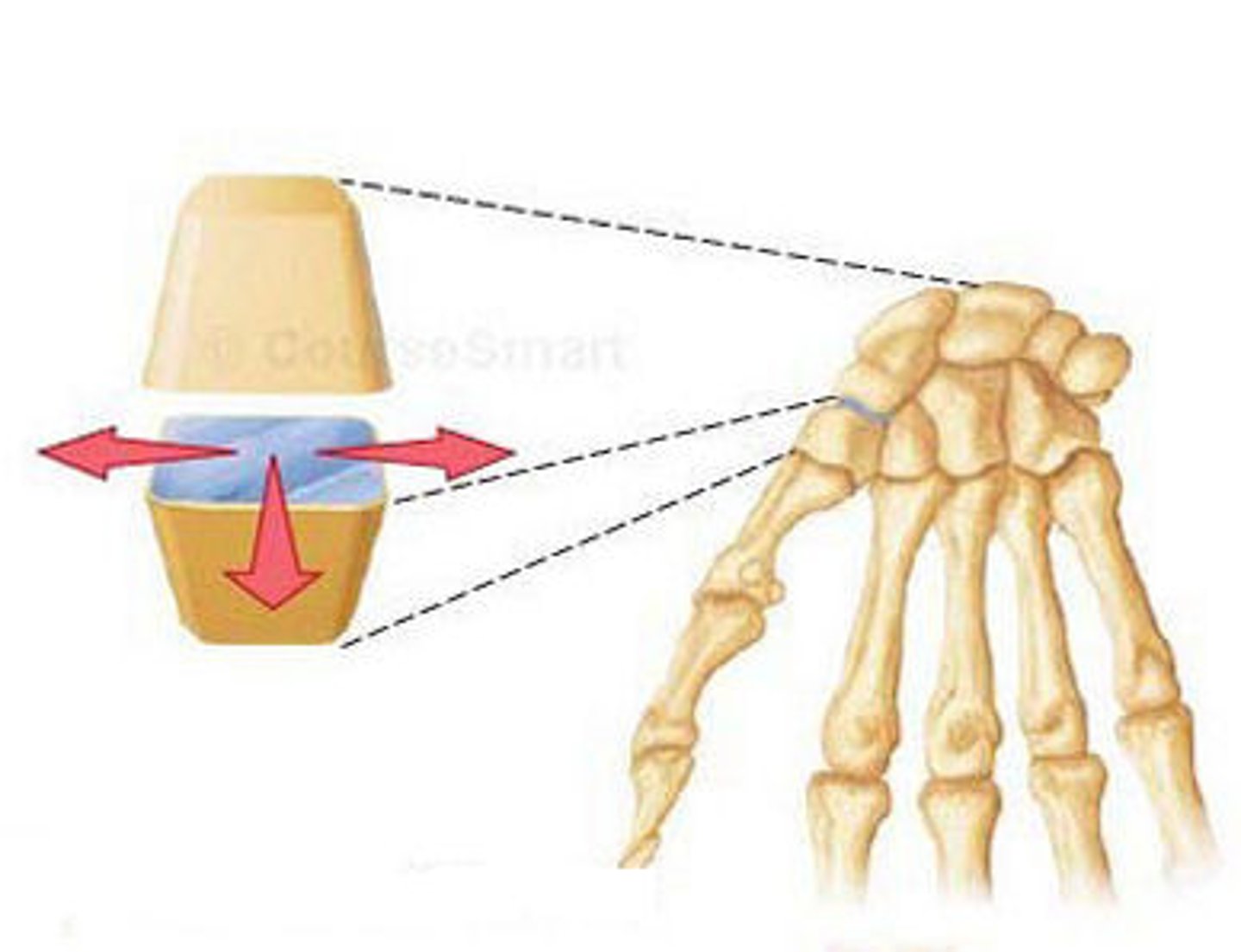
Condyloid / ellipsoidal joint
- between metacarpals and phalanges
- between radius and carpals
Plane / gliding joint
- between carpals
- between tarsals
- between facets of adjacent vertebrae
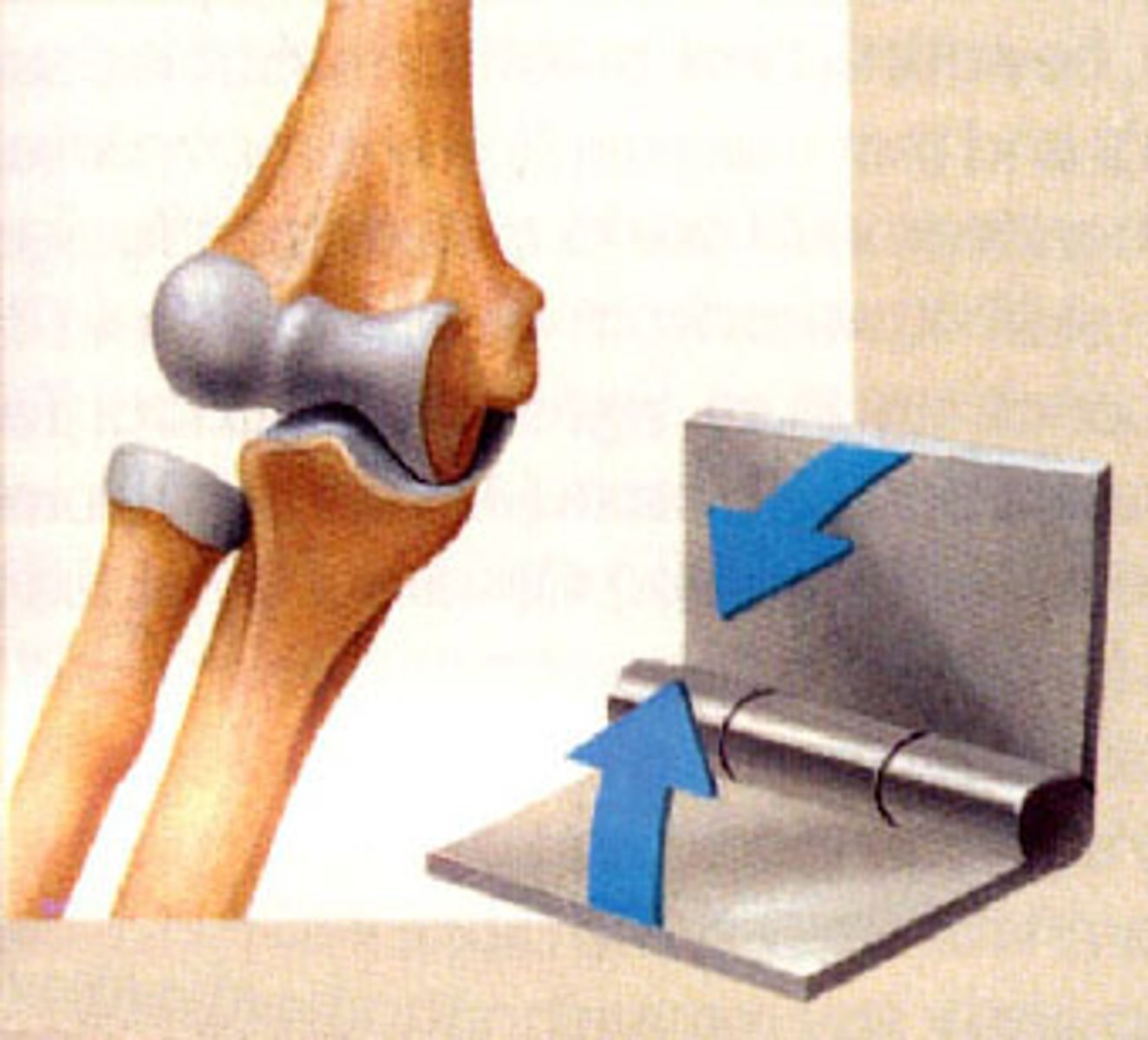
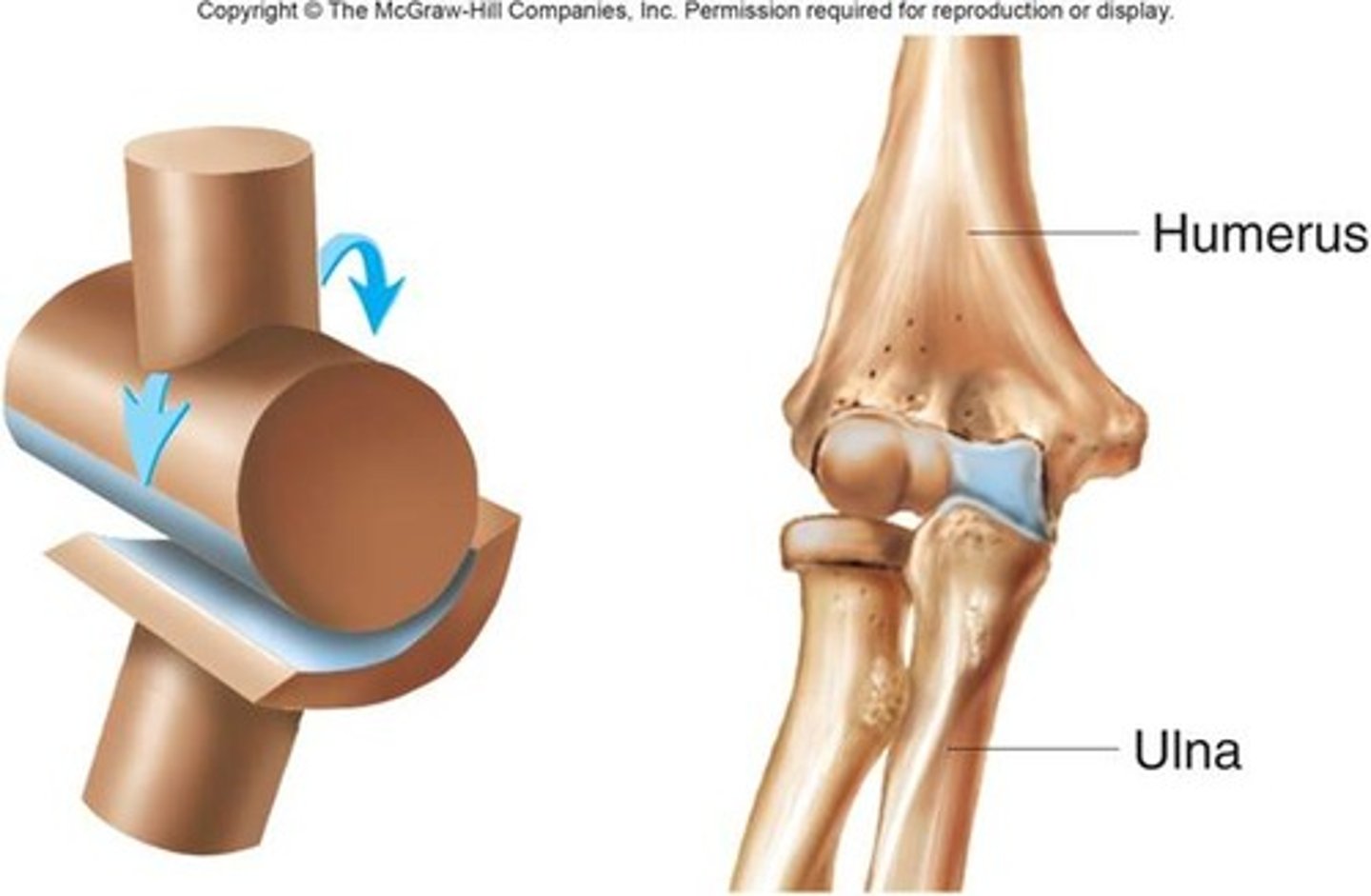
Hinge joint
- elbow joint
- between phalanges
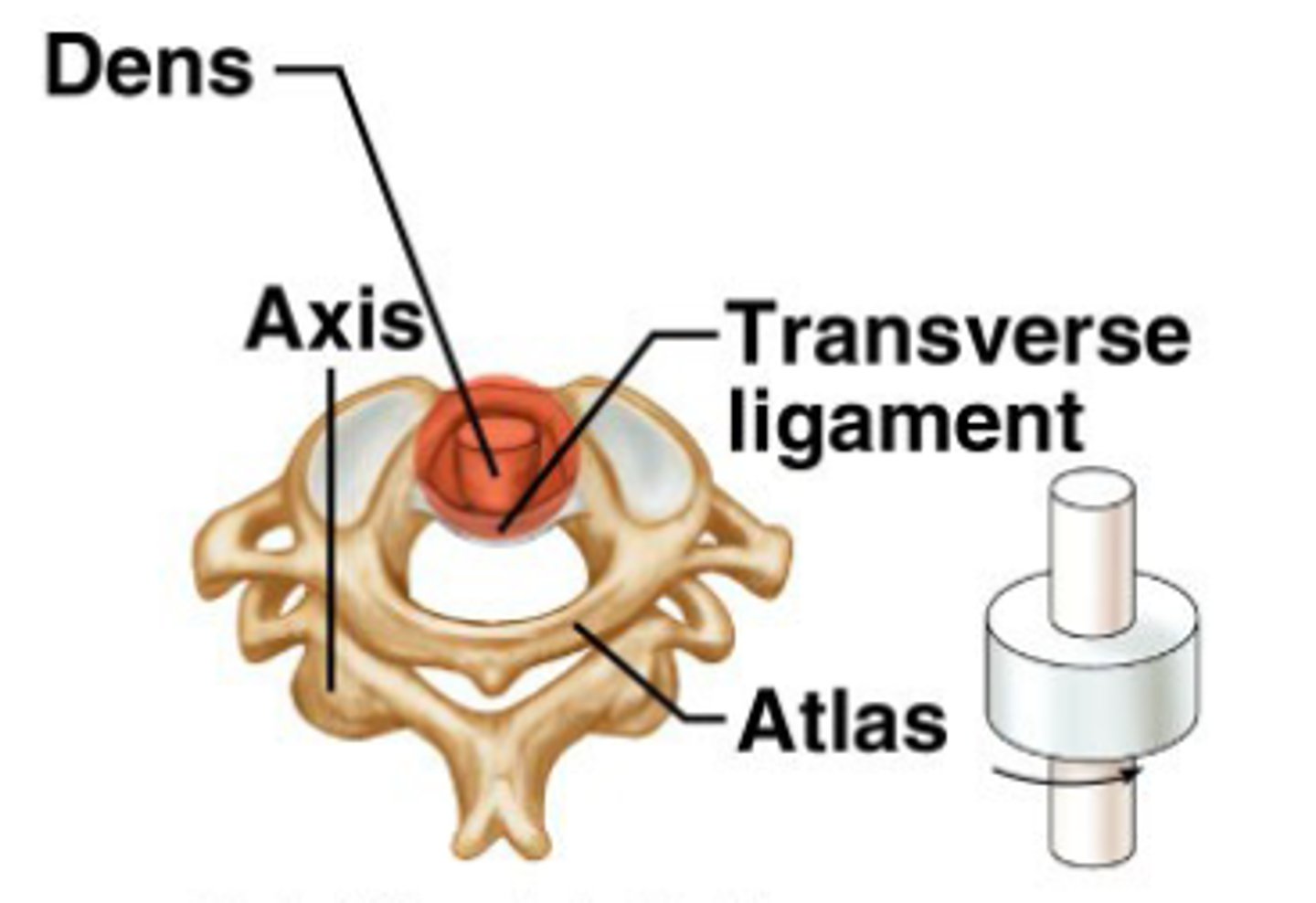
Pivot joint
neck and head
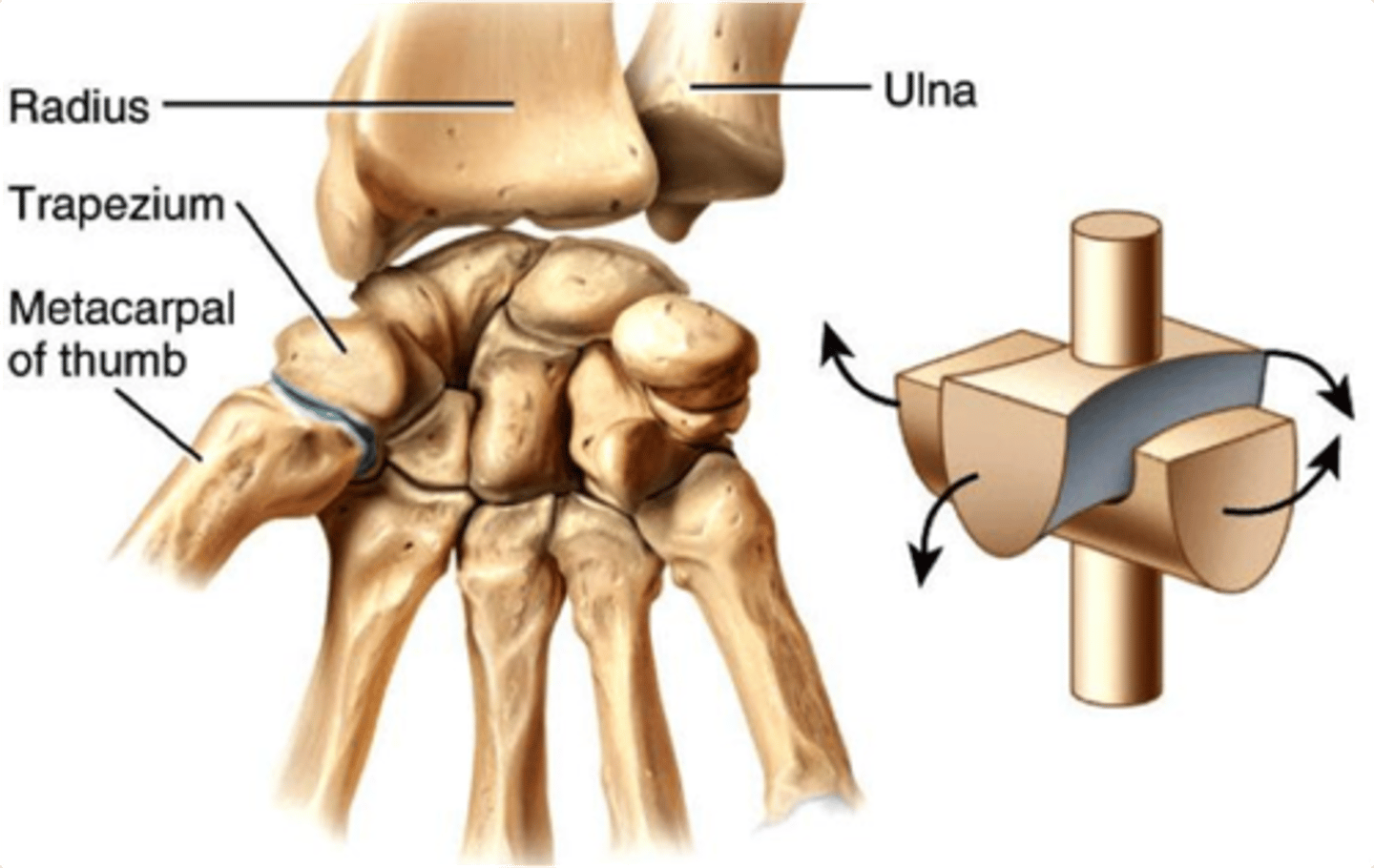
Saddle joint
between carpal and 1st metacarpal of thumb
Insertion
moveable end of muscle
Origin
fixed end of muscle
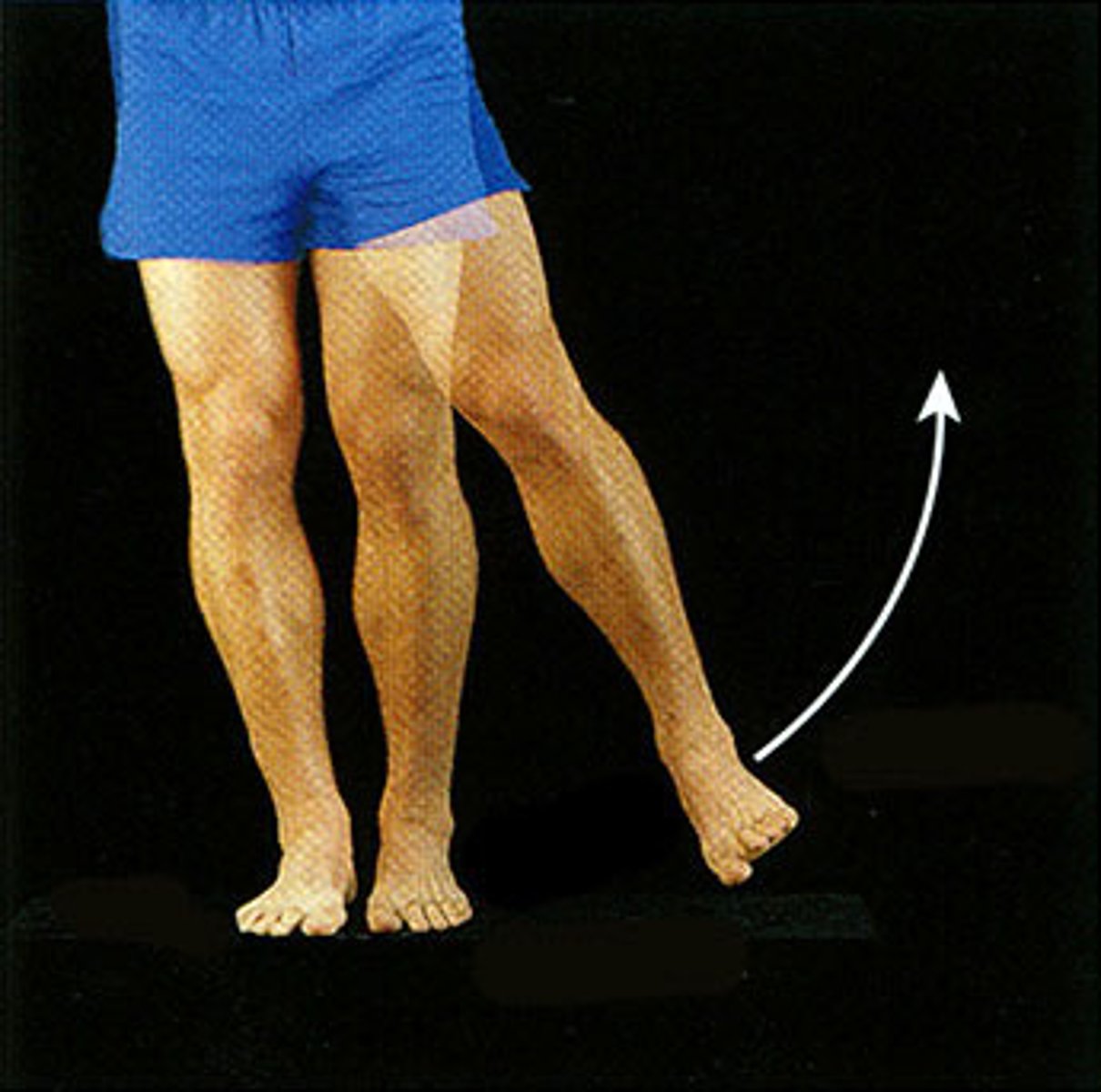
abduction
moving away from body
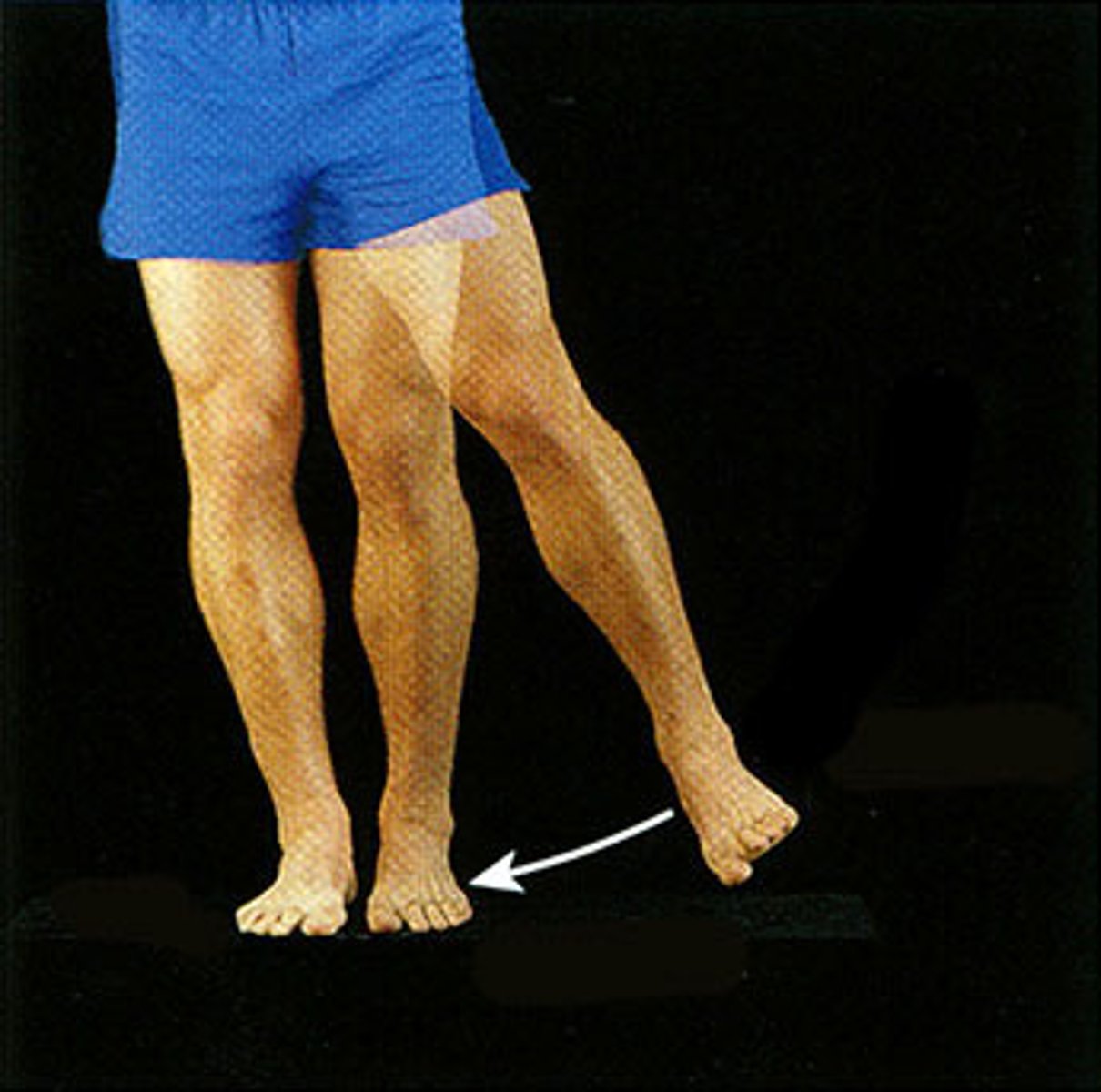
adduction
moving towards body
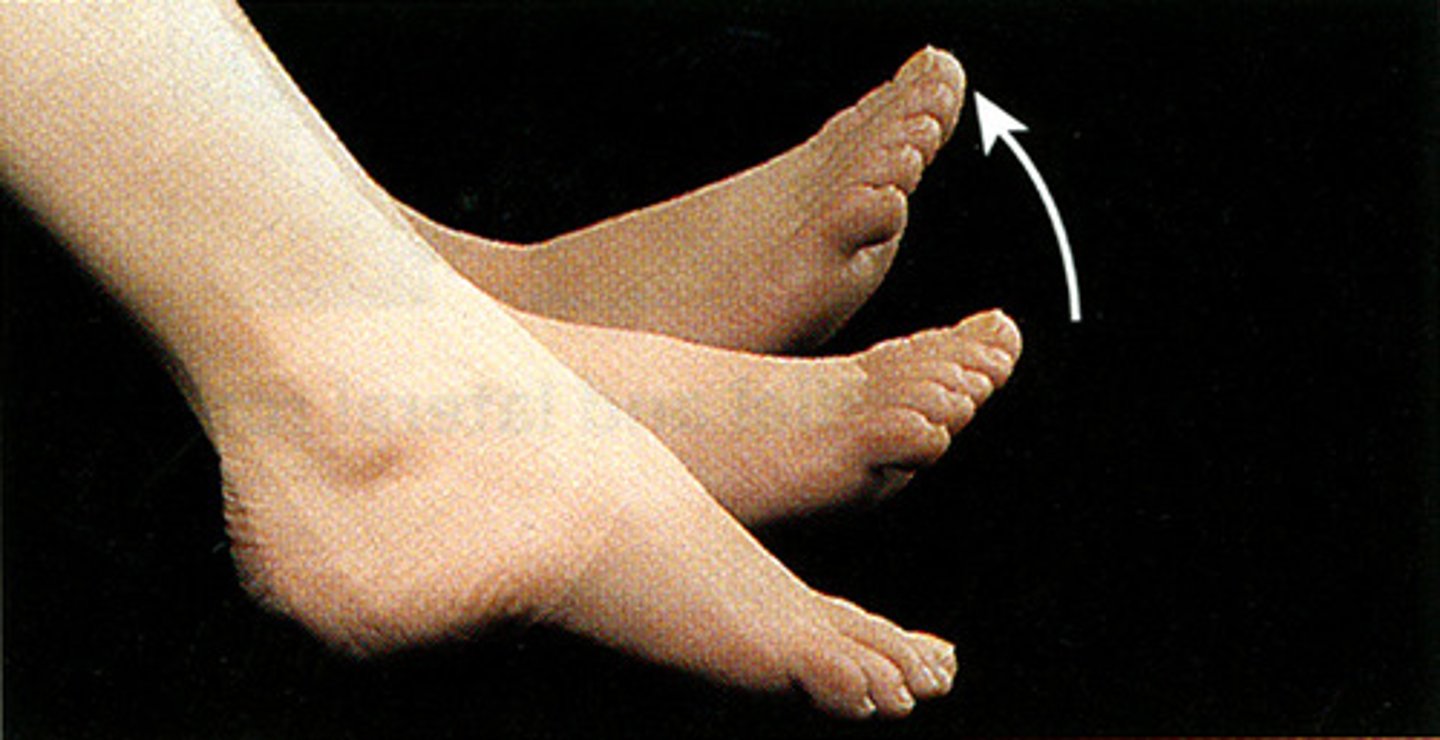
dorsiflexion
bending foot up towards ankle
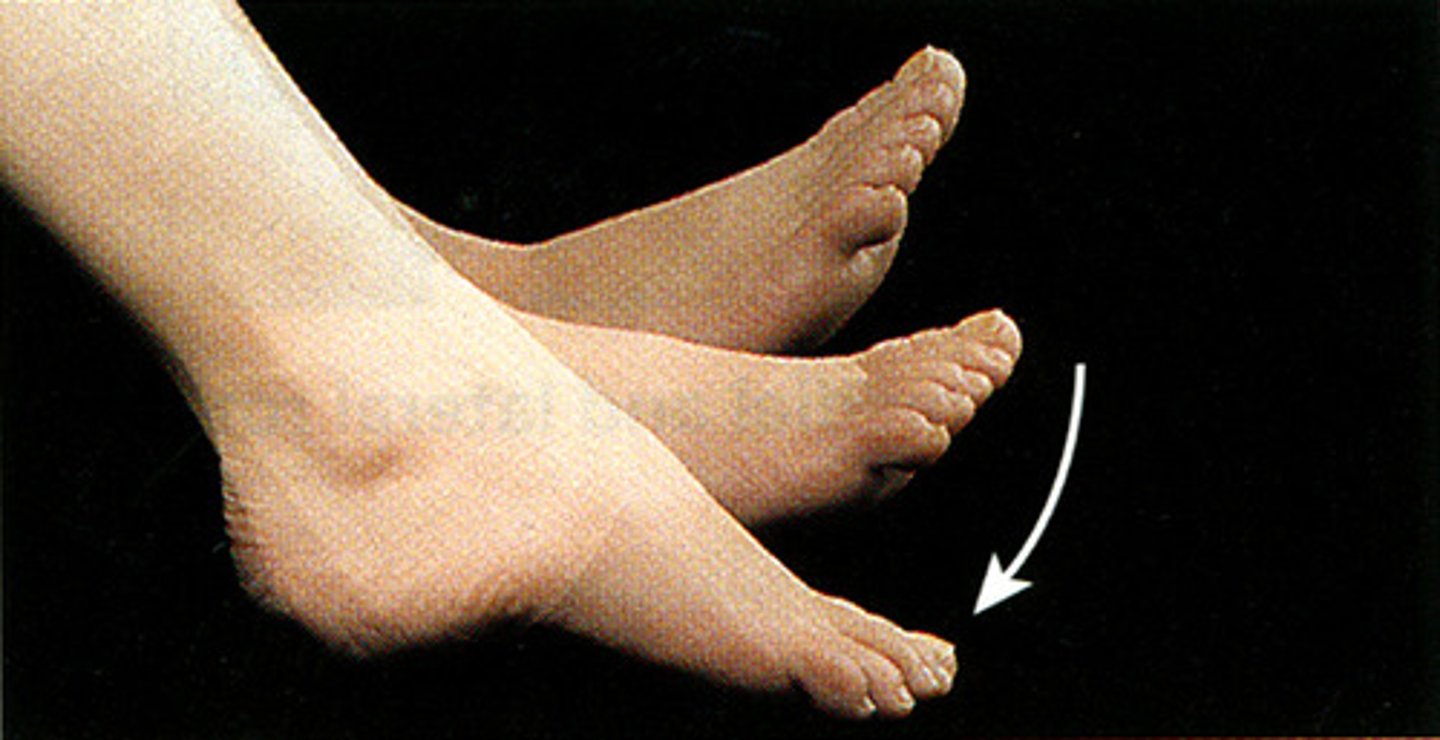
plantar flexion
pointing toe
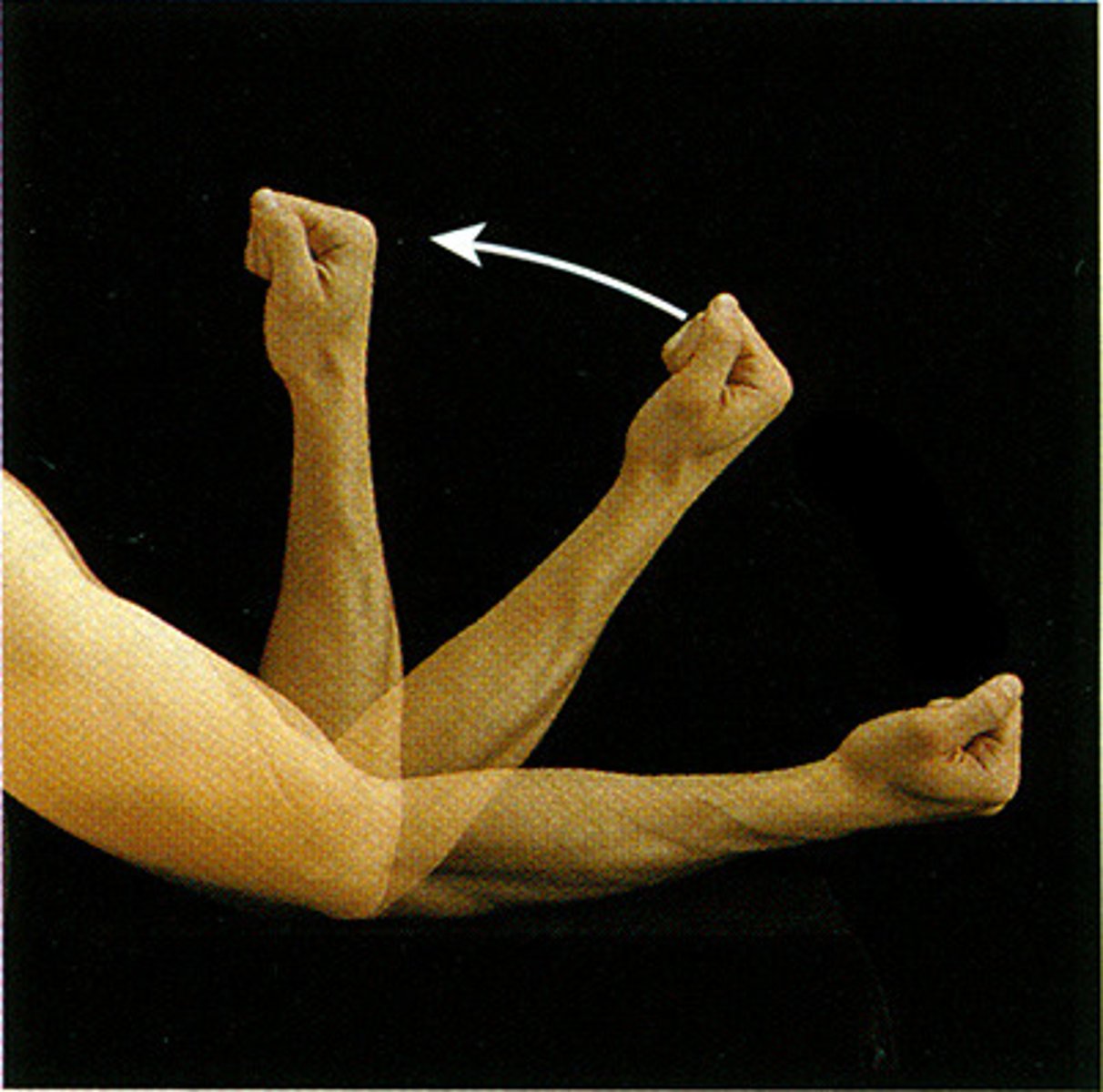
Flexion
bending a part
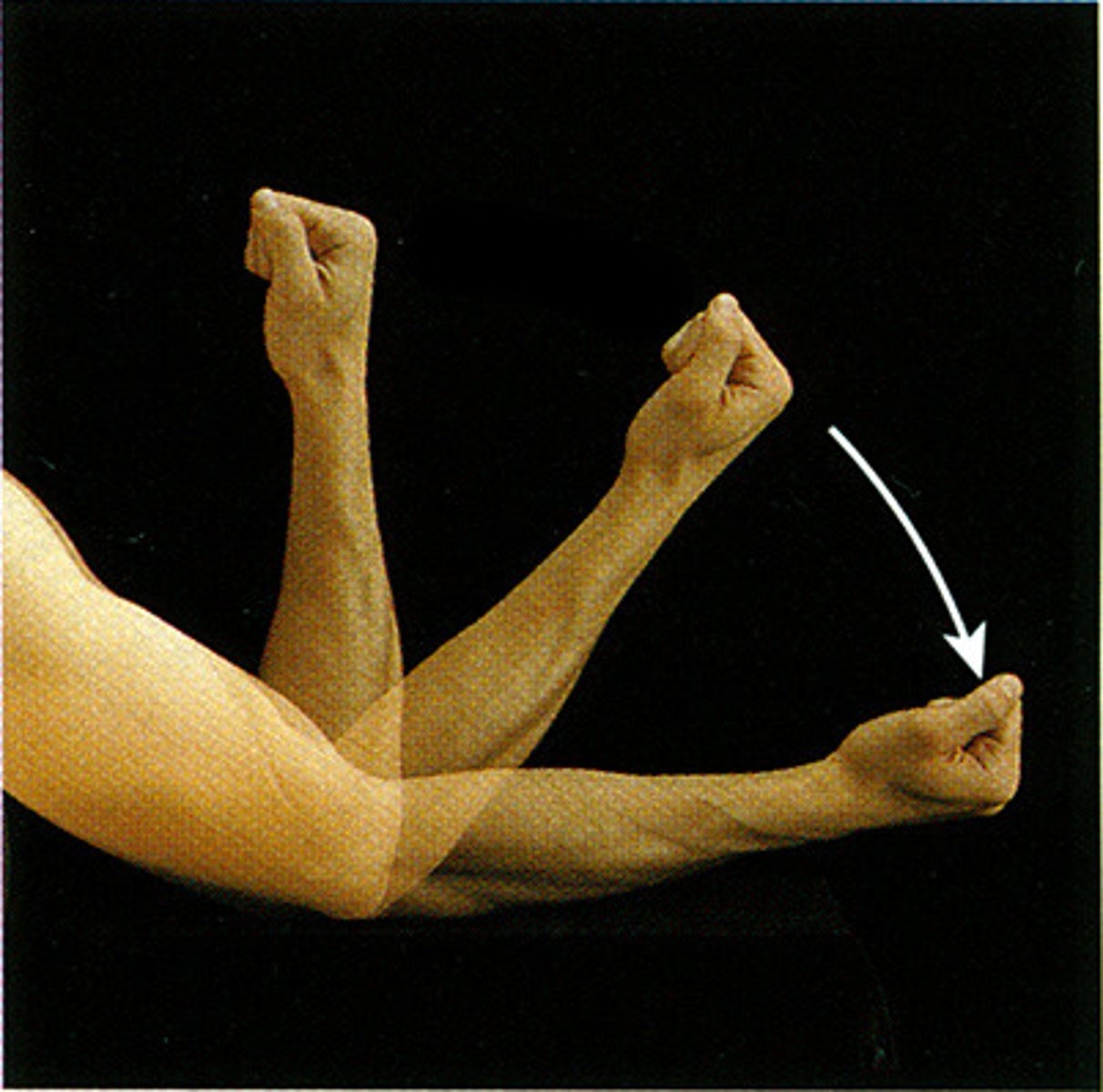
Extension
straightening a part
Hyperextension
excessive extension
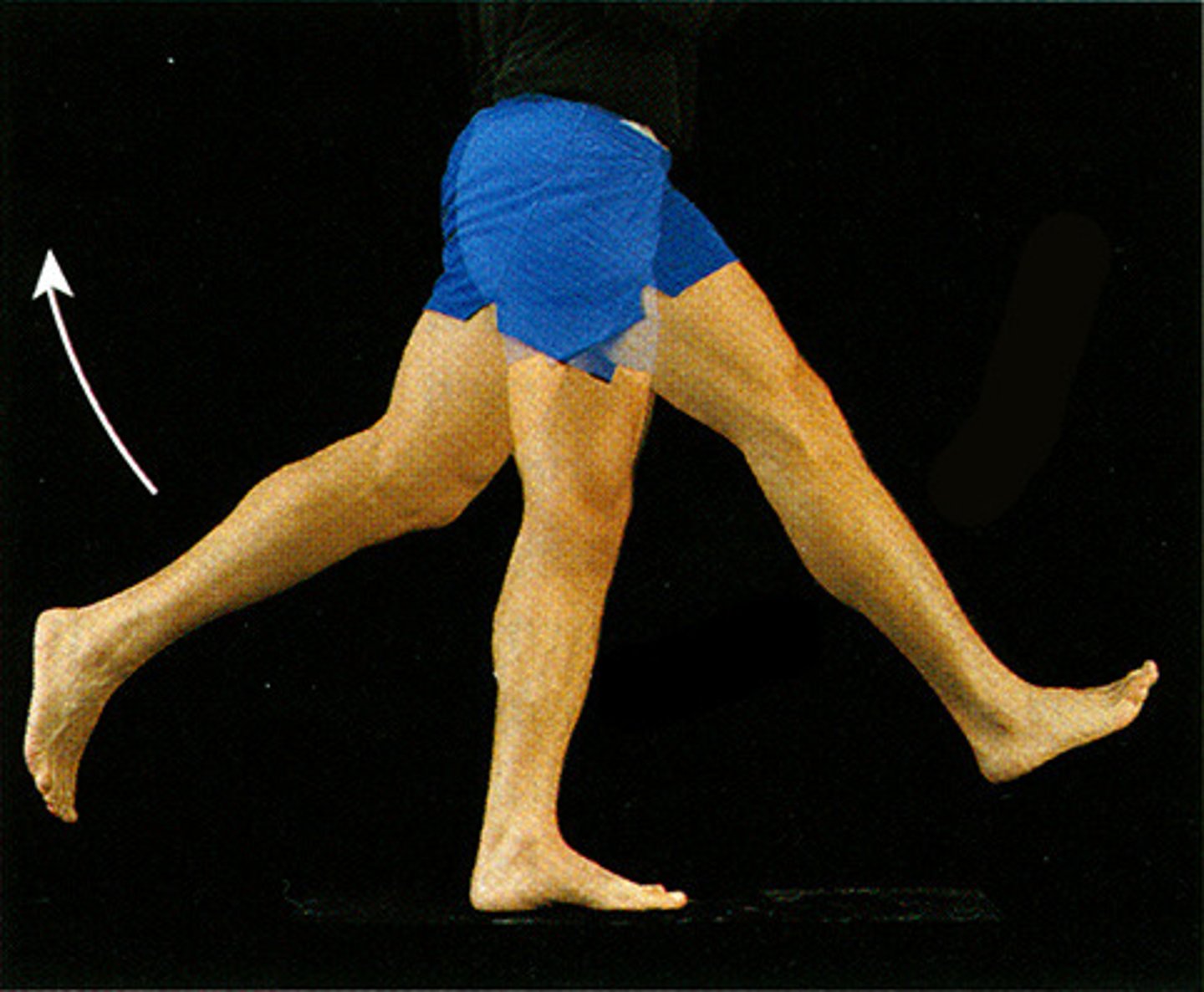
Rotation
moving a part around an axis
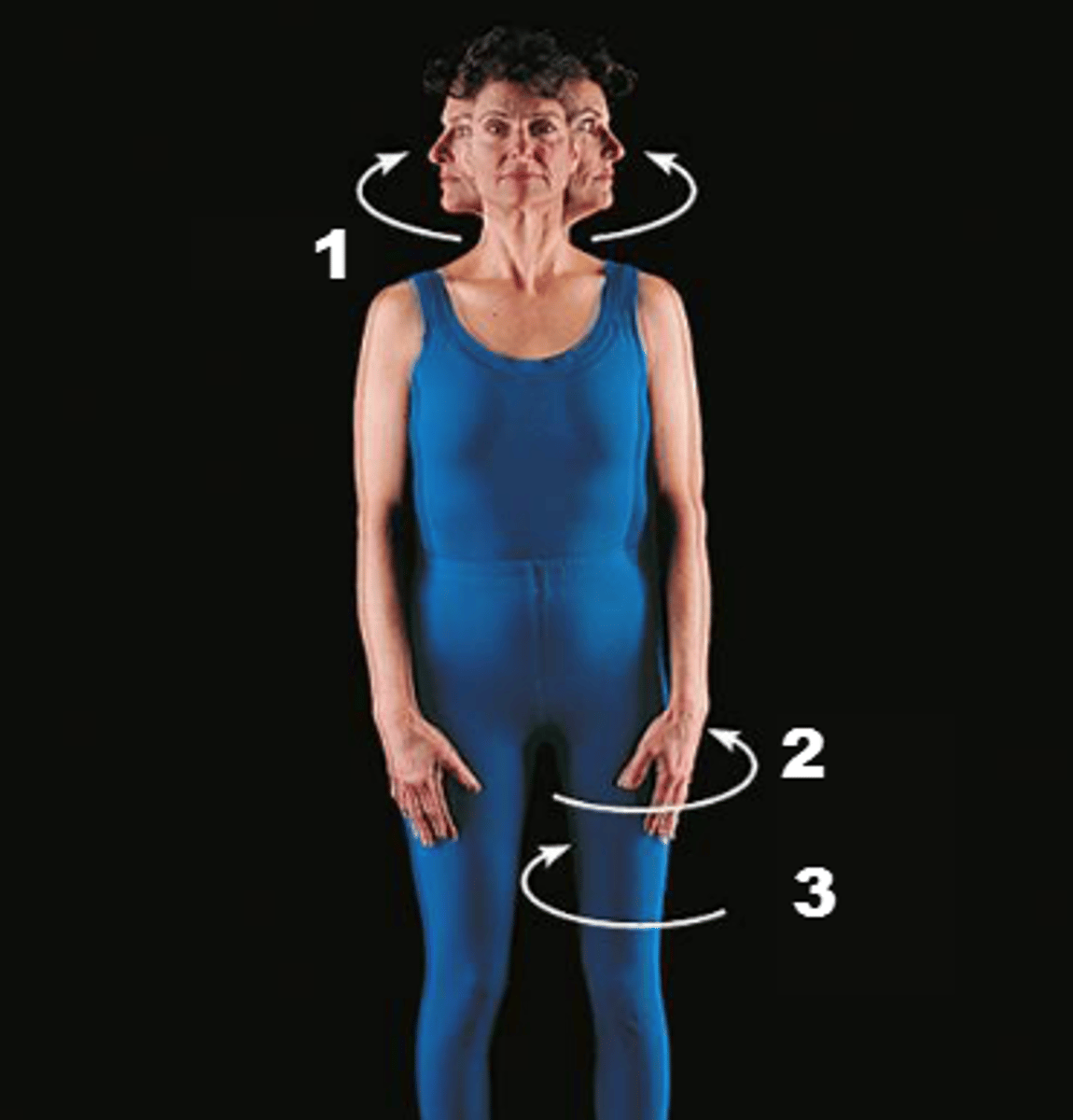
Circumduction
moving a part so that it follows a circular part
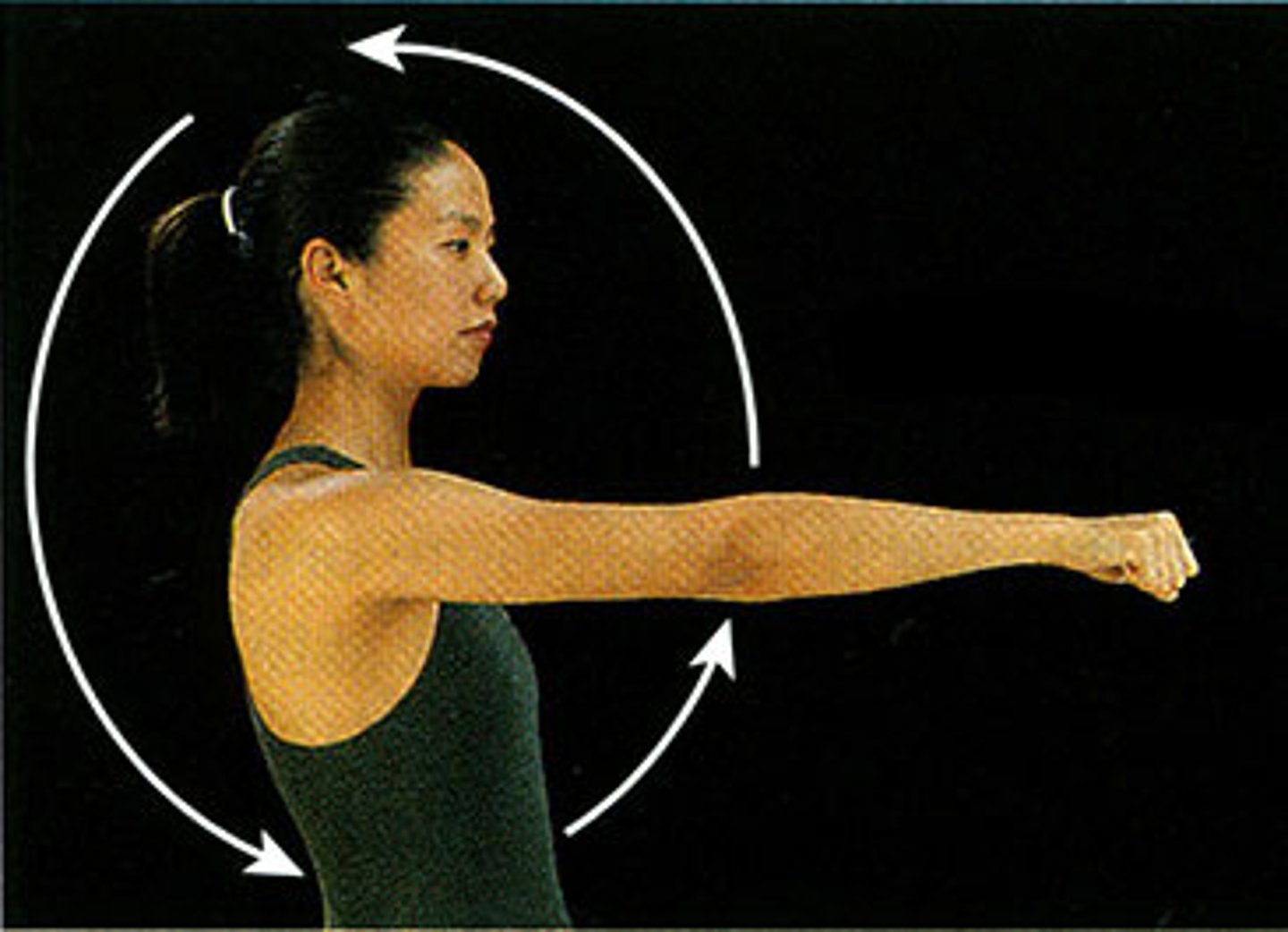
Supination
turning hand so palm is upward
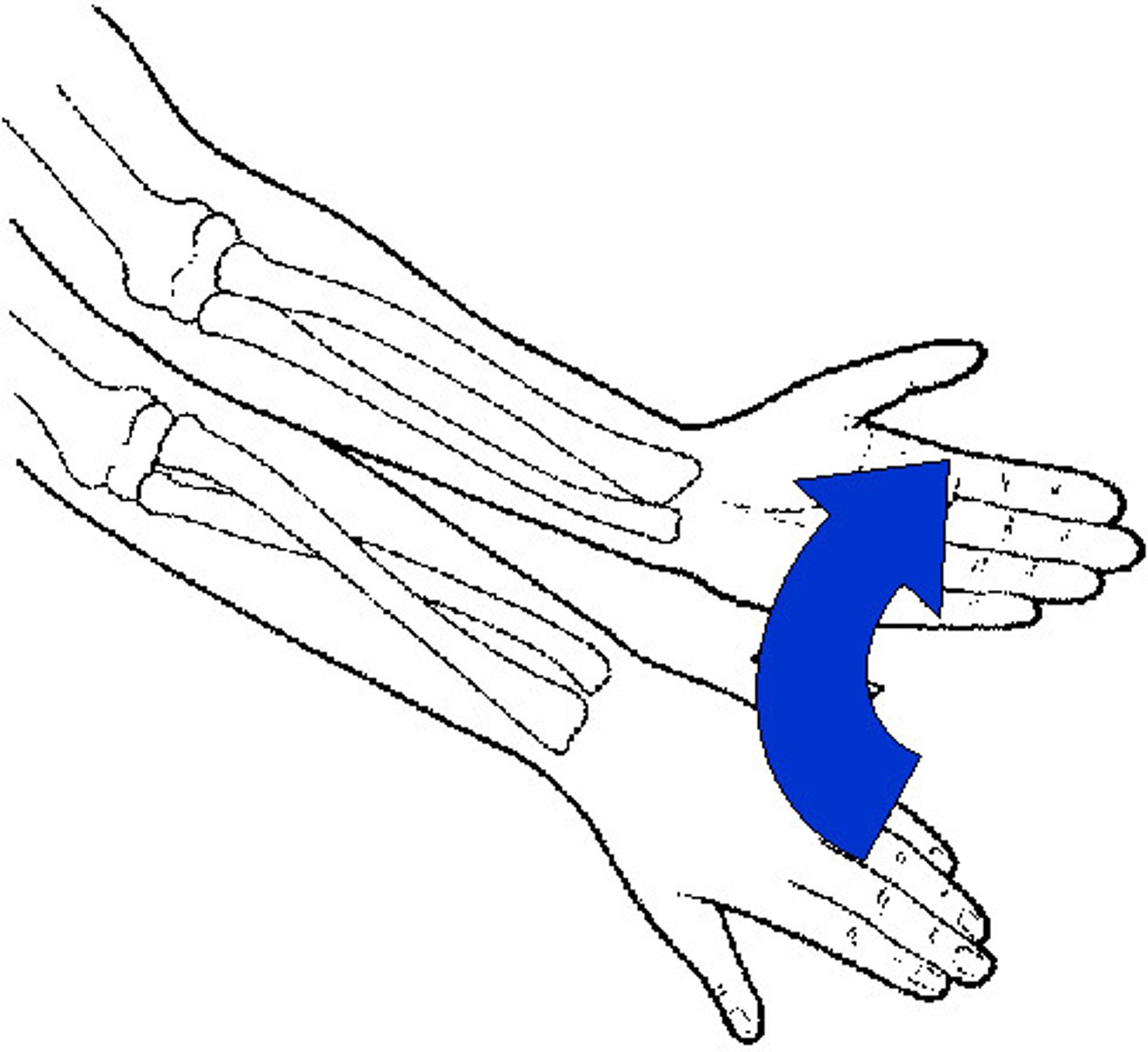
Pronation
turning hand so palm is downward
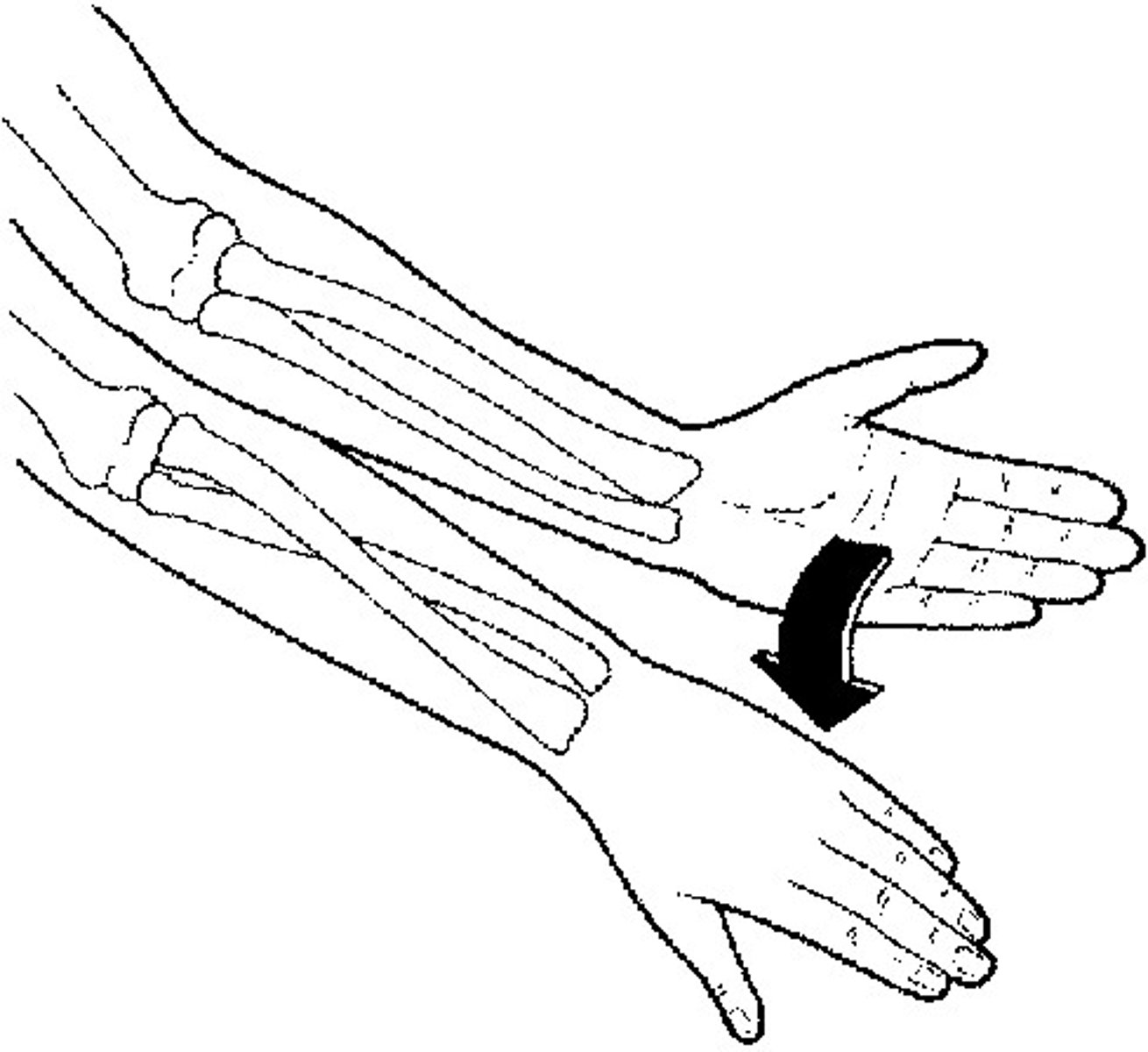
Eversion
turning sole of foot out
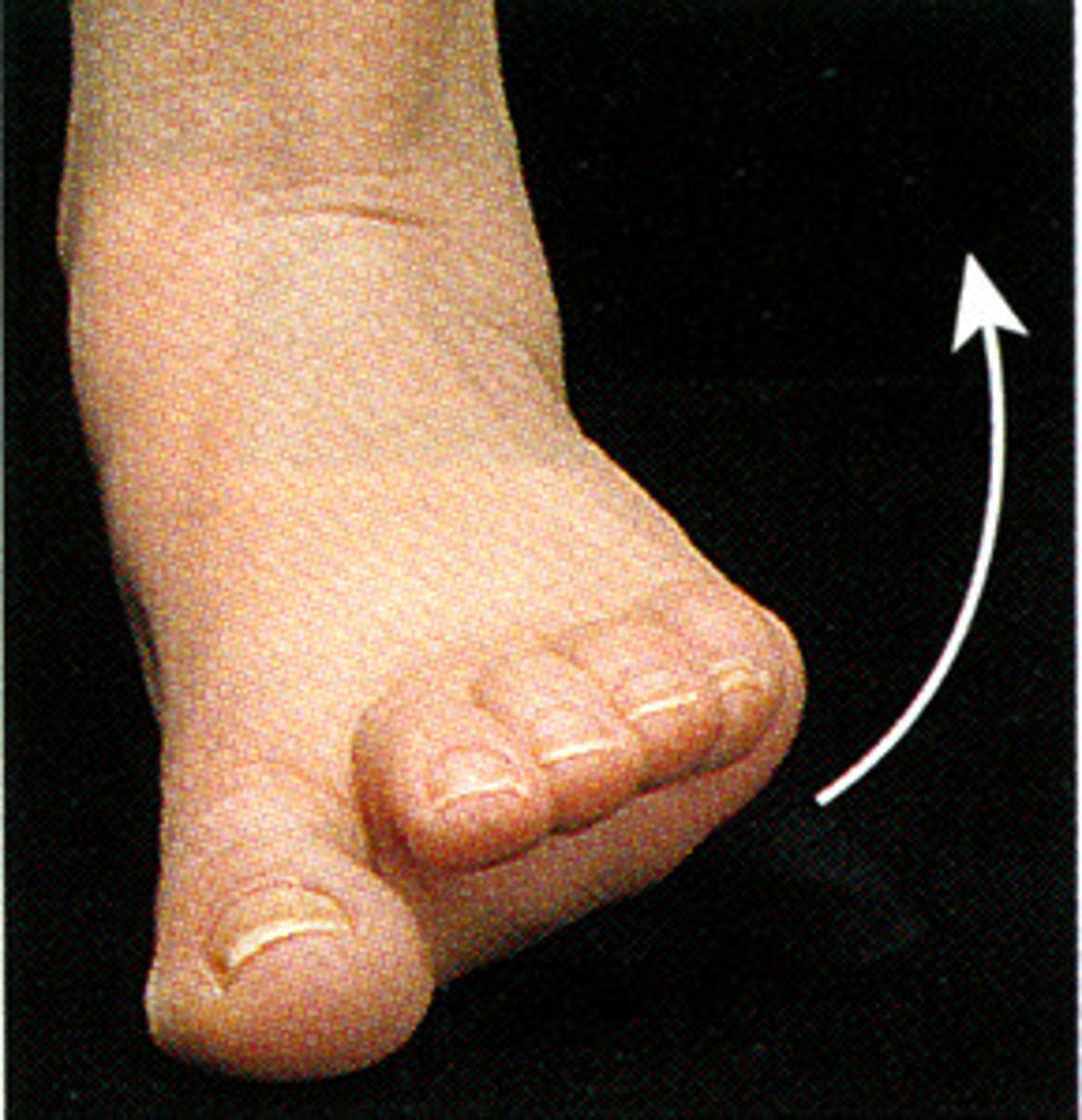
Inversion
turning sole of foot in
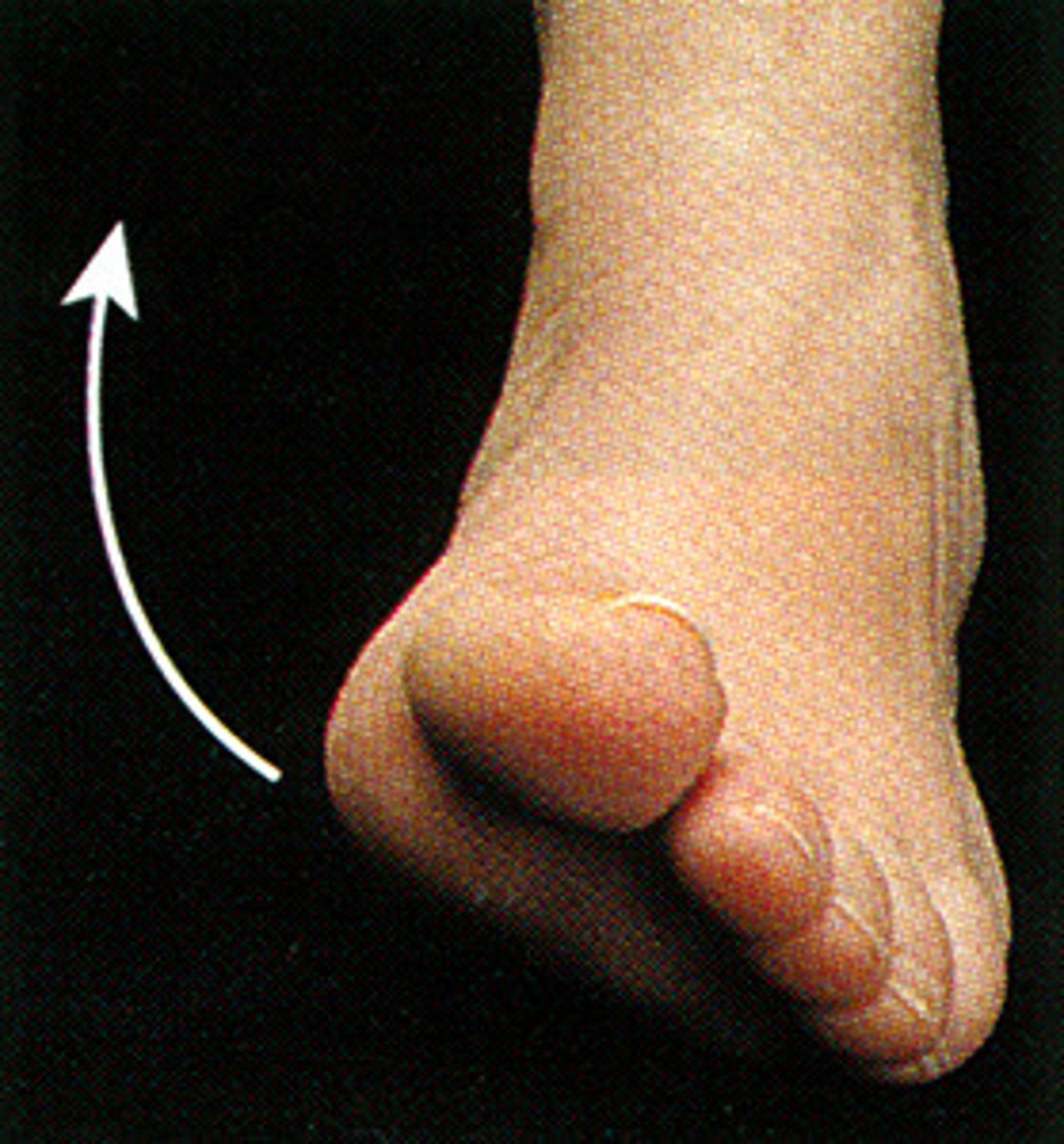
Protraction
thrusting the chin forward
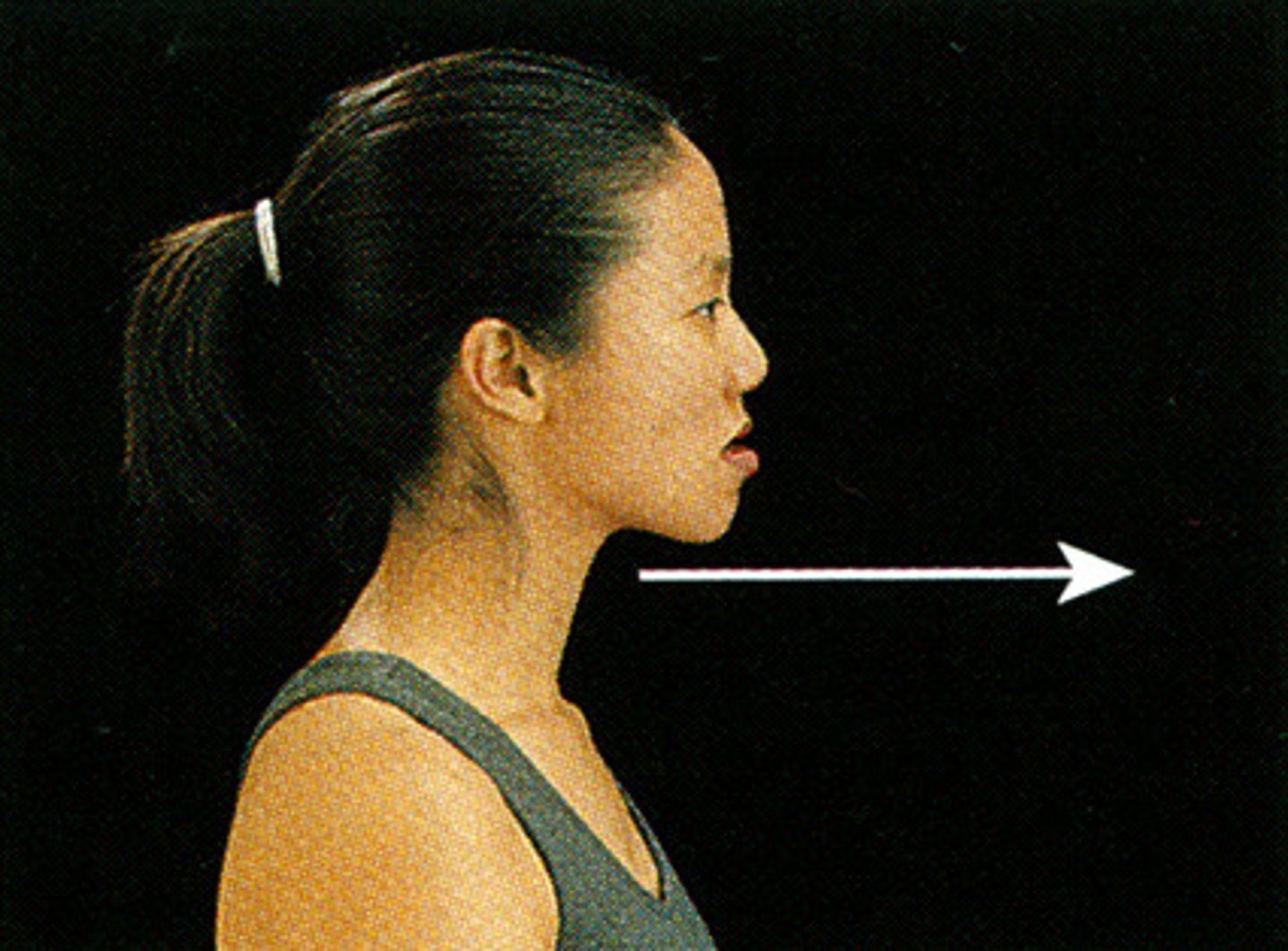
Retraction
pulling the chin backward
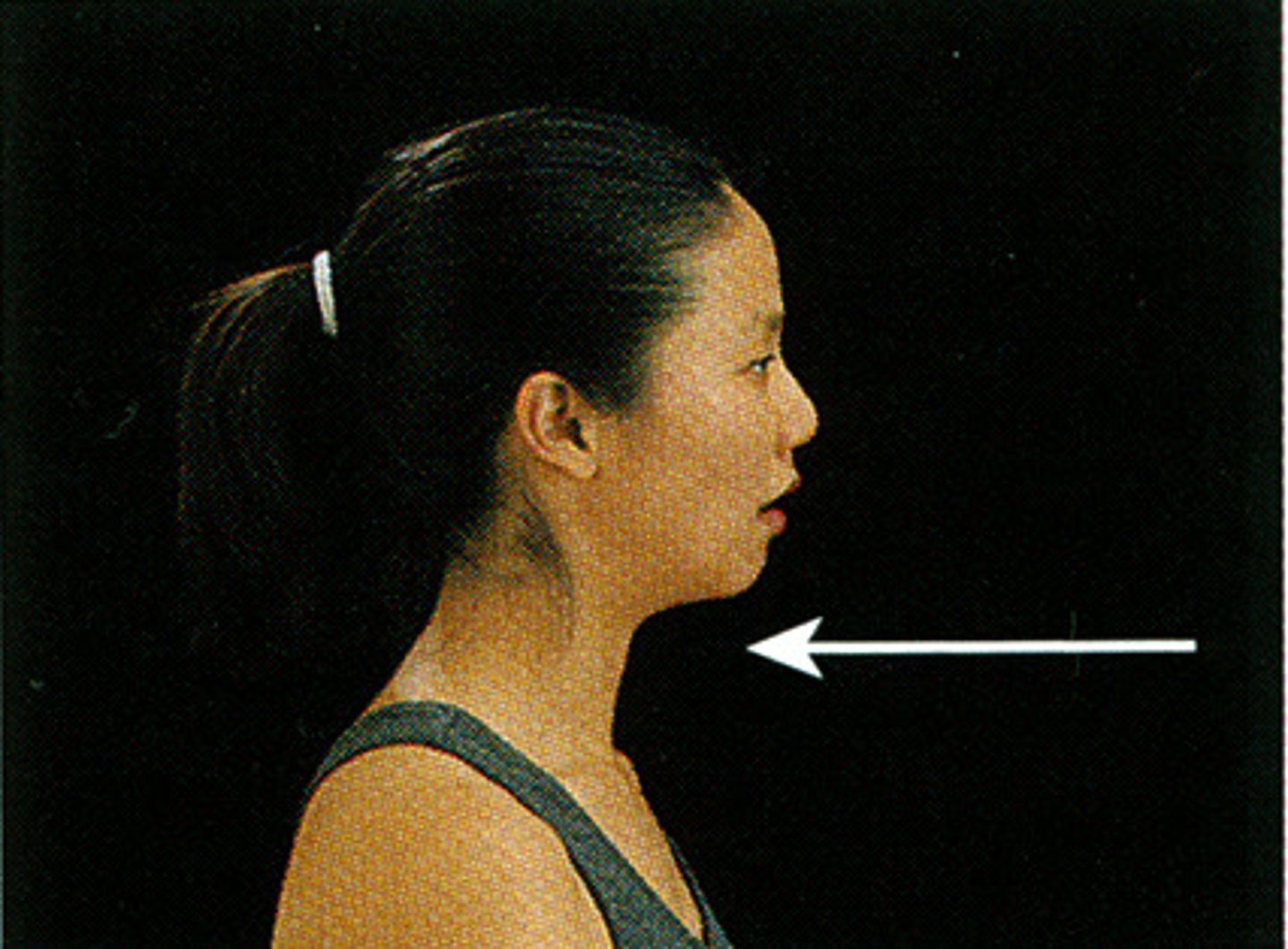
Elevation
shrugging the shoulders
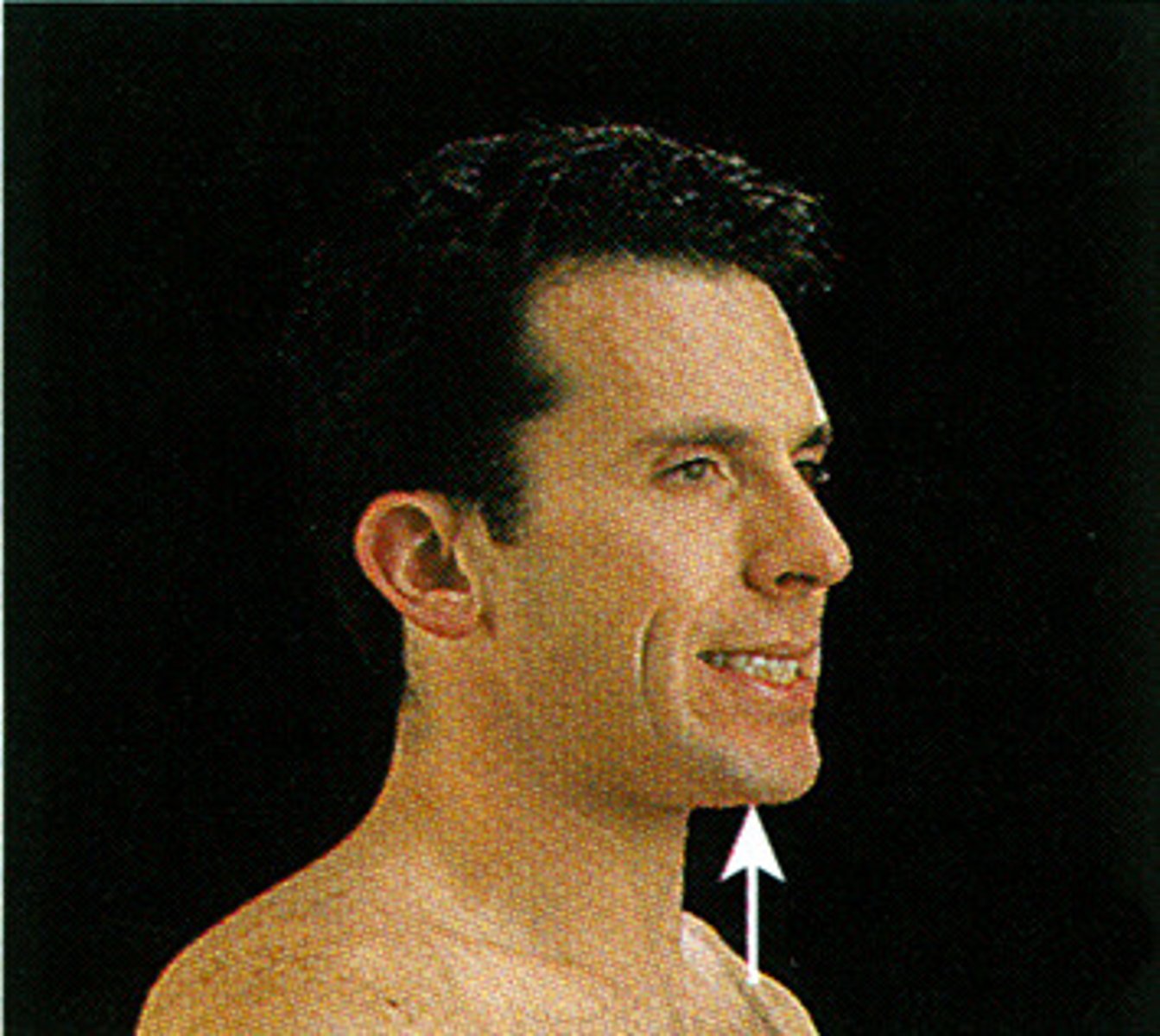
Depression
dropping the shoulders