Chapter 11 - Little-Seen Kingdoms
1/69
Earn XP
Description and Tags
BJU Press, 3rd edition
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
Archaebacteria
the kingdom whose members live in EXTREME environments
Eubacteria
the kingdom that contains TRUE bacteria and CYANObacteria
What are the ONLY prokaryotic organisms?
Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
What to prokaryotic organisms NOT have?
nucleus and many of the organelles found in the eukaryotic organisms
cyanobaceteria
once known as a blue-green algae
What does cyano mean?
dark blue
How do viruses reproduce?
By being reproduced by INFECTED cells
How does a person or animals get rabies?
By getting bit by an infected animal
What are some well known viruses?
chicken pox, cold sores, rabies, warts and the flu
How can you prevent getting viruses?
Washing your hands, coughing and sneezing in your elbow, and not sharing food with someone who is sick.
Bacterium is plural for the word____.
bacteria
bacerium
all organisms, or living things, that can be found in all natural environments. They are made of a single cell. Most bacteria can be seen only with a microscope. Bacteria do not have most of the structures found in the cells of other organisms.
What is a virus smaller than?
A bacterium (a single bacteria)
What does your body release to protect you from viruses?
a chemical called interferon
How to vaccines work?
They contain a weakened virus and when it’s injected into your body, your body will make antibodies to protect you against infection. Then, if you come around the virus in the world, your body will already know how to defend itself.
What is a virus exactly?
a nucleic acid (DNA or RNA) core with a protein coat. They are nonliving.
How does a virus make you sick?
It infects your cells by attaching to them and injecting viral nucleic acid. Then, the nucleic acid directs the cell to make MORE viral nucleic acids and protein coats. So actually then, the CELL reproduced the virus. The virus does not reproduce itself.
strep
bacteria arranged end to end in long chains
What’s a common strep bacteria?
strep throat
What are the 3 shapes of bacteria?
spherical (called coccus)
spiral (called spirillum)
rod (called bacillus)
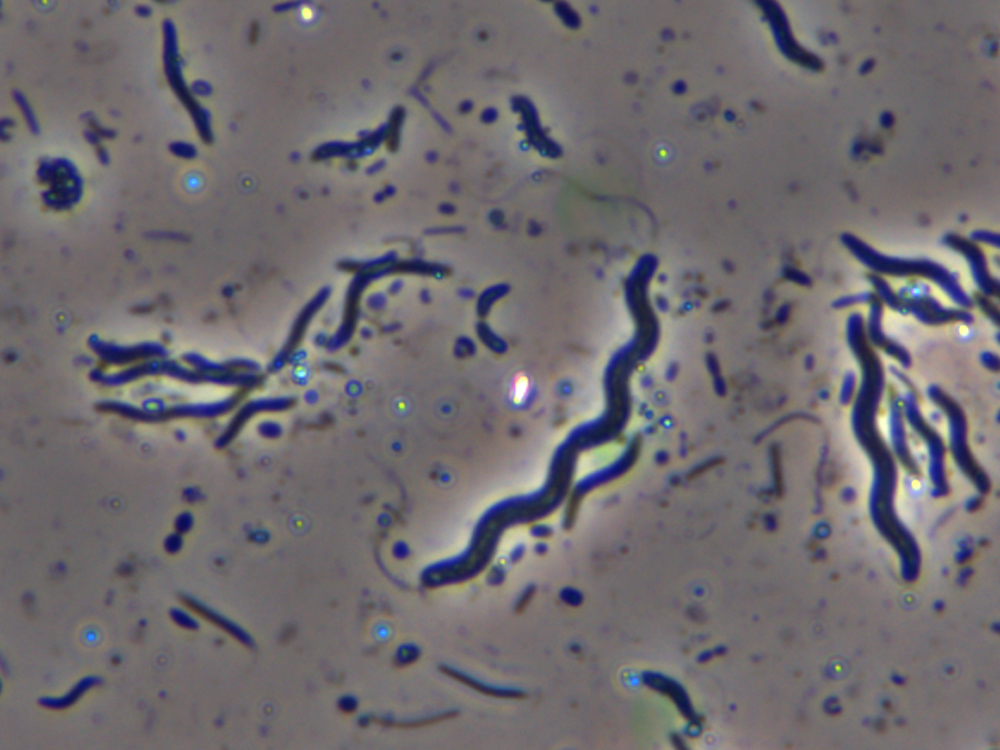
spiral shaped bacteria
spirillum
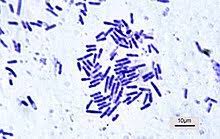
rod-shaped bacteria
bacillus
Benefits of fungi and bacteria
They decompose wastes such as fallen leaves, shed skin and dead bodies.
flagellum
a long whip like hairs that acts like a propeller, causing some bacteria to move
detritus feeders
creatures that eat dead organisms
How are bacteria helpful?
They decompose wastes we produce and they are used to make yogurt, pickles, and cheese. They also are used to make antibiotics and many chemicals.
How are bacteria harmful?
They can make you sick with plague, leprosy, strep throat and food poisoning.
Are bacteria more helpful or harmful?
helpful
Why are viruses not classified in a kingdom?
They are not living.
Kingdom Protista
A kingdom of species that move, obtain food, and reproduce. They ALL have a nuclei and are unicellular (or if they are multicellular, they do not form water-conducting tissues). They contain the organisms, algae and protozoans.
2 groups of the Kingdom Protista
Protozoa and algae
What kingdom does bacteria fall under?
Kingdoms Archaebacteria and Eubacteria
colony
A group of unicellular protists living together. Each IS capable of living separately though.
tissues
special group of cells that perform specific tasks. This would occur in multicellular protists.
algae
the most plantlike protists that perform photosynthesis and are usually unable to move themselves.
Protozoa
more animal-like protists are usually move themselves and capture prey.
psudepodia
The bulges in cytoplasm that serves as an anchor for the cell to pull itself forward on. It’s one way a protist can move. Amoebas move in this way, so the movement has been named, amoeboid movement.
3 general ways protists can move themselves
flagella
cilia
forming bulges, called pseudopodia
spirogyra
A protists with no mouth. Because it has no mouth, it uses its chloroplasts to use sunlight to make its food.
cilia
short, hairlike projections that help with movement
food vacuoles
also known as a digestive vacuole, is an organelle that helps some protists get food.
plankton
Microscopic organisms that float or drift near the ocean’s surface. They are the most abundant food in the ocean. They are in the Kingdom Protista because and they are a type of algae.
What are 2 diseases that protists can cause?
Malaria and African sleeping sickness
dinoflagellates
are mostly marine plankton, but they also are common in freshwater habitats. They are a protist.
What can happen when dinoflagellates overpopulate?
They give the ocean a reddish color called red tide, which is deadly to fish because of a toxin that they produce. Shellfish that get the toxin, are then eaten by humans, can in turn, poison humans.
red tide
an overpopulation of dinoflagellates that is deadly to fish and can poison humans who eat the fish with the toxin.
fragmentation
A form of asexual reproduction where a broken filament from a spirogyra has been broken off and then forms two new spirogyra.
conjugation
A form of sexual reproduction where two protists of the same species come together and form a temporary union. They exchange genetic material during this union. When the two protists separate, they are genetically different from the original organisms.
zygote
If two protist spores are close together, they can fuse to form a diploid zygote.
malaria
mosquito-borne disease caused by a parasite. The blood that mosquito’s suck, contain the protists that cause this disease. People with malaria often experience fever, chills, and flu-like illness. Left untreated, they may develop severe complications and die.
African sleeping sickness
is a disease caused by a protist parasite. People can get this parasite when an infected Tsetse fly bites them. Symptoms include fatigue, high fever, headaches, and muscle aches. If the disease is not treated, it can cause death.
Kingdom Fungi
All contain spores and most contain hyphae. Mushrooms and black mold fall into this kingdom.
hyphae
long filaments that are most fungal cells. Black bread mold in an example of this.
stalk of a mushroom
an example of hyphae grouped together to form a much larger and more complex structure that the hyphae in bread mold.
3 types of hyphae in bread mold
rhizoids (rootlike)
stolons
sporangia (spore-bearing)
How does bread mold grow/reproduce?
by spores
Parts of a mushroom
cap
spores
hypae
gills
stalk
Where are the spores in a mushroom?
in the gills that are under the cap
Where is the hyphae in a mushroom?
attached to the stalk. They look like roots in the ground
mycelia
densely packed hyphae that makes up mushrooms
How do fungi get energy?
They DO NOT have chloroplasts or vacuoles so they secrete a digestive enzyme into the area around them. Thier food is called either a saprophyte (dead) or a parasite (alive).
They can also get energy from lichen.
parasite
a fungus food that is alive
lichen
an organism that is made of a fungus and alga. This is one way fungi get energy.
The function of a mushroom’s gills
maximize the surface area where the spores are produced
to help hold up the cap of the mushroom.
mycorrhizae
a fungus which grows in association with the roots of a plant in a symbiotic relationship
symbiotic relationship
close associations formed between pairs of species.
parasitic relationship
an organism that lives all or part of its life in or on a living host. It usually benefits from it’s hose, but it harms the host in some way.
saprophyte
a fungus or other organism that absorbs food from dead material
penicillin
an extract from the fungus, mold, that is used to make medicine to treat fungal skin diseases
Fungal products that we use
Mushrooms, blue cheese, yeast bread, and chocolate.