AnaChem: Gravimetric & Volumetric Analysis & Potentiometry
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
Gravimetric analysis
is a quantitative method to determine an analyte concentration by weighing a pure, solid form of the analyte.
measurement of mass
Solid
The ____ form is obtained by adding a precipitating reagent to a solution containing the analyte
Theodore W. Richards
Gravimetric analysis was developed by
Analyte
a substance whose chemical constituents are being identified and measured.
Precipitant
also known as the precipitating agent refers to the chemical that is used to cause precipitation
Precipitate
the insoluble substance formed in the gravimetric method
Size
Particle retention depends on the ____ of the filter’s pores.
Suspended solids
suppose you are to determine the total suspended solids in water released from a sewage-treatment facility.
_____ are just that solid matter that has yet to settle out of its solution matrix. The analysis is easy.
You collect a sample and pass it through a pre-weighed filter that retains the suspended solids. After drying to remove any residual moisture, you weigh the filter. The difference between the filter’s original mass and final mass gives the mass of _____.
Cellulose fiber filters
commonly referred to as filter paper, range in pore size from 30 µm to 2–3 µm.
Glass fiber filters
constructed from chemically inert borosilicate glass, range in pore size from 2.5 µm to 0.3 µm.
Membrane filters
which are made from a variety of materials, including cellulose nitrate and PTFE, are available with pore sizes from 5.0 µm to 0.1 µm.
Recrystallization
If the analyte is an aqueous ion, use
In this case we cannot isolate the analyte by filtration because the ion (Pb2+ ion) is dissolved in the solution’s matrix. We can still measure the analyte’s mass by chemically converting it to a solid form.
With use of Pt electrodes, The Pb2+ ion in solution oxidizes to PbO2 and deposits on the Pt electrode serving as the anode. If we weigh the Pt before and after, the difference in the two measurements gives the mass of PbO2 (calculated using reaction’s stoichiometry).
Precipitation
easiest way using the precipitation process (the reaction that creates an insoluble solid product from the reaction of two soluble solid products)
Analyte is converted to sparingly soluble precipitate.
Solution preparation, precipitate formation, filtering, washing, heating, weighing
Key steps in precipitation
Volatilization
using thermal or chemical energy to determine their masses
____ gases (that can be easily evaporative), like carbon dioxide, chlorine, etc., can be separated with the help of _____ gravimetry.
Example: In determining the moisture content of food, thermal energy vaporizes the H2O.
Larger particles, supersaturated
Particle size and filterability of precipitates
Selective, specific, readily filtered, low solubility, known composition
Properties of precipitant (precipitating agent)
Errors
There are different causes of ___ in gravimetric analysis:
Inaccurate weighing
Incomplete and imperfect precipitation
Use of substandard reagent and apparatus.
Haste and impatience
Volumetric Analysis
Measurement of the volume of a solution whose concentration is known and applied to determine the concentration of the analyte.
Titration or Titrimetric method
delivery of a solution of known concentration into a solution of unknown concentration
Acid–base titrations
in which an acidic or basic titrant reacts with an analyte that is a base or an acid
Complexometric titrations
involving a metal–ligand complexation reaction
Redox titrations
where the titrant is an oxidizing or reducing agent
Precipitation titrations
in which the analyte and titrant react to form a precipitate
Equivalence point.
For a titration to be accurate we must add a stoichiometrically equivalent amount of titrant to a solution containing the analyte. We call this stoichiometric mixture the
a theoretical point reached when the amount of added titrant is chemically equivalent to the amount of analyte in the sample
Titrant/standard solution
solution of known concentration used in titration (added from burette)
Titrate/Analyte
unknown solution which we determine its concentration
End point
physical change associated with the condition of chemical equivalence.
Indicators
are often added to the analyte solution to produce an observable physical change (signaling the end point) at or near the equivalence point.
Complex organic compound which shows clear visual change after the reaction between titrant and titrate is just complete.
Phenolphthalein
Methyl orange, blue
Thymol blue
Titration error
The difference between the end point volume and the equivalence point volume is a determinate method error, often called the ____.
If the end point and equivalence point volumes coincide closely, then the ____ is insignificant and can be safely ignored. Clearly, selecting an appropriate end point is critical
Buret
Typical setup for carrying out a titration. The apparatus consists of a ___, a ____ stand and clamp with a white porcelain base to provide an appropriate background for viewing indicator changes, and a wide-mouth Erlenmeyer flask containing a precisely known volume of the solution to be titrated. The solution is normally delivered into the flask using a pipet.
Erlenmeyer flask
Typical setup for carrying out a titration. The apparatus consists of a buret, a buret stand and clamp with a white porcelain base to provide an appropriate background for viewing indicator changes, and a wide-mouth ____ containing a precisely known volume of the solution to be titrated. The solution is normally delivered into the flask using a pipet.
0.01 mL
Detail of the buret graduations. Normally, the puret is filled with titrant solution to within 1 or 2 ml. of the zero position at the top. The initial volume of the buret is read to the nearest ____.
Pink
Before the titration begins. The solution to be titrated an acid in this example, is placed in the flask, and the indicator is added as shown in the photo. The indicator in this case is phenolphthalein, which tums ____ in basic solution.
Over titrate
If you overshoot the endpoint, it will cause an error in the calculation of the solution being titrated. If the volume of titrant is in error because it is higher than it should be, the moles of titrant will be incorrect and the resulting calculation for the solution titrated will not be accurate.
Potentiometry
It measures the electric potential across the substance.
It is used to measure the potential of an electrochemical cell to determine the concentration of a solution.
It's used in many fields, including pharmaceuticals, food, beverages, clinical chemistry, environmental chemistry, and agriculture:
Potential
amount of work to move a unit of charge
Current
flow of electricity, amount of electricity flowing in a circuit.
Charge
property of sub atomic particles
Electrode
The electrochemical cell is divided into two half-cells, each containing an ___ immersed in a solution containing ions whose concentrations determine the electrode’s potential.
Redox reaction
This separation of electrodes is necessary to prevent the ____ from occurring spontaneously on the surface of one of the electrodes, short-circuiting the electrochemical cell and making the measurement of cell potential impossible.
Anode
electrode where oxidation occurs
Electrons flow from the
A negative electrode
Cathode
electrode where reduction occurs
Electron flows to the
Positive electron
Reference Electrode
electrode potential is known
Indicator Electrode
unknown electrode potential
Salt Bridge
to maintain electrical neutrality in an electrochemical cell by allowing ions to flow between the solutions in the cell's half-cells
Electric circuit
A salt bridge containing an inert electrolyte, such as KCl, connects the two half-cells. The ends of the salt bridge are fixed with porous frits, allowing ions to move freely between the half-cells and the salt bridge, while preventing the contents of the salt bridge from draining into the half-cells. This movement of ions in the salt bridge completes the
Electrochemistry
Relationship between Chemical Reactions and Electricity
Certain chemical reactions can create electricity
Electricity can make certain chemical reactions happen
Oxidation-Reduction Reactions
Also known as Redox Reaction
In an _____, electrons are transferred from one reactant to another. An example is the oxidation of iron(II) ions by cerium(IV) ions. The reaction is described by the equation

Oxidation
An increase in oxidation number
Reduction
A decrease in oxidation number
Two half-reactions
We can split any oxidation/reduction equation into ____that show which species gains electrons and which loses them.
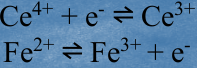
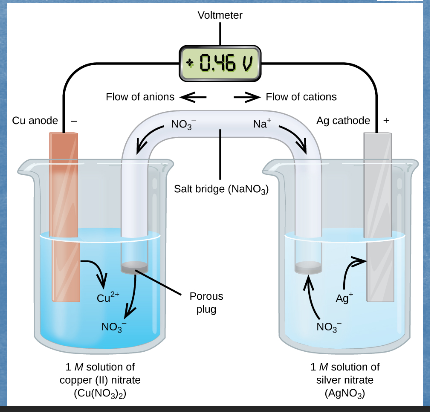
Galvanic Cell or Voltaic Cell
is an electrochemical cell where chemical energy is transformed into electrical energy.
Loses
Zn ___ electrons = oxidation
Gains
Cu ___ electrons = reduction
Electric current
Here the redox reaction has been physically separated into two half-cells, each corresponding to one half-reaction.
The flow of electrons from the anode to the cathode produces _____.
Oxidation number
is a positive or negative number assigned to an atom to indicate its degree of oxidation or reduction.
Zero
The oxidation number of any uncombined element is
Equals its charge
The oxidation number of a monatomic ion
-2
The oxidation number of oxygen in compounds is ___, except in peroxides, such as H2O2 where it is -1.
Hydrogen
The oxidation number of ___ in compounds is +1 if it is combined with nonmetals and -1 if it is combined with metals.
Sum
The ___ of the oxidation numbers of the atoms in the compound must equal 0.
Ionic charge
The sum of the oxidation numbers in the formula of a polyatomic ion is equal to its
+1, +2
The Group 1 metals have an oxidation state of ___ and Group 2 an oxidation state ___
-1, -2, -3
Group 17 elements have an oxidation state of ___, Group 16 elements of , and Group 15 elements of _.