Virginia Tech BMSP 2135 RAT #15
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
what are the 2 divisions of the nervous system?
CNS, PNS
what organs comprise the CNS?
brain, spinal cord
what organs comprise the PNS?
spinal nerves and their branches, cranial nerves
CNS: brain
- Enclosed completely by the skull
- Composed primarily of ___________ _________
- Consists of 100 billion neurons/nerve cells
- Lots of functions from the regulation of breathing and the processing of algebra to performing in the creative arts
nervous tissue
CNS: spinal cord
- Connects the brain with the peripheral NS and performs certain integrative functions
- Brain merges with the spinal cord at the __________ _______________
- Passes through the vertebral foramen of the 1st cervical vertebra and continues inferiorly to the 1st or 2nd lumbar vertebra
- Contains fewer cells than the brain (~100 million neurons)
- Enables the brain to communicate with most parts of the body below the head and neck
- Also able to carry out certain functions on its own
foramen magnum
PNS
- _____________ = most numerous organs of the NS
- Consist of bundles of axons, CT sheaths, and blood vessels
- Carry signals to and from the CNS
nerves
what are the 2 types of nerves?
cranial, spinal
cranial nerves
- originating from or traveling to the brain
- _____ pairs
12
spinal nerves
- originating from or traveling to the spinal cord
- _____ pairs
31
What are the three basic functional processes of the nervous system?
sensory functions, integrative functions, motor functions
basic functions of the NS
_____________ functions involve gathering information about the internal and external environments of the body
sensory
basic functions of the NS
________________ functions: analyze and interpret the detected sensory stimuli and determine an appropriate response
integrative
basic functions of the NS
integrative functions are performed entirely by the _______, mostly by the brain
CNS
basic functions of the NS
_____________ functions: the actions performed in response to integration
motor
basic functions of the NS
motor output is performed by the motor (efferent) division of the ________
PNS
Sensory input is gathered by the sensory (_____________) division of the PNS
afferent
sensory input
- carried from sensory receptors to the where? by cranial and spinal nerves of the PNS
- sensory stimuli are first detected by sensory receptors = specialized part of a neuron that detects changes in the internal and/or external environment
spinal cord and/or brain
what are the 2 ways to classify sensory information?
somatic, visceral
somatic sensory division
- consists of neurons that carry signals from skeletal muscles, bones, joints, and skin
- also includes sensory neurons that transmit signals from the organs of vision, hearing, taste, smell, and balance
- sometimes these particular neurons are referred to as the _____________ sensory division
special
visceral sensory division
consists of neurons that transmit signals from viscera (____________) such as the heart, lungs, stomach, intestines, kidneys, and urinary bladder
organs
The PNS __________ ____________ consist of motor neurons that carry out the motor functions of the NS
motor division
motor output
travels from the brain and/or spinal cord via cranial and spinal nerves of the PNS to muscle cells or __________ for secretion
glands
organs that carry out the effects of the NS
effectors
the motor division may be further classified based on the organs that the neurons contact
2 divisions: ___________ motor division, ____________ motor division
somatic, visceral
somatic motor division
- also called the voluntary motor division
- consists of neurons that transmit signals to __________ _____________
- skeletal muscle tissue is under conscious control
skeletal muscles
visceral motor division
- also called the ANS/involuntary motor division
- consists of neurons that carry signals primarily to where?
- the ANS regulates secretion from certain glands, the contraction of smooth muscle, and the contraction of cardiac muscle in the heart
thoracic and abdominal viscera
what are the 2 primary types of cells in nervous tissue?
neurons, neuroglial cells
Neurons are generally __________ = at a certain point in development, they lose their centrioles and after that lack the ability to undergo mitosis
amitotic
what are the 3 main parts of a neuron?
dendrites, cell body (soma), axon
organelle composition → level of biosynthetic activity
- Free ribosomes and rough ER are found in abundance, reflecting the commitment of the cell body to protein synthesis
- Other organelles involved in protein synthesis (Golgi apparatus and one or more prominent nucleoli) are present
- __________________ are numerous, indicating the high metabolic demands of the neuron
- The cytoplasm of the cell includes lysosomes, smooth ER, and other organelles found in most cells
Mitochondria
dendrites
- Short, highly forked processes that resemble the branches of a tree limb
- Receive input from other neurons, which they transmit in the form of electrical impulses toward the cell body
- Do not generate or conduct ___________ ________________
Huge receptive surface area
action potentials
_________ = nerve fiber = processes that can generate and conduct APs
1 axon per neuron
axon
the initial portion of an axon where an AP is generated
axon hillock
branches that extend from some axons that typically arise at right angles
axon collaterals
small branches at the end of an axon that are a result of the splitting of both the axon and its collaterals
telodendria
location of termination of telodendria; also called synaptic knobs; role is to communicate with a target cell; each axon generally splits into >1000
axon terminals
the plasma membrane of the axon
axolemma
cytoplasm of the axon
axoplasm
what are the 3 functional regions of the neuron?
receptive region, conducting region, secretory region
receptive region of neuron
consists of what 2 structures?
dendrites and cell body.
conducting region of neuron
The received signals are collected in the cell body, which then may transmit a signal to the ________, the conducting region of the neuron.
axon
secretory region of neuron
When the signal reaches the axon terminals of the secretory region, they secrete chemicals that trigger changes in their __________ cells.
target
what are the 3 structural classifications of neurons?
multipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar
multipolar neuron
- A neuron with 1 axon and >2 ____________
- Over 99% of neurons in the body
- Widest variety in terms of shape and size
- motor (efferent) neurons, interneurons
dendrites
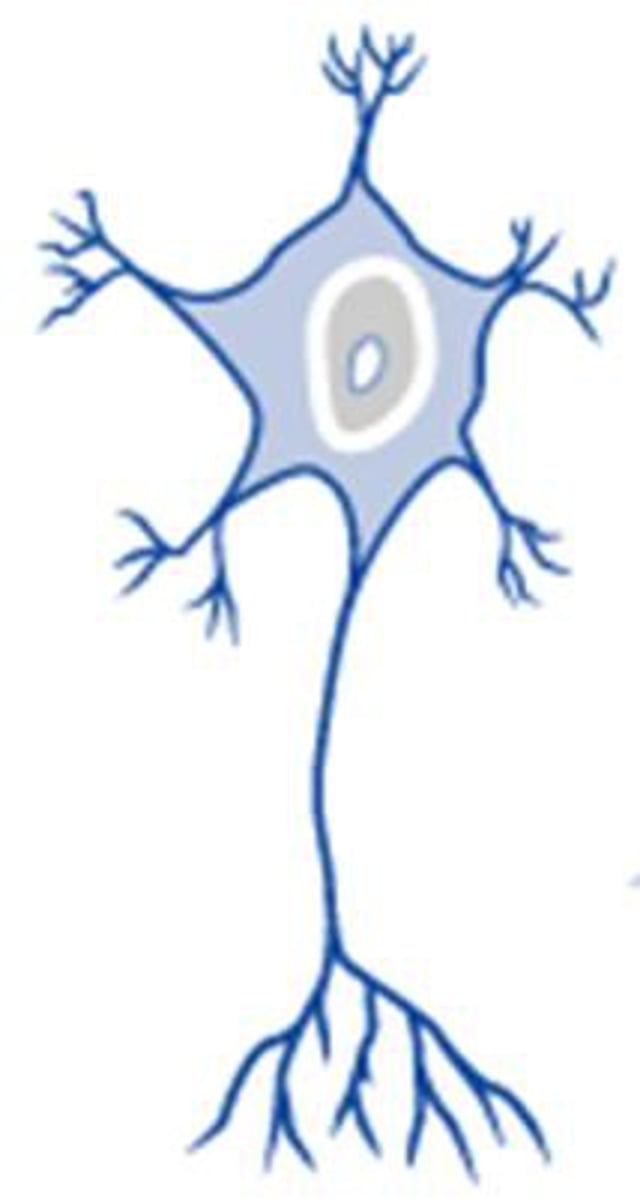
bipolar neurons
- how many axons and dendrites do bipolar neurons have?
- cell body in middle
- In humans, the majority of bipolar neurons are sensory neurons, located in places such as the retina of the eye and the olfactory epithelium of the nasal cavity
1 axon, 1 dendrite
pseudounipolar neurons
how many axons does pseudounipolar neurons have?
2
pseudounipolar neurons
- 2 axons: a _____________ process that brings input to the cell body and a ____________ process that brings input to a target cell; formerly referred to as unipolar neurons
- sensory neurons that detect stimuli such as touch, pressure, and pain
peripheral, central
what are the 3 functional classifications of neurons?
sensory (afferent), interneuron, motor (efferent)
cluster of neuron cell bodies in the CNS
nuclei
cluster of neuronal cell bodies in the PNS
ganglia
bundles of axons in the CNS
tracts
bundles of axons in the PNS
nerves
____________ = type of neuroglial cells in the CNS that anchor neurons and blood vessels, regulate extracellular environment, facilitate formation of BBB, repair damaged tissue
astrocytes
____________ = type of neuroglial cells in the CNS that myelinate certain axons in the CNS
oligodendrocytes
____________ = type of neuroglial cells in the CNS that act as phagocytes
microglia
____________ = type of neuroglial cells in the CNS that line cavities, cilia circulate fluid around brain and spinal cord, some secrete CSF
ependymal cells
____________ = type of neuroglial cells in the PNS that myelinate certain axons
Schwann cells
____________ = type of neuroglial cells in the PNS that surround and support cell bodies
satellite cells
____________ is composed of repeating layers of the plasma membrane of the neuroglial cell, so it has the same substance as any plasma membrane: phospholipids, other lipids like cholesterol, and proteins
Myelin
myelin sheath
- plays an important role in the electrophysiology of many neurons
- in unmyelinated axons, the electric current "leaks" out of the axon and has to be continually regenerated
- however, ions do not pass easily through the hydrophobic portion of the phospholipid bilayer → the high lipid content of myelin makes it an excellent insulator, akin to the rubber tubing around a copper wire
- overall effect of this insulation is to increase the speed of _______________ of action potentials: Myelinated axons conduct action potentials about 15-150 times faster than unmyelinated axons.
conduction
the myelinated segment of an axon; covered by neuroglia
internodes
are more than 1 cell needed to myelinate an axon in the CNS and PNS?
yes (axons are generally much longer than a single oligodendrocyte or Schwann cell)
the unmyelinated segment of an axon between two internodes
node of Ranvier (myelin sheath gap)
collections of myelinated axons that appear white
white matter
collections of unmyelinated axons, dendrites, and cell bodies that appear gray
gray matter
Can damaged neurons in the CNS regenerate?
no (damaged axons and dendrites in the CNS almost never regenerate)
Neural tissue in the PNS is capable of regeneration to some extent, but only if the ______ _________ remains intact
cell body
which of the 3 functions of the NS (sensory, integrative, motor) are carried out by the PNS?
sensory, motor
internal cavities of the brain that are filled with a protective cerebrospinal fluid
ventricles
the brain is (richly/poorly) supplied with blood vessels
richly
what are the 4 divisions of the brain?
cerebrum, diencephalon, cerebellum, brainstem
4 divisions of brain
______________
- higher mental functions
- interprets sensory stimuli
- plans and initiates movement
cerebrum
4 divisions of brain
_______________
- processes, integrates, and relays information
- maintains homeostasis
- regulates biological rhythms
diencephalon
4 divisions of brain
____________________ monitors and coordinates movement
cerebellum
4 divisions of brain
______________
- maintains homeostasis
- controls certain reflexes
- monitors movement
- integrates and relays information
brainstem
where does the spinal cord begin?
foramen magnum (of the occipital bone)
the spinal cord is encased within and protected by what?
vertebral cavity
Like the brain, the spinal cord has an internal cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid; its cavity, the ___________ ___________, is continuous with the ventricles of the brain.
central canal
in the brain, the gray matter is on the (outside/inside) and the white matter is on the (outside/inside)
outside, inside
in the spinal cord, the gray matter is on the (outside/inside) and the white matter is on the (outside/inside)
inside, outside
white matter in the spinal cord is called what?
tracts
gray matter in the spinal cord is called what?
nuclei
name 4 things that help protect the brain
cranial cavity (skull), cranial meninges, CSF, BBB
the cranial meninges, CSF, and BBB are (inside/outside) the skull
inside
what is the singular form of meninges?
meninx
List the three cranial meninges from outermost to innermost.
dura mater, arachnoid mater, pia mater (DAP)
What are the three spaces related to the meninges?
epidural space, subdural space, subarachnoid space
Spaces of the meninges
potential space between the dura mater and the cranial bones
epidural space
Spaces of the meninges
narrow space deep to the dura that houses a thin layer of serous fluid and certain veins that drain the brain
subdural space
Spaces of the meninges
narrow, fluid-filled space between the arachnoid mater and pia mater that contains CSF and major blood vessels of the brain
subarachnoid space
What are the two layers of the dura mater?
periosteal dura, meningeal dura
layers of the dura
____________ dura = outer layer that is attached to the inner surface of the cranial cavity, functions as the periosteum of the bones and has an extensive blood supply that resides in the epidural space
periosteal
layers of the dura
____________ dura = inner layer that is avascular; lies superficial to the arachnoid mater
meningeal dura
the set of venous channels that are located between two layers of dura mater (periosteal layer, meningeal layer) and drain the cerebral veins of the brain
dural sinuses
a double fold of meningeal dura that dives into the longitudinal fissure and separates the 2 cerebral hemispheres
falx cerebri
the ________ ______________ separates the left and right cerebellar hemispheres
falx cerebelli
this is the the partition between the cerebellum and the occipital lobe of the cerebrum; named for its resemblance to a tent covering the cerebellum
tentorium cerebelli
the arachnoid mater resembles a what?
spider web
inward extensions made of bundles of collagen fibers and fibroblasts that anchor the arachnoid mater to the deeper pia mater
arachnoid trabeculae
arachnoid granulations = arachnoid _________: play an important role in returning CSF to the bloodstream
villi