Sediment sources, cells and budgets
1/12
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
13 Terms
Fetch
The distance of the sea, over which the wind has traveled
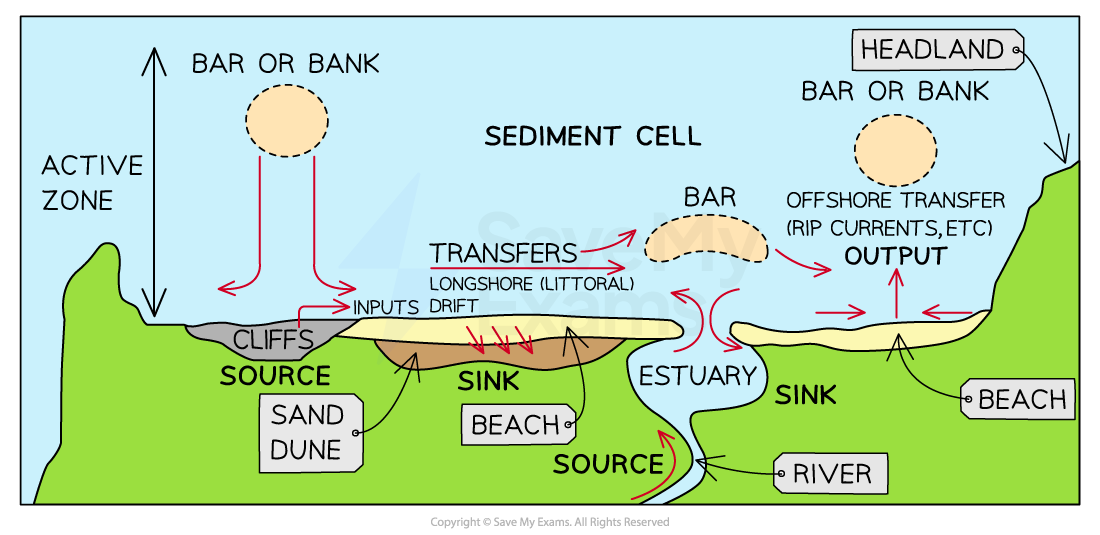
Sediment cell
An isolated system of sources, transfers and sinks of sediment along a section of coastline. The coastline of England and Wales is divided into 11 primary sediment cells, with sub-cells within each primary cell. The boundaries are formed by major headlands or large estuaries. A sediment cell operates a closed system, with virtually no inputs or outputs of sediment from the cell.
Human influences on the coastal sediment budget
construction of major dams
residencies
sedimentary budgets
Sedimentary budgets
Sedimentary budgets are a coastal management tool used to analyse and describe the different sediment inputs (sources) and outputs on the coasts. Within a coastal environment, the rate of change of the sediment depends on the amount of sediment brought into the system compared to the ammount of sediment that leaves the system.
Residencies
Over 5.3 million residents live in coastal towns in England and Wales, of which 3.5 million live in seaside towns (those with a beach and visitor attractions) and 1.9 million in other coastal towns
Construction of major dams
The construction of major dams or rivers can trap river sediment de hind the dam wall. This then starves the coast of sediment source leading to serious consequences
The construction of the Aswan high dam on the river nile in 1964 reduces sediment volume from 130 million tonnes to about 15 million tonnes per year. Erosion rates jumped from 20-25m per year to over 200m per year as the delta was starves of sediment
Dredging
This is the removal of sediment from a beach, sea or river.
Sands or gravels are scooped/sucked up for use by construction industry
dreging of river mouths and estuaries often to maintain channels for ship transport
Coastal zone
Coastal zones include:
Backshore
Foreshore
In shore
Offshore
Nearshore
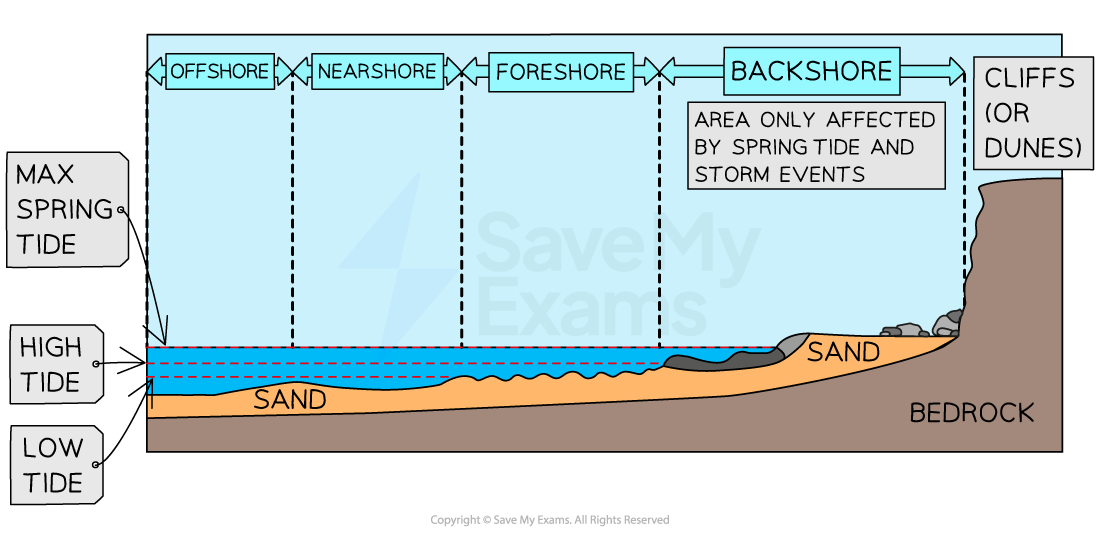
Backshore
Changes usually take place during storm activity
Foreshore
Most important zone for marine processes in times that aren’t influenced by storm activity
In shore
Waves cease to have any influence on the land below them
Offshore
Activity is limited to deposition of sediments
Near shore
Waves begin to break
Swash zone - turbulent layer of water washes up the beach following the wave breaking
Surf zone - Waves break forming a foamy, bubbly surface and where waves move up the beach as swash
Breaker zone - Waves approaching the coastline begin to break, water depth is 5-10m