Accessory Radiology Equipment (Cram)
1/40
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
41 Terms
Fill in the blank: The beam of x–rays leaving the port consists of two types: _____ ________ x–rays can penetrate the body and reach the film. While ____ _______ x–rays if allowed to leave the tube housing, are only absorbed by the first few centimetre’s of tissue. They contribute nothing to the exposure of the film.
High energy, low energy
What are the two types of filtration?
- Inherent filtration
- Added filtration
This type of filtration includes the glass envelope, cooling gas or oil chamber, lead shielding, and housing which surrounds the x–ray tube and the window
Inherent filtration (glass envelope pictured)

Added filtration is accomplished by placing something between the window of the x–ray tube and the collimator, what is it?
Aluminum filter
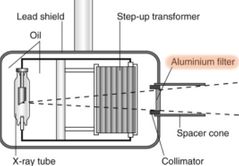
True or false: The collimator enhances the safety of the x–ray machine by focusing the x–ray beam and changing its direction
False. The collimator improves safety by controling the size of the primary beam by absorption of radiation into the lead plates. It does NOT focus or change the direction of x–rays
What are the three benefits when using a collimator?
- Improves image quality (reduces scatter)
- Decreases exposure to the patient
- Decreases exposure to personnel
What type of collimator is found in older x–ray machines?
Cone type
What type of collimator is found in newer x–ray machines?
Lead shutter type

The grid ratio is defined as the height of the lead strips to the distance between them (R = h/d). What is the relationship between the height and distance betweeen the lead strips in a 8:1 grid?
The lead strips are 8 times as high as the distance between them
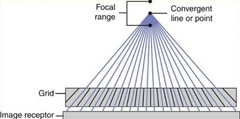
What kind of grid is this? The lead strips are angled, which allows the x–rays at the edge of the primary beam to pass through the grid
Focused grid

What kind of grid is this? The lead strips run parallel to each other. This grid is only useful for a very small x–ray field
Non–focused grid
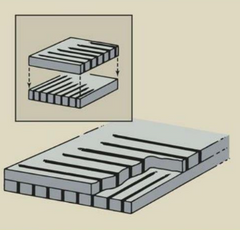
What kind of grid is this? It consists of two focused grids on top of one another.
Crossed grid
Which type of grid can be used at many different source image distances?
Non–focused grid
Which type of grid is made to be used at a specified source image distance?
Focused grid
Which type of grid can't be used with oblique views?
Crossed grid
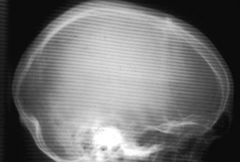
What is the problem with this x–ray?
Lines indicate that the grid is damaged

What kind of grid is this? It moves when the exposure is made. This movement blurs the grid lines. Why isn't it commonly used in veterinary medicine?
Potter–Bucky. The noise of the motor that moves the grid is loud and may startle animals
Fill in the blank: The _______ _______ utilizes the property of x–rays to cause certain materials to fluoresce.
intensifying screen
Fill in the blank: _________ crystals in the intensifying screen absorb x–rays and covert that energy to light which in turn exposes the _______ _______ crystals in the x–ray film.
Phosphor, silver halide
How are intestifying screens placed in order to increase efficiency?
The intensifying screens sandwich the film in the cassette
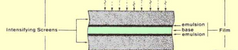
What percent of the exposure in an x–ray film is due to light produced by the intensifying screen?
95%, only 2–5% is due directly to x–ray photons
What are the three factors which determine the intensity or speed of the intensifying screen?
- Thickness of the layer of phosphor crystals
- The size of the phosphor crystals
- The type of crystal (there are several types)
True or false: Like a collimator, the purpose of an intensifying screen is to increase detail on a radiograph
False. Intensifying screens reduce the amount of detail
If intensifying screens reduce the amount of detail, why are they used?
They decrease exposure times, this is a big safety feature and especially useful in veterinary medicine when patients can move
What are the four different kinds of intensifying screens?
- Fast screens
- Slow screens
- Medium screens
- Rare earth screens
What kind of intensifying screen is this: It has small crystals, which increases exposure times but has better detail?
Slow screen
What kind of intensifying screen is this: It contains special phosphor crystals (containing lanthanum), it has a very rapid rate of fluorescence. They emit a green light
Rare earth screen
What kind of intensifying screen is this: It is commonly used in veterinary medicine
Medium screen
What kind of intensifying screen is this: It has large crystals and a thicker layer of crystals. It has very a fast exposure times but the detail on the radiograph is reduced
Fast screen
The film and the screen are not in close contact, this allows the fluorescent light to spread unevenly and produce and image which is not sharp. What could cause this?
Fur buildup between the film and the screen
What are the six advantages to using an intensifying screen?
- Decreases the chance of patient motion
- Decrease patient exposure
- Decrease scatter radiation
- Greater KvP selection
- Increase life or x–ray tube (lower mAs)
- Permits use of smaller focal spot
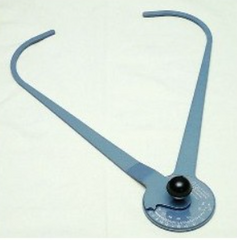
What x–ray accessory instrument is this. They are used to measure the thickest part being radiographed?
Calipers
What are some positioning aids (know some)?
Sedation/tranquillizer, foam blocks or wedges, v–trough, ties, tape, and sandbags
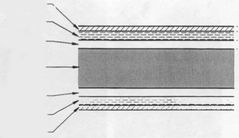
Label this diagram of x–ray film
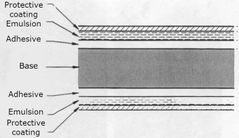
What are the three film speed groups? Speed refers to the exposure required to produce an image with suitable density
- Fast film
- Medium film
- Slow film
Put these film types in order from largest to smallest silver halide crystals: Medium film, slow film, fast film
Fast film > Medium film > Slow film
Put these film types in order from most to least exposure required: Medium film, slow film, fast film
Slow film > Medium film > Fast film
What are the two basic kinds of film?
- Screen film
- Non–screen film
Which basic type of film requires intensifying screens?
Screen film
How should you store film: in a vertical or horizontal position?
Vertical, in a horizontal position they will be crushed
What are the six things that decrease scatter radiation?
Remember: I Avoid Getting Cancer In Lifetime
Intensifying screen
Aluminum filter
Grids
Collimator
Inherent filtration
Lead sheets (laid around patient/table)