DPT Human Anatomy Exam 1
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
112 Terms
Regional Anatomy
method of studying the body's structure by focusing attention on a specific part and examining the arrangement and relationships of the various systemic structures within it.
Surface Anatomy
provides knowledge of what lies under the skin and what structures are perceptible to touch in the living body at rest and in action
System Anatomy
the study of the body's organ systems that work together to carry out complex functions
Body Systems (11)
integumentary (protective physical barrier), skeletal (bones), articular (joints), muscular, nervous, circulatory (heart and blood), alimentary (digestive tract), respiratory, urinary, genital, and endocrine (hormone)
Clinical Anatomy
emphasizes aspects of bodily structure and function important in the practice of medicine, dentistry, and all the allied health sciences
Human Movement System
a physiological system that functions to produce motion of the body as a whole or of its component parts
Effector Systems
muscular, skeletal, nervous
Support Systems
cardiovascular, endocrine, pulmonary, integumentary
Anatomical Planes and Sections
median, saggital, coronal, transverse, oblique
median
divides the body into right and left halves through the midline
saggital
divided the body into right and left parts by passing through parallel to the median plane
coronal
divides the body into anterior and posterior parts
transverse
divides the body into superior and inferior parts
oblique
slices of the body
superior/cranial
closer to the head
inferior/cadual
closer to the feet
posterior/dorsal
closer to the backside of the body
anterior/ventral
closer to the frontside of the body
medial
closer to the midline
lateral
away from the midline
dorsal foot
top of foot
plantar foot
bottom of foot
palmar hand
palm of hand
dorsal hand
back of hand
superficial
closer to the surface
intermediate
between a superficial and deep structure
deep
further from the surface
external
outside of or father from the center of an organ or cavity
internal
inside or closer to the center, independent of direction
proximal
closer to the point of origin or trunk
distal
further away from the point of origin or trunk
unilateral
Occurring only on one side
bilateral
occurring on both sides
ipsilateral
occurring on the same side
contralateral
occurring on the opposite side
anatomical variations
doesn't have any effect on normal function. they are often discovered during imaging, surgical procedures, autopsy's, or studies in individuals unaware of an adverse effect from the variation
conventional radiography
plain film studies or X-rays
radiodensity
dense to x-rays or radiation
when something is denser it tends to show up whiter
radiolucency
void areas in imaging that appear because of the tissue is less dense
when something is less dense it tends to show up darker
Computerized Tomography (CT)
uses x-rays in the construction of 2D/3D images
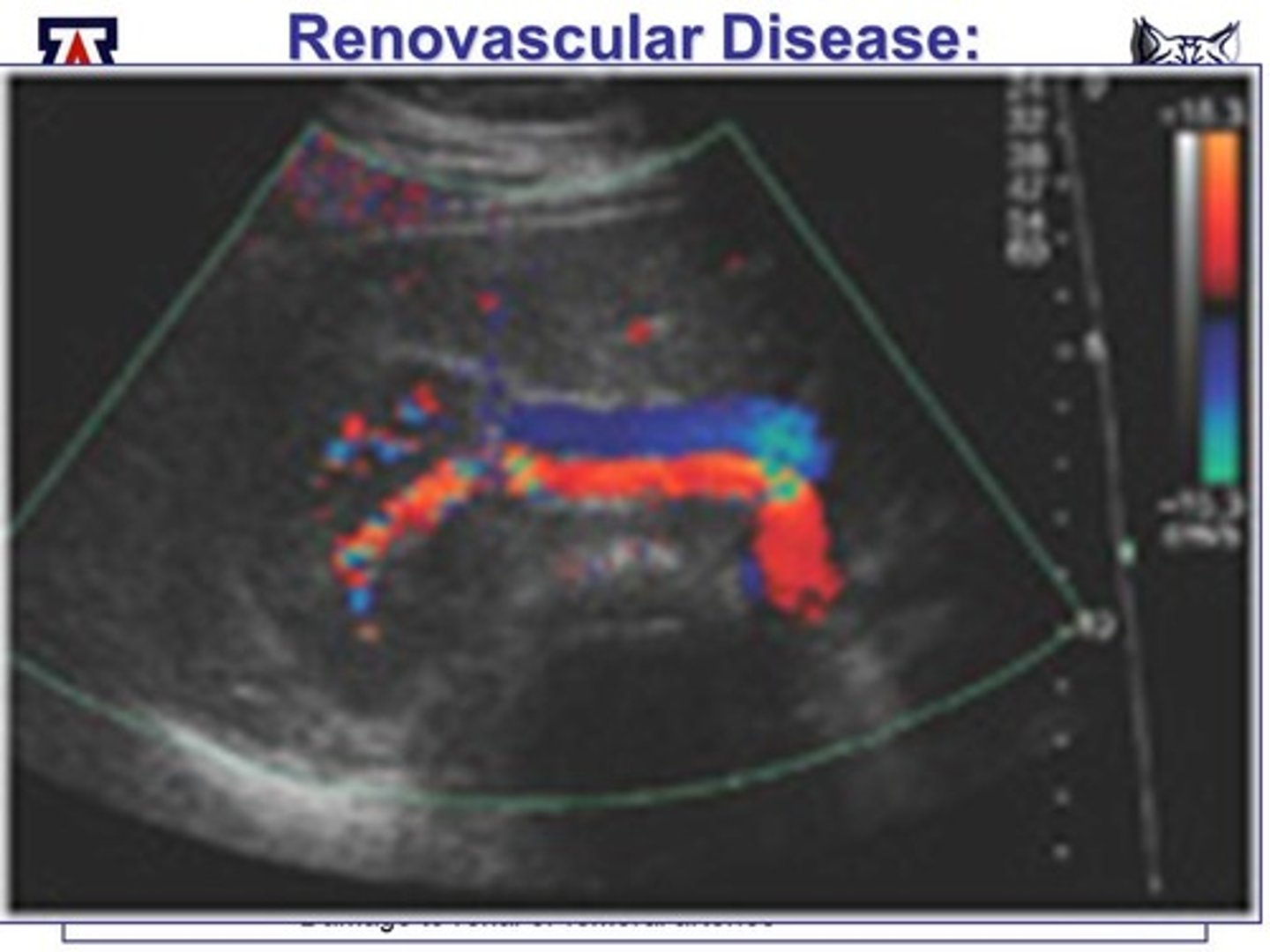
ultrasonography
allows for visualization of movement and blood flow in real time without the use of radiation
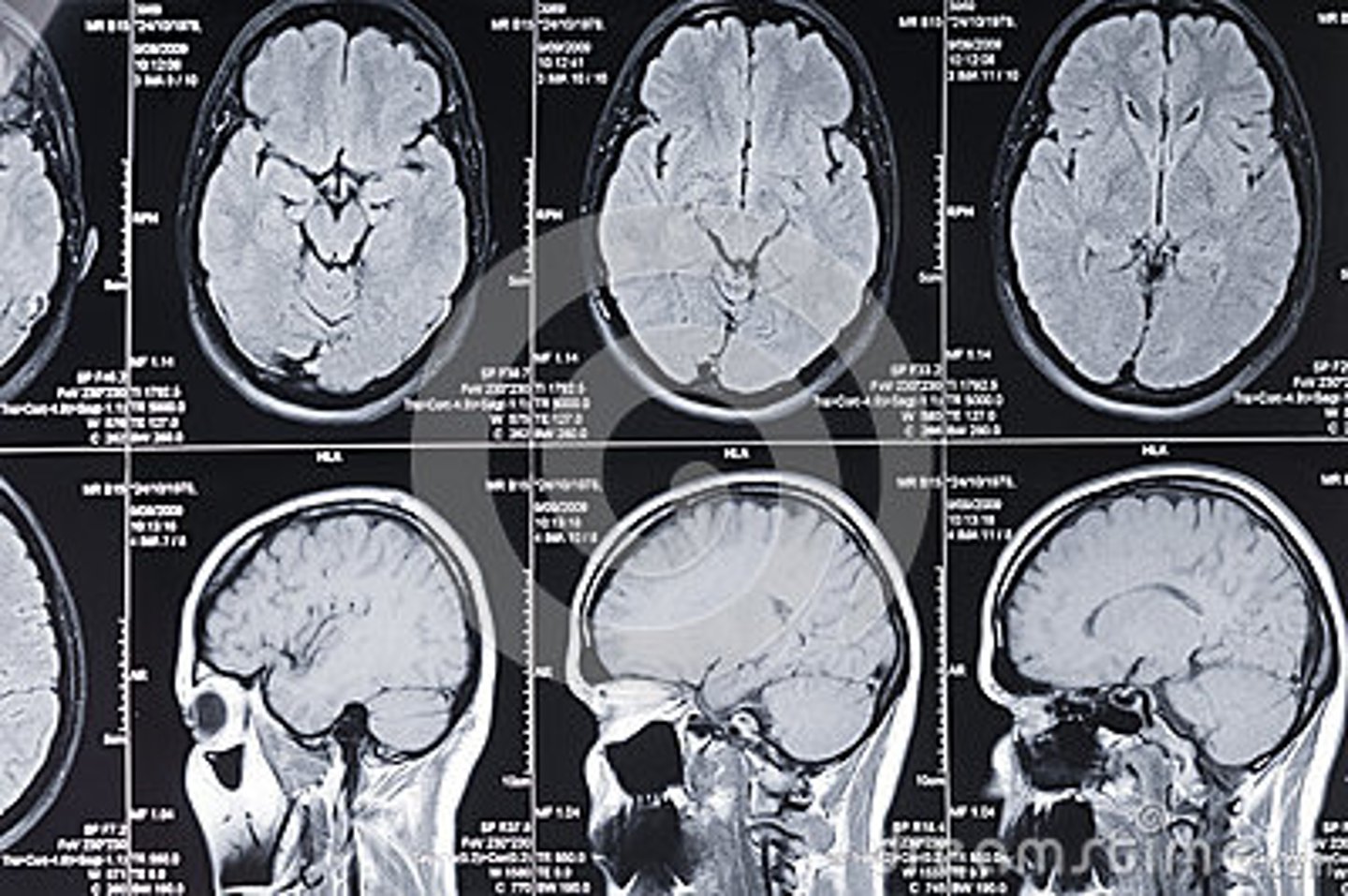
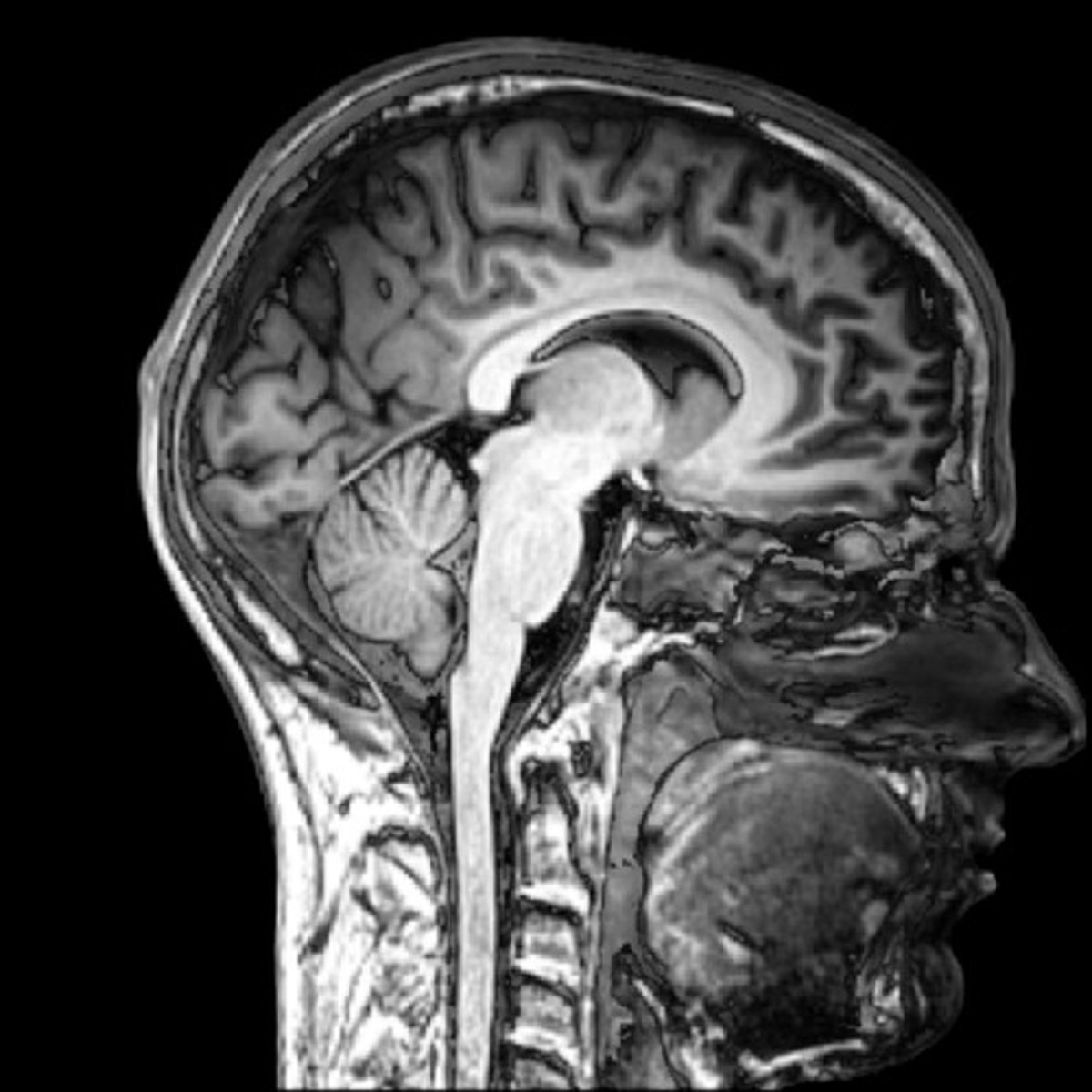
magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
provides for greatest structural differentiation
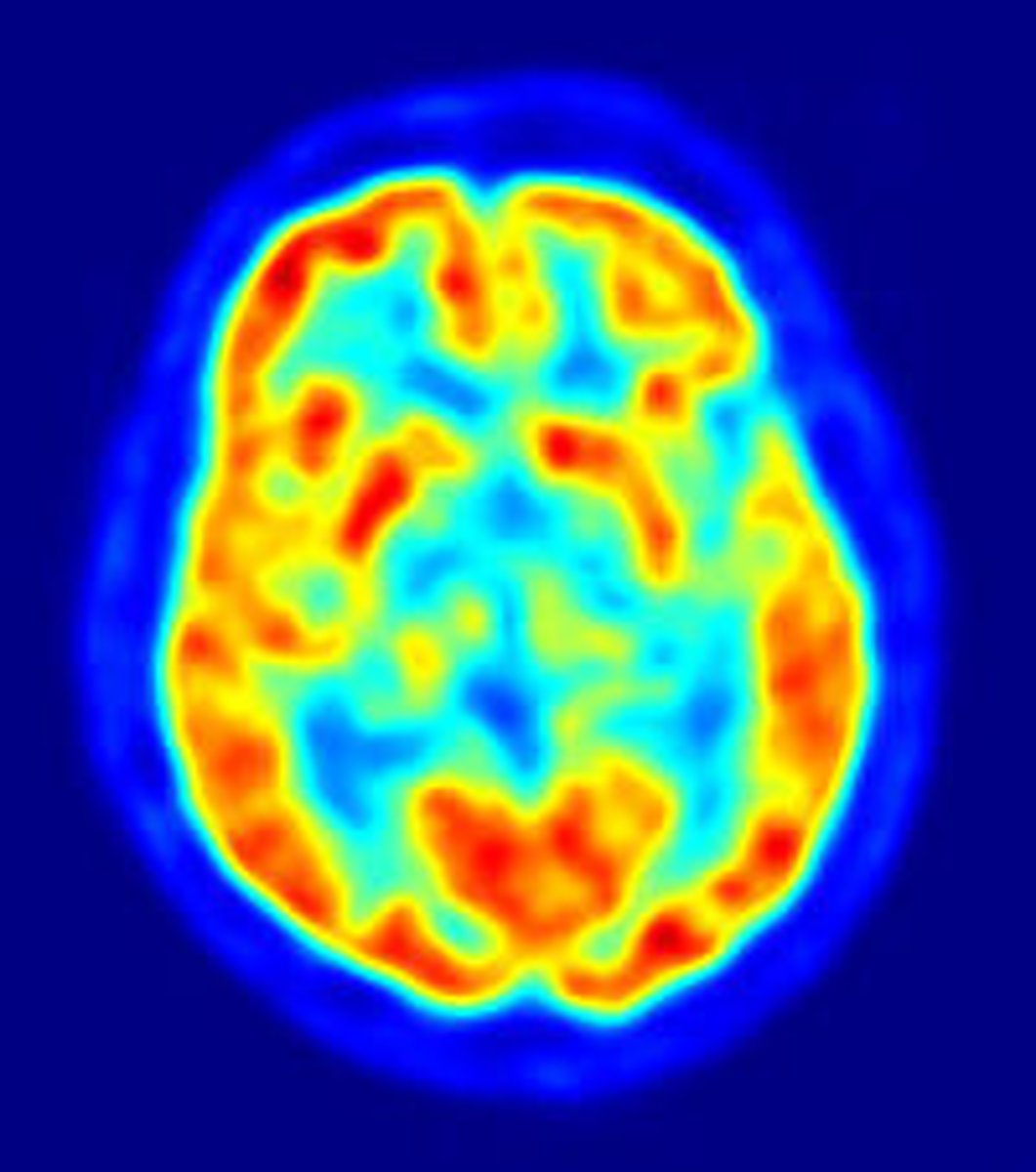
Positron Emission Tomography (PET)
utilized to evaluate physiologic function on a dynamic basis
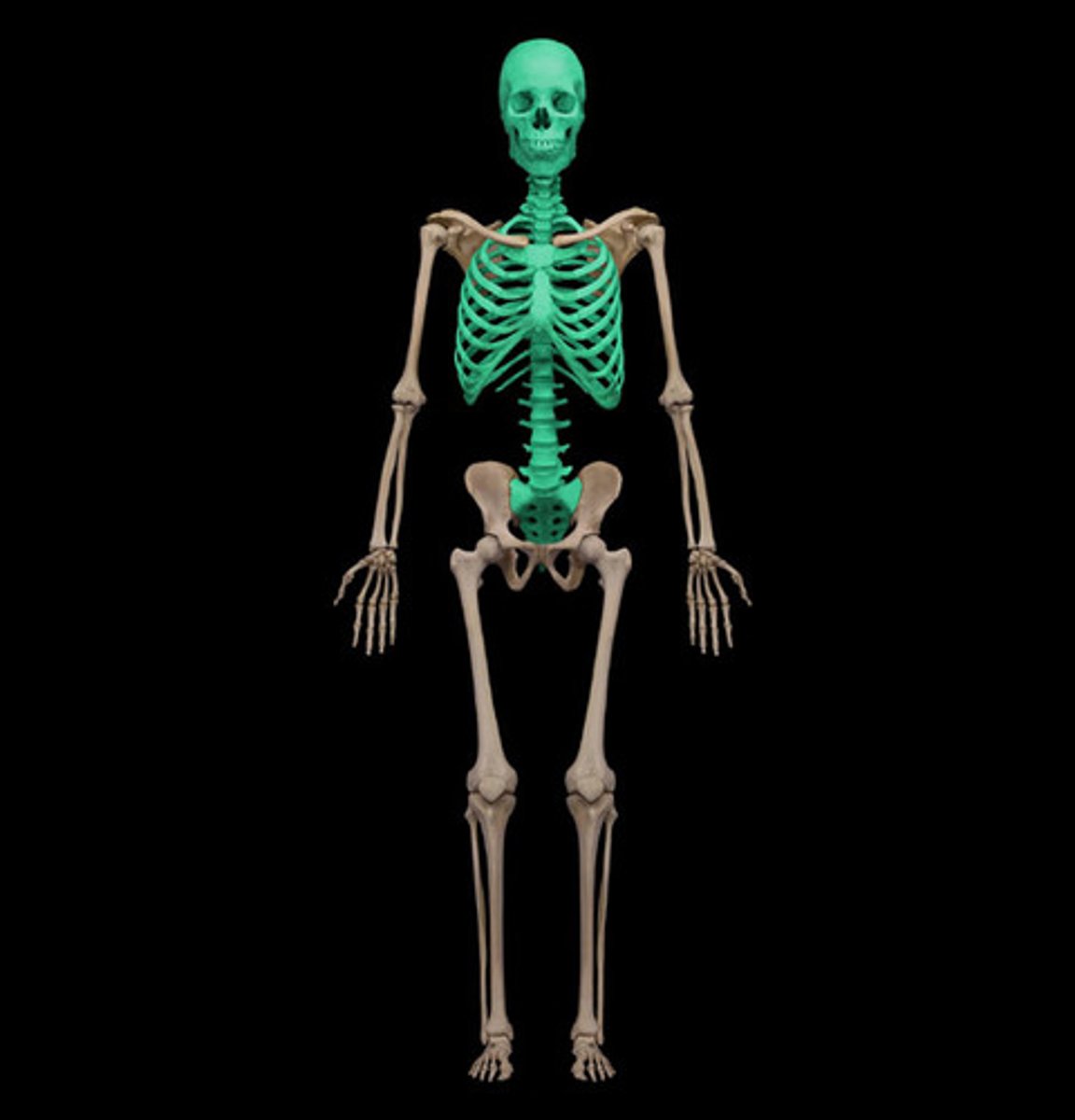
axial skeleton
consists of the bones of the cranium, hyoid bone, cervical vertebrae, ribs, sternum, and sacrum
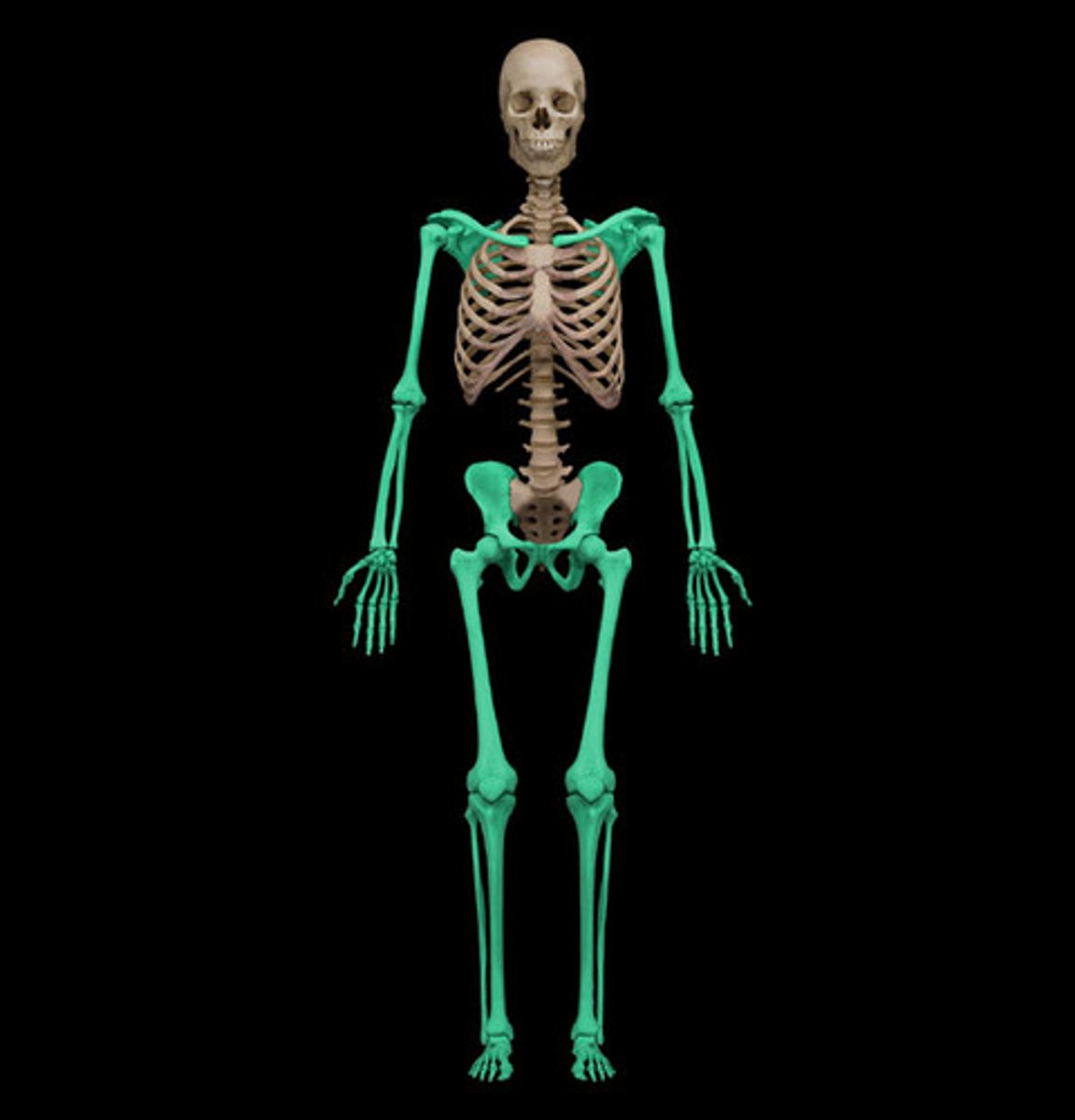
appendicular skeleton
consists of the bones of the limbs, including the scapula, clavicle, and pelvic girdles
cartilage
a resilient, semi rigid form of connective tissue that forms parts of the skeleton where more flexibility is required
avascular
articular cartilage (hyaline)
covers ends of bones
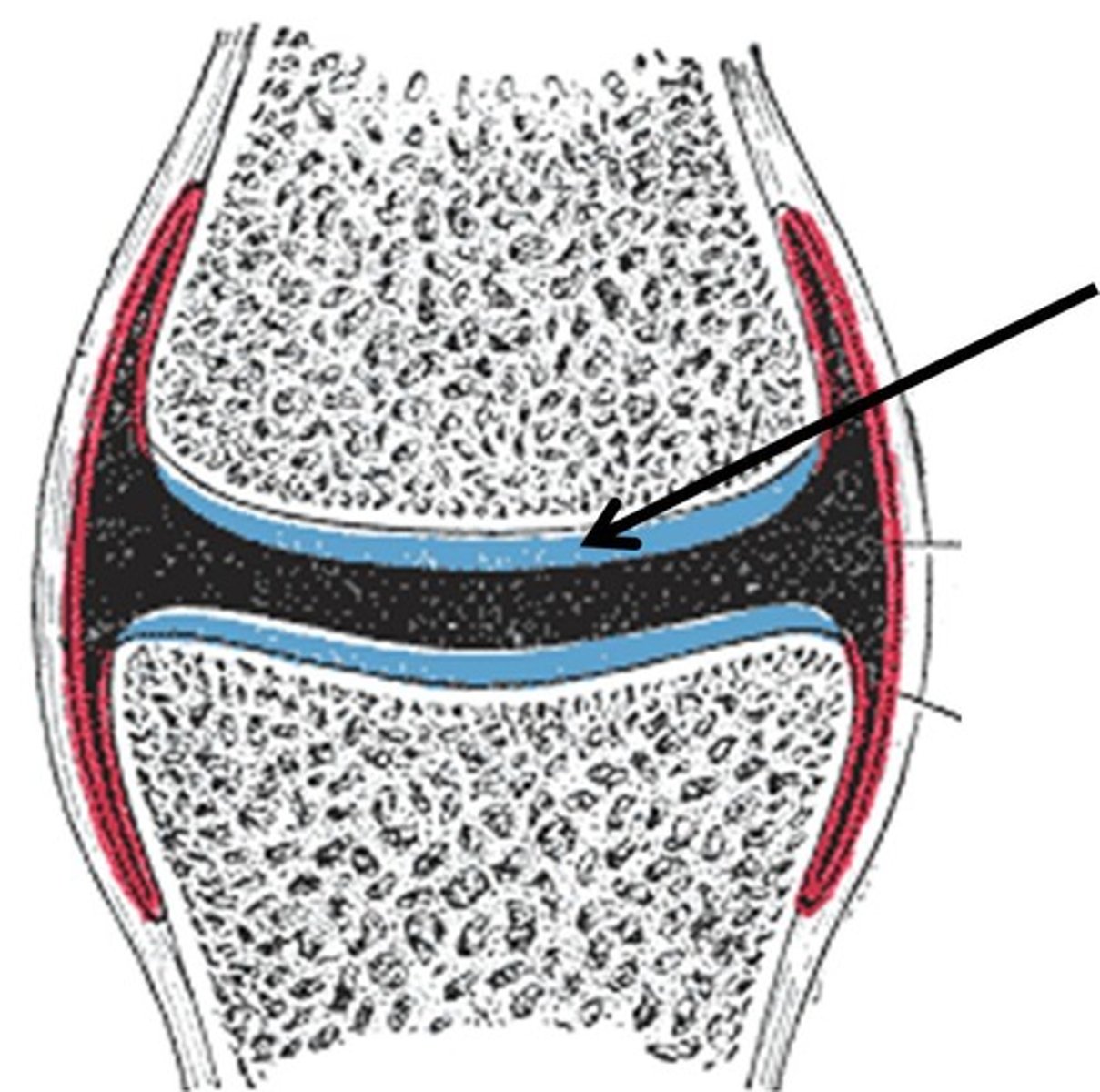
articular surfaces
capped in articular cartilage, which provides smooth, low-friction, gliding surfaces for free movement
bone
living tissue
hard form of connective tissue
skeletal system functions
provides support, protection, mechanical basis for movement, storage (Ca2+), and continuous supply of new blood cells
skeletal system components
compact bone, spongy bone, medullary cavity, periosteum, perichondrium
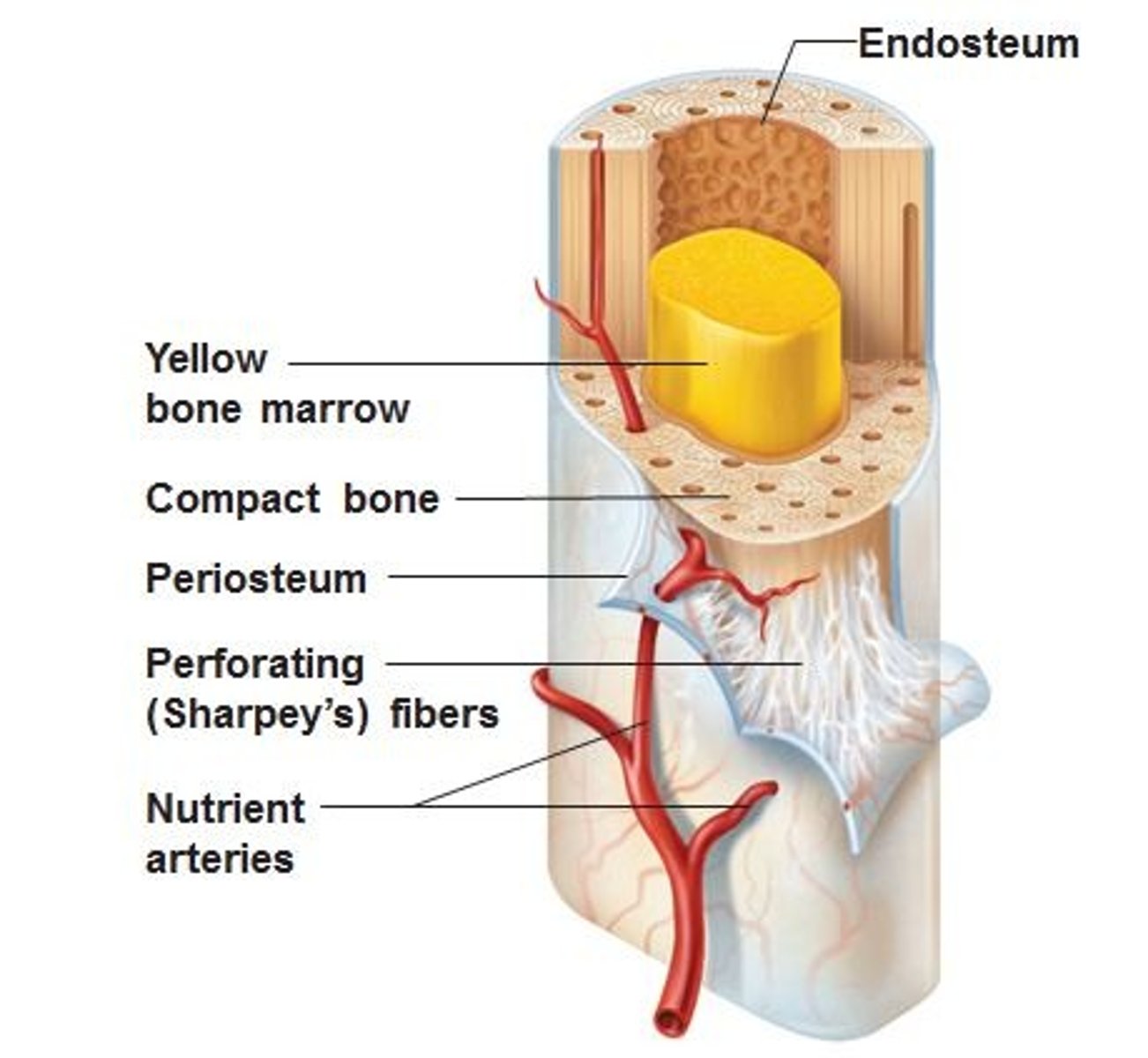
compact bone
dense bone in which the bony matrix is solidly filled with organic substances leaving only tiny spaces that contain osteocytes or bone cells
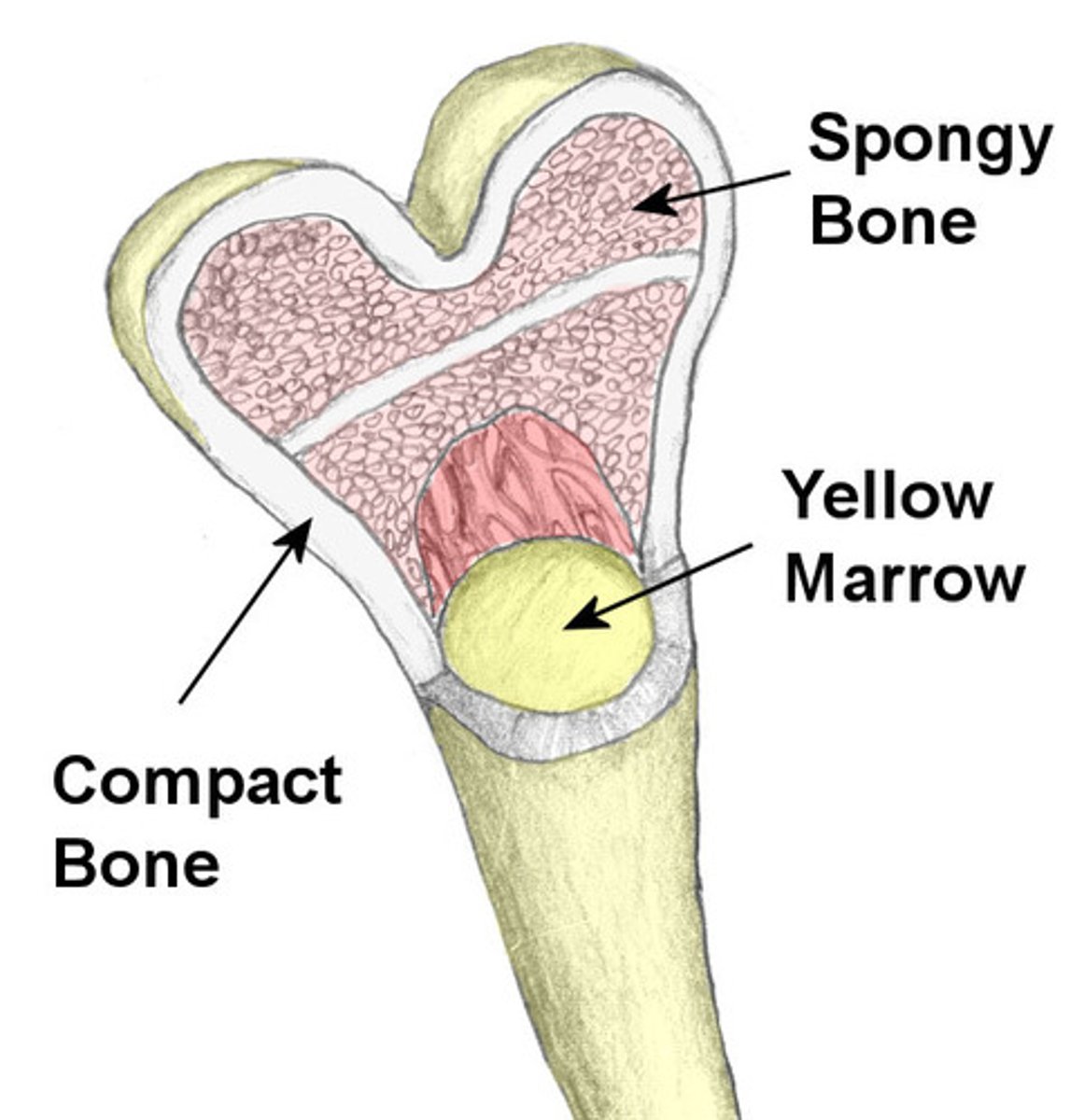
spongy bone
spongy, porous bone tissue composed of hard and soft tissue components
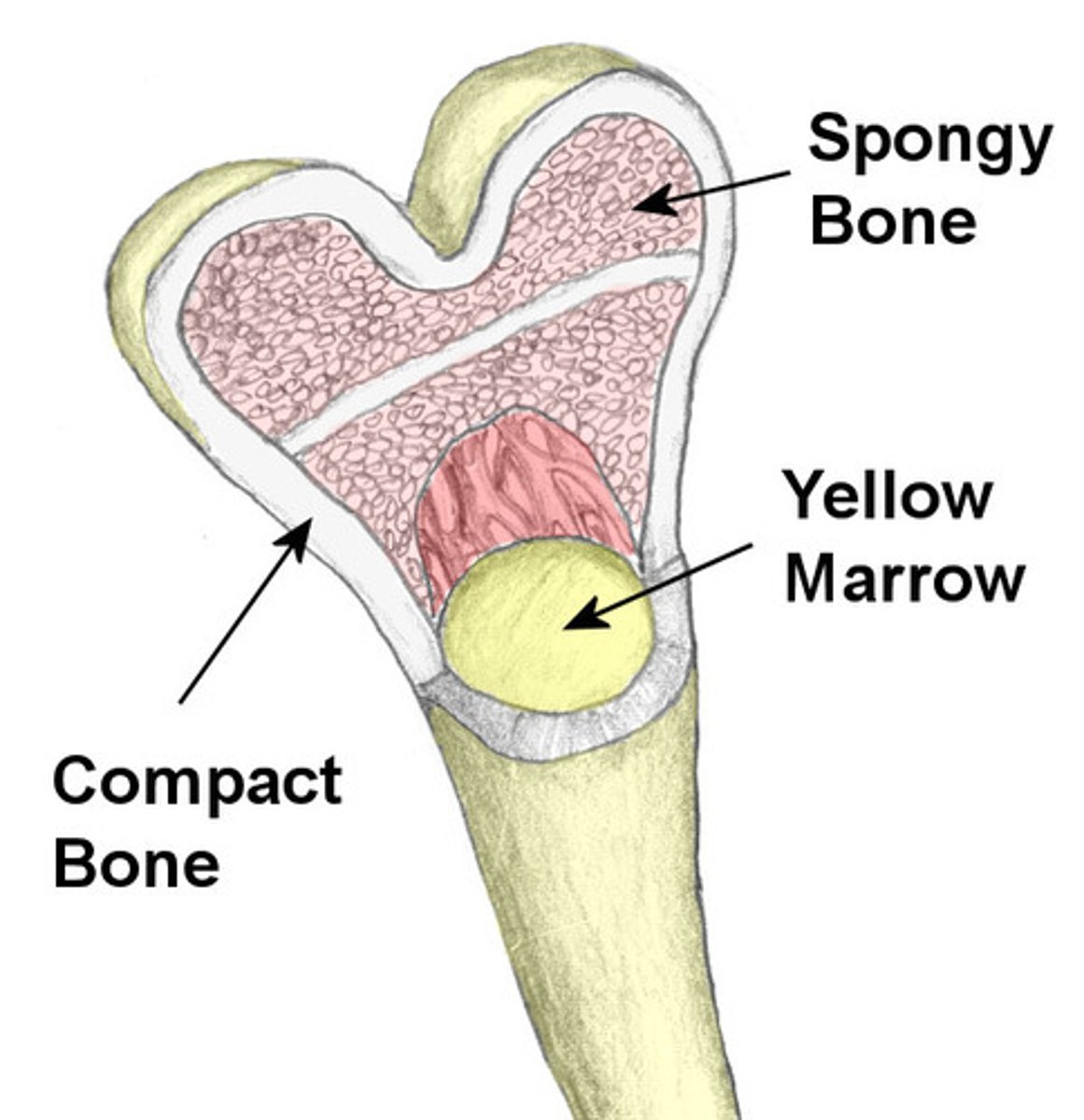
medullary cavity
the hollow part of bone that contains bone marrow
periosteum
a fibrous connective tissue covering that surrounds each skeletal element like a sleeve
serves as an attachment for tendons and muscles
perichondrium
dense irregular connective tissue membrane covering the cartilage
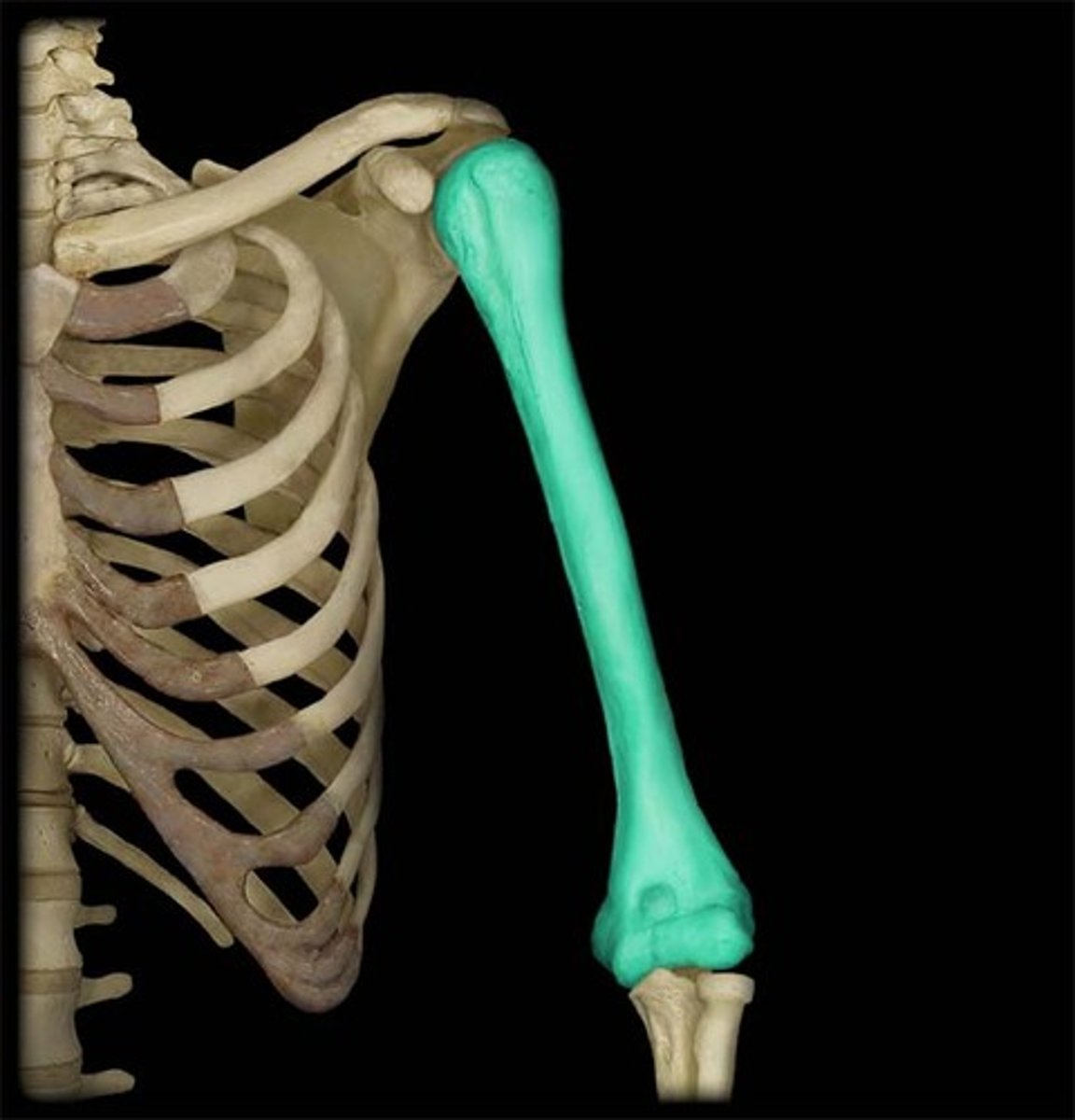
long bones
tubular
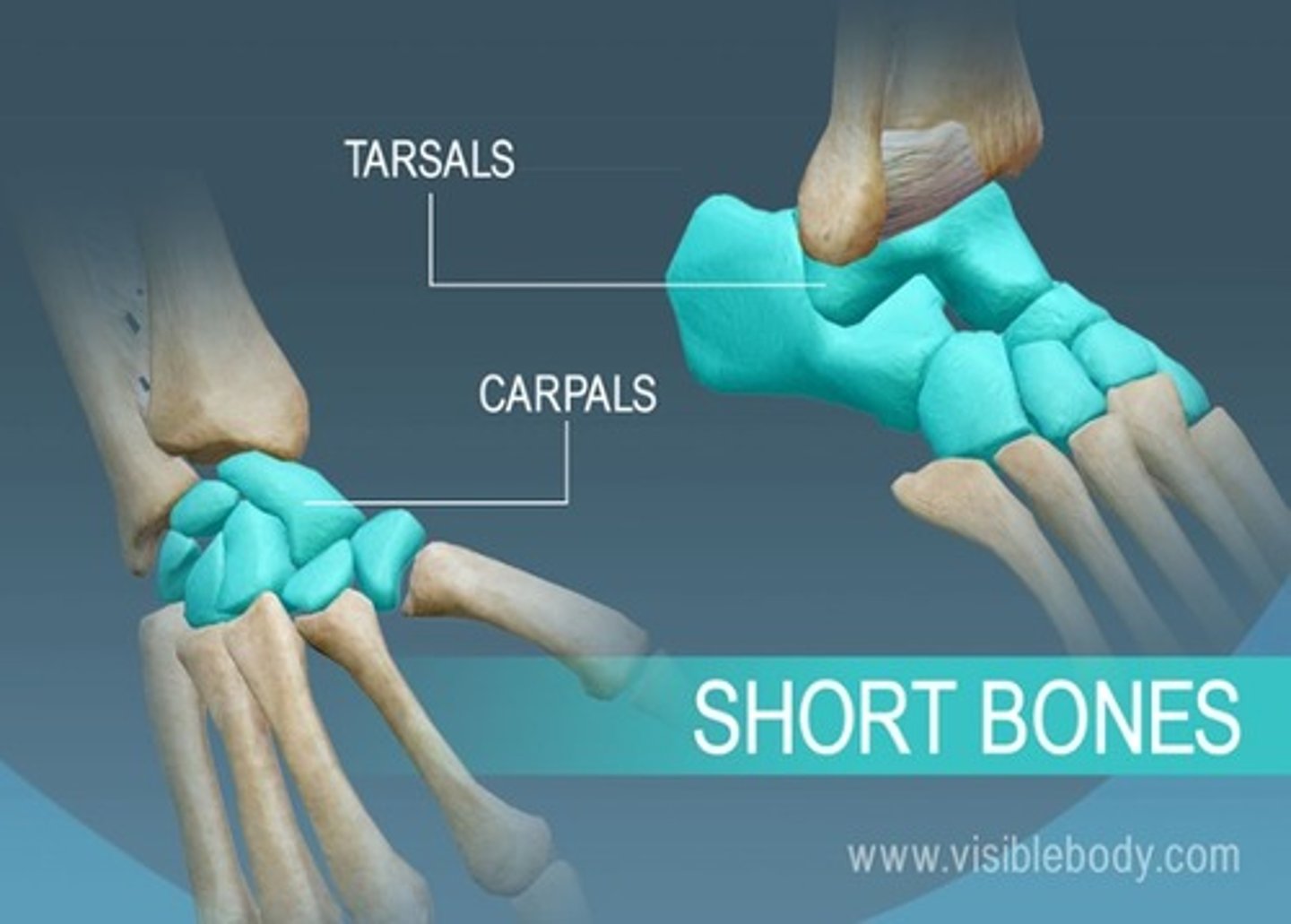
short bones
cuboidal
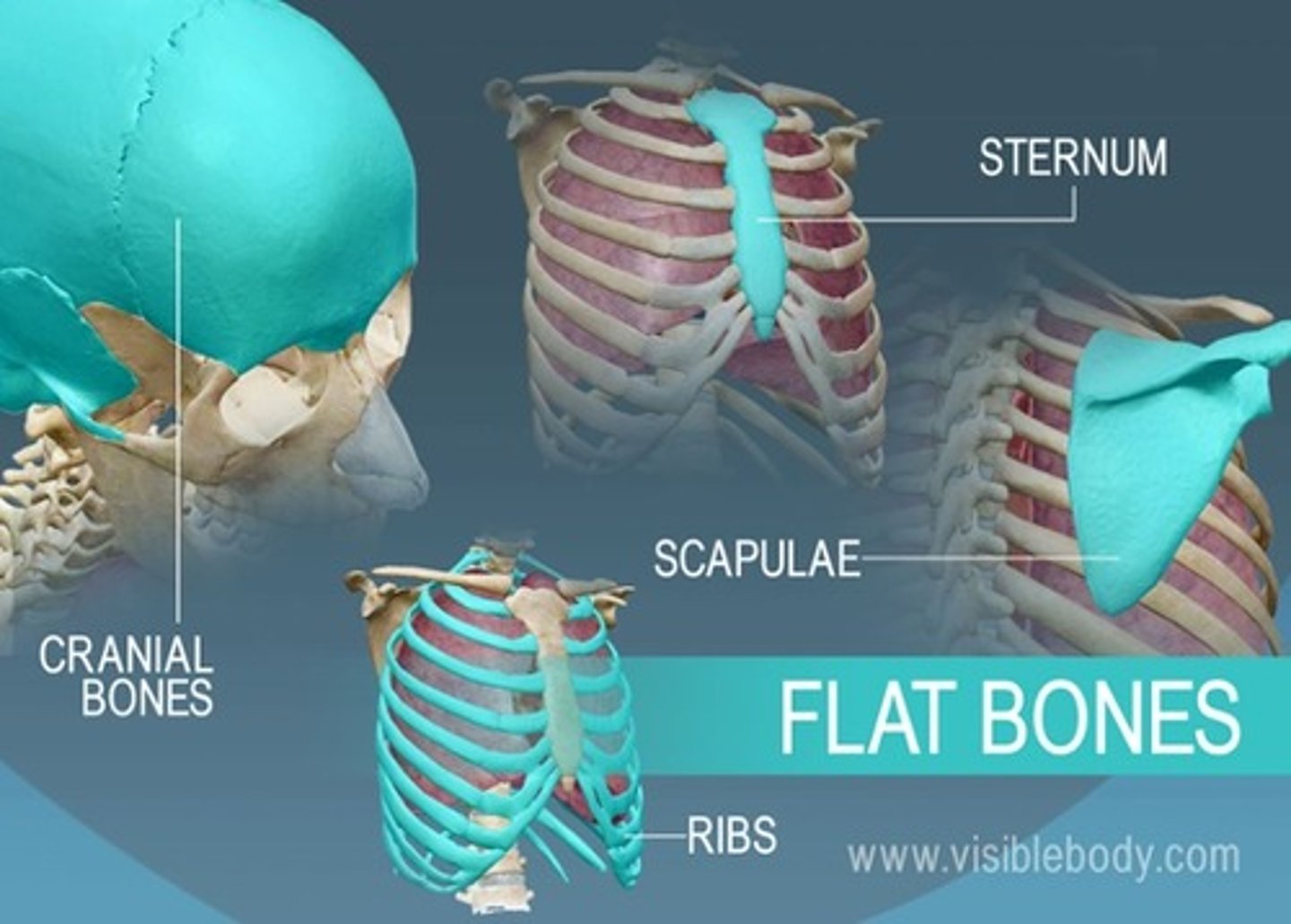
flat bones
serve protective functions
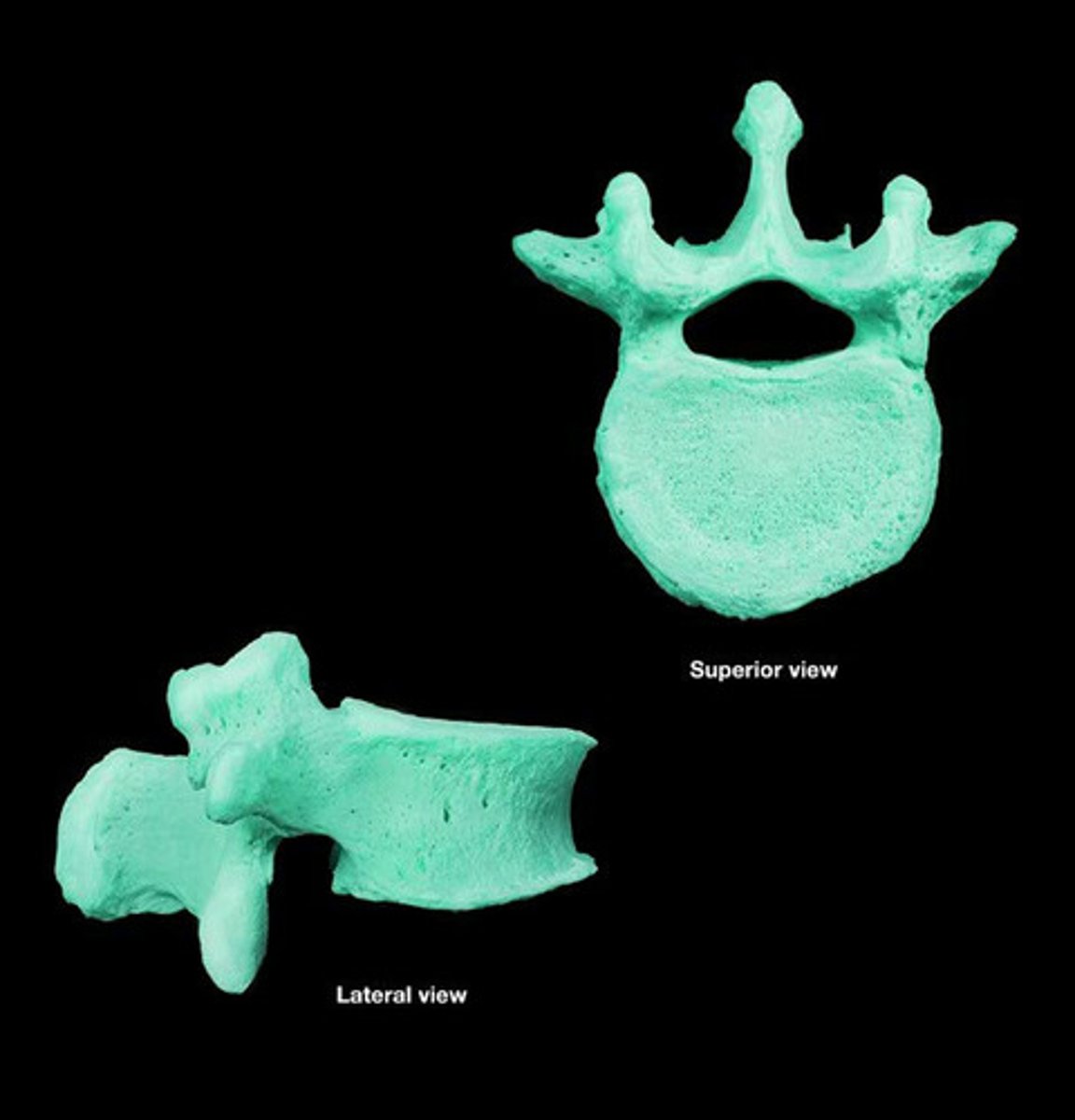
irregular bones
have various shapes
sesamoid bones
develop in certain tendons
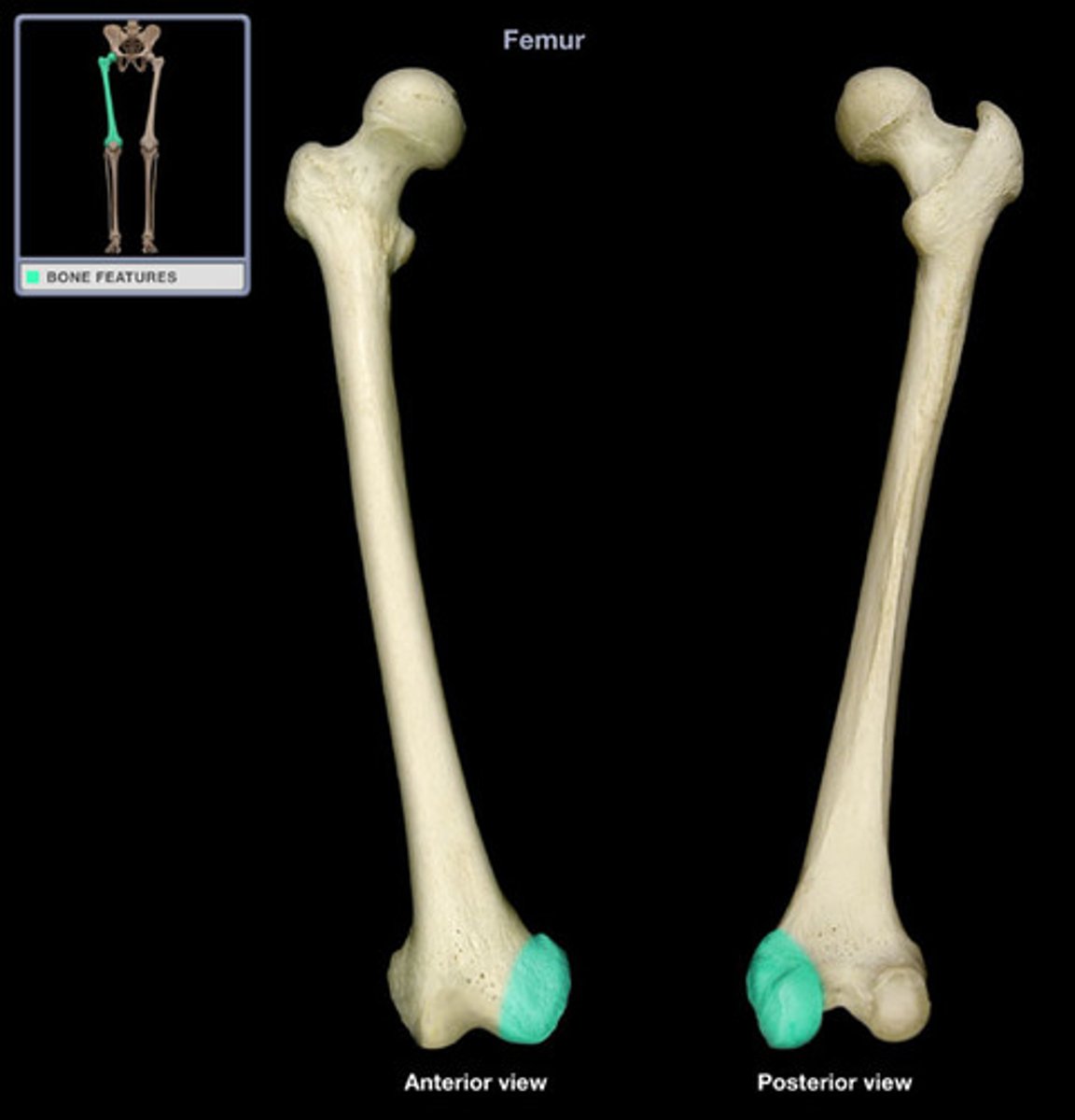
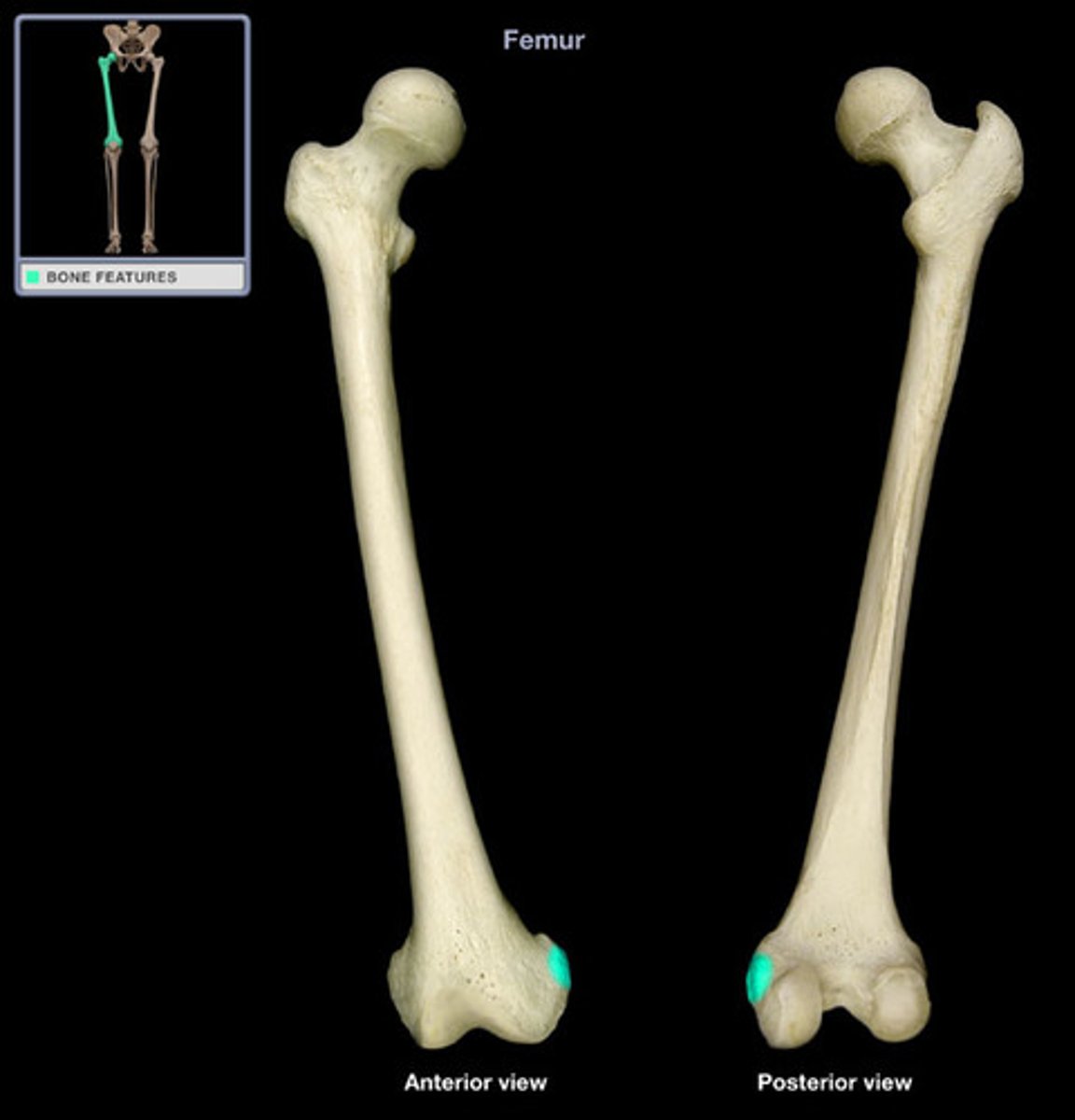
condyle
rounded, knuckle-like articular area, often occurring in pairs
crest
ridge of bone
epicondyle
eminence superior or adjacent to a condyle
facet
smooth flat area, usually covered with cartilage, where a bone articulates with another bone
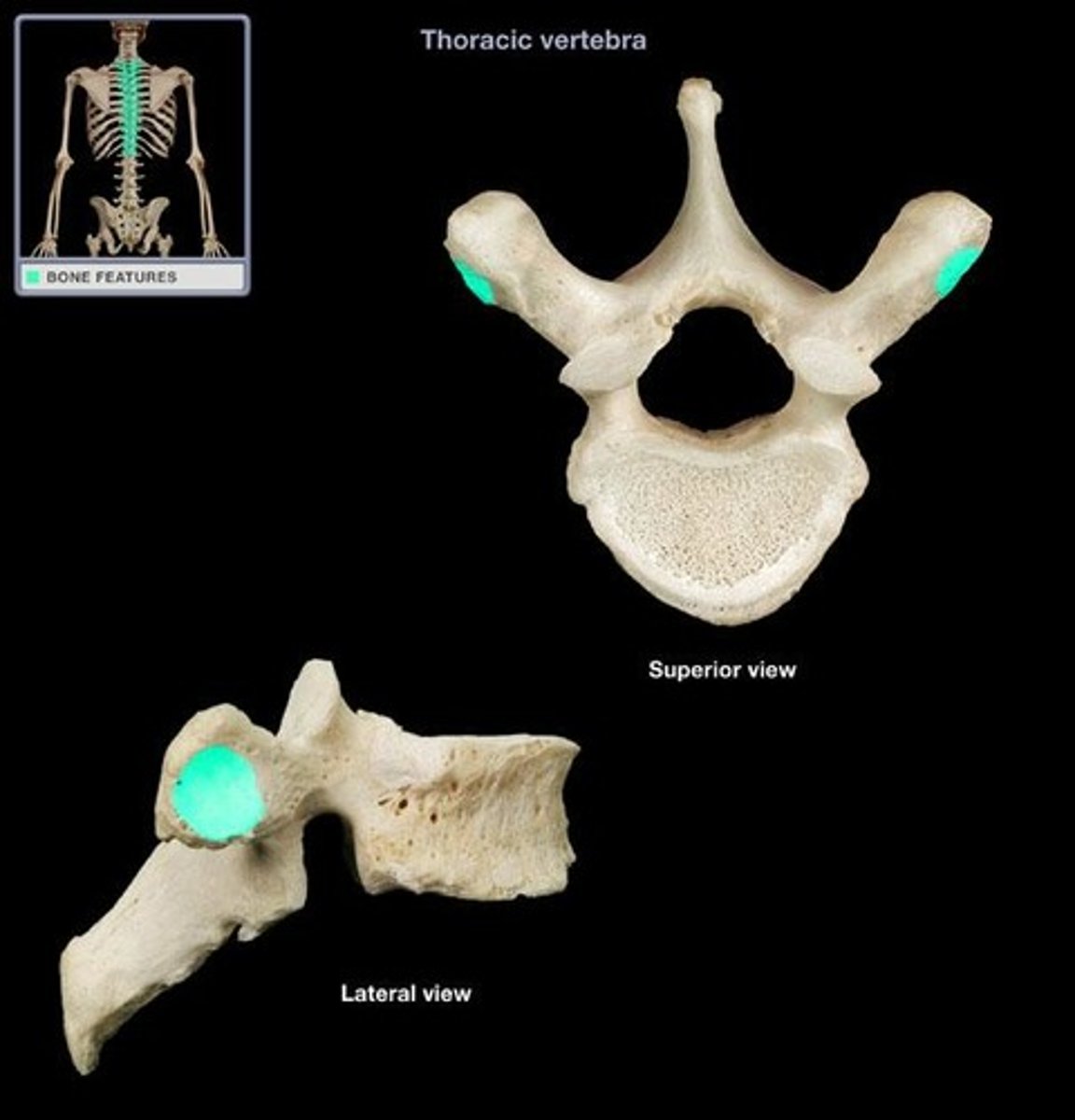
foramen
passage through a bone
fossa
hollow or depressed area
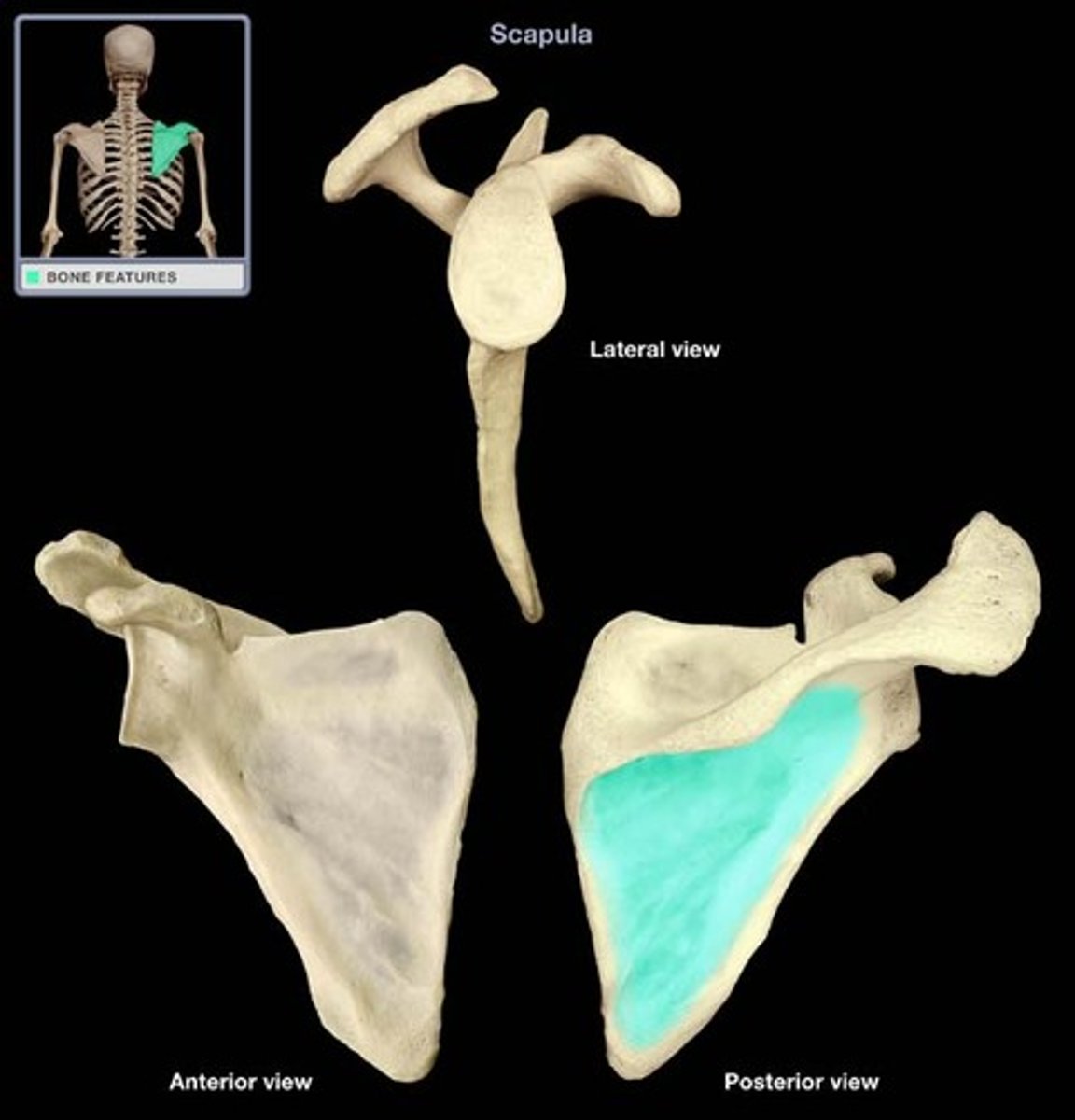
linea
linear elevation, sometimes called a ridge
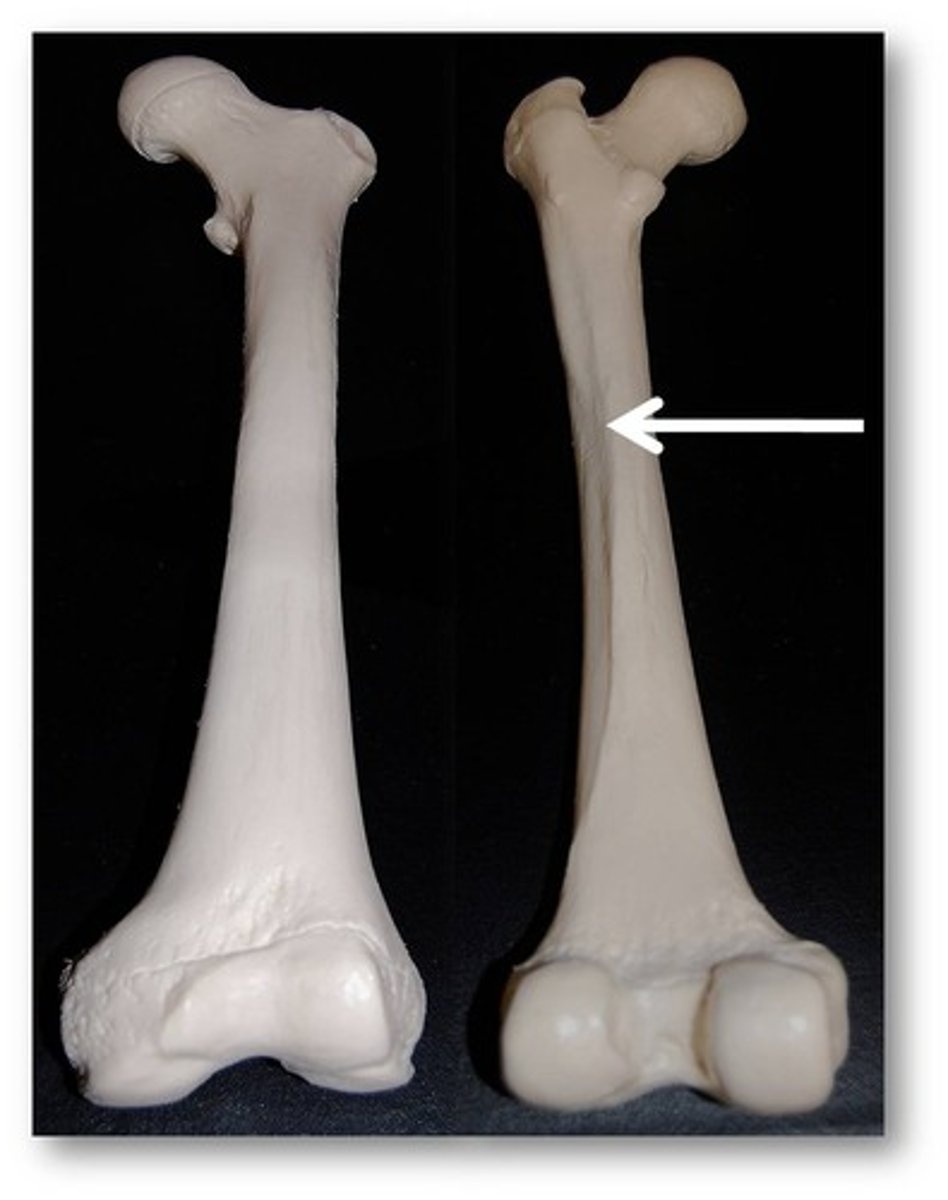
malleolus
rounded process
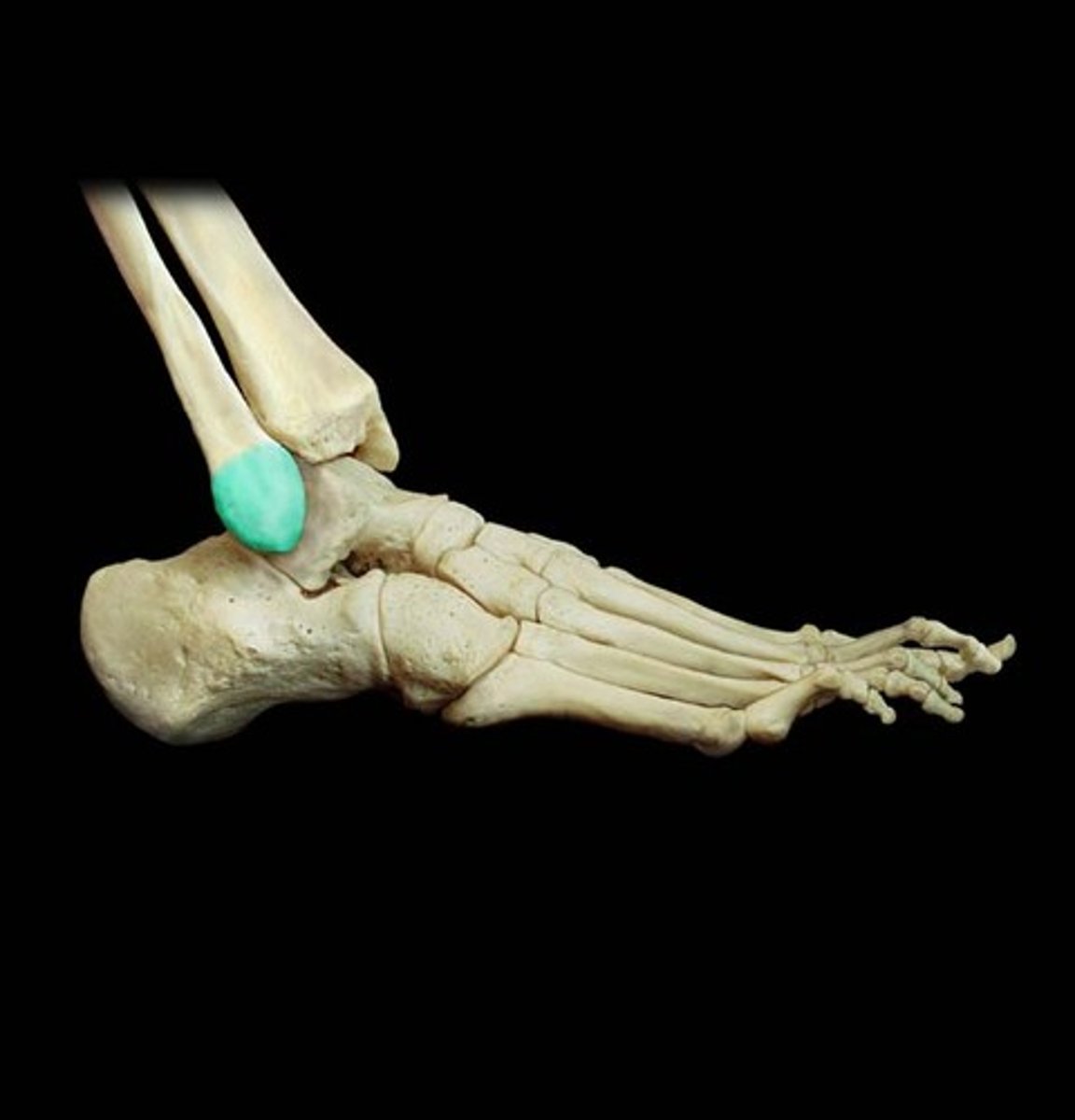
notch
indentation at the edge of a bone
process
an extension or projection serving a particular purpose having a characteristic shape, or extending in a particular direction
protuberance
a bulge or projection of the bone
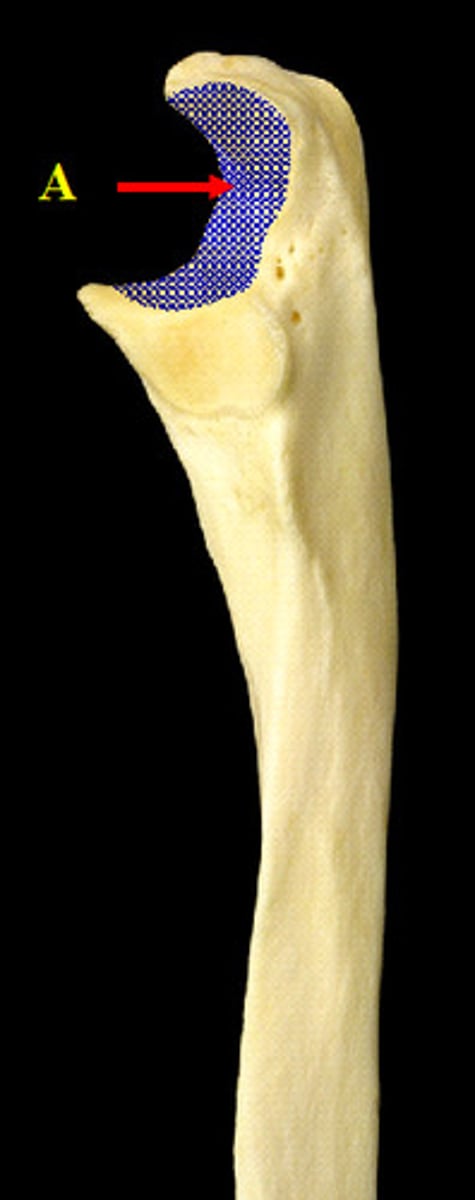
spine
thorn-like process
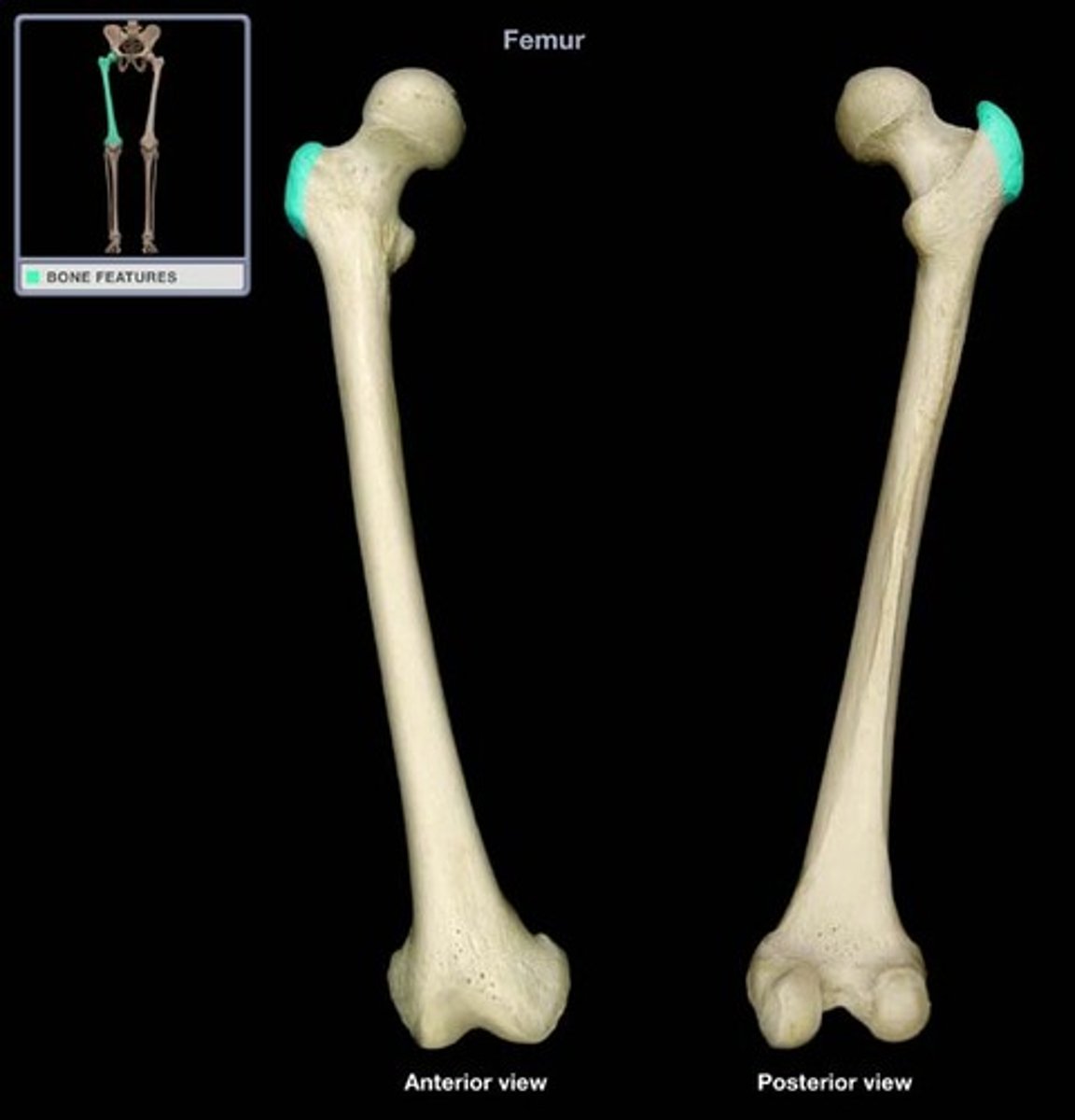
trochanter
large blunt elevation
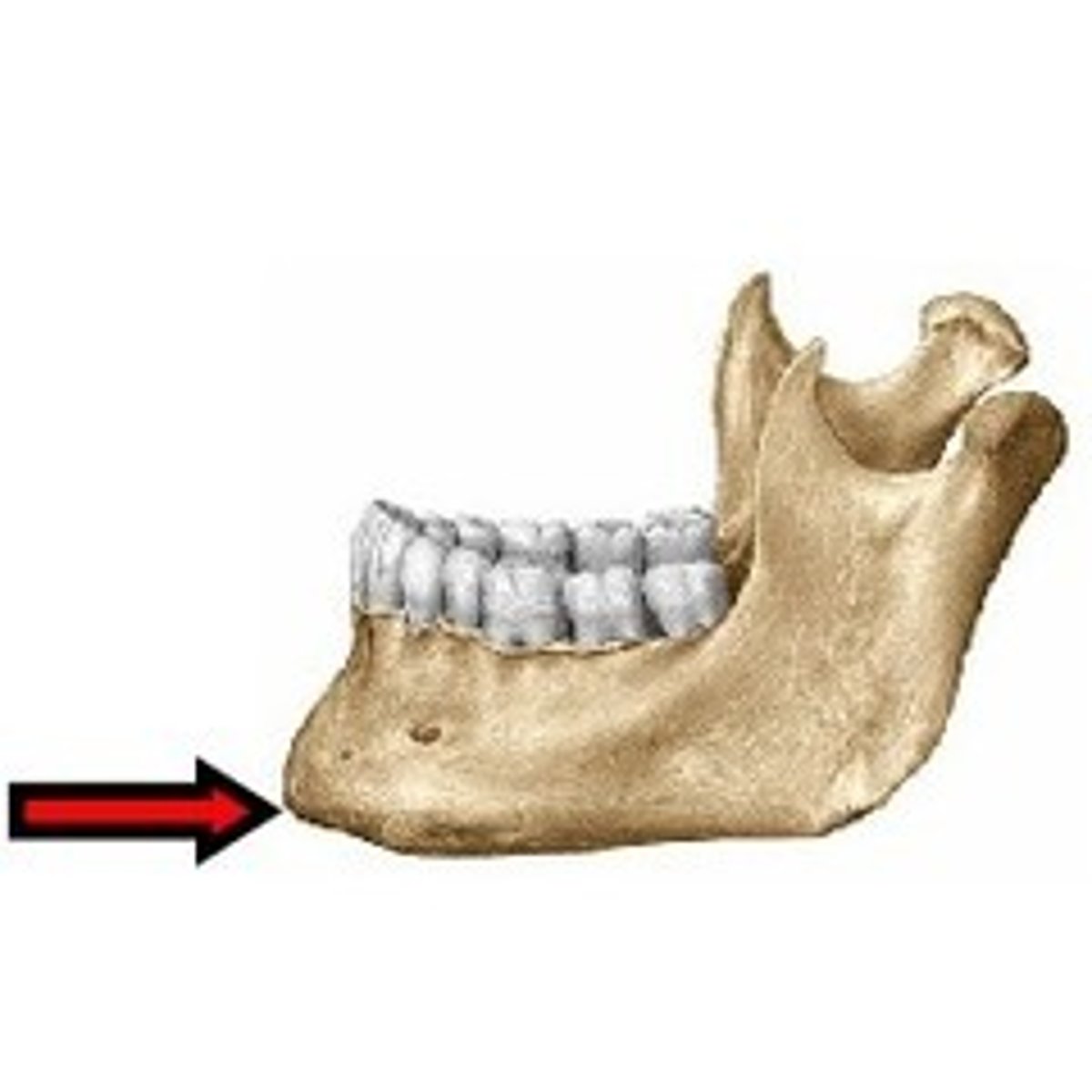
tubercle
small raised eminence
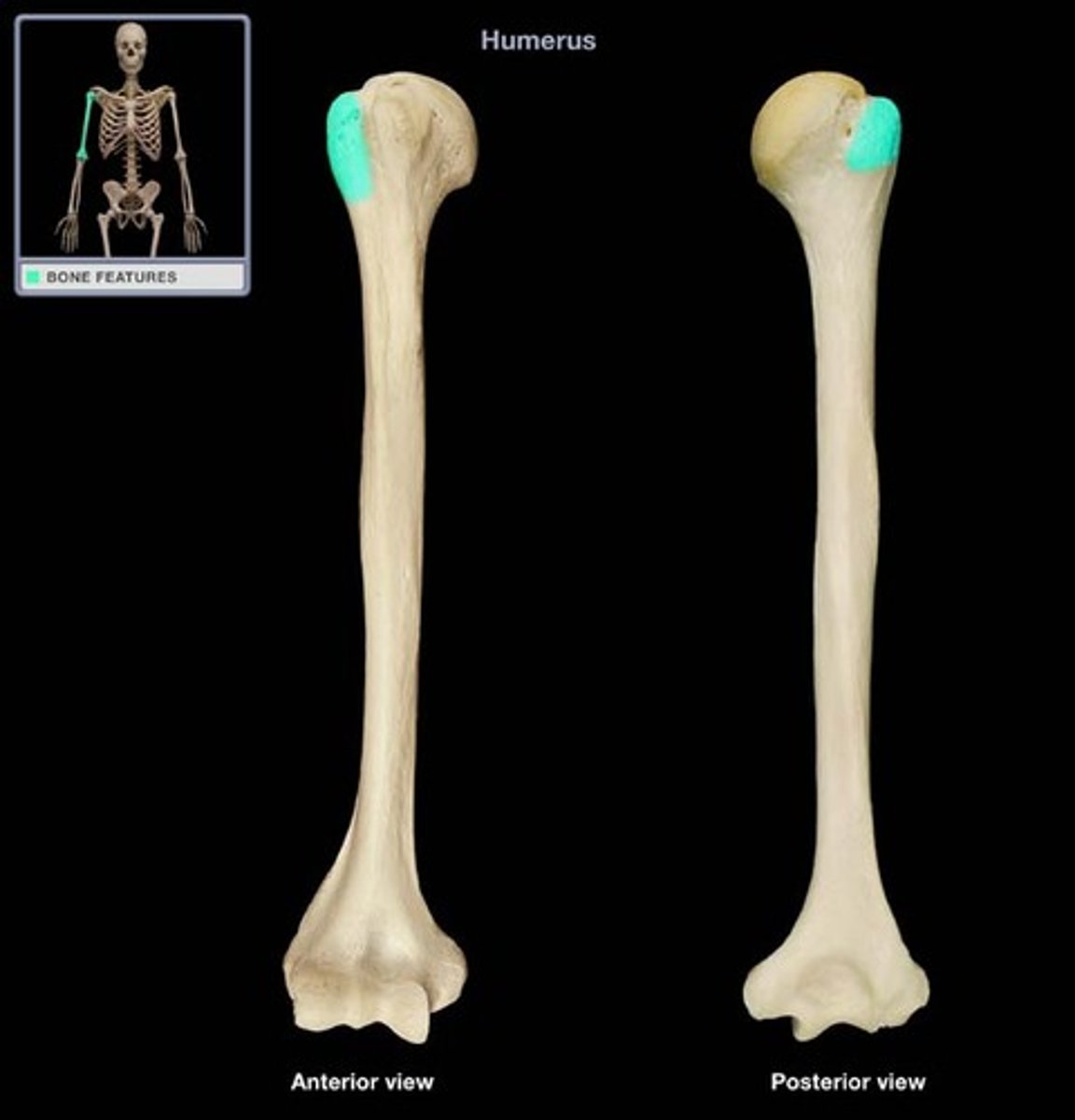
tuberosity
large rounded elevation
mesenchyme
Embryonic connective tissue from which all tissues develop
intermembranous ossification
mesenchymal models of bones form during the embryonic period, and direct ossification of the mesenchyme begins in the fetal period
enter chondral ossification
cartilage models of bones form from the mesenchyme during the fetal period and bone subsequently replaces most of the cartilage
primary ossification center
the first area of a bone to start ossifying
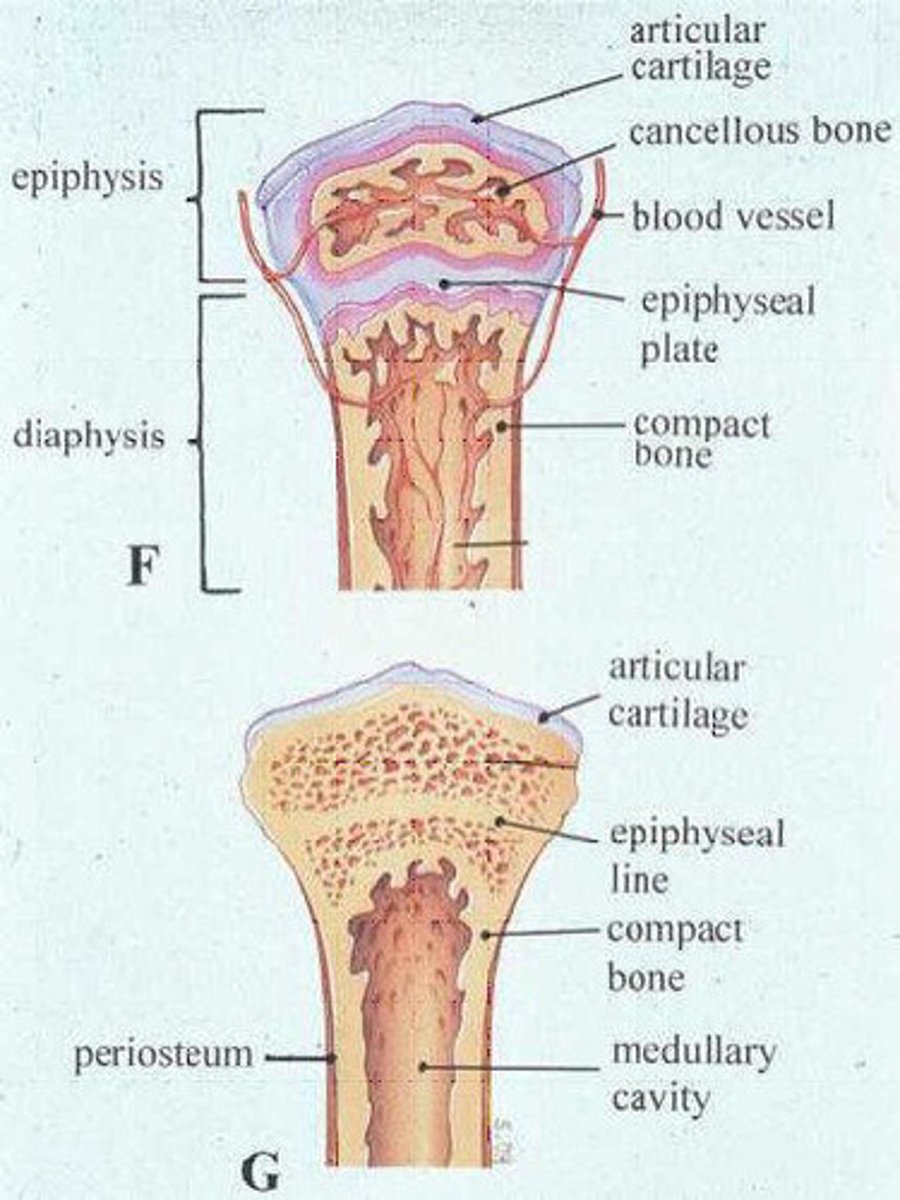
diaphysis
the shaft of a bone ossified from the ossification center
secondary ossification center
an area of ossification that appears after the primary (usually epiphyses)
epiphyses
the parts of the bone ossified from the secondary center of ossification (end of long bone)
epiphyseal plate
growth plates that intervene between the diaphysis and epiphyses
epiphyseal line
the seam formed during the fusion process (synostosis) is particularly dense and is recognizable in section bone of radiographs
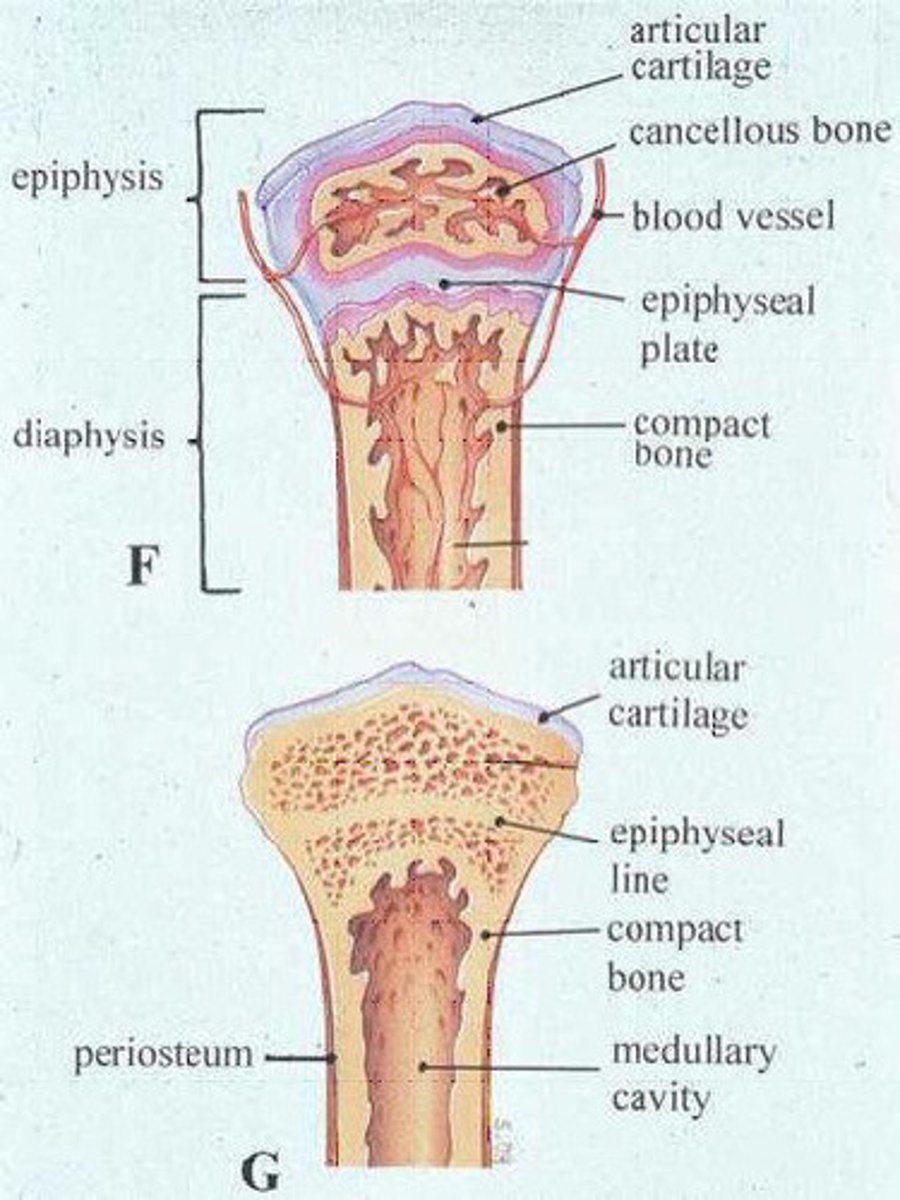
metaphysis
Flared part of the diaphysis nearest to the epiphysis
vasculature
arteries and veins
arteries
carry blood away from the heart
nutrient arteries arise as independent branches outside the periosteum
there is more than 1 per bone
many small branches of periosteal arteries of the periosteum
veins
accompany arteries through nutrient foramina
large veins leave through foramine near the articular ends of bones
periosteal nerves
periosteum is rich with sensory nerves that carry pain fibers
vasomotor nerves
cause constriction or dilation of blood vessels regulating blood flow through marrow
joints
fibrous, cartilaginous, synovial
fibrous
joints unified by fibrous tissue
movement depends on the length of fibers connecting the articulating bone
suture, gomphosis, syndesmosis
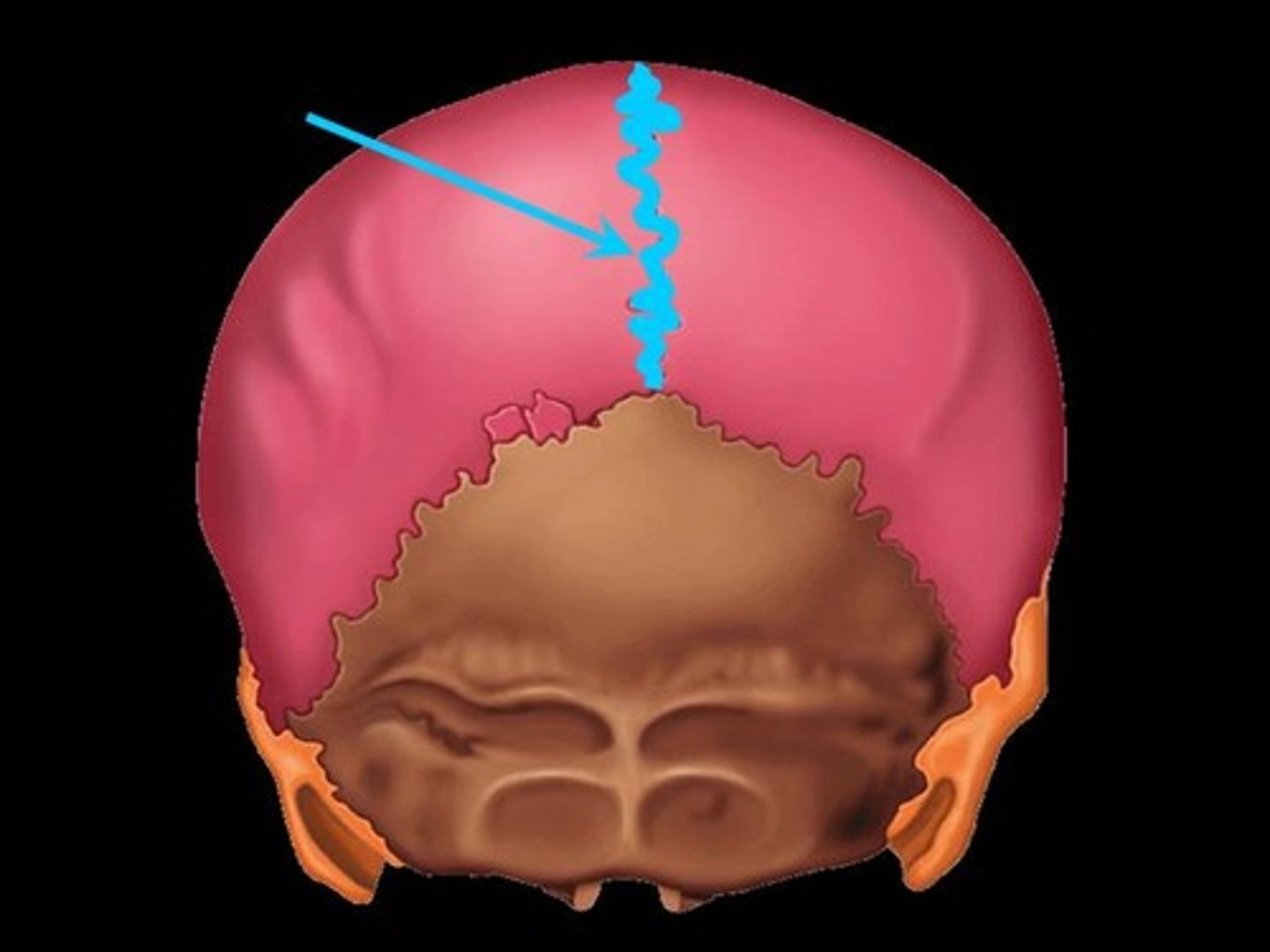
suture
fibrous joints of the cranium that hold bony plates together
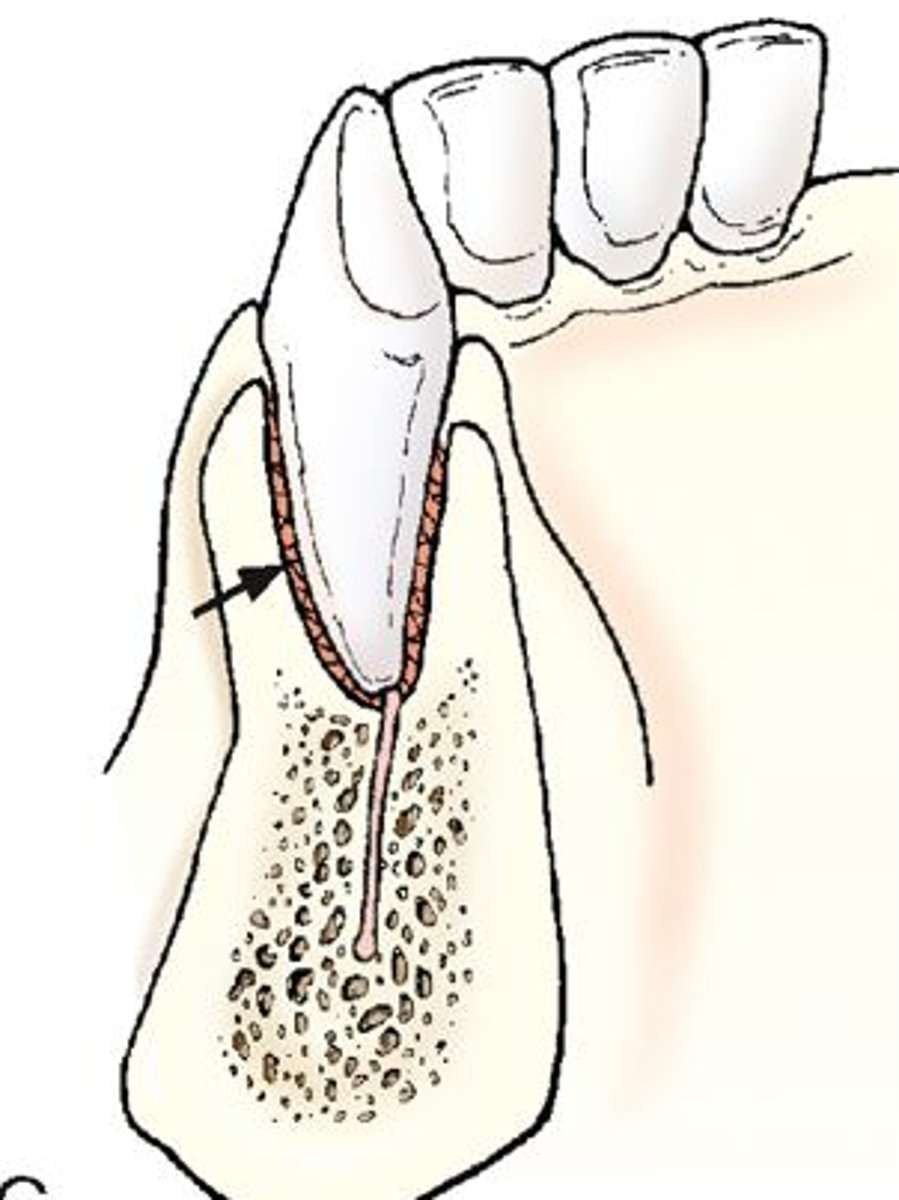
gomphosis
peg and socket type joint with little movement
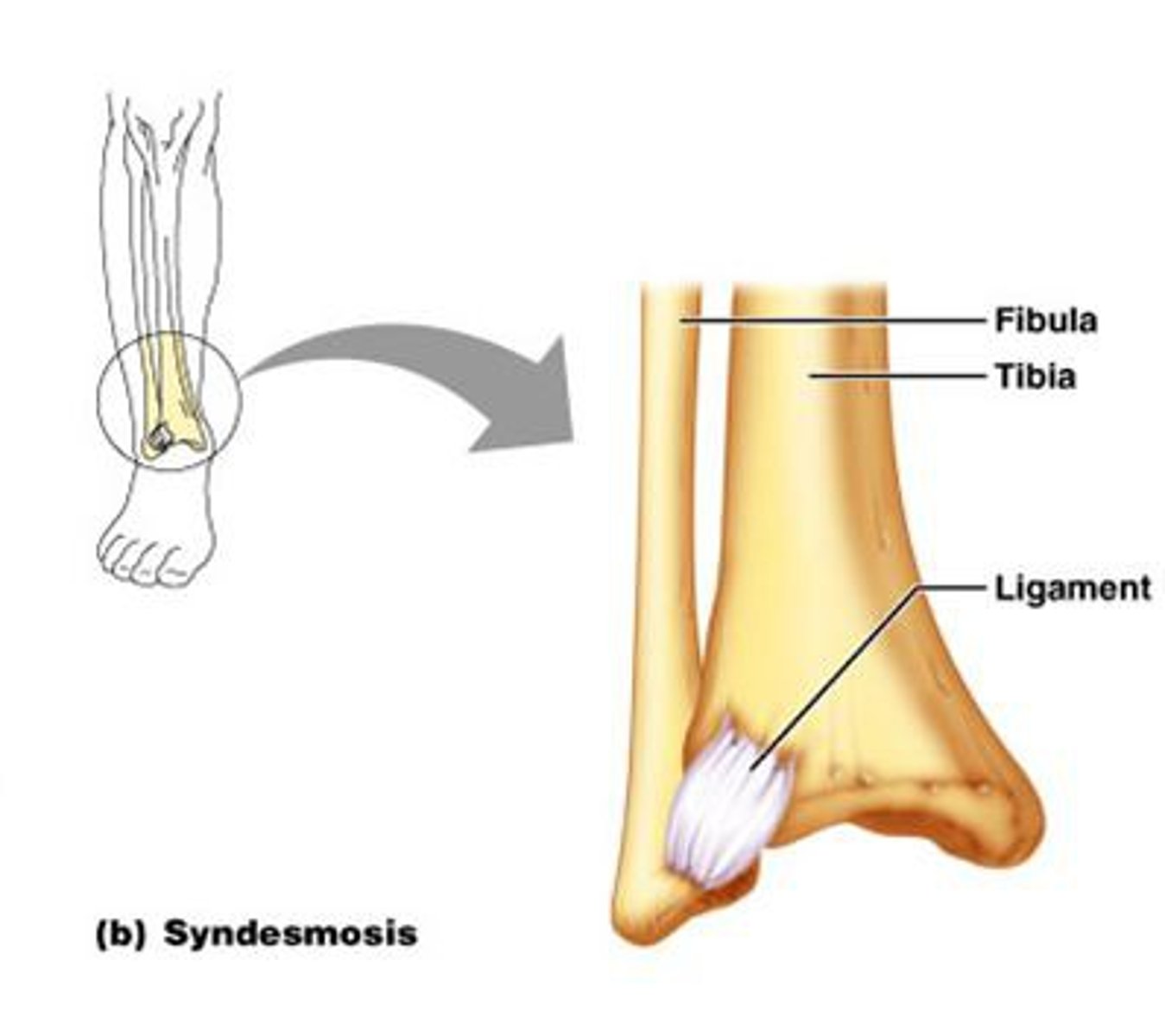
syndesmosis
unites the bones with a sheet of fibrous tissue, either a ligament or fibrous membrane
cartilaginous
united by hyaline cartilage or fibrocartilage
synchondroses
symphysis
synchondroses
primary cartilaginous
bones are united by hyaline cartilage, which permits slight bending in early life
symphysis
secondary cartilaginous
strong, slightly movable joints united by fibrocartilage
synovial
most common type of joint and provide free movement between the bones they join
usually reinforced by accessory ligaments that are either extrinsic or are a thickening of a joint capsule