Urinalysis: Types, Collection, and Interpretation for Clinical Practice
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
What is the purpose of urine microscopy?
To examine urine for cells, crystals, bacteria, and other components that may indicate disease.
Do stones form in alkaline or acidic?
alkaline
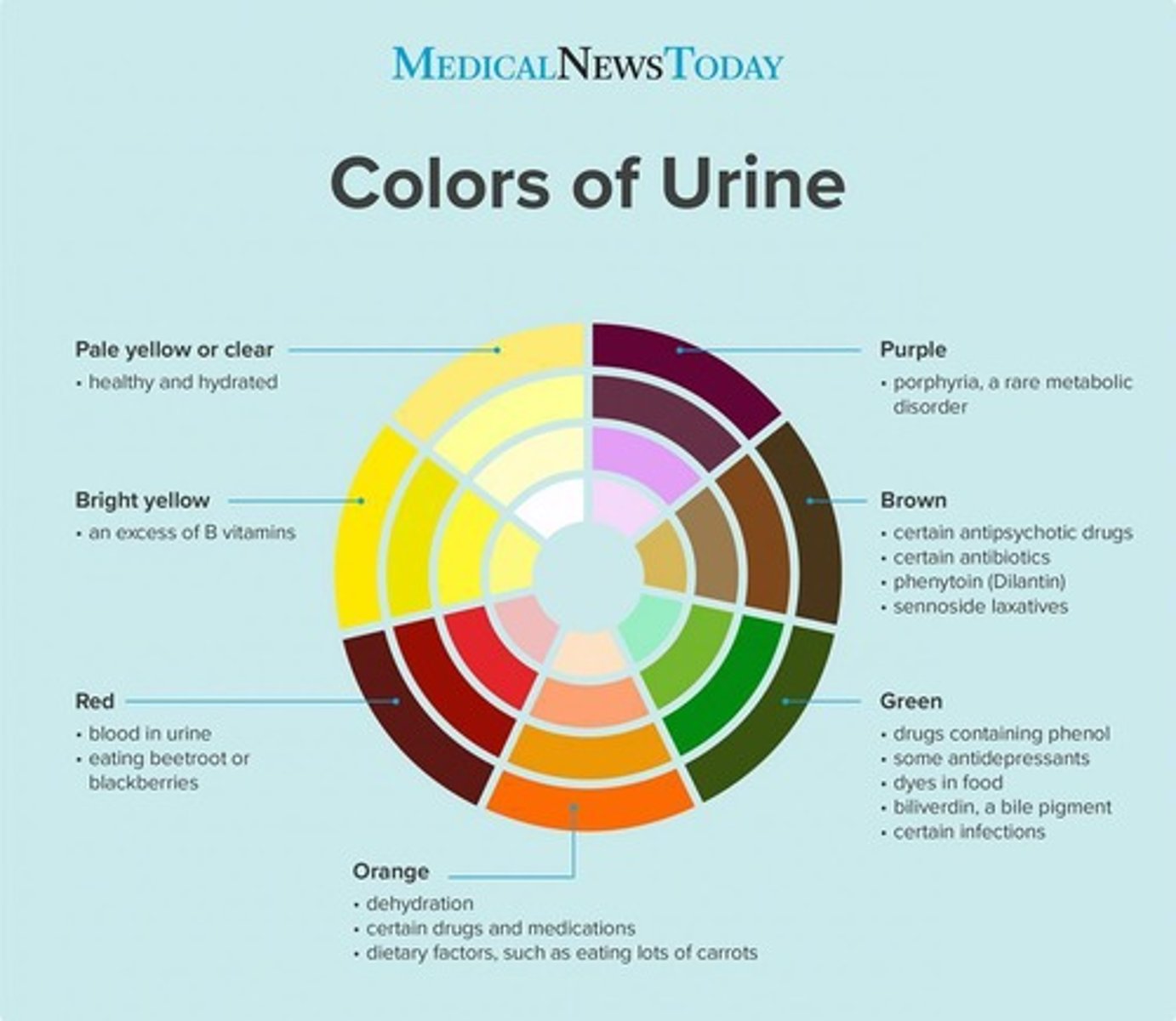
What are some abnormal findings on a urinalysis?
Cloudy appearance, dark yellow color, presence of protein, glucose, or blood.
What components are typically tested in a urine dipstick?
pH, protein, glucose, specific gravity, leukocyte esterase, nitrites, ketones, bilirubin, and hemoglobin/blood.
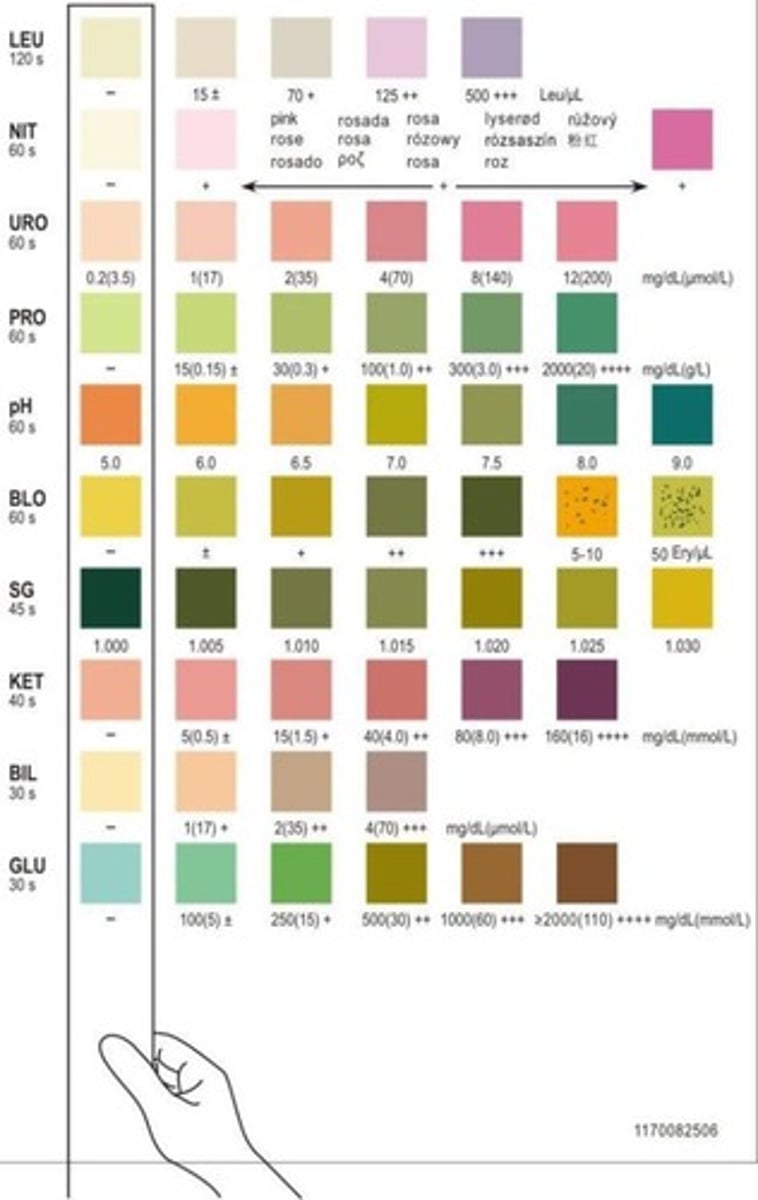
What is the normal pH range for urine?
Normal urine pH is between 4.6 and 8.0. average is 6.0
What factors can affect urine pH?
Diet, hydration status, and certain medications can influence urine pH.
What causes elevated urine pH (alkaline urine)?
Bacterial infections, a diet rich in citrus, or alkalemia can cause elevated pH.
What causes decreased urine pH (acidic urine)?
Starvation, dehydration, a meat-rich diet, or metabolic/respiratory acidosis can lead to decreased pH.
What conditions can cause proteinuria?
Kidney disease, diabetes mellitus complications, and pre-eclampsia in pregnancy.
What causes glucosuria?
blood glucose is >180 mg/dL.
What is the normal range for urine specific gravity?
1.010 - 1.025
What does increased specific gravity indicate?
More concentrated urine, often due to dehydration.
What does decreased specific gravity indicate?
More dilute urine, which can be caused by overhydration or renal disease.
What is the normal result for nitrites in urine?
None/negative; a positive result indicates a urinary tract infection.
What does a positive leukocyte esterase test indicate?
The presence of leukocytes in urine, suggesting a urinary tract infection, especially if nitrites are also positive.
What are ketones and when are they present in urine?
Byproducts of fat metabolism present when glucose is unavailable, often seen in uncontrolled diabetes.
What is the normal level of bilirubin in urine?
None/negative; bilirubin is a waste product from hemoglobin degradation.
How is bilirubin excreted from the body?
Primarily through the stool, but conjugated bilirubin can also be excreted by the kidneys.
What is the solubility of unconjugated bilirubin?
Unconjugated bilirubin is NOT water soluble.
What happens when there is an inability to dispose of conjugated bilirubin?
Blood levels increase, leading to bilirubinemia that spills into the urine.
What does a positive bilirubin test in urine indicate?
It may indicate obstructive biliary disease due to conditions like gallstones or tumors.
What is the normal finding for hemoglobin in urine?
Normal: none/negative; blood cells and hemoglobin should not be excreted.
What could cause blood or hemoglobin to be present in urine?
Possible causes include urinary tract infection, kidney inflammation, kidney stones, or bladder cancer.
What is considered normal for red blood cells in urine microscopy?
Normal: <2 RBC per high powered field (hpf).
What indicates microscopic hematuria?
Microscopic hematuria is defined as >2 RBC/hpf without visible changes to urine color.
What indicates gross hematuria?
Gross hematuria involves a significant number of RBCs resulting in visible color changes in urine.
What could the presence of RBCs in urine indicate?
It may indicate contamination, urinary tract infection, kidney stones, or bladder cancer.
What is the normal range for white blood cells in urine microscopy?
Normal: <4 WBC per high powered field (hpf).
What does >4 WBC/hpf indicate?
It is indicative of bacteriuria.
What is the normal finding for epithelial cells in urine microscopy?
Normal: <5 epithelial cells/hpf.
What does >5 squamous epithelial cells in urine indicate?
It indicates contamination of the specimen.
What are casts in urine microscopy?
Casts are formed when cells clump together in renal tubules and are flushed out into the urine.
What are hyaline casts indicative of?
Hyaline casts are generally nonspecific and can be seen in renal disease or may be normal after exercise.
What do granular casts indicate?
Granular casts are indicative of renal disease but may also be normal after exercise.
What are muddy brown casts associated with?
Muddy brown casts are associated with acute tubular necrosis, a common acute kidney injury.
What are waxy casts indicative of?
Waxy casts indicate degeneration of granular casts and are seen more often in chronic kidney disease.
What do fatty casts indicate?
Fatty casts are associated with glomerular diseases and nephrotic syndrome.
What are renal tubule cell casts associated with?
They are associated with renal tubular disease such as acute tubular nephritis and proliferative glomerulonephritis.
What are white blood cell casts associated with?
Infection in the kidney, such as pyelonephritis or interstitial nephritis.
What condition are red blood cell casts classically associated with?
Glomerulonephritis.
What are the types of crystals that may be seen on microscopy?
Calcium, Magnesium (struvite), Uric Acid, and Cysteine.
What shape are calcium oxalate crystals, and what is their significance?
Envelope or dumbbell shaped; they are the most common cause of kidney stones.
What shape do calcium phosphate crystals take, and in what urine condition do they form?
Rosette shaped; they form more readily in alkaline urine.
What are magnesium crystals associated with?
Struvite kidney stones, seen with increased ammonia levels and increased pH due to urea-splitting bacteria.
What are the microbes that magnesium crystals are associated with?
Proteus mirabilis and Kelebsiella pneumoniae
What is the characteristic appearance of struvite stones on microscopy?
Coffin lid appearance; they can form staghorn calculi.
What is uric acid a byproduct of, and what shape do uric acid crystals have?
Nucleic acid breakdown; the crystals are ovoid or rhomboid in shape.
What condition causes hexagonal cysteine crystals?
Cystinuria, a genetic disorder that results in kidney stones.
What is the purpose of a urine culture and sensitivity test?
To isolate and grow bacteria in patients with urinary tract infection symptoms.
What indicates a positive urine culture?
Presence of more than 100,000 colony-forming units (CFU).
What does the Minimum Inhibitory Concentration (MIC) measure?
The lowest concentration of antibiotic that prevents visible growth of bacteria.