energy resources and transfers
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Last updated 4:12 PM on 9/25/25
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
73 Terms
1
New cards
1- kinetic
2- thermal
3- chemical
4- GPE
5- elastic potential
6- electrostatic
7- magnetic
8- nuclear
2- thermal
3- chemical
4- GPE
5- elastic potential
6- electrostatic
7- magnetic
8- nuclear
what are the eight types of energy stores?
2
New cards
anything moving has energy in its kinetic energy store
what happens in kinetic?
3
New cards
any object- the hotter the more energy it has in it's store
what happens in thermal?
4
New cards
anything that can release energy by a chemical reaction e.g food and fuels
what happens in chemical?
5
New cards
anything that is in a gradational field (anything that can fall)
what happens in GPE?
6
New cards
anything stitched like springs and rubber bands
what happens in elastic potential?
7
New cards
two charges that attract or repel
what happens in electrostatic?
8
New cards
two magnets that attract or repel
what happens in magnetic?
9
New cards
atomic nuclei releases energy from this store in nuclear reactions
what happens in nuclear?
10
New cards
1- mechanically
2- electrically
3- by heating
4- by radiation
2- electrically
3- by heating
4- by radiation
what are the four main ways that energy can be transferred between?
11
New cards
an object moving due to a force acting on it e.g push or pull
what happens in mechanically?
12
New cards
a charge moving through a potential difference e.g charges moving through a circuit
what happens in electrically?
13
New cards
energy transferred from a hotter object to a cooler object
what happens in heating?
14
New cards
energy transferred by light/sound waves
what happens in radiation?
15
New cards
energy cannot be created or destroyed but it can be transferred from one store to another
what is the principle of conservation of energy?
16
New cards

what is efficiency defined as?
17
New cards
radiation, conduction and convection
what are the 3 ways energy can be transferred by heating?
18
New cards
the transfer of energy by heating by infrared electromagnetic waves
what is thermal radiation?
19
New cards
the main form of energy transfer by heating in solids
what is conduction?
20
New cards
the main form of energy transfer by heating in liquids and gases
what is convection?
21
New cards
emission of electromagnetic waves
what does thermal radiation involve?
22
New cards
infrared radiation, consists of electromagnetic waves of different frequencies .
what can thermal radiation also be called as?
23
New cards
emit and absorb infrared radiation
what do all objects continually do?
24
New cards
it emits more radiations that it abosrbs as it cools down
if an object is hotter than its surrounding what happens?
25
New cards
it absorbs more radiation that it emits as it warms up
if an object is cooler than its surrounding what happens?
26
New cards
the particles are held tightly together. when one particle vibrates, it collides with other particles nearby.
is a solid is heated what happens?
27
New cards
the process where vibrating particles transfer energy from their kinetic energy store to the kinetic energy stores of neighbouring particles.
definition of thermal conduction?
28
New cards
convection occurs when the more energetic particles move from the hotter region to the cooler region and transfer energy only in liquids and gases.
definition of convection?
29
New cards

what happens in an immersion heater?
30
New cards
in roundish or squarish containers because they allow the convection current to work best.
where is convection most efficient?
31
New cards
coloured crystals:
1- place some purple potassium permanganate crystals in a beaker of cold water. put the crystal to one side of the beaker.
\
2- use a bunsen burner and gently heat the side of the beaker with the crystals at the bottom.
\
3- as the temperature of the water increases the crystals with dissolve forming a bright purple solution.
\
4- it will then be carried by convection.
1- place some purple potassium permanganate crystals in a beaker of cold water. put the crystal to one side of the beaker.
\
2- use a bunsen burner and gently heat the side of the beaker with the crystals at the bottom.
\
3- as the temperature of the water increases the crystals with dissolve forming a bright purple solution.
\
4- it will then be carried by convection.
what is a practical that you can see convection currents?
32
New cards
how well it can transfer energy by conduction.
what does the thermal conductivity of an object describe?
33
New cards
use materials with low thermal conductivity
if you want to reduce energy transfers by conduction what should you do?
34
New cards
stop the fluid from moving and prevent convection currents forming
if you want to reduce energy transfers by convection what should you do?
35
New cards
object should be desgined with a surface that is a poor emitter
\
clothes, blankets and foam cavity wall insulation all work by trapping pockets of air.
air cannot move so energy conducts slowly and material which has low thermal conductivity.
\
clothes, blankets and foam cavity wall insulation all work by trapping pockets of air.
air cannot move so energy conducts slowly and material which has low thermal conductivity.
if you want to reduce energy transfers by insulation what should you do?
36
New cards
black is better than white
dull is better than shiny
dull is better than shiny
what colours absorb and emit IR radiation better than others?
37
New cards
energy transferred
what does work done mean?
38
New cards
when a force moves an object through a distance, work is done on the object and energy is transferred.
definition of work done
39
New cards
you are doing work against frictional forces. energy is being transferred to the kinetic energy store because the object starts moving, and some is being transferred to the thermal energy store due to friction. temp will increase. ( e.g rubbing your hands together will warm them up).
what happens when you push something along a rough surface?
40
New cards
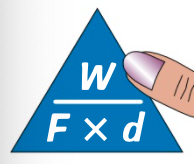
formula for work done
41
New cards
power is a measure of how quickly work is being done
power is the rate at which energy is transferredpow
power is the rate at which energy is transferredpow
definition of power
42
New cards

\
power formula
43
New cards

kinetic energy formula
44
New cards

GPE formula
45
New cards
non renewable
what type of energy resource will run out one day?
46
New cards
non renewable
what type of energy resource will do damage to our planet?
47
New cards
non renewable
what type of energy resource provides most of our energy?
48
New cards
1- coal
2- natural gas
3- oil
4- nuclear fuels
2- natural gas
3- oil
4- nuclear fuels
what are example of non renewable resources?
49
New cards
steam
what do most power stations use to drive a turbine?
50
New cards
from the 4 non renewable resources In big power station.
where is our electricity generated?
51
New cards
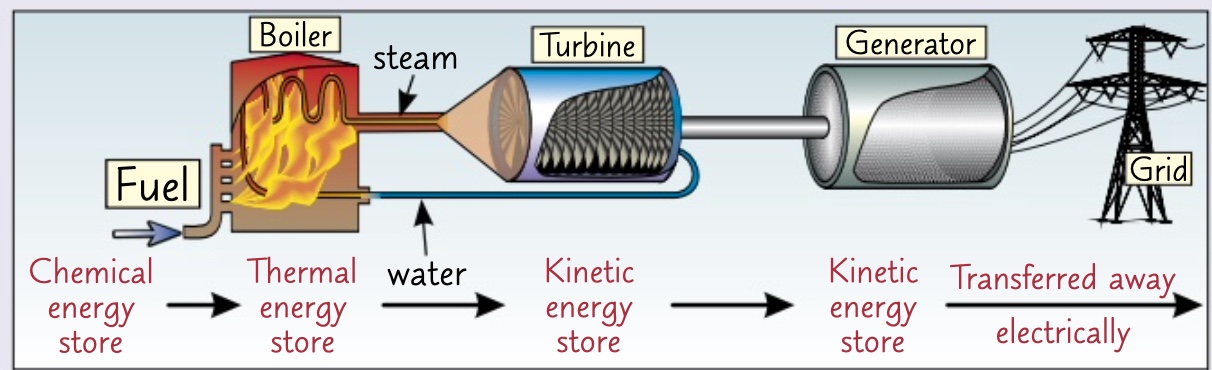
1- as the fossil fuel burns in oxygen the energy in it’s chemical energy store is transferred to the thermal energy store of the water by heating.
2- water boils to form steam. the steam turns the turbine transferring energy mechanically the kinetic energy store of the turbine.
3- as the turbine rotates also the generator which produces an electric current. It transfers the energy electrically away from power station to natural grids to homes.
2- water boils to form steam. the steam turns the turbine transferring energy mechanically the kinetic energy store of the turbine.
3- as the turbine rotates also the generator which produces an electric current. It transfers the energy electrically away from power station to natural grids to homes.
how does a power station work?
52
New cards
1- burning them releases lots of energy quite cheap
2- energy from fossil fuels don’t rely on weather - RELIABLE ENERGY SOURCE
3- lots of power stations for fossil fuels dont need to spend more money or new technology to use them
\
2- energy from fossil fuels don’t rely on weather - RELIABLE ENERGY SOURCE
3- lots of power stations for fossil fuels dont need to spend more money or new technology to use them
\
what are the advantages of fossil fuels?
53
New cards
1- fossil fuels release carbon dioxide into atmosphere when burned. contributes to global warming and climate change.
2- burning COAL & IRON releases sulfur dioxide, causes acid rain. acid rain damages trees and soils, huge impact on wildlife.
3- they will eventually run out
2- burning COAL & IRON releases sulfur dioxide, causes acid rain. acid rain damages trees and soils, huge impact on wildlife.
3- they will eventually run out
what are the disadvantages of fossil fuels?
54
New cards
use energy from the kinetic energy store of moving air to generate electricity. the wind turns the blades, which turns a generator inside of it.
how do wind turbines work?
55
New cards
* quite cheap to run
* very tough and reliable
* renewable will never run out
* doesn’t produce any polluting waste
* very tough and reliable
* renewable will never run out
* doesn’t produce any polluting waste
what are the advantages of wind turbines?
56
New cards
* they spoil the view. many of them need.
* - very noisy can disturb people
* expensive to set up especially out at sea
* - very noisy can disturb people
* expensive to set up especially out at sea
what are the disadvantages of wind turbines?
57
New cards
heat from underground
what is geothermal power?
58
New cards
* only possible where hot rocks lie near the surface
* water is pumped in pipes down to the hot rocks and forced back due to pressure to turn a turbine and drive a generator.
* energy transferred from thermal to kinetic to generate electricity
\
* water is pumped in pipes down to the hot rocks and forced back due to pressure to turn a turbine and drive a generator.
* energy transferred from thermal to kinetic to generate electricity
\
how does geothermal power work?
59
New cards
* used to heat building directly
* free renewable energy no environmental problems.
* free renewable energy no environmental problems.
what is geothermal energy used for?/advantages
60
New cards
* cost of drilling down several km
* cost of building a power plant
* cost of building a power plant
what are the disadvantages of geothermal power process?
61
New cards
solar cells
what type of cells can you capture the sun’s energy?
62
New cards
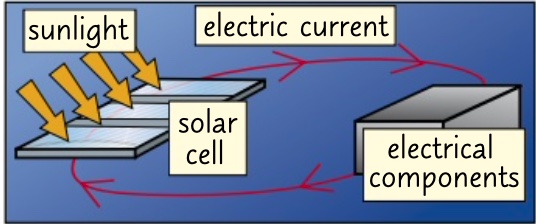
photocells
* use energy from the sun to directly generate electricity.
* generate direct current
\
* use energy from the sun to directly generate electricity.
* generate direct current
\
what is the other name for solar cells and how do they work?
63
New cards
* sun provides a renewable energy resource
* no pollution involved
* when there is no sunlight cells can be linked to rechargeable batteries to create a system that can store energy from the day to use at night
* no pollution involved
* when there is no sunlight cells can be linked to rechargeable batteries to create a system that can store energy from the day to use at night
what are the advantages for using solar cells?
64
New cards
* expensive
* not practical to connect them to national grid- very expensive
* they can only generate electricity when there is enough sunlight- problem at night.
* not practical to connect them to national grid- very expensive
* they can only generate electricity when there is enough sunlight- problem at night.
what are the disadvantages for using solar cells?
65
New cards
* simpler than solar cells
* black water piper inside a glass box.
* glass allows energy from sun, absorbed by black pipes and heats up water
* cost money to set up but they are renewable and free after
* used for small scale energy production
* black water piper inside a glass box.
* glass allows energy from sun, absorbed by black pipes and heats up water
* cost money to set up but they are renewable and free after
* used for small scale energy production
what are solar water heating panels?
66
New cards
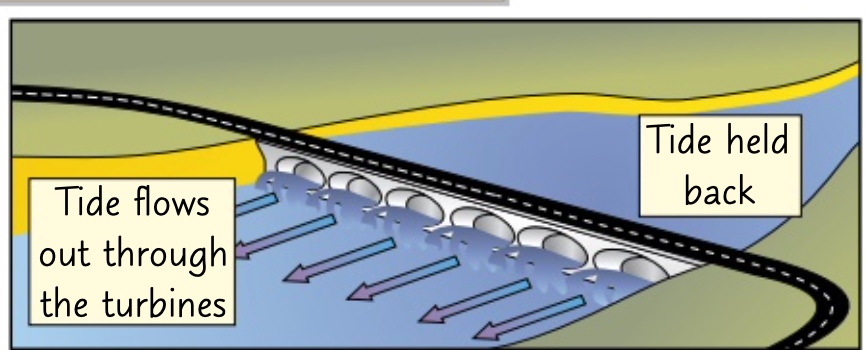
* generate energy when the tide goes in and out
* big dams built across rivers, with turbines inside.
* as the tide comes in it fill us the estuary and then the water can be allowed out through turbines at a controlled speed
* big dams built across rivers, with turbines inside.
* as the tide comes in it fill us the estuary and then the water can be allowed out through turbines at a controlled speed
how do tidal barrages work?
67
New cards
* no pollution
* renewable
\
* renewable
\
what are the advantages of tidal barrages?
68
New cards
* preventing boats
* spoiling view
* altering habitat of wildlife
* lower tides will provide less energy than higher ones
* initial costs are high
* spoiling view
* altering habitat of wildlife
* lower tides will provide less energy than higher ones
* initial costs are high
what are the disadvantages of tidal barrages?
69
New cards
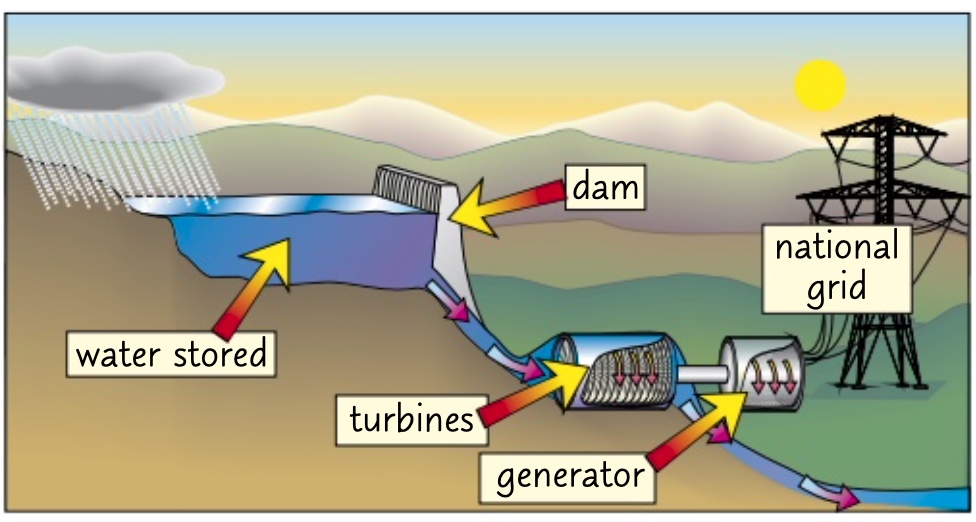
* requires flooding of a valley by building a big dam
* rainwater is caught and allowed out through turbines
* energy transferred is GPE-KE to generate electricity h
* rainwater is caught and allowed out through turbines
* energy transferred is GPE-KE to generate electricity h
how does hydroelectric power work?
70
New cards
* renewable
* no pollution
* immediate response to increase in demand
* no pollution
* immediate response to increase in demand
what are the advantages of hydroelectric power?
71
New cards
* flood valley
* rotting vegetation releases carbon dioxide and methane
* loss of habitat for some species
* dont look very good when they dry up
* costs are high
* rotting vegetation releases carbon dioxide and methane
* loss of habitat for some species
* dont look very good when they dry up
* costs are high
what are the disadvantages of hydroelectric power?
72
New cards
* extra supply when needed
what does pumped storage give?
73
New cards
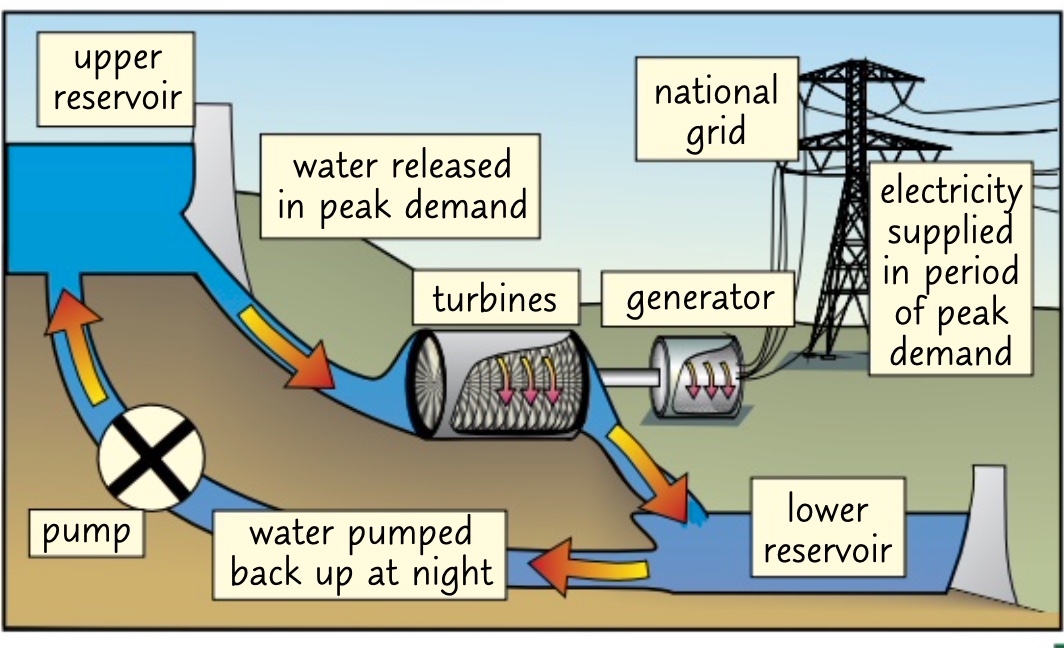
* spare night time electricity is used to pump water up to a higher reservoir
* released quickly when high demands
* spare electricity used to transfer energy back to water GPE so more electricity can be generated
* released quickly when high demands
* spare electricity used to transfer energy back to water GPE so more electricity can be generated
how does pumped storage work?