L12: structure and function of forelimb joints
1/148
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
149 Terms
simple joint
joint has articulations between 2 articulating bones
compound joint
joint has more than 2 articulating bones
what are the further classifications of fibrous joints?
syndesmosis
sutures
gomphosis
syndesmosis joint
ligamentous joint united by fibrous tissue that permits only slight movement
where are syndesmosis joints present?
coastal cartilage on coastal arch
between radius and ulna
sutures joint
fibrous joint between bones of the skull
gomphosis joint
specialized articulation in the teeth with the mandible and maxilla
what are the types of cartilagenous joints?
synchrondosis
symphyses
what type of cartilage makes up synchrondosis joints?
hyaline cartilage
what is an example of a synchrondosis joint?
growth plate
what cartilage makes up symphyses joint?
fibrocartilage
where can symphyses joints be found in the body?
between pelvic bone and pelvic symphisis
mandibular symphysis
between vertebra
what is only type of joint with a joint cavity?
synovial joint
what is the only joint that is freely moveable?
synovial joint
what is another name for the elbow joint?
cubital
what is another name for the metocarpophalangeal joint?
fetlock
what is another name for the proximal interphalangeal joint?
pastern
what is another name for the distal interphalangeal joint?
coffin
MCQ: how are joints in dogs primarily classified?
function and structure
MCQ: what is an example of a fibrous joint in dogs?
sutures of the skull
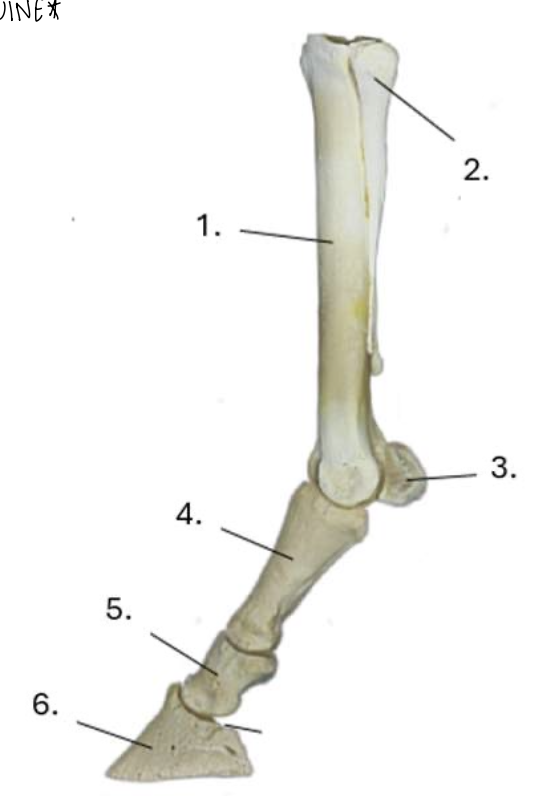
what is 1?
cannon bone
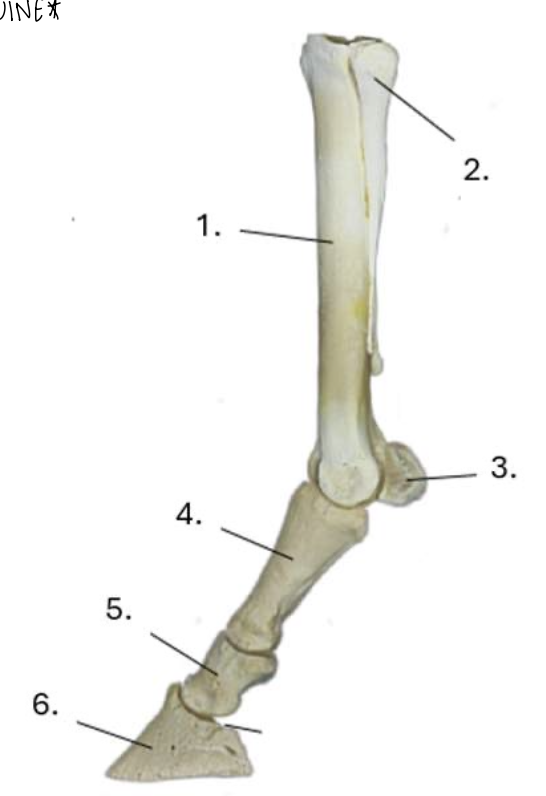
what is 2?
lateral splint bone
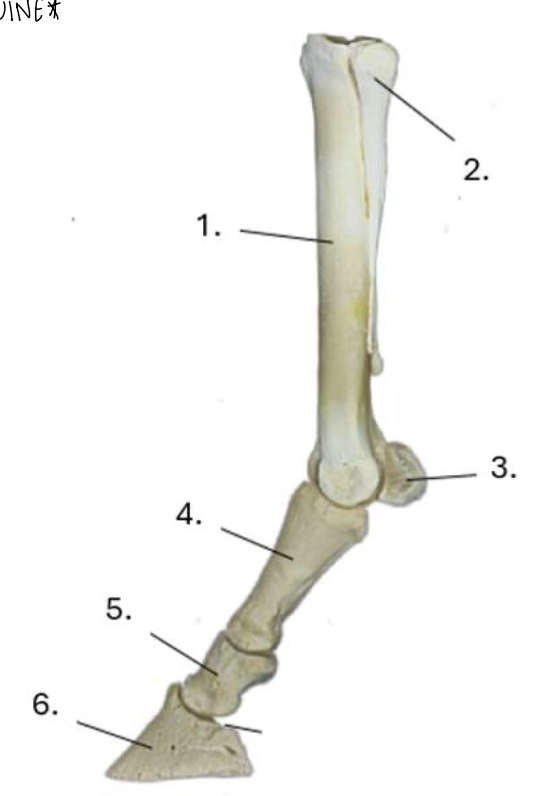
what is 3?
proximal sesamoid bone
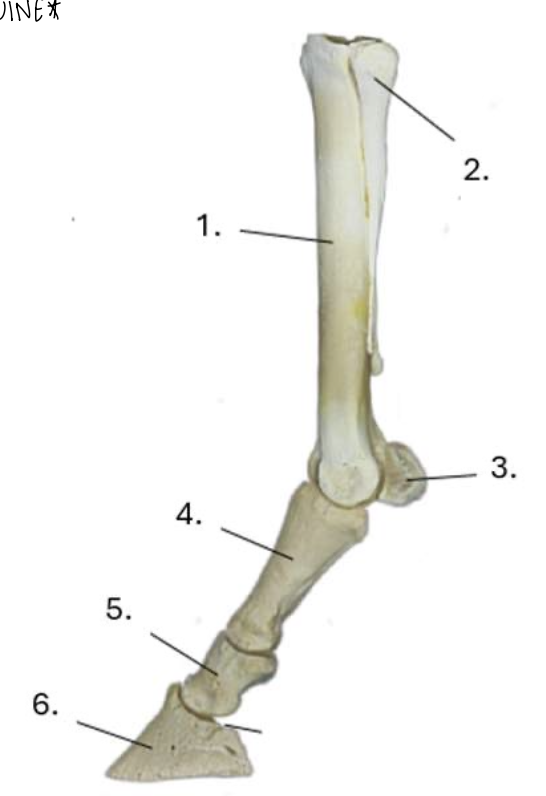
what is 4?
proximal phalanx (long pastern bone)
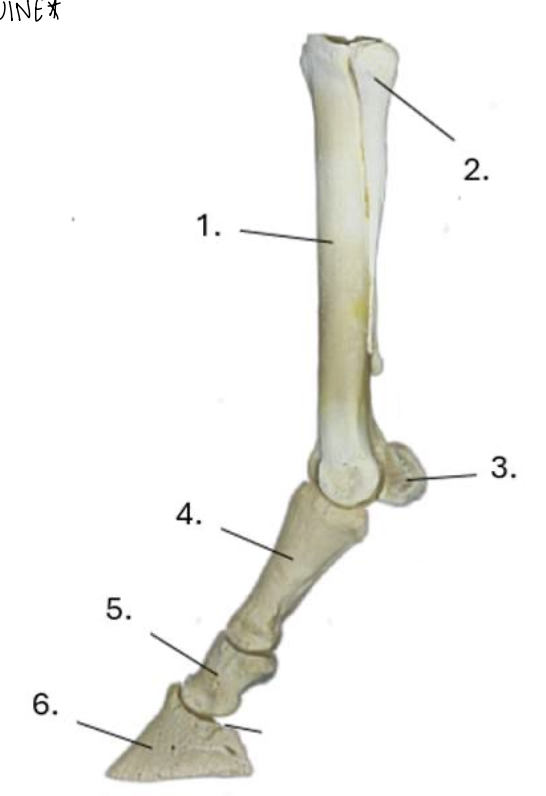
what is 5?
middle phalanx (short pastern bone)
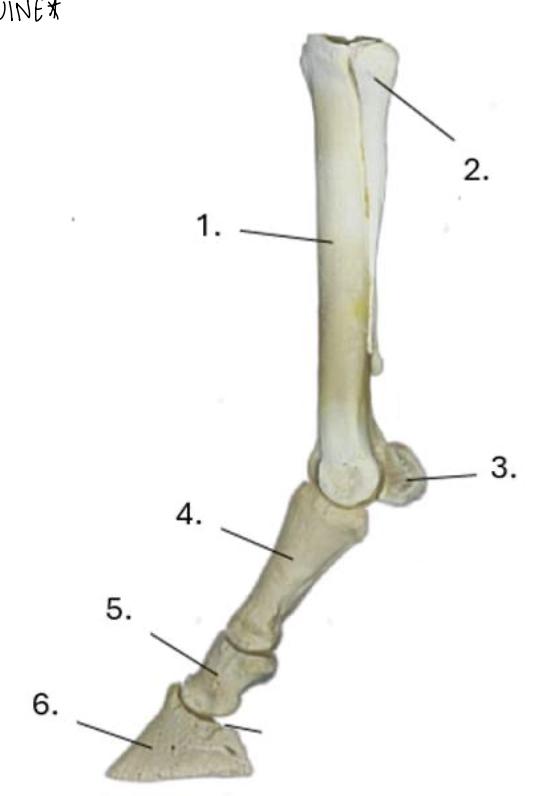
what is 6?
distal phalanx (coffin bone)
what type of joint attaches the forelimb to the trunk?
synsarcosis
which limb bears more weight and is involved more in the animal landing?
forelimb
reflex angle
more than 180 degrees
how do muscles prevent overextension or overflexion of a limb>
via equilibrium of flexors and extensors
what structure in the limb prevents the opposite action?
ligaments
what will ligaments on the flexor surface prevent?
hyperextension of the limb
active range of motion (AROM)
the movement a joint can perform when the animal moves it voluntarily using their own muscles
passive range of motion (PROM)
movement achieved when an external force (vet or therapist) moves the joint without muscle effort from the animal
what bones are involved with the shoulder joint?
glenoid cavity of scapula
head of proximal humerus
what type of joint is the shoulder joint?
simple synovial ball and socket joint
glenoid lip
fibrocartilaginous rim along the articular cartilage that deepens and widens the glenoid cavity
where does the joint cavity of the shoulder joint extend?
extends medially and laterally
bicipital bursa
extension of the shoulder joint in dogs
what is the clinical significance of the bicipital bursa?
due to connection to shoulder, you can inject into shoulder joint and it will reach bicep bursa
where is the joint cavity of the shoulder joint?
from the glenoid lip to the neck of the humerus
what are the ligaments of the shoulder joint?
transverse humeral ligament
lateral and medial glenohumeral ligaments
what is the function of the transverse humeral ligament?
hold the tendon of the bicep in the intertubercular groove
what are movements of the shoulder joint in quadrupeds limited to?
flexion and extension due to muscles surrounding shoulder joint
what movement helps with shock absorption of the shoulder?
gliding of glenoid cavity and humeral head
what is the function of the active ligaments of the shoulder
provide stability
what assists the active ligaments of the shoulder laterally?
teres minor
what assists the active ligaments of the shoulder medially?
teres major
what makes up the active ligaments of the shoulder>
tendons of the:
subscapularis muscle
supraspinatus muscle
infraspinatus muscle
what causes sweeny shoulder in horses?
damage to the suprascapular nerve
which shoulder muscles atrophy during sweeny shoulder?
infraspinatus muscles
supraspinatus muscles
MCQ: what feature is always present in all synovial joints?
articular capsule
MCQ: which is an additional feature of a synovial joint?
ligament
what bones are involved with the cubital joint?
distal humerus
proximal radius and ulna
what type of joint is the cubital joint?
compound synovial condylar joint
what are the component articulations of the cubital joint?
humeroradial joint
humeroulnar joint
proximal radioulnar joint
what is the olecranon tuberosity also known as?
point of the elbow
what are the components of the cubital joint capsule?
cranial joint capsule
lateral joint capsule
medial joint capsule
what are the ligaments of the cubital joint?
collateral ligaments
oblique ligament
annular ligament of the radius
olecranon ligament
what is the function of the collateral ligaments in the cubital joint?
stabilize elbow joint
prevent valgus and varus
what is the function of the oblique ligament of the cubital joint?
prevent overextension of elbow joint
what is the function of the annular ligament in the cubital joint?
hold radius and ulna together (absent in ruminants)
what is the function of the olecranon ligament of the cubital joint?
prevent overflexion of the elbow joint
what species is the olecranon ligament of the cubital joint present in?
small animals only
which collateral ligament of the cubital joint is branched in the horse?
medial collateral ligament
what is the lateral collateral ligament in the horse a component of?
the stay apparatus
MCQ: which ligament prevents bending of the cubital joint outward (laterally) or inward (medially)?
collateral ligaments
what lesions are associated with elbow dysplasia?
un-united anconeal process of the ulna
fragmentation of the medial coronoid process of ulna
osteochondrosis of medial aspect of humeral condyle
which ligament in any joint restrict the movement to extension and flexion only?
lateral and medial collateral ligaments
what are the functional digits in the pig?
2 and 3
what is the functional digit in bovine?
digits 3 and 4
what is the most stressed joint in the forelimb of horses?
fetlock
how many functional digits does the dog have?
4 (digits 2-5)
what bones are involved in the carpal joint of the dog?
distal ends of radius and ulna
7 carpal bones
5 metacarpal bones
what type of joint is the carpal joint?
compound synovial hinge joint
what bones are involved in the carpal joint of the horse?
distal end of radius
7 carpal bones
3 metacarpal bones
what are the joint articulations of the carpal joint?
antebrachiocarpal joint cavity
middle carpal joint cavity
carpometacarpal joint cavity
antebrachiocarpal joint
isolated joint cavity present between the antebrachium and carpus
which joint cavities communicate with one another in the carpus?
middle carpal joint cavity and carpometacarpal joint cavity
how many injections would be needed for the carpus?
2
synovial sheaths
protective layer around the tendon to reduce friction
what is the function of the acessory metacarpal ligaments?
stabilization of the accessory carpal bone
what is the function of the distal ligaments of the accessory carpal bone in horses?
stabilize accessory carpal bone against the pull exerted by carpal flexor muscle
what ligaments are present in the carpus of the horse?
collateral ligaments
intercarpal ligaments
antebrachiocarpal joint
most moveable joint meaning its cavity will open widest upon flexion
middle carpal joint cavity movement
very little movements
carpometacarpal cavity movements
no movements and cavity will not open at all
what is the function of the palmar carpal ligament?
to prevent overflexion of carpus joint
what is the function of the flexor retinaculum?
stabilize tendons of superficial and deep flexor muscles
what joints do you take fluid from for the carpus?
radiocarpal joint
middle carpal joint
what do we call the antebrachocarpal joint in the horse?
radiocarpal joint since horse lack ulna
what bones are involved in the fetlock joint?
distal end of cannon bone
proximal end of proximal phalanx
proximal sesamoid bone
what type of joint is the fetlock?
compound, synovial hinge joint
what structure will often be injured after the fetlock has been injured?
coffin joint
what side of the forelimb is the fetlock large and thick?
palmar side
where do the dorsal and palmar pouches of the fetlock project proximally between?
between the cannon bone and interosseus muscle on the palmar surface
where do the dorsal and palmar pouches of the fetlock project proximally below?
below the extensor tendons on the dorsal surface
what is pathological distension of the fetlock joint capsule known as?
articular windgalls
wind puffs
galls
what are the ligaments of the fetlock?
medial collateral ligament
lateral collateral ligament
proximal sesamoidean ligament
middle sesamoidian ligament
distal sesamoidean ligament
what makes up the proximal sesamoidean ligament?
interosseus muscle