Exam 3 chpt 14+15
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
C
Leopold’s maneuvers are often performed before assessing the fetal heart rate (FHR). These maneuvers help identify the best location to obtain the FHR. A pH test or fern test can be performed to determine the status of the fetal membranes. Dilation and effacement are best determined by vaginal examination. Assessment of fetal position is more accurate with vaginal examination
The nurse is preparing to perform Leopold’s maneuvers. Please select the rationale for the consistent use of these maneuvers by obstetric providers?
a. To determine the status of the membranes
b. To determine cervical dilation and effacement
c. To determine the best location to assess the fetal heart rate
d. To determine whether the fetus is in the posterior position
A
Frequent maternal position changes reduce the discomfort from constant pressure and promote fetal descent. A full bladder intensifies labor pain. The bladder should be emptied every 2 hours. Women in labor become very hot and perspire. Cool cloths will provide greater relief. Soft indirect lighting is more soothing than irritating bright lights.
Which comfort measure should the nurse utilize in order to enable a laboring woman to relax?
a. Recommend frequent position changes.
b. Palpate her filling bladder every 15 minutes.
c. Offer warm wet cloths to use on the patient’s face and neck.
d. Keep the room lights lit so the patient and her coach can see everything.
A
An increasing pulse rate is an early sign of excessive blood loss. If the blood volume were diminishing, the blood pressure would decrease. A firm fundus indicates that the uterus is contracting and compressing the open blood vessels at the placental site. Saturation of one pad within the first hour is the maximum normal amount of lochial flow. Two pads within 4 hours is within normal limits.
Which assessment finding is an indication of hemorrhage in the recently delivered postpartum patient?
a. Elevated pulse rate
b. Elevated blood pressure
c. Firm fundus at the midline
d. Saturation of two perineal pads in 4 hours
A
Helping a patient manage the pain is an essential part of nursing care because pain is an expected part of normal labor and cannot be fully relieved. Labor pain cannot be fully relieved. The labor nurse should always be assessing for unpredictable occurrences. Decreasing anxiety is important; however, managing pain is a top priority.
Which intervention is an essential part of nursing care for a laboring patient?
a. Helping the woman manage the pain
b. Eliminating the pain associated with labor
c. Feeling comfortable with the predictable nature of intrapartal care
d. Sharing personal experiences regarding labor and birth to decrease her anxiety
C A trickle of fluid from the vagina may indicate rupture of the membranes, requiring evaluation for infection or cord compression. Decreased or the lack of fetal movement requires further assessment. Irregular contractions are a sign of false labor and do not require further assessment. Bloody show may occur before the onset of true labor. It does not require professional assessment unless the bleeding is pronounced.
A patient at 40 weeks’ gestation should be instructed to go to a hospital or birth center for evaluation when she experiences
a. increased fetal movement.
b. irregular contractions for 1 hour.
c. a trickle of fluid from the vagina.
d. thick pink or dark red vaginal mucus.
D
Multiparous women usually have shorter labors than do nulliparous women. The woman described in option D is multiparous with a history of rapid labors, increasing the likelihood that her infant might be born in uncontrolled circumstances. A gravida 2 would be expected to have a longer labor than the gravida in option C. The fact that she lives close to the hospital allows her to stay home for a longer period of time. A gravida 1 will be expected to have the longest labor. The gravida 2 would be expected to have a longer labor than the gravida 3, especially because her first labor was 16 hours.
Which patient at term should proceed to the hospital or birth center the immediately after labor begins?
a. Gravida 2, para 1, who lives 10 minutes away
b. Gravida 1, para 0, who lives 40 minutes away
c. Gravida 2, para 1, whose first labor lasted 16 hours
d. Gravida 3, para 2, whose longest previous labor was 4 hours
B
All options describe relevant intrapartum nursing assessments, but the focus assessment has priority. If the maternal and fetal conditions are normal and birth is not imminent, other assessments can be performed in an unhurried manner. Contraction pattern, amount of discomfort, and pregnancy history are important nursing assessments but do not take priority if the birth is imminent. Last food intake, when labor began, and cultural practices the couple desires is an assessment that can occur later in the admission process, if time permits. Identification of ruptured membranes, the woman’s gravida and para, and her support person are assessments that can occur later in the admission process if time permits.
A woman who is gravida 3, para 2 enters the intrapartum unit. The most important nursing assessments include
a. contraction pattern, amount of discomfort, and pregnancy history.
b. fetal heart rate, maternal vital signs, and the woman’s nearness to birth.
c. last food intake, when labor began, and cultural practices the couple desires.
d. identification of ruptured membranes, the woman’s gravida and para, and access to a support person.
D
The situation describes a patient with normal assessments who is probably in false labor and will probably not deliver rapidly once true labor begins. The patient will probably be discharged, and there is no indication that a sedative is needed. These are all indications of false labor; there is no indication that further assessment or observations are indicated. These are all indications of false labor without fetal distress. There is no indication that a cesarean birth is indicated.
A primigravida at 39 weeks of gestation is observed for 2 hours in the intrapartum unit. The fetal heart rate has been normal. Contractions are 5 to 9 minutes apart, 20 to 30 seconds in duration, and of mild intensity. Cervical dilation is 1 to 2 cm and uneffaced (unchanged from admission). Membranes are intact. The nurse should expect the patient to be
a. discharged home with a sedative.
b. admitted for extended observation.
c. admitted and prepared for a cesarean birth.
d. discharged home to await the onset of true labor.
D
When fetal oxygen is compromised, relaxation of the rectal sphincter allows passage of meconium into the amniotic fluid. Active fetal movement is an expected occurrence. The expected FHR range is 120 to 160 bpm. The fetus should be able to tolerate contractions lasting 90 seconds if the resting phase is sufficient to allow for a return of adequate blood flow
Which clinical finding would be an indication to the nurse that the fetus may be compromised?
a. Active fetal movements
b. Fetal heart rate in the 140s
c. Contractions lasting 90 seconds
d. Meconium-stained amniotic fluid
B
A bulging vulva that encircles the fetal head describes crowning, which occurs shortly before birth. Bloody show occurs throughout the labor process and is not an indication of an imminent birth. Rupture of membranes can occur at any time during the labor process and does not indicate an imminent birth. Birth of the head occurs when the station is +4. A zero station indicates engagement.
Which nursing assessment indicates that a patient who is in the second stage of labor is almost ready to give birth?
a. Bloody mucous discharge increases.
b. The vulva bulges and encircles the fetal head.
c. The membranes rupture during a contraction.
d. The fetal head is felt at 0 station during the vaginal examination
D
The transition phase of labor is often associated with an abrupt change in behavior, including increased anxiety and irritability. This change of behavior is an expected occurrence during the transition phase. If she is in the transitional phase of labor, analgesia may not be appropriate if the birth is near. Hyperventilation will produce signs of respiratory alkalosis.
A 25-year-old primigravida patient is in the first stage of labor. She and her husband have been holding hands and breathing together through each contraction. Suddenly, the patient pushes her husband’s hand away and shouts, “Don’t touch me!” This behavior is most likely
a. a sign of abnormal labor progress.
b. an indication that she needs analgesia.
c. normal and related to hyperventilation.
d. common during the transition phase of labor.
C
The Apgar score is 9 because 1 point is deducted from the total score of 10 for the infant’s blue hands and feet. The baby received 2 points for each of the categories except color. Because the infant’s hands and feet were blue, this category is given a grade of 1. The baby received 2 points for each of the categories except color. Because the infant’s hands and feet were blue, this category is given a grade of 1. The infant had 1 point deducted because of the blue color of the hands and feet.
At 1 minute after birth, the nurse assesses the newborn to assign an Apgar score. The apical heart rate is 110 bpm, and the infant is crying vigorously with the limbs flexed. The infant’s trunk is pink and the hands and feet are blue. The Apgar score for this infant is
a. 7.
b. 8.
c. 9.
d. 10.
A
Infants are wet with amniotic fluid and blood at birth, which accelerates evaporative heat loss. Rubbing the infant does stimulate crying but is not the main reason for drying the infant. The main purpose of drying the infant is to prevent heat loss. Drying the infant after birth does not remove all of the maternal blood.
The nurse thoroughly dries the infant immediately after birth primarily to
a. reduce heat loss from evaporation.
b. stimulate crying and lung expansion.
c. increase blood supply to the hands and feet.
d. remove maternal blood from the skin surface.
C
Normal early maternal-infant behaviors are tentative and include fingertip touch, eye contact, and using a high-pitched voice when talking to the infant. There is no indication at this point that a social service consult is necessary. The signs are of normal attachment behavior. These are signs of normal attachment behavior; no other assessment is necessary at this point. The mother may be fatigued but is interacting with the infant in an expected manner.
The nurse notes that a patient who has given birth 1 hour ago is touching her infant with her fingertips and talking to him softly in high-pitched tones. Based on this observation, which action should the nurse take?
a. Request a social service consult for psychosocial support.
b. Observe for other signs that the mother may not be accepting of the infant.
c. Document this evidence of normal early maternal-infant attachment behavior.
d. Determine whether the mother is too fatigued to interact normally with her infant.
D
A primipara is experiencing the birthing event for the first time and may experience anxiety due to fear of the unknown. It would be important to recognize this because the patient is alone in the labor-birth room and will need additional support and reassurance. Although FVD may occur as a result of fluid loss, prospective management of labor patients includes the use of parenteral fluid therapy; the patient should be monitored for FVD and, if symptoms warrant, receive intervention. Because the patient has been in labor for 4 hours, this is not considered to be a prolonged labor pattern for a primipara patient. Although the patient may be tired, this nursing diagnosis would not be a priority unless there were other symptoms manifested. The patient is entering the second stage of labor; therefore she will be allowed to push with contractions. In terms of pain management, medication will not be administered at this time because of imminent birth.
Which nursing diagnosis would take priority in the care of a primipara patient with no visible support person in attendance? The patient has entered the second stage of labor after a first stage of labor lasting 4 hours.
a. Fluid volume deficit (FVD) related to fluid loss during labor and birth process
b. Fatigue related to length of labor requiring increased energy expenditure
c. Acute pain related to increased intensity of contractions
d. Anxiety related to imminent birth process
B
When a patient has not had prenatal care, the nurse must determine through interviewing and examination the presence of any pregnancy or labor risk factors, obtain admission labs, and discuss birth plan choices. Explaining the importance of prenatal care can be accomplished after the patient’s history has been completed.
A nursing priority during admission of a laboring patient who has not had prenatal care is
a. obtaining admission labs.
b. identifying labor risk factors.
c. discussing her birth plan choices.
d. explaining importance of prenatal care.
A
Charting related to membrane rupture includes the time, FHR, and character and amount of the fluid. Pain is not associated with this event. When it is obvious that the fluid is amniotic fluid, which is anticipated during labor, it is not necessary to verify this by testing. The patient’s understanding of the event would only need to be documented if it presents a problem.
The patient in labor experiences a spontaneous rupture of membranes. Which information related to this event must the nurse include in the patient’s record?
a. Fetal heart rate
b. Pain level
c. Test results ensuring that the fluid is not urine
d. The patient’s understanding of the event
B
After the head emerges, it realigns with the shoulders (restitution). External rotation occurs as the fetal shoulders rotate internally, aligning their transverse diameter with the anteroposterior diameter of the pelvic outlet. Expulsion occurs when the baby is completely delivered. Internal rotation occurs prior to birth of the head
The nurse is reviewing the cardinal maneuvers of labor and birth with a group of nursing students. Which maneuver will immediately follow the birth of the baby’s head?
a. Expulsion
b. Restitution
c. Internal rotation
d. External rotation
C
The maneuver that determines whether the presenting part is engaged (widest diameter at or below a zero station) in the maternal pelvis is performed by palpating the suprapubic area. Next, an attempt is made to grasp the presenting part gently between the thumb and fingers. If the presenting part is not engaged, the grasping movement of the fingers moves it upward in the uterus. If the presenting part is engaged, the fetus will not move upward in the uterus. Palpating the uterine fundus distinguishes between a cephalic and breech presentation. Holding the left hand steady on one side of the uterus while palpating the opposite side of the uterus determines on which side of the uterus is the fetal back and on which side are the fetal arms and legs. Placing your hands on each side of the uterus with fingers pointed toward the inlet determines whether the head is flexed (vertex) or extended (face).
The nurse is performing Leopold’s maneuvers on her patient. Which figure depicts the Leopold’s maneuver that determines whether the fetal presenting part is engaged in the maternal pelvis? Refer to Figures A to D.
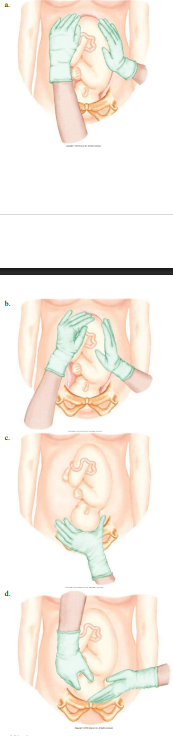
D
The nurse should monitor for edema and discoloration. Using a cold application to the labia and perineum reduces pain by numbing the area and limiting bruising and edema for the first 12 hours. An episiotomy is performed as the fetal head distends the perineum. The pain with vaginal hematoma is severe and constant. The pain associated with vaginal hematoma is severe.
After a forceps-assisted birth, the patient is observed to have continuous bright red lochia and a firm fundus. Which other data would indicate the presence of a potential vaginal wall hematoma?
a. Lack of an episiotomy
b. Mild, intermittent perineal pain
c. Lack of pain in the perineal area
d. Edema and discoloration of the labia and perineum
D
Internal version is used only during vaginal birth to manipulate the second twin into a presentation that allows it to be born vaginally. For internal version to occur, the cervix needs to be completely dilated. For internal version to occur, the cervix needs to be dilated. Internal version is done to turn the second twin after the first twin is born.
The nurse is explaining the technique of internal version to a nursing orientee. Which statement best describes the technique of internal version?
a. Manipulation of the fetus from a breech to a cephalic presentation before labor begins
b. Manipulation of the fetus from a transverse lie to a longitudinal lie before cesarean birth
c. Manipulation of the second twin from an oblique lie to a transverse lie before labor begins
d. Manipulation of the second twin from a transverse lie to a breech presentation during vaginal birth
B
The patient who is exhausted will be unable to assist with the expulsion of the fetus. With a wide pelvic outlet, vacuum extraction would not be necessary. With a rapid birth, vacuum extraction would not be necessary. A station of 0 is too high for a vacuum extraction
A maternal indication for the use of vacuum extraction is
a. a wide pelvic outlet.
b. maternal exhaustion.
c. a history of rapid deliveries.
d. failure to progress past 0 station.
A
Forceps birth can result in local irritation, bruising, or lacerations of the fetal scalp. This would put the infant at risk for cold stress and would be contraindicated. Prophylactic antibiotics are not necessary with a forceps birth. Measuring the circumference of the head is part of the initial nursing assessment.
Immediately following the forceps-assisted birth of an infant, which action should the nurse implement?
a. Assess the infant for signs of trauma.
b. Apply a cold pack to the infant’s scalp.
c. Give the infant prophylactic antibiotics.
d. Measure the circumference of the infant’s head.
C
Fetal bradycardia may indicate fetal distress and may require immediate intervention. Maternal pulse rate may increase due to the pushing process. Blood pressure of 120/70 mm Hg is within expected norms for this stage of labor. Decreased intensity of uterine contractions indicates the birth is imminent at this point.
While assisting with a vacuum extraction birth, which alteration should the nurse immediately report to the obstetric provider?
a. Maternal pulse rate of 100 bpm
b. Maternal blood pressure of 120/70 mm Hg
c. Persistent fetal bradycardia below 100 bpm
d. Decreased intensity of uterine contractions
C
Fetal bradycardia may indicate fetal distress and may require immediate intervention. Maternal pulse rate may increase due to the pushing process. Blood pressure of 120/70 mm Hg is within expected norms for this stage of labor. Decreased intensity of uterine contractions indicates the birth is imminent at this point.
While assisting with a vacuum extraction birth, which alteration should the nurse immediately report to the obstetric provider?
a. Maternal pulse rate of 100 bpm
b. Maternal blood pressure of 120/70 mm Hg
c. Persistent fetal bradycardia below 100 bpm
d. Decreased intensity of uterine contractions
D
Prostaglandins are contraindicated in patients who have had a previous surgery in the upper uterus, such as a previous classic cesarean incision or extensive surgery for uterine fibroids. A side effect of prostaglandin administration is hyperstimulation of the uterus. A Bishop’s score of 5, 42 weeks of gestation, or a previous low transverse cesarean birth are not contraindications for cervical ripening.
The nurse is preparing to administer a vaginal prostaglandin preparation to ripen the cervix of her patient. With which patient should the nurse question the use of vaginal prostaglandin as a cervical ripening agent?
a. The patient who has a Bishop’s score of 5
b. The patient who is at 42 weeks of gestation
c. The patient who had a previous low transverse cesarean birth
d. The patient who had previous surgery in the upper uterus
C
An external cephalic version (changing the fetal presentation from breech to cephalic) is more successful when the pregnancy is at least 37 weeks and there is still adequate room and fluid to manipulate the fetus but prior to term or onset of labor. A low-lying placenta, previous cesarean birth, and uterine fibroids are contraindications for version.
Which breech presentation should the nurse recognize as being favorable for an external cephalic version?
a. 36-week gestation with low-lying placenta
b. 38-week gestation with one previous cesarean
c. 37-week gestation with fetal weight of 7lb
d. 40-week gestation with several uterine fibroids
B
Reassurance of fetal lung maturity is essential before elective procedures such as induction or cesarean. The cervix must be favorable for dilation but need not be dilated prior to induction. Prior rupture of membranes is not necessary for induction. Uterine hypertonia is a risk factor associated with induction of labor
The pregnant patient expresses a desire to schedule birth during the baby’s father’s furlough from military service. The nurse explains that prior to induction of labor, it is essential to determine which clinical finding?
a. Dilated cervix
b. Fetal lung maturity
c. Rupture of membranes
d. Uterine hypertonia
B
The woman’s temperature should be assessed at least every 2 to 4 hours after the membranes rupture. Elevations above 38C (100.F) should be reported. A rising FHR and fetal tachycardia (above 160 bpm) may precede maternal fever. The fetal heart rate is at the high end of the acceptable range and the maternal temperature is slightly above normal. These parameters warrant watching closely with more frequent vital signs. The WBC is often falsely elevated in labor, largely related to the stress of labor. The FHR with a baseline of 150 to 160 bpm demonstrates moderate variability, and fetal acoustic stimulation is not warranted. Amniotic fluid is emitted from the vagina at variable rates and the underpad needs to be changed as needed
The labor nurse is developing a plan of care for a patient admitted in active labor with spontaneous rupture of the membranes 6 hours prior to admission with clear fluid. On admission, vital signs were as follows: maternal heart rate (HR) 92 bpm; fetal rate (FHR) baseline, 150 to 160 bpm; blood pressure, 124/76 mm Hg; temperature 37.2C (99F). What is the priority nursing action for this patient?
a. Fetal acoustic stimulation
b. Assess temperature every 2 hours
c. Change absorption pads under her hips every 2 hours
d. Review white blood cell count (WBC) drawn at admission
A, B, C
Delayed pushing has been shown to result in less maternal fatigue and decreased pushing time. Pushing vigorously sooner than the onset of the reflexive urge may contribute to birth canal injury because her vaginal tissues are stretched more forcefully and rapidly than if she pushed spontaneously and in response to her body’s signals. A brief slowing of contractions often occurs at the beginning of the second stage
A laboring patient is 10 cm dilated; however, she does not feel the urge to push. The nurse understands that according to laboring down, the advantages of waiting until an urge to push are which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
a. Less maternal fatigue
b. Less birth canal injuries
c. Decreased pushing time
d. Faster descent of the fetus
e. An increase in frequency of contractions
B, C, E
Following birth, the newborn is at risk for hypothermia. Therefore nursing interventions are aimed at maintaining warmth. Drying the infant off, in addition to maintaining warmth, helps stimulate crying and lung expansion, which helps in the transition period following birth. Placing a cap on the infant’s head helps prevent heat loss. Removal of wet linens helps minimize further heat loss caused by exposure. Newborns should not be covered while in a radiant warmer with blankets because this will impede birth of heat transfer. Bathing a newborn should be delayed for at least a few hours so that the newborn temperature can stabilize during the transition period.
Which interventions should be performed in the birth room to facilitate thermoregulation of the newborn? (Select all that apply.)
a. Place the infant covered with blankets in the radiant warmer.
b. Dry the infant off with sterile towels.
c. Place stockinette cap on infant’s head.
d. Bathe the newborn within 30 minutes of birth.
e. Remove wet linen as needed.
B,C,D
Nursing care of the normal laboring patient would include monitoring and documentation of vital signs as part of the labor assessment, documentation the FHR, checking patterns to look for assurance of fetal well-being by evaluating baseline and the fetal response to contraction patterns, and noting any position changes on the monitor tracing to evaluate the fetal response. Providing dietary offerings during the course of labor is not part of the nursing care plan because the introduction of food may lead to nausea and vomiting in response to the labor process and might affect the mode of birth.
When caring for a patient in labor who is considered to be at low risk, which assessments should be included in the plan of care? (Select all that apply.)
a. Check the DTR each shift.
b. Monitor and record vital signs frequently during the course of labor.
c. Document the FHR pattern, noting baseline and response to contraction patterns.
d. Indicate on the EFM tracing when maternal position changes are done.
e. Provide food, as tolerated, during the course of labor.
A, C, D
Conditions associated with fetal compromise include maternal hypotension (may divert blood flow away from the placenta to ensure adequate perfusion of the maternal brain and heart), meconium-stained (greenish) amniotic fluid, and maternal fever (38C [100.4F] or higher). Fetal heart rate of 110 to 160 bpm for a term fetus is normal. Complete uterine relaxation is a normal finding.
The nurse is monitoring a patient in the active stage of labor. Which conditions associated with fetal compromise should the nurse monitor? (Select all that apply.)
a. Maternal hypotension
b. Fetal heart rate of 140 to 150 bpm
c. Meconium-stained amniotic fluid
d. Maternal fever—38C (100.4F) or higher
e. Complete uterine relaxation of more than 30 seconds between contractions
A, C, D
Assessment findings that may indicate a potential complication in the fourth stage include a soft boggy uterus, high uterine fundus displaced to the right, and intense vaginal pain unrelieved by analgesics. The maternal temperature may be slightly elevated after birth because of the inflammation to tissues, and half of a lochia pad saturated in the first hour after birth is within expected amounts
The nurse is caring for a patient in the fourth stage of labor. Which assessment findings should the nurse identify as a potential complication? (Select all that apply.)
a. Soft boggy uterus
b. Maternal temperature of 37.2C (99F)
c. High uterine fundus displaced to the right
d. Intense vaginal pain unrelieved by analgesics
e. Half of a lochia pad saturated in the first hour after birth
A, B, C, E
Fetal death, postterm pregnancy, rupture of members, and chorioamnionitis are all acceptable indications for induction. Other conditions include intrauterine growth retardation (IUGR), maternal-fetal blood incompatibility, hypertension, and placental abruption. Elective inductions for convenience of the patient or her provider are not recommended; however, they have become common. Factors such as rapid labors and living a long distance from a health care facility may be a valid reason in such a circumstance.
Induction of labor is considered an acceptable obstetric procedure if it is a safe time to deliver the fetus. The charge nurse on the labor and birth unit is often asked to schedule patients for this procedure and therefore must be cognizant of the specific conditions appropriate for labor induction, including which of the following? (Select all that apply.)
a. Fetal death
b. Postterm pregnancy
c. Rupture of membranes at or near term
d. Convenience of the patient or her health care provider
e. Chorioamnionitis (inflammation of the amniotic sac)
C
The tocotransducer monitors uterine activity and should be placed over the fundus, where the most intensive uterine contractions occur. The tocotransducer is for external use. The tocotransducer monitors uterine contractions. The most intensive uterine contractions occur at the fundus; this is the best placement area.
Proper placement of the tocotransducer for electronic fetal monitoring is
a. inside the uterus.
b. on the fetal scalp.
c. over the uterine fundus.
d. over the mother’s lower abdomen.
A
Beat-to-beat variability cannot be determined by auscultation because auscultation provides only an average fetal heart rate (FHR) as it fluctuates. Tachycardia can be determined by any of the FHR monitoring techniques. Bradycardia can be determined by any of the FHR monitoring techniques. The fetal response to the contractions is usually noted by an increase or decrease in fetal heart rate. These can be determined by any of the FHR monitoring techniques.
Which clinical finding can be determined only by electronic fetal monitoring?
a. Variability
b. Tachycardia
c. Bradycardia
d. Fetal response to contractions
C
The periodic pattern described is early deceleration that is not associated with fetal compromise and requires no intervention. This is a Category I tracing which is a normal pattern. Repositioning the patient, applying a fetal scalp electrode, or administering oxygen would be interventions performed for Category II or III patterns.
When the deceleration pattern of the fetal heart rate mirrors the uterine contraction, which nursing action is indicated?
a. Reposition the patient.
b. Apply a fetal scalp electrode.
c. Record this normal pattern.
d. Administer oxygen by nasal cannula.
B
When the membranes rupture, amniotic fluid may carry the umbilical cord to a position where it will be compressed between the maternal pelvis and the fetal presenting part, resulting in a variable deceleration pattern. Early declarations are considered reassuring; they are not a concern after rupture of membranes. Accelerations are considered reassuring; they are not a concern after rupture of membranes. Increase in baseline variability is not an expected occurrence after the rupture of membranes.
When the mother’s membranes rupture during active labor, the fetal heart rate should be observed for the occurrence of which periodic pattern?
a. Early decelerations
b. Variable decelerations
c. Nonperiodic accelerations
d. Increase in baseline variability
C
Late decelerations indicate fetal compromise (uteroplacental insufficiency) and are considered to be a significant event requiring immediate assessment and intervention. Of all the options listed, changing maternal position may increase placental perfusion. In the presence of late decelerations, Pitocin infusion should be stopped. Contacting anesthesia for epidural administration will not solve the existing problem of late decelerations. There are no data to support the administration of Narcan and because patient is still in early labor, birth is not imminent.
The patient presenting at 38 weeks’ gestation, gravida 1, para 0, vaginal exam 4 cm, 100% effaced, +1 station vertex. What is the most likely intervention for this fetal heart rate pattern?
a. Continue oxytocin (Pitocin) infusion.
b. Contact the anesthesia department for epidural administration.
c. Change maternal position.
d. Administer Narcan to patient and prepare for immediate vaginal delivery.
B
Amnioinfusion is a procedure utilized during labor when cord compression or the detection of gross meconium staining is found in the amniotic fluid. An isotonic (Lactated Ringers or normal saline) solution is used as an irrigation method through the IUPC (intrauterine pressure catheter).
The physician has ordered an amnioinfusion for the laboring patient. Which data supports the use of this therapeutic procedure?
a. Presenting part not engaged
b. +4 meconium-stained amniotic fluid on artificial rupture of membranes (AROM)
c. Breech position of fetus
d. Twin gestation
C
Decelerations that begin at the peak of the contractions and recover after the contractions end are caused by uteroplacental insufficiency. When the patient is in the supine position, the weight of the uterus partially occludes the vena cava and descending aorta, resulting in hypotension and decreased placental perfusion. Increasing the IV infusion, elevating the lower extremities, and administering O2 will not be effective as long as the patient is in a supine position.
Which of the following is the priority intervention for a supine patient whose monitor strip shows decelerations that begin after the peak of the contraction and return to the baseline after the contraction ends?
a. Increase IV infusion.
b. Elevate lower extremities.
c. Reposition to left side-lying position.
d. Administer oxygen per face mask at 4 to 6 L/minute.
A
Decelerations that mirror the contraction are early decelerations caused by fetal head compression. Early decelerations are not associated with fetal compromise and require no intervention. Administering O2, increasing the IV flow rate, and assessing for hypotension are not necessary within early decelerations.
Decelerations that mirror the contractions are present with each contraction on the monitor strip of a multipara who received epidural anesthesia 20 minutes ago. The nurse should
a. maintain the normal assessment routine.
b. administer O2 at 8 to 10 L/minute by face mask.
c. increase the IV flow rate from 125 to 150 mL/hour.
d. assess the maternal blood pressure for a systolic pressure below 100 mm Hg.
C
Fetal scalp stimulation helps identify whether the fetus responds to gentle massage. An acceleration in response to the massage suggests that the fetus is in normal oxygen and acid-base balance. Monitoring fetal oxygen saturation using fetal pulse oximetry is no longer available in the United States. Obtaining a fetal scalp blood sample is invasive and the results are not immediately available. Increasing the rate of nonadditive IV fluid would not clarify the fetal condition.
To clarify the fetal condition when baseline variability is absent, the nurse should first
a. monitor fetal oxygen saturation using fetal pulse oximetry.
b. notify the physician so that a fetal scalp blood sample can be obtained.
c. apply pressure to the fetal scalp with a glove finger using a circular motion.
d. increase the rate of nonadditive IV fluid to expand the mother’s blood volume.
A
A thick layer of abdominal fat absorbs energy from uterine contractions, reducing their apparent intensity on the monitor strip. Contraction patterns of 2 to 3 minutes lasting 60 seconds and every 2 minutes lasting 60 to 70 seconds indicate accurate measurement of uterine activity. Irregular and mild contractions are common in the latent phase.
Which patient is a candidate for internal monitoring with an intrauterine pressure catheter?
a. Obese patient whose contractions are 3 to 6 minutes apart, lasting 20 to 50 seconds
b. Gravida 1, para 0, whose contractions are 2 to 3 minutes apart, lasting 60 seconds
c. Multigravida whose contractions are 2 minutes apart, lasting 60 to 70 seconds
d. Gravida 2, para 1, in latent phase whose contractions are irregular and mild
A
A deceleration that returns to baseline after the end of the contraction is a late deceleration caused by placental perfusion problems. Administering oxygen will increase the patient’s blood oxygen saturation, making more oxygen available to the fetus. Decreasing the IV rate, repositioning the ultrasound transducer, and performing a vaginal exam to assess for cord prolapse are not effective interventions to improve fetal oxygenation.
Which of the following is the priority intervention for the patient in a left side-lying position whose monitor strip shows a deceleration that extends beyond the end of the contraction?
a. Administer O2 at 8 to 10 L/minute.
b. Decrease the IV rate to 100 mL/hour.
c. Reposition the ultrasound transducer.
d. Perform a vaginal exam to assess for cord prolapse.
D
Variable decelerations are caused by conditions that reduce flow through the umbilical cord. The patient should be repositioned when the FHR pattern is associated with cord compression. The knee–chest position uses gravity to shift the fetus out of the pelvis to relieve cord compression. Administering oxygen will not be effective until cord compression is relieved. Increasing the IV fluids and placing a wedge under the right hip are not effective interventions for cord compression.
When a pattern of variable decelerations occur, the nurse should immediately
a. administer O2 at 8 to 10 L/minute.
b. place a wedge under the right hip.
c. increase the IV fluids to 150 mL/hour.
d. position patient in a knee-chest position.
A
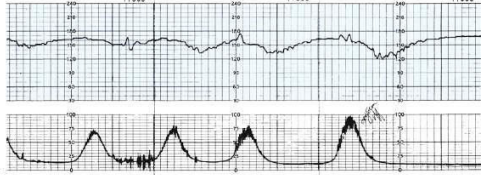
Late decelerations are similar to early decelerations in that the FHR slows (30 to 40 bpm); however, the decelerations are shifted to the right in relation to the contraction. They often begin after the peak of the contraction. They reflect possible impaired placental exchange (uteroplacental insufficiency). Administration of 100% oxygen through a snug face mask makes more oxygen available for transfer to the fetus. A commonly suggested rate is 8 to 10 L/minute. The pattern is abnormal, so repositioning the fetal ultrasound transducer, assisting the patient to the bathroom, or continuing to monitor the pattern will not correct the problem.
The nurse is monitoring a patient in labor and notes this fetal heart rate pattern on the electronic fetal monitoring strip (see figure). Which is the most appropriate nursing action?
a. Administer oxygen with a face mask at 8 to 10 L/minute.
b. Reposition the fetal monitor ultrasound transducer.
c. Assist the patient to the bathroom to empty her bladder.
d. Continue to monitor the patient and fetal heart rate patterns.
The nurse is monitoring a patient in labor and notes this fetal heart rate pattern on the electronic fetal monitoring strip (see figure). Which is the most appropriate nursing action at this time?
a. Decrease the rate of the IV fluids.
b. Document the fetal heart rate pattern.
c. Explain to the patient that the pattern is normal.
d. Perform a vaginal exam to detect a prolapsed cord.
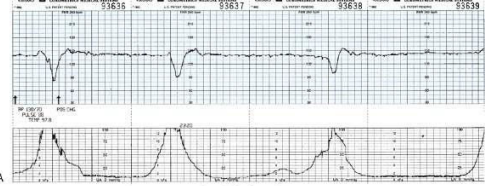
A
To apply internal monitoring devices, the membranes must be ruptured. Cervical dilation of 4 cm would permit the insertion of fetal scalp electrodes and an intrauterine catheter. A compromised fetus should be monitored with the most accurate monitoring devices. An internal electrode should not be placed if the patient has hemophilia, maternal HIV, or genital herpes.
Which maternal condition should be considered a contraindication for the application of internal monitoring devices?
a. Unruptured membranes
b. Cervix dilated to 4 cm
c. Fetus has known heart defect
d. Maternal HIV
B
When the membranes rupture, amniotic fluid may carry the umbilical cord to a position where it will be compressed between the maternal pelvis and the fetal presenting part, resulting in a variable deceleration pattern. Early declarations are considered reassuring; they are not a concern after rupture of membranes. Accelerations are considered reassuring; they are not a concern after rupture of membranes. Increase in baseline variability is not an expected occurrence after the rupture of membranes.
When the mother’s membranes rupture during active labor, the fetal heart rate should be observed for the occurrence of which periodic pattern?
a. Early decelerations
b. Variable decelerations
c. Nonperiodic accelerations
d. Increase in baseline variability