Clinical Optometry III Final exam - Everything else (Refractive error, etc.)
1/306
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
307 Terms
Direct
This is the equation for ____________ ophthalmoscopy.

17.5x
What is the magnification during direct ophthalmoscopy for a 10D myope?
Indirect
This is the equation for ____________ ophthalmoscopy magnification. (Essentially step 1 times step 2).
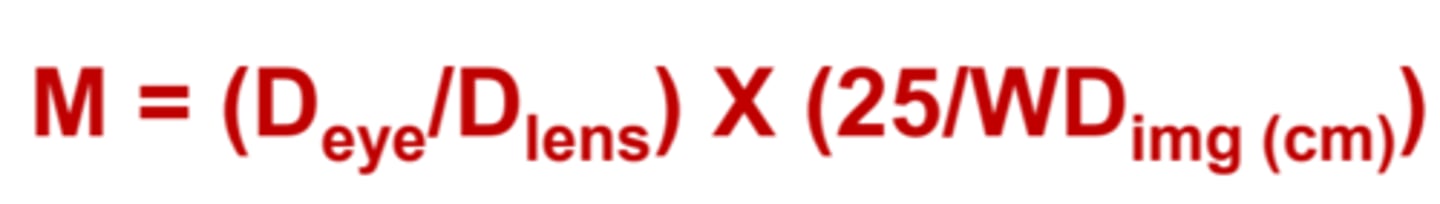
2.188x
What is the magnification during indirect ophthalmoscopy on a 10D myope using a 20D lens that creates an image 40cm from the observer?
0.83x
What is the magnification during indirect ophthalmoscopy on a 10D hyperope using a 30D lens that creates an image 50cm from the observer?
WDlens
The _____________ is the viewing distance from the lens to the observer.
WDimg
The _____________ is the viewing distance from the image to the observer.
WDimg
This equation is needed to calculate the ___________.

2.38x
Find the magnification during BIO when using a 20D lens held on a 10D myope at 40cm from the observer:
flens
This equation is used to find the __________.

2.14x
Find the magnification during BIO when using a 20D lens held on an emmetropic patient at 40cm from the observer:
Increase
As you decrease the power of the condensing lens (30D to 20D), the magnification will _________________.
Decrease
As you decrease the power of the condensing lens (30D to 20D), the FOV will _________________.
Increase
As you increase the working distance during BIO, the FOV will _________________.
Decrease
As you increase the working distance during BIO, the magnification will _________________.
180
Your head should be placed ________ degrees away from the meridian that you wish to examine during BIO.
8
The FOV of a 20D lens is about ______ disc diameters.
Decrease
As BIO lens power increases (20D to 30D), retinal irradiance will _____________.
10
Clinically, we should minimize continuous exposure of a single area of the fundus to a max of _____ seconds during SLE.
BIO
The _______ provides a real, inverted, and laterally reversed image of the fundus.
40
Clinically, we should minimize continuous exposure of a single area of the fundus to a max of _____ seconds during BIO.
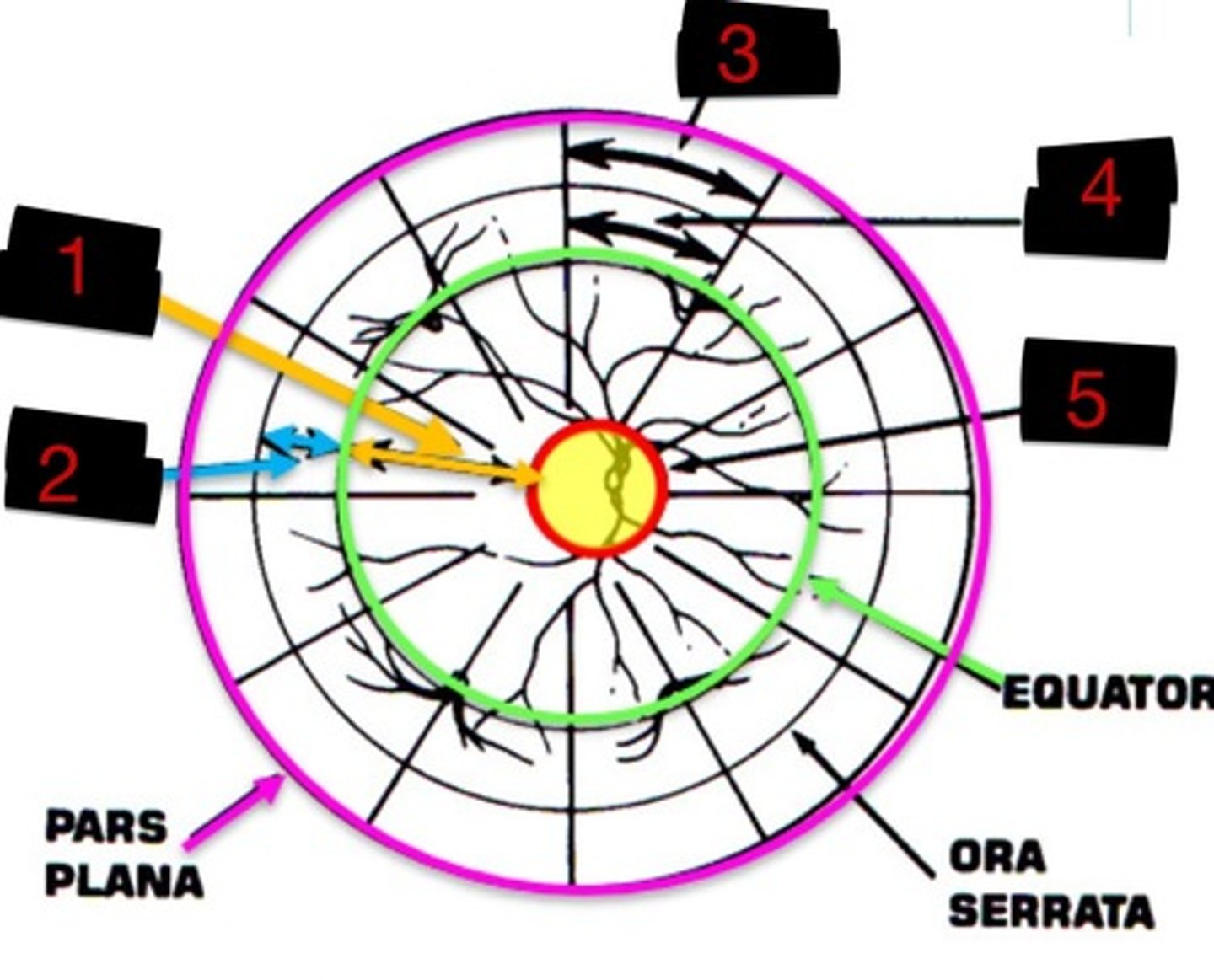
10DD
Label 1
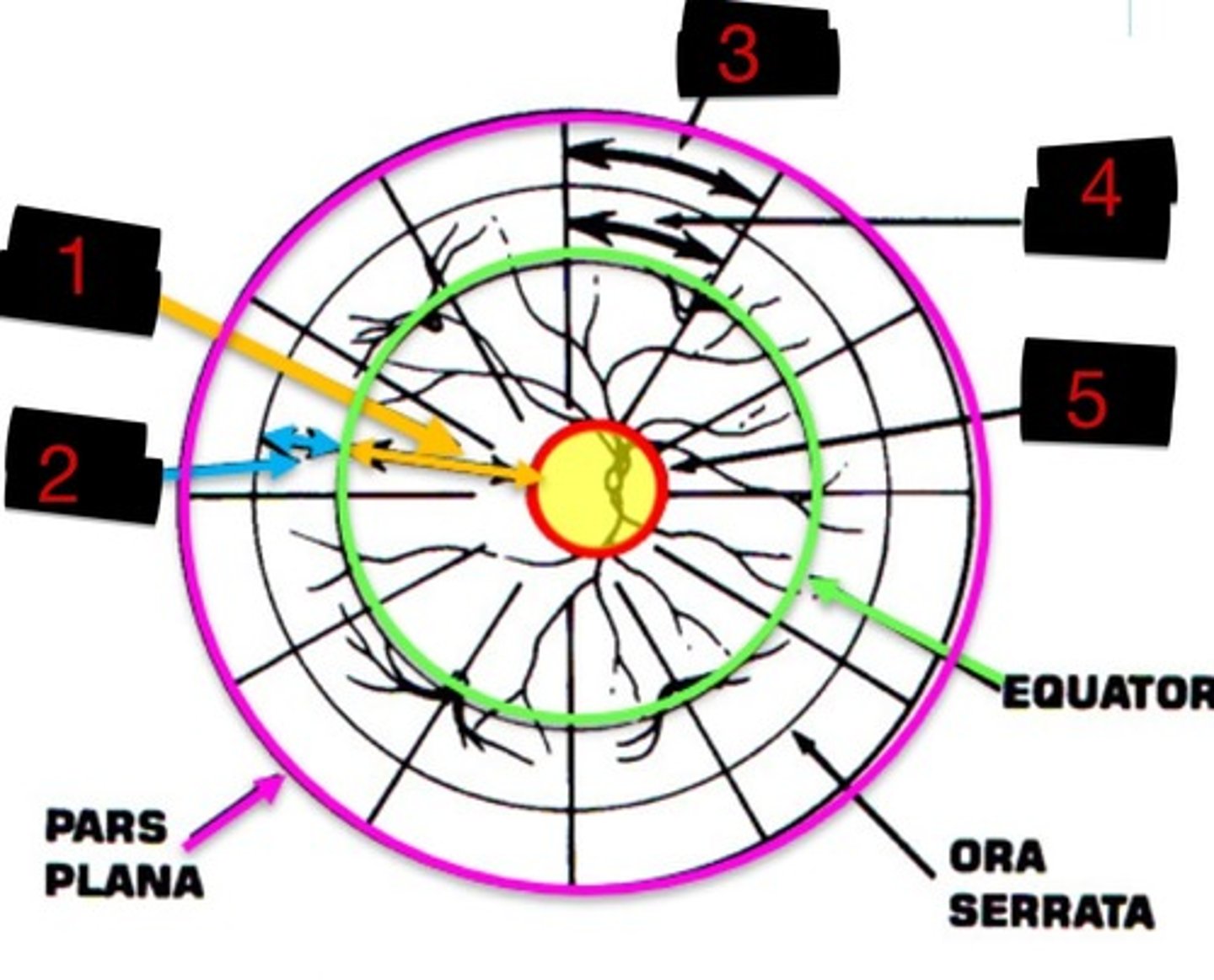
4DD
Label 2
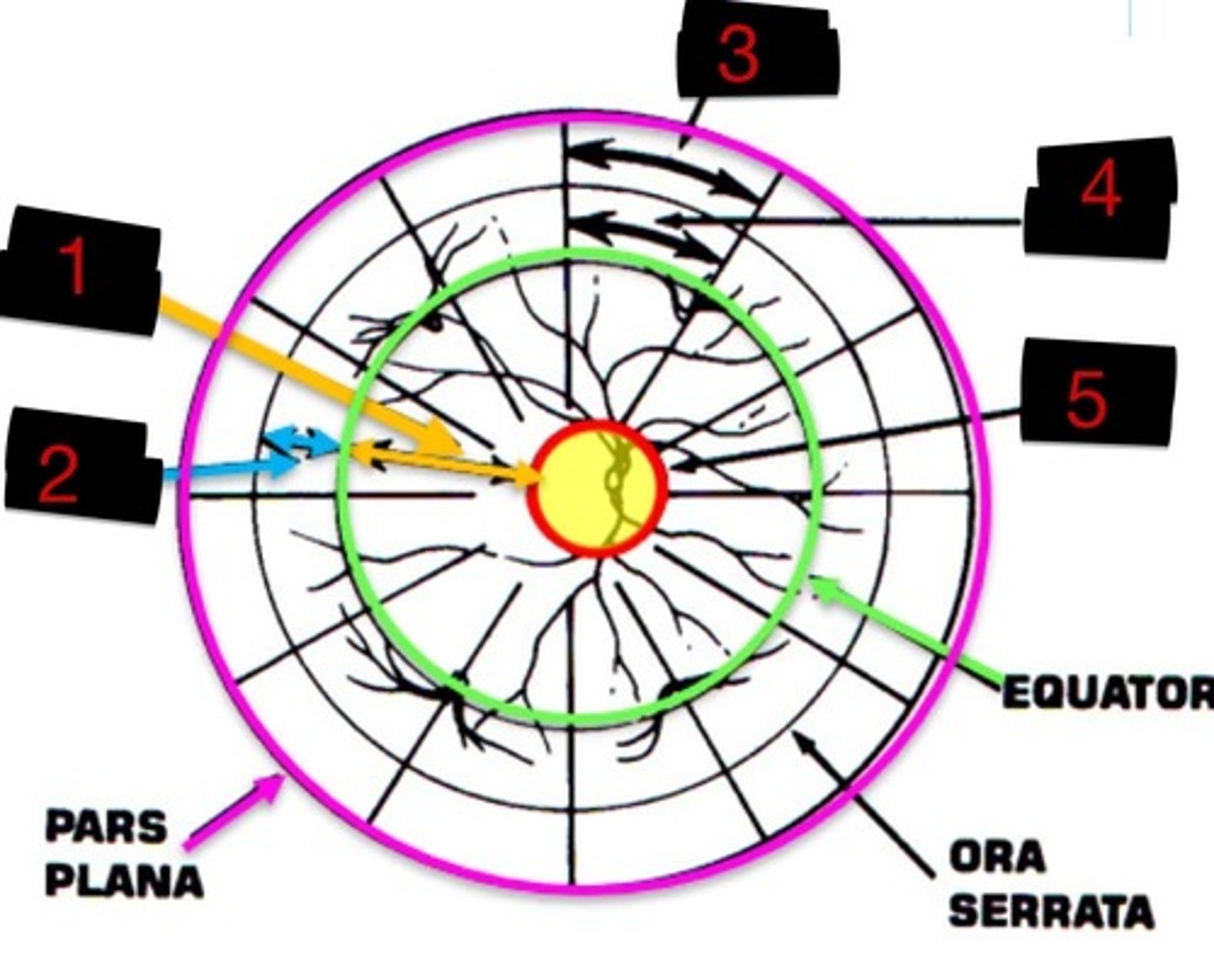
3DD
Label 3
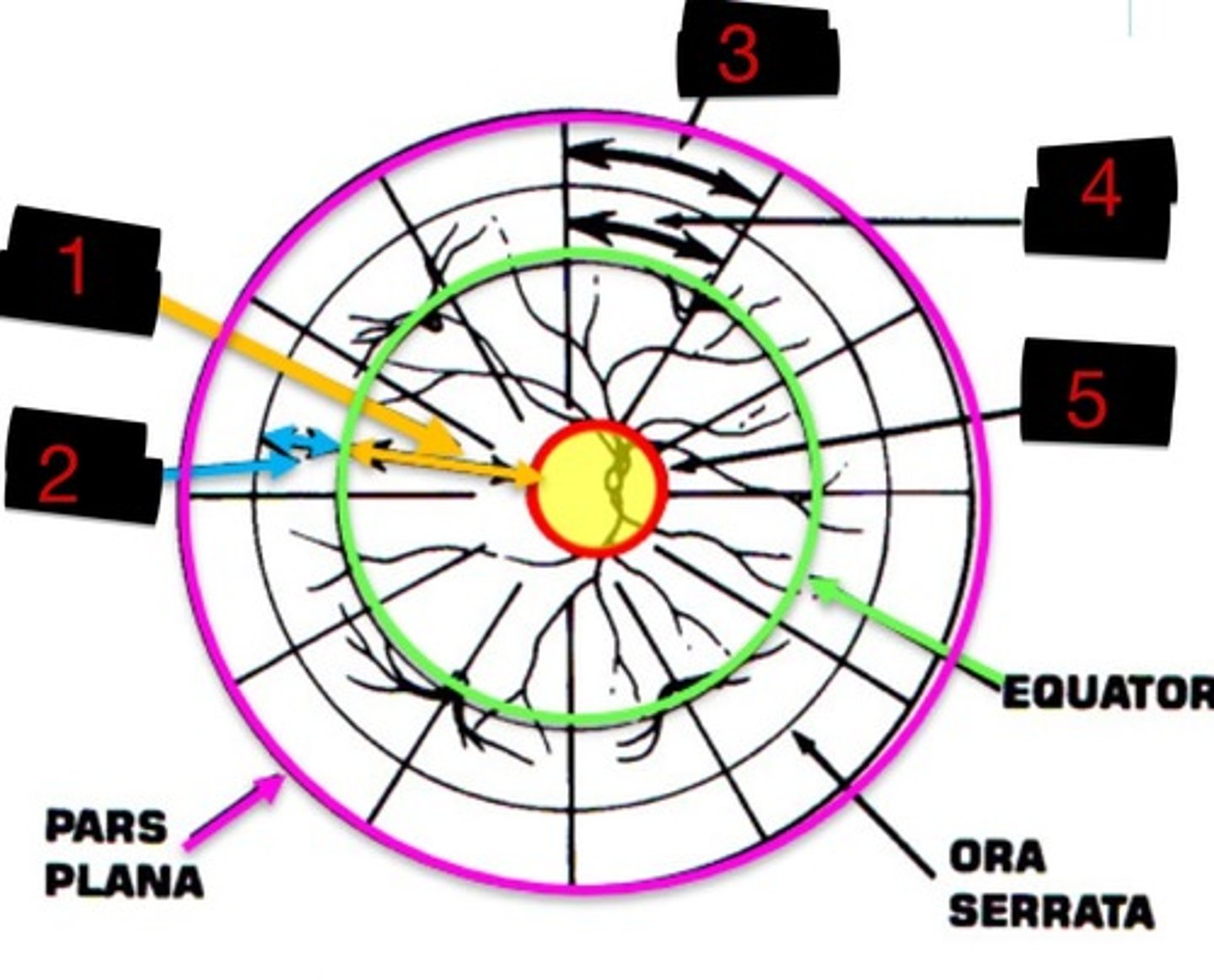
6DD
Label 4
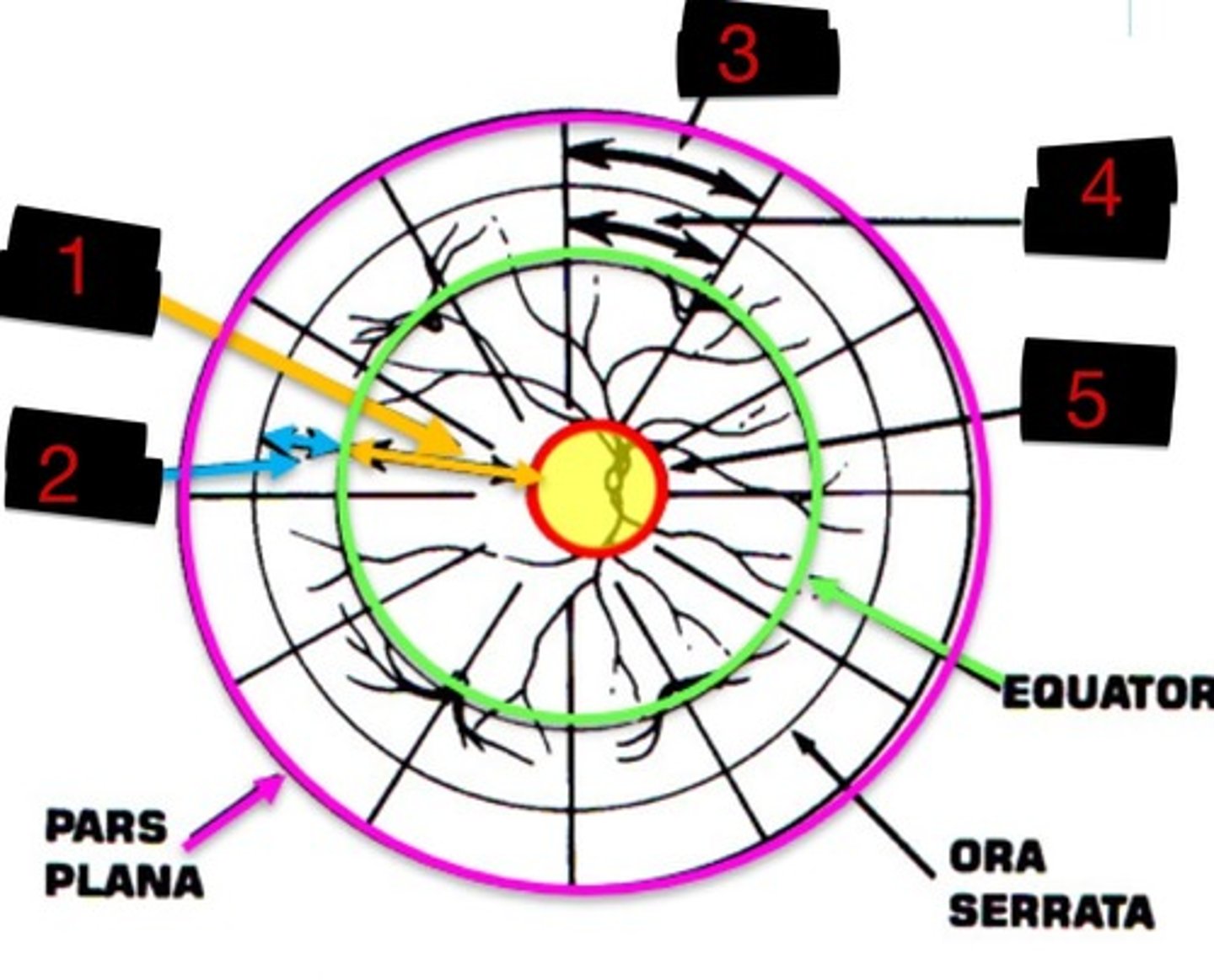
8DD
Label 5
Topical anesthetic
Benoxinate would be considered a ____________________________.
Topical anesthetic
Proparacaine would be considered a ____________________________.
Topical anesthetic
The mechanism of action for a ________________________ is to prevent the generation and conduction of nerve impulses.
Ester
All topical anesthetics used in optometry have an _______________ functional group.
Amide
If the functional group of an anesthetic is an ____________, it will have a longer duration of action and be metabolized by the liver.
Increase
As the length of the structure of the topical anesthetic increases, the potency will _____________.
Desquamation
For topical anesthetics, a complication can be _____________________ of the corneal epithelium which is more severe in patients with dry eye.
Retardation
For topical anesthetics, a complication can be _____________________ of the epithelial healing which inhibits epithelial mitosis.
False
T/F: It is okay to prescribe a topical anesthetic like proparacaine for patient take home use.
Self-administration
Due to corneal toxicity, ______________________ of a topical anesthetic is a contraindication due to the possibility of corneal scarring which can lead to permanent vision loss.
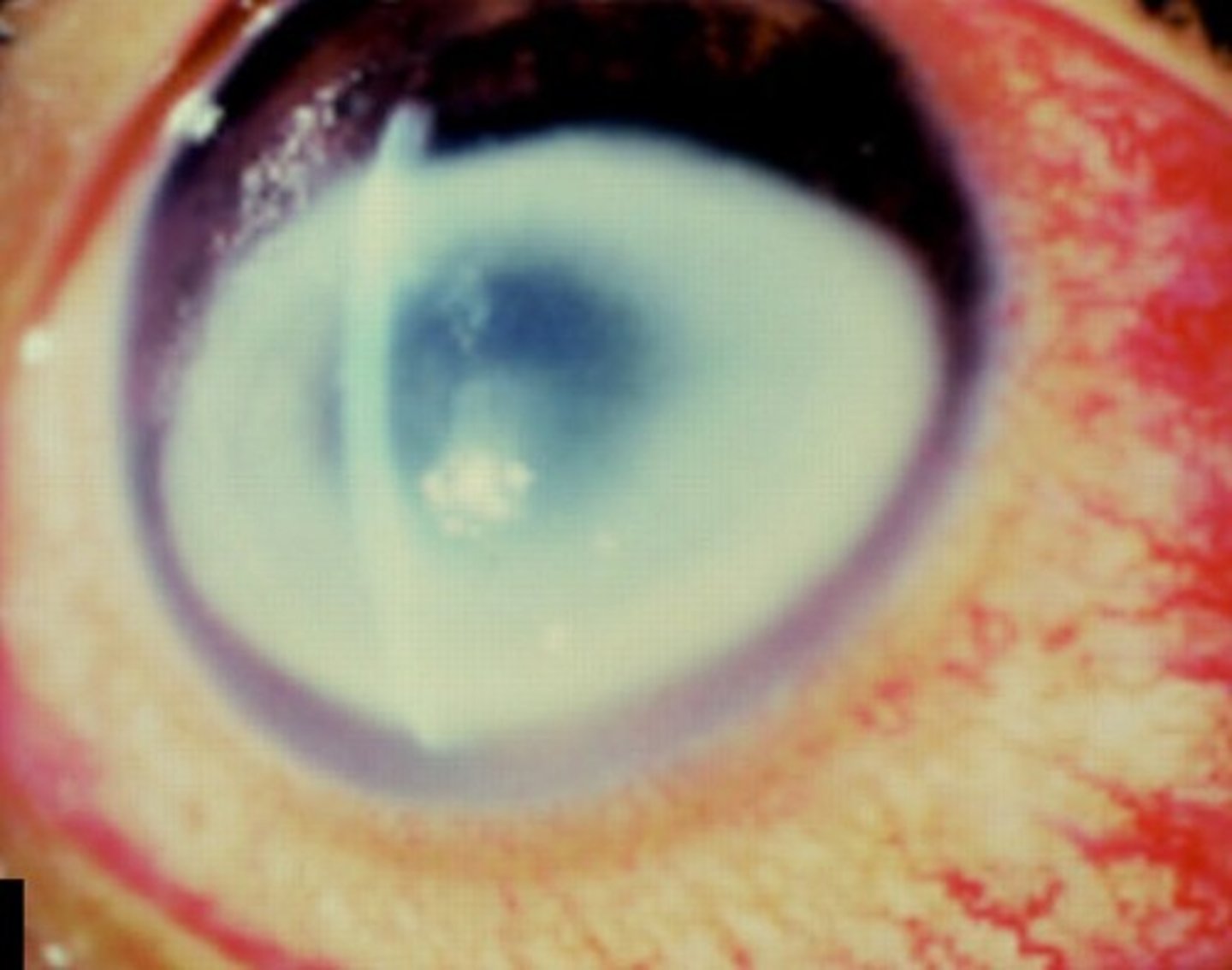
Topical anesthetic
Intense pain, severe tearing, and photophobia were the most common symptoms of patients who are abusing a _________________________.
Ring-shaped
57.7% of patients with anesthetic abuse keratopathy have a ____________________ opacification.
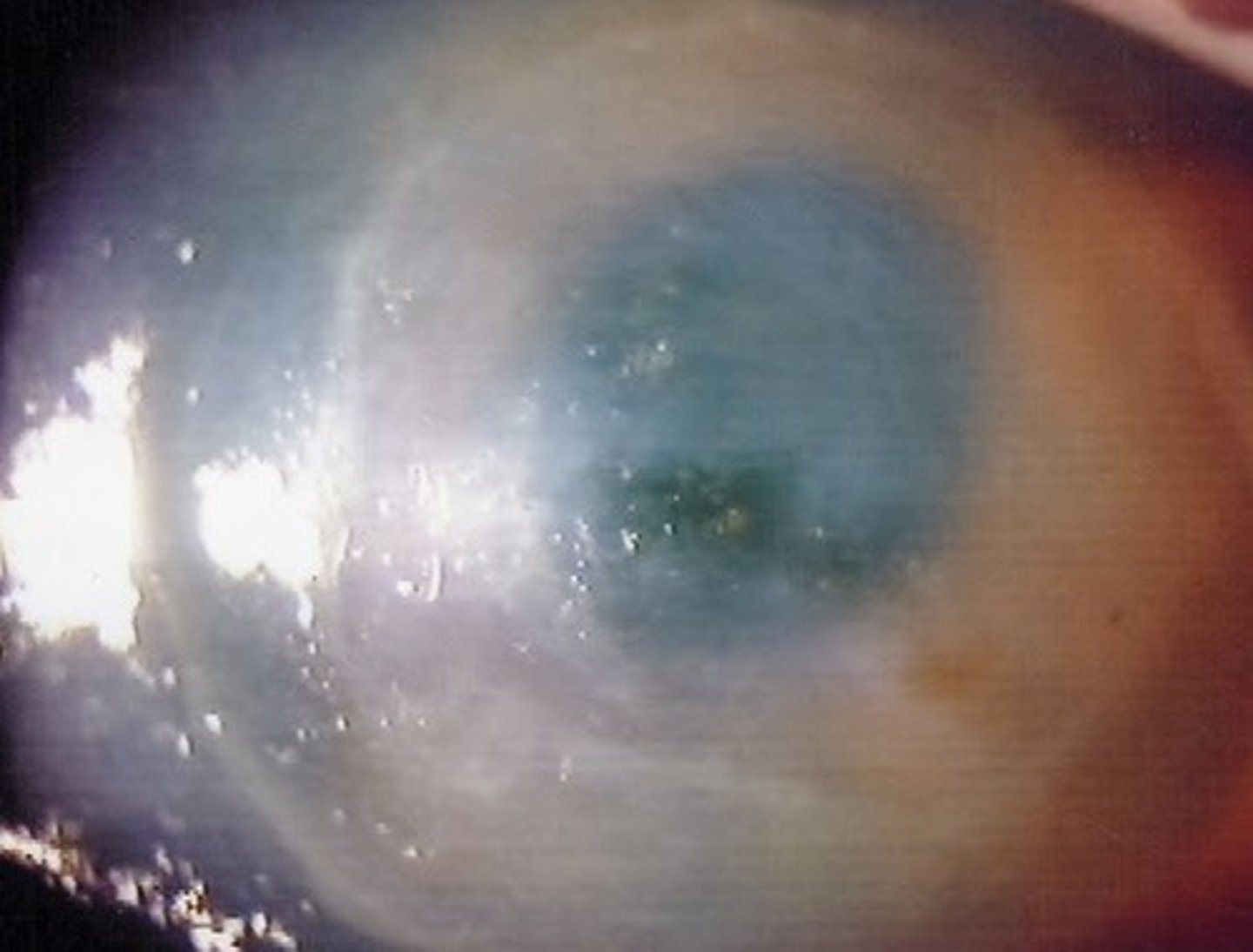
Hypopyon
An accumulation of pus in the anterior chamber of the eye is called a _________________ which is common in topical anesthetic abuse cases.
Proparacaine
Which topical anesthetic is least toxic to microorganisms?
Benoxinate
Which topical anesthetic is only available combined with fluorescein?
Fluorescein
Which dye absorbs blue (493nm) light and emits green (520nm) light?
Tight junctions
Disruption of _______________ at the epithelial surface leads to ingress around cells which can cause hyperfluorescence when using fluorescein dye.
False
T/F: Fluorescein stains the damaged cells themselves.
False
T/F: Fluorescein binds to cells to stain them.
Fluorescein
Which dye can only enter the epithelium where there is interrupted continuity of the epithelial surface?
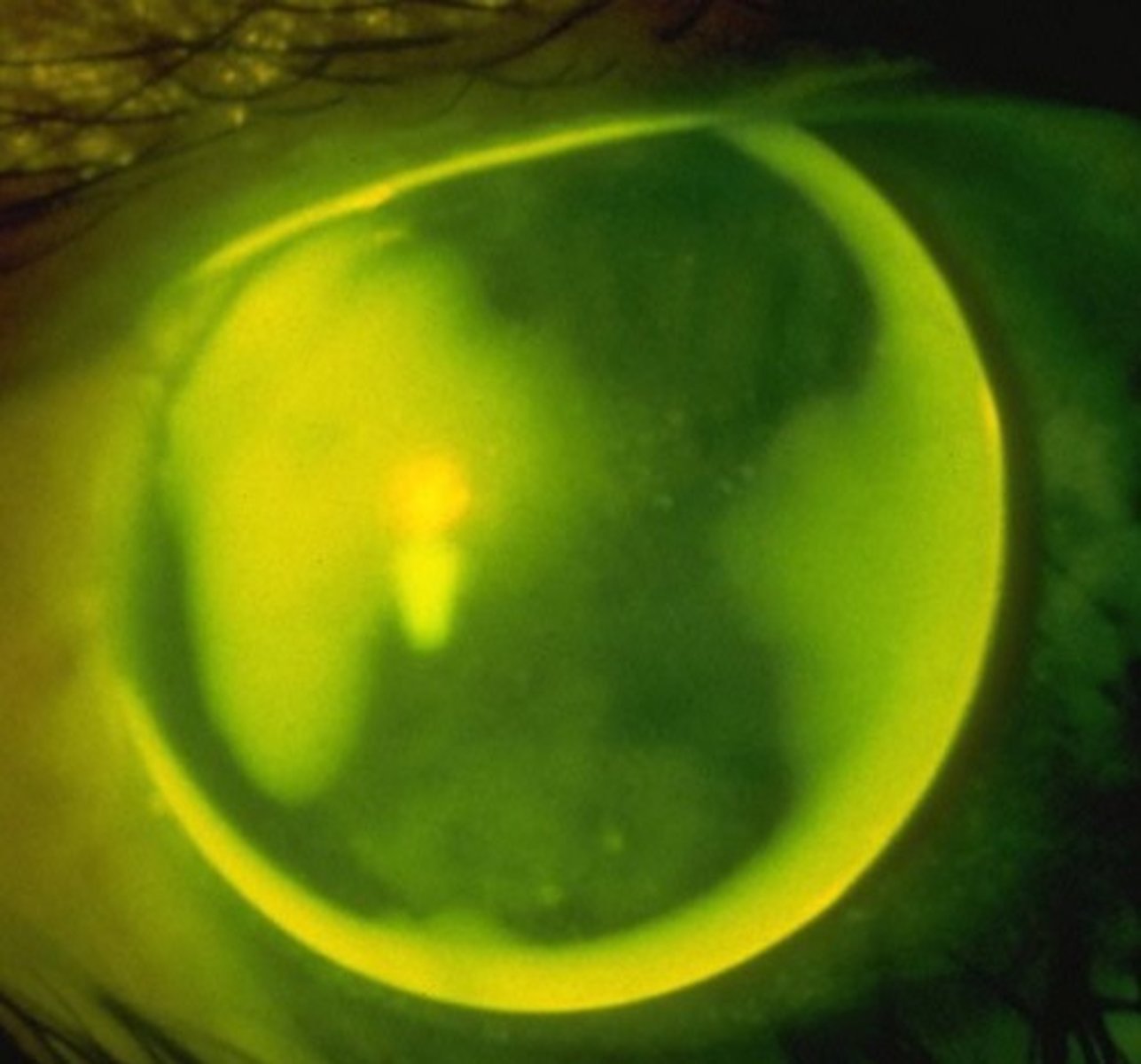
Against the rule
What type of astigmatism is shown here?
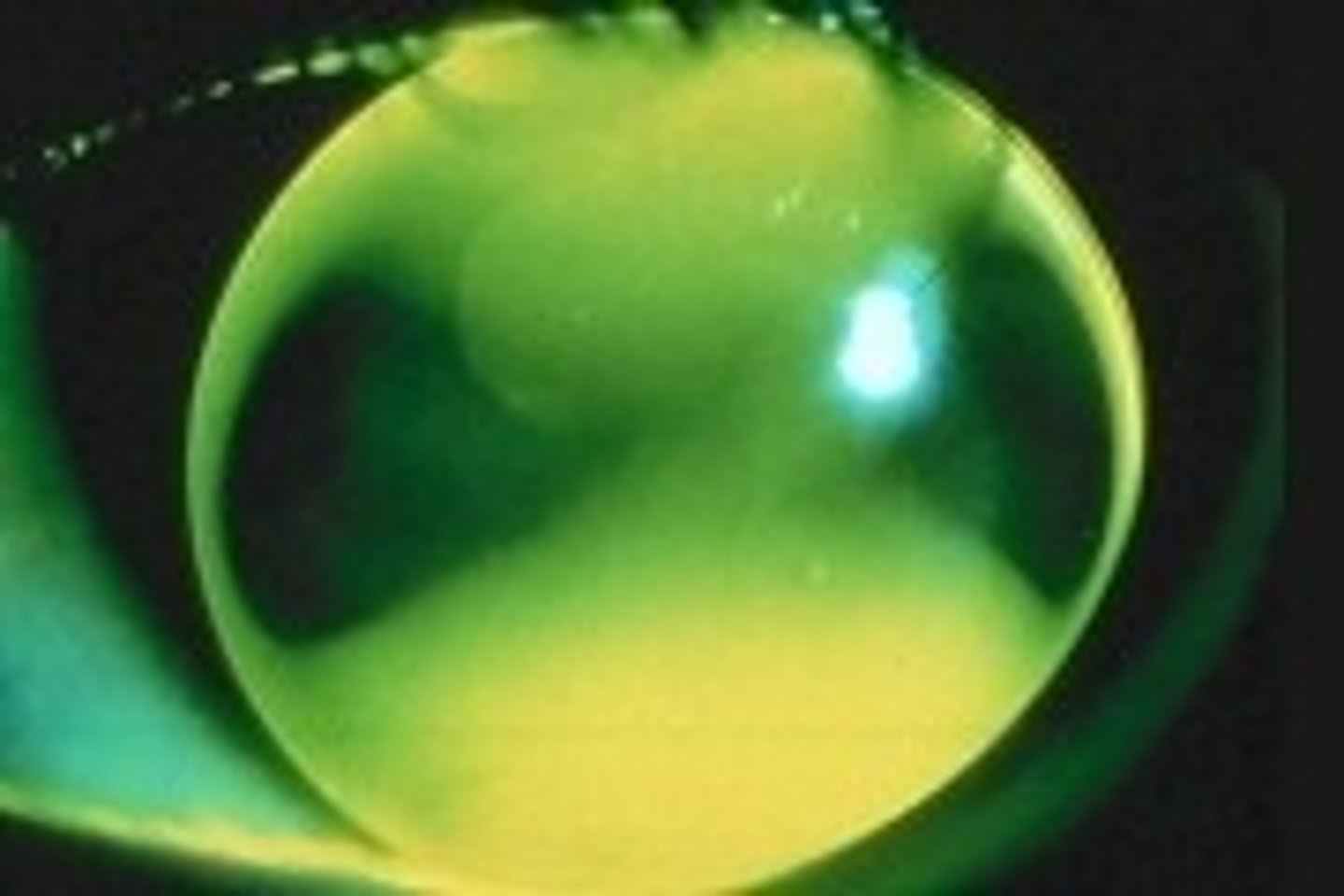
With the rule
What type of astigmatism is shown here?
Fluorescein
Which dye do we use for Jones test and TBUT?
Benoxinate
The presence of which topical anesthetic with fluorescein helps prevent bacterial contamination?
False
T/F: Rose bengal is a vital dye.
Rose bengal
Which dye is an iodine derivative of fluorescein that stains tissue pink or magenta?
Rose bengal
Which dye will instantly kill and then stain unprotected cells that are exposed to it?
Glycocalyx
The toxicity of rose bengal can be blocked by an intact ________________.
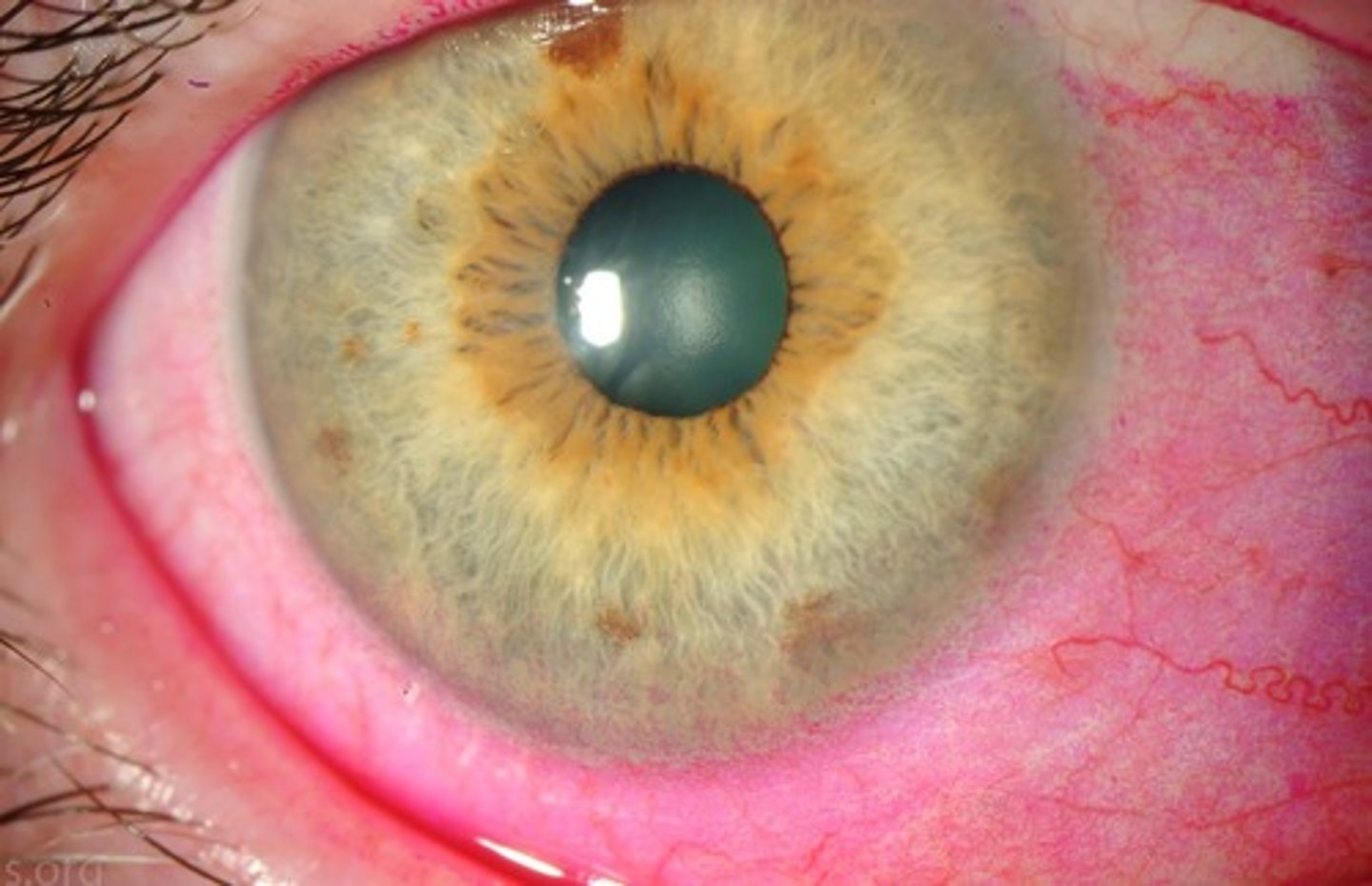
Rose bengal
Which dye is this:
Lissamine green
Which dye stains identically to rose bengal but is a vital dye?
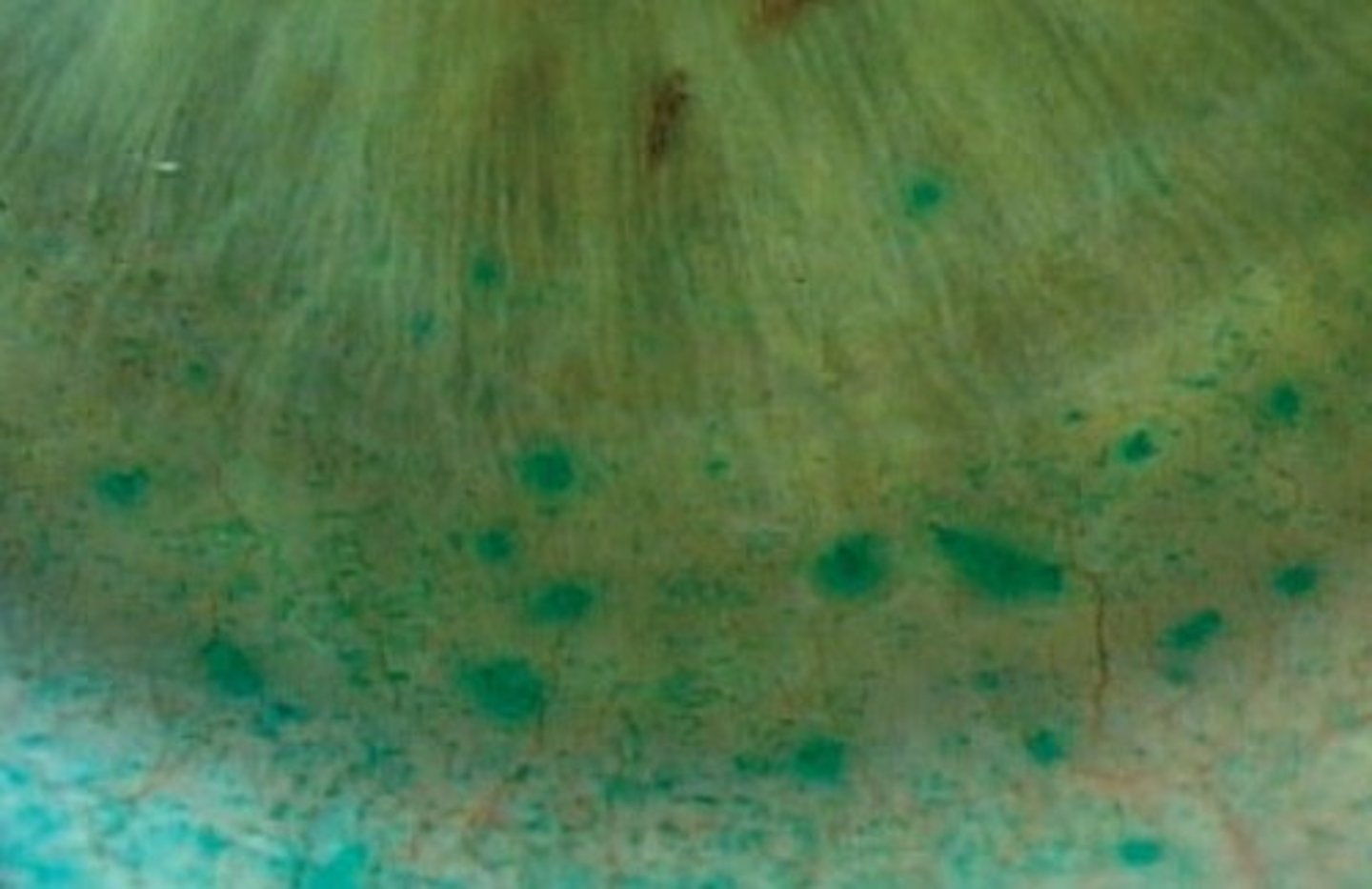
Lissamine green
Which dye is this:
Ester
If the functional group of an anesthetic is an ____________, it will have a shorter duration of action and be metabolized locally.
Lissamine green
Which dye is the best one to use for staining the conjunctiva?
Pilocarpine
What drug with a green cap is a muscarinic agonist?
Antimuscarinic
Tropicamide, cyclopentolate, and atropine are all considered what type of drug?
Tropicamide
Which antimuscarinic only lasts about 4-6 hours?
Antimuscarinic
Tropicamide is what type of drug?
Antimuscarinic
Cyclopentolate is what type of drug?
Antimuscarinic
Scopolamine is what type of drug?
Category C
All mydriatic/cycloplegic drugs are what pregnancy category?
Antimuscarinic
Spastic paralysis and brain injury are risk factors for potential CNS side effects from _________________ agents.
Atropine
The most potent and longest acting anticholinergic:
Antimuscarinic
Hot as a hare, Blind as a bat, Dry as a bone, Red as a beet, and Mad as a hatter - all describe systemic overdose symptoms of _________________ drugs.
Cyclopentolate
What is the drug of choice for routine cycloplegic refraction and commonly comes in a 1% solution?
Cyclopentolate
Which antimuscarinic readily crosses the blood-brain barrier and can cause transient psychotic reactions?
Cycloplegic refraction
A ________________ is necessary to diagnose latent hyperopia and pseudomyopia.
Phenylephrine
What drug is a DIRECT alpha-adrenergic agonist?
Cocaine
Which drug inhibits the reuptake of norepinephrine?
False
T/F: Phenylephrine is a cycloplegic agent.
10%
The __________ solution of phenylephrine is used to break posterior synechiae.
Phenylephrine
Tricyclic antidepressants and MAO inhibitor use are contraindications for use of which mydriatic drop?
Phenylephrine
Orthostatic hypotension and Malignant hypertension are contraindications for use of which mydriatic drop?
Phenylephrine
Systemic side effects of ______________________ include acute systemic hypertension, ventricular arrhythmia, tachycardia, and subarachnoid hemorrhages.
Hydroxyamphetamine
What alpha-adrenergic agonist is used for localizing lesions in Horner’s syndrome?
Apraclonidine
The process of developing super-sensitivity takes weeks to occur, therefore _________________ would not be a good differential in EARLY diagnosis of horner’s.
Hydroxyamphetamine
Dilation with __________________________ indicates the cause for the honer’s syndrome lies with either the 1st or 2nd order neuron.
Apraclonidine
Which drug does NOT dilate the normal pupil in Horner’s and relies upon norepinephrine supersensitivity because it is a very weak direct agonist?
False
T/F: Tropicamide is a pregnancy category B drug.
Dynamic contour tonometer
What type of tonometry is designed to be less affected by corneal properties even though it is still transcorneal?
False
T/F: Diaton tonometry requires an anesthetic.
3 mmHg
You have decided to start glaucoma therapy on the left eye of a patient. The baseline IOP is 25 mmHg and 28 mmHg in the right and left eyes, respectively. At the follow-up visit you find the IOP to be 20 mmHg OU. What is the treatment effect?
6 mmHg
You have decided to start glaucoma therapy on the right eye of a patient. The baseline IOP is 22 mmHg and 22 mmHg in the right and left eyes, respectively. At the follow-up visit you find the IOP to be 24 mmHg OD and 30mmHg OS. What is the treatment effect?
7 mmHg
You have decided to start glaucoma therapy on the right eye of a patient. The baseline IOP is 25 mmHg and 21 mmHg in the right and left eyes, respectively. At the follow-up visit you find the IOP to be 28 mmHg OD and 31mmHg OS. What is the treatment effect?
Manometry
The only method that is capable of recording the true intraocular pressure (invasive):
Pressure phosphene
The Provue tonometer is provided for home use and measures the ___________________ ("eclipse" or dark circle) in order to determine IOP.
Impact-rebound tonometry
A device with a ballistic-like mechanism that measures the return bounce of an object after impacting the eye:
Impact-rebound tonometry
Both iCARE and the Diaton tonometer are examples of _____________________________.
iCare
Which form of Impact-rebound tonometry is transcorneal?
Diaton tonometer
Which form of Impact-rebound tonometry is transpalpebral?
iCare
For use of the ________________________ device, no anesthetic or fluorescein is required, it has a disposable tip, and it records the average of 6 reliable readings.
Central corneal thickness
The iCARE tonometer has a good correlation with GAT and both devices are equally affected by __________________________.
True
T/F: iCare is a great option for pediatric patients.
iCare
Which tonometer is a useful screening tool that does NOT require a smooth regular cornea and is more comfortable than an air puff?
Diaton tonometer
Which tonometer analyzes the deceleration of a free-falling metal rod after impacting the eyelid?