ALL OF EDEXCEL PHYSICS PAPER 2
1/96
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
97 Terms
What are the different energy stores?
- Gravitational potential
- Elastic potential
- Electrostatic energy
- Kinetic energy
- Nuclear energy
- Magnetic energy
- Thermal energy
- Chemical energy
What are the different ways in which energy is transferred?
By heating
By electrical equipment
Through work done by forces acting over a distance
What is a sankey diagram?
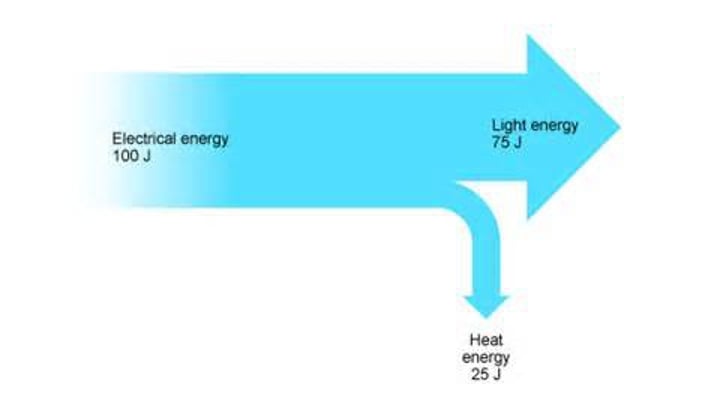
Explain conservation of energy.
Energy cannot be created or destroyed, only transferred between stores. When there are energy transfers in a closed system, then there is no net change to the total system.
What is the equation for work done?
Work done (J) = force x distance
What is equal to work done?
Energy transferred
1 J = 1 NM
What is the equation for gravitational potential energy?
GPE = m x g x h
What is the equation for kinetic energy?
KE = 1/2 x v^2 x m
What always happens to some of the energy in system changes?
Some of the energy is dissipated to the surroundings as waste energy, usually as heat energy
What is power?
Power is the rate at which energy is transferred, measured in watts.
Example: an electric heater with a power of 600W transfers 600J of energy per second.
What is the equation for power?
work done or energy / time taken.
What is one watt equal to?
One joule per second.
What is efficiency?
Useful/total
What are the non-contact forces?
- Gravity
- Electrostatic forces
- Magnetic attraction and repelling
What are the contact forces?
- Normal contact force
- Friction
What is the difference between vector and scalar?
Scalar has a magnitude only wheras vector has a magnitude and a direction
How do you draw free body force diagram?
It is all the forces acting on an isolated body with the sizes of the arrows showing the relative magnitudes of the forces.
What is the reactant force?
The reactant force is the total overall force on an object
What does a vector diagram look like if the object is in equilibrium?
The tip of the last force should end where the tail of your first force begins
What does it mean to split a force into it's components?
Forces can be split into the vertical and horizontal forces at right angles from each other. Acting together, these forces have the same effect as the single force.
How do you reduce unwanted energy transfer?
Through lubrication, which reduces energy transferred by friction in moving parts.
What way does conventional current flow in?
From the positive terminal to the negative terminal
What are the different circuit symbols?
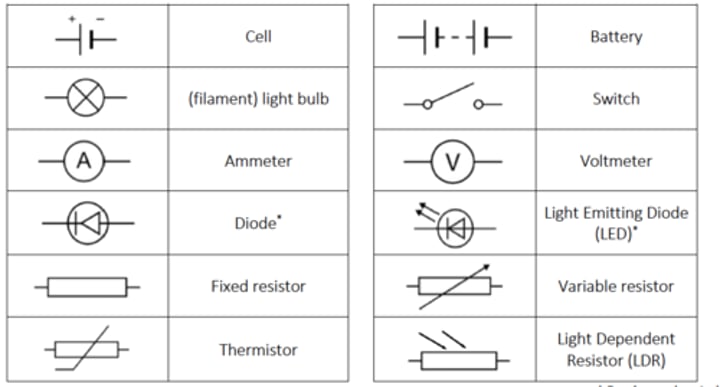
What are the differences between a series and parallel circuit?
- Series circuits only have one path around the circuit, which means that if you remove or disconnect a component it is broken and stops working completely.
The current is the same everywhere and the p.d. is shared.
- Parallel circuits have more than one path and each component is connected separately. Current conserved at a junction and p.d. the same
What is potential difference?
Potential difference is the energy transferred per unit charge and must be connected in parallel because the energy is used between two points.
It is measured in volts, a volt is therefore a joule per coulomb.
What is the equation for energy transferred?
Energy transferred = charge x potential difference (E = Q x V or E = I x T x V)
What is current?
Current is rate of flow of charge and is the flow of electrons in a metal.
Current is created when you have a source of potential difference and a closed circuit.
Current is also conserved at a junction.
What is the equation for charge?
Q = I x V
How does changing the resistance change the current and how can this be achieved using a variable resistor?
Due to Ohm's law, I = V x R so if the resistance increases, then the current must decrease (if p.d. is kept constant). They are inversely proportionate. This relationship can be shown through using a variable resistor to change the resistance and see how this affects the current.
What is the equation for potential difference?
V = I x R
Explain Ohm's law.
Ohm's law is the equation V = I x R. This means that if the potential difference increases, then the current also increases and they are directly proportionate. This also means that if the resistance increases, the current decreases. They have an inversely proportionate relationship.
What is resistance?
Resistance is the opposition to current. When there is more resistance, the current is lowered (due to Ohm's law)
Why, if two resistors are in series, the net resistance is increased?
- The potential difference is shared across all the components in a series circuit
- Therefore the potential difference across each resistor is lower, which means the current across each resistor is also lower (due to Ohm's Law V=I x R).
- Current is the same everywhere in a series circuit, so the total current is reduced.
- If the current is lowered, then the resistance is increased
Why does the total resistance decrease when you add resistors to a parallel circuit?
- The potential difference is the same across all branches/components in a parallel circuit.
- By adding more loops (in the parallel circuit), the current has more than one direction to go in which means that the total current in the circuit increases as more charge can flow through in a shorter amount of time.
- As potential difference is the same across all branches and due to ohm's law (V= I x R or rearranged I= V/R),if the current increases then the total resistance must decrease.
Why should you not let a circuit heat up?
Heat increases the resistance as it causes the current to decrease. The electrons move faster, colliding more with the metal lattice structure in the components which increases the resistance as it is harder for them to get through the components.
How does current also cause heat energy?
When an electric current flows through a resistor, it has to do work against resistance. This causes an electrical transfer of energy due to the electrons colliding with the lattice structure.
How does current vary with potential difference in a filament lamp?
The increasing p.d. and current increases the temperature of the filament because there are more electrons colliding with the lattice structure. This causes the resistance to increase as it's harder for the electrons to get through and therefore the current decreases as p.d. does.
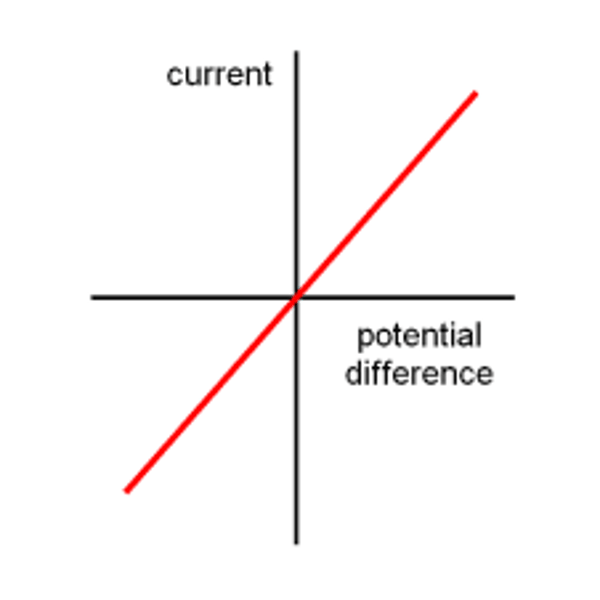
How does current vary with potential difference in a fixed resistor?
Follows Ohm's law and maintains a directly proportionate relationship. This is as long as the temperature stays the same (temperature increases the resistance).
The resistance is equal to 1/gradient.
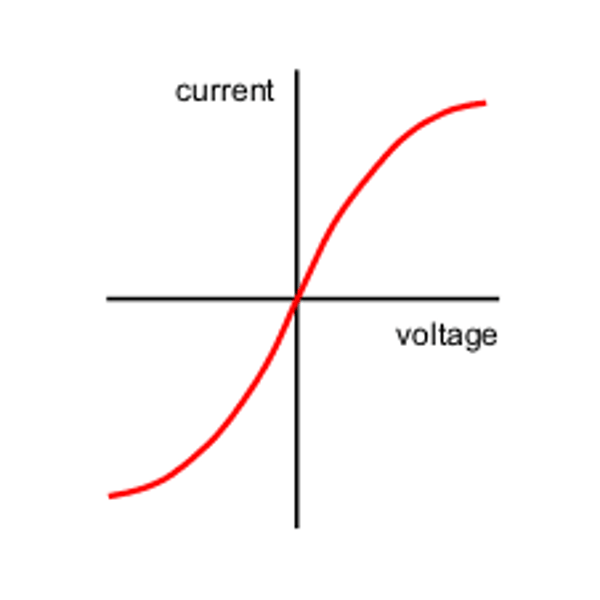
How does current vary with potential difference in a diode?
Current will only flow in one direction because of the high resistance in the opposite direction. This means that current cannot flow there. The resistance is very low in the other direction which allows current to decrease.
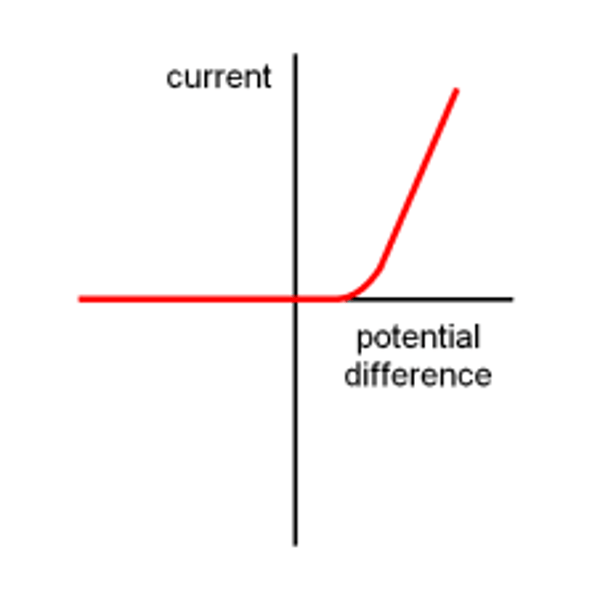
How does the resistance of a light-dependent resistor vary with light intensity?
The resistance decreases as the light intensity increases. This means that more current can flow through, and the energy transfer is greater. (E = I x T x V). It is used in outdoor lighting and automatic night lights as the current flow can be controlled by the light.
How does the resistance of a thermistor vary with change of temperature?
The resistance decrease as the temperature increases. This means more current can flow which means that more energy can be transferred. This is useful in thermostats and central heating devices as the current flow can be controlled by the temperature.
How can you reduce unwanted energy in a circuit?
Through using low resistance wires - less energy lost as heat as more current can pass through the component without heating it up (lattice structure)
What are the advantages and disadvantages of the heating effect of an electric current?
ADVANTAGES:
Electric heaters, used in fuses, filament bulbs and toasters work with a really high resistance wire so that it heats up.
DISADVANTAGES:
Reduces it's efficiency as less energy is transferred to the useful energy stores, components not working
What are the second equations for power?
P = I x V
P = I^2 x R
What is the difference between direct and alternating voltage?
Alternating voltage is where the positive and negative ends of the potential difference keep changing - this induces an alternating current and in direct voltage the potential difference is positive or negative
What is direct current?
Direct current is the movement of charge in one direction only and cells and batteries supply direct current (d.c.)
What is alternating current?
In alternating current (a.c.) the movement of charge changes direction
What is the UK mains supply?
An alternating current at 230 V and 50Hz
Describe the plug.
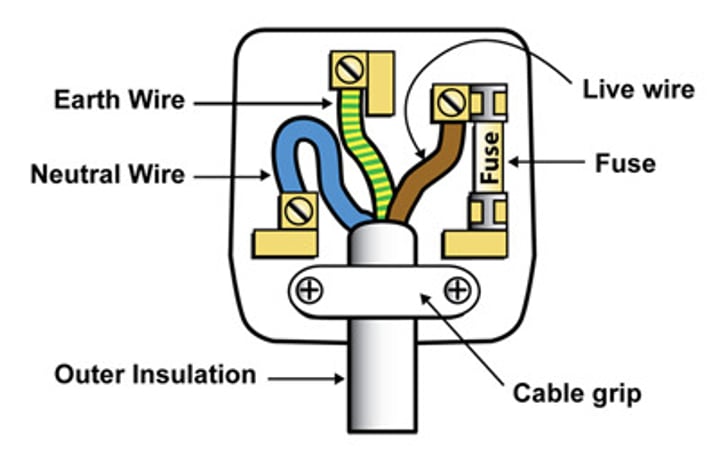
What is the function of the live wire?
The live wire carries the voltage to the appliance (230 V)
What is the function of the neutral wire?
The neutral wire completes the circuit as electricity flows out of this wire. (0 V)
What is the function of an earth wire?
If a fault develops which means that the live wire touches the metal case, then because the case is earthed, the current can flow through the case and out of the earth wire.
The earth wire connects to the metal parts of the plug and provides a direct route to the earth.
What is the function of a fuse?
A surge in current created by a fault melts the fuse when the amount of current is greater than the rating (as the current increases, heat also increases). This connects to the live wire so that the circuit is broken.
What is the function of circuit breakers?
A large current can 'trip' a circuit breaker, breaking a circuit. The large current creates a magnetic field around a coil of wire and iron bolt, which electro magnetises an iron bolt. This causes part of the circuit to move away from the closed position, breaking the circuit
Why is it dangerous to provide a connection between the live wire and the earth?
If you touch the live wire then a potential difference is produced across your body to the earth and a current can flow through you. This may kill or injure you. Even if the plug socket or a light switch is off, there is still potential difference in the live wire so if you made contact, your body would provide a link between live and the earth and a current would flow through you.
Any current flowing through towards the earth can cause a fire
What is a power rating?
This is the maximum safe power it can operate with, so it is the maximum amount of energy transferred between energy stored in a second.
What repels and what attracts?
Unlike magnetic poles attract and like magnetic poles repel
What are three main magnetic materials?
- Iron (looses magnetism very quickly)
- Nickel
- Cobalt
What are some of the uses of magnetic materials?
Fridge doors contain a permanent magnet in order to keep it closed
Cranes use induced electromagnets to attract and move magnetic materials
Doorbells use electromagnets which turn on and off repeatedly to attract and release an arm which strikes a metal bell
What is the difference between permanent and induced magnets?
Permanent magnets produce their own magnetic field all the time, whereas induced magnets only produce a magnetic field while they are in another magnetic field. This is why the force between a magnet and a magnetic material is always attractive as the south pole induces a north pole in the material.
What is the shape and field lines of a magnetic field around a bar magnet?
The field lines always go from north to south.
The closer the lines are, the stronger the magnetic field
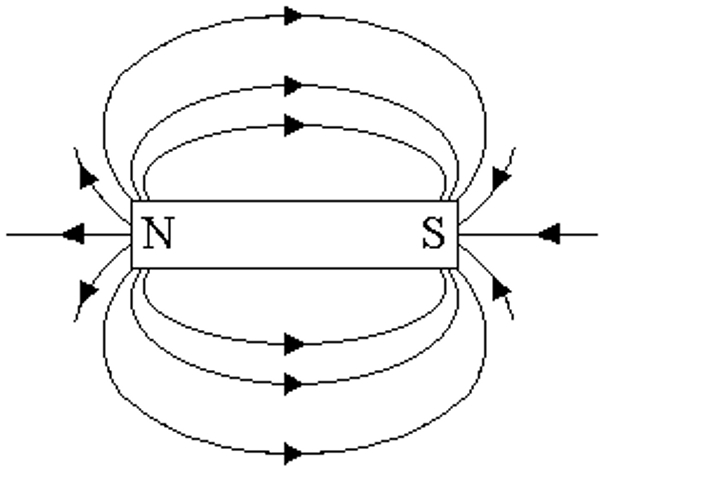
What is a uniform field?
Placing the north and south poles of two bar magnets creates a uniform field between the two poles.
How can you use plotting compasses to show the shape and direction of the field of a magnet?
- Put the magnet on a piece of paper and draw round it
- Place a compass on the paper and the needle will point in the direction of the field line
- Mark the direction of the compass needle and then placing it in a different direction
- Join up points to show the field lines
How is the behaviour of a magnetic compass related to evidence that the core of the earth must be magnetic?
Compasses always point to the earth's north pole because the earth generates it's own magnetic field (North pole is actually a magnetic south pole)
What can current do?
An electric current moving through a wire creates a magnetic field. This is made up of circles perpendicular to the wire.
Changing the direction of the current changes the direction of the field line (use the right hand thumb rule)
How can you increase the strength of the field?
- Increase the current going through the wire
- the shorter the distance from the wire, the stronger the field
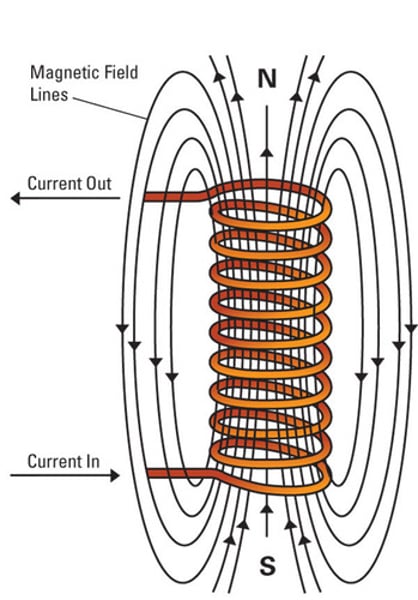
What is a solenoid?
A solenoid is a long coil of wire that a current flows through in order to produce magnetic field lines. The field lines add together to form a very strong almost uniform field along the centre. On the outside, the overlapping field lines cancel out to give a weaker field.
What is the motor effect?
The motor effect occurs when a current carrying conductor is placed near a magnet and the two magnetic fields interact to produce a force. To experience the full force, the wire has to be 90 degrees to the field
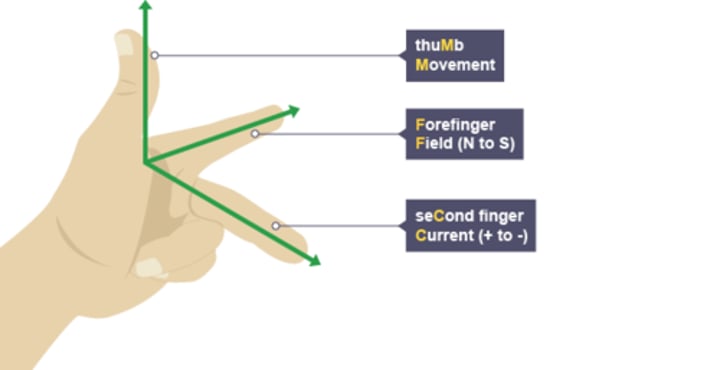
What is fleming's left hand rule?
Thumb = Motion
First finger = Field
Second finger = Current
What is electromagnetic induction?
Electromagnetic induction is where a wire is moved through a magnetic field and a changing potential difference is induced, or a magnet is moved through a coil of wire - this is because every time direction is reversed, potential difference is also reversed.
You also get an induced potential if the wire is kept still and the magnetic field is moved through the wire, but the magnetic field must be cut by the wires for the p.d. to be induced.
You can also induce a p.d. when the magnetic field changes
What are the factors that effect the size of the induced potential difference?
- The strength of the magnetic field/magnet
- The speed of movement
- Coils in a wire (creates a stronger magnetic field, as shown in a solenoid)
How does the induced current from the induced potential difference induce it's own magnetic field and how does this oppose the magnet's own field?
When a current is induced using electromagnetic induction, this current produces it's own magnetic field (as current going through a wire always induces a field). This magnetic field opposes the change that made the magnet, so a south pole will induce a south pole in the wire. When the south pole is moved out, the pole in the wire becomes a north pole which attracts the south pole.
Why do more coils increase the strength of the magnetic field?
Because of the field lines lining up to create an almost uniform field.
How can an alternating current in one circuit induce a current in another circuit in a transformer?
An alternating current in the primary coil induces an alternating magnetic field in an iron core (which is used because it looses its magnetism quickly) because the current in the wire produces a magnetic field and then the iron core becomes a temporary magnet.
Due to the generator effect, the alternating magnetic field induces a potential difference in the secondary coil, which then allows an alternating current to pass through the circuit
What do the transformers do?
Changes the p.d. (increases or decreases it).
A step-up transformer increases the potential difference (which increases the current)
A step-down transformer decreases the potential difference (which decreases the current).
Why are different transformers used in the national grid?
The national grid has to transfer lots of energy per second, which means that it needs a high power. In order to do this, there must be a high voltage or a high current. However, increasing the current makes wires heat up and increases the resistance, which reduces efficiency and wastes energy. So the voltage must be increased instead using a step up tranformer. At the end of the national gird, there is a step down transformer to reduce the potential difference (and increase current) so that it is usable for consumers
Describe the different states of matter in terms of the movement and arrangement of particles.
SOLIDS: Strong forces of attraction hold the particles together n a fixed, regular arrangement. They don't have much energy so can only vibrate around a fixed point
LIQUIDS: forces of attraction are weaker, particles are still close together but can move past each other to form regular arrangements. Random directions at low speeds
GASES: Almost no forces of attraction between the particles, particles have more energy and travel in random directions at higher speeds
What is the equation for density?
Mass/Volume
What is the experiment used to investigate the densities of solids and liquids?
- Measure the mass of the object using a mass balance
- Fill a eureka can with a known volume of water
- Place the object into the can, with the spout over a beaker
- Measure the displacement of water by pouring the water into a measuring cylinder
- Plug values into the equation
What are the differences in density between the different states of matter?
Particles in a solid are the most dense as the particles remain close together when they are a solid as opposed to a liquid - the volume is greater in a solid which also increases the density
What happens to mass during changes of state?
Nothing. Material also recovers it's original properties when it is reversed.
Explain how heating a system will change the energy stored within the system or cause a change in state
When a substance is changing state, you're still putting energy in but the temperature does not increase because the energy is being used to break intermolecular bonds, or bonds are being formed which releases energy so the temperature doesn't decrease until this is done
Define specific heat capacity.
Specific heat capacity refers to the amount of energy needed to increase the temperature of 1kg of a substance by 1 degree.
Define specific latent heat.
Specific latent heat is the amount of energy needed to change the state of one kg of a substance
How can you reduce unwanted energy transfer?
Through using thermal insulators such as polystyrene, which contains air pockets which trap the heat and prevent it from dissipating to the surroundings
Describe an experiment to measure the specific heat capacity.
1) Use a mass balance to measure the mass of the insulating container and then repeat with water inside and take this away from container to find the mass
2) Set up the equipment with a thermometer, an immersion heater that is connected to a joulemeter. Place a lid on the container and rhen measure temperature and record. Turn on the heater and wait until the temperature has increased by 10 degrees and then plug in values into equation
Explain the pressure of a gas in terms of the motion of it's particles.
As gas particles move about, they randomly bump into each other and the walls of the container. When they collide, they exert a force on the surface. This is pressure. The more particles there are in a given area, the more often they will collide with the walls of the container.
Explain the effect of changing the temperature of a gas
Energy is transferred to the kinetic stores of the gas particles and they move faster, so more particles hit the wall harder and more often, increasing the pressure
What is absolute zero?
Absolute zero is -273 degrees and is as cold as anything can get. At this temperature, there is no particle movement at all
How can you convert from kelvin to celsius and back again?
C to K you add 273 degrees
K to C you take away 273
What do you need for stretching, bending and compressing?
More than one force
What is the difference between elastic and inelastic distortion?
Elastic distortion is when the object can go back to it's original shape and length after the force has been removed.
Inelastic distortion is when the object does not return to it's original shape and length after the force has been removed.
What is the elastic limit?
The elastic limit is the point where an object stops distorting elastically and begins to distort inelastically.
What are the elastic relationships?
Extension is directly proportionate to force
What is the equation?
F = k x X
What stops after a while?
The relationship. As more force is applied, the object become inelastically distorted. There is a maximum point above which the graph curves. This is the limit of proportionality.
Describe an experiment to investigate the extension and force.
1) Measure the natural length of the spring with a ruler clamped to a stand. Add markers for greater accuracy
2) Add a mass to the reading and measure the new reading.
3) Repeat and plot in a graph.
To calculate work done, it's the area under the graph andthe gradient is the spring constant