Anatomy and Physiology Exam 1 content
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
germ cells (Haploid)
somatic cells (Diploid)
what are the two classifications of cells
plasma membrane
cytoplasm
nucleus
What are the three basic structures that all animal cells contain
The phosphorus head
What part of the phospholipid makes it hydrophilic?
integral or transmembrane proteins
ex. channel proteins
peripheral proteins
ex. enzymes
What are the two types of membrane proteins?
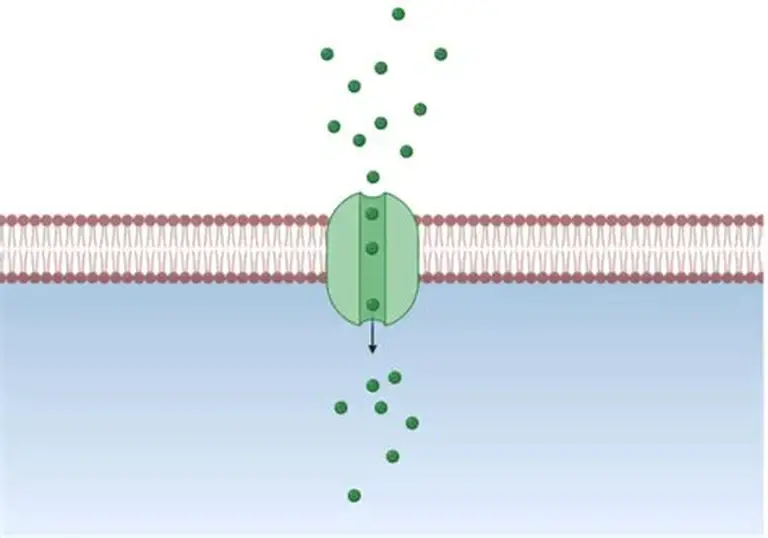
creates a channel in the membrane for facilitated diffusion (passive transport) of solutes
what is the role of channel proteins?
lipids, specifically phospholipids
What is the most critical part of the cell membrane?
lubricates and protects the plasma membrane as well as cell recognition
what is the role of glycocalyx?
integral proteins which join adjacent cells to create a tight seal between cells
prevents the movement of fluid and molecules in between cells
What are tight junctions?
link cells together like a zipper
prevents cells from breaking apart
what are desmosomes?
the use of ATP (energy)
what is the difference between passive and active transport?
diffusion
facilitated diffusion
osmosis
what are the three types of passive transport?
distance
molecule size
temperature
gradient size
electrical forces
what are 5 factors that influence diffusion?
the movement of water across a membrane
what is osmosis?
active transport
vesicular transport
What are the two active transport processes?
when large molecules need to be moved from an area of low concentration to high conecentration
When is active transport used?
creates a concentration gradient for sodium to enter the cell
what is the role of the sodium potassium pump?
Na- is pushed into the extracellular space to increase the difference in concentration (requiring ATP)
sodium potassium pump is phosphorylated creating ADP, changing the shape of the pump
allows for K+ to enter the ICF
rebinds ATP to the pump
describe the processes of the sodium potassium pump
an ion gradient created from primary active transport (sodium potassium pump)
What does secondary active transport rely on to take place?
the movement of large substances across a cell membrane using vesicles (active transport)
what is vesicular transport?
phagocytosis
pinocytosis
receptor mediated endocytosis
what are the three types of endocytosis?
Substances bind to specific receptor proteins which then get ingested into the vesicle
What is receptor mediated endocytosis?
the cell “gulps” ECF containing solute which is then brought into the cell (non-specific)
What is pinocytosis?
the cell engulfs a large particle using receptors which binds the cell around large micro-organisms
What is phagocytosis?
cytoplasm
the organelle found between the plasma membrane containing cytosol and organelles
cytosol (ICF)
contains dissolved ions, soluble and insoluble proteins and waste products
microfilaments (actin)
Intermediate filaments (keratin)
microtubules (mechanism for changing shape)
what are the three components of the cytoskeleton?
Endoplasmic Reticulum
a network of canals and sacs made of cell membrane, extends from the nucleus throughout the cytosol to the plasma membrane
lipid synthesis
detox
glycogen storage
calcium ion storage
what are the 4 functions of the smooth ER
synthesized proteins are packaged for transport
what is the function of the rough ER
Ribosome
organelle in charge of protein synthesis
proteasomes
organelles that contain protein digesting enzymes to remove denatured proteins
Golgi Apparatus
organelle that modifies and packages substances, renews the plasma membrane and packages special enzymes within vesicles for use in the cytosol
Cell recognition
What is the glycocalyx’s primary function?
what is the afferent pathway
the pathway before the “control centre” in homeostatic feedback loops
what is the efferent pathway
the pathway after the “control centre” in homeostatic feedback loops
extrinsic regulation
regulation that occurs in the nervous and/or endocrine system.
autoregulation (intrinsic regulation)
when an internal structure reacts to the stimulus. a change in the cell, tissue or organ. happening within.
Negative feedback consists of the system “shutting off” whereas positive feedback systems consist of "overloading” the system.
explain the difference between positive and negative feedback mechanisms
increased risk of disease
complications with aging
increased risk of destructive positive feedback loops
what are some of the issues associated with chronic homeostatic imbalance
Labour and Blood clotting
what are two examples of a positive feedback loop
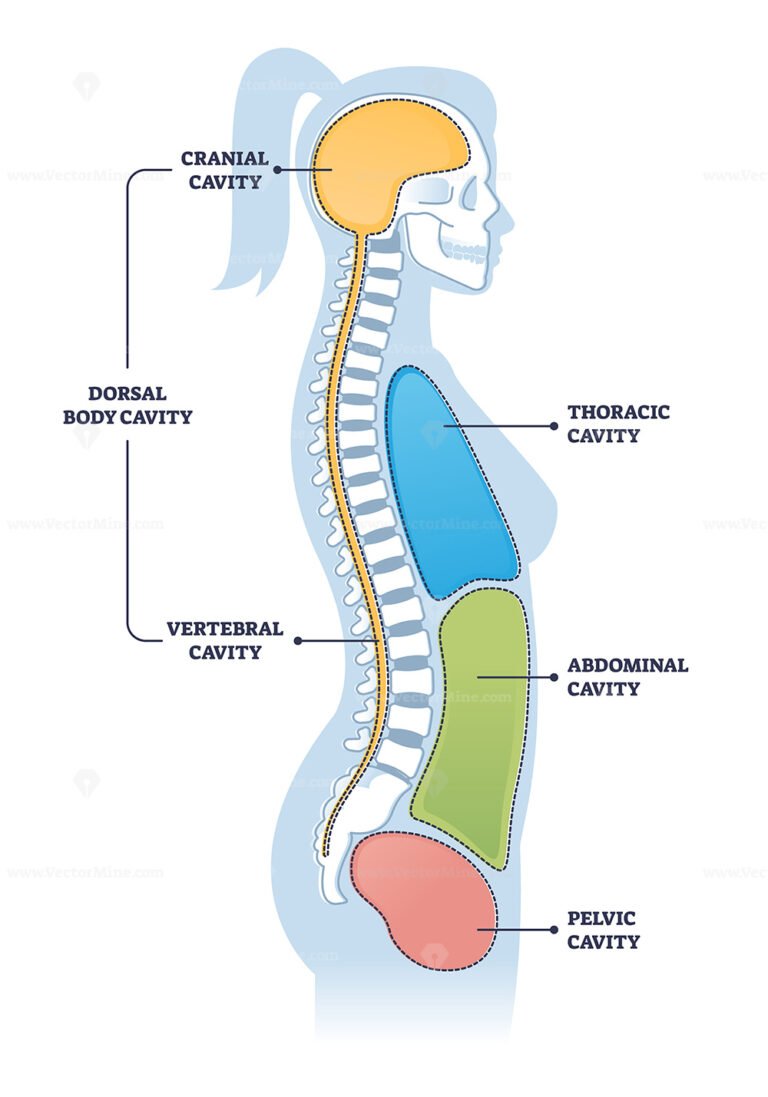
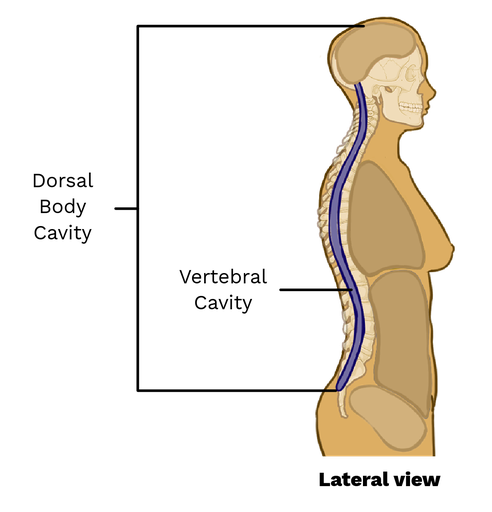
dorsal cavity
consists of the vertebral cavity and the cranial cavity which protects the central nervous system.
ventral cavity
consists of the thoracic and abdominopelvic cavities which protects the viscera
vertebral cavity
the cavity within the vertebral column that houses the spinal cord.
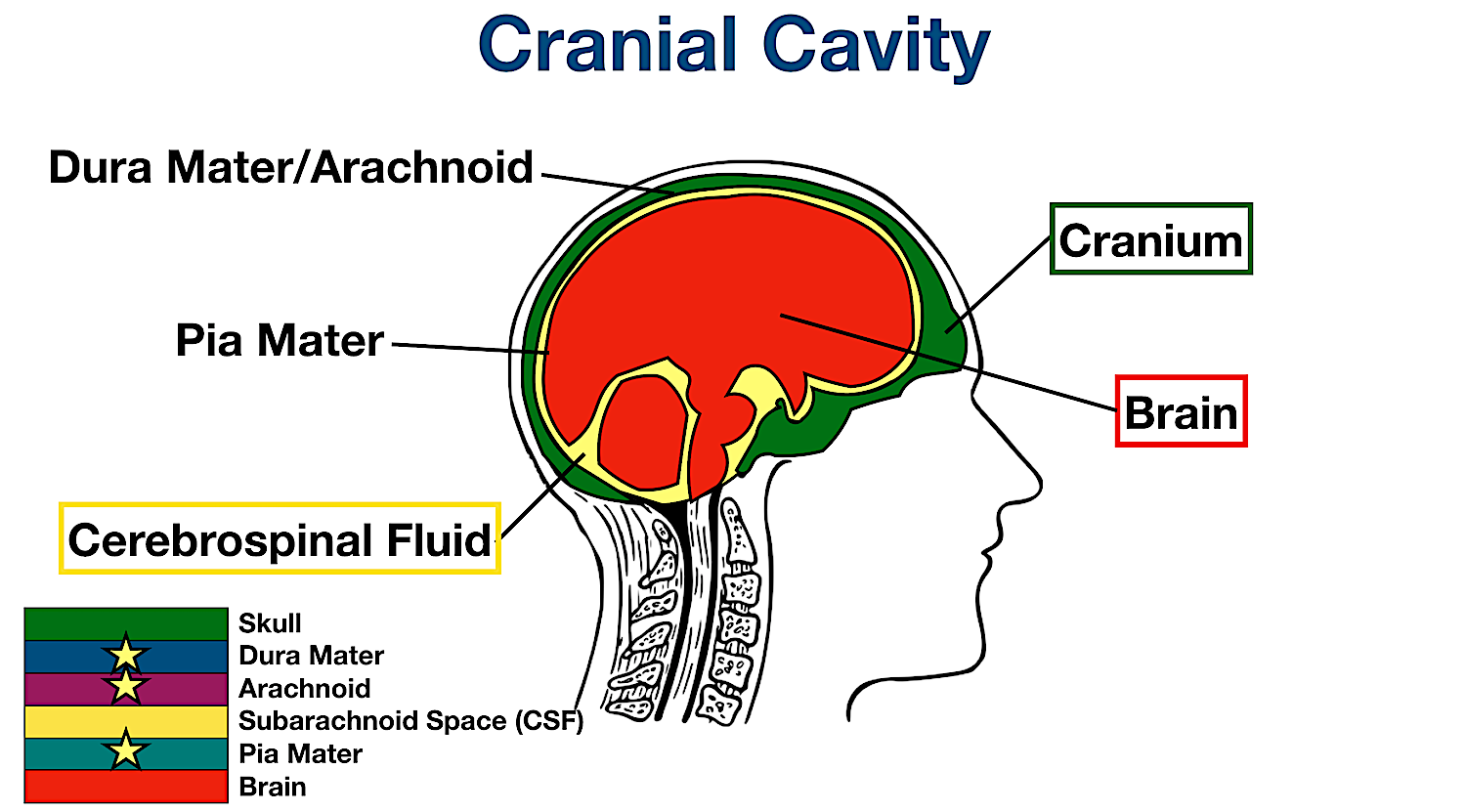
cranial cavity
the cavity that houses the brain and is surrounded by the skull.
thoracic cavity
The part of the ventral cavity located above the diaphragm, containing the lungs and heart.
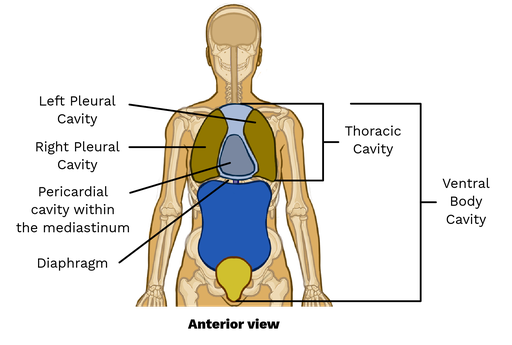
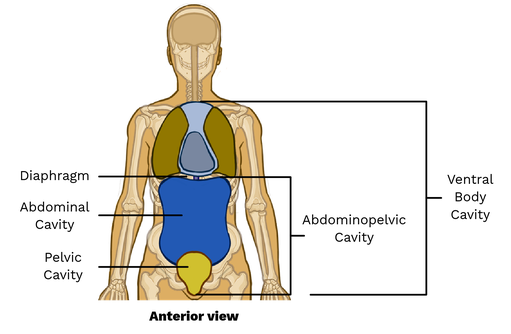
abdominopelvic cavity
the cavity located below the diaphragm that contains the digestive organs, urinary bladder, and reproductive organs.
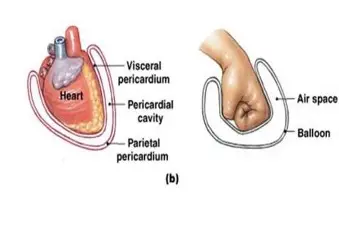
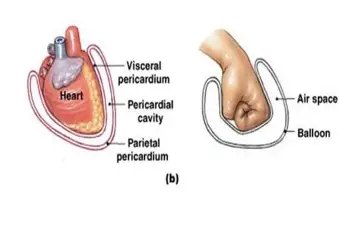
visceral
referring to the serous membrane directly touching the organ(s)
parietal
reffering to the serous membrane lining the cavity
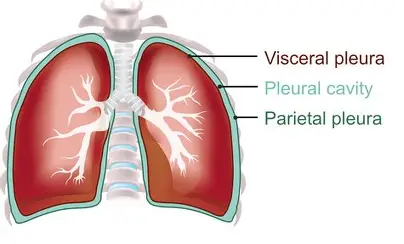
pleura
a serous membrane lining the thoracic cavity and covering the lungs.
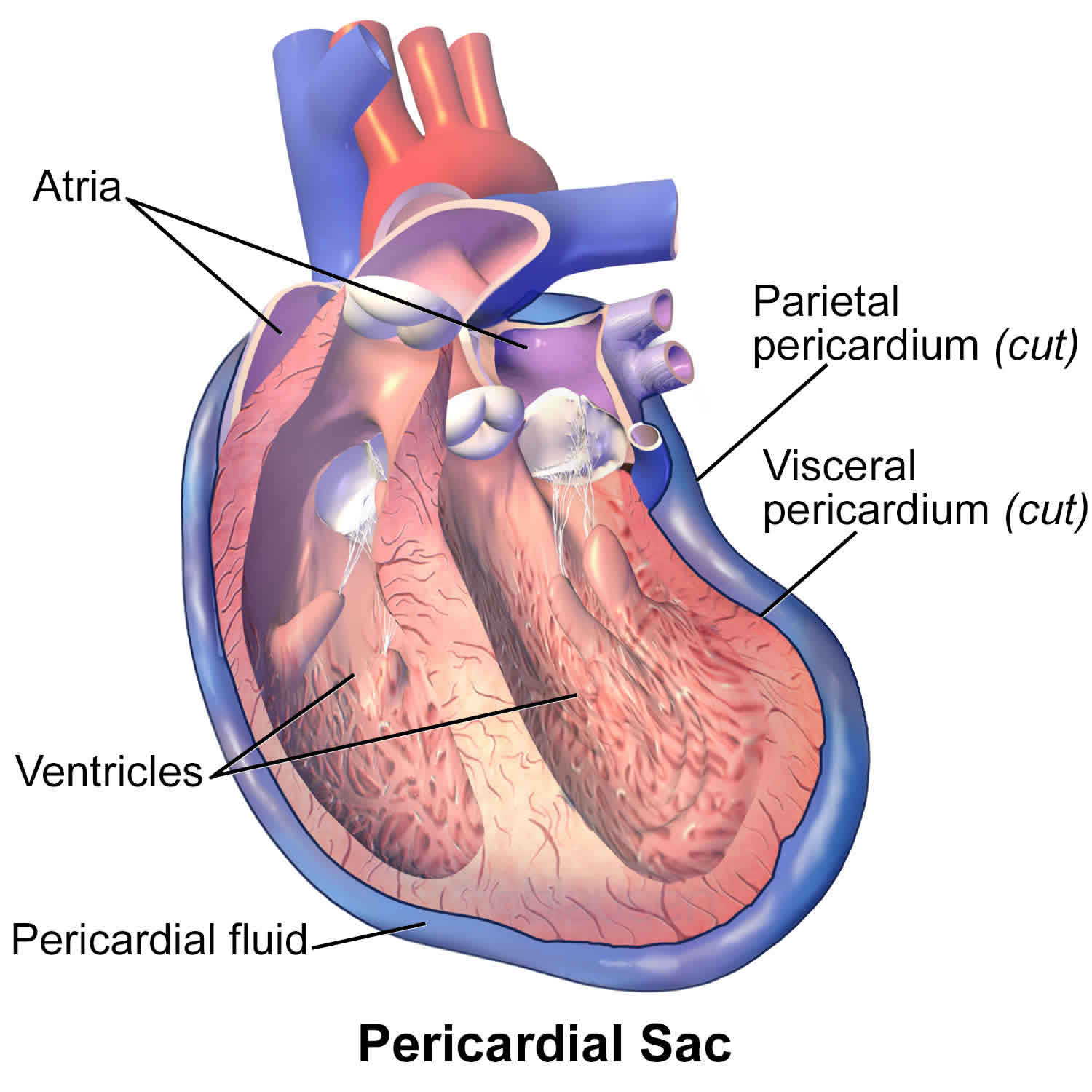
pericardial
referring to the serous membrane around the heart
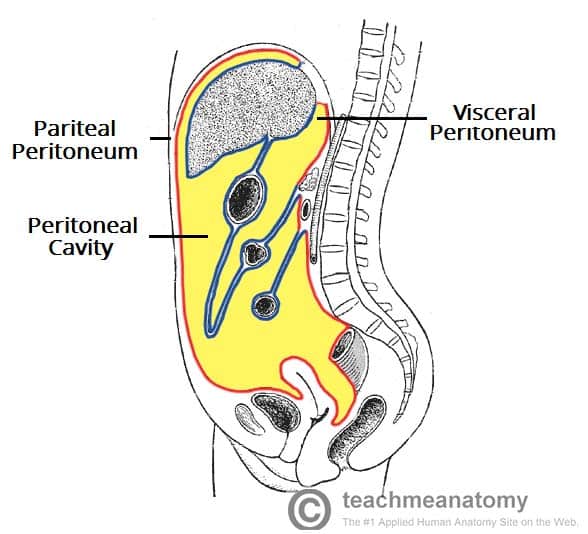
peritoneum
relating to the serous membrane around the digestive organs
perspiration and thermoregulation
what function does high heat vapourization provide for humans?
prevents accessive fluctuation in core body temperature to prevent things like frostbite.
what is the function of a high heat capacity in the human body
Carbohydrates (sugars)
which macromolecules are hydrophilic
Lipids (fats)
which Macromolecules are Hydrophobic
Diabetes Mellitus
What is the cause of Ketoacidosis
bicarbonate buffer system
respiratory compensation
carbonic acid- bicarbonate
what are the three types of buffer systems
Acidosis
when the blood pH drops below 7.35
Alkalosis
when the blood pH rises above 7.45
7.35-7.45
What is the homeostatic range of blood pH
Monosaccharides
What is the monomer of a Carbohydrate?
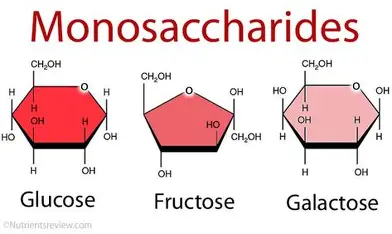
Glucose, Fructose and Galactose
What are the three monosaccharides?
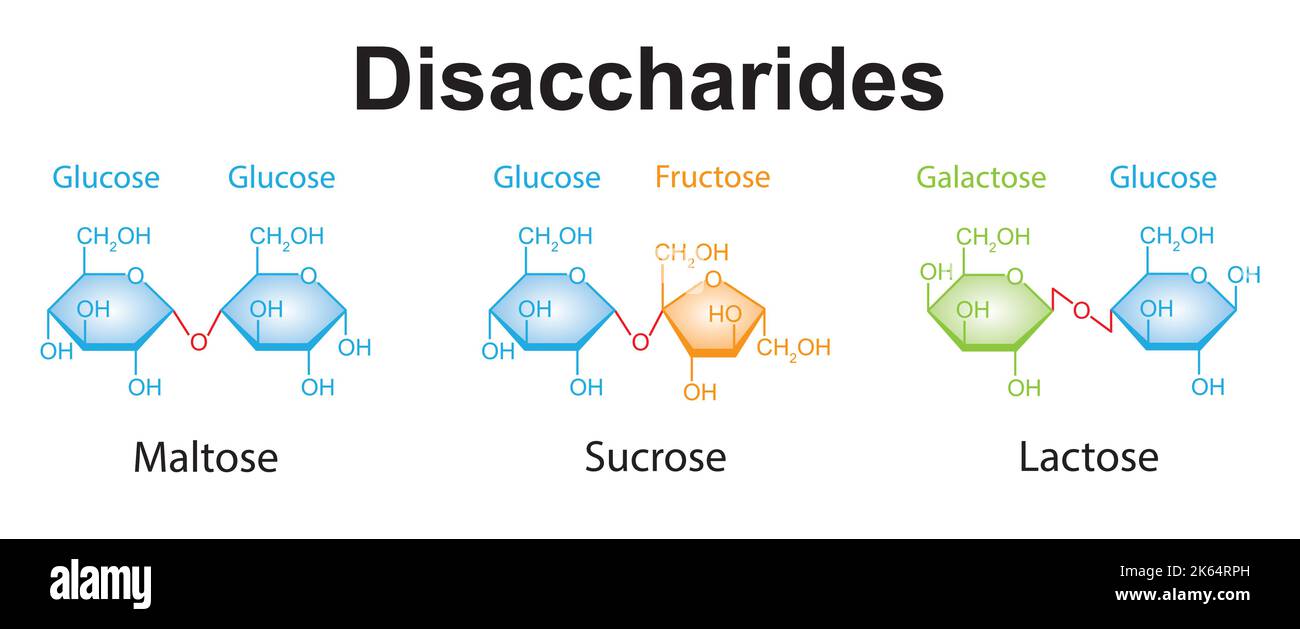
Sucrose, Lactose and Maltose
What are the three Disaccharides that we need to know?
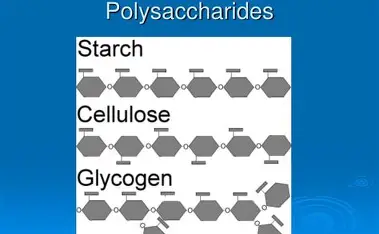
Cellulose, Glycogen, and Starch
What are the three polysaccharides that we need to know?
The middle Monomer in cellulose is mirrored which makes it difficult for animals to digest.
What is the difference between Cellulose and Starch?
Saturated fats contain only single bonds and are found in solid form at room temperature
unsaturated fats contain double bonds and are liquid at room temperature
Trans fats contain an extra Hydrogen (hydrogenated fats) to “fix” the structure of an unsaturated fat to remain solid at room temperature (ex. margarine)
What are the differences between a saturated, unsaturated and trans fats
fatty acids
eicosanoids
glycerides
phospholipids
glycolipids
steroids
what are the 6 classes of Lipids
Amino Acids
What are the monomers of Proteins?
Nucleotides
What are the monomers of Nucleic Acids?
an unsaturated fat has a bend at the double bond between carbons
What is the difference in structure between saturated and unsaturated fats?
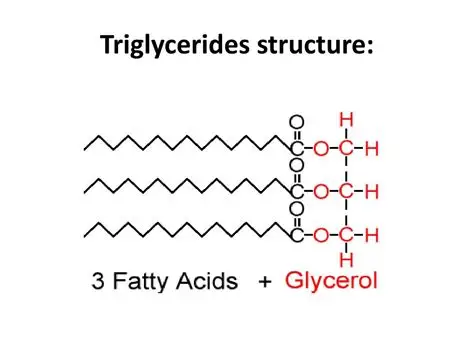
a glycerol and three fatty acid groups
What are triglycerides formed from
Cholesterol
What is the most important steroid in the body
Peripheral protein
what type of membrane protein is bound to the inner or outer surface of the membrane and can be separated easily
it strengthens the membrane while providing flexibility
what is the role of cholesterol in the cell membrane?
to prevent passage of materials between cells
What is the primary function of a tight junction
Cardiac muscle
What tissue type are gap junctions important in?
counter transport
What is it called when carrier proteins transport two molecules in opposite direction
Intermediate filaments
what part of the cytoskeleton provides tensile strength?
to propel substances across the surface of the cell
what is the role of cilia
Sperm cell
What is the only type of human cell with flagellum?
Lysosomes
which organelle contains digestive enzymes?
peroxisomes
which organelle functions to “detoxify” the cell?
synthesize proteins to be embedded into the cell membrane or exported to other parts of the body
what is the role of ribosomes in the rough ER?
nucleolus
Which organelle is in charge of ribosome synthesis
chemical
cell
tissue
organ
organ system
organism
what are the organizations of the body from smallest to largest
Before Control Centre: afferent
stimulus
receptor
input
After Control Centre: efferent
output
response
describe the 5 points on the “teeter totter” of homeostasis
specialized to specific substrates
saturation limits
what are the limitations on enzymes?
Fatty Acids
which type of lipid are the building blocks of all fat in the body and are made up of long hydrocarbon chains with a carboxylic acid group
Eicosanoids
which lipids are derived from arachidonic acids and are found in cell membranes
glycerides
which lipids are the result of a dehydration synthesis reaction between glycerol and fatty acids
steroids
which lipid is a large molecule with a 4 hydrocarbon ring skeleton. These lipids function in plasma membranes, sex hormones, tissue metabolism, mineral balance and bile salts
phospholipids
which lipids are formed from modified triglycerides with an added phosphorus head in place of a fatty acid chain. present in the cell membrane
glycolipids
which lipids have a structure of fatty acid chains, glycerol and a carbohydrate group
crenation
What is it called when a red blood cell is placed in a hypertonic solution causing contraction of the red blood cell?
Hemolysis
what is it called when a red blood cell is “ruptured” from being placed in a hypotonic solution?
Dehydration synthesis (synthesis meaning formation)
what is the process called in which the body creates large molecules from smaller ones. Ex. two monosaccharides form a disaccharide
hydrolysis (lysis meaning to break down)
what is the process called in which the body breaks down large molecules into smaller ones. Ex. breaking down polysaccharides into glucose through digestion
high heat capacity
high heat of vapourization
polar solvent
reactivity
lubrication
What are the 5 properties of water
Globular Proteins
proteins which are compact, soluble and found in the blood. Ex. antibodies, hormones and enzymes
fibrous proteins
tough, durable and insoluble proteins found in tertiary and quaternary structures. Ex. keratin, collagen