Lecture 16 - Amino Acids as Biosynthetic Precursors
1/56
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
57 Terms
Synthase vs. Synthetase
Synthetases: use ATP in the reaction
Synthases: do not use ATP
What is the goal of the one-carbon and methyl cycle?
To produce methyl groups for the various methylation reactions in the body
One-carbon cycle overview
- serine to glycine
- 5,10-methylene-THF reduction
- Transfer of the methyl group from 5-methyl-THF to homocysteine
Serine to glycine conversion enzyme
SHMT
- transfers hydroxymethyl group from serine
Does SHMT have catalytic activity?
No
What does SHMT rely on?
it relies on its cofactors, PLP and tetrahydrofolate (THF)
Role of PLP in SHMT activity
PLP takes the hydroxymethyl away from the serine forms formaldehyde (short-lived) and glycine
Role of THF in SHMT activity
Stores hydroxymethyl group after PLP has taken it off
Methyl group stored b/w N5 and N10 of THF
Reduction of 5, 10-methylene-THF
- Forms 5-methyl-THF
'Cut' a bond by reducing it and changes the cyclo- group to a methyl group
Reduction of 5,10-methylene THF enzyme
MTHFR
Where do the electrons come from for the reduction of 5,10-methylene THF?
Electrons for this reduction come from NADH that passes it to FADH2 that passes it to MTHFR
FAD is bound to MTHFR
After 5,10-methylene-THF is reduced...?
its methyl groups is transferred to homocysteine
Methyl cycle overview
- Homocysteine to methionine
- Formation of S-Adenosyl Methionine (SAM)
- S-Adenosyl homocysteine recycling
Homocysteine to methionine conversion
5-methyl-THF transfers a methyl group to homocysteine to form methionine.
Once 5-methyl-THF loses its methyl group it becomes..?
it becomes THF
Homocysteine to methionine enzyme
methionine synthase
What coenzyme is required for the conversion of homocysteine to methionine?
Coenzyme B12 (vitamin B12)
Where can we get vitamin B12
from a balanced diet
- Vitamin B12 is mainly found in dairy products, eggs, meat, fish and seafood
S-Adenosyl methionine (SAM) synthesis
Condensation b/w methionine and 5' carbon of a ribose to create SAM
- Frees 3 phosphate groups (pyrophosphate + ppi)
SAM synthesis enzyme
Methionine adenosyl transferase
What is the purpose of SAM?
SAM is the major methyl donor in many transmethylation reactions
What reactions in our body use SAM?
All methylation reactions in our body
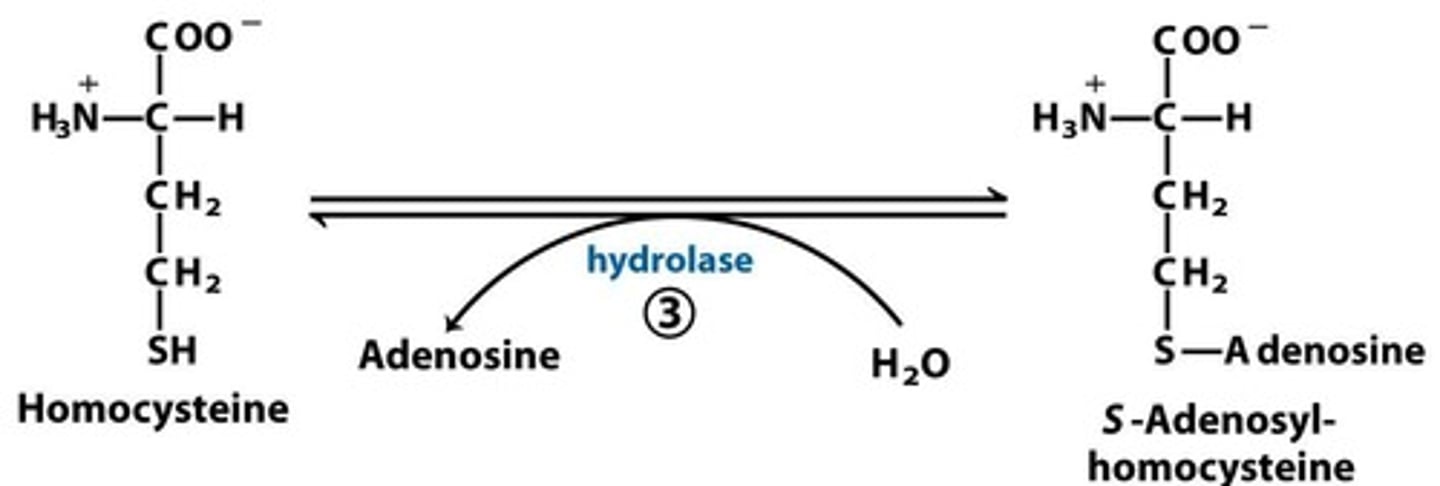
S-adenosyl-homocysteine recycling
S-adenosyl-homocysteine is hydrolyzed into homocysteine
Hyperhomocysteinemia (the methyl 'trap')
an accumulation of homocysteine because we can’t convert methionine to homocysteine w/o coenzymes
What causes hyperhomocysteinemia
low levels of:
Vitamin B12
Folate (THF)
Vitamin B6!!!
Risks associated with hyperhomocysteinemia
- Cardiovascular risks
- Neuropsychiatric illness (Alzheimer's schizophrenia, etc.)
Folate and B12 in pregnancy
Canadian women are given folic acid supplements during pregnancy to reduce the risk of neural tube defects (NTDs).
ex: Spina Bifida
MTHFR deficient alleles
Reduced methylation efficiency overall
high conc Serine regulation of pyruvate kinase (PK)
Serine is a positive allosteric regulator of pyruvate kinase
It increases the rate of glycolysis and shutdown the synthesis of serine.
Low conc Serine regulation of pyruvate kinase (PK)
the activity of PK will decrease leading to an increase of serine biosynthesis
How does inhibiting PK, promote serine synthesis?
When you inhibit PK, all the intermediates of glycolysis build up and the increased 3PG can go towards serine biosynthesis.
Serine regulation of PK is...
Completely independent of glucagon and insulin
Serine, glycine and cancer
In many cancers, the allosteric control of serine over PK is lost
Regardless of serine concentration, PK will be inhibited and serine biosynthesis will go on uncontrolled which allows for the uncontrolled proliferation of cancer cells.
Role of methylation
fine tune transcription
Example of methylation
X-chromosome inactivation
Methylation of histone proteins occurs at which amino acid residues?
Occurs at Arg or Lys residues in the protein sequence
How can Arg be methylated?
Arg can be methylated once (monomethylated) or twice (asymmetrically or symmetrically dimethylated)
How can Lys be methylated?
Lys can be methylated once, twice, or three times
Deregulation of DNA methylation was shown to play a role in...?
- Cancer genesis
- Ageing
Amino acids can also be precursors to or are...?
neurotransmitters
Excitatory neurons
cause other neurons to fire
Inhibitory neurons
prevent other neurons from firing
Amino acid neurotransmitters include...?
glycine, aspartate, and glutamate
Neurotransmitters derived from amino acids include...?
dopamine
GABA
Histamine
Serotonine
Which of the amino acid derived NTs are excitatory?
Aspartate
Glutamate
Histamine
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine
Which of the amino acid derived NTs are inhibitory?
GABA
Serotonin
Glycine
Which of the amino acid derived NTs are both excitatory and inhibitory?
L-Dopa
Dopamine
Tryptophan as a precursor of neurotransmitters
produces serotonin
Serotonin functions
Feel good neurotransmitter
regulation of intestine movement
Tyrosine as a precursor of neurotransmitters
produces..
- L-Dopa
- Dopamine
- Norepinephrine
- Epinephrine
Dopamine functions
Low levels of dopamine will affect your mood and energy level
The loss of 80% of dopaminergic neurons in the brain substantia nigra leads to development of Parkinson disease symptoms
What NTs are also hormones?
Epinephrine
Norepinephrine
Epinephrine & norepinephrine as neurotransmitters
Limited functions as NTs
Anxiety
Sleep
Metabolism
Histidine as a precursor of neurotransmitters
produced histamine
Glutamate as a precursor of neurotransmitters
produces
- Glutamate
- GABA
Glycine as a precursor of neurotransmitters
produces glycine
Aspartate as a precursor of neurotransmitters
produces aspartate