Market Efficiency & Elasticity
1/61
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
62 Terms
Market Efficiency
Producing the goods & services that society wants at the lowest possible cost.
Efficient Outcome
It is not possible to make someone better off without making someone else worse off.
Consumer Surplus
The difference between what a consumer is willing to pay and what they actually pay.
Producer Surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to accept for a good versus what they actually receive.
Total Surplus
The sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus in a market.
Deadweight Loss
The loss of economic efficiency that occurs when the equilibrium outcome is not achievable or not achieved.
Price Ceiling
A maximum price set by the government that can be charged for a good or service.
Price Floor
A minimum price set by the government that must be paid for a good or service.
Marginal Benefit Curve
A demand curve that reflects the maximum price a consumer is prepared to pay for a good.
Net Gain
The difference between the total benefit received and the total cost incurred.
Consumer Surplus
The difference between what consumers are willing to pay for a good or service and what they actually pay.
Marginal Benefit
The additional satisfaction or utility that a consumer receives from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
Willingness to Pay
The maximum amount that a consumer is willing to spend on a good or service.
Producer Surplus
The difference between what producers are willing to accept for a good or service and what they actually receive.
Supply Curve
A graphical representation that shows the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied.
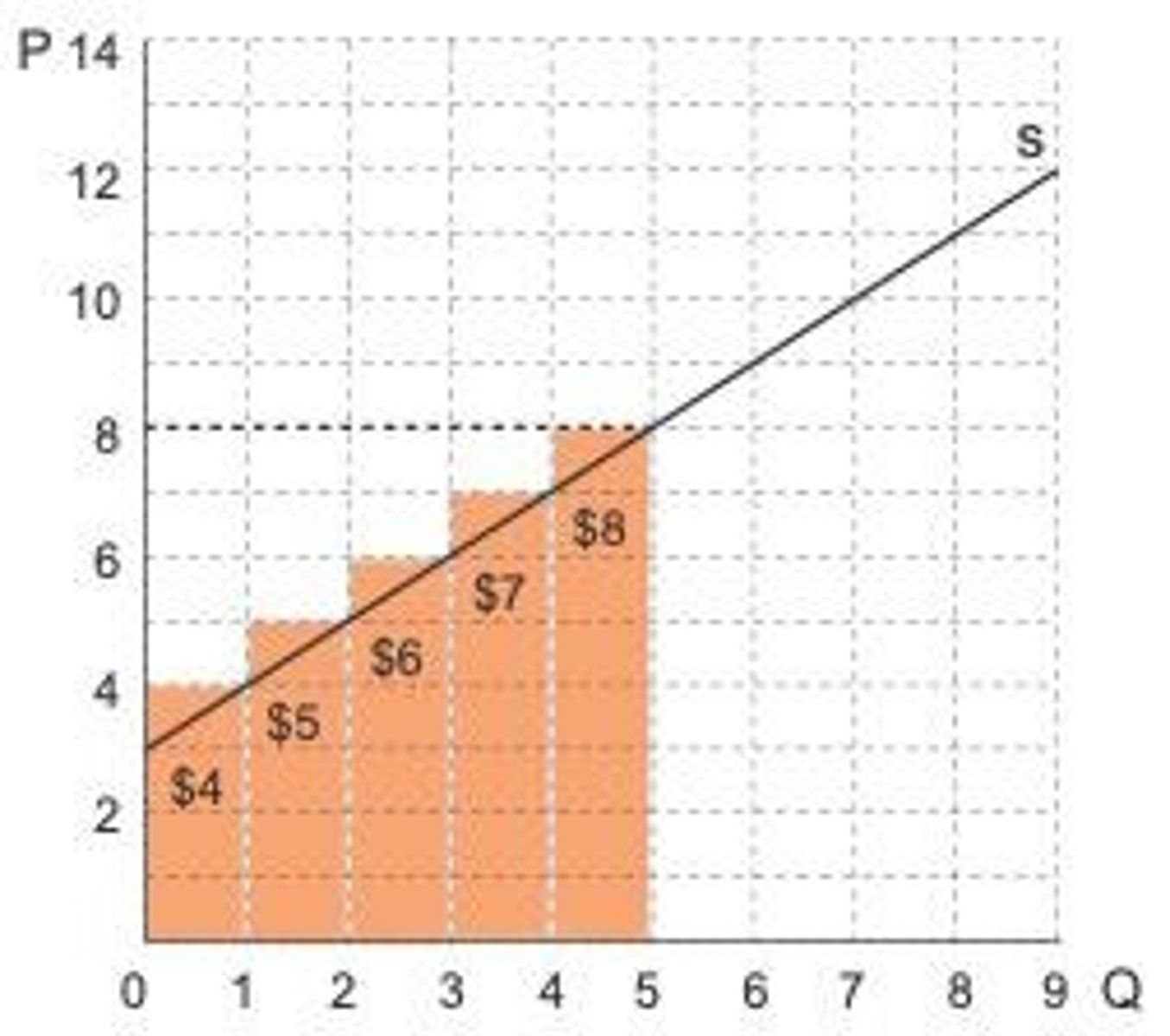
Marginal Cost Curve
A curve that reflects the minimum price a producer is prepared to receive for a good, representing the cost of producing one more unit.
Total Revenue
The total amount of money a firm receives from selling its goods, calculated as price multiplied by quantity sold.
Net Gain
The difference between total revenue and total costs, indicating profit.
Market Efficiency
A situation in which resources are allocated in a way that maximizes total surplus, which is the sum of consumer and producer surplus.
Economic Welfare
The overall well-being of individuals in an economy, often measured by the levels of consumer and producer surplus.
Allocation Method
The process by which goods and services are distributed among consumers.
First-Come, First-Served
An allocation method where goods are distributed based on the order in which consumers arrive.
Sharing Equally
An allocation method where goods are divided equally among consumers.
Contest
An allocation method where goods are distributed based on competition among consumers.
Market Price
The price at which a good or service is sold in a competitive market.
Consumer Surplus Calculation
For James, if he pays $42 for 7 pizzas and his total benefit is $63, his consumer surplus is $21.
Increase in Producer Surplus
If the price rises, there will be an increase in producer surplus because producers will sell more at a higher price.
Supply Curve
The supply curve shows the minimum price that firms must receive to supply a certain quantity of a good.
Producer Surplus Condition
Producer surplus will be positive when the price exceeds marginal cost.
Total Surplus
Total surplus is a measure of the economic welfare that a market creates for consumers and producers.
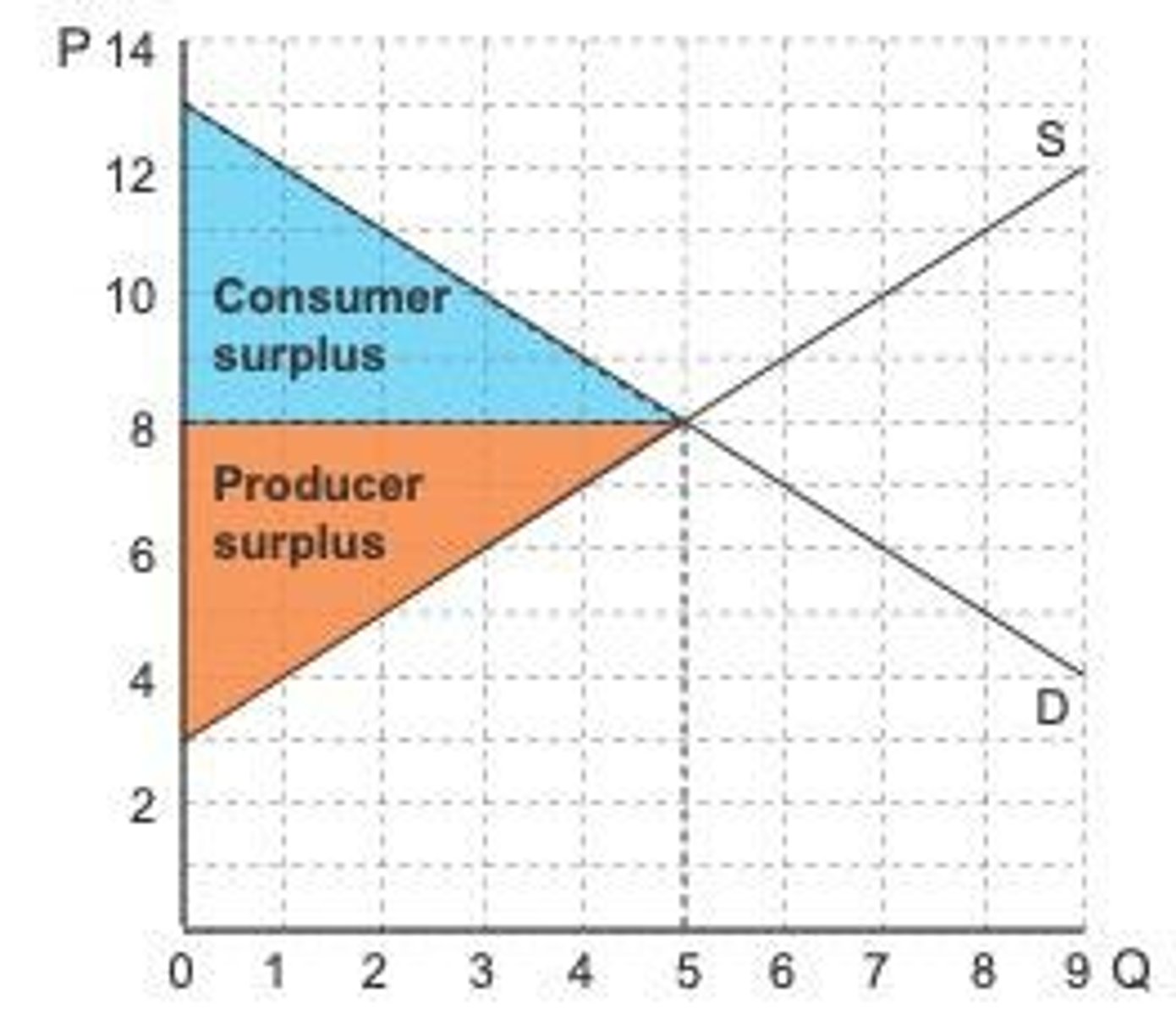
Total Surplus Formula
Total surplus = consumer surplus + producer surplus.
Economic Efficiency
Economic efficiency occurs when total surplus is maximised.
Equilibrium Price & Quantity
Total surplus equals a maximum only at the equilibrium output.
Deadweight Loss
When total surplus is reduced because of either under or overproduction, it is referred to as a deadweight loss.
Government Intervention
When governments intervene in markets they may decrease economic efficiency.
Market Restrictions
Examples include market restrictions, price ceilings, price floors, taxes, and subsidies.
Price Ceiling Definition
A price ceiling is a legislated maximum price that sellers are allowed to charge in the market.
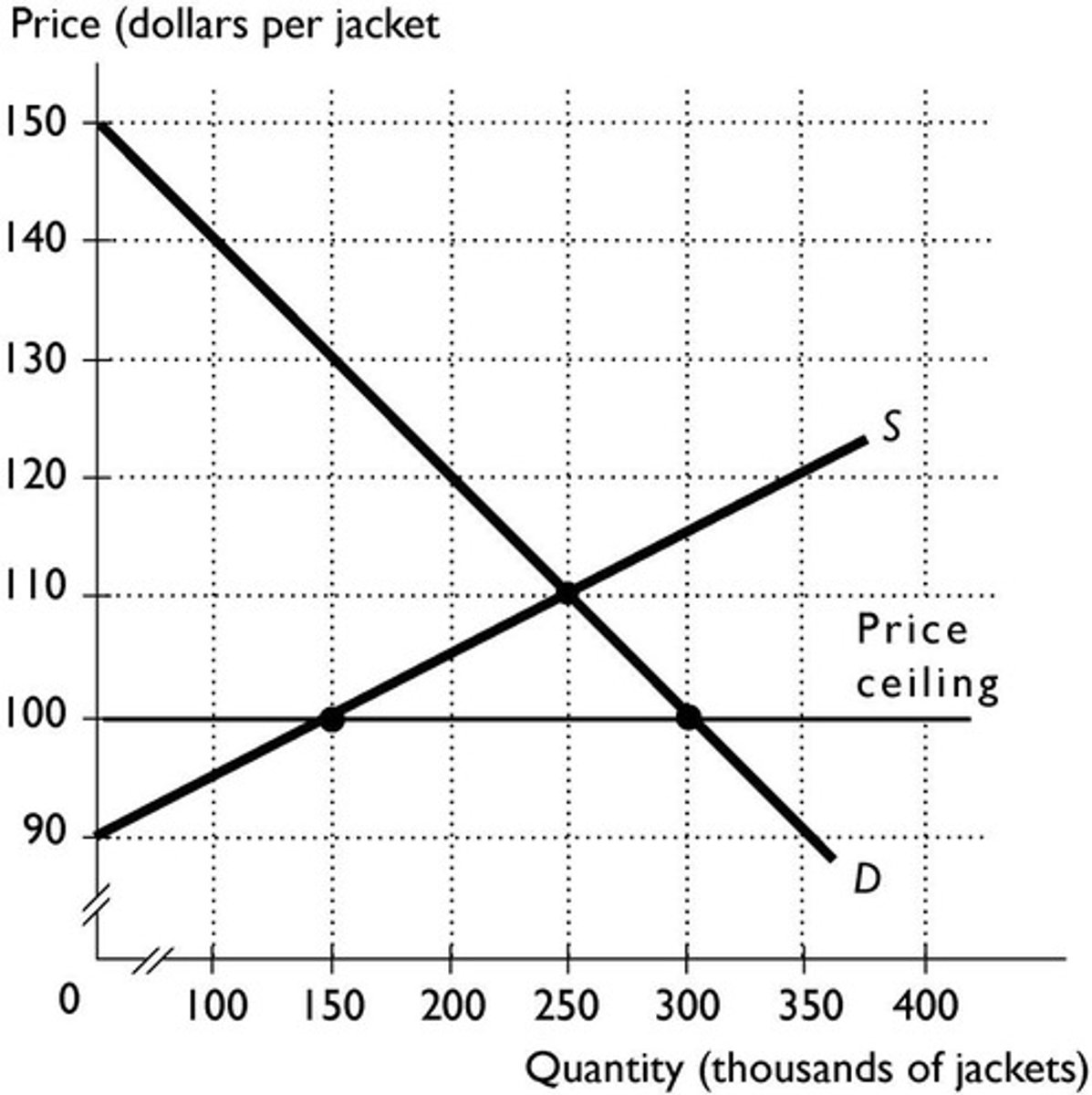
Price Ceiling Purpose
A price ceiling is designed to benefit consumers by keeping the price below the market clearing or equilibrium price.
Price Ceiling Effect
A price ceiling results in a shortage because the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
Price Ceiling Impact
A price ceiling will create a deadweight loss - total surplus is decreased because quantity has fallen.
Price Floor Definition
A price floor is a legislated minimum price that sellers are allowed to charge in the market.
Price Floor
A minimum price that is set above the equilibrium price.
Surplus
A situation that results when the quantity supplied exceeds the quantity demanded.
Consumer Surplus
The benefit consumers receive when they pay less than what they are willing to pay.
Producer Surplus
The benefit producers receive when they sell at a higher price than the minimum they would accept.
Marginal Benefit
The additional benefit received from consuming one more unit of a good or service.
Marginal Cost
The additional cost incurred from producing one more unit of a good or service.
Shortage
A situation that occurs when the quantity demanded exceeds the quantity supplied.
Black Market
An illegal market in which the price exceeds a legally imposed price ceiling.
Price Ceiling
A maximum price that is set below the equilibrium price.
Market Efficiency
Occurs when the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus is maximized.
Tax
A financial charge imposed by the government on goods and services to raise revenue.
Total Surplus
The total benefit to society, calculated as the sum of consumer surplus and producer surplus.
Price Elasticity
A measure of how much the quantity demanded or supplied responds to changes in price.
Price Inelastic
A situation where the quantity demanded or supplied is relatively unresponsive to price changes.
Equity Grounds
Justifications for economic policies based on fairness and income distribution.
Government Intervention
Actions taken by the government to affect the economy, such as setting price floors or ceilings.
Quantity Supplied
The total amount of a good that producers are willing and able to sell at a given price.
Quantity Demanded
The total amount of a good that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price.
Consumer surplus effect from tax
Buyers pay more & consume less - consumer surplus decreases.
Producer surplus effect from tax
Sellers receive less & sell less - producer surplus decreases.
Subsidy definition
A subsidy is a grant paid by the government to a producer with the purpose of reducing costs and increasing output.