policy 210 quiz one
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
public policy
a decision for the community
policies have no power unless they are voted on and executed by people chosen by the people - representative government
NEED TEETH
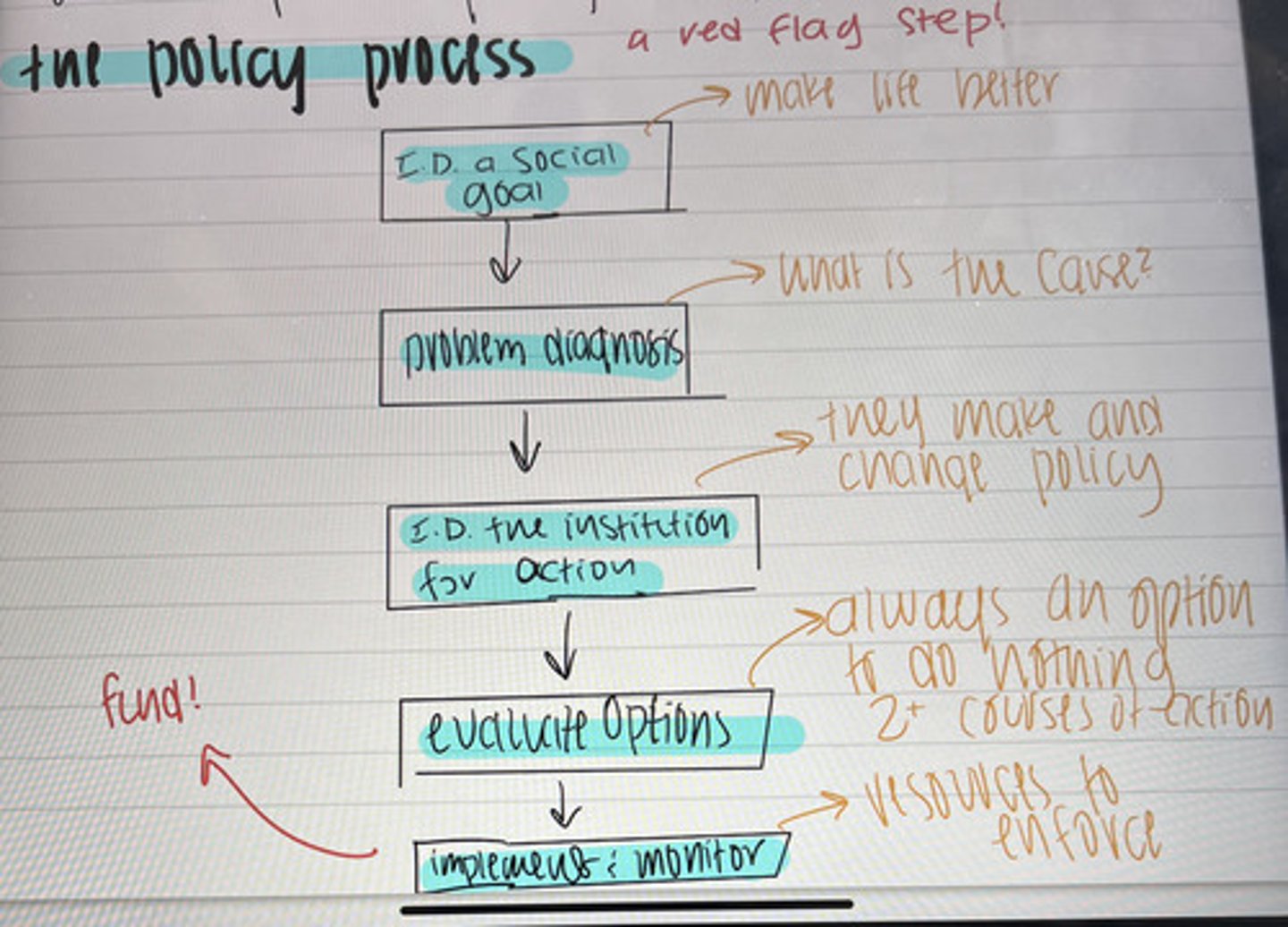
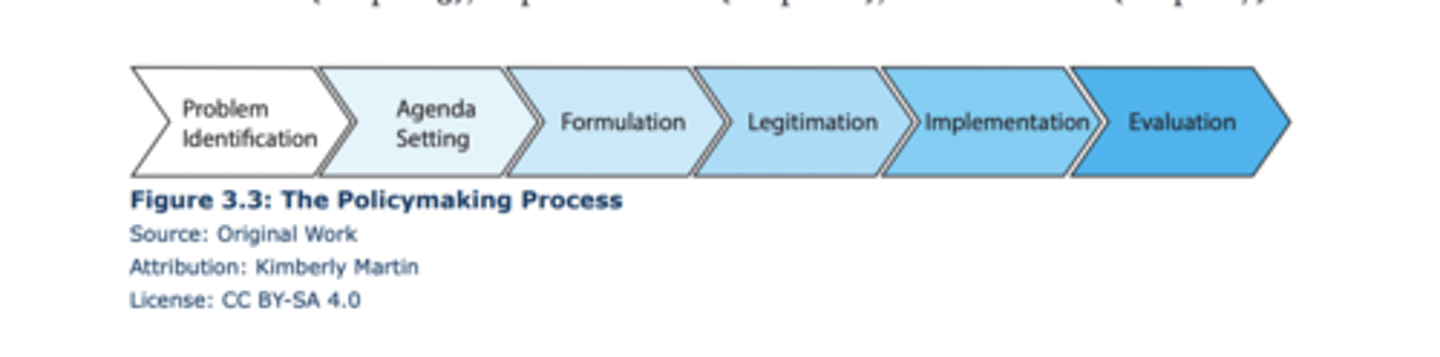
policy process
gather information -> analyze it -> set a policy
for-profit institutions
want to make a profit for their cowoners
revenues > costs
usually means they are in the private sector
nonprofit
they don't generate income - rely on donations, govt subsidies and funding
revenues < costs
501(c)(3) - tax code
government
exercises authority - aka can make people do things
markets
self-regulating economic machines
free rider
get to just hang out on the payment of others
tax evasion, etc.
real figures
adjusted for inflation
nominal - adjustment for price change
nominal figures
no inflation adjustment - just as they are
positive analysis
analysis on data without opinions
personal work and work opportunity reconciliation act
expanded welfare into the program it is today
moved into lifetime caps, changed the pay structure, etc.
New Deal
President Roosevelt's program for getting the United States out of the depression
added jobs, regulated banks and the stock market, created a minimum wage and retirement income
normative analysis
analysis on what "should" be done
government actors
anyone who acts on the part of the government
distributive policy
provide goods and services to the majority, funded by taxpayer money
redistributive policy
move wealth among the system (class-based)
tries to even out wealth or social status
regulatory policy
encourage some behaviors and discourage others
constituent policy
creation and running of government agencies
bureaucrats
an official in a federal government department
responsible for carrying out policies (sometimes they know more than the officials themselves)
statutory laws
a law enacted by a legislative body
constitutions
establish powers of government actors while allowing access of non-govt actors to limited policy decisions
confederate government
power in the states moved to a central big power
federalism
a combination of state and national governments
feds get explicitly defined powers, states get reserved (those not already covered)
when did big government start
after the Great Depression and World War 2, people wanted more federal government involvement
the New Deal really started it all
enumerated powers
held by the federal government
- regulate interstate commerce
- coin money
- declare war
- make laws: execute their powers
concurrent powers
shared by the states and federal governments
- collect taxes
- incur debt
- make and enforce laws
- establish courts and charter corporations
reserved powers
held by the states alone
- ratify constitutional amendments
- establish logistics of national electrions
- wield police power
- everything else not denied to states or given to the Feds
the Great Society
policies that changed social inequity
branches of government
legislative: make the laws
executive: enforce the laws (elastic language - executive orders)
judiciary: interpret the laws
powers of Congress
passes laws, appropriates $ spent, oversees all executive branches
judicial review
is the law constitutional?
established by Marbury v. Madison
judicial restraint
courts shouldn't push their views
opposite: judicial activism
ACA
Affordable Care Act
- expanded Medicaid
- people with pre-existing conditions should always have coverage
- stay on parents' insurance till 26
- insurers cannot limit coverage
- basic all plan requirements
- all Americans have to have insurance
- added subsidies
conference committees
made up of members both from the house and the senate who meet up to reconcile the legislation once it has passed through both houses successfully
filibuster
60 Senator majority usually needed to pass some legislation through the body
arab human development report
5% of the world lacks prosperity
very slow economic growth
poor public policy: freedom, women's empowerment, knowledge acquisition
welfare
originally intended to help out widows and single mothers with children (first expansion)
provides basic assistance to those populations (Temporary Assistance for Needy Families (TANF) for the most dire of situations)
concerns about welfare queens, lifetime limits, wedlock
liberal democracy
the freedom to fulfill your dreams
heuristic
a proxy, a formula for how we see the world
opinion policy congruence
key points of the players making the policy matching up
congressional budget office
data on cost for Congress
market failures
goods and services are not efficiently allocated
reasons for market failures
public goods: tragedy of the commons
externalities: policies that impact a third party by accident
information asymmetry: one party has better information than the other
why do governments fail
- inability to defend welfare
- limits of democracy and voting
- inability to define outstanding public goods costs
- political constraints
- cultural constraints
- institutional constraints
- legal constraints
- knowledge constraints
- analytical constraints
- policy timing
the goal of public policy
1) defend people and property while keeping social order
2) support/make effective non-government actors
3) promote thriving
stages model of public policy
very similar to bardach's eightfold path
technocratic policy
the "Deep State", the big machine of government
caps
a classic policy tool that prevents people from having too much fun with things
zimbabwe
program to transfer land from white farmers to black farmers
was doing well but going slow, government interfered and it became a mess - land was seized, the country went into a famine
implied powers
powers that congress has that are not stated explicitly in the constitution
models
simplified illustrations of how systems operate
ceteris paribus
all other things being equal
the assumption in most social science research
utility
loosely equals well being
opportunity cost
what you give up to get something else
power of incentives
explain human behavior
if you change incentives you can change behavior
rational individuals won't do anything to make themselves worse off
policies that aren't rational can have unintended consequences
human capital
we think about our investments the same way that firms do
three basic policy questions
who is affected
how are they affected
what is their likely response
moral hazard
individuals/firms are protected so they act with less caution and make an unfortunate outcome more likely
information asymmetry
situation in which one party is more informed than another because of the possession of private information
principal agent problems
conflicts that arise when tasks are delegated by one group of people (principals) to another group of people (agents)
adverse selection
individuals use private information to put themselves in or out of a market transaction
signaling
when firms/individuals undertake options with no direct value
investing in fancy furniture in a law firm, for example
certification
a third party attests to the quality of the good or service
branding
when firms build an identity for their products
screening
one party investigates the other before entering into a transaction
behavioral econ
we are rational?
- revenge
- assessing risk
- planning and saving for retirement wrong
what governments do
taxes, regulation, subsidies and grants, provides services, agency budgets, information, modify structure of private rights, economic framework notification, education and consultation, financing and contracting, bureaucratic and political reforms