Unit 1 AP Psych
1/129
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
130 Terms
Behaviour Genetics
the scientific study of how genes and the environment influence individual differences in behavior.
Natural Selection (eugenics)
inherited traits that enable an organism to survive and reproduce in an environment will be passed on to succeeding generation
Mutation
random error in gene replication that leads to a change
heredity
nature
genetic transfer of characteristics from parent to offspring
environment
nurture
every non-genetic influence (prenatal pills to the people and things around us.)
monozygotic twins
a single fertilized egg splits into two, creating two genetically identical organisms
dizygotic twins
separate fertilized eggs share a maternal prenatal environment, but are basically like siblings.
epigenetics
study of environmental influences on gene expression that occur without a DNA change
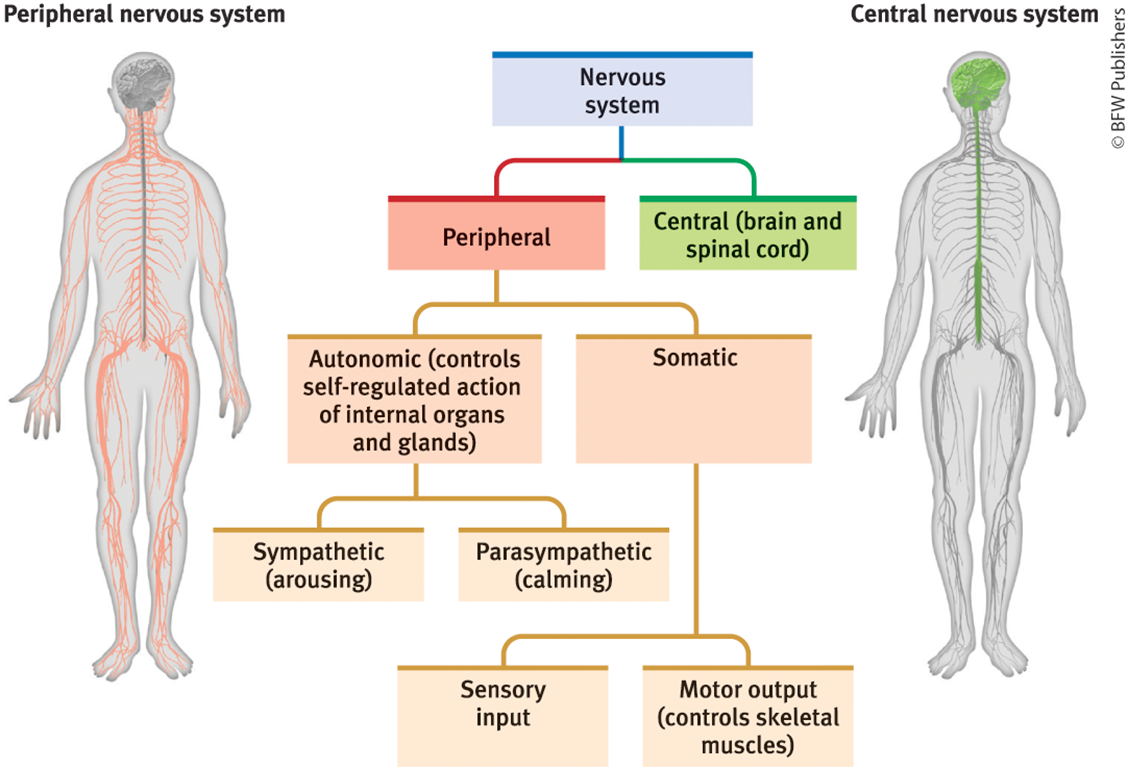
What is the nervous system?
the body’s speedy, electrochemical communication network consisting of nerve cells of the peripheral (PNS) and central (CNS)
Made up of neurons that communicate using neurotransmitters (NT). neurons release NT
nerves
sensory neurons
motor neurons
interneurons
bundles of axons that link the CNS to muscles, glands, and sense organs.
bring sensory info to the CNS
send the info from CNS to the body
connect neurons within the CNS
CNS
brain and spinal cord
coordinate incoming sensory messages and outgoing motor messages
brain’s neurons get into groups called neural networks
spinal cord controls reflex in the reflex arc
reflex arc
Touching something hot:
Skin senses heat → sends signal through a sensory neuron to the spinal cord.
Interneuron in spinal cord passes the message to a motor neuron.
Motor neuron tells muscles to pull your hand away.
It’s a reflex—your brain reacts (feels pain) after your body moves.
peripheral nervous system (PNS)
made up of sensory and motor neurons
All the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. It connects the CNS to the rest of the body.
somatic nervous system
part of PNS
voluntary skeletal muscle control
autonomic nervous system
part of PNS
involuntary control of glands and muscles (heart, lungs, etc.)
sympathetic (symp)
part of ANS
arouses the body, mobilizing its energy
fight, flight, or freeze
dilating pupils, fast heartbeat, digestions stops, bladder holds, adrenal glands stimulate release of neurotransmitters
maintains body’s homeostasis
parasympathetic
part of ANS
calms the body, conserving its energy
rest/digest
pupils contract, heartbeat slows, digestion stimulated, bladder goes
maintains body’s homeostasis
neurons
a nerve cells that is the basic building block of the nervous system (queen bees)
resting potential (1.3a)
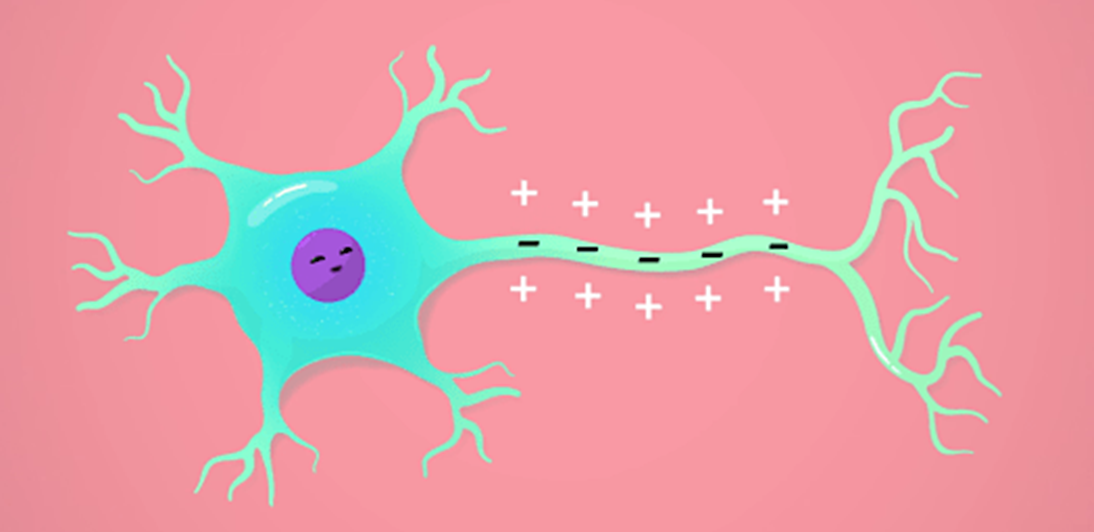
the resting state of the neuron
the charge is positive outside, and negative inside
excitatory signals
inhibitory signals
action potential
Excitatory signals = like pressing the gas pedal — they tell the neuron to go (send a message).
Inhibitory signals = like pressing the brake — they tell the neuron to stop.
If excitatory signals outnumber inhibitory ones enough to reach the threshold, the neuron fires an action potential (sends an electrical message down the axon).
all-or-none response
fire or u dont
like a lightswitch
depolarization
The inside of a neuron is more negative than the outside. When Na⁺ (sodium) ions enter, it makes the inside less negative, causing depolarization — a small loss of the normal charge difference.
repolarization
Repolarization happens after depolarization. K⁺ (potassium) ions flow out of the neuron, making the inside more negative again and bringing it back to its resting state.
refractory period
neurons need short breaks.
during a resting pause (refractory period), subsequent action potentials cant occur until the axon returns to its resting state.
the neurons fire again after it rests
How do neurons communicate with each other
sending neuron releases neurotransmitters across a synapse to the receiving neuron
synapse
the junction between the axon tip of the sending neuron and the dendrite or soma of receiving neuron
Neurotransmitters
chemical messengers that cross the synaptic gap, received by neurons
reuptake
unused NT taken back up to the the sending neuron
endorphines
“Morphine-within”
group of natural, opiate-like neurotransmitters.
linked to pain control and pleasure!
agonists
A chemical or drug that mimics a neurotransmitter and activates its receptor, increasing its effect
antagonists
inhibiting neuron firing
stops/blocks neurotransmitter’s actions
endocrine system
slow chemical communication system. set of glands and fat tissue that secrete hormones into bloodstream. regulate bodily functions, growth and development
hormones
chemical messengers manufactured by the endocrine glands. travels thru bloodstream.
adrenal gland
when the sympathetic nervous system activates, adrenal glands release epinephrine (adrenaline) and norepinephrine (noradrenaline) to energize the body.
pituitary gland
endocrine system’s most influential gland.
hypothalamus (part of the CNS and endocrine system) direct the pituitary gland to regulate growth and control other endocrine glands.
psychoactive drugs (1.5B)
alter perceptions and mood.
depressants
downers that calm neural activity and slow body functions
stimulants
uppers that temporarily excite neural activity and arouse body functions
hallucinogens
distort perceptions and evoke sensory images in the absence of sensory input
“mind-manifesting” drugs
tolerance/withdrawal
tolerance: user requires more doses to experience the drug’s effect because the user’s brain experiences neuro-adaptation.
withdrawal: stopping the drug will make it hard for user
addiction
lack of control/social functioning/too much usage
want the drug more than like the drug
substance use disorder
continued substance craving and use despite significant life disruption/physical risk.
alcohol
depressant type
slows brain’s activity (judgment, inhibitions, memory, processing of experience, less self-awareness and less sexual inhibitions)
opioids
opium and its derivatives (morphine and heroin) depress neural functioning. lessens pain for temporary period of relief but makes effects worse
too much use of this will cause brain to stop producing endorphines, which can even cause death
what are considered stimulants
nicotine, caffeine, cocaine
speeds up body functions. helps to stay awake, lose weight or boost mood/performance. but ofc, there’s addiction and withdrawal issues.
nicotine
stimulating and highly addictive psychoactive drug found in tobacco
signals the CNS to release neurotransmitters.
cocaine
powerful and addictive stimulant. produces temporary increased alertness and euphoria, depleting brain’s supply of neurotransmitters dopamine, serotonin, and norepinphrine
marijuana (cannabis) and THC
amplifies sensitivity to colors, sounds, tastes and smells.
form of mild hallucinogen. causes delusions and anxiety
marijuana relaxes and produces euphoric high.
sleep (1.5)
a periodic of natural loss of consciousness
circadian rhythm
It's your body's natural 24-hour clock that helps control when you feel awake or sleepy, and it also affects things like body temperature, hormones, and digestion. It helps your body sync with day and night.
jetlag
This causes symptoms (daytime fatigue, lack of alertness, poor coordination, increased risk of diabetes/cancer) that result from crossing multiple timezones at highspeed.
alpha waves
in bed with eyes closed, relaxed but awake state
NREM-1 and Hypnogogic Sensations
During this brief NREM-1 sleep you may experience fantastic images resembling hallucinations.
You may have a sensation of falling or floating weightlessly. Sometimes a leg or arm may jerk.
These hypnagogic sensations may later be incorporated into your memories.
NREM-2 stage
there are periodic sleep spindles, bursts of rapid, rhythmic brain-wave activity.
you could be awoken without too much difficulty, but asleep.
NREM-3
lasts for 30 minutes.
brain emits large, slow delta waves and it’s hard to wake up
REM stage sleep
a reoccurring sleep stage where vivid dreams commonly occur
aka paradoxical sleep; muscles are relaxed but other body systems are active
motor cortex is active, but brainstem blocks its message. if ur awake during this time, there will be sleeping paralysis.
heart rate rises, irregular breathing, eyes dart around rapidly
REM rebound
tendency for REM sleep to increase following REM sleep deprivation
information-processing theory
dreams help sift, sort and consolidate the day’s experiences in our memory
brain scans have confirmed the link between rem sleep and memory
activation synthesis theory
Your brain gets random activity while you sleep, and it tries to turn that into a story—that’s your dream
Freud’s Wish-Fulfillment Dream Theory
Freud believed that dreams help people express hidden desires, especially ones that might be unacceptable in real life.
He divided dreams into two parts:
Manifest Content – What happens in the dream (the storyline).
Latent Content – The hidden meaning behind the dream.
Freud also thought that many adult dreams, even if they don’t seem sexual, are connected to deep, hidden desires.
dopamine
reward and movement
oversupply: schizophrenia
undersupply: parkinson’s
serotonin
moods and emotion
undersupply: depression
norepinephrine/noradrenaline
hormone and neurotransmitter
sympathetic (fight/flight) nervous system arousal
glutamate
excitatory signal in nervous system
gaba
major inhibitory signal in nervous system
endorphines
pain control, happiness
acetylcholine (ACh)
memory, muscle action
under supply: Alzheimer’s
blocked receptors: Myasthenia gravis
Substance P
pain signals
cell body (soma)
glial cells: support/nourish/protect neurons (worker bees)
contains nucleus. produces genetic info
dendrites
receives incoming messages. conducts impulses towards cell body
axon
attached to soma, passes msgs away from cellbody to other neurons,muscles,glands. action potential travels down this
myelin sheath
fatty tissue encasing the axons of neurons. speeds up signal down axon, provides insulation to prevent impulse interfereing
terminal branches
store neurotransmitters. allows communication across synapse (junction where neurons communicate)
adrenaline
fight or flight
leptin
suppress hunger
Ghrelin
Stimulate hunger
Melatonin
causes sleep
Oxytocin
Love and bonding
Higher level consciousness
Controlled processes- totally aware
Lower-level consciousness
Automatic processing (day dreaming, phone numbers)
Altered states
Produced through drugs, fatigue, hypnosis
Circadian rhythm
24-hour biological clock
Body temps and awareness change due to this
Controlled by superchiasmatic nucleus in the brain
beta waves
Awake
Stage 1 nrem
Light sleep
Consolidation theory
Help us sort out the days events and consolidate our memories
Activation synthesis theory
Rem triggers neural activity that evokes random visual memories, which our sleeping brain turns into stories
Insomnia
Inability to fall asleep
Narcolepsy
Fall asleep out of nowhere due to orexin defeciency
Rem sleep behaviour disorder
Acting out the content of dreams while asleep
Somnambulism
Sleep walking due to fatigue, drugs, and alcohol
Sleep apnea
Stop breathing suddenly while asleep (associated with obesity)
what is sensation
How we detect physical energy from the environment and encode it as neural signals
Absolute threshold
Detection of signal 50% of the time
faint sound in a small room
Difference threshold / Just noticeable difference (JND)
Minimum difference between two stimuli required for detection 50% of the time
noticing when the volume goes up or down
Webber’s law
Small originals → small change is noticeable.
Large originals → need a bigger change to notice.
Signal detection theory
We don't just sense things automatically—we detect them based on our attention, motivation, and expectations.
Sensory adaptation
Diminished sensitivity as a result of constant stimulation (you can’t feel ur underwear)
Frequency (wavelength)
What colour (hue)?
Amplitude (wave height)
How bright?
Pathway of vision
“Lazy Cats Play Like Real Runners By Going Over Open Oceans.”
Light → cornea → pupil/iris → lens → retina → rods/cones → bipolar cells → ganglion cells → optic nerve → optic chiasm → occipital lobe
“Lazy Cats Play Like Real Runners By Going Over Open Oceans.”