ALL (1, 2, 3)
1/167
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Topic 1: Foundations of environmental systems and societies Topic 2: Ecosystems and ecology Topic 3: Biodiversity and conservation
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
168 Terms
enviromental value system
Worldview or paradigm that shapes the way individuals or groups perceive and evaluate environmental issues
Influenced by cultural, religious, economic, and socio-political contexts
ecocentrism
views ecology and nature as central to humanity
emphasizes a less materialistic approach to life
prioritizes biorights, emphasizes the importance of education, and encourages self-restraint in human behavior
athropocentrism
argues that humans must sustainably manage the global system
through the use of taxes, environmental regulation, and legislation
debate to reach a consensual, pragmatic approach
technocentrism
argues that technological developments can provide solutions to environmental problems
scientific research is encouraged
pro-growth agenda
systems approach
a way of visualizing a complex set of interactions which may be ecological or societal
system
an assemblage of parts and their relationship, forming a functioning entirity or whole
comprised of storages and flows
flows
movevement of matter and energy - either transfers or transformations (arrows)
transfer
matter or energy moves through a system without changing state or form (flow)
transformation
a change in state or form (flow)
open system
exchanges both energy and matter across its boundary (ECOSYSTEMS)
closed system
exchanges only energy across its boundary (only experimental)
isolated system
hypothetical concept in which neither energy nor matter is exchanged across the boundary
storages
where energy or matter is held (boxes)
first law of thermodynamics
the principle of conservation of energy - energy in an isolated system can be transformed but cannot be created or destroyed
second law of thermodynamics
the entropy of a system increases over time
(explains the inefficiency and decrease in available energy along a food chain)
entropy
a measure of the amount of disorder in a system
negative feedback loop
STABILIZING - occurs when the output of a process inhibits or reverses the operation of the same process in such a way as to reduce change - it counteracts deviation
positive feedback loop
DESTABILIZING - will tend to amplify changes and drive the system toward a tipping point where a new equilibrium is adopted
resiliance of a system
its tendency to avoid tipping points and maintain stability
(contributed to by diversity and the size of storages)
delay in feedback loop
make it difficult to predict tipping points and add to the complexity of modelling systems
affected by diversity and the size of storages within systems
sustainablility
the use and management of resources that allows full natural replacement of the resources exploited and full recovery of the ecosystems affected by their extraction and use
natural capital
natural resources that can produce a sustainable natural income of goods or services
natural income
the yield obtained from natural resources
ecosystems provide:
life-supporting services (water replenishment, flood, and erosion protection)
goods (timber, fisheries, and agricultural crops)
environmental indicators of sustainability
biodiversity, pollution, population or climate
enviromental impact assesment (EIA)
assess environmental, social and economic impacts of a project (provides decision-makers with info)
predicts and evaluates possible impacts
suggests mitigation strategies
before - baseline studies
after - an audit and continued monitoring
critisms of EIAs
lack of a standard practice or training for practitioners
lack of a clear definition of system boundaries
lack of inclusion of indirect impacts
not necessarily binding - can be ignored
ecological footprint
the area of land and water required to sustainably provide all resources at the rate at which they are being consumed by a given population
pollution
the addition of a substance or an agent to an environment through human activity, at a rate greater than that at which it can be rendered harmless by the environment, and which has an appreciable effect on the organisms in the environment
non-point or point source
persistent or biodegradable
acute or chronic
pollutants
organic or inorganic substances, light, sound, or thermal energy, biological agents, or invasive species (i.e. from combustion of fossil fuels)
primary (active on emission)
secondary (arising from primary pollutants undergoing physical or chemical change).
DDT
insecticide and toxin
→ example of a conflict between the utility of a “pollutant” and its effect on the environment
intrinsic value
when an object or place has a worth irrespective of its economic value
biorights
all life has a right to exist
ecosphere
the planetary ecosystem, including all the earth’s living organisms and their physical environment
litosphere
the rigit outer layer of the earth, about 75 km of the earth’s crust
example of a small system
bromeliad plant in the Amazon river
example of a medium system
a small lake in the Šumava forest
example of a large system
the earth
model
a simplified description designed to show the structure or workings of an object, system or concept
steady state equilibrium
the ability to return to a balance after a disturbance
static equilibrium
no inputs, outputs of energy or matter and no change over time (doesn’t occur in nature)
stable equilibrium
if a system returns to its original equilibrium after a disturbance
unstable equilibrium
system that does not return to the same equilibrium after a disturbance, but forms a new equilibrium
tipping point
a critical threshold when even a small change can have a dynamic effect on a system
resilience
the tendency to avoid tipping points and maintain stability through a steady state equilibrium
species
a group of organisms that share common characteristics and that interbreed to produce fertile offspring
biosphere
the part of the planet where organisms live, including the ground and the air
ecology
study of living organisms in relationship to their environment
habitat
the environment in which a species normally lives
niche
the particular set of abiotic and biotic conditions and resources to which an organism or population responds
fundamental niche
the full range of conditions and resources in which a species could survive and reproduce
realized niche
the actual conditions and resources in which a species exists due to biotic interactions
abiotic factors
the non-living, physical factors that influence the organisms and ecosystems
(temperature, sunlight, pH, salinity, and precipitation)
biotic factors
living components of an ecosystem
the interactions between organisms
predation, herbivory, parasitism, mutualism, disease, and competition
population
a group of organisms of the same species living in the same area at the same time, and which are capable of interbreeding
S and J curves
a generalized response of populations to a particular set of conditions (abiotic and biotic factors)
S curve
(ex.: mammals)
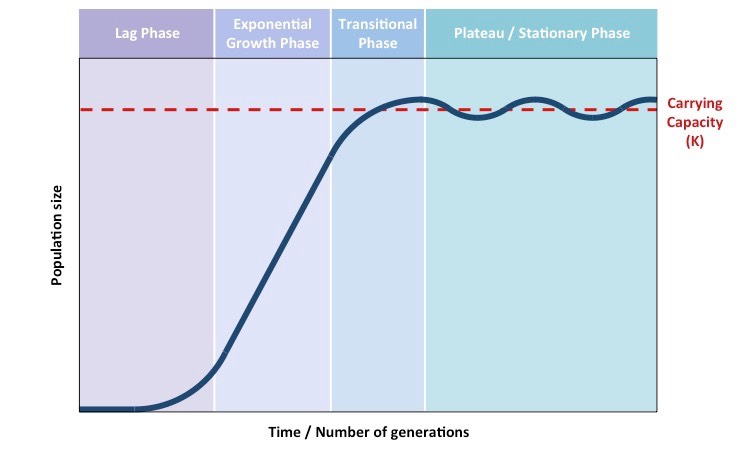
J curve
exponential growth (ex.: colonizing populations - roaches)
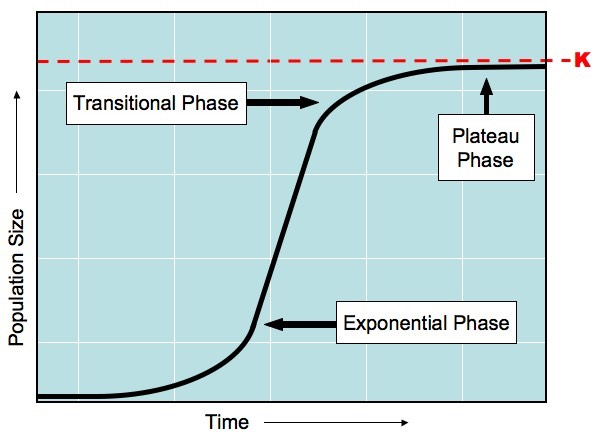
carrying capacity (K)
the maximum number of specific organisms a habitat can sustain
limiting factors
slow population growth as it approaches the carrying capacity of the system
(water availability)
community
a group of populations living and interacting with each other in a common habitat
ecosystem
a community and the physical environment with which it interacts
food web
a complex series of interactions showing the feeding relationships between organisms in an ecosystem
respiration
the conversion of organic matter into carbon dioxide and water in all living organisms, releasing energy
glucose + oxygen → carbon dioxide + water
aerobic respiration word equation
photosynthesis
produces the raw material for producing biomass
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
photosynthesis word equation
primary producers
produce their own food using photosynthesis
form the first trophic level in a food chain
(autotrophs)
→ typically plants or algae
trophic level
the position that an organism occupies in a food chain, or the position of a group of organisms in a community that occupy the same position in food chains
feeding relationships
producers
consumers
decomposers
modelled using:
food chains
food webs
ecological pyramids
ecological pyramids
quantitative models (usually measured for a given area and time)
pyramids of numbers
pyramids of biomass
pyramids of productivity
bioaccumulation
the build-up of persistent or non-biodegradable pollutants within an organism or trophic level because they cannot be broken down
biomagnification
the increase in concentration of persistent or nonbiodegradable pollutants along a food chain
toxins
accumulate along food chains due to the decrease of biomass and energy
→ DDT, mercury
pyramid of numbers
(can sometimes display different patterns when individuals at lower trophic levels are large)

pyramid of biomass
represents the standing stock or storage of each trophic level (g m–2 or J m-2)
(can show greater quantities at higher trophic levels because it’s measured at a fixed point in time)
pyramid of productivity
the flow of energy through a trophic level, indicating the rate at which biomass is being generated

productivity
the conversion of energy into biomass for a given period of time
solar energy unavailable for ecosystems
solar radiation (insolation) that is absorbed by inorganic matter or reflected back into the atmosphere
pathways of energy through an ecosystem
conversion of light energy to chemical energy
transfer of chemical energy from one trophic level to another with varying efficiencies
overall conversion of ultraviolet and visible light to heat energy by an ecosystem
re-radiation of heat energy to the atmosphere
net primary productivity (NPP)
total amount of energy stored as biomass in producers (energy available for consumers)
NPP
= GPP – R
= gross primary productivity - respiratory losses
gross secondary productivity (GSP)
total energy assimilated by consumers
GSP
= food eaten – fecal loss
net secondary productivity (NSP)
total amount of energy stored as biomass in consumers (energy available for next trophic level)
NSP
= GSP – R
= gross secondary productivity - respiratory losses
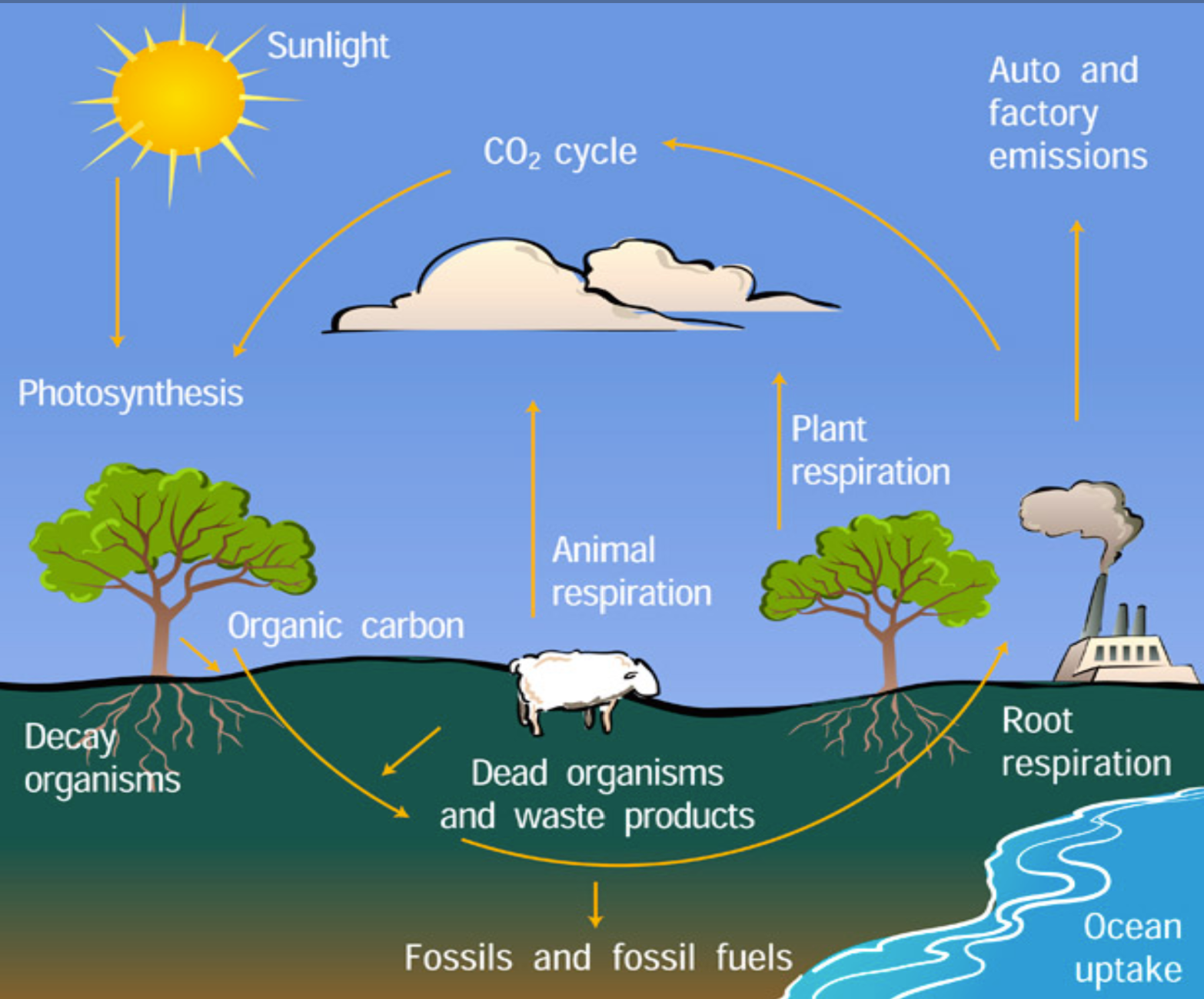
carbon cycle
storages:
organic - organisms and forests
inorganic - the atmosphere, soil, fossil fuels and oceans
flows:
consumption (feeding)
death and decomposition
photosynthesis
respiration
dissolving
fossilization
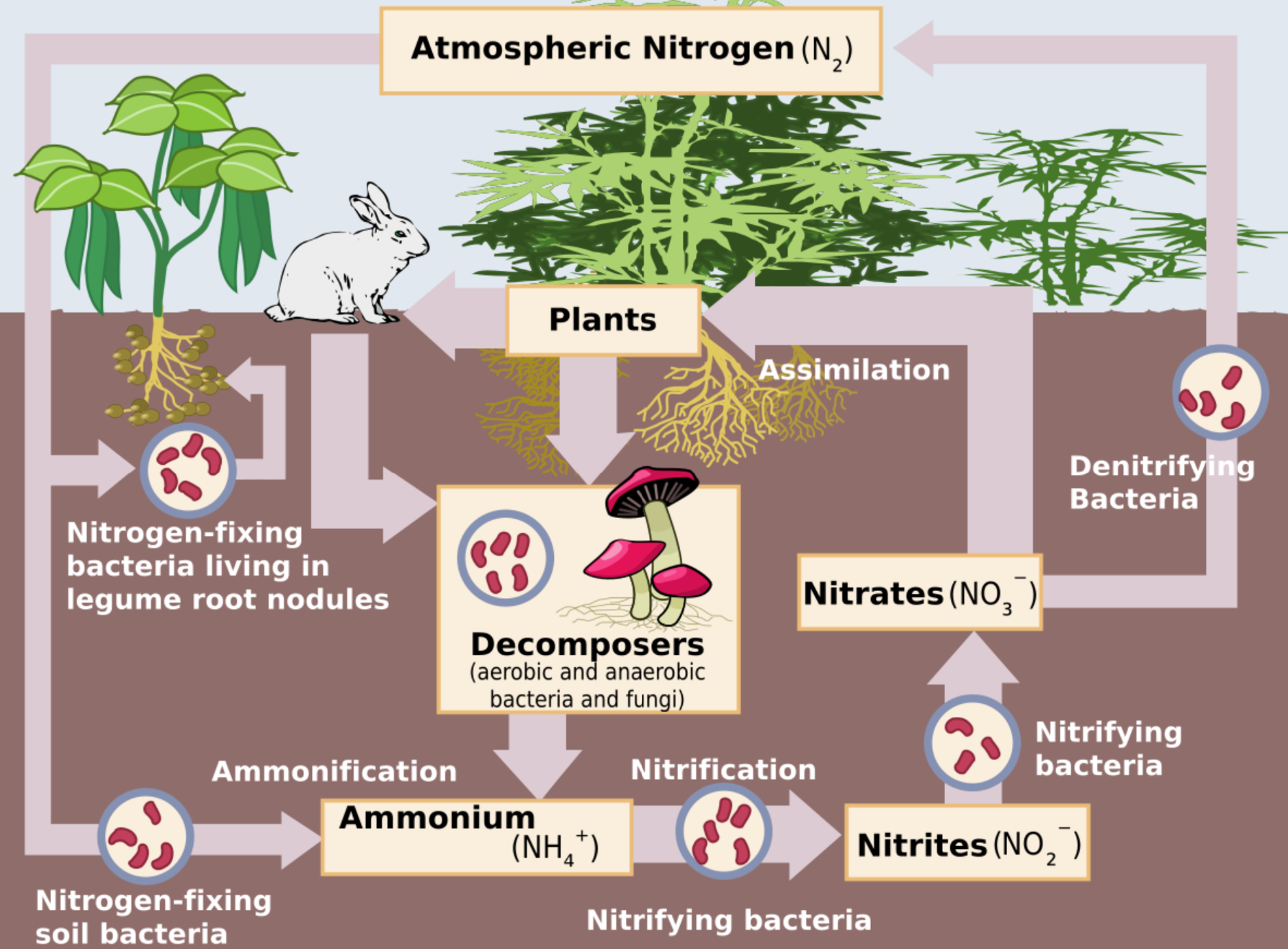
nitrogen cycle
stores:
organic - organisms
inorganic - soil, fossil fuels, atmosphere and water bodies
flows:
nitrogen fixation by bacteria and lightning
absorption
assimilation
consumption (feeding)
excretion
death and decomposition
denitrification by bacteria
biomes
collections of ecosystems sharing similar climatic conditions
aquatic
forest
grassland
desert
tundra
insolation, precipitation and temperature
3 main factors governing the distribution of biomes
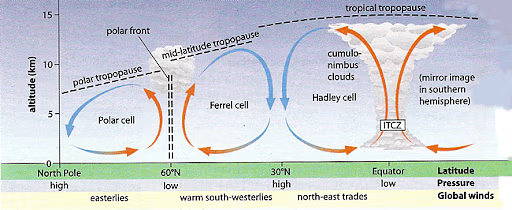
tricellular model of atmospheric circulation
explains the distribution of precipitation and temperature and how they influence structure and relative productivity of different terrestrial biomes
zonation
changes in community along an environmental gradient
→ due to changes in altitude, latitude, tidal level or distance from shore (coverage by water)
succession
the process of change over time in an ecosystem involving pioneer, intermediate and climax communities
(patterns of energy flow, gross and net productivity, diversity, and mineral cycling change over time)
early stages of succession
low biomass
low gross productivity
low proportion of energy lost through respiration
high net productivity
later stages of succession (climax community)
high biomass
high gross productivity - balanced by respiration
~0 net productivity
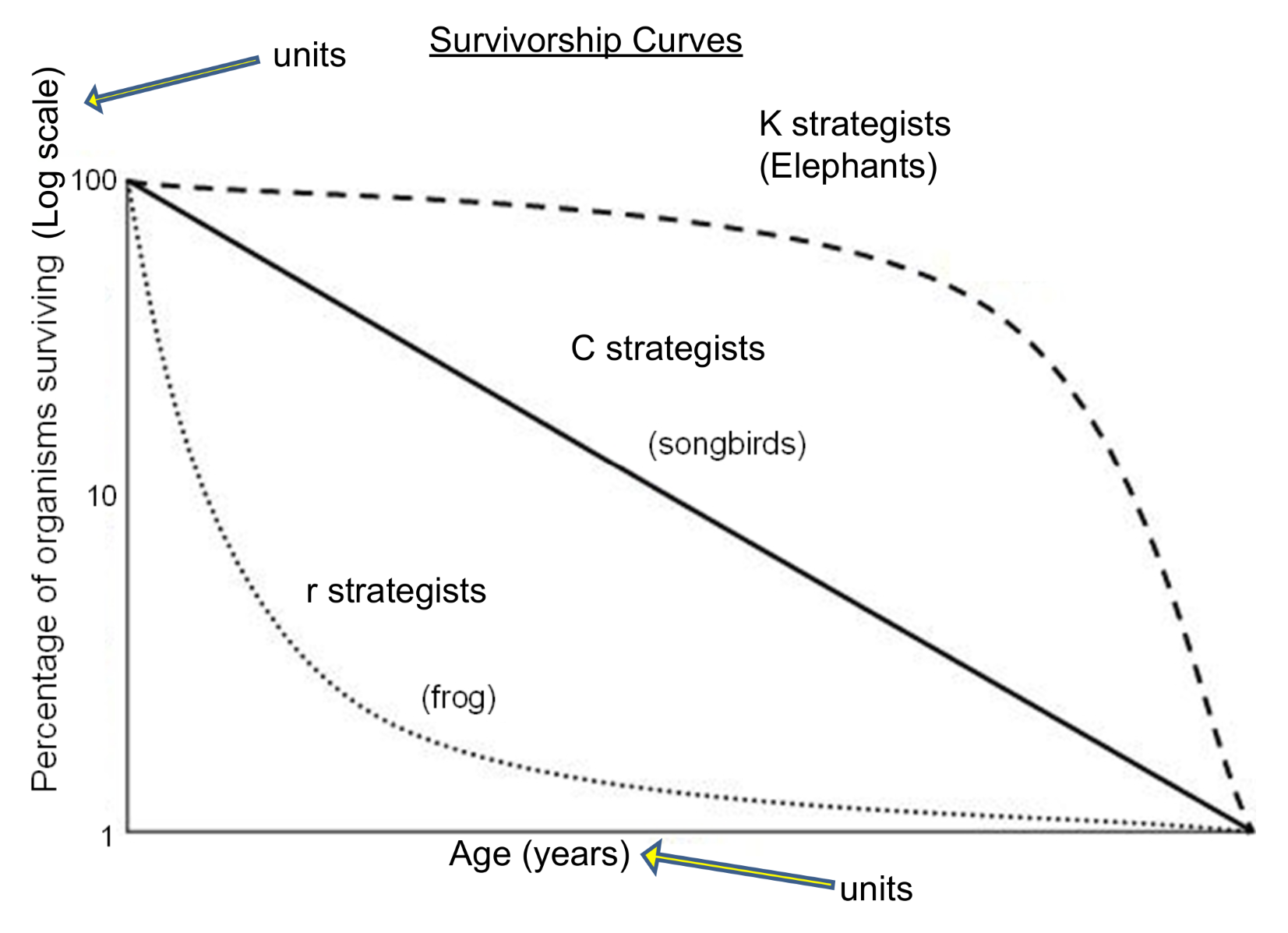
r-strategists
grow fast
mature early
produce many small offspring
give little care to young
→ cockroaches, frogs
favored by natural selection - pioneer communities
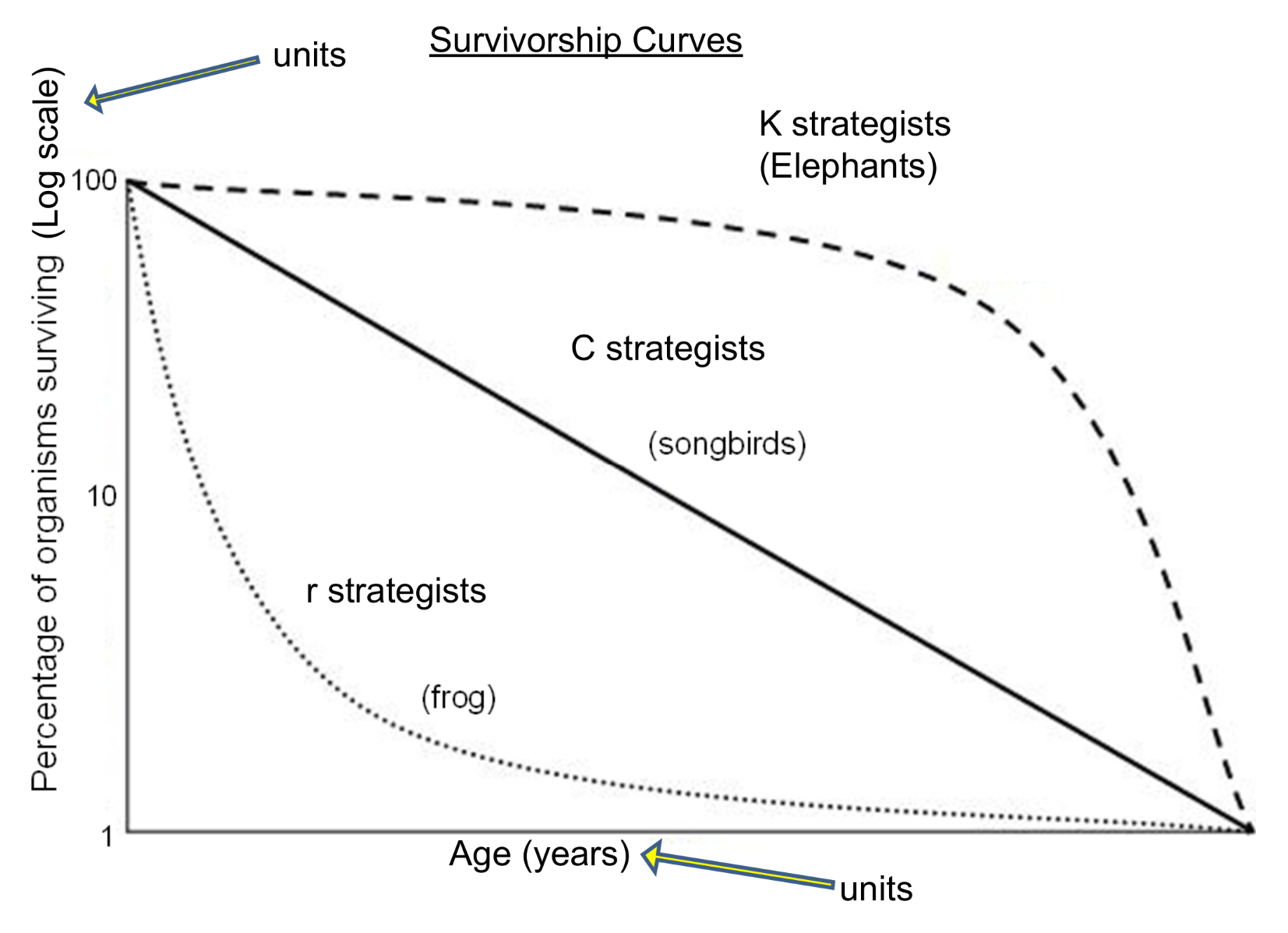
K-stategists
slow growing
usually large
have few large offspring
mature slowly
→ hippopotamus, dolphin, elephant
favored by predictable environments - climax communities
tools for identifying organisms in an ecosystem
keys
comparison to herbarium or specimen collections
technologies
scientific expertise
Secchi disk
for measuring turbidity