Chapter 25 - Neonatal and Infant Head
1/105
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
106 Terms
D
Dysgenesis of the fourth ventricle results in which one of the following malformations?
A) corpus callosum
B) cystic dilation of the lateral ventricle
C) holoprosencephaly
D) Dandy-Walker
A
What is the name of the structure that forms between the corpus callosum and the anterior horn of lateral ventricle?
A) septum pellucidum
B) massa intermedia
C) fourth ventricle
D) lateral ventricle
A
Cyclopia is associated with which one of the following?
A) holoprosencephaly
B) hydrocephalus
C) hydraencephaly
D) Dandy-Walker malformation
B
Bilateral occlusion of the carotid arteries may result in ______.
A) hydrocephalus
B) hydranecephaly
C) holoprosencephaly
D) intraventricar hemorrhage
D
Which three mechanisms account for the development of hydrocephalus?
A) outflow obstruction, increased absorption, and overproduction
B) inflow obstruction, decreased absorption, and underproduction
C) inflow obstruction, increased absorption, and overproduction
D) outflow obstruction, decreased absorption, and overproduction
D
The junction of the anterior, occipital, and temporal horns is called the ______.
A) cistern
B) brainstem
C) choroid plexus
D) atrium (trigone)
C
The most important causes of abnormal neurodevelopment sequelae in premature infants is which one of the following?
A) hydrocephalus
B) choroid plexus cyst
C) white matter necrosis
D) alobar holoprosencephaly
D
The part of the brain that connects the forebrain and the spinal cord is which one of the following?
A) pons
B) trigone
C) cerebrum
D) brainstem
A
The portion of the brain that forms the lateral borders of the frontal horns of the lateral ventricles and lies anterior to the lateral ventricles and thalamus is which one of the following?
A) caudate nucleus
B) cisterna
C) corpus callosum
D) fontanelle
B
A thin, triangular space filled with CSF that lies between the anterior horn of the lateral ventricles is:
A) interhemispheric fissure
B) cavum septi pellucidi
C) trigone
D) caudate nucleus
A
The portion of the brain that lies posterior to the cranial fossa under the tentorium is called which one of the following?
A) cerebellum
B) corpus callosum
C) lower recess
D) cavum septum pellucidum
B
Sonography of the neonatal brain is evaluated through which one of the following?
A) inferior temporal lobe
B) anterior fontanelle
C) superior temporal lobe
D) posterior fontanelle
C
A mass of special cells located in the atrium of the lateral ventricles is which one of the following?
A) corpus callosum
B) caudate nucleus
C) choroid plexus
D) cisterna
D
The periventricular tissue, which may bleed easily before 32 weeks' gestation, is the _____.
A) caudate nucleus
B) corpus callosum
C) brainstem
D) germinal matrix
D
The area in which the falx cerebri sits that separates the two cerebral hemispheres is which one of the following?
A) tentorium
B) corpus callosum
C) lateral ventricles
D) interhemispheric fissure
A
The two ovoid brain structures located on either side of the third ventricle superior to the brainstem make up the _____.
A) thalami
B) choroid plexus
C) gyri
D) fontanelle
B
The brain coverings are known as which one of the following?
A) subendymomas
B) meninges
C) parenchyma
D) ependyma
B
Approximately 40% of CSF is produced by which one of the following?
A) extracellular fluid
B) choroid plexus
C) corpus callosum
D) cerebrum
D
The largest subarachnoid space demonstrated sonographically is ______.
A) suprasellar cistern
B) pontine cistern
C) quadrigeminal cistern
D) cistern magnum
C
Convolutions on the surface of the brain are called which one of the following?
A) sulci
B) fissures
C) gyri
D) lobes
B
The most common causes of congenital hydrocephalus is which one of the following?
A) papilloma if the choroid plexus
B) aqueductal stenosis
C) overproduction of CSF
D) agenesis of the corpus callosum
C
Acute neonatal brain hemorrhage appears _____.
A) echolucent
B) hypoechoic
C) echogenic
D) complex
A
Periventricular leukomalacia is defined as which one of the following?
A) white matter necrosis
B) focal brain necrosis
C) thickened ependyma
D) an epidural hemorrhage
D
The primary brain vesicle, rhombencephalon, is located in which one of the following?
A) hypothalamus
B) forebrain
C) midbrain
D) hindbrain
B
Which one of the following is most likely the result of a germinal matrix hemorrhage?
A) cerebral cyst
B) subependymal cyst
C) subarachnoid cyst
D) periventricular leukomalacia
D
Which of the following brain structures are part of the hindbrain?
A) Cerebral hemispheres, thalamus, and hypothalamus
B) Spinal cord, cisterna magna, and nerve roots
C) Mastoid fontanel, temporal lobe, and lateral ventricle
D) Pons, cerebellum, and medulla oblongata
Lateral Ventricles
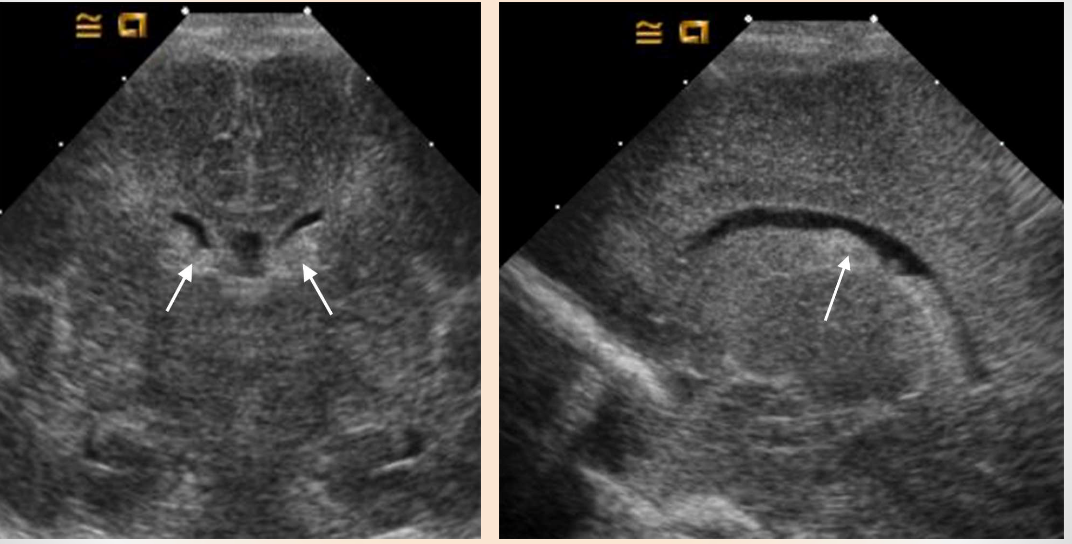
What are the arrows pointing to?
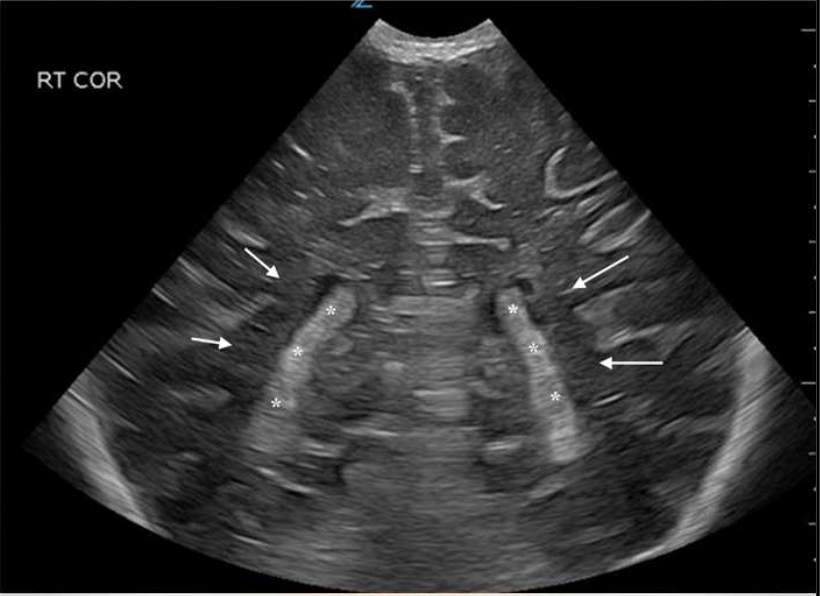
Choroid Plexus
What are the stars?
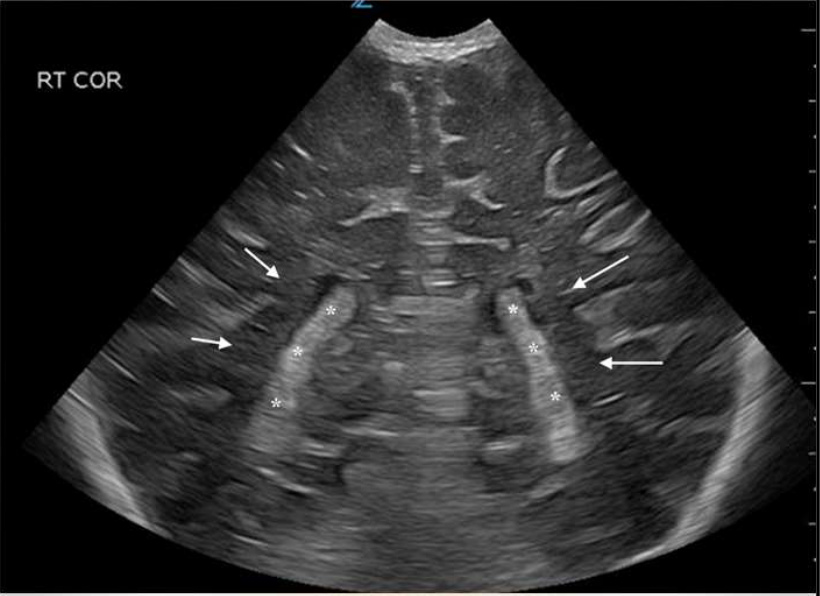
Cavum Septum Pellucidum
What is the arrows pointing to?
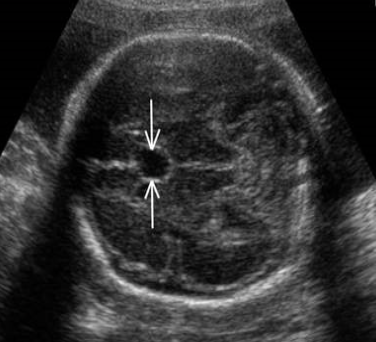
Lateral Ventricle
What is the anechoic structure?
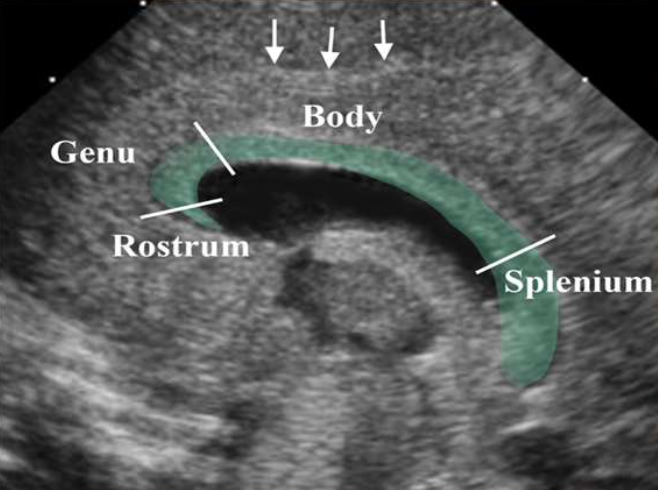
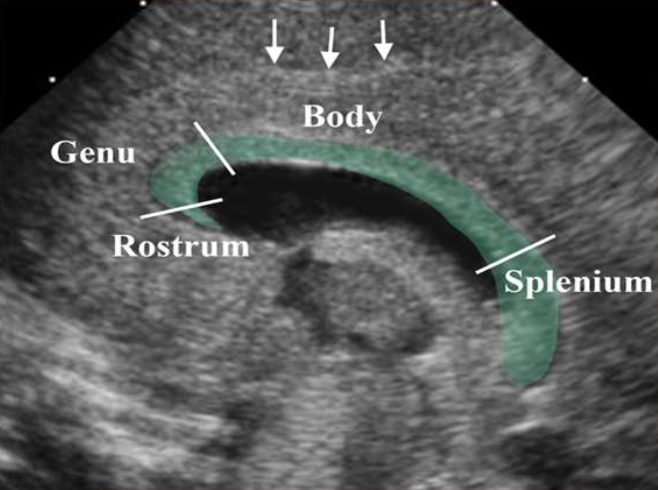
Corpus Callosum
What is the green highlighted structure?
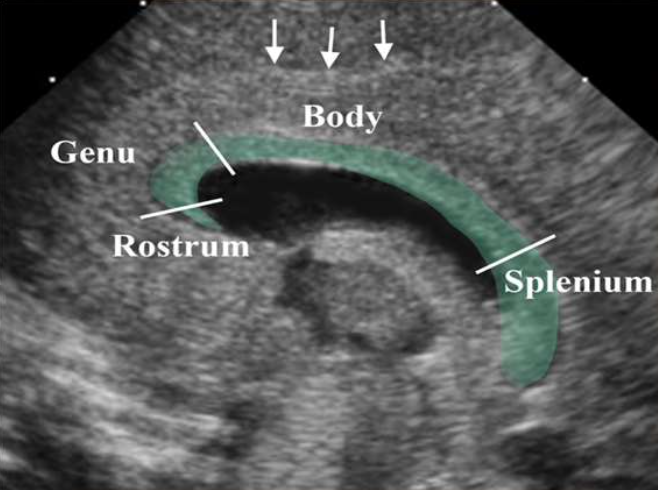
Sagittal
What view is this image?
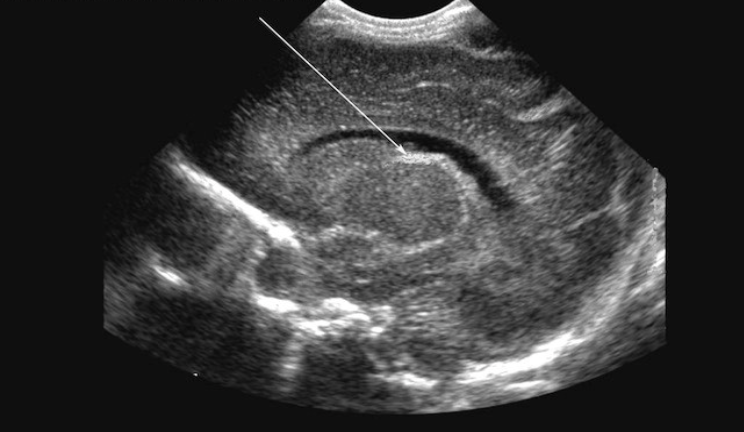
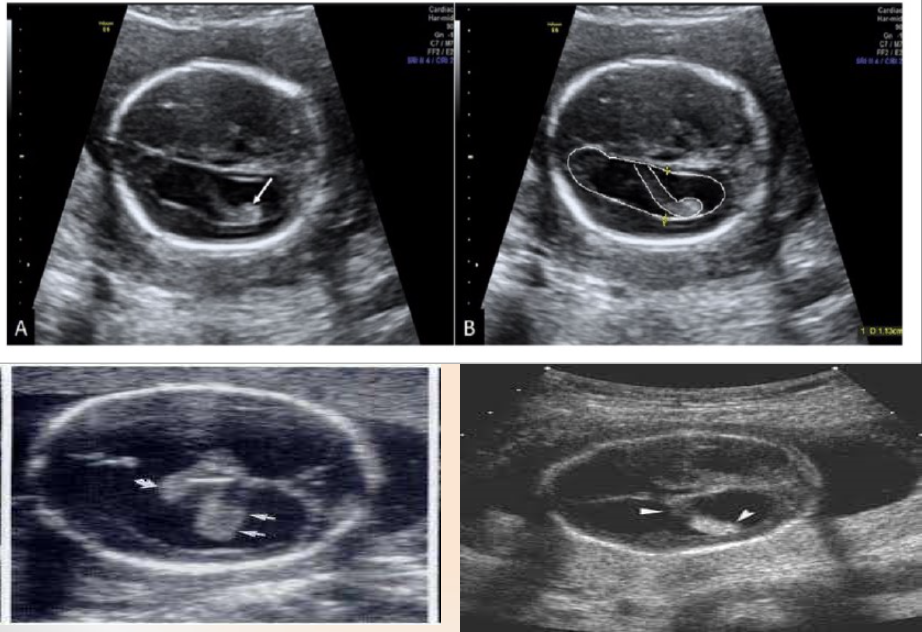
Germinal Matrix at the Caudothalamic Groove
What is the arrow pointing to?
Caudothalamic Groove
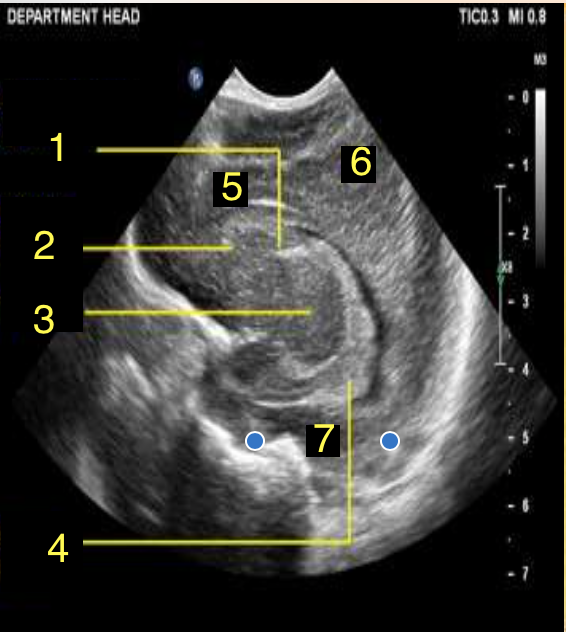
What is number 1?

Caudate Nucleus
What is number 2?
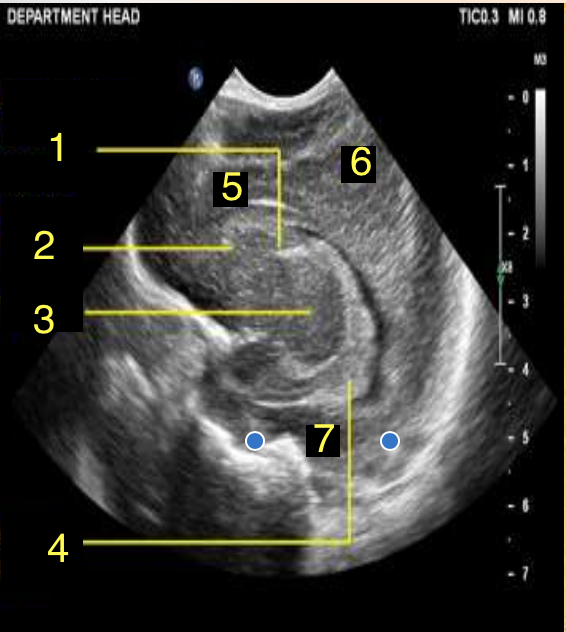
Thalamus
What is number 3?
Choroid Plexus
What is number 4?
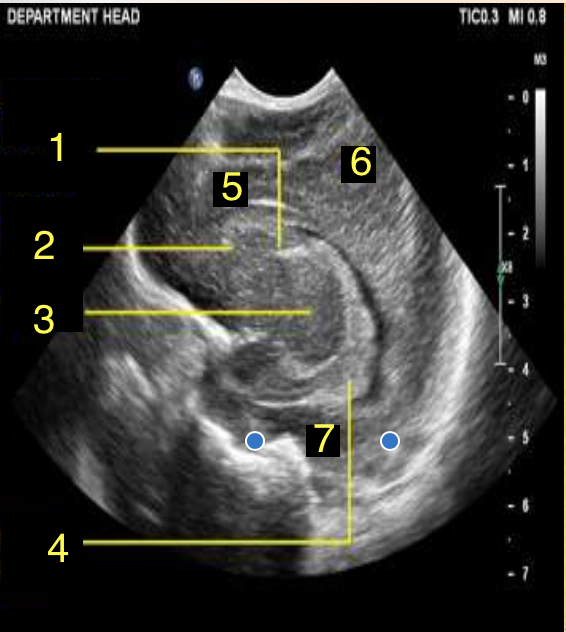
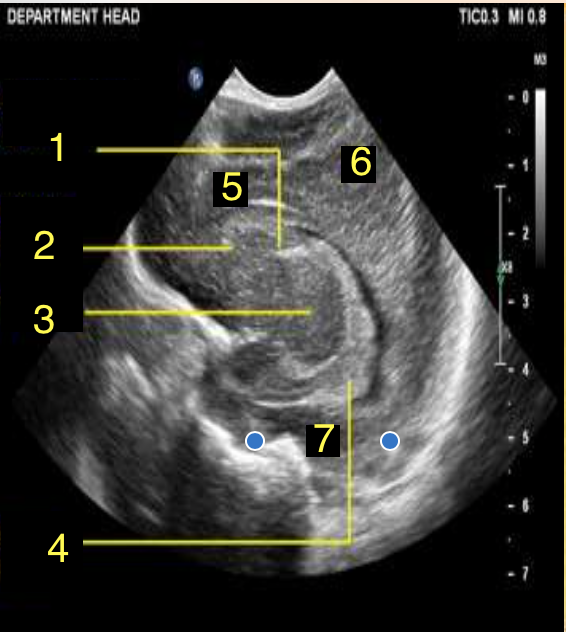
Frontal Lobe
What is number 5?
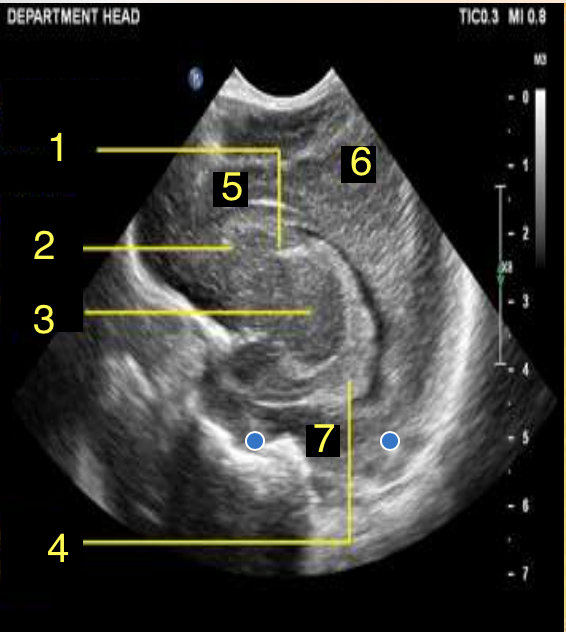
Parietal Lobe
What is number 6?
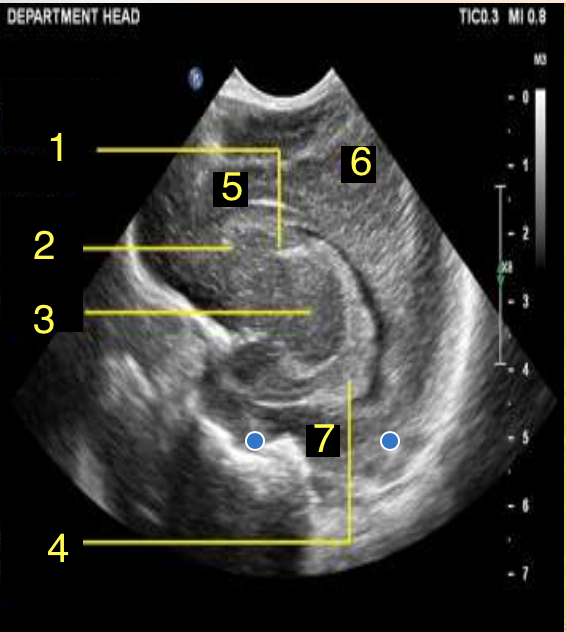
Temporal Lobe
What is number 7?
Corpus Callosum
What is the color pink?
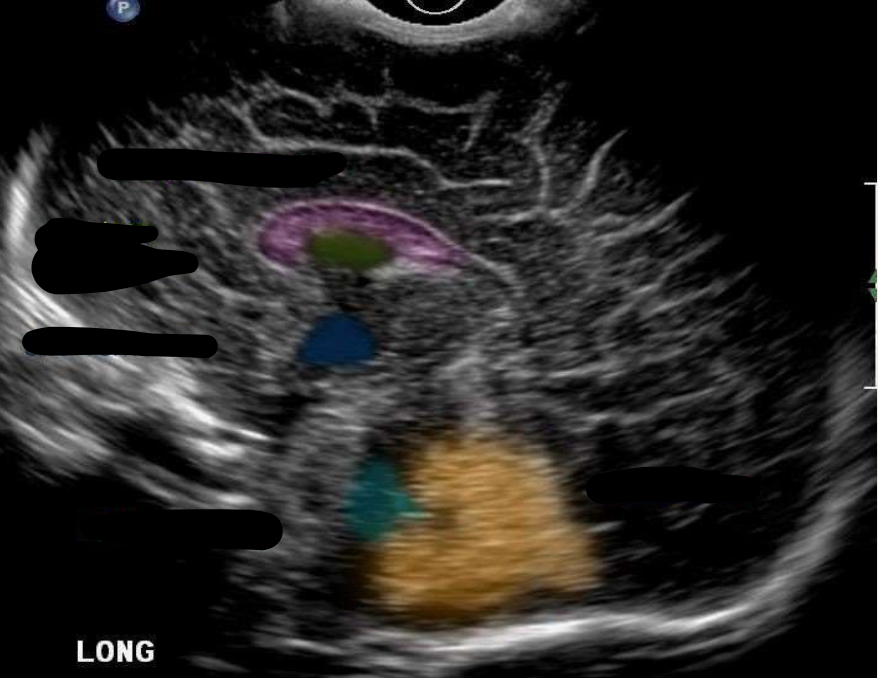
Cavum Septum Pellucidum
What is the color green?
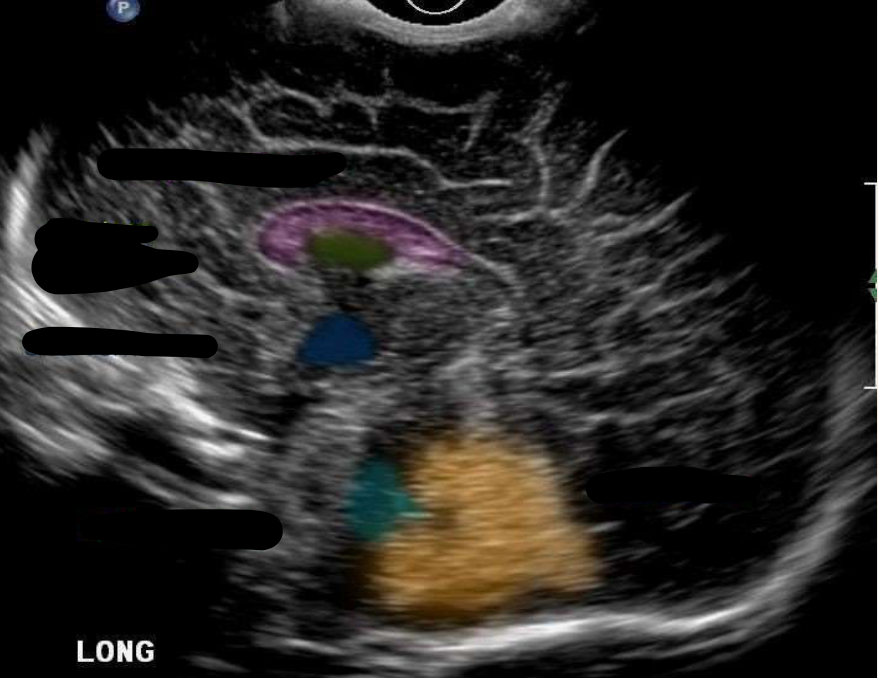
Third Ventricle
What is the color navy?
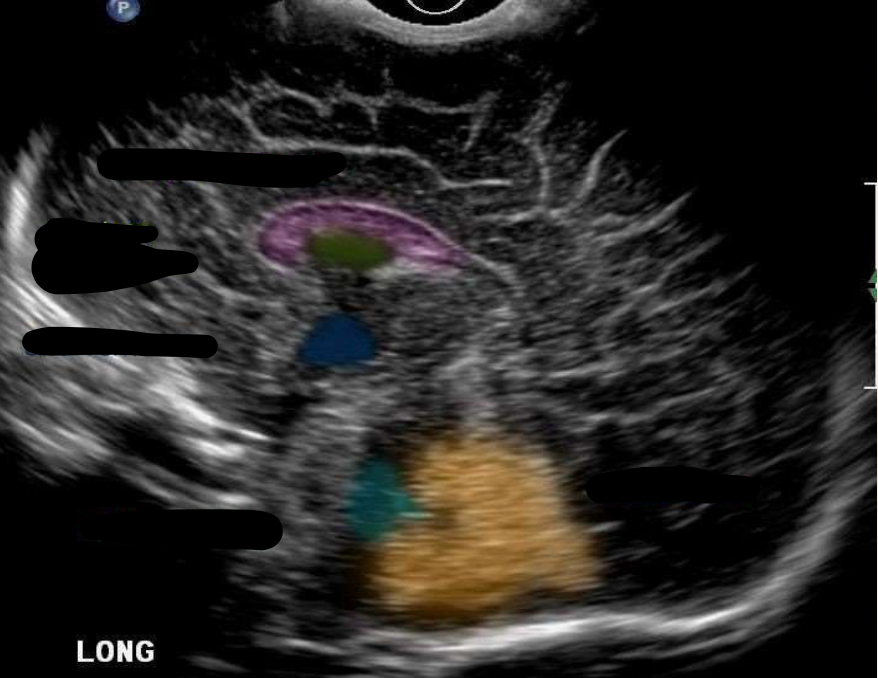
Fourth Ventricle
What is the color aqua?
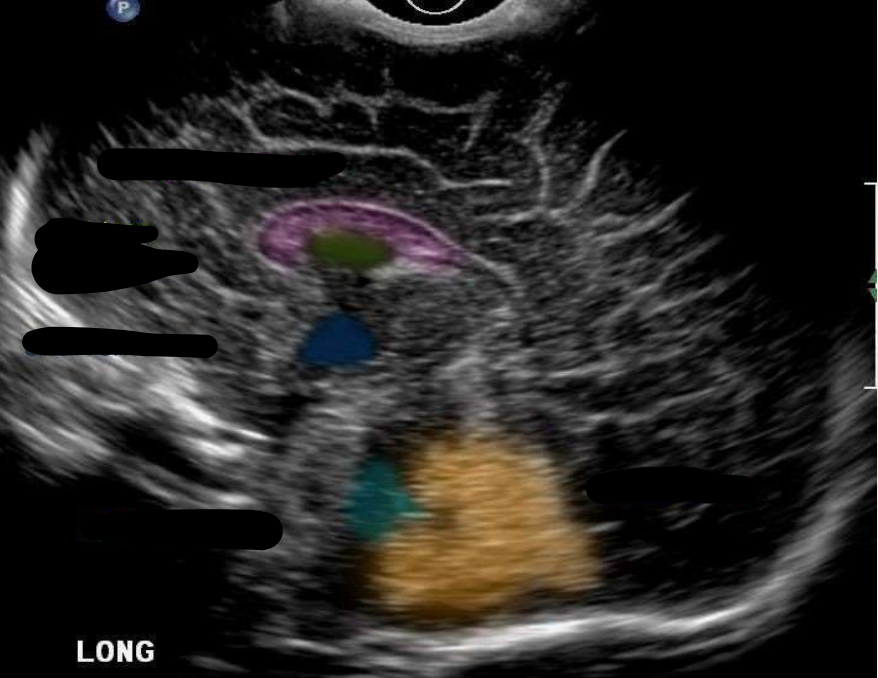
Cerebellum
What is the color orange?
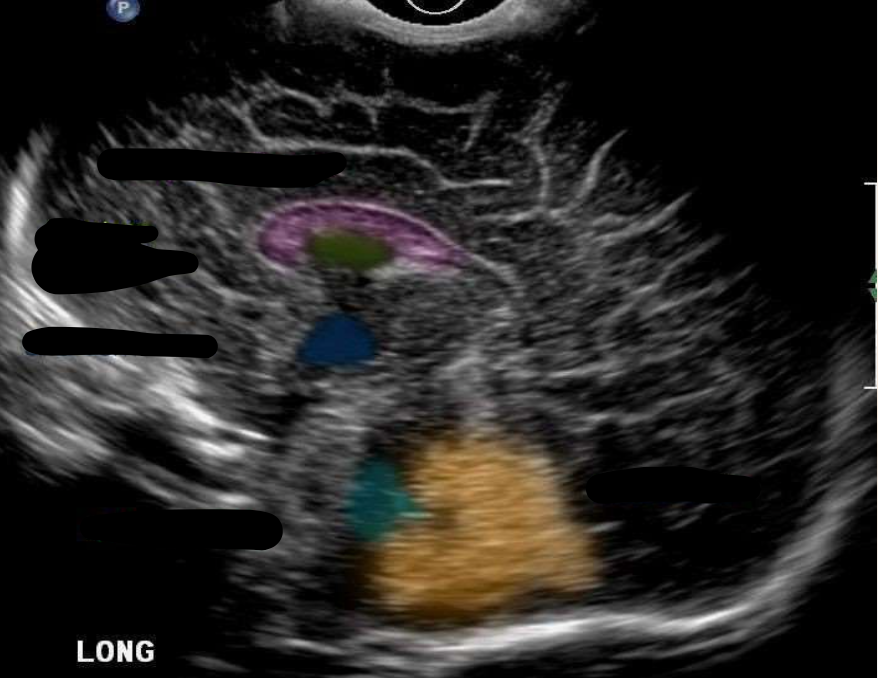
“Dangling” Choroid Plexus
What is this imaging showing?
Aqueductal Stenosis/Hydrocephalus
What is this imaging showing?
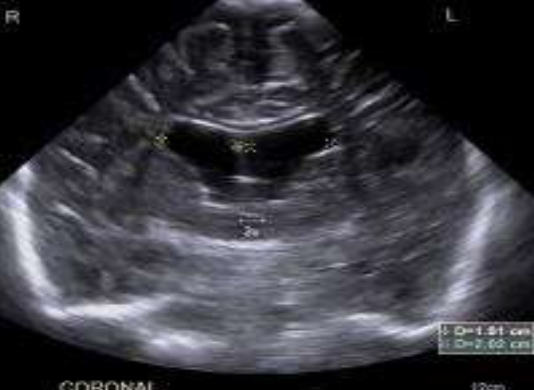
Ventricular Index
What is being measured?
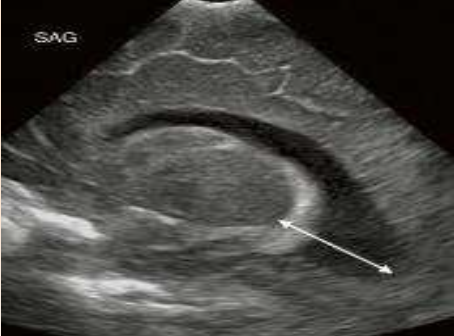
Anterior Horn Width
What is being measured?
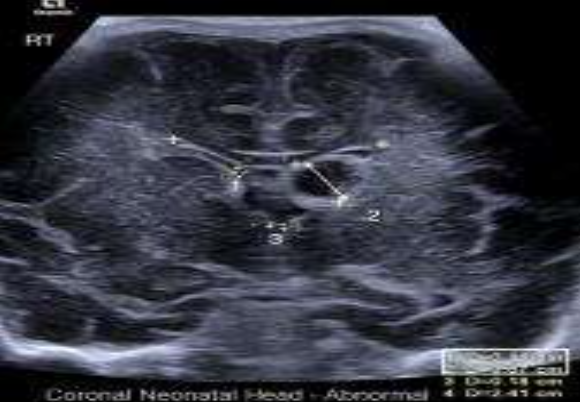
Frontal Temporal Horn Ratio
What is being measured?
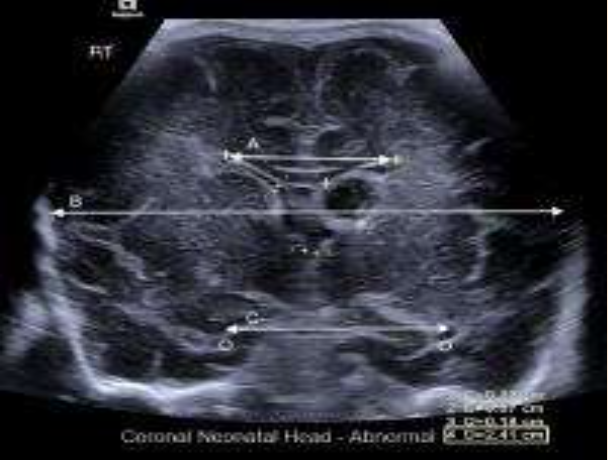
Thalsmo-Occipital Distance
What is being measured?
Grade I Subependymal Hemorrhage (Intracranial Hemorrhage)
What pathology is shown in this image?
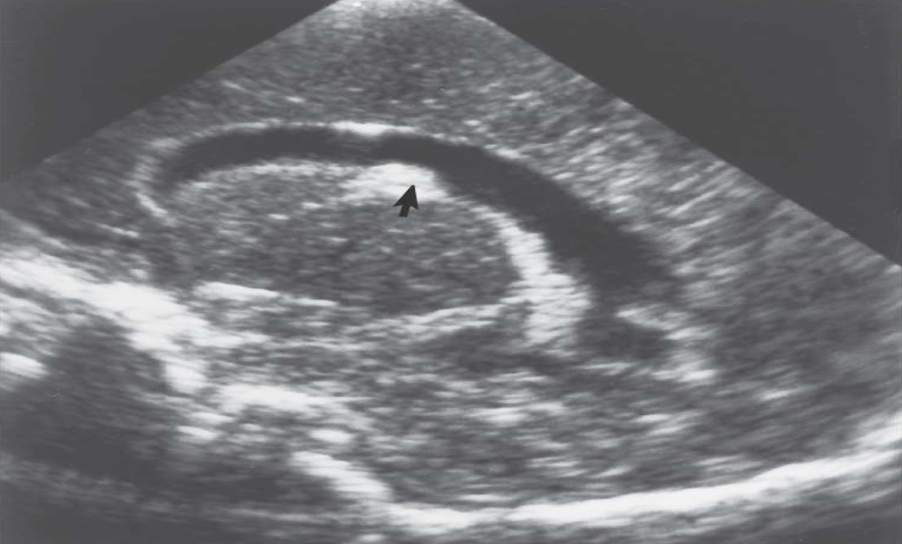
Caudothalmic Groove
Where is this bleed located?
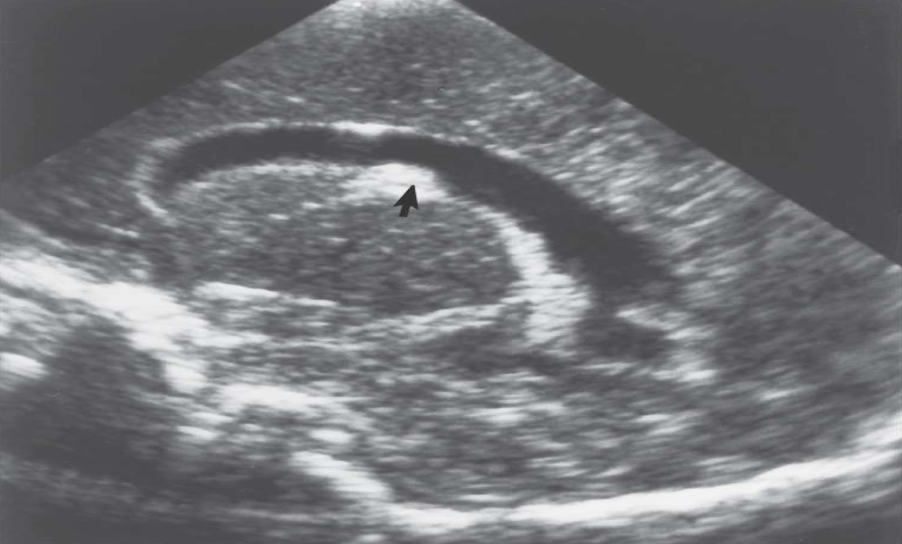
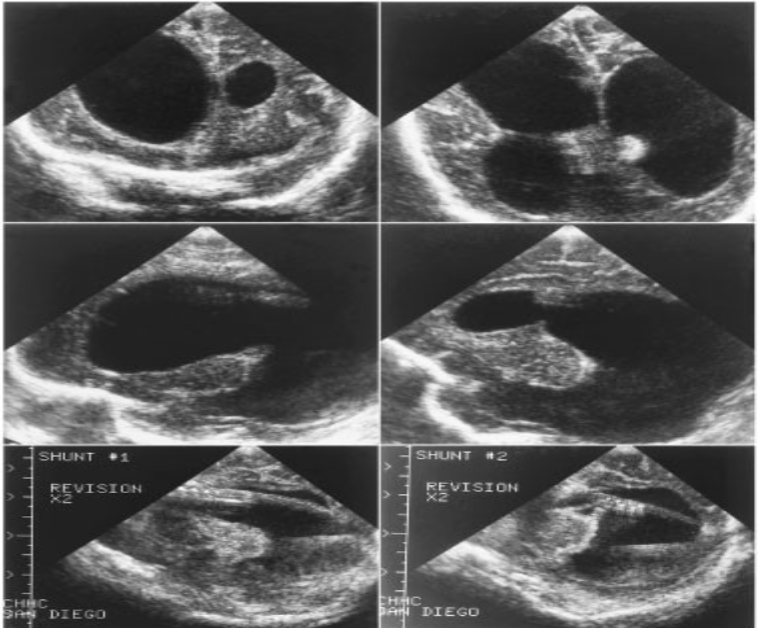
Grade I Intraventricular Hemorrhage
What pathology is being shown?
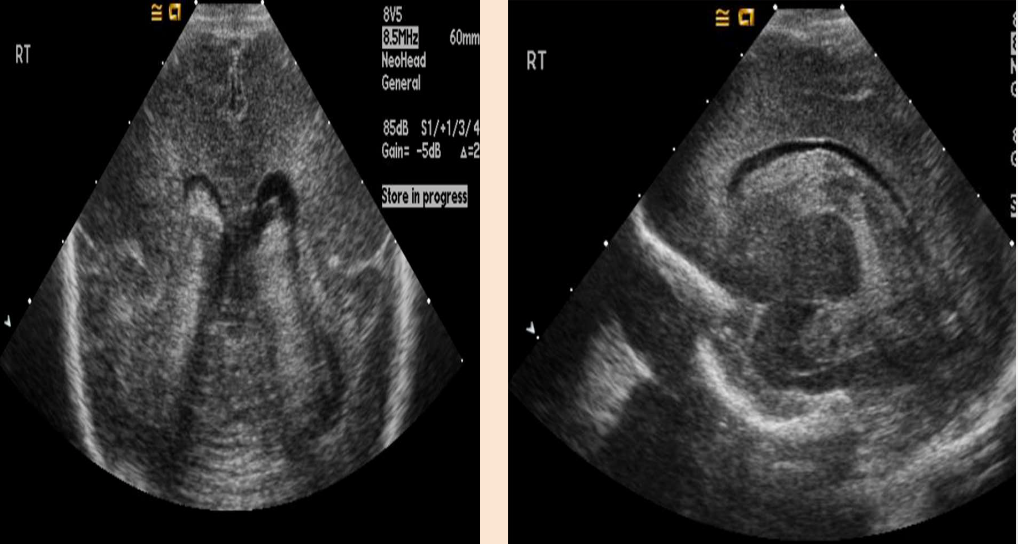
Grade II & III Intraventricular Hemorrhage
What pathology is being shown?
Grade IV Intraventricular Hemorrhage
What pathology is being shown?
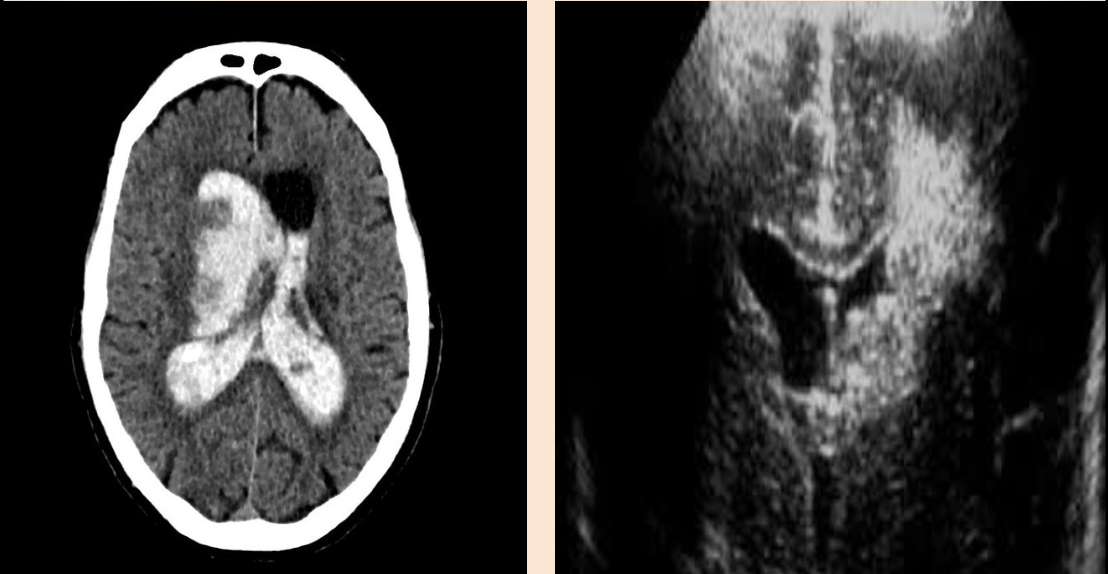
Intracerebellar Hemorrhage
What pathology is being shown?
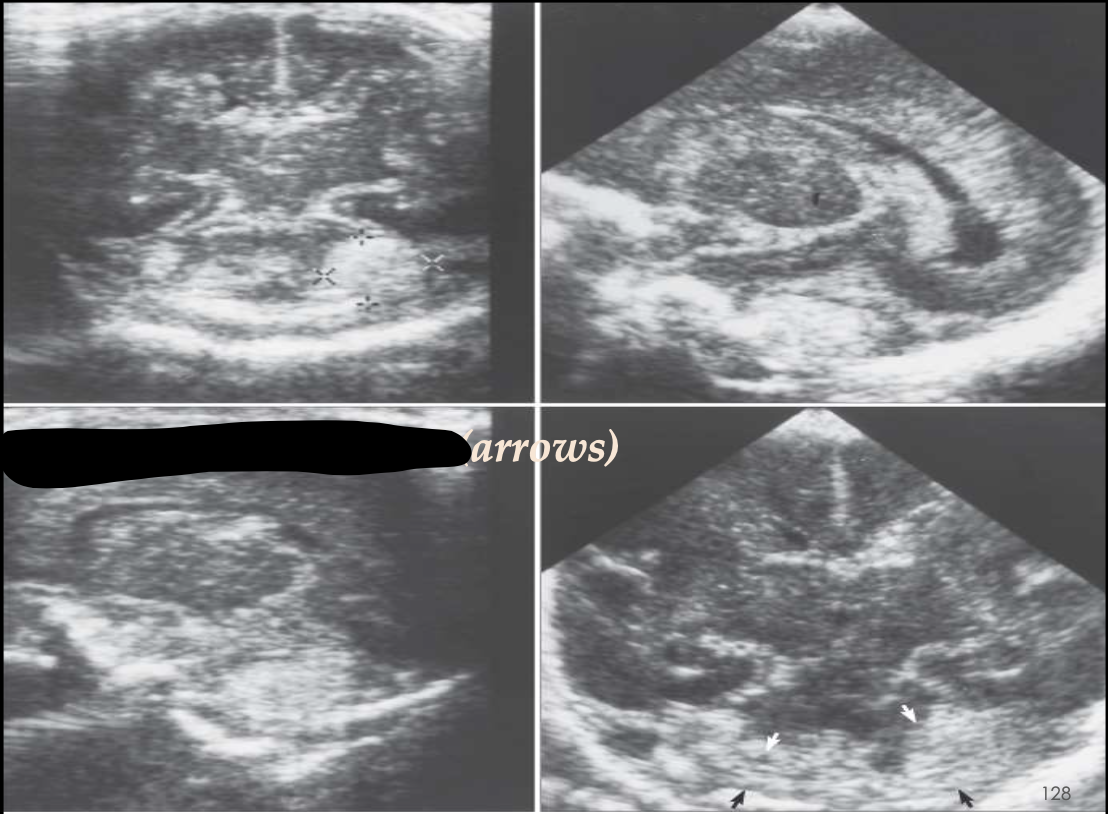
Periventricular Leukomalcia (PVL)
What pathology is being shown?
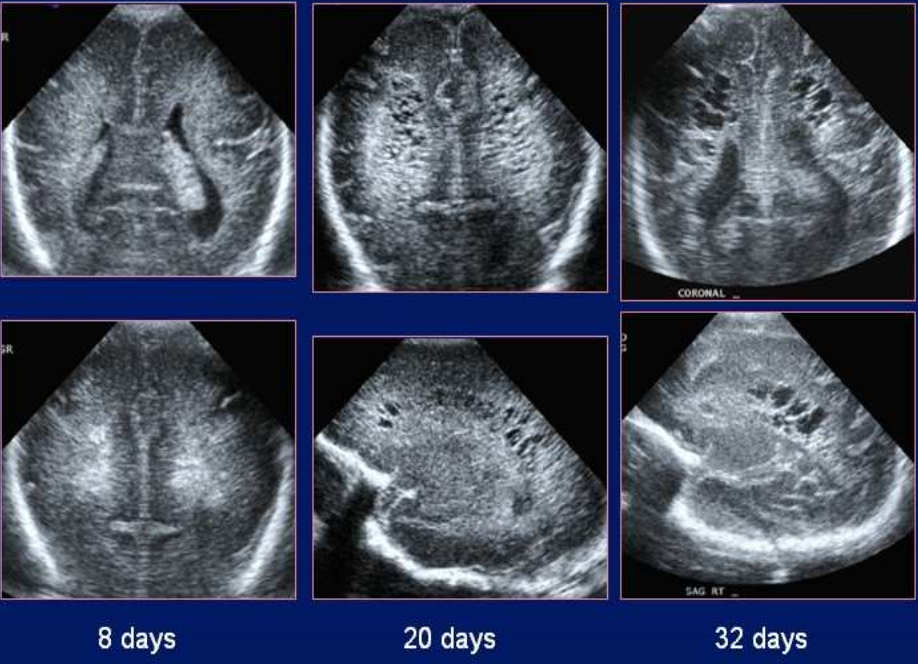
Arnold Chiari II Malformation
What pathology is being shown?
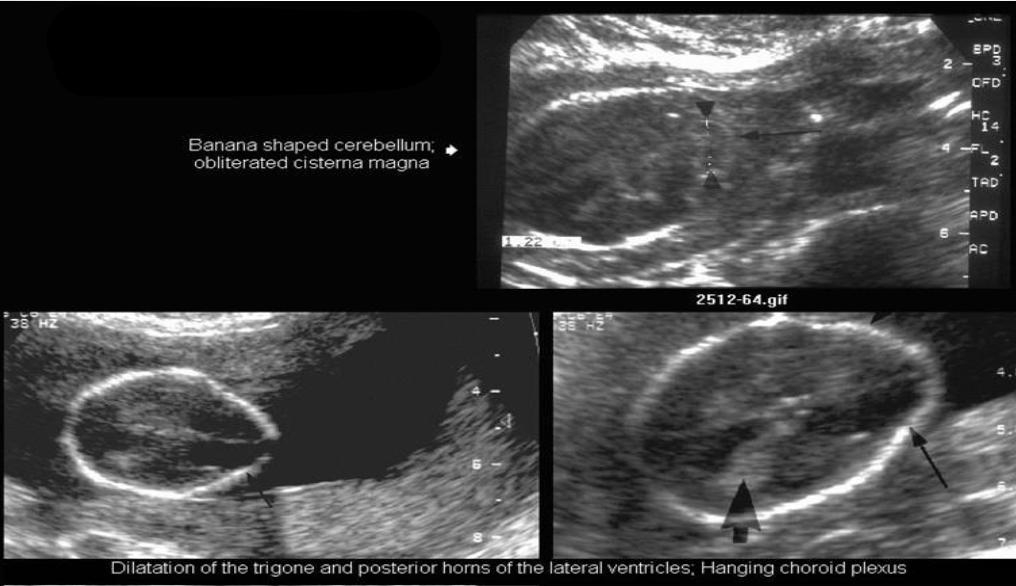
Arnold Chiari Malformation
What pathology is being shown?
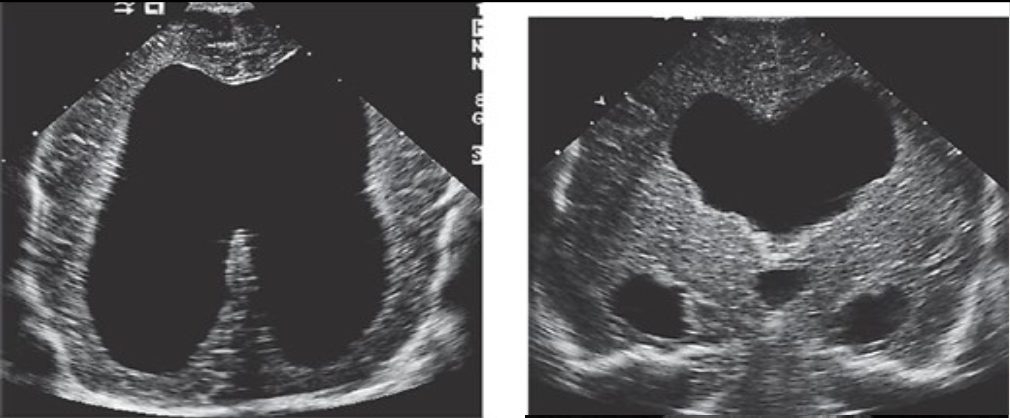
Dandy Walker Malformation
What pathology is being shown?
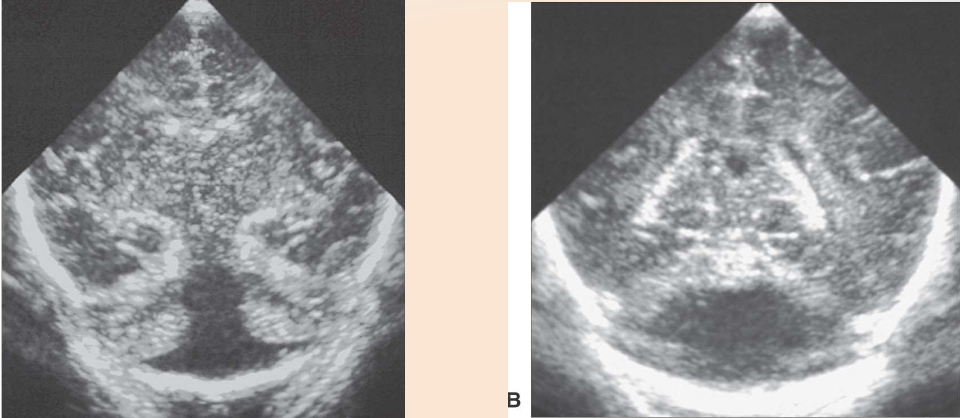
Dandy Walker Malformation
What pathology is being shown?
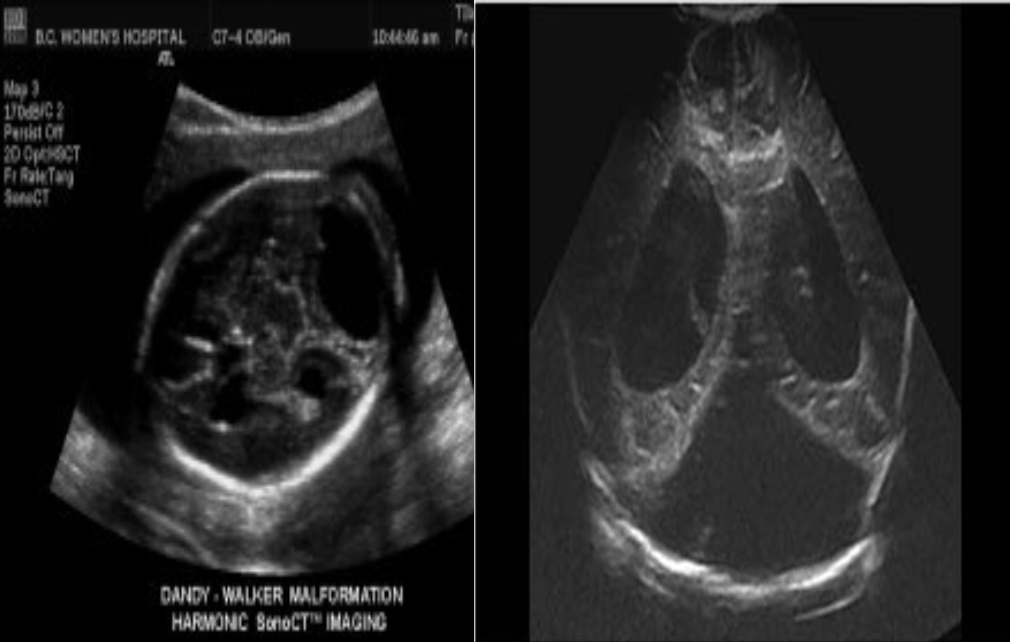
Alobar Holoprosencephaly
What pathology is being shown?
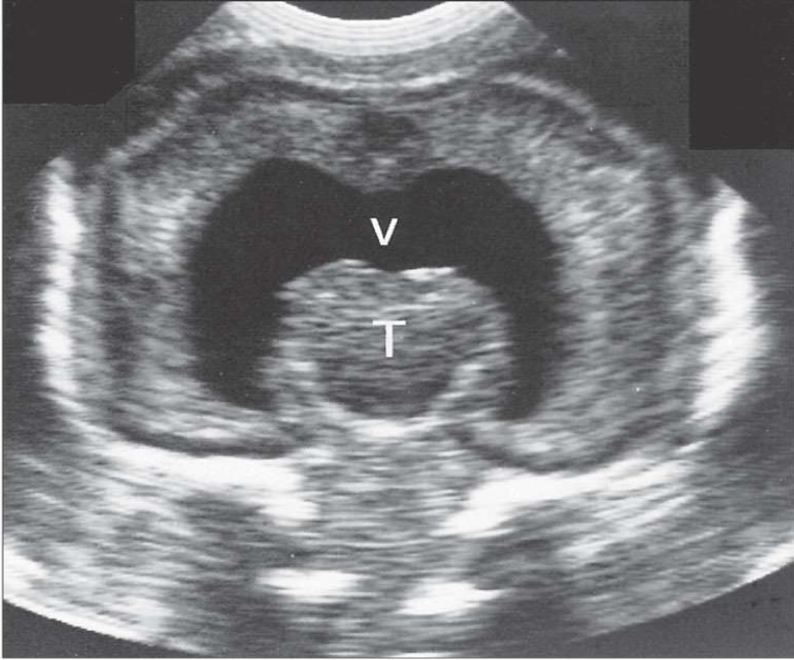
Fused Thalami
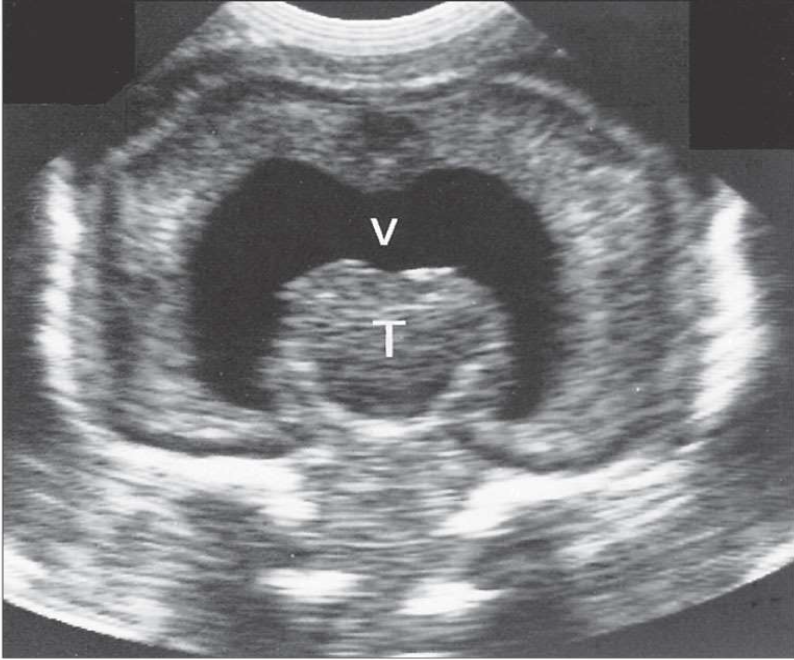
What is the structure labeled T?
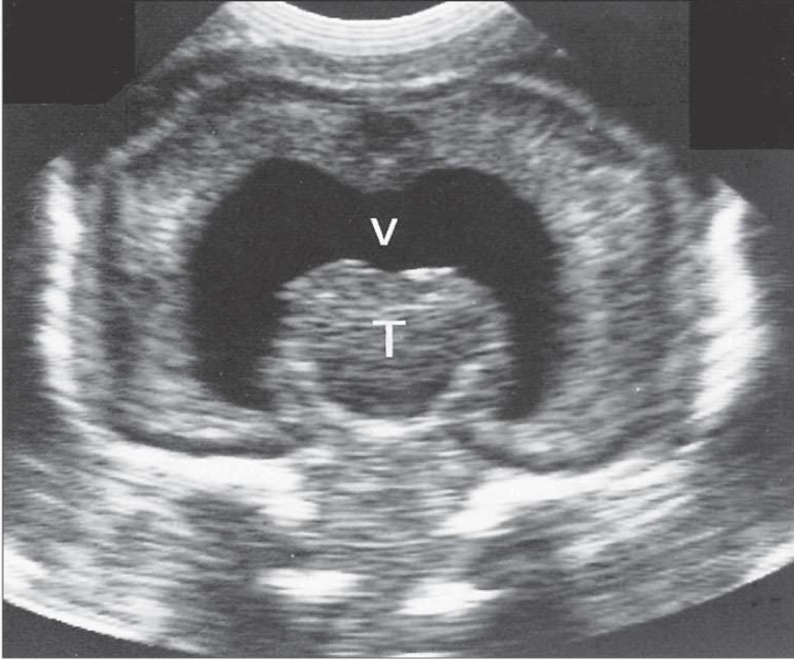
Common Ventricle
What is the structure labeled V?
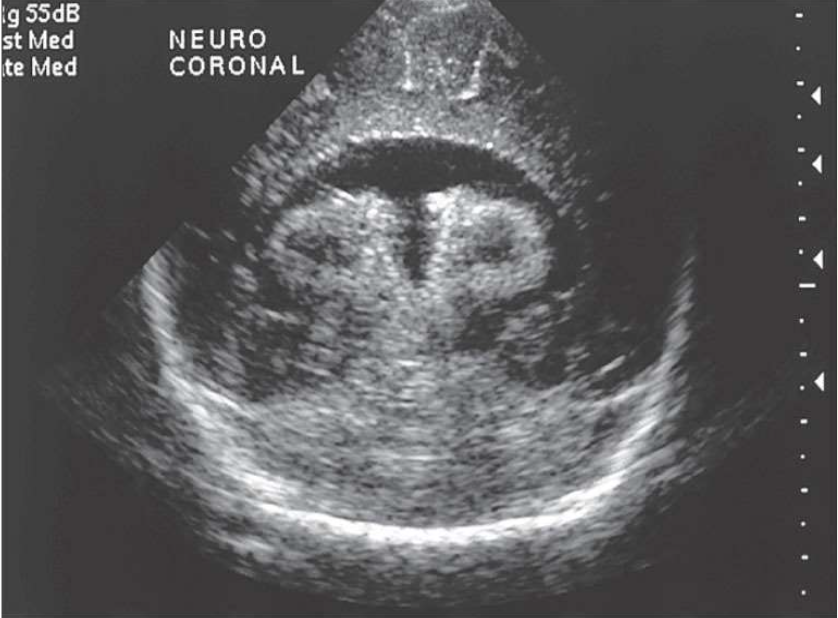
Semilobar Holoprosencephaly
What pathology is being shown?
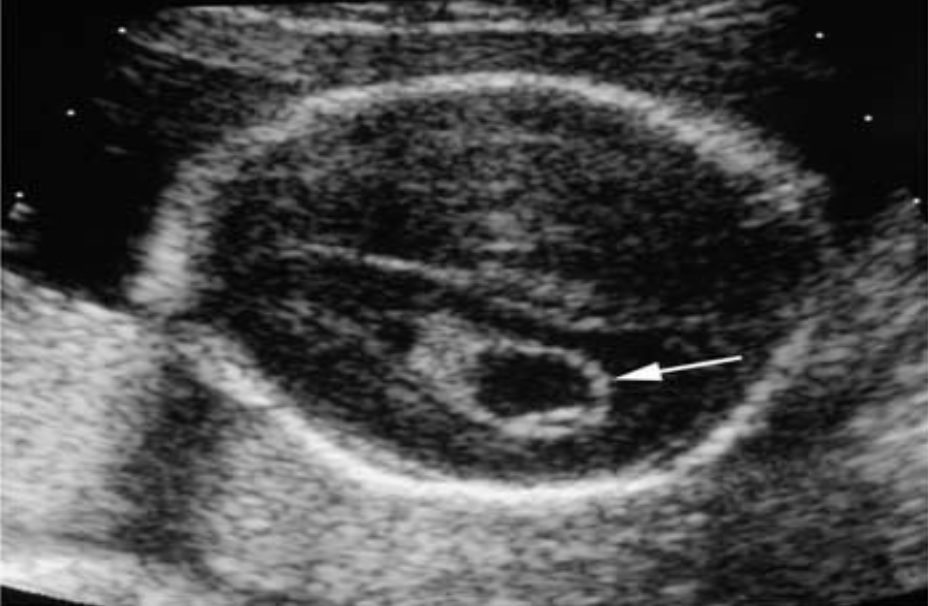
Choroid Plexus Cyst
What pathology is being shown?
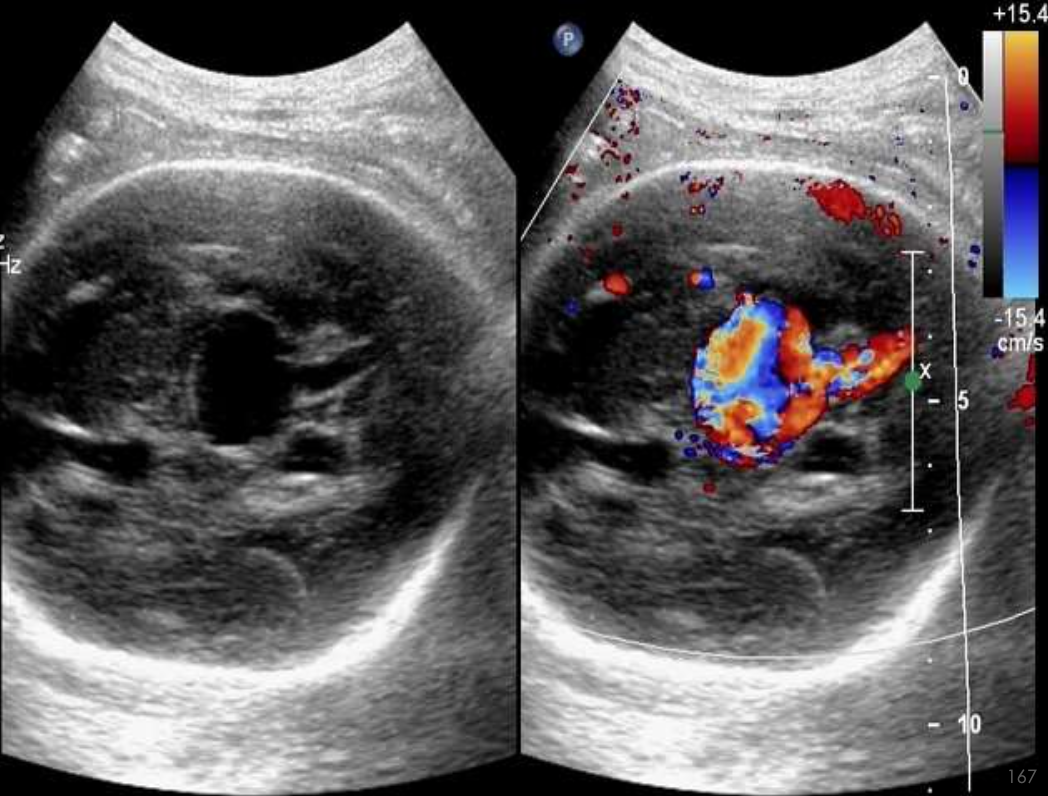
Galenic Venous Malformation
What pathology is being shown?
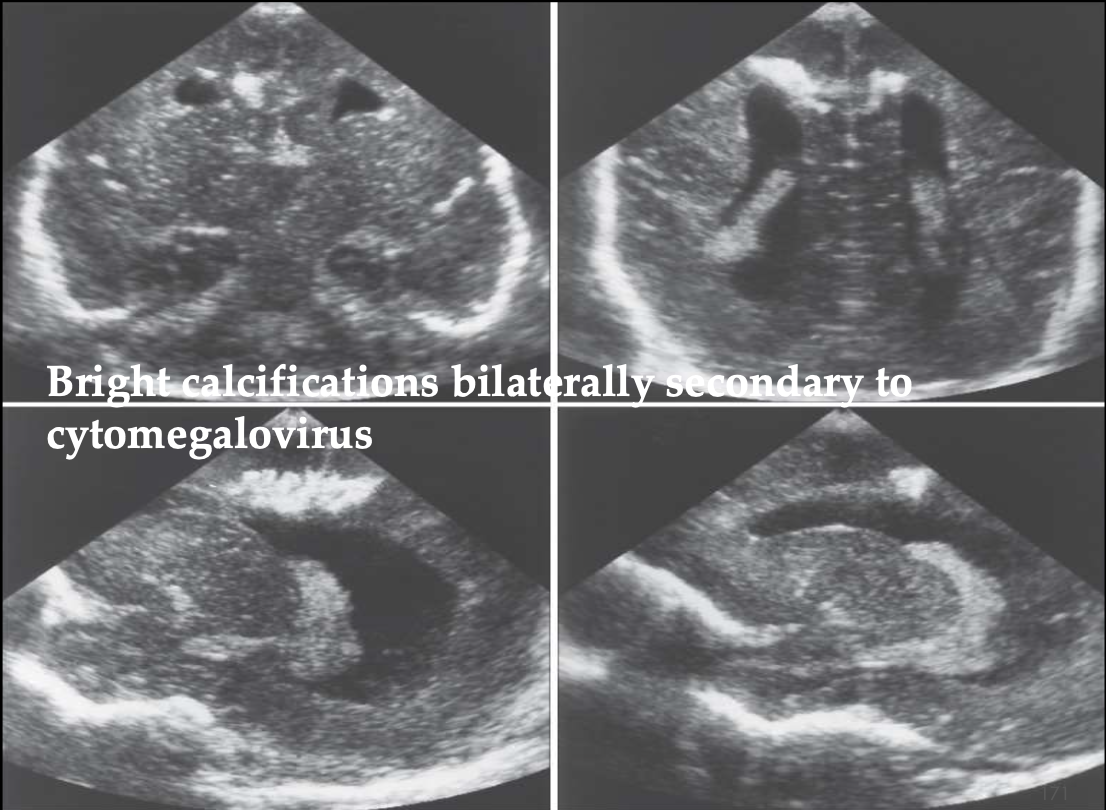
Ventriculitis
What pathology is being shown?
Interhemispheric Falx
What is the highlighted structure?
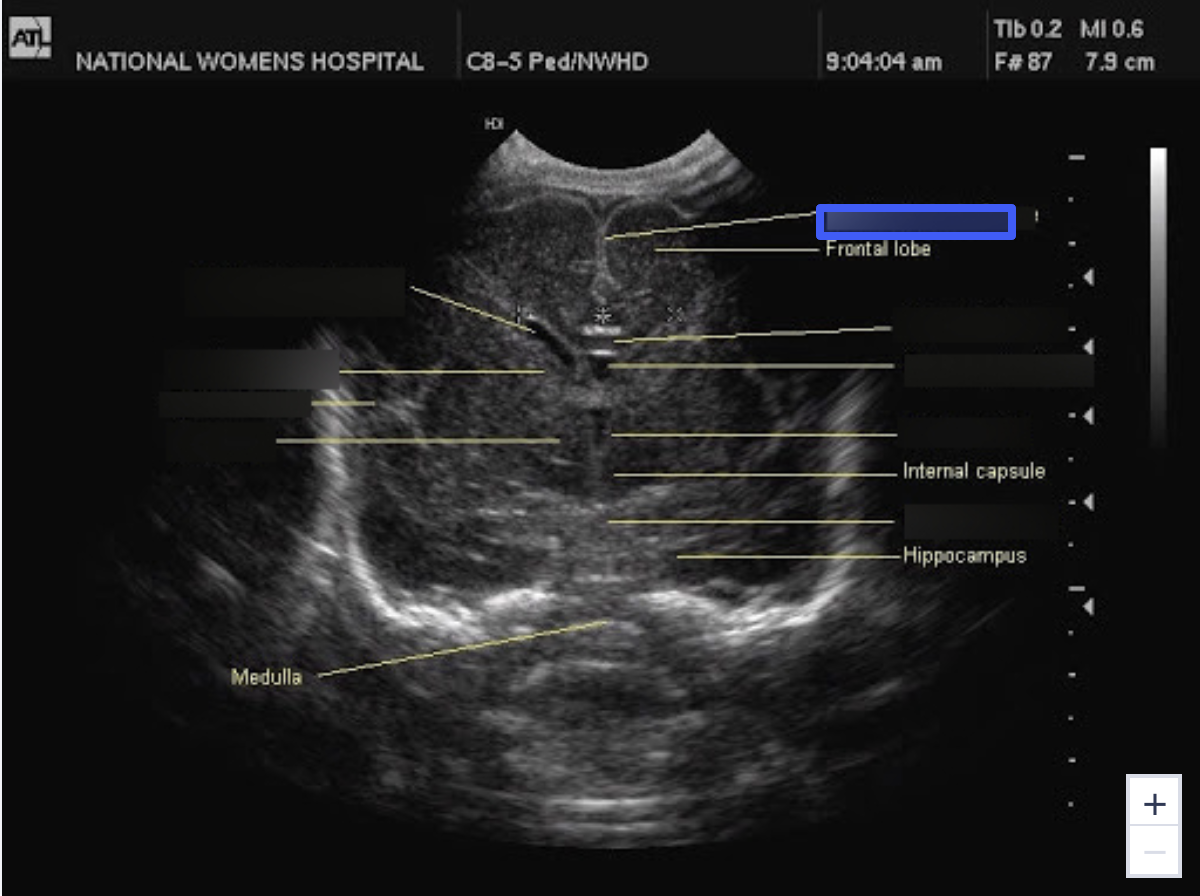
Corpus Callosum
What is the highlighted structure?
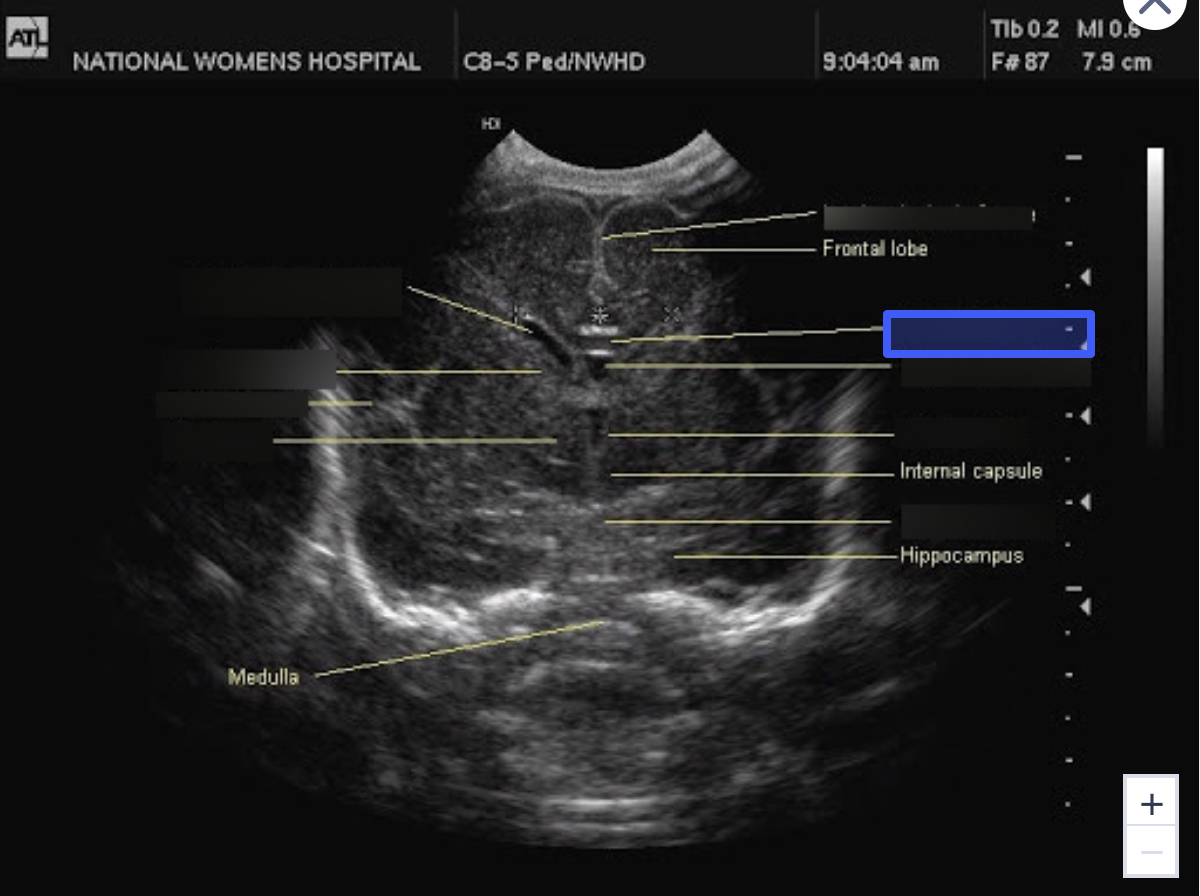
Cavum Septum Pellucidum
What is the highlighted structure?
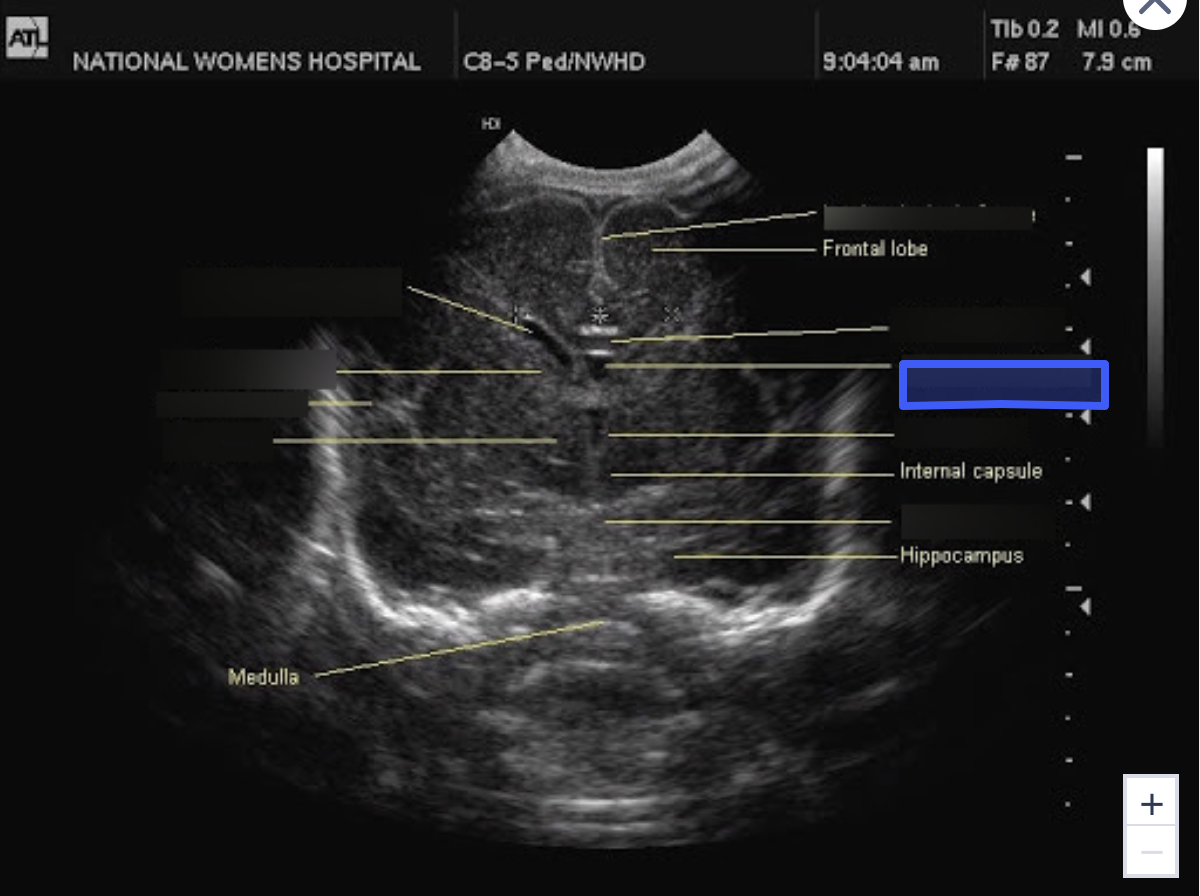
Third Ventricle
What is the highlighted structure?
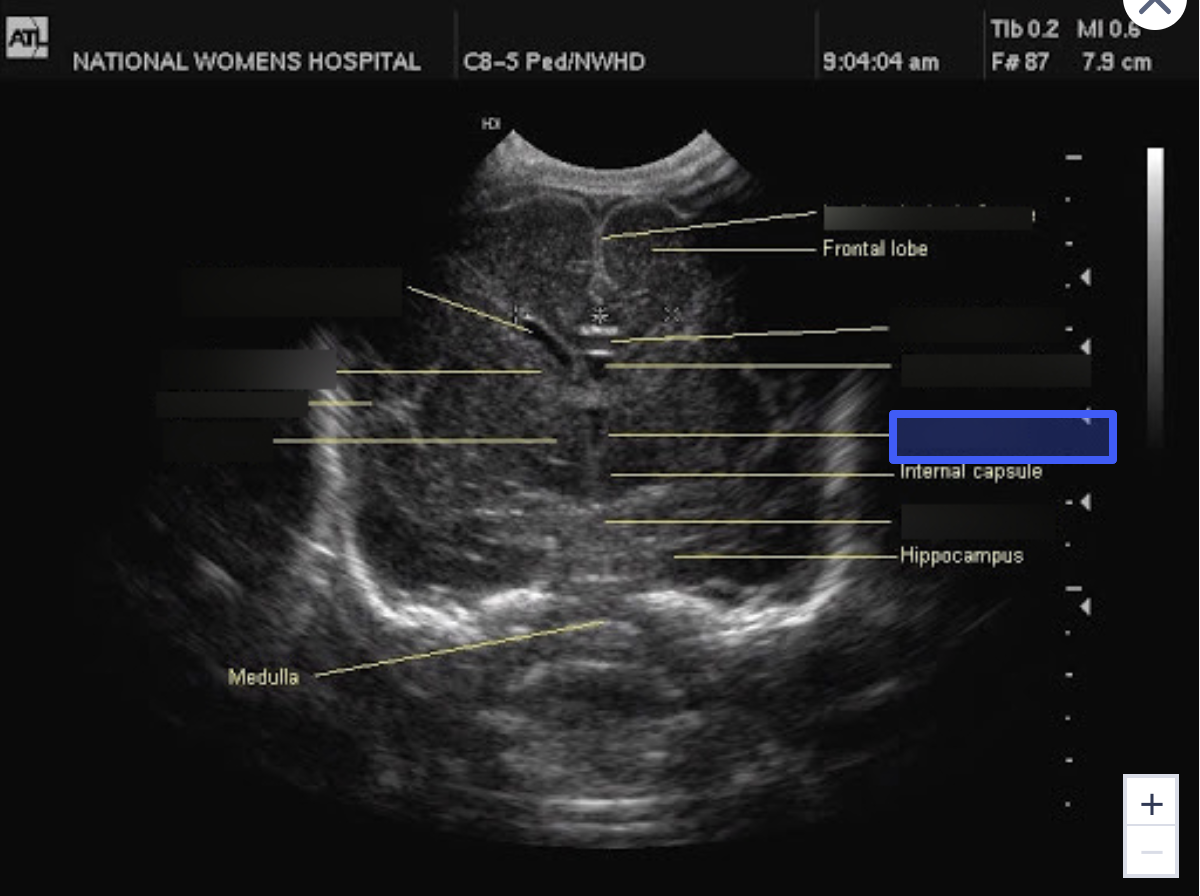
Pons
What is the highlighted structure?
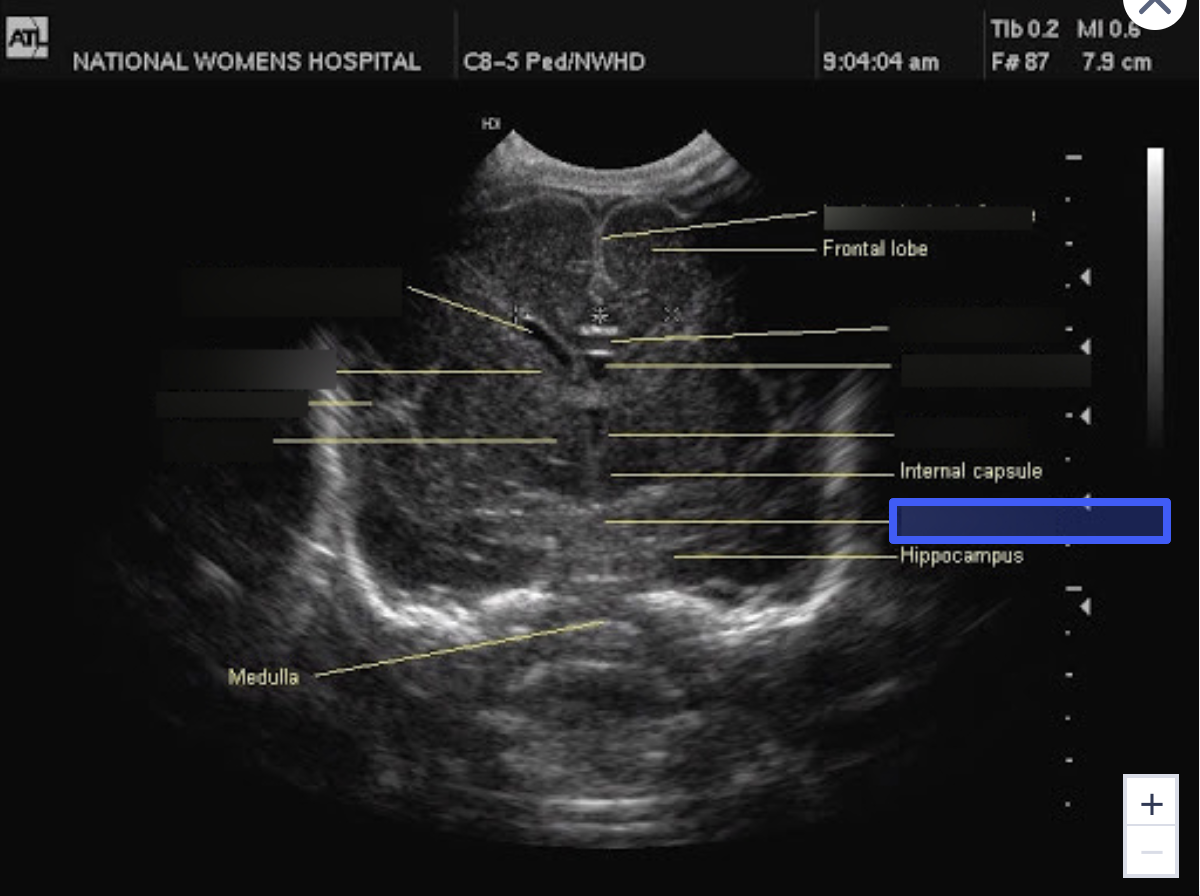
Thalamus
What is the highlighted structure?
Sylvian Fissure
What is the highlighted structure?
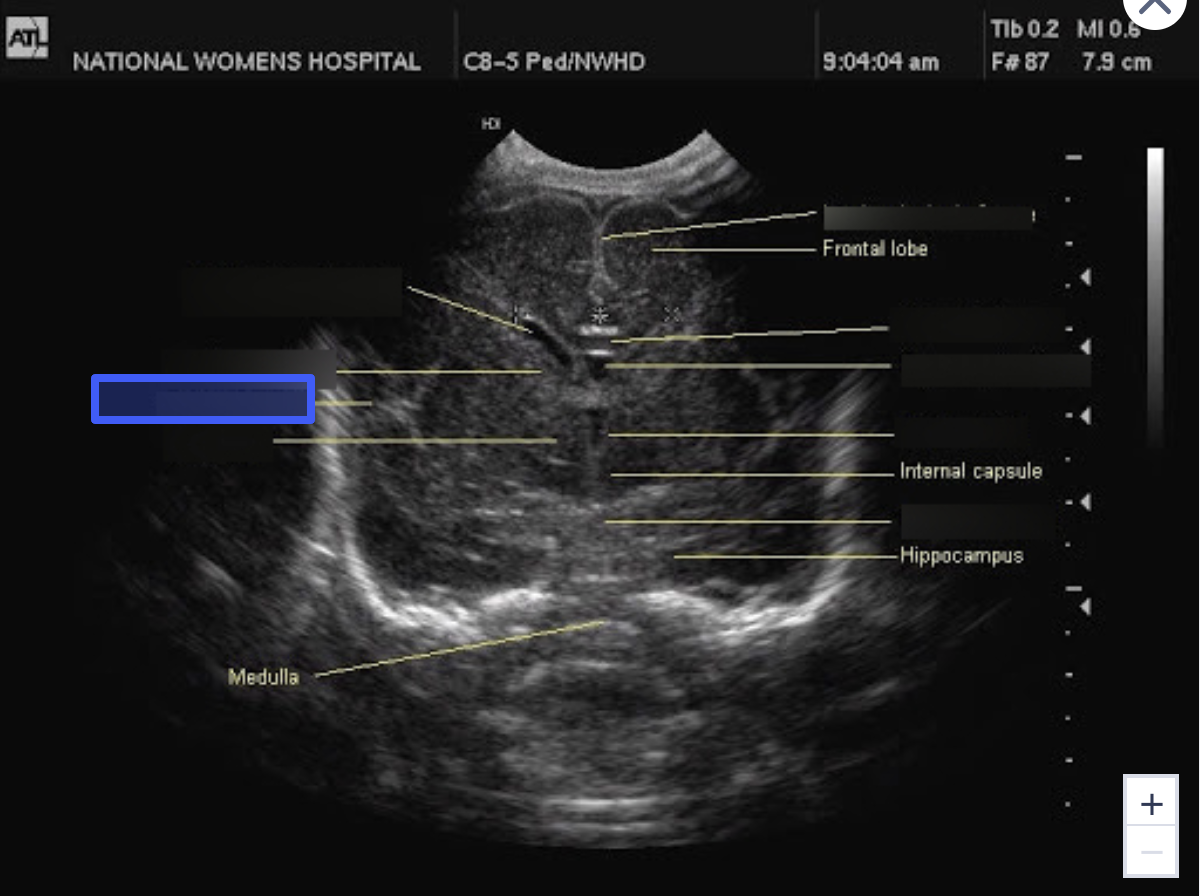
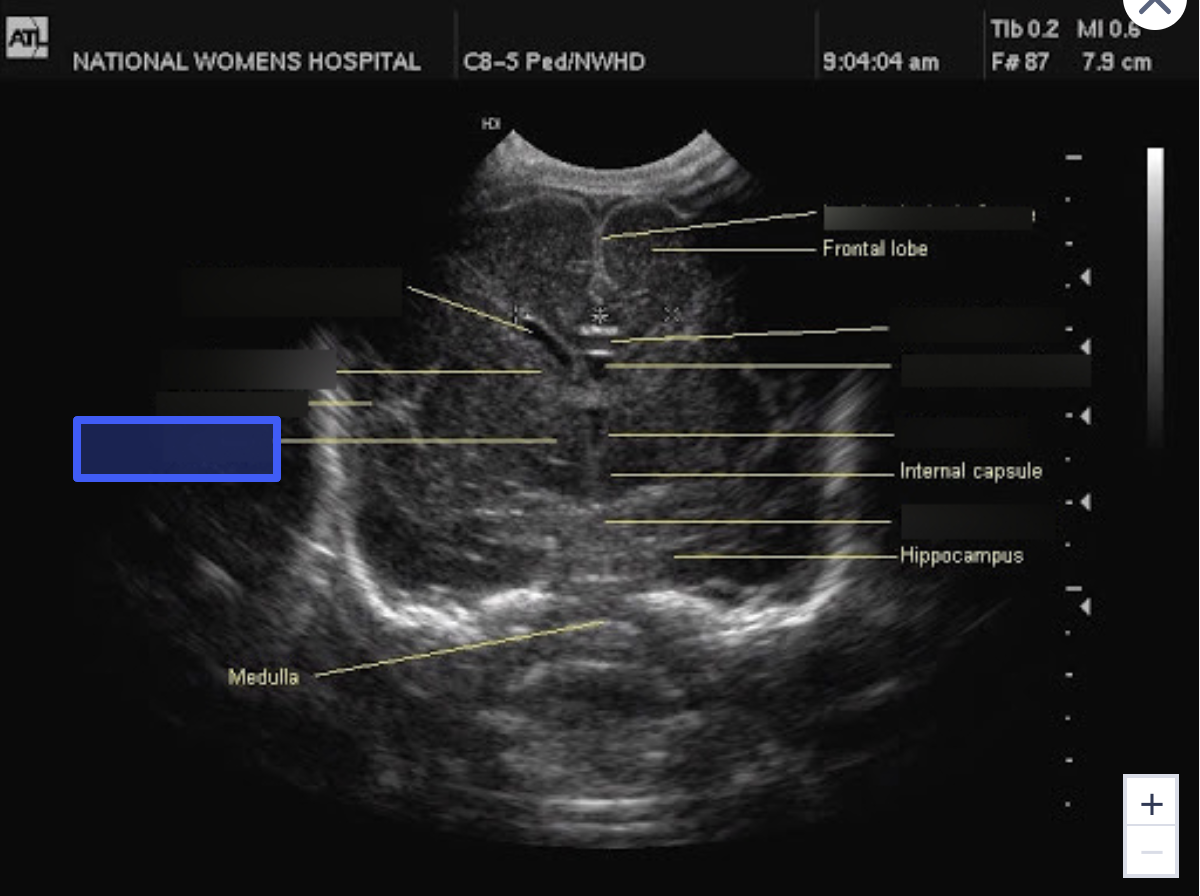
Caudate Nucleus
What is the highlighted structure?
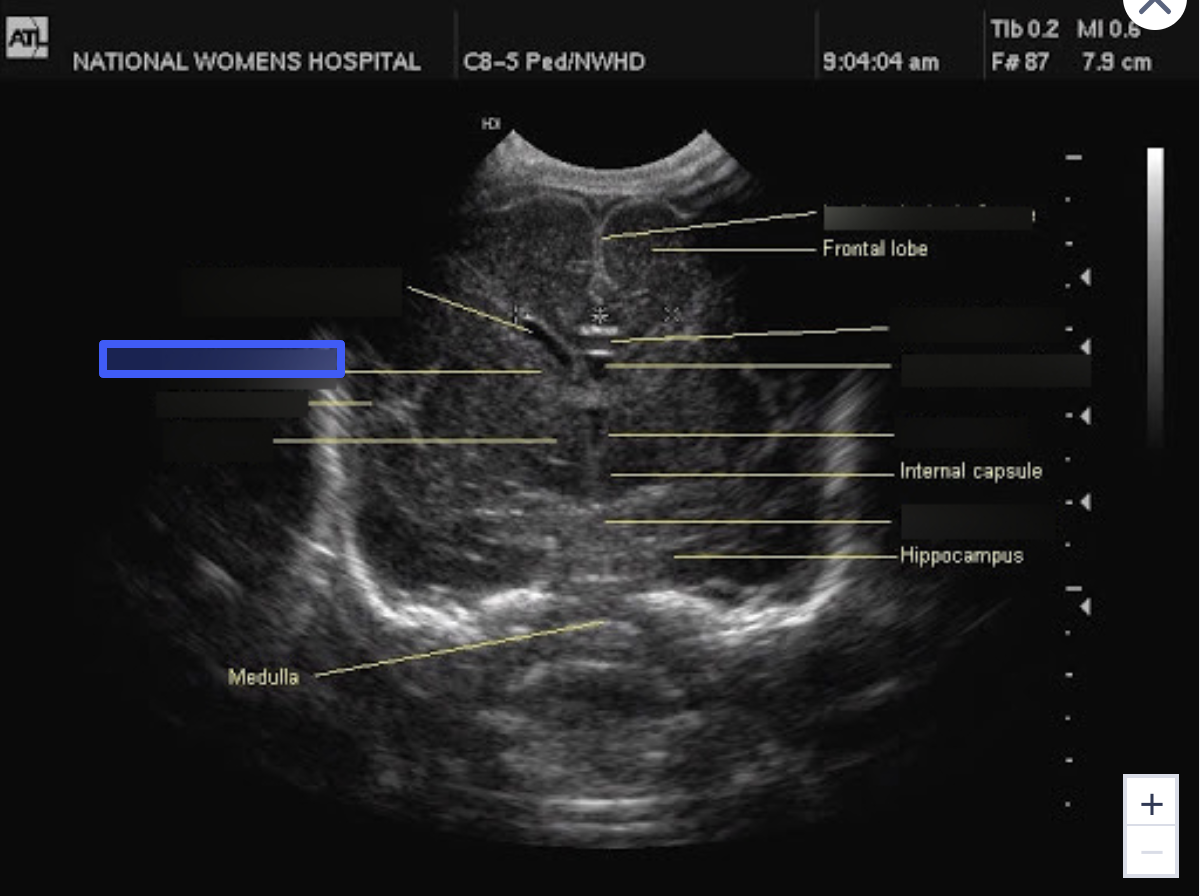
Lateral Ventricle
What is the highlighted structure?
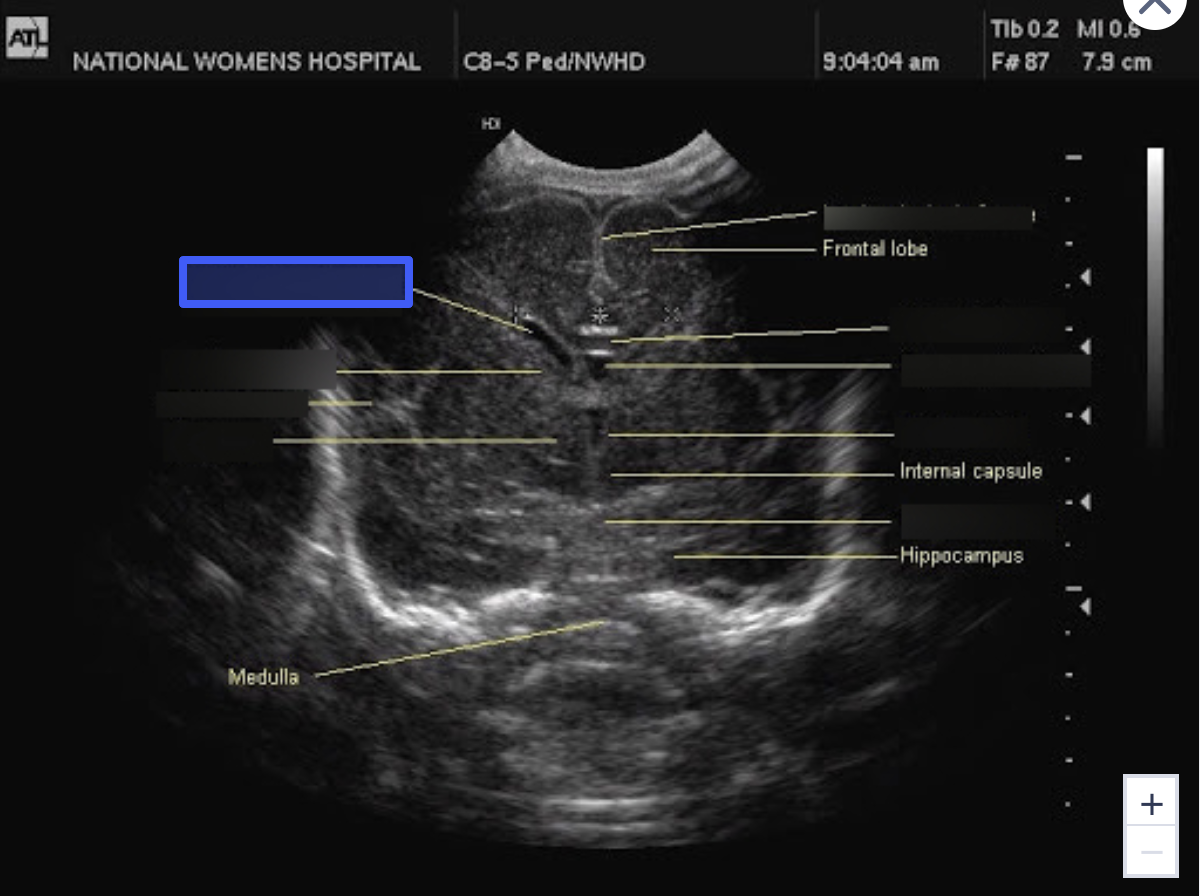
Corpus Callosum
What is the highlighted structure?
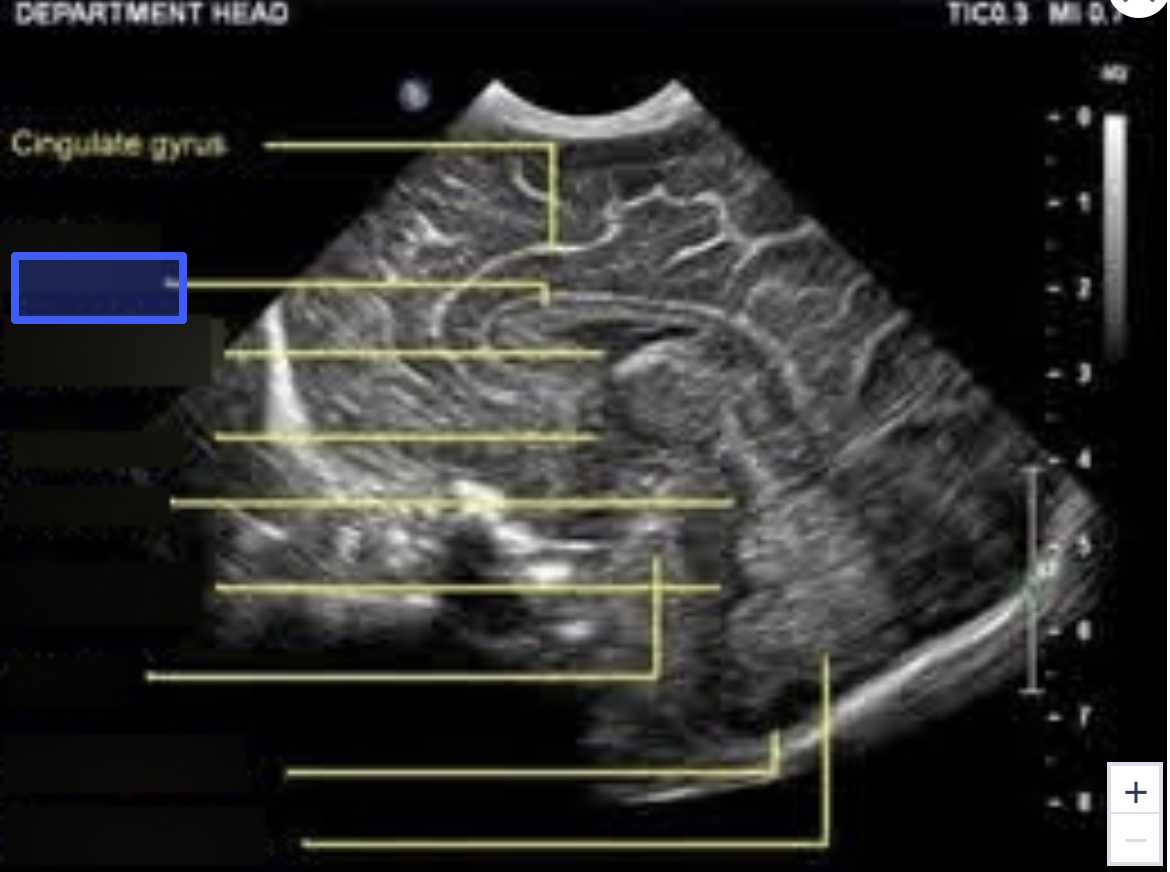
Cavum Septum Pellucidum
What is the highlighted structure?
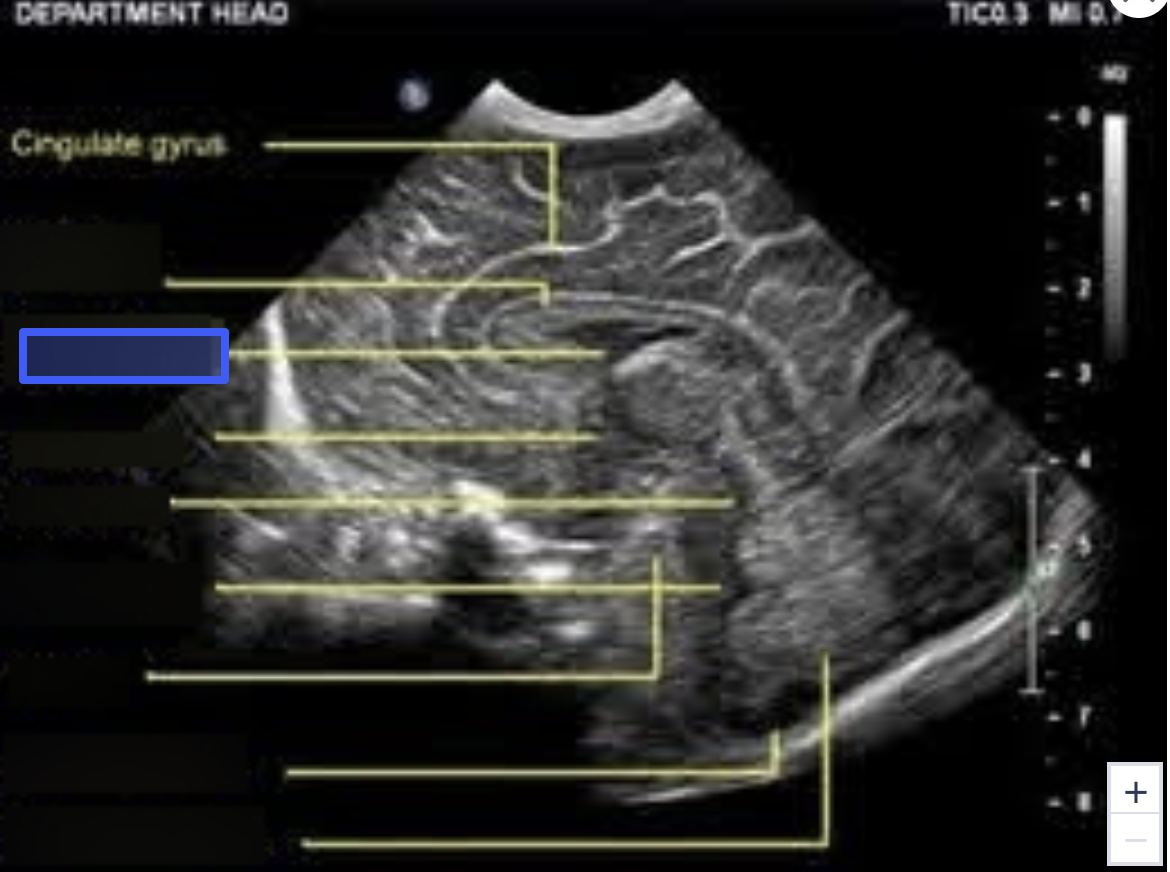
Third Ventricle
What is the highlighted structure?
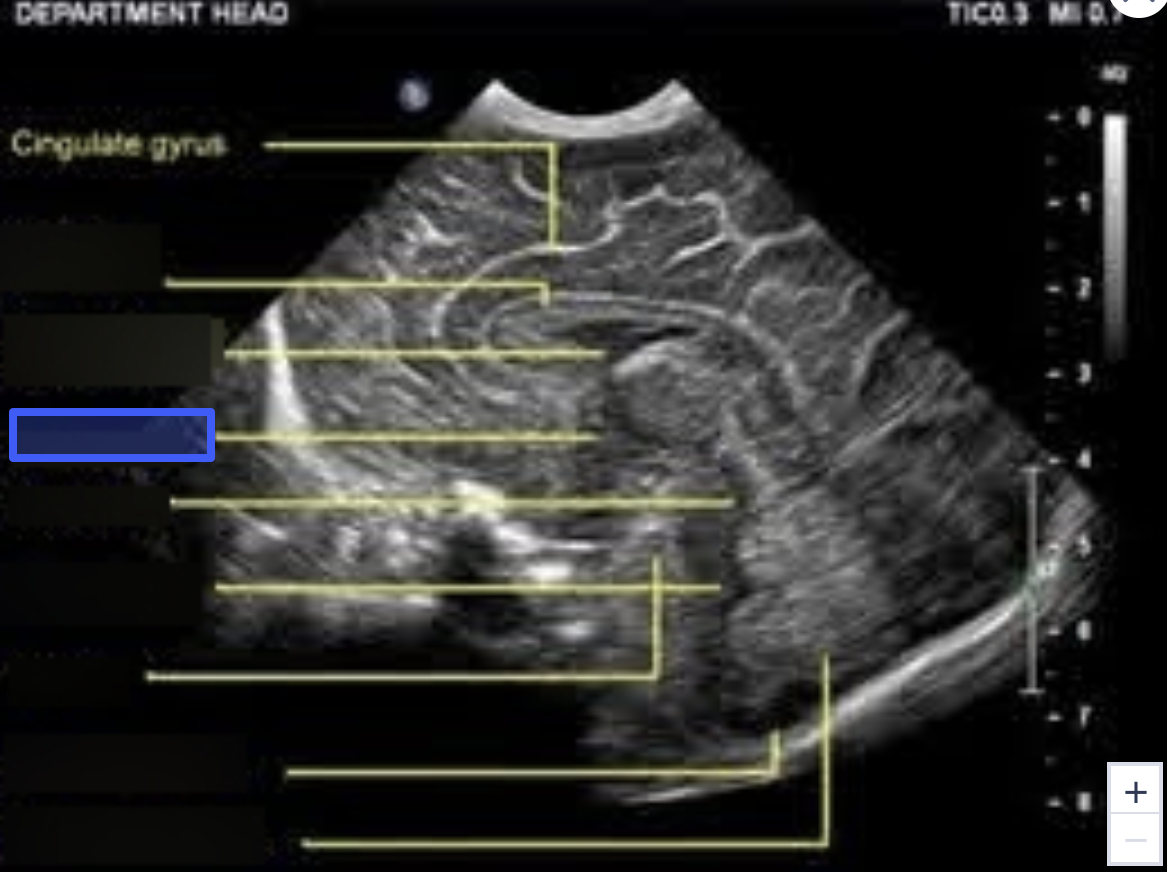
Aqueduct of Sylvius
What is the highlighted structure?
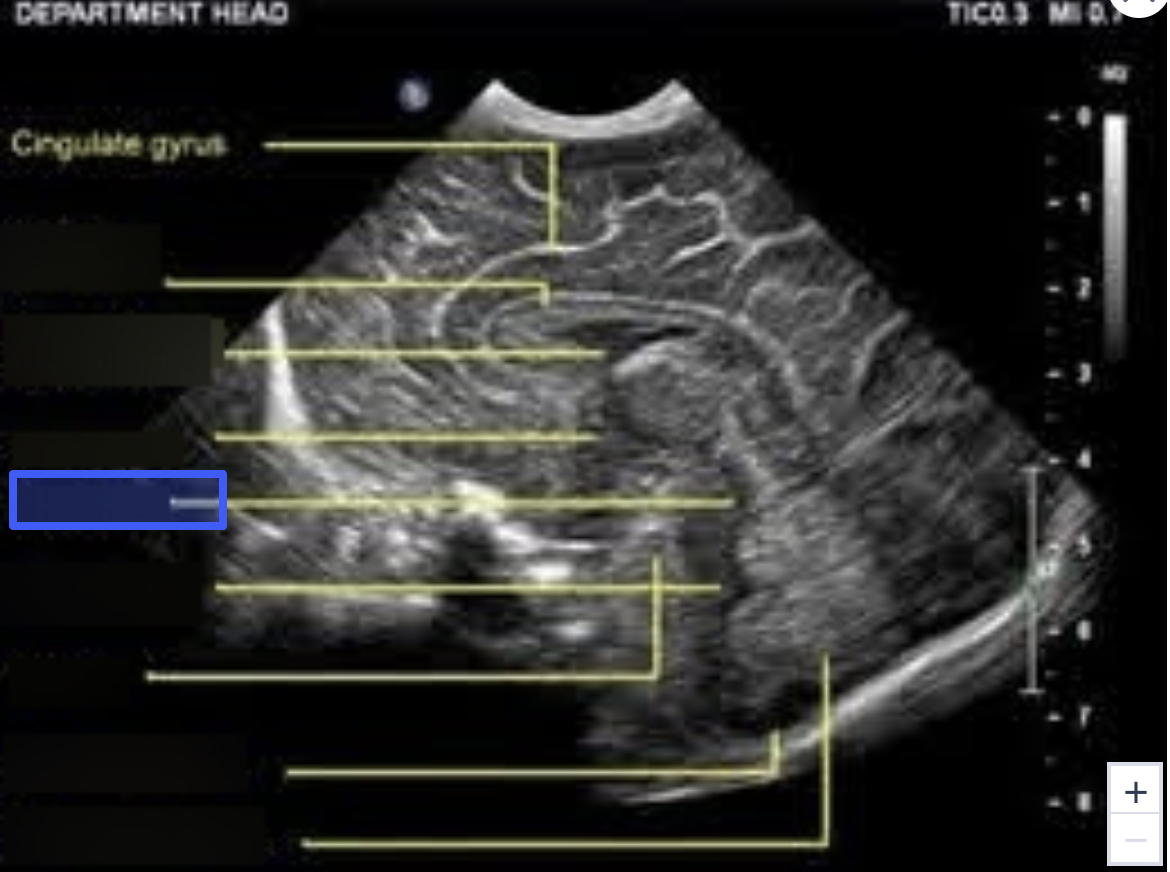
Fourth Ventricle
What is the highlighted structure?
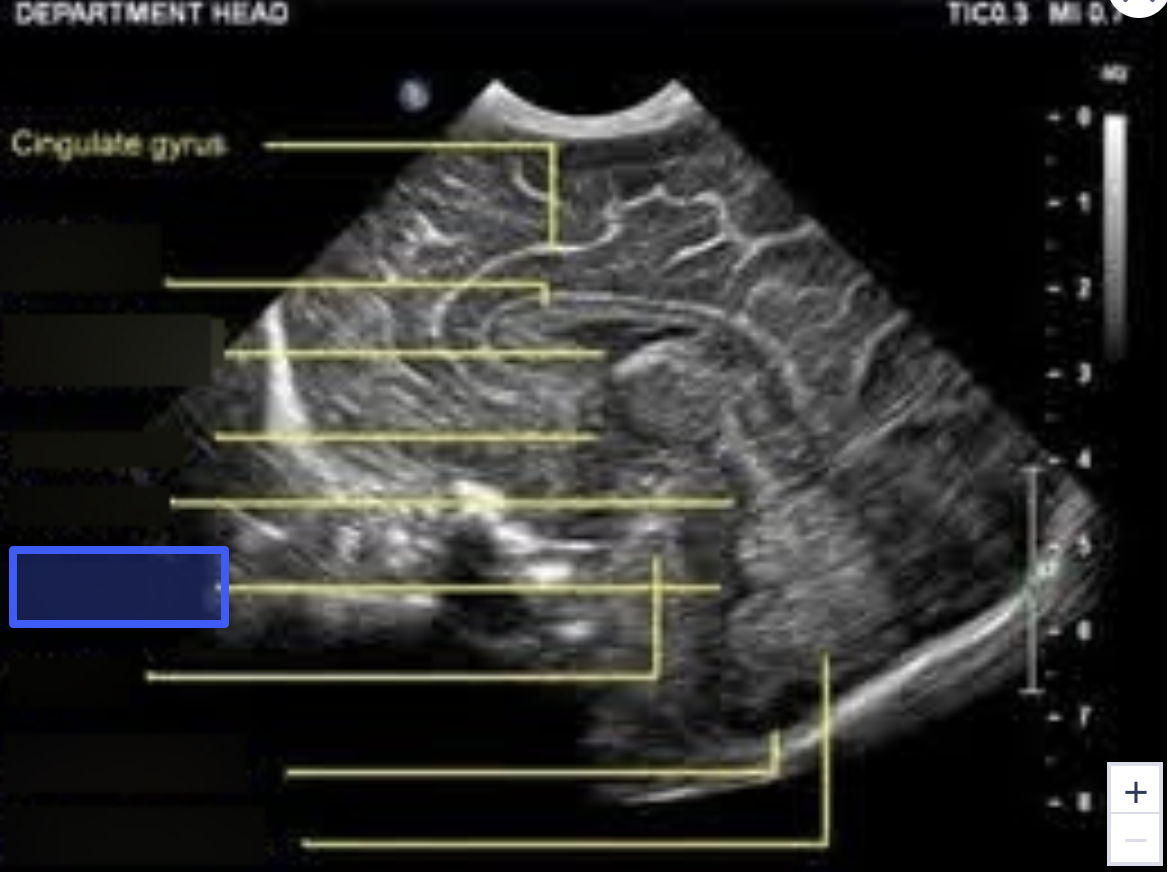
Pons
What is the highlighted structure?
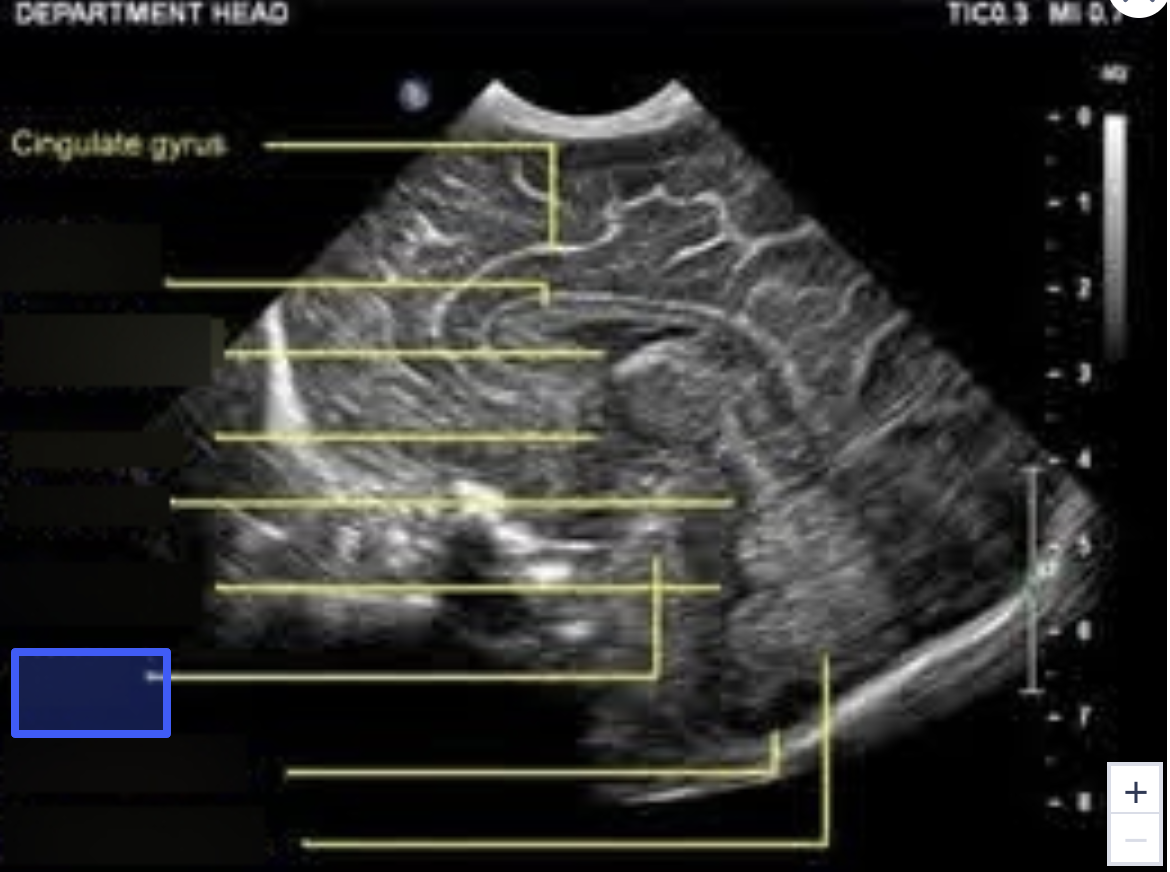
Cisterna Magna
What is the highlighted structure?
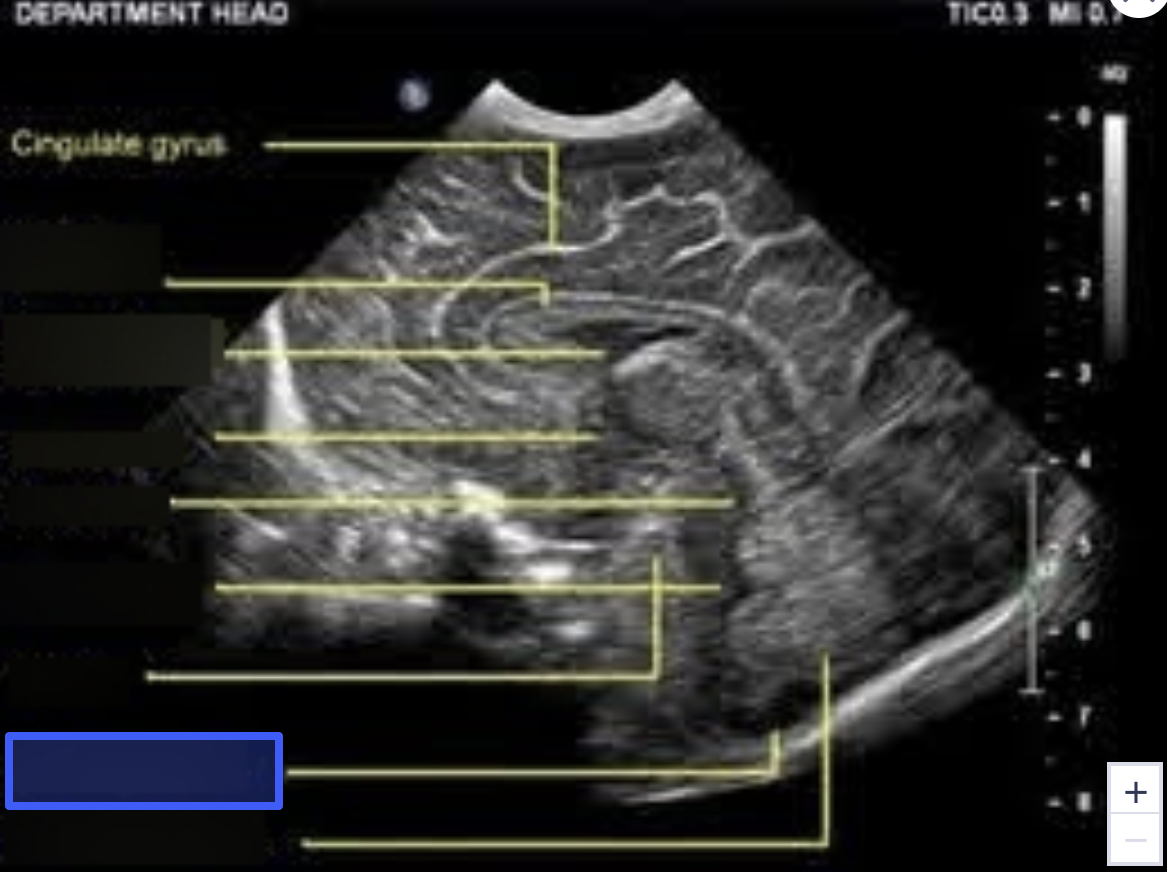
Cerebellar Vermis
What is the highlighted structure?
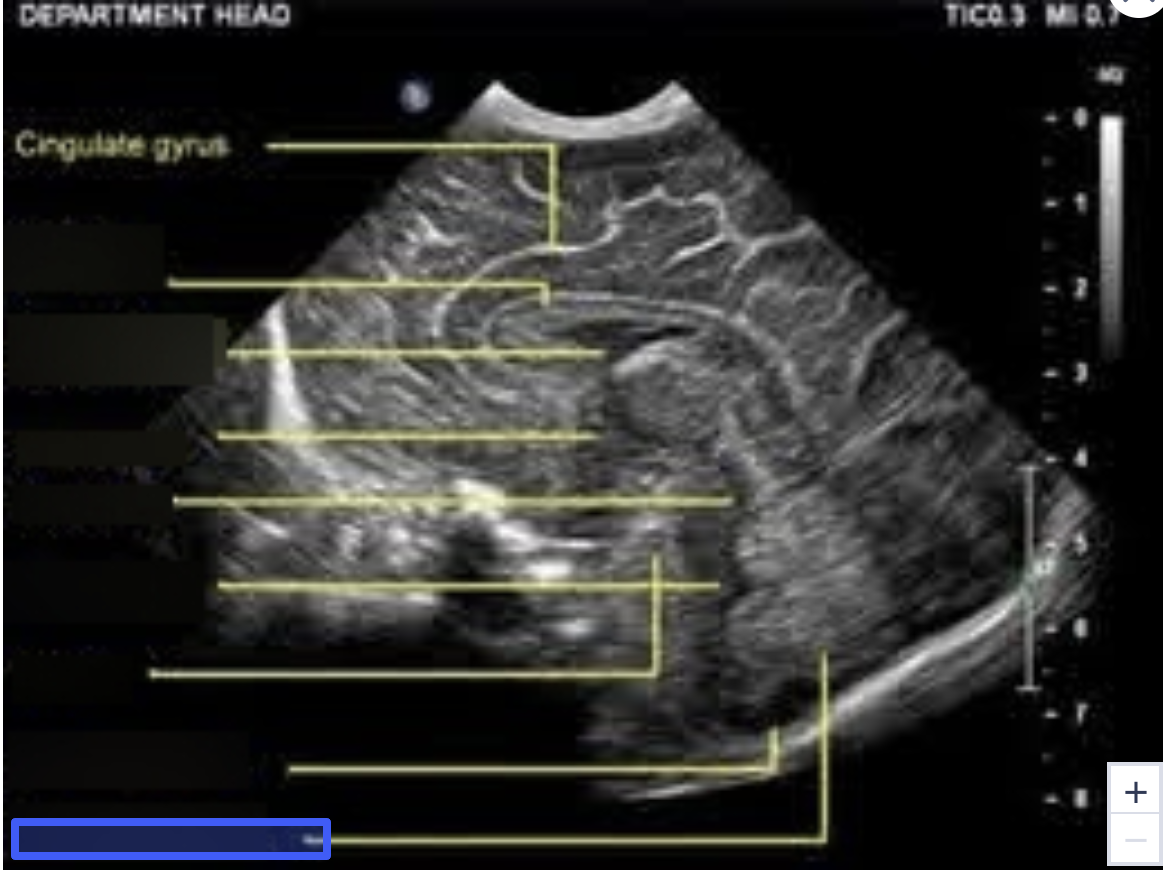
B
The cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) travels from the lateral ventricles to the third ventricle via which one of the following structures?
a. Foramina of Luschka
b. Foramen of Monro
c. Aqueduct of Sylvius
d. Foramina of Magendie
C
The cavum septum pellucidi is observed anterior to the ____.
a. Peduncles
b. Cerebellum
c. Thalamus
d. Corpus callosum
B
Dilation of the entire ventricular system, including the fourth ventricle, is associated with which one of the following abnormalities?
a. Aqueductal stenosis
b. Spinal defects
c. Cardiac defects
d. Foramen Monro stenosis
A
The normal atrium of the lateral ventricle measures _____ mm.
a. 6.5
b. 8
c. 10
d. 11
D
The size of the cistern magna is obtained by measuring from the ____ to the ____.
a. Cerebellar lobe; skin line
b. Vermis; skin line
c. Cerebellar lobe; occipital bone
d. Vermis; occipital bone
D
The cisterna magna should not exceed _____ in the transcerebellar plane.
a. 4 mm
b. 2 mm
c. 8 mm
d. 10 mm
D
Premature closure of the fetal cranial sutures is which of the following conditions?
a. Encephalocele
b. Meningocele
c. Myelomeningocele
d. Craniosynostosis
D
Cerebrospinal fluid passes from the third ventricle to the fourth ventricle via the:
a. Lateral Aperture
b. Median Aperture
c. Interventricular Foramen
d. Aqueduct of Sylvius
D
Which of the following is a membrane that separates the fetal cranium into two equal hemispheres?
a. Lateral Fissure
b. Rolandic Fissure
c. Sylvian Fissure
d. Falx Cerebri
A
Ventriculomegaly is defined by measuring the internal width of the atrium of the lateral ventricles and having the diameter measure greater than 10 mm.
a. True
b. False
D
Which one of the following neural tube defects is characterized by a lack of development of the cerebral and cerebellar hemispheres and cranial vault and is an abnormality that is incompatible with life?
A) acrania
B) cephalocele
C) Dandy-Walker malformation
D) anencephaly
D
Which one of the following central nervous anomalies demonstrates splaying of the cerebellar hemispheres on ultrasound?
A) hydraencephaly
B) cephalocele
C) vein of Galan malformation
D) Dandy-Walker malformation
B
A condition in which a complete or partial absence of the cranial bones is demonstrated is which one of the following?
A) cebocephaly
B) acrania
C) holoprosencephaly
D) hydraencephaly
A
Which one of the following anomalies may be characterized by the presence of colpocephaly?
A) agenesis of the corpus callosum
B) Arnold-Chiari malformation
C) Dandy-Walker malformation
D) holoprosencephaly