AP Calculus AB Semester 1 Exam Review
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
71 Terms
Definition of the Derivative (i.e. the Difference Quotient)

Average Rate of Change of f(x) on [a,b]
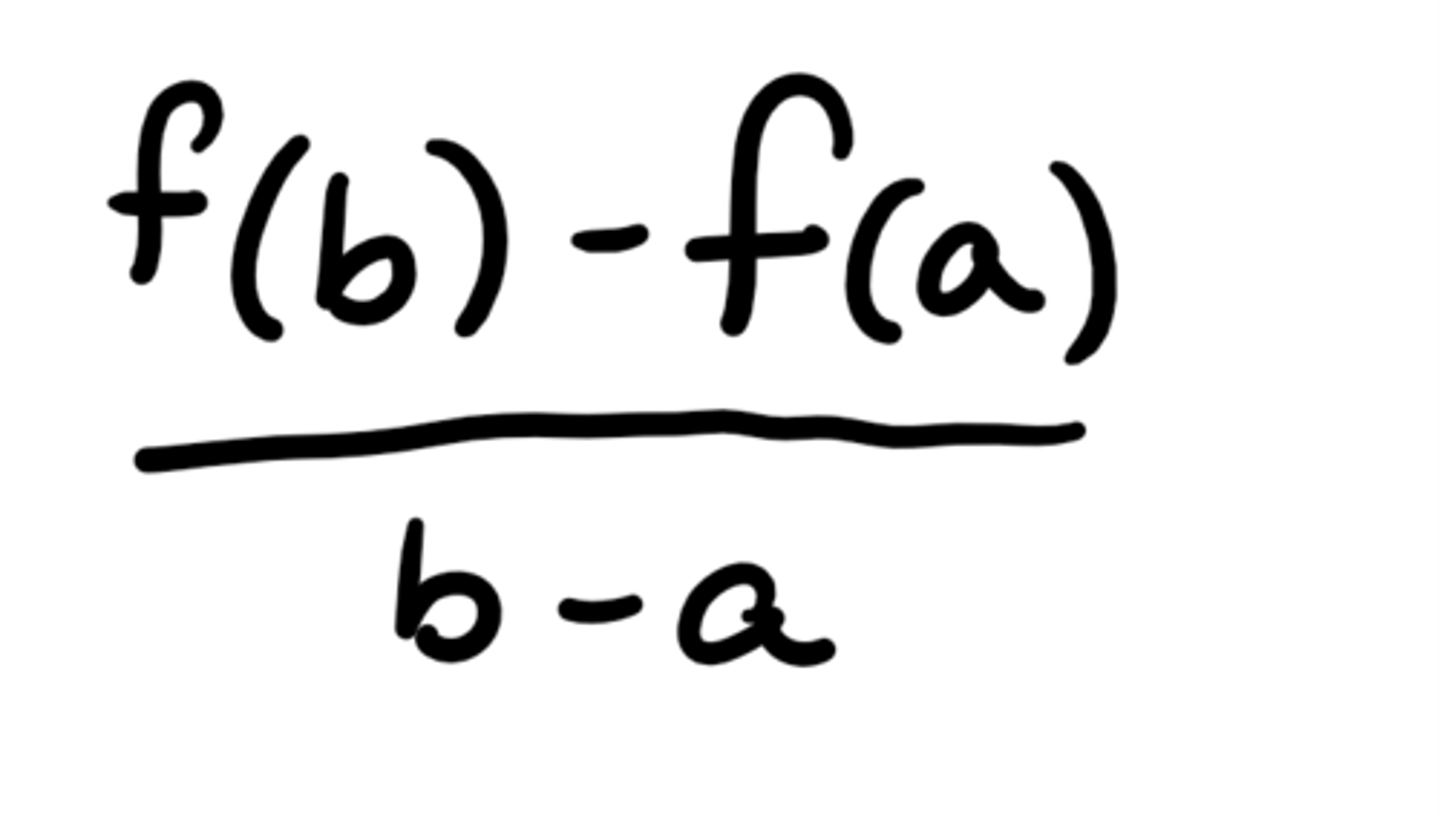
Instantaneous Rate of Change at x=a
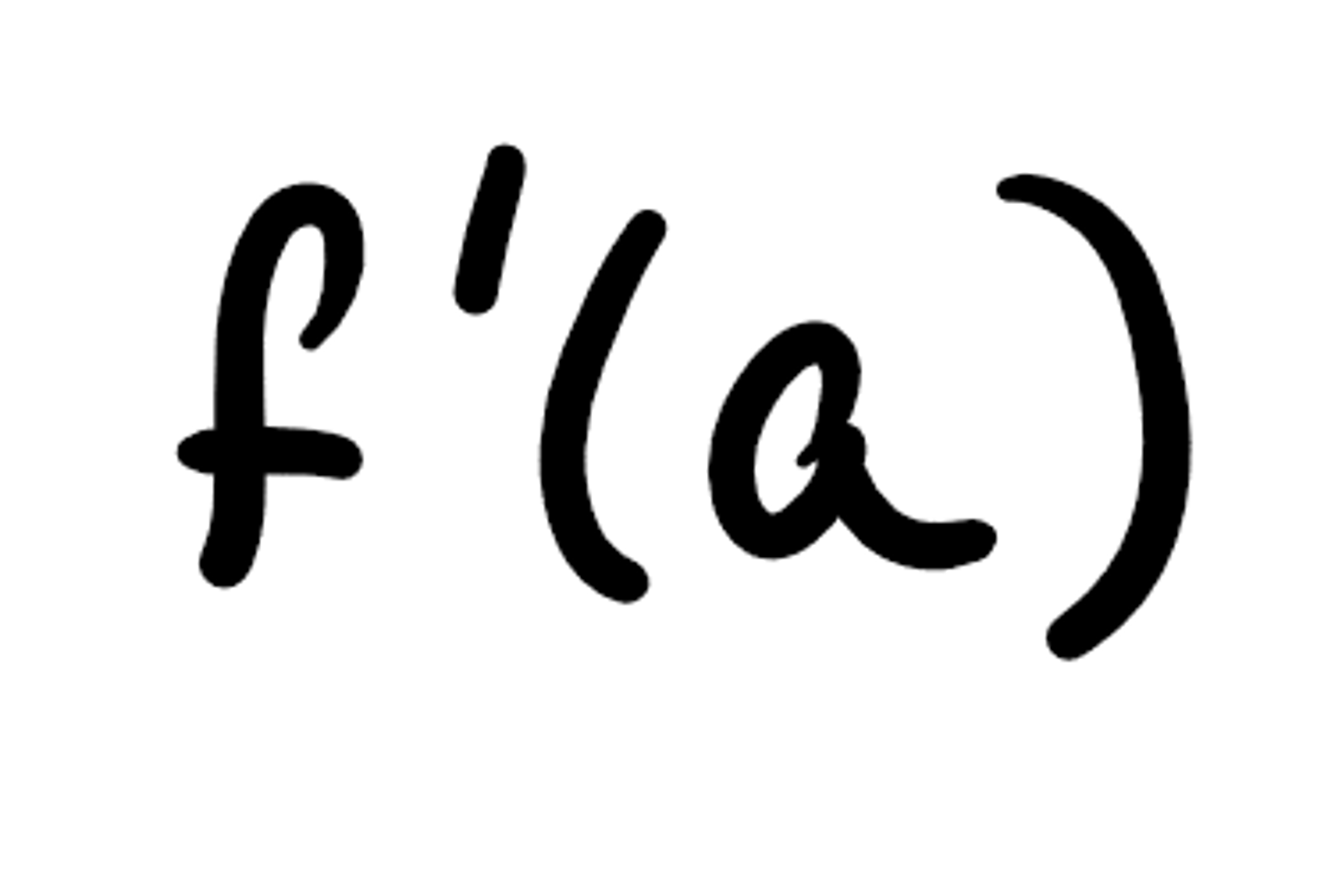
A function is continuous if and only if; (aka "The Definition of Continuity")
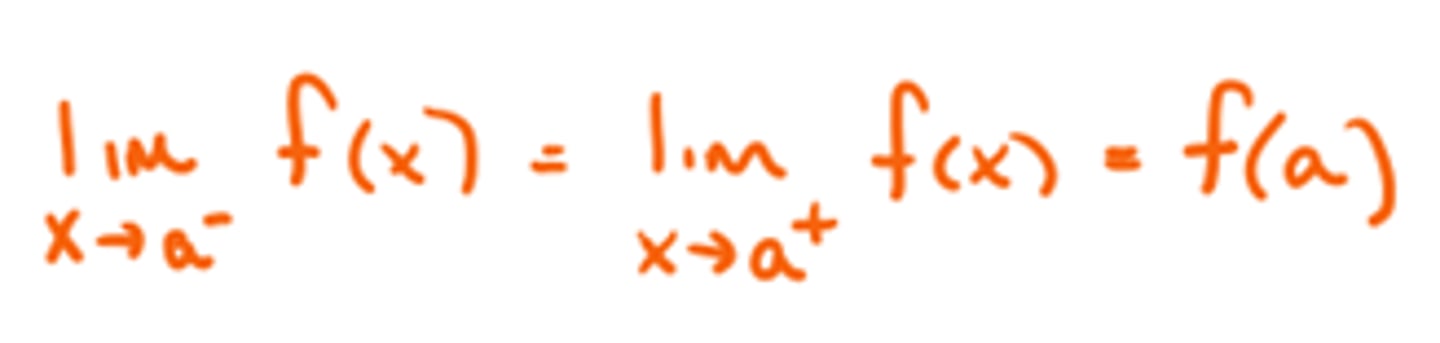
A Piecewise Function is "differentiable" at x=c if
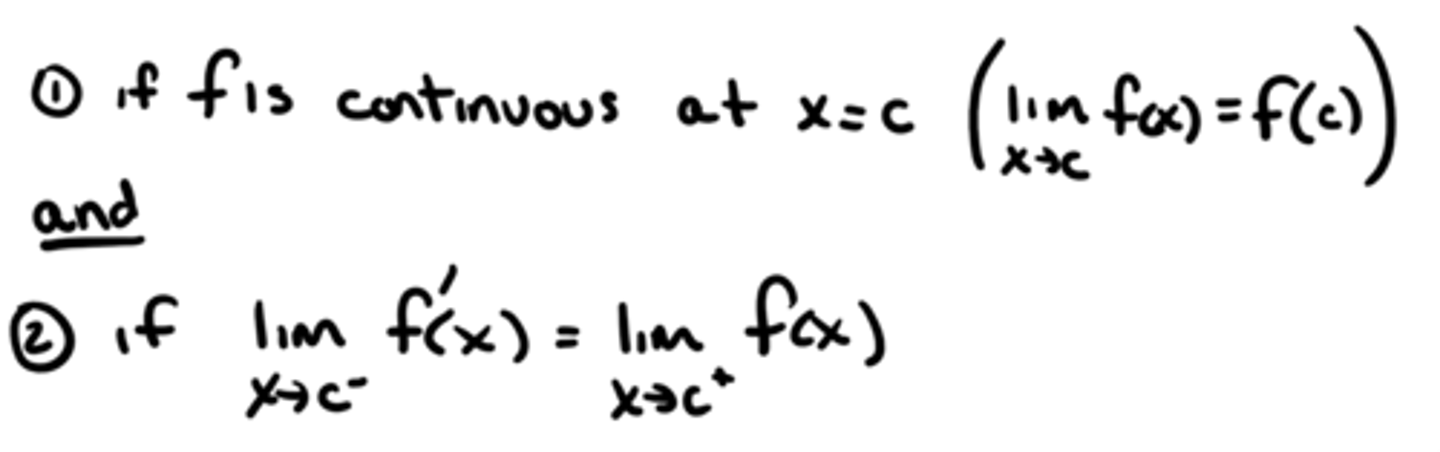
If a function is "differentiable" then,
It must also be continuous
Derivative of a constant
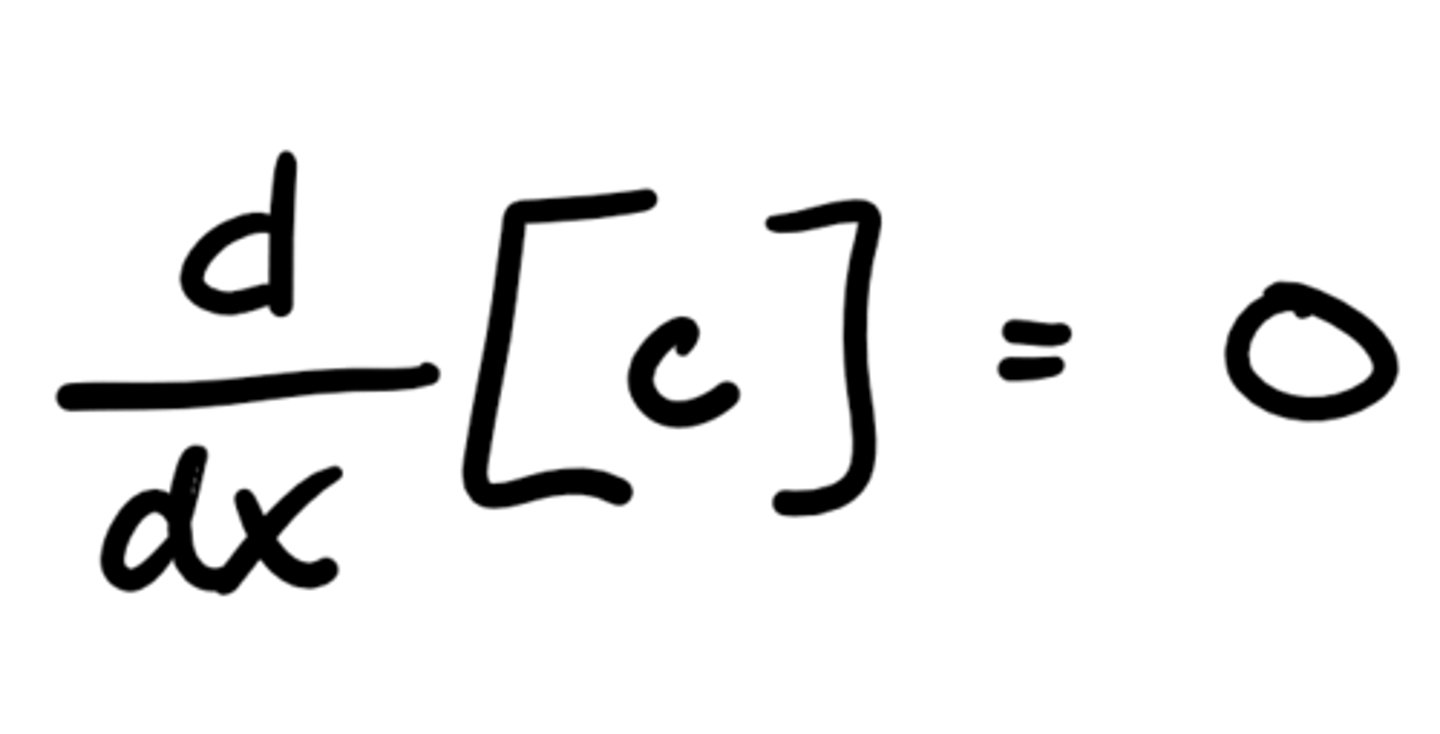
Derivative of kx
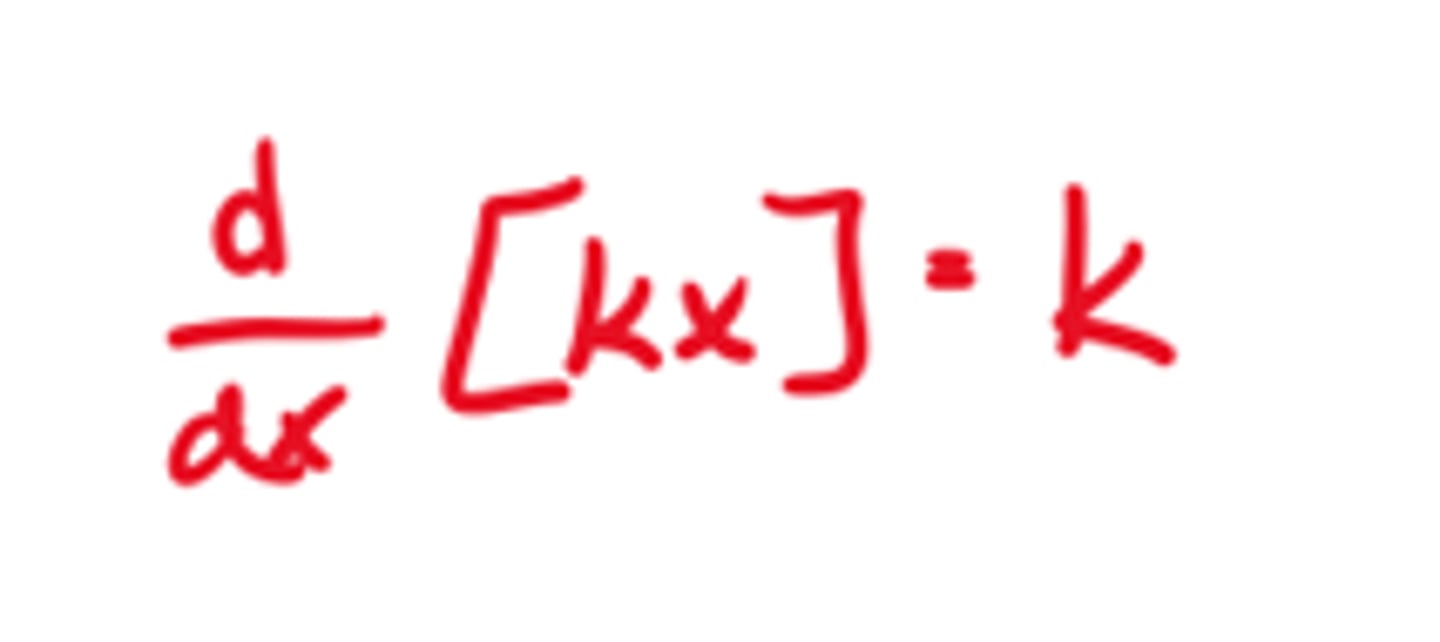
Derivative of x^n
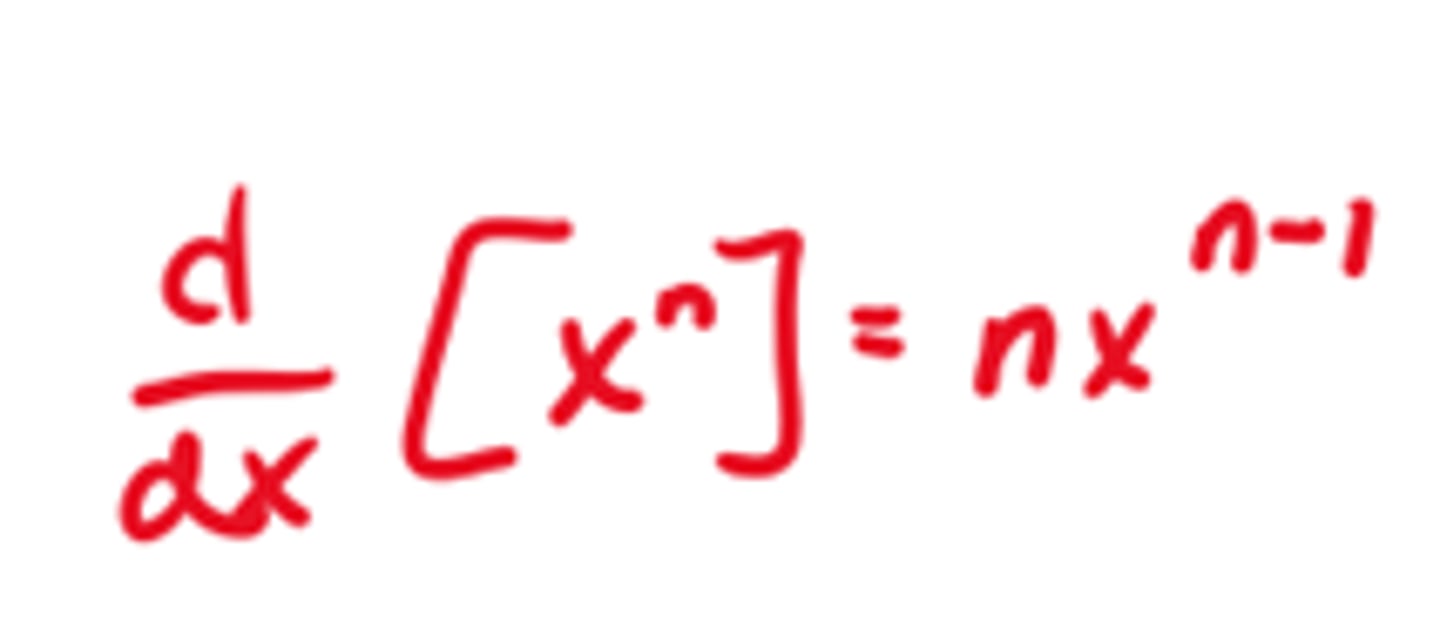
Derivative of e^x
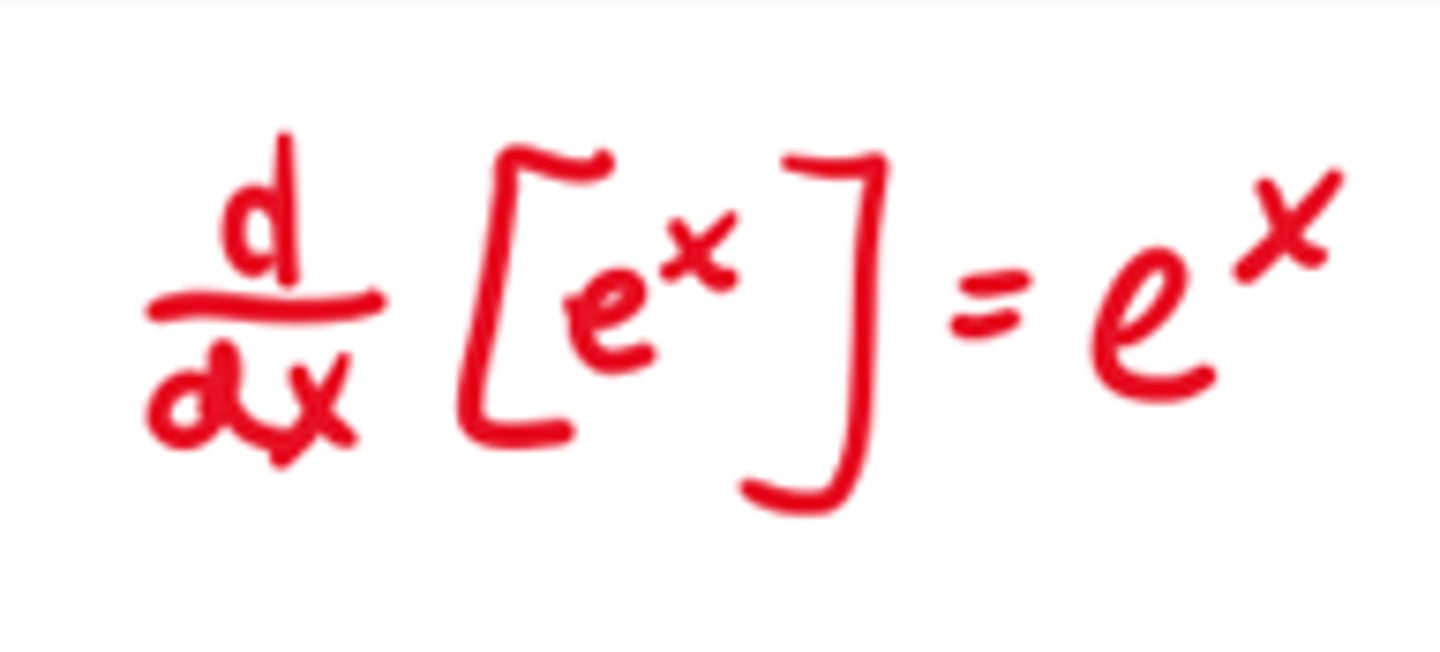
Derivative of a^x
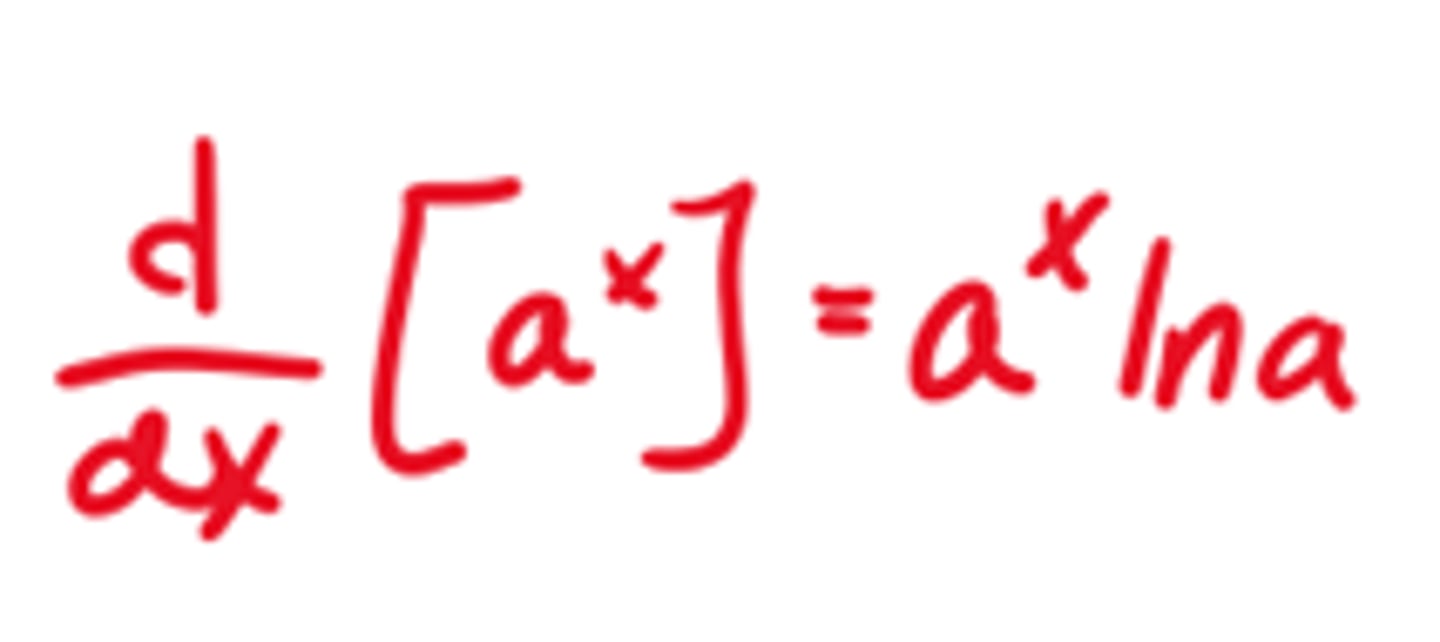
Derivative of square root of x
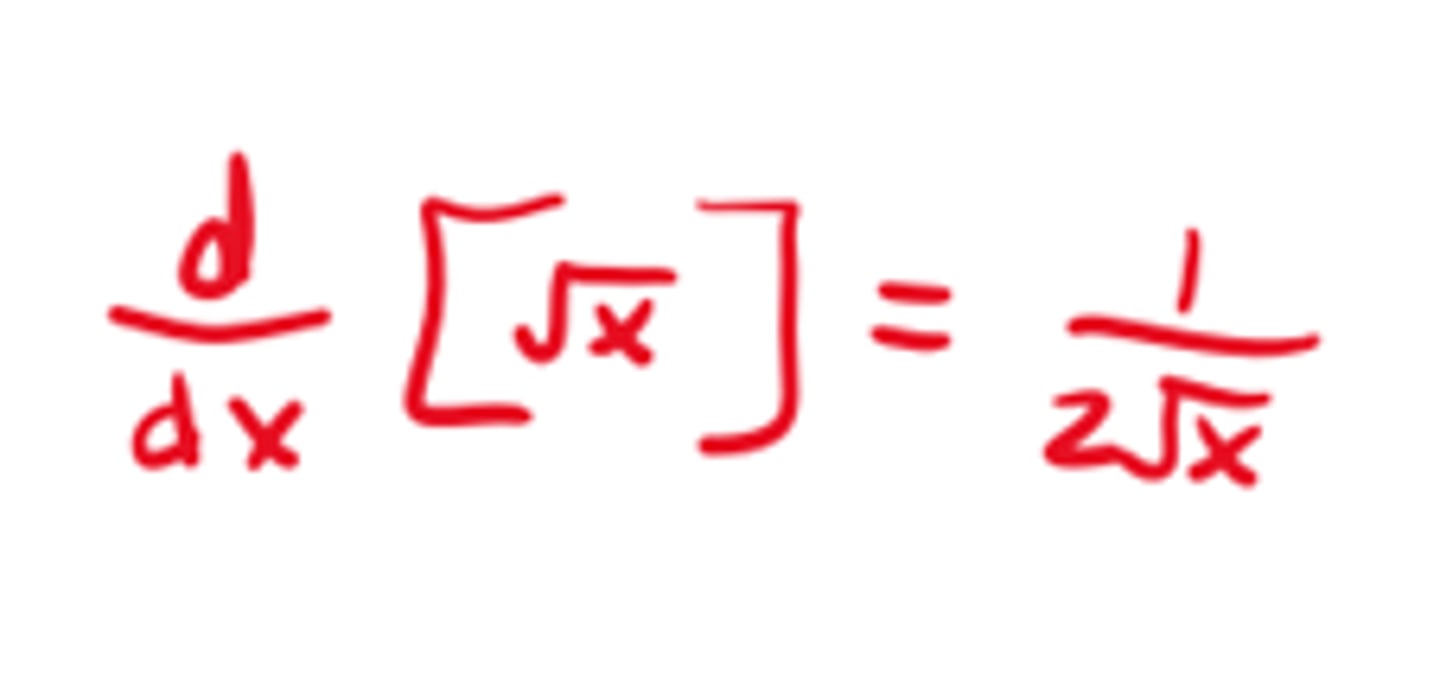
Derivative of sinx
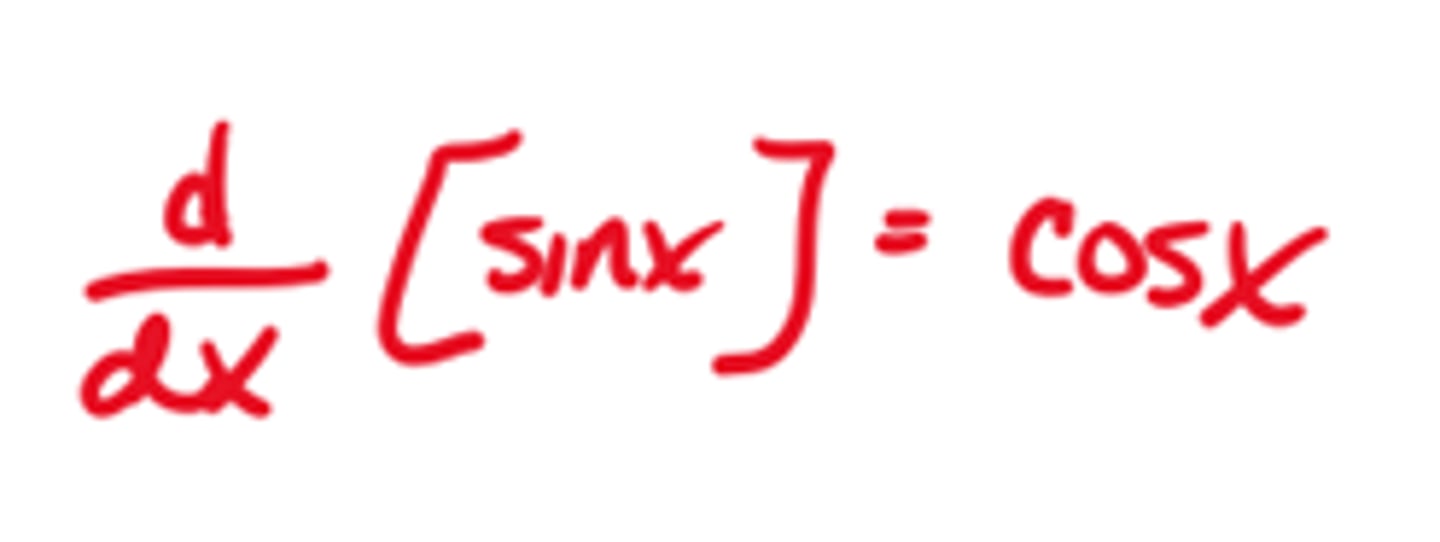
Derivative of cosx
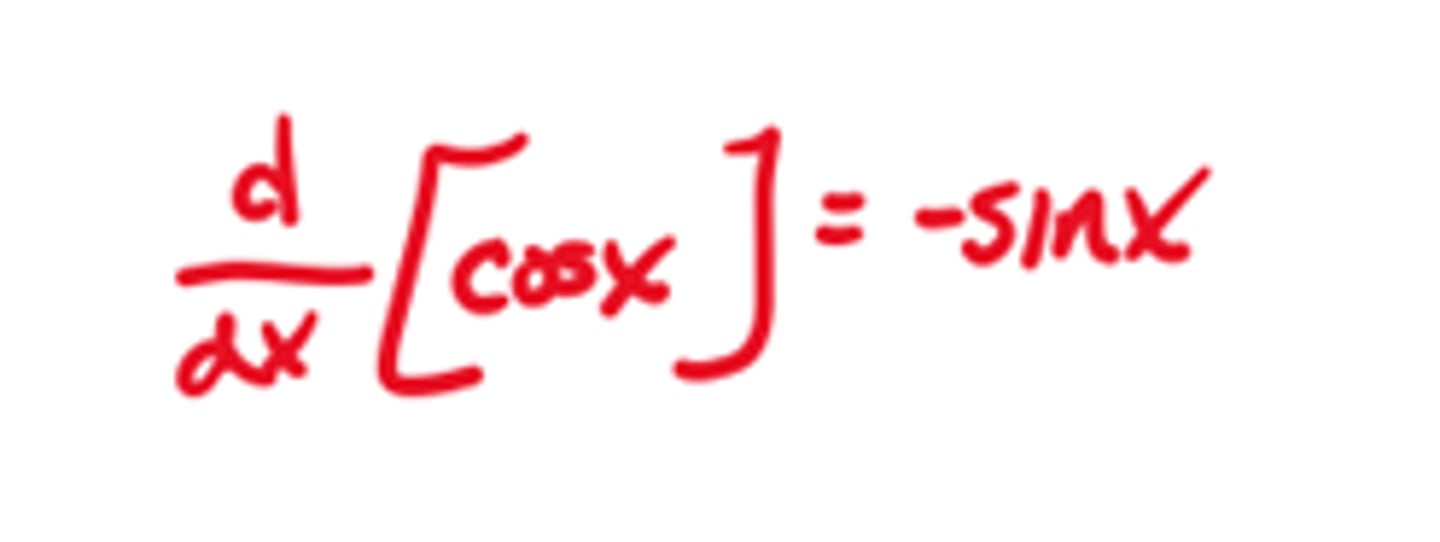
Derivative of tanx
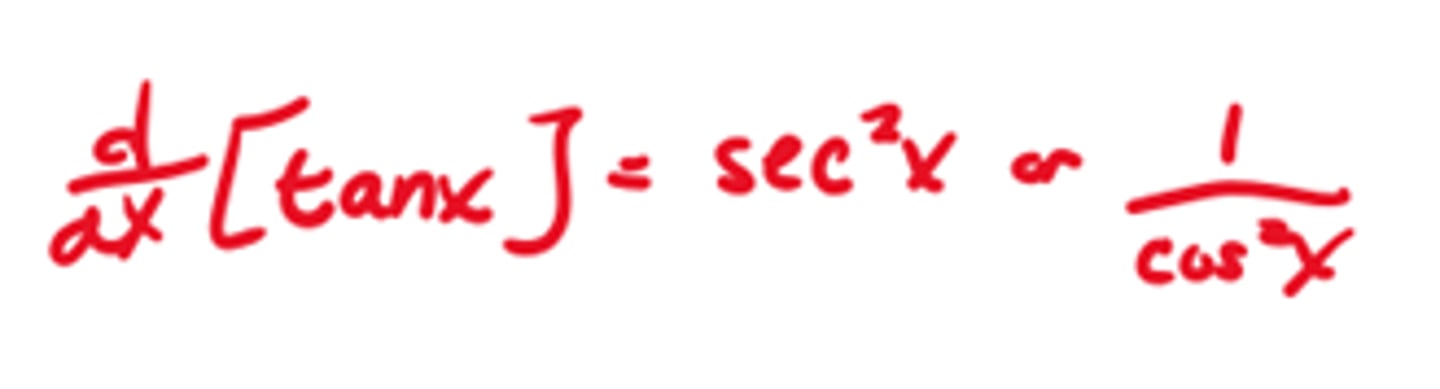
Derivative of sec(x)

Derivative of csc(x)
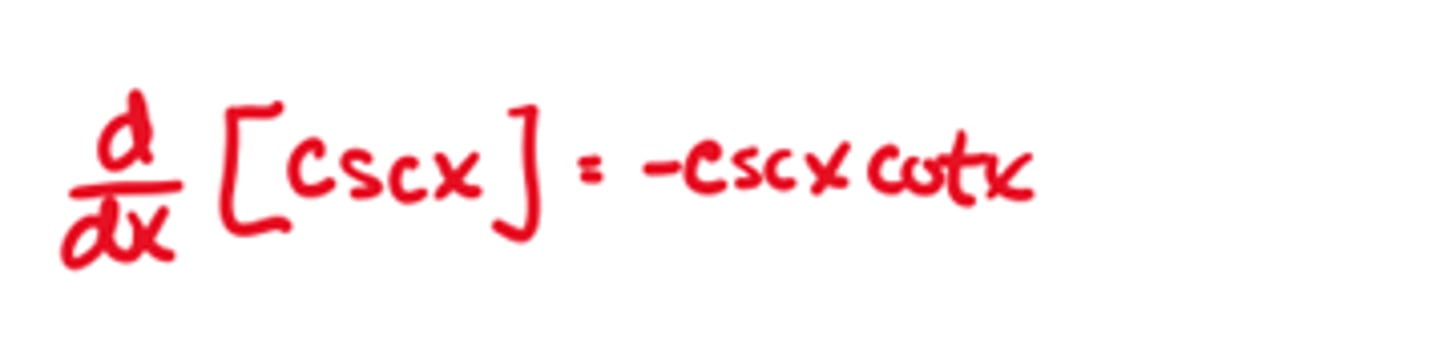
Derivative of cot(x)
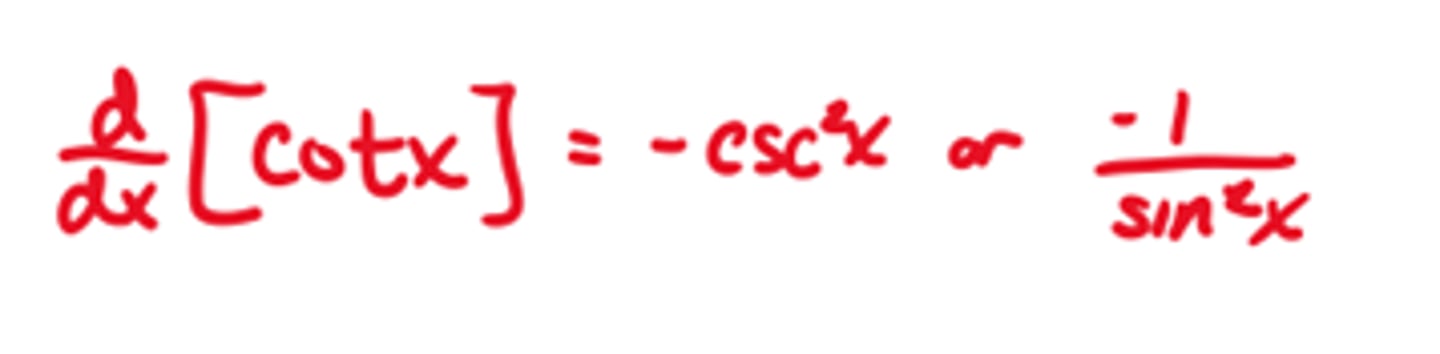
Derivative of k*f(x)
Constant Multiple Rule
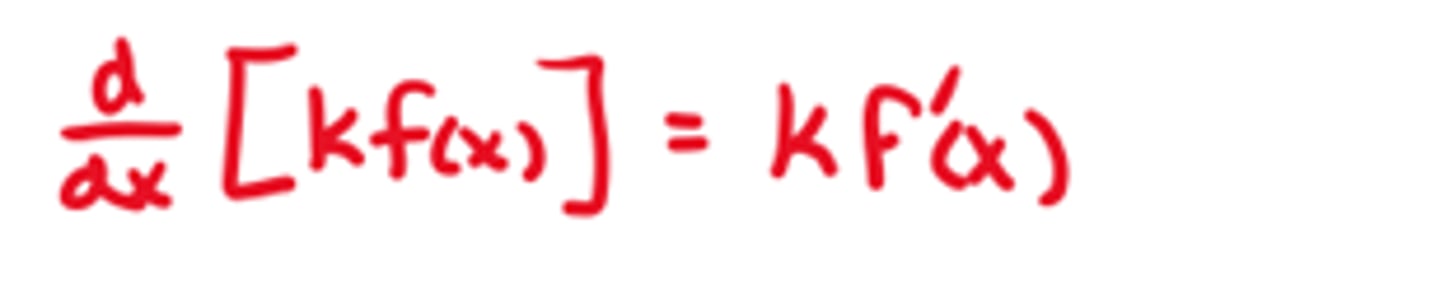
Derivative of f(x)+/-g(x)
Sum and Difference rule
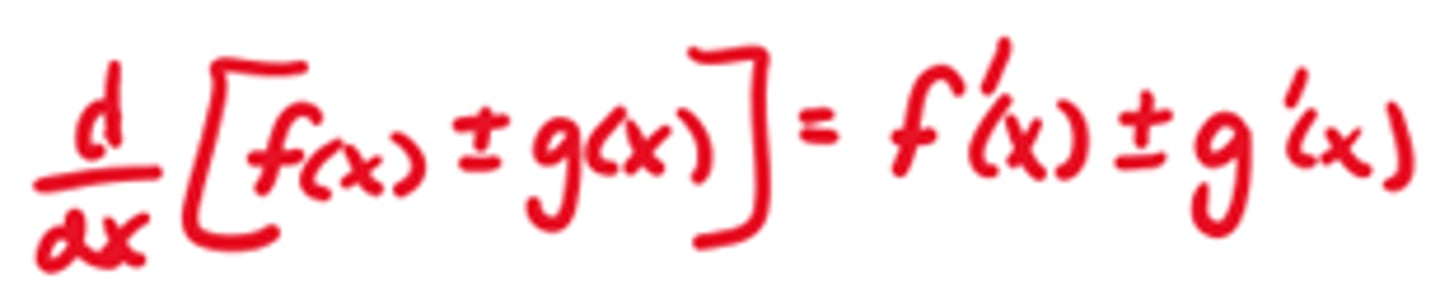
Derivative of f(x)g(x)
Product Rule
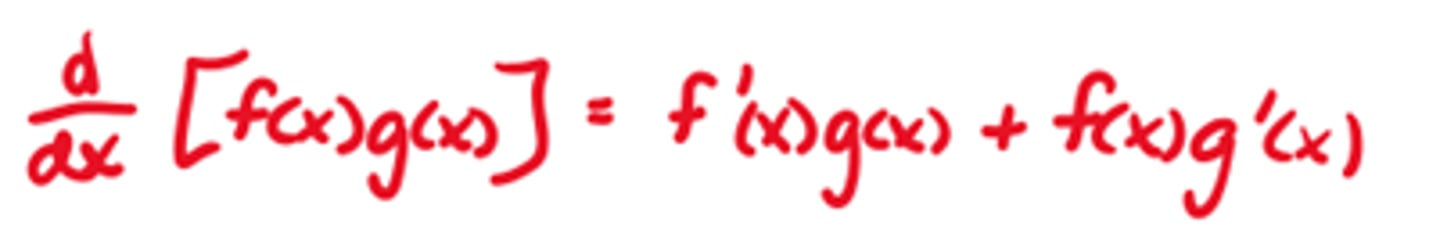
Derivative of f(x)/g(x)
Quotient Rule
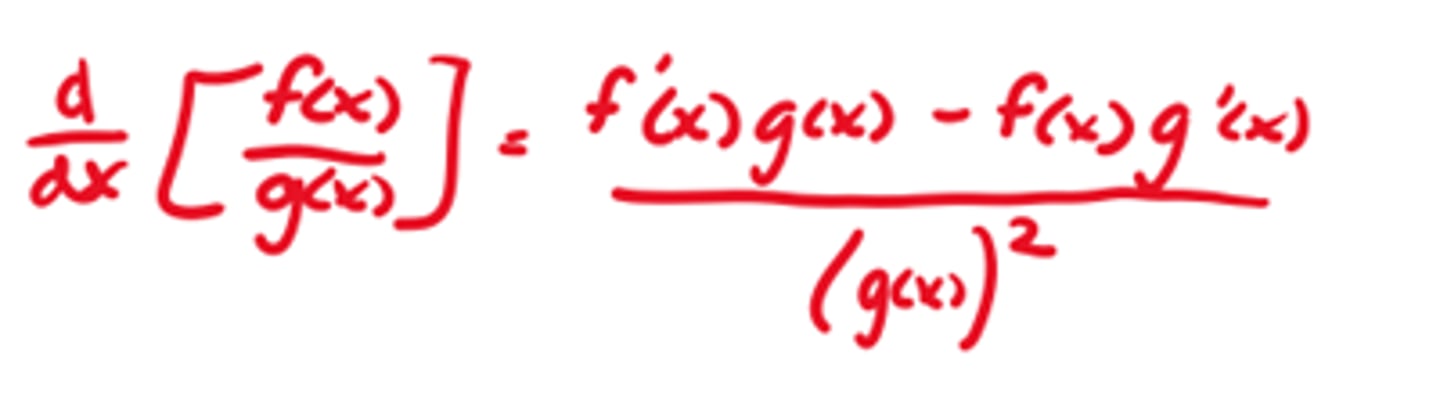
Derivative of f(g(x))
Chain Rule
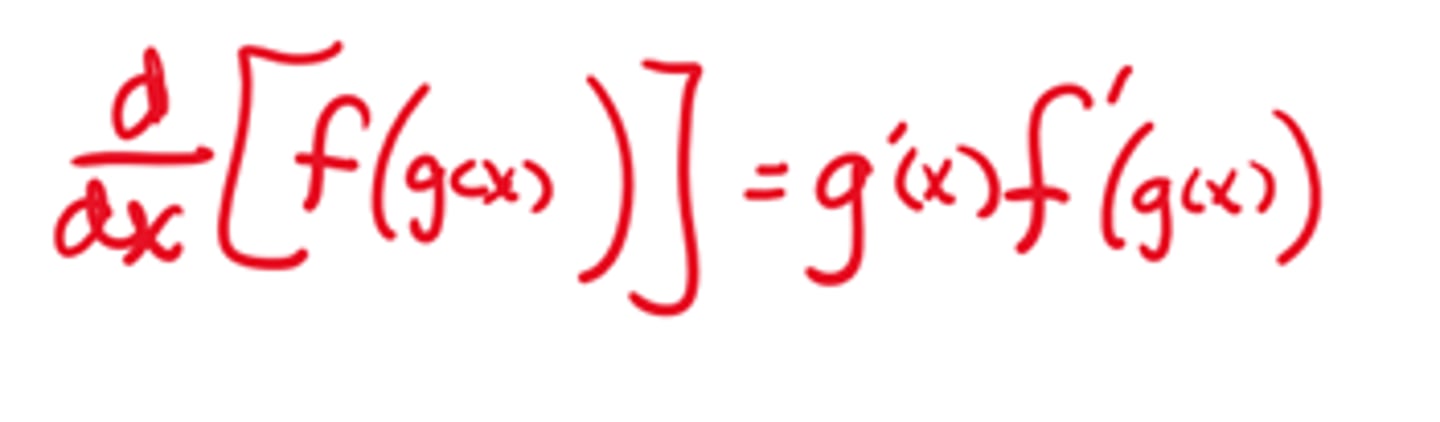
Derivative of lnx
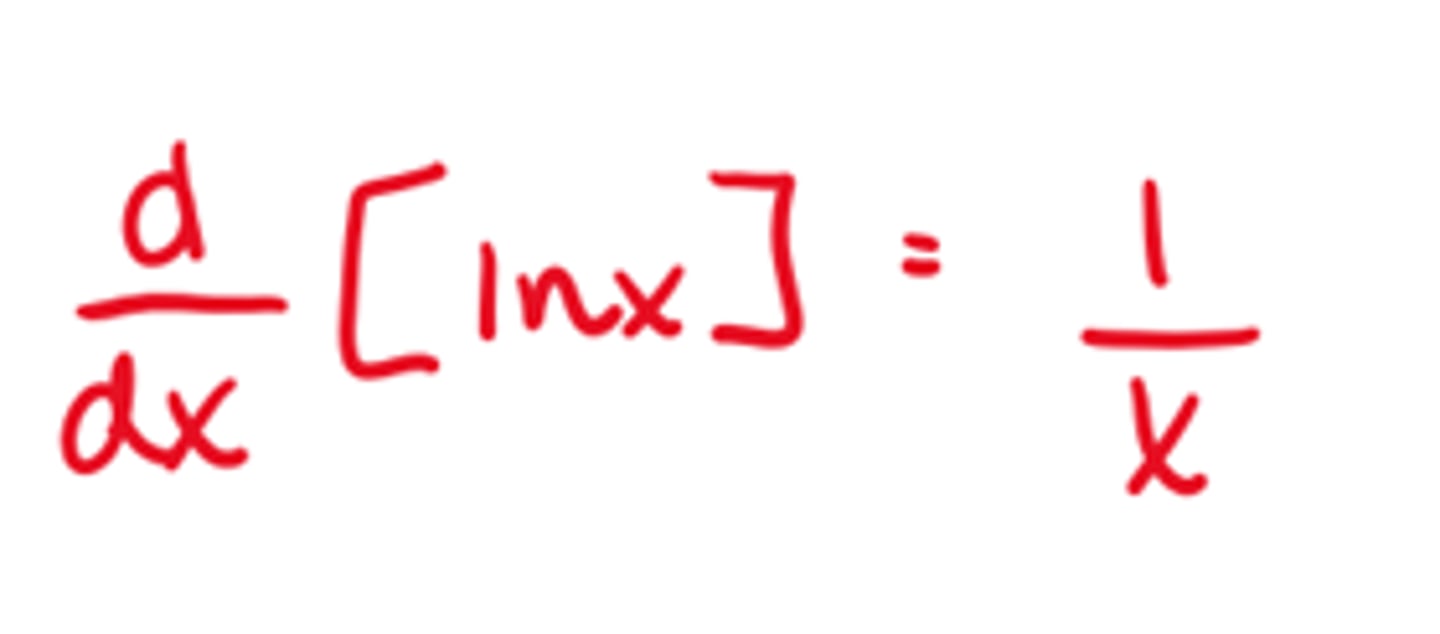
Derivative of arcsinx
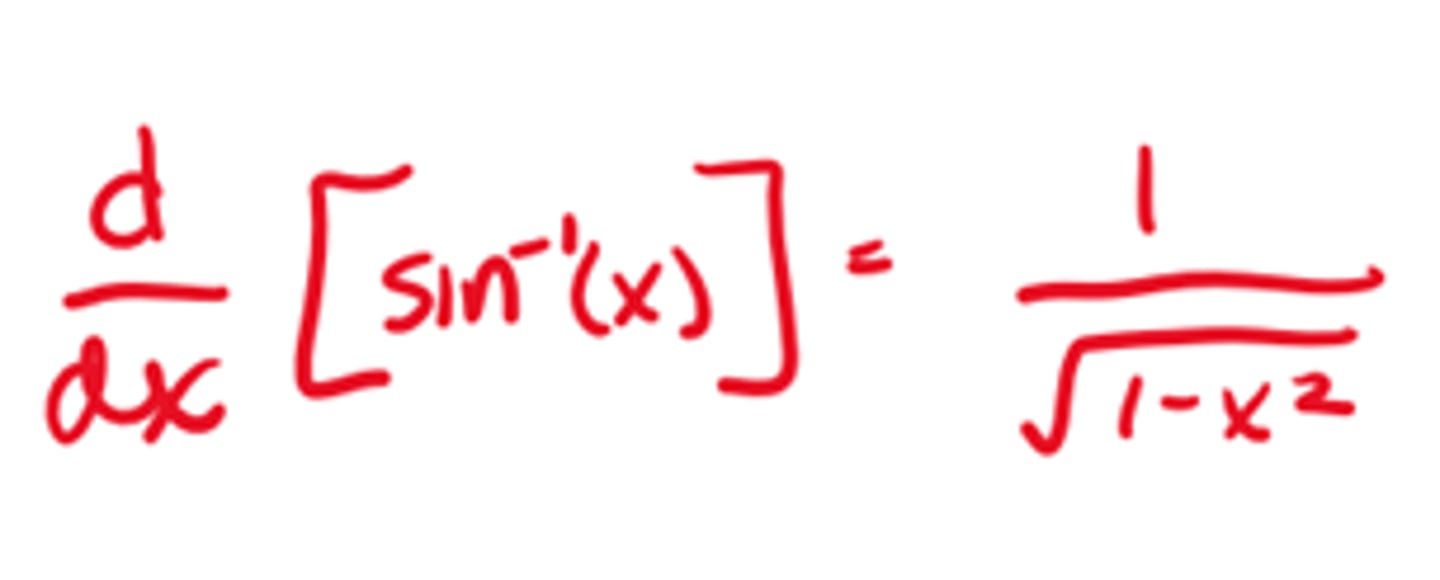
Derivative of arctanx
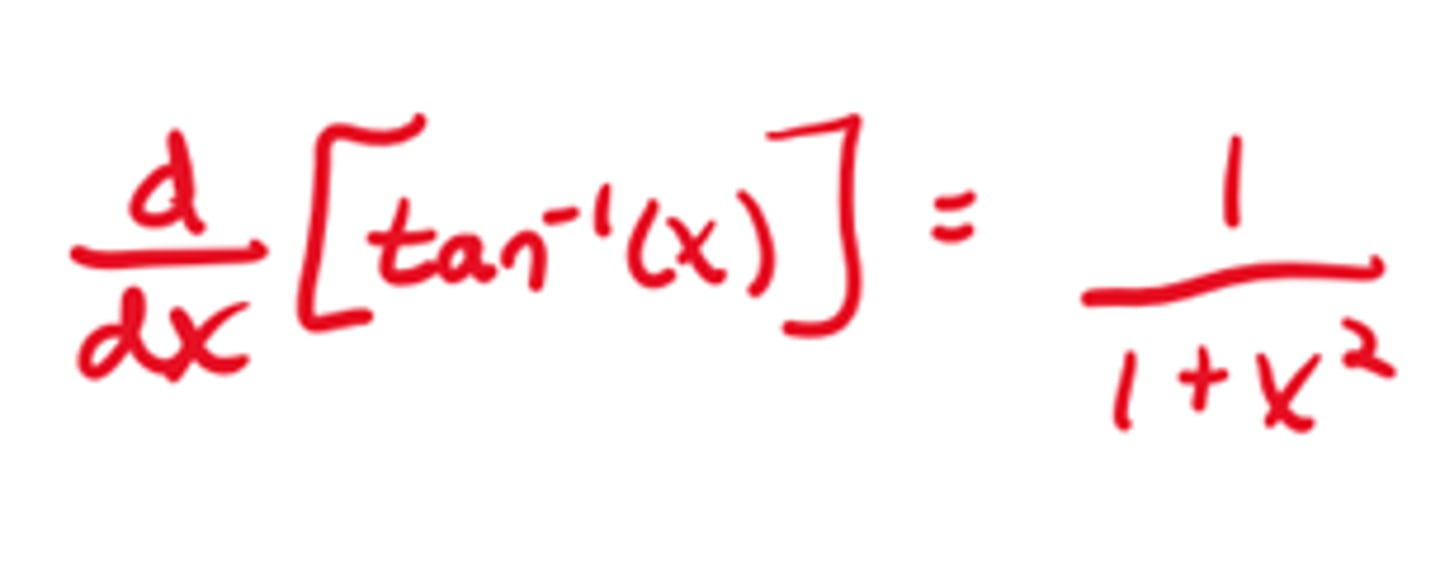
Derivative of arccosx
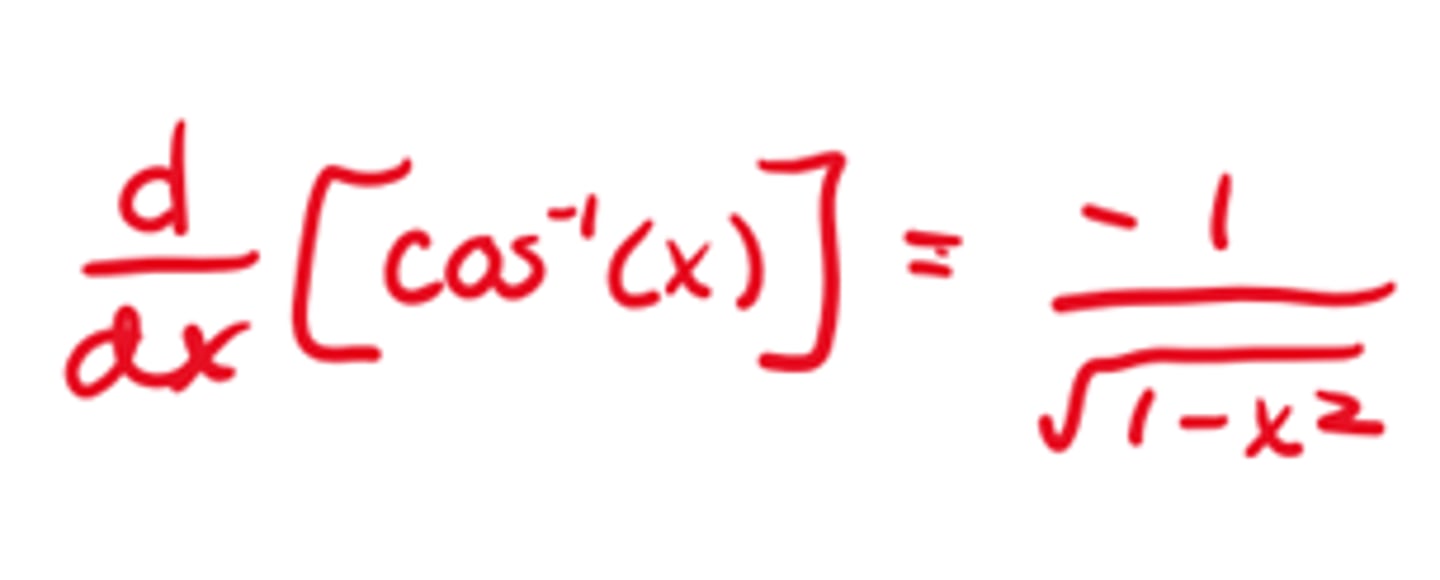
Derivative of f inverse of x
1. Fill out formula with indicated x-coord.
2. Evaluate interior (f inverse) first. (reminder: since this is an inverse you are given a y-value and want to find the x associated with that y)
3. Find f' of the answer to step 2
4. Make sure you write your answer as 1/f'
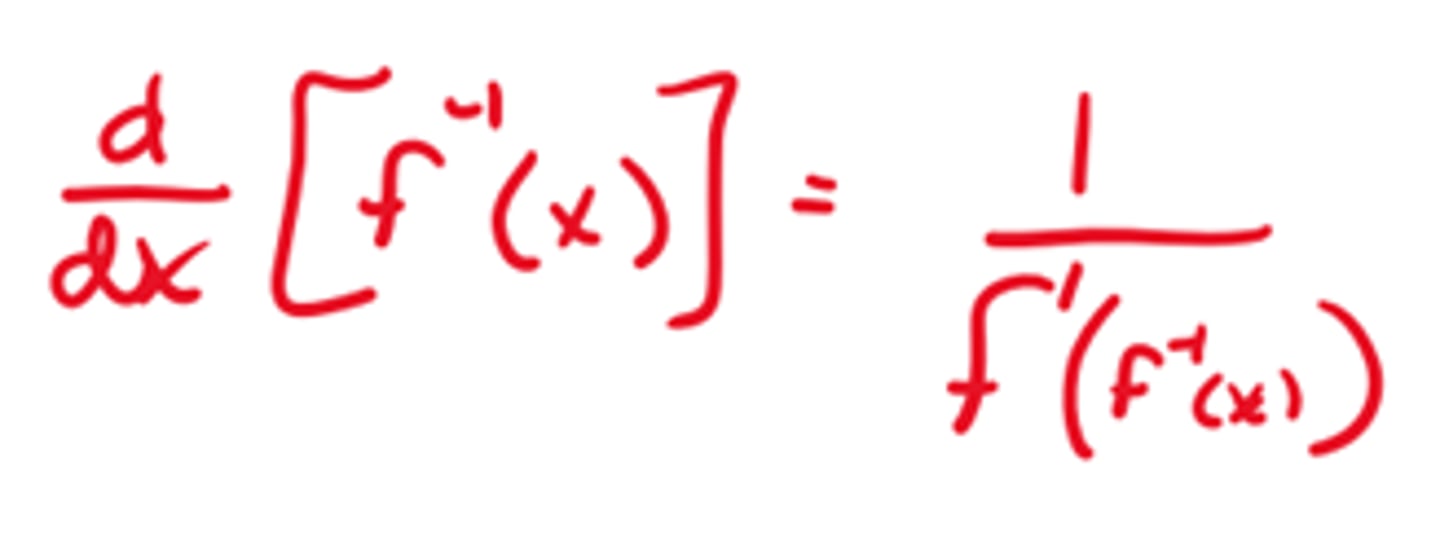
Equation of the Line Tangent to f(x) at x=a
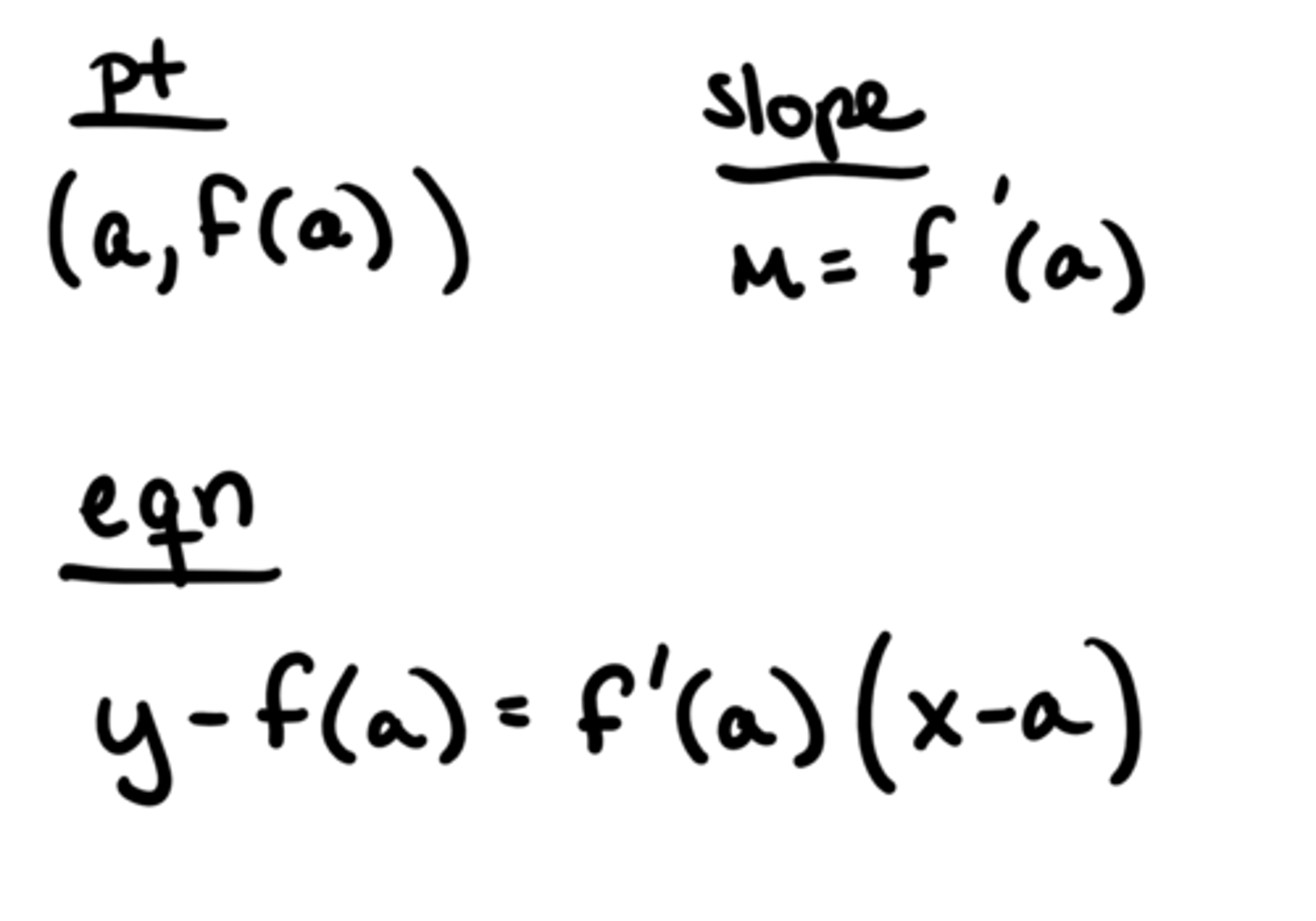
Intermediate Value Theorem
When to Use:
Prove a y-value f(c)=k exists.
Requirements:
1. f(x) is continuous on [a, b]
2. Given 2 known points (a, f(a)) and (b, f(b)).
Conclusion:
If f(c)=k is between f(a) and f(b), then f(c)=k must exist.
Mean Value Theorem
When to Use:
Prove a derivative f'(c) exists.
Requirements:
1. f(x) is differentiable on an interval (a, b)
Conclusion:
f'(c) = (f(b)-f(ab))/(b-a)
*The derivative must equal the slope between two given points.
Absolute value functions

Points where f(x) is "discontinuous"

Points where f(x) is "non-differentiable"

Implicit Differentiation
1. Take derivative of every term using normal shortcuts/rules.
- x-term derivatives = normal derivative
- y-term derivatives = (normal derivative)*dy/dx
2. Move all dy/dx terms to the left side of the equal sign, and all non-dy/dx terms to the right side.
3. Factor dy/dx from the left side.
4. Divide to solve for dy/dx
Implicit Second Derivative
(Find d^2y/dx^2)
1. Take derivative of dy/dx equation, and include dy/dx for any y-term derivatives.
2. Substitute original dy/dx equation into the 2nd derivative for any dy/dx terms.
Find "Vertical" Tangents
1. Set Denominator of dy/dx = 0
2. Substitute result into the original curve/equation
Find "Horizontal" Tangents
1. Set Numerator of dy/dx = 0
2. Substitute result into the original curve/equation
The Differential
dy=[f'(x)]*dx
Linear Approximation
Use the equation of the tangent line to approximate some value f(c)
1. Write tangent line equation: y-f(a)=f'(a)(x-a)
2. Plug x-coord of approximation (x=c) into tangent line equation
3. Solve tangent line equation for y
Critical Point of f(x)
Where f'(x)=0 or f'(x) is undefined
f is increasing when;
f' > 0 (positive)
f is decreasing when;
f' < 0 (negative)
f is concave up when;
f'' > 0 (positive)
f is concave down when;
f'' < 0 (negative)
Inflection Point of f(x)
Where f''(x) changes sign
Relative Maximum (First Derivative Test)
Where f'(x) changes from positive to negative
Relative Minimum (First Derivative Test)
Where f'(x) changes from negative to positive
Relative Maximum (Second Derivative Test)
Where f'(a)=0 and f''(a)<0
Relative Minimum (Second Derivative Test)
Where f'(a)=0 and f''(a)>0
A tangent approximation is an "underestimate" when...
f is concave up (f''>0)
A tangent line approximation is an "overestimate" when...
f is concave down (f''<0)
Extreme Value Theorem
Requirements:
1. f(x) is continuous on [a,b]
Conclusion:
f(x) will always have a absolute/global max and min because the closed end points can be the absolute/global extrema.
or
closed end points are always considered "candidates" for absolute max/min.
Note:
Critical points, sign changes in f'(x), and/or specific signs of f'' do NOT have to occur.
Candidates Test for Absolute/Global Extrema
"Candidates" are considered all critical points and closed end points
1. Find critical points (f'=0 and f'=undefined)
2. Create a table of f(x) values by plugging all "candidates" in to the original f(x) equation
3. Take the limit as x approaches any open end points
4. Classify global/absolute extrema
Absolute/Global Maximum
x=candidate is a global/absolute maximum because it is the largest value of f(x).
Note: if the limit as x approaches an open end point is the largest value, then no global max exists.
Absolute/Global Minimum
x=candidate is a global/absolute minimum because it is the smallest value of f(x).
Note: if the limit as x approaches an open end point is the smallest value, then no global min exists.
Absolute Max (Only Critical Point)
If x=c is the only critical point and is a relative max because f' goes from positive to negative then it is also the absolute max.
Absolute Min (Only Critical Point)
If x=c is the only critical point and is a relative min because f' goes from negative to positive then it is also the absolute min.
L'Hopital's Rule
Given lim f(x)/g(x) if,
- lim f(x) = 0
- lim g(x) =0
the lim f(x)/g(x)=lim f'(x)/g'(x)
Notes:
- Take separate derivatives of numerator and denominator (NOT the quotient rule)
- also applies if the numerator and denominator both go to infinity.
Closest Point
Minimize Distance Between 2 Points
d=sqrt((x2-x1)^2+(y2-y1)^2)
Find velocity v(t) given position x(t)
v(t)=x'(t)
Find acceleration a(t) given position x(t)
a(t)=x''(t)
Find acceleration a(t) given velocity
a(t)=v'(t)
A particle is "at rest" when
v(t)=0
A particle moves to the "right" when
v(t)>0
A particle moves to the "left" when
v(t)<0
A particle is "farthest right" when
position has an absolute maximum
A particle is "farthest left" when
position has an absolute minimum
Speed
Absolute value of velocity, speed = Iv(t)I
Speed increases (speeding up)
when a(t) and v(t) have the same sign
Speed decreases (slowing down)
when a(t) and v(t) have opposite signs