light microscope
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
26 Terms
what type of image is produced by a light microscope
an absorption image
what is the Dmin?
the resolution limit, the smallest distance at which two points can still be distinguished
what does resolution of the lens mean
the ability of the lens to distinguish between two close together points as separate
what is the equation for Dmin
1/R = Dmin
R = the resolution (unitless or in mm / lines)
Dmin = the resolution limit
is the dmin and resolution proportional or inversely proportional?
inversely proportional
better resolution (smaller Dmin), lower resolution (higher Dmin)
what is abbe’s equation?
dmin = 0.5 * λ / NA
λ = wavelength of light in nm or micrometers
NA = numerical apperture
What’s Abbe’s equation when numerical aperture is not given directly
dmin = 0.5 λ / n * sina
n = refractive index of medium between object and lens
a = semiangle of the maximum cone of light entering the lens
does a higher NA result in a better or worse dmin?
a better dmin, as a higher NA due to the equation means a smaller dmin
e.g. if the top part of the equation was 10 and the bottom part 5 dmin would be 2 which is better if the top part of the equation was 10 and the bottom part 2 then the dmin would be 5 which would be worse.
why would immersion oil be used
to match the refractive index of the medium to the glass slide of the specimen and the lens of the microscope → minimises light refraction and maximises light capturing resulting in a clear image
e.g. air has a refractive index of 1.003, and the glass slides
what is NA
How much light a lens can collect from a specimen and how finely it can resolve detail
does resolution depend on NA
yes
why is using blue light better for resolution over using red light?
due to Abbe’s equation; a smaller wavelength → smaller λ -→ smaller dmin → better resolution
blue light has a smaller wavelength (470nm) than red light (700nm)
what is the equation for total magnification?
magnification of objective lens (4,10,40) x magnification of occular lens (which is always x10)
does increased magnification mean better resolution?
not all the time, it depends on the image produced
what is a useful magnification and what is an empty magnification
useful magnification is when increased magnification provides an image that is detailed and clearer
empty magnification is when increased magnification leads to an image that is blurred / provides no new information
light passes through the specimen and as a result some wavelengths are absorbed differently depending on tissue density and stain,
how do more dense areas look compared to less dense areas / clear areas and why?
dense areas absorb more transmitted light → appear darker
clear areas absorb less transmitted light → appear brighter
describe the image from the objective lens
real, inverted and magnified
describe the image from the eyepiece
virtual, inverted, magnified
which part of the microscope is responsible for the resolution
objective lens
which part of the microscope is responsible for the contrast
condenser
which parts of the microscope is responsible for the magnification
objective lens and ocular lens
what is the resolving power of a microscope?
(same as dmin) the smallest distance between two points that a microscope can distinguish as separate
why do we apply immersion oil outside of it improving resolution at a higher magnification
to increase and match the refractive index of the medium to the refractive index of the glass slide of specimen and objective lens to minimise light refraction to prevent blurring in the image produced
how do we apply immersion oil
apply small drop of immersion oil on the cover slip after focusing at a low power, rotate the 100x objective oil immersion lens so that it contacts the immersion oil.
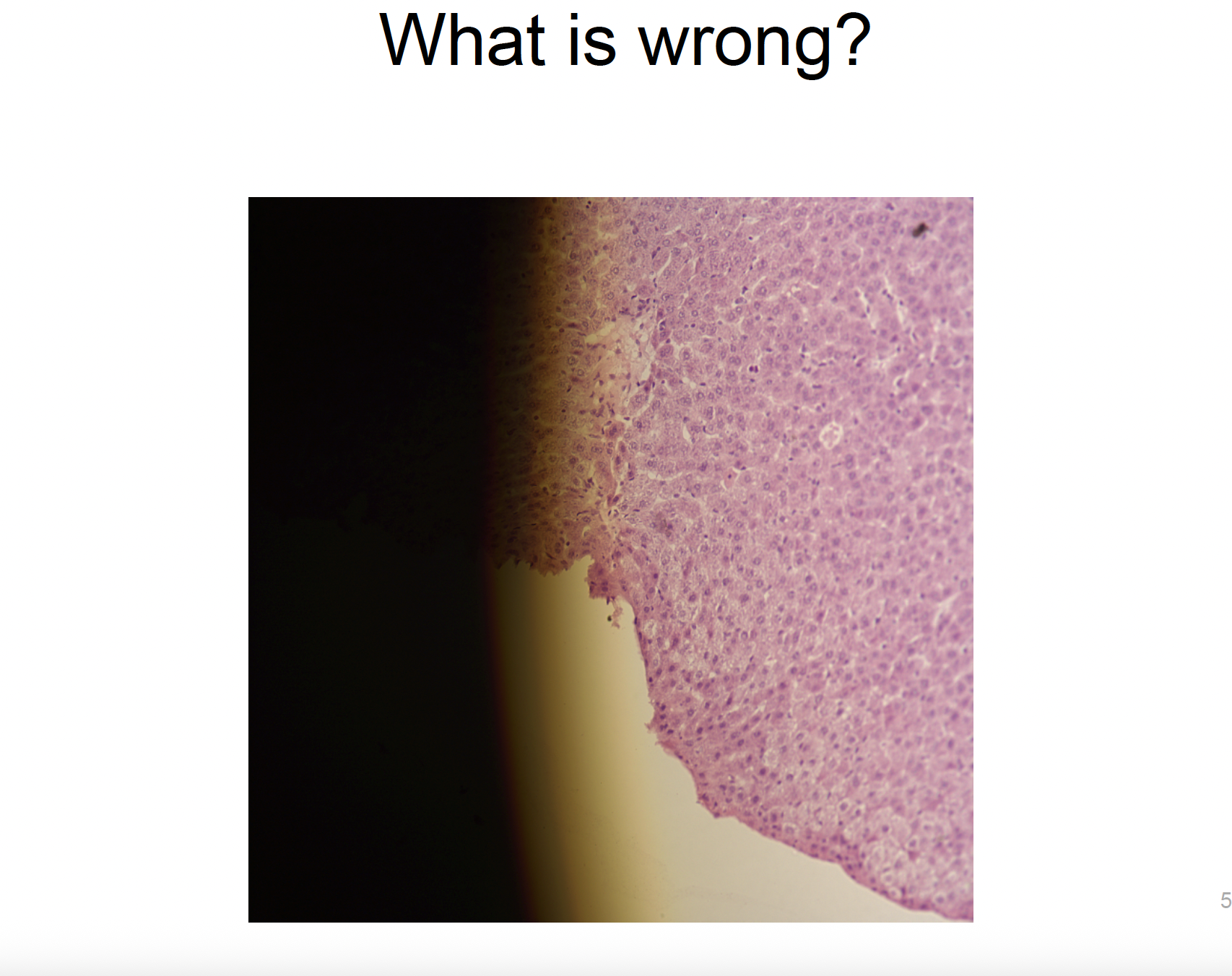
the condenser (or maybe light source) isn’t centred properly → uneven illumination
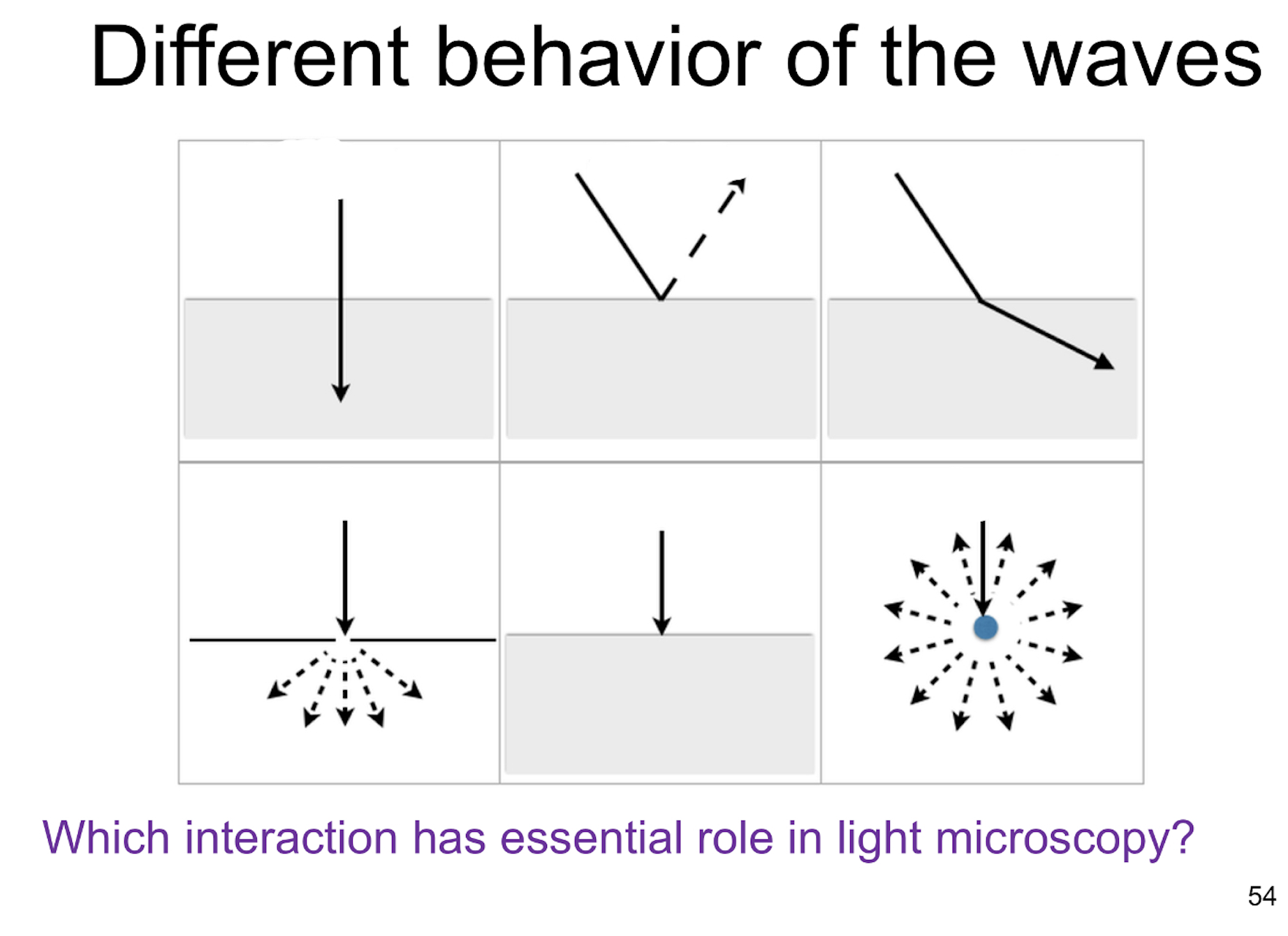
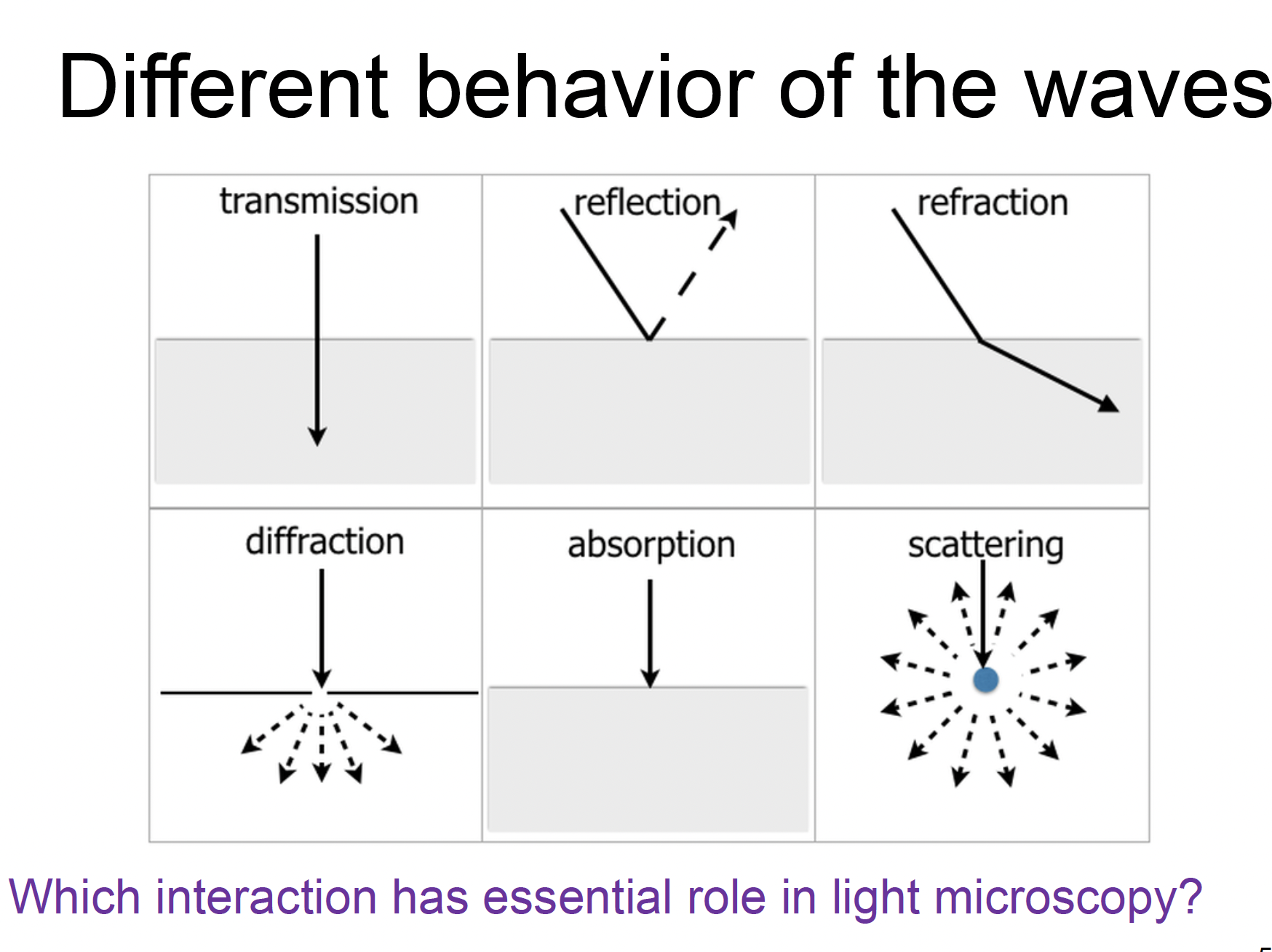
name the different behaviours and state which one is essential for light microscopy
transmission
refraction (light bends when passing through materials of different RIs like from glass slide to air and then lens)
absorption (diff parts of the specimen absorb light differently → contrast)