Variations in economic activity: macroeconomic equilibrium
1/14
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Unit 3, Macroeconomics
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
15 Terms
Monetarist / new classical counter revolution
An economic school of thought arguing that the price mechanism along with well-functioning competitive markets are sufficient to lead the economy to full employment. In this school of thought, government intervention is not necessary to manage the level of aggregate demand.
Keynesian revolution
An economic school of thought based upon the works of John Maynard Keynes, challenging the classical (laissez faire) viewpoint and advocating an interventionist role for the government in managing the level of aggregate demand and thus of economic activity.
Keynesian aggregate supply curve
An aggregate supply curve that shows the level of planned real output produced in an economy in relation to the average price level over time which consists of three sections: a horizontal section, an upward-sloping section and a vertical section. Changes in real GDP or the price level depend on aggregate demand and how close to (full) capacity the economy is operating.
Full employment level of output
The level of output that is produced by the economy when there is only natural unemployment.
Potential output
Output produced by an economy when it is at full employment equilibrium, or long-run equilibrium according to the monetarist/new classical model.
Deflationary/ recessionary gap
Arises when the equilibrium level of real output is less than potential output as a result of a decrease in AD.
Inflationary gap
The case where equilibrium real output exceeds potential output as a result of an increase
in AD.
Keynesian AS curve
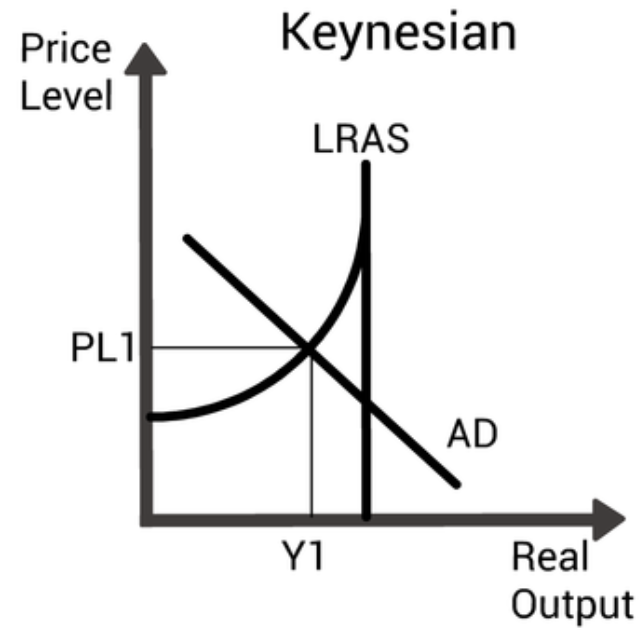
Monetarist AS curve
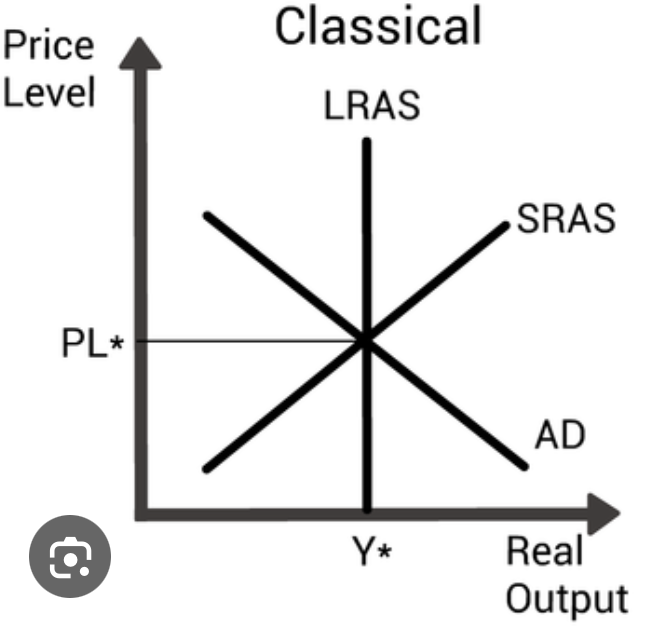
Short run in macroeconomics
´
The period of time when the prices of factors of production, especially wages, are considered fixed.
Short-run aggregate supply (SRAS)
The total quantity of real output (real GDP) offered at different possible price levels in the short run (when wages and other resource prices are constant).
Supply-side policies
Government policies designed to shift the long-run aggregate supply curve to the right, thus increasing potential output in the economy and achieving economic growth.
Costs
All the expenditure by a firm(s) to produce a certain good, service or output; is a determinant of SRAS.
Cost-push inflation
Inflation that is a result of increased production costs (typically because of rising money wages or rising commodity prices) and illustrated by a leftward shift of the SRAS curve.
Indirect taxes (macroeconomics)
Payments to the government based on the spending on goods and services, included in or added to the selling price; is a determinant of SRAS