Botany Krosnick Exam 2
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/124
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 10:35 PM on 11/10/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
1
New cards
Asexual Reproduction
Homosporous
2
New cards
Sexual Reproduction
Heterosporous in seeds in flowering and cone bearing seeds
3
New cards
Meiosis in plants
-In all plants and in may protists, meiosis results in the formation of haploid cells that can divide vegetatively without undergoing fertilization
-These cells are referred to as spores
-In these groups, gametes are produced by mitosis
-These cells are referred to as spores
-In these groups, gametes are produced by mitosis
4
New cards
Meiosis in animals
Diploid → Meiosis → 2 Haploid → Mitosis → 4 Haploid
Results directly in gametes
Results directly in gametes
5
New cards
Mitosis vs Meiosis
Mitosis: one division forming 2 identical cells (clones); Meiosis: two divisions forming 4 genetically different cells
6
New cards
Haploid (1n)
-One copy of each chromosome
-Gametes
-Gametes
7
New cards
Diploid (2n)
-Two copies of each chromosome
-Zygotes
-Zygotes
8
New cards
Polyploid
-Having three or more of each type of chromosome
-Triploid (3n)
-Tetraploid (4n)
-Hexaploid (6n)
-Triploid (3n)
-Tetraploid (4n)
-Hexaploid (6n)
9
New cards
Alternation of Generations
Life cycle involving sexual reproduction that alternates between diploid sporophyte phase and haploid gametophyte phase
10
New cards
Sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism
11
New cards
Gametophyte
Haploid, or gamete-producing, phase of an organism
12
New cards
Haplobiontic
Life history where only one stage (haploid or diploid) is dominant, and multicellular
13
New cards
H, h
Starts with a 2n zygote, spends multicellular generation as haploid
14
New cards
H, d
Starts with a 2n zygote, goes through mitosis and spends multicellular generation as diploid
15
New cards
Diplobiontic
Life cycle with both haploid and diploid multicellular generation (alternation of generation, D, h + d)
16
New cards
Cyanobacteria
Photosynthetic, oxygen-producing bacteria (formerly known as blue-green algae).
17
New cards
Cyanobacteria vs chloroplasts
chlorophyll is stored in thylakoids in their cytoplasm
18
New cards
Cyanobacteria vs green algae
green algae are a eukaryotic organism having a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles while cyanobacteria are prokaryotes having no nucleus and membrane-bound organelles
19
New cards
Cyanobacteria vs blue-green algae
Bacteria that can photosynthesize, but do not have bound membranes or nuclei
20
New cards
Isogamous gametes
both sperm and eggs are motile and equal in size
21
New cards
Anisogamous gametes
sperm and egg differ in size
22
New cards
Oogamous gametes
One is a large, non-motile egg and the sperm is small and motile
23
New cards
Gametangia
A reproductive organ that houses and protects the gametes of a plant
24
New cards
Antheridium
Male reproductive structure in some algae and plants
25
New cards
Sporangium
spore capsule in which haploid spores are produced by meiosis
26
New cards
Viridiplantae
Kingdom ____________would include green algae and land plants.
27
New cards
Chlorophyta
phylum of green algae
28
New cards
Streptophyta
green algae clade that gave rise to land plants; charophytes and liverworts
29
New cards
Charophyte
A member of the green algal group that are considered the closest relatives of land plants.
chlorophyll a and b, store carbohydrates as starch, have cell walls consisting of cellulose, and undergo similar cell-division processes.
life cycles are usually characterized as haploid with zygotic meiosis
chlorophyll a and b, store carbohydrates as starch, have cell walls consisting of cellulose, and undergo similar cell-division processes.
life cycles are usually characterized as haploid with zygotic meiosis
30
New cards
Coleochaete
Disk-shaped (with hairs) member of the Charophyta whose cells produce a phragmoplast during cell division
31
New cards
Green algal ancestry
Filamentous cells developed 2D and 3D growth, creating parenchyma, eggs become large, became archegoniate (egg chamber).
32
New cards
Water-To-Land difficulties
-Drying out
-Ultraviolet rays
-Temperature variation
-Obtaining nutrients
-Gravity
-Ultraviolet rays
-Temperature variation
-Obtaining nutrients
-Gravity
33
New cards
Byrophytes
Nonvascular plants - examples are liverworms, hornworts, and mosses.
34
New cards
Byrophyte characteristics
-No vascular tissue
-Grow in damp and frozen/hot climates
-Rhizoids, not roots!
-Diplobiontic life cycle/ dominant haploid (gametophyte) generation
-Grow in damp and frozen/hot climates
-Rhizoids, not roots!
-Diplobiontic life cycle/ dominant haploid (gametophyte) generation
35
New cards
Compared to green algae?
-Oogamous reproduction only
-Archegonium
-Embryo from zygote
-Sporophytes are differentiates
-Heteromorphic alternation of generation
-Archegonium
-Embryo from zygote
-Sporophytes are differentiates
-Heteromorphic alternation of generation
36
New cards
Bryophyte examples
mosses, liverworts, hornworts
37
New cards
byrophyte structure
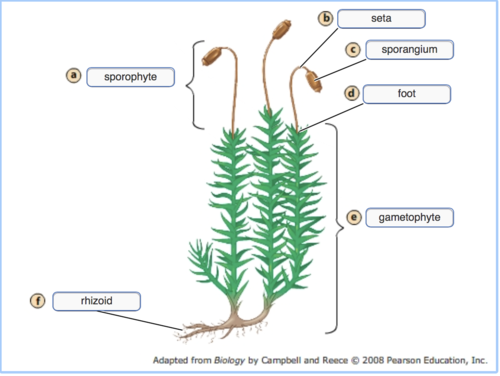
38
New cards
Archegonia
Female reproductive part of a nonvascular plant
39
New cards
Antheridia
Structures in nonvascular plants that produce male gametes
40
New cards
Protonema
A mass of green, branched, one-cell-thick filaments produced by germinating moss spores.
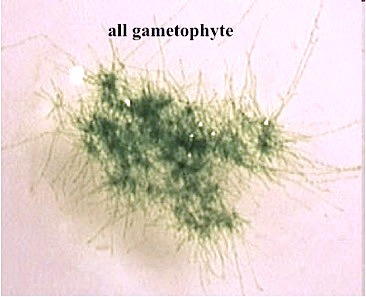
41
New cards
Peristomal teeth
Opens when air is dry enough to release pores

42
New cards
Microphylls
leaves with a single vein
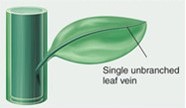
43
New cards
Sporophyte
Diploid, or spore-producing, phase of an organism
44
New cards
gametophyte
Haploid, or gamete-producing, phase of an organism
45
New cards
Bryophyta
-True mosses
-Have protonema
-Haploid, dominant gametophyte generation
-Budding sometimes
-Paraphyses collect water
-Several chloroplast per cell
-Have protonema
-Haploid, dominant gametophyte generation
-Budding sometimes
-Paraphyses collect water
-Several chloroplast per cell
46
New cards
Hepatophyta
-Liverworts
-Leafy (dichotomous branching)
-Pores for gas exchange, static unlike stomata
-Thallose (no stem/leaf distinction, elevated gametophytes, chimney cells)
-Sperm use raindrops
-Leafy (dichotomous branching)
-Pores for gas exchange, static unlike stomata
-Thallose (no stem/leaf distinction, elevated gametophytes, chimney cells)
-Sperm use raindrops
47
New cards
Anthocerophyta
-Hornworts
-Thalloid gametophyte
-Cyanobacteria present (nitrogen fixation)
-Stomata on sporophyte
-Gametophytes are within small cavities
-Thalloid gametophyte
-Cyanobacteria present (nitrogen fixation)
-Stomata on sporophyte
-Gametophytes are within small cavities
48
New cards
hydroids and leptoids
-Inside vs outside
-H for water (X)
-L for nutrients (P)
-H for water (X)
-L for nutrients (P)
49
New cards
Fern allies
Lycophyta, Sphenophyta, and Psilophyta
50
New cards
Fern ally characteristics
-Seedless
-Vascular
-Shed spores to initiate alternation of generation
-Xylem and Phloem
-Sporophyte dominate multicellular stage
-Vascular
-Shed spores to initiate alternation of generation
-Xylem and Phloem
-Sporophyte dominate multicellular stage
51
New cards
Pteridopsida
-True ferns
-Sporangia arise from single epidermal cell
-Sporangia arise from single epidermal cell
52
New cards
Sorus
cluster of sporangia on the underside of a fern frond

53
New cards
Annulus
-Curved sporangium covering that ejects spores when walls break
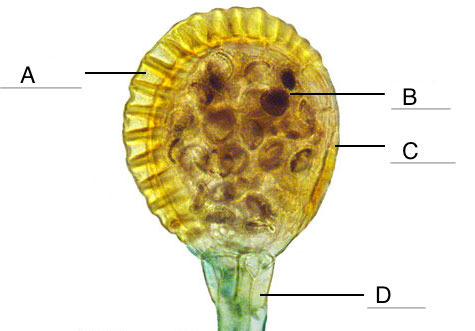
54
New cards
Sporocytes
-Undergo meiosis and produces spores that are released in the spring
55
New cards
Prothallus
-Heart-shaped gametophyte form of a fern that can make its own food and absorb water and nutrients from the soil
-Produces archegonia and antheridia
-Produces archegonia and antheridia
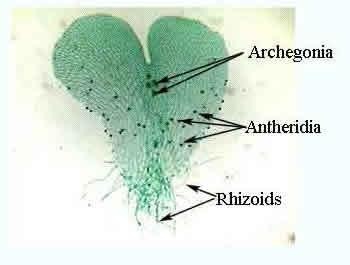
56
New cards
Antheridum in ferns
-Along root like rhizoids
-Circular
-Produces sperm
-Circular
-Produces sperm
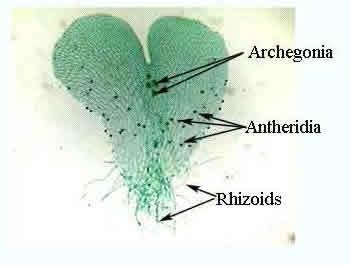
57
New cards
Archegonium in ferns
-Short neck
-Single egg close to notch of prothallus
-Single egg close to notch of prothallus
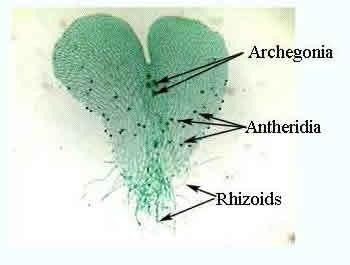
58
New cards
Fern life cycle
1). Zygote develops into leafy fern plant. 2) the sporophyte. 3) Spores are released from spore cases and grow into tiny, heart-shaped gametophytes. Each gametophyte has both male and female structures. 4) Sperm swim to another gametophyte to fertilize eggs.
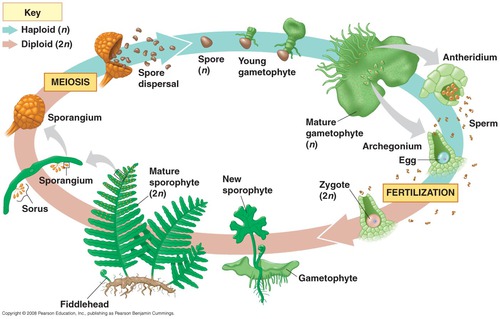
59
New cards
Enations
Tiny, green, superficially leaflike, veinless, photosynthetic flaps of tissue

60
New cards
Microphylls in ferns
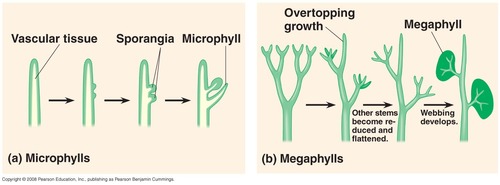
61
New cards
Homospory vs. Heterospory
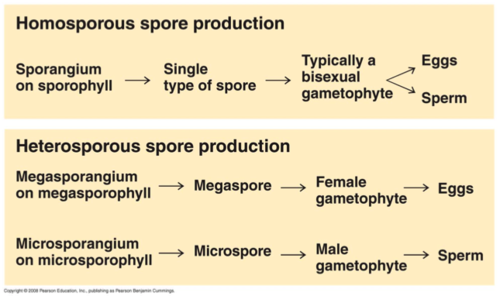
62
New cards
Exospory vs Endospory
-spore germinates and grows as an external gametophyte; ancestral condition
-Inside!
-Inside!
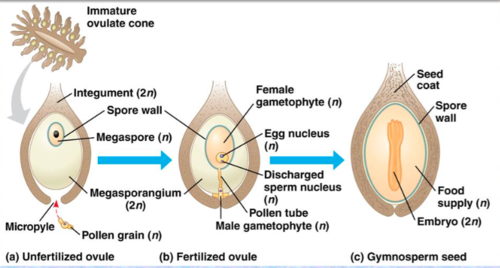
63
New cards
Strobilli
cone-like structures formed from groups of sporophylls
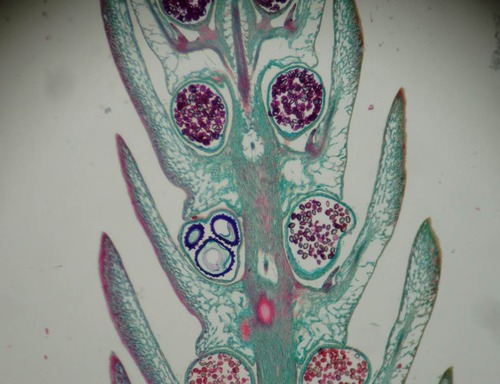
64
New cards
rhizoids
A thin, rootlike structure that anchors a moss and absorbs water and nutrients.
65
New cards
Rhyniophytes
A group of early vascular plants that appeared in the Silurian and became extinct in the Devonian. Possessed dichotomously branching stems with terminal sporangia but no true leaves or roots.
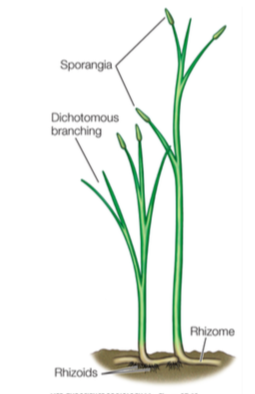
66
New cards
Ferns need water
-Spores do not have moisture storage, so humid environments are required
67
New cards
Bryophytes water needs
-Have swimming sperm, needs water to reach egg
68
New cards
Node
Place where leaves, branch, and stems originate
69
New cards
Internode
A segment of a plant stem between the points where leaves are attached.
70
New cards
petiole
the stalk of a leaf
71
New cards
blade
Broad, flat portion of a leaf.
72
New cards
phyllotaxy vennation
Spiraling from a center axis or stem
73
New cards
what the difference between edicot and monocot stems
Monocot leaves are narrow, slender, and longer than dicot leaves. Dicot leaves are broad and relatively smaller than monocot leaves.
74
New cards
asexual reproduction
produces plants that are genetically identical to the parent plant because no mixing of male and female gametes
75
New cards
sexual reproduction
through pollination when a male and female (two parent plants) come together to make a new plant containing both DNAs
76
New cards
What is the end result of meiosis in plants vs. animals?
Meiosis in animals produce the gametes (sperms and eggs), whereas meiosis in plants produce spores
77
New cards
What is the purpose of meiosis?
Meiosis is the process of chromosomal reduction in eukaryotic cells, which leads to the production gametes needed for sexual reproduction.
78
New cards
how does mitosis differ from meiosis
Mitosis results in two identical daughter cells, whereas meiosis results in four sex cells
79
New cards
What is alternation of generations?
the regular alternation between two distinct forms. The generations are alternately sexual and asexual
80
New cards
What is the significance of the cyanobacteria for land plants?
They are able to carry out nitrogen fixation.
81
New cards
what features do cyanobacteria share with chloroplasts
hey both have cell membranes constructed from a phospholipid bilayer and both have a cell wall
82
New cards
How are cyanobacteria similar to green algea
they occur in terrestrial and aquatic habitats. and evolved from algae and can be photosynthetic
83
New cards
How do cyanibacteria and green agea differ
cyanibacteria can produce and use their own food through sunlight where as green algea provide for zooplankton
84
New cards
Why should we not call cyanobacteria "blue-green algae"
blue-green algae aren't quite plants or algae
85
New cards
Haplobiontic versus diplobiontic life cycles
diplohaplontic is describing a life cycle that has alternating haploid and diploid phases while haplodiplontic is having multicellular diploid and haploid stages.
86
New cards
Isogamous
Similar
87
New cards
anisogamous
fusion of two gametes that differ in size and/or form.
88
New cards
oogamous gametes
Large female gamete is immobile while the small male gamete is mobile
89
New cards
what are the closest relative to land plants
Green-algea
90
New cards
Viridiplantae
Made up of green algea/ where land plants originated
91
New cards
Chlorophyta?
green algea that survive in extreme enviroments
92
New cards
Streptophyta?
aquatic green algea that live in
93
New cards
What are the characteristics of the charophytes that make them a good potential precursor to land plants?
have chlorophyll a and b, store carbohydrates as starch, have cell walls consisting of cellulose, and undergo similar cell-division processes.
94
New cards
What type of life cycle do charophytes display?
a haplontic life cycle where the only diploid cell is the zygote that then undergoes meiosis to produce haploid spores
95
New cards
Is Charophytes life cycle similar or different from land plants?
they are different as they dont undergo alternation of gennerations
96
New cards
gametophyte
gamete-producing and usually haploid phase, producing the zygote from which the sporophyte arises
97
New cards
sporophyte
asexual and usually diploid phase, producing spores from which the gametophyte arises
98
New cards
List several characteristics of the bryophytes.
Vascular tissues are absent, sexual reproduction is oogamete type, they have a heteromorphic or heterologous alternation of generations, Bottom half is haploid and upper half is diploid.
99
New cards
How are Bryophytes similar to the green algae, and how are they different?
Both algae and bryophytes lack a vascular system. The main difference between algae and bryophytes is the division of the plant body
100
New cards
Which organisms are classified within the Bryophytes?
liverworts, hornworts and mosses