1. alginate
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
95 Terms
what structure provides legal proof of pt current occlusion?
mounted diagnostic case on an articulator
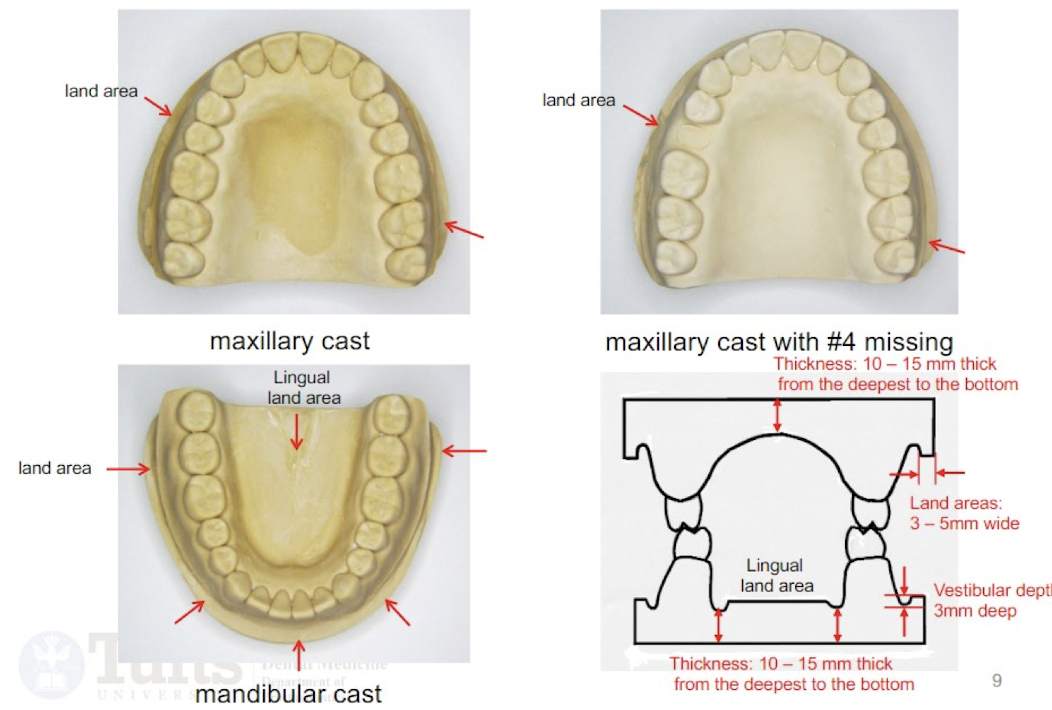
explain the land areas and thickness requirements for a trimmed cast:
maxillary lingual land area thickness
mandibular lingual land area thickness
peripheral land area thickness
vestibular depth
maxillary lingual land area: 10-15mm deepest part
mandibular lingual land area thickness: 10-15 mm
peripheral land area thickness: 3-5mm
vestibular depth: 3mm
what are the two materials most commonly used to make impressions?
hydrocolloids
synthetic elastomeric polymers
impressions create positive or negative reproductions of the tissue?
negative
filling an impression with dental stone or other model material makes a negative or positive cast?
positive
what are the some desirable qualities of impression materials?
Pleasant odor, taste, and color
Absence of toxic or irritant constituents
Adequate shelf life
Economic
Easy to use
Good setting characteristics
Satisfactory consistency and texture
Readily wets oral tissues
Resistance to permanent distortion
Adequate strength
Dimensional stability over temperature and humidity normally found in clinical and laboratory setting
Compatibility with cast and die materials
Accuracy in clinical use
Readily disinfected without loss of accuracy
No release of gas during the setting of the impression or cast and die material
what are the six types of impression materials?
Alginate hydrocolloid (A.K.A. irreversible hydrocolloid)
Agar hydrocolloid (A.K.A. reversible hydrocolloid)
Elastomeric materials Zinc oxide-eugenol materials
Gypsum
Compound impression material
what is the most widely used impression material in dentistry?
alginate (hydrocolloids)
which an an advantge and disadvantage of alginate hydrocolloids?
adv: accurate if handled properly
disadv: dimensionally unstable (syneresis vs inhibition)
alginate powder composed of what substances:
Sodium or Potassium alginate (12 to 15%)
Calcium sulfate dehydrate (8 to 12%)
Sodium phosphate (2%)
Reinforcing filler (~70%)
Potassium sulfate or alkali zinc fluorides (~10%)
Coloring and flavoring agents
what are the two main reactions of alginate hydrocolloids?
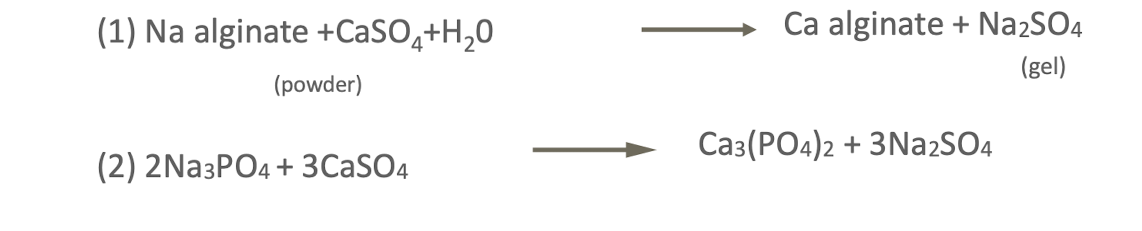
what slows alginate reaction?
retarders/chelating agents ike trisodium phosphate or sodium hexametaphosphate - bind to free calcium ions preventing immediate cross-link of alginate chains delaying reaction
how to manipulate alginate:
Powder should be lightly shaken for aeration
One scoop of powder should be used for one measure of water
Always add water to the mixing bowl first
One minute of thorough mixing for the regular setting and 45 seconds for fast-set
Set time is around 3.5 minutes after mixing
add powder or water to bowl first
water
how long to mix for regular vs fast-set?
regular: 1 min
fast-set: 45 sec
set time for alginate after mixing
3.5 min
1 scoop of powder in grams vs water in ml
1 scoop of powder = 16g
1 measure of water = 38 ml
lower or higher W/P ratio: increase in strength
lower W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: increase in tear strength (resisatnce to pulling)
lower W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: “better” consistency
lower W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: decrease in working time
lower W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: decrease in setting time
lower W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: decreased flexibility
lower W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: decrease in strength
higher W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: decrease in tear strength
higher W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: runny consistency
higher W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: increase in working time
higher W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: increase in setting time
higher W/P
lower or higher W/P ratio: increased flexibility
higher W/P
(cold/hot) water will increase the working and setting times
cold
syneresis
storage in air
loss of water due to hydration that causes shrinkage
syneresis
imbitbition
storage in water
tendency to absorb water that results in swelling
imbibition
how long can an impression be stored in 100% himidty?
30 min prior to pouring
disinfection of impression accomplished by immersion in what two substances?
sodium hypochlorite or iodophors
water temp should be btwn
65-75℉
undercuts and not enough material could lead to
tearing
consistency is related to what three things?
water-powder ratio
water temp
spatulation
porosity can be related to what
incorrect spatulation
poor stone surface is related to what?
extended contact btwn gypsum and alginate - separate 45-60 min after pouring
what are the features of ideal mandibular and maxillary impressions?
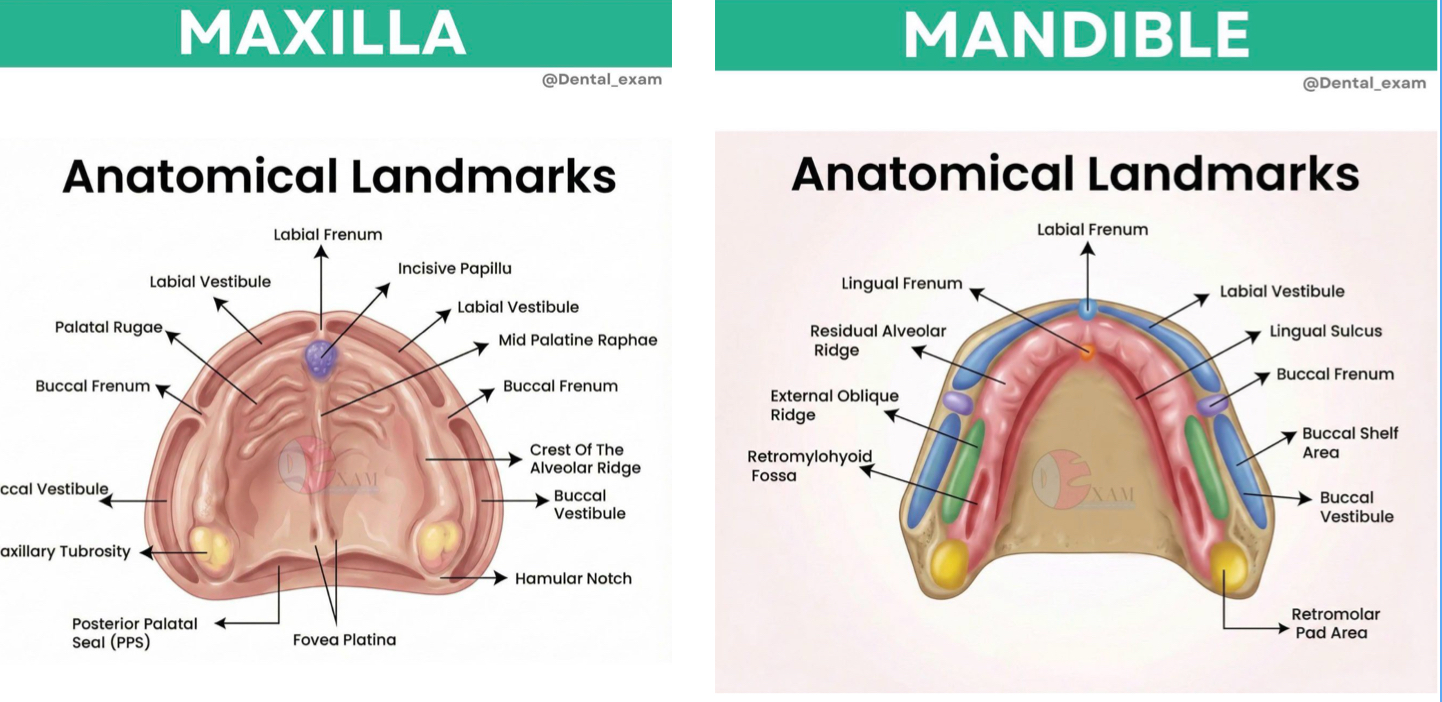
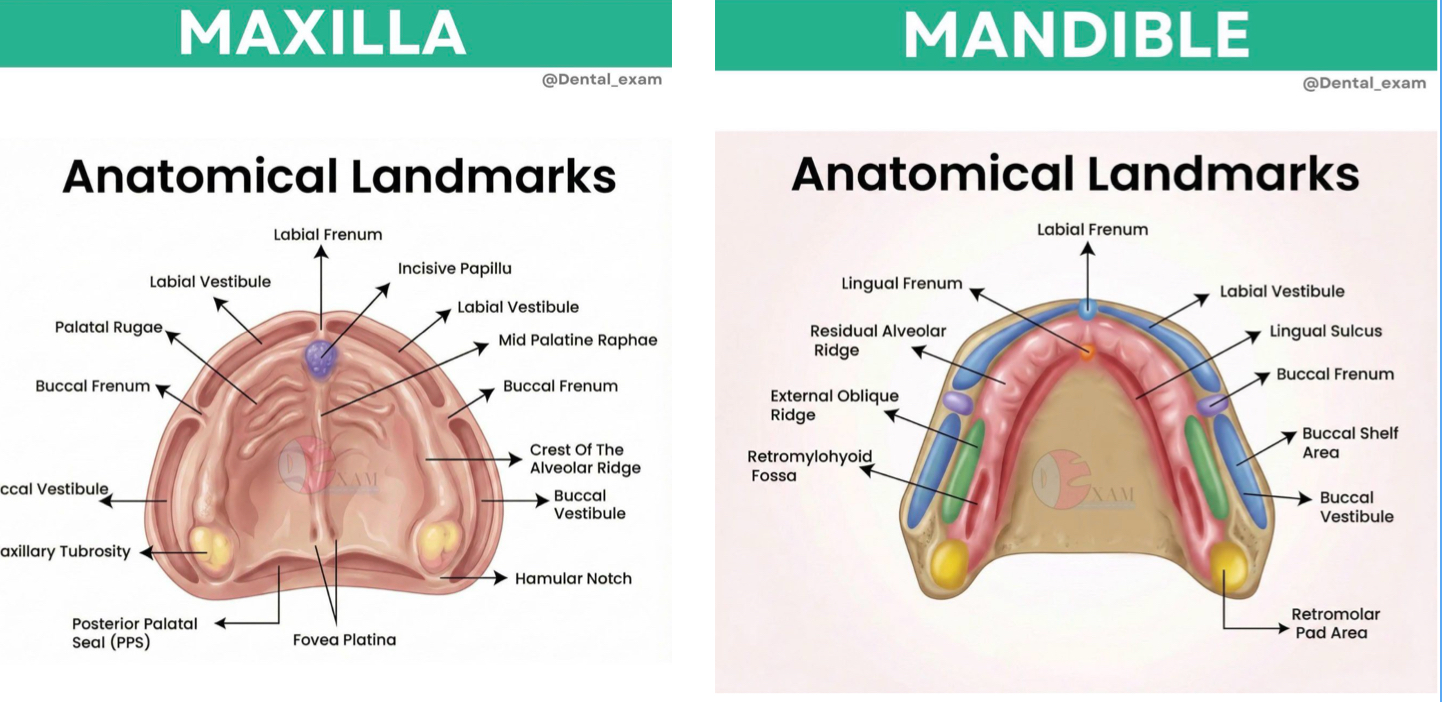
infection control of impression in operatory:
Rinse impression using cold running water to remove blood and debris
Rub impression using Cavi Wipe
Wrap it with Cavi-Wipe and place in plastic bag
infection control in lab
Place impression on a paper towel
Spray with Cavicide in 4th Fl Lab and leave it for 3 mins
Rinse impression using cold running water
Pour impression with Type III or IV dental stone
gypsum or alignate: refer to various forms of calcium sulfate (hydrous and anhydrous)
gypsum
gyspum or alginate: manufactured by the calcination of calcium sulfate
gypsum
gypsum products are manufactured by the (BLANK) of calcium sulfate dihydrate
calcination
what are the five gypsum products?
impression plaster - ISO type 1
(white) plaster - ISO type 2
high strength plasters:
(yellow) stone - ISO type 3
stone, high-strength, low-expansion - ISO type 4
stone, high-strength, high expansion - ISO type 5
what is the worst thing about acrylic resin?
shrinkage
for metal base, crowns and bridges what ISO type used
4 bc low expansion 0-0.15%
white impression plaster
1
white mounting plaster of Paris
2
yellow stone study class
3
working cast for C&B
4
green working cast aka Die Keen aka C&B (tooth/implants), metal rpd frame
5
type 1 setting expansion % and compressive strength psi
0-0.15%
580-1160 psi
type 2 setting expansion % and compressive strength psi
0-0.30%
1300 psi min
type 3 setting expansion % and compressive strength psi
0-0.20%
2900 psi min
type 4 setting expansion % and compressive strength psi
0-0.15%
5100 psi min
type 5 setting expansion % and compressive strength psi
0.16-0.30% 5100 psi min
yellow stone
3
green stone
5
for a maxillary complete denture what stone is used?
3
for a mandibular metal base rpd what stone is used?
5
for a mandibular acrylic resin (shrinkage) rpd what stone is used?
3
for immediate maxillary complete and mandibular resin based rpd what stone should be used?
3
type ? allows expansion to compensate for acrylic shrinkage
3
type ? provides limited expansion - good for prosthesis that require high precision like crown and bridge, fixed prosth like dental implant restoration and metal based rpd
4 or 5
what are the two products of partial dehydration of gypsum
plaster and stone
traditional hemihydrate plaster is produced by
dry calcination (Beta Hemihydrate)
medium and high strength plasters/stoens manufactured by wet calcination havea (stronger/weaker) set mass
stronger Alpha Hemihydrate
setting process
2 stages, thick slurry
reverse of first stage of dehydration & exothermic
slurry water defined as
saturated calcium sulfate solution made by placing stone debris in a container of water
using tap water or slurry water for gypsum:
decrease setting time or shorten setting time
decrease compressive strength (not good)
increase dimensional change (not good)
slurry water
lab plaster W/P ratio and ISO (gypsum setting process)
47, 2
dental stone W/P ratio and ISO (gypsum setting process)
30, 3
mounting stone W/P ratio and ISO (gypsum setting process)
26, 3
microstone W/P ratio and ISO (gypsum setting process)
28, 3
die-keen W/P ratio and ISO (gypsum setting process)
21, 4
four stages of gypsum setting process
fluid
plastic
friable
carvable
setting reaction causes a (decrease/increase) in true volume of reactants
decrease
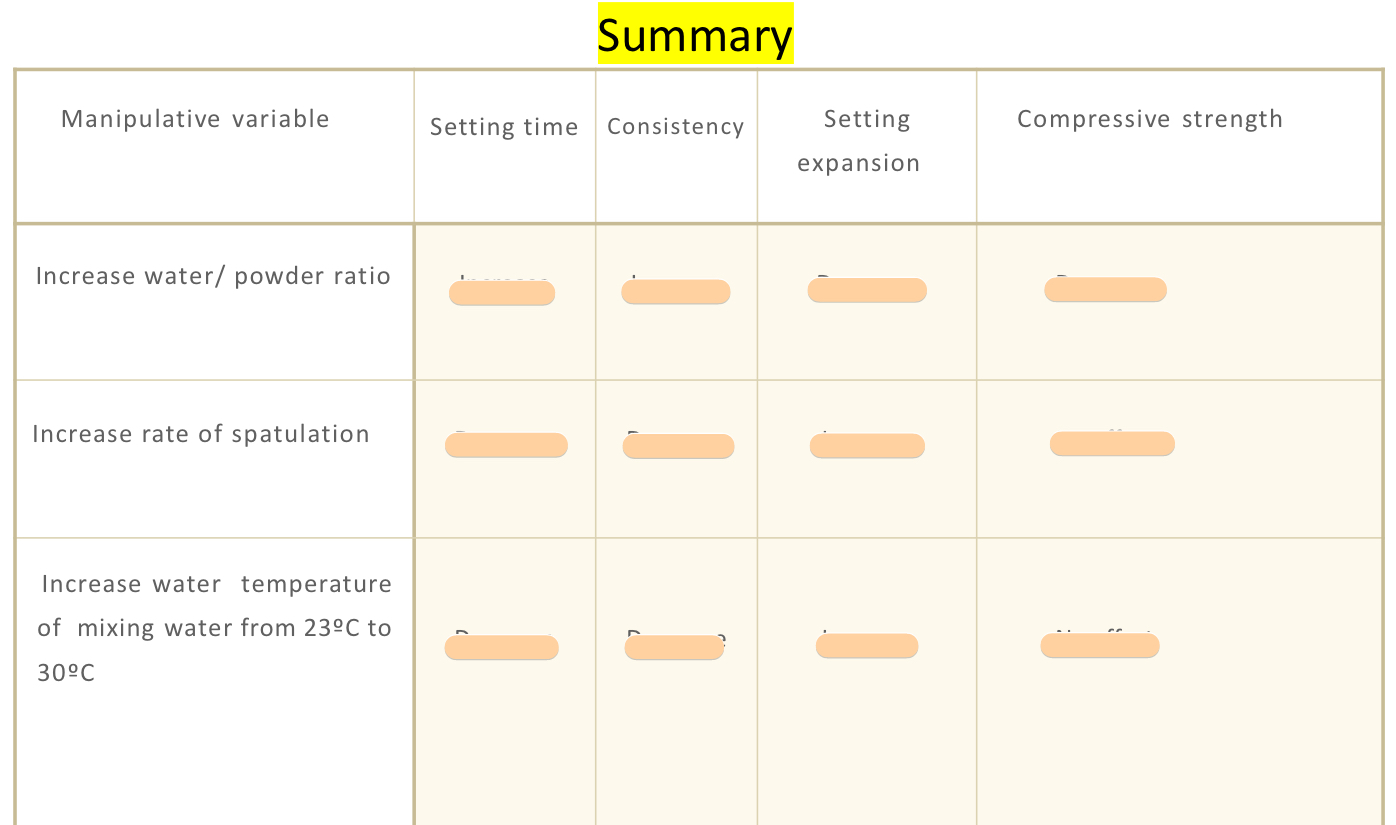
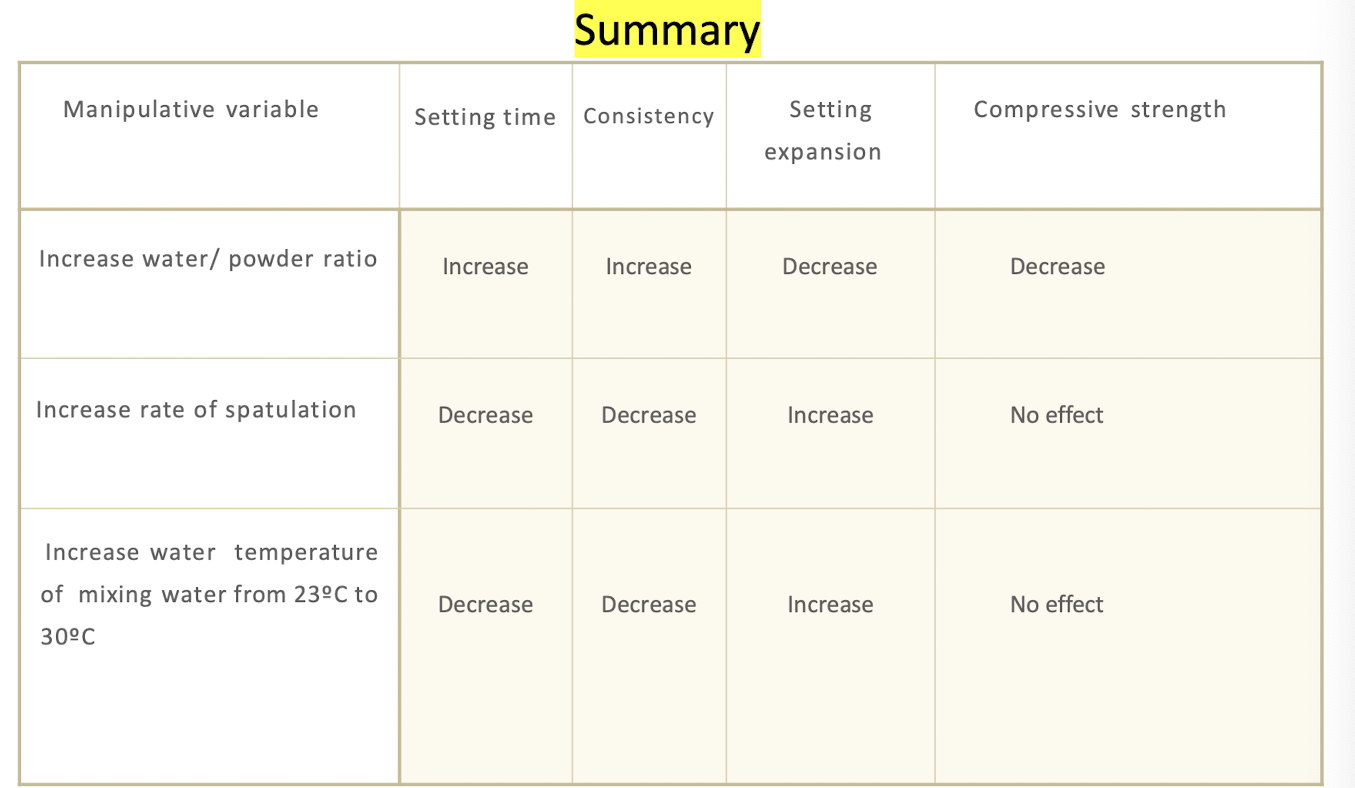
what will affect the chemical reaction during the setting of gypsum products?
water/powder ratio
↑ temp of water
↓ setting time
(high/low) water/powder ratio harden more quickly, and will produce less microporosities related to residual unreacted water
]It will, however, (decrease/increase) microporosity related to crystal growth
low, increase
(more/less) spatulation turns = lower setting time
more
setting expansion is (inversely/proportional) to w:p
inversely
strength is (inversely/proportional) to w:p
inversely proportional
using (low/high) w:p for maximum strength also increases setting expansion
low
Removal of uncombined water from cast gypsum by low-temperature drying approximately (halves/doubles) the strength
doubles
hand mix or power-driven mix w vacuum:
lower setting time
higher compressive strength
lower setting expansion %
lower viscosity
power-driven mix w vacuum
what:
serves as complement tool to clinical exam
provides legal proof pf pt current occlusion
allows clinician to modify occlusal pre-tx plan prior to definitive tx plan
evaluate pt occlusion in centric and eccentric positions
determine interarch distance - make alterations to clinician’s desire w/o pt
mounted cast on an articulator
what is the relationship between teeth and alveolar ridge?
interarch distance