Types of Joints BIO-201L GCU
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Synostosis
Fused bones, immovable
fibrous joints (synarthrosis)
connected by dense connective tissue consisting mainly of collagen; immovable
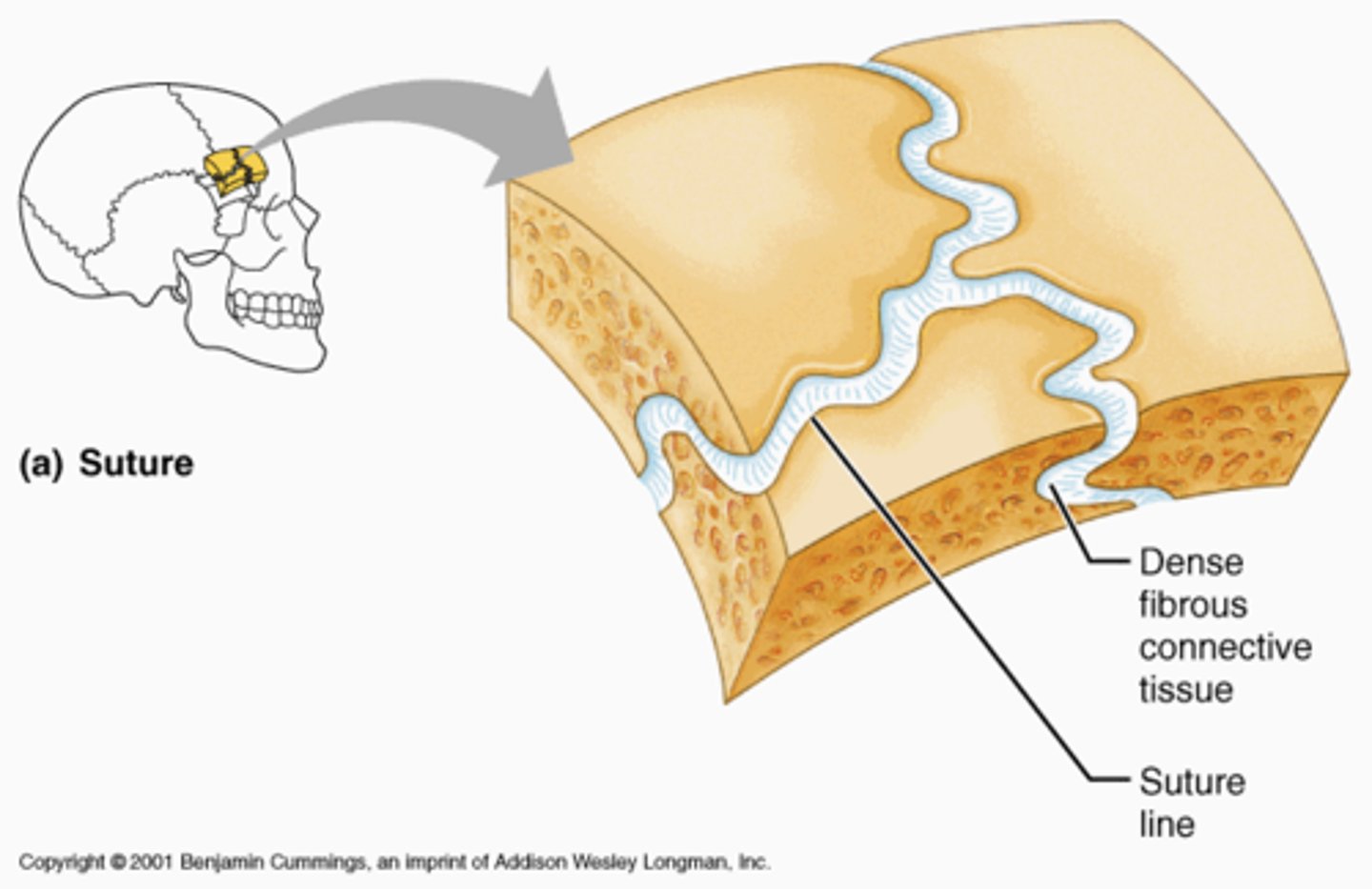
suture joint
fibrous joint only found in the skull
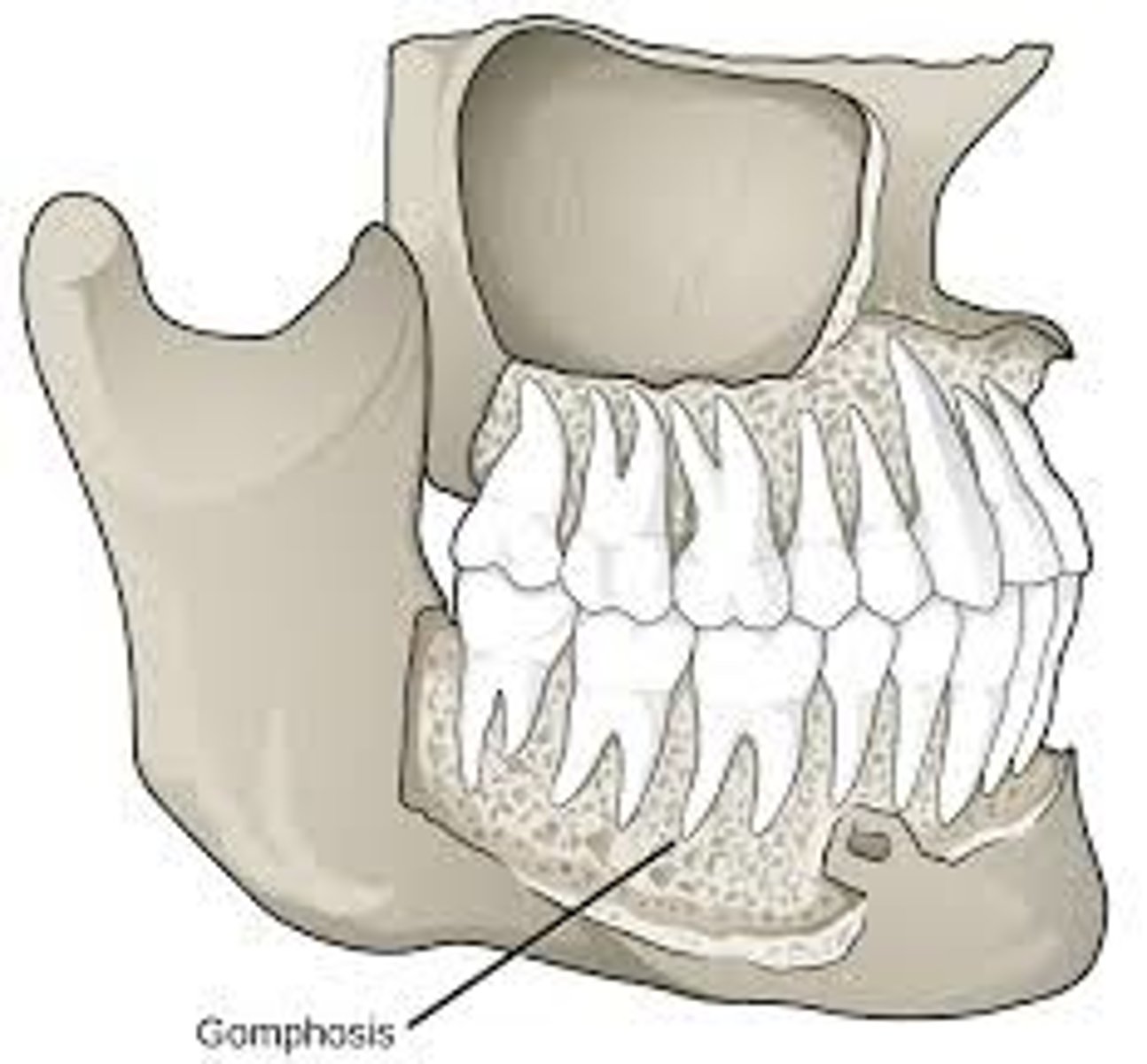
gomphoses joint
fibrous joint that attaches the tooth to its socket
Syndesmosis
a fibrous joint held together by a ligament
cartilaginous joints (amphiarthrosis)
allow only slight movement and consist of bones connected entirely by cartilage
Synchondrosis
cartilaginous joint in which the connecting material is hyaline cartilage
Symphesis
connected by a wedge or pad of fibrocartilage
Synovial (diarthrosis)
freely movable; located at ends of long bones
monoaxial (diarthrosis)
movement in one plane (elbow, ankle)
biaxial (diarthrosis)
movement in two planes (ribs, wrist)
triaxial (diarthrosis)
movement in three planes (shoulder, hip)
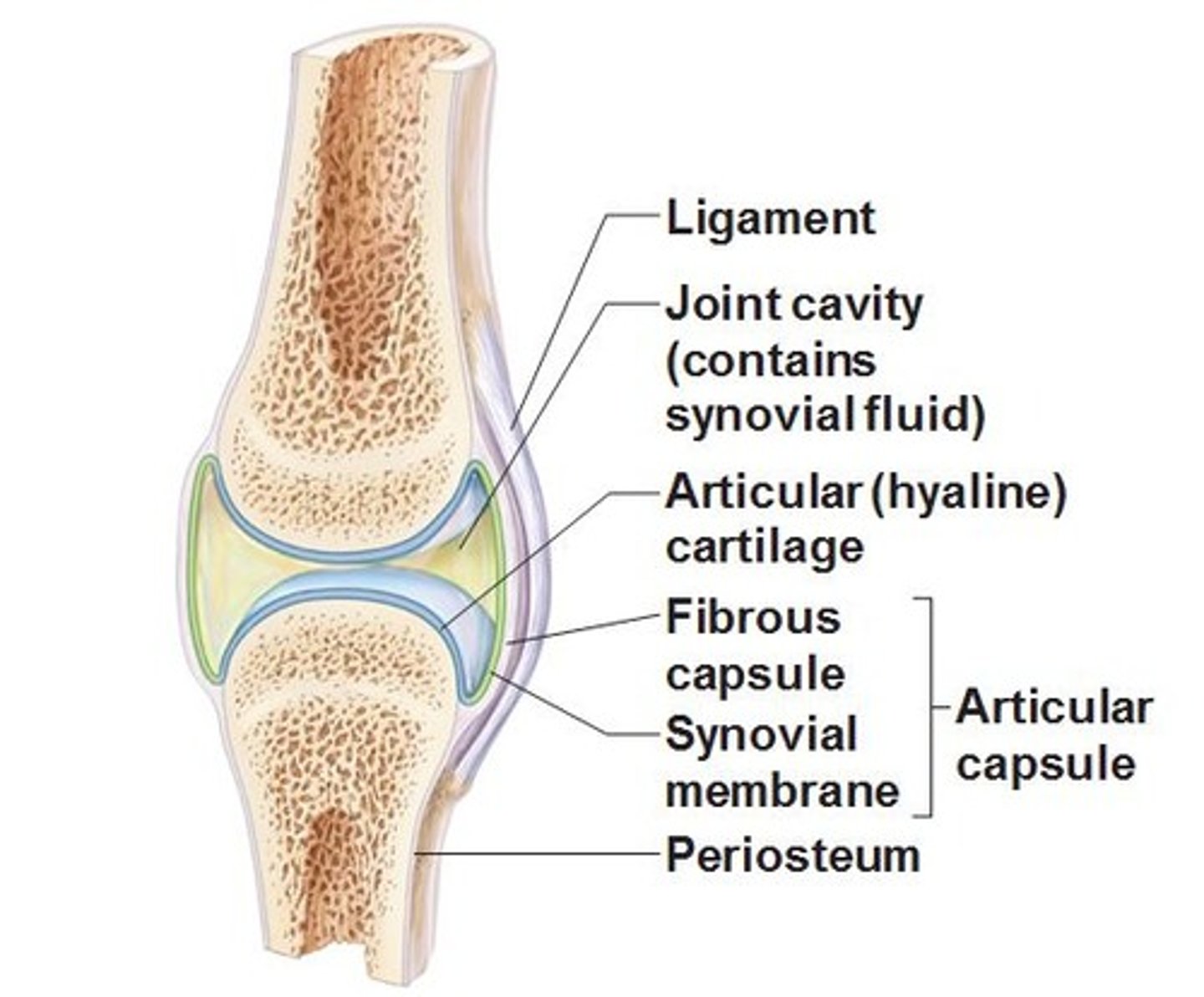
synovial joint: articular capsule
surrounds the joint
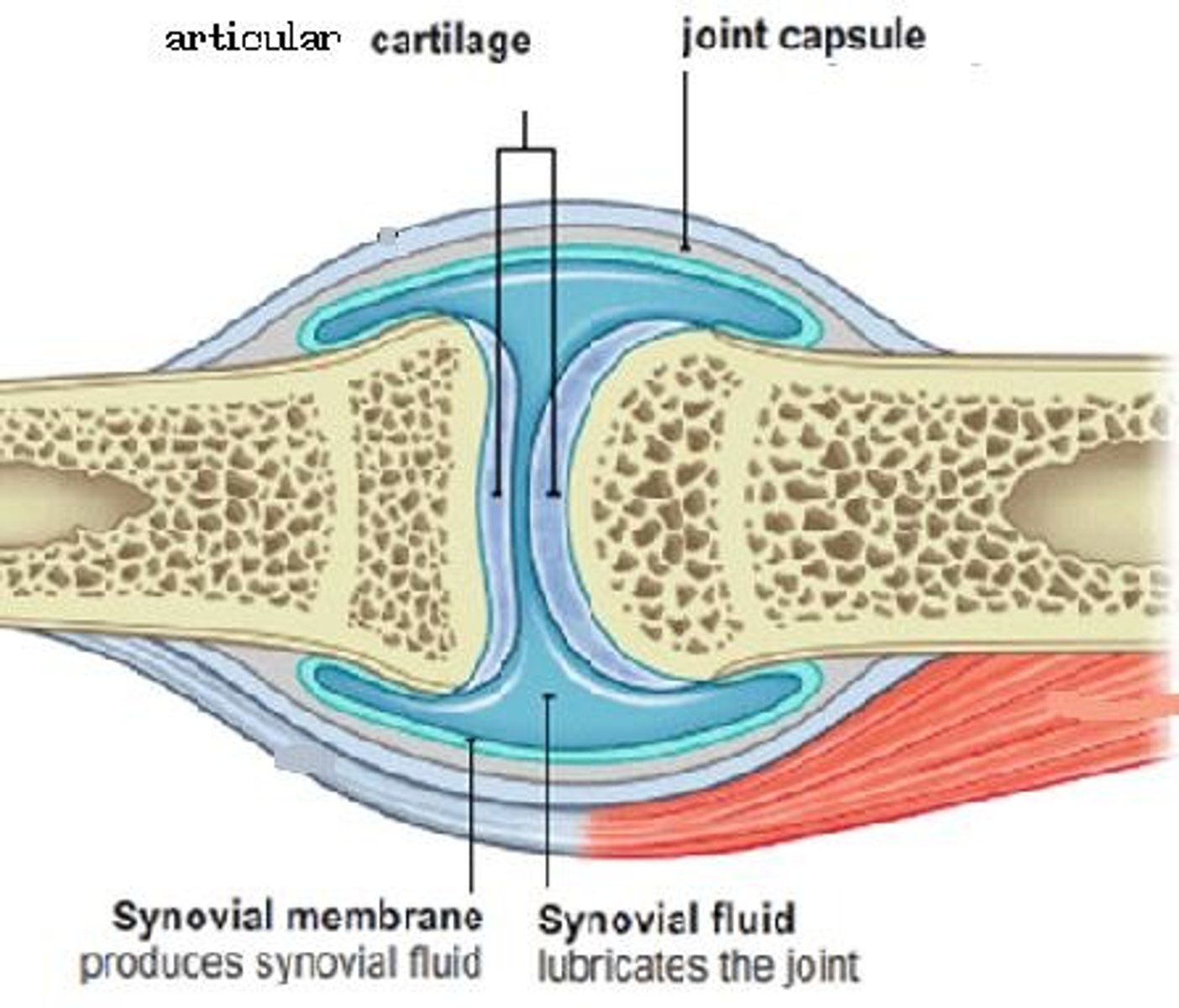
synovial joint: synovial cavity
space between bones at a synovial joint
synovial joint: synovial fluid
the fluid inside a joint
3 Functions: Lubrication, Distribution of Nutrients, Shock
Absorption
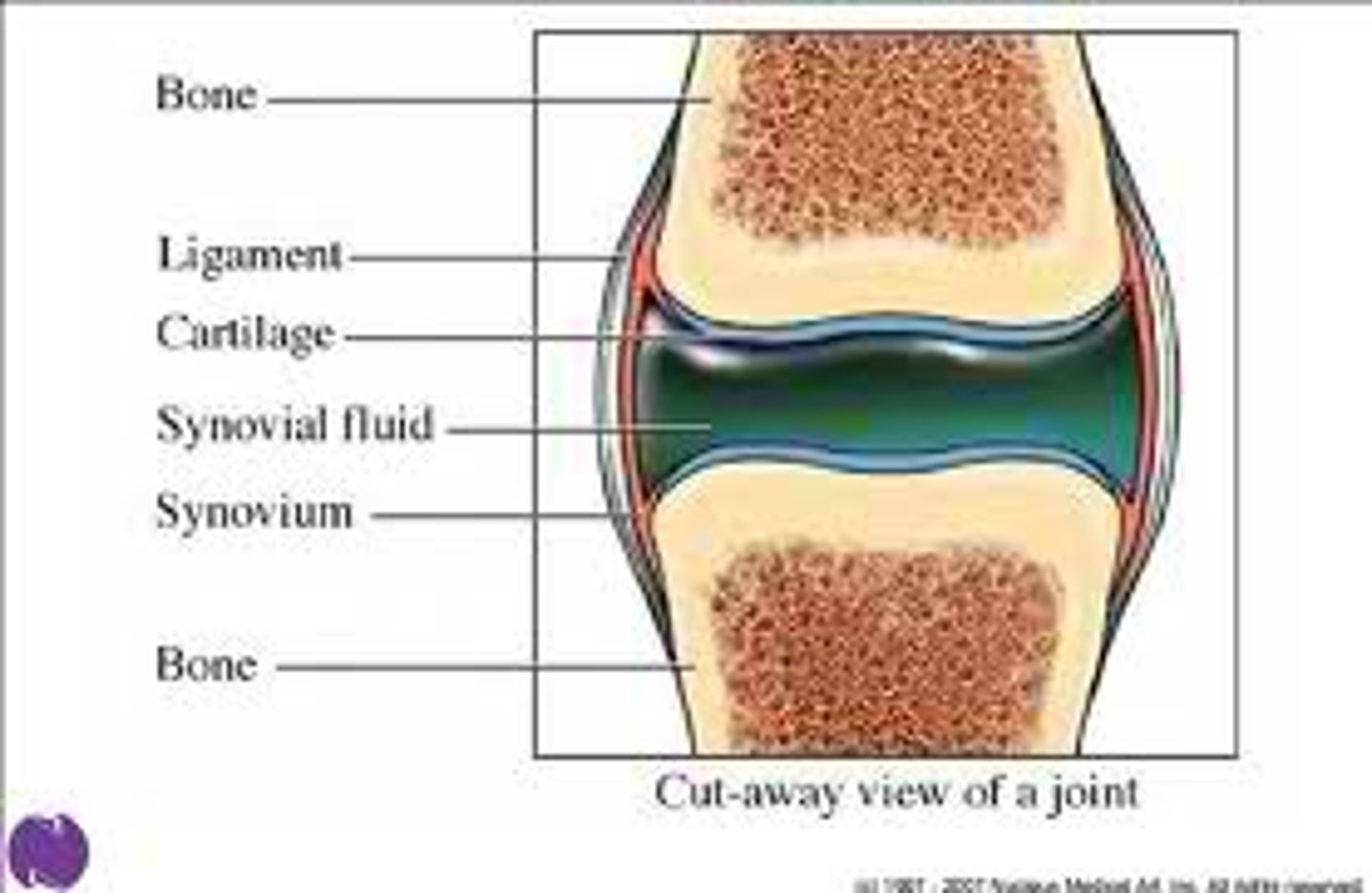
synovial joint: articular cartilage
hyaline cartilage
covers the articulating surfaces of bone
Helps reduce friction
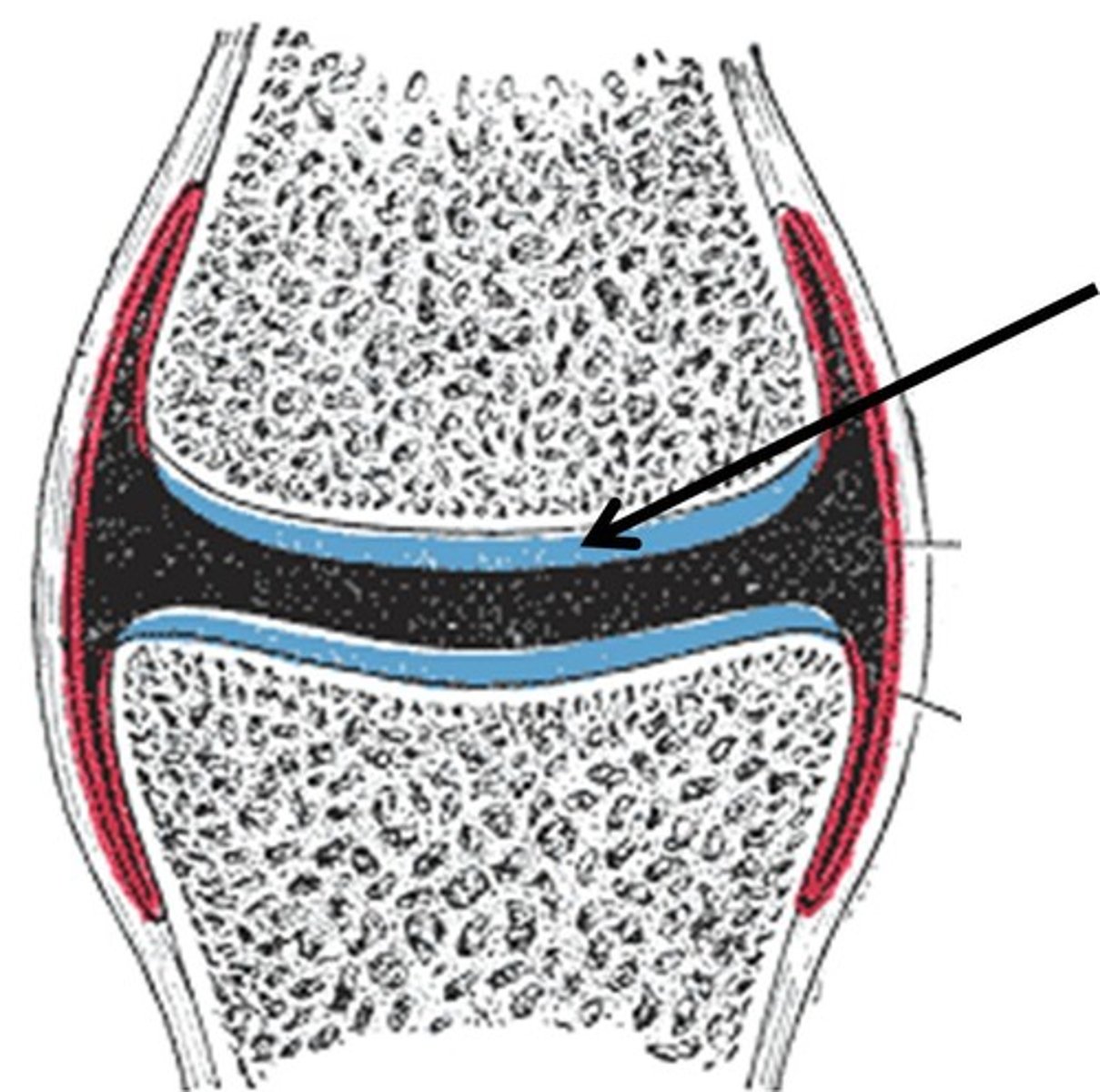
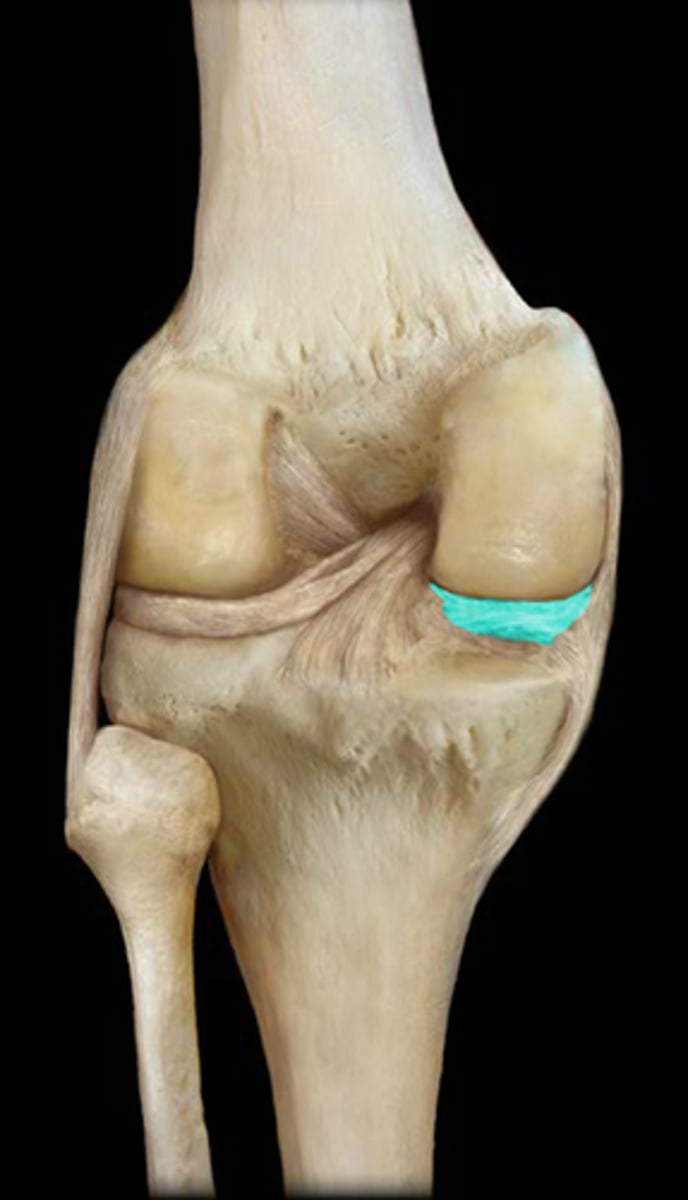
synovial joint: menisci
fibrocartilaginous pads in the knee
synovial joint: fat pads
adipose tissue superficial to joint capsule
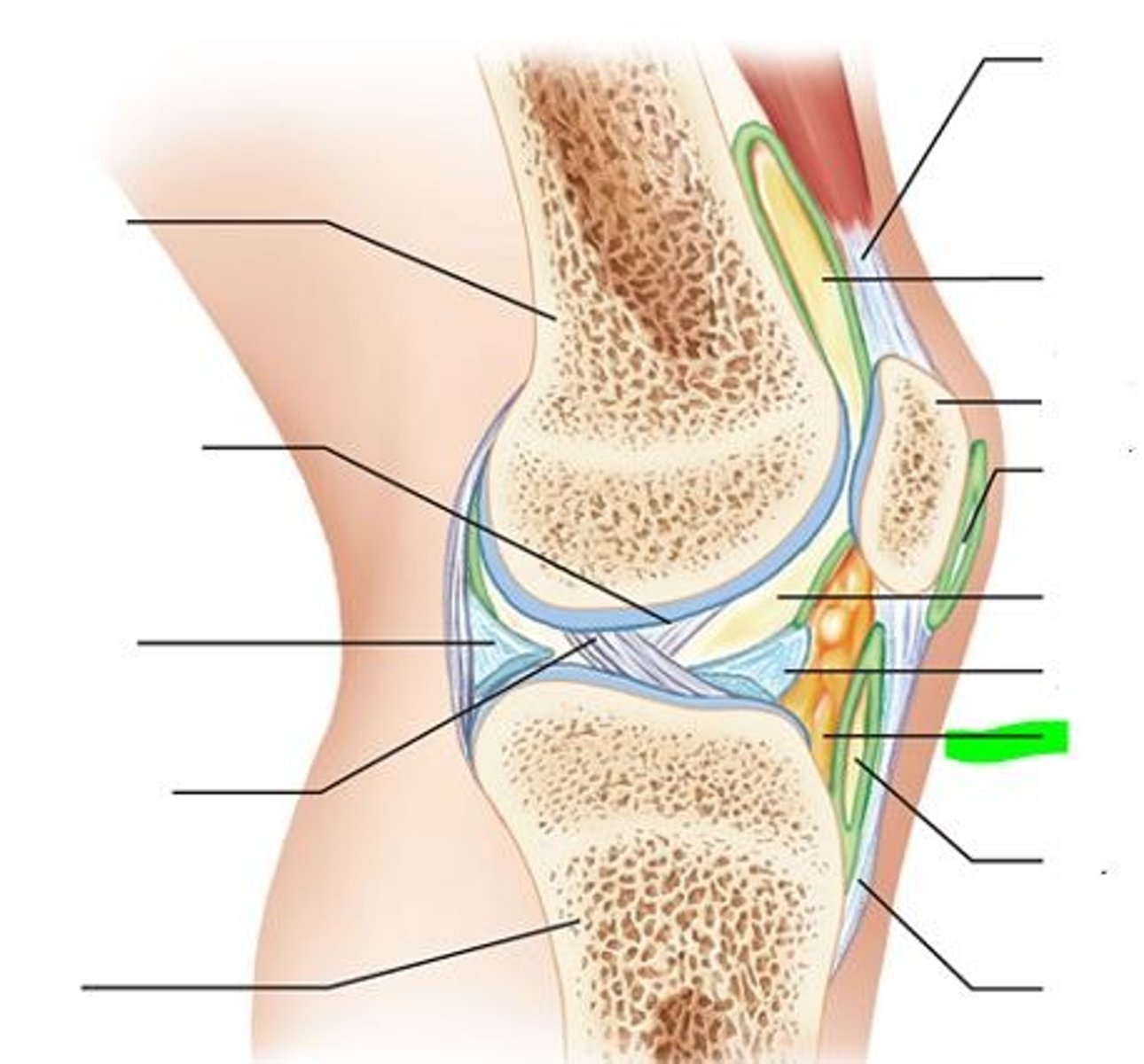
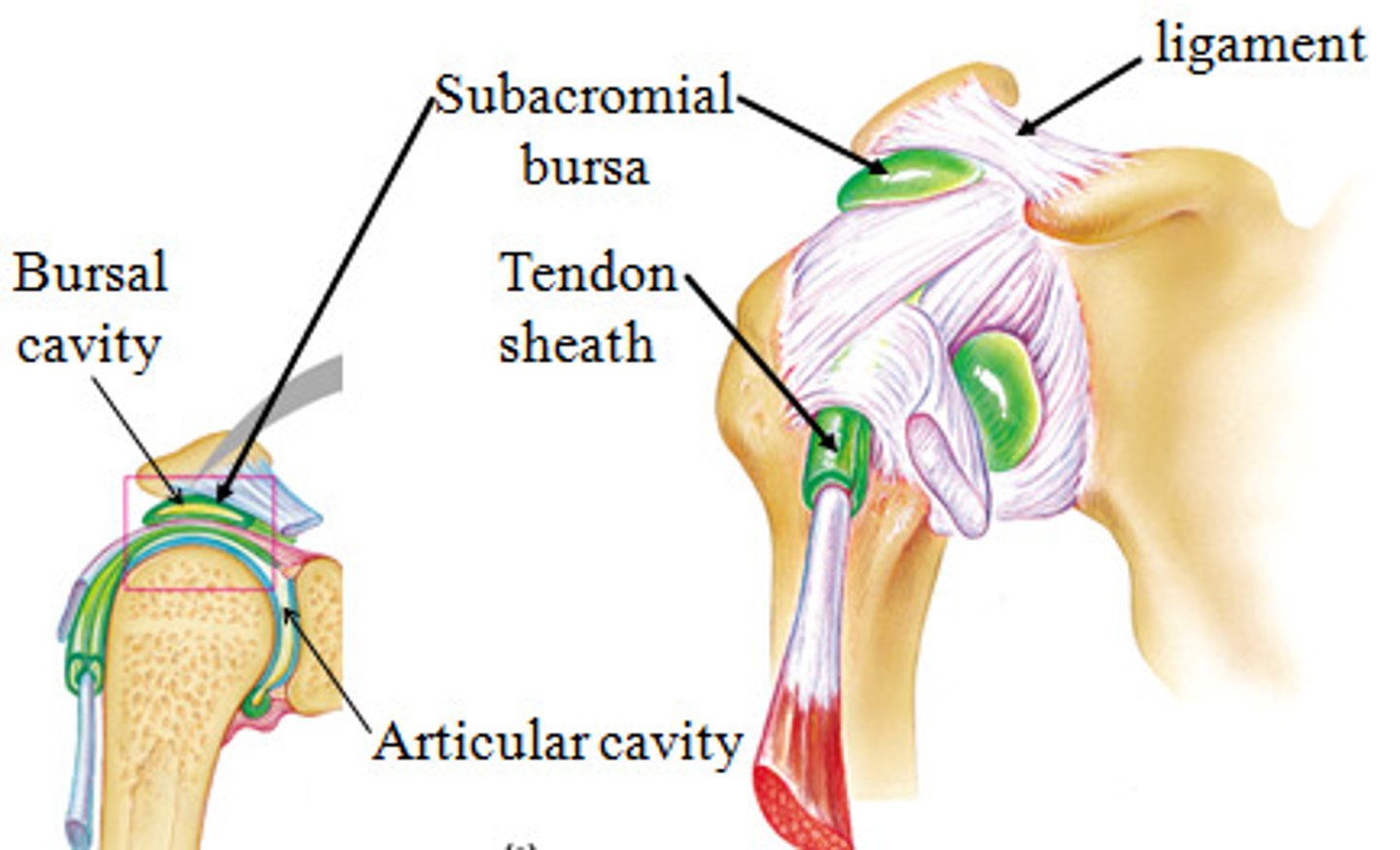
synovial joint: bursae
small fluid filled pouches by joints - helps to reduce
friction, and act as a shock absorber
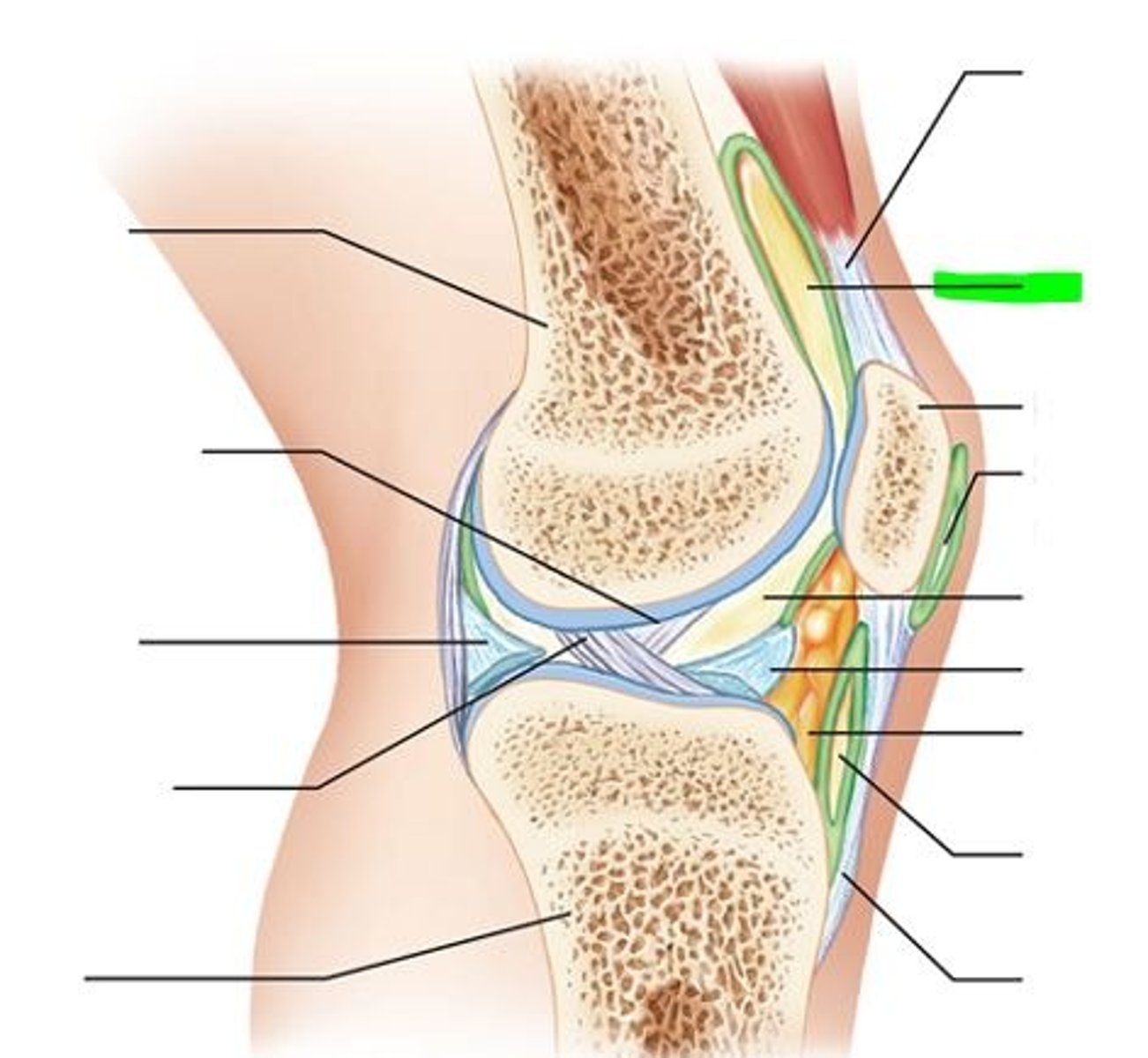
synovial joint: tendon sheath
elongated bursa that wraps around a tendon