Wing Design Layout
1/37
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
38 Terms
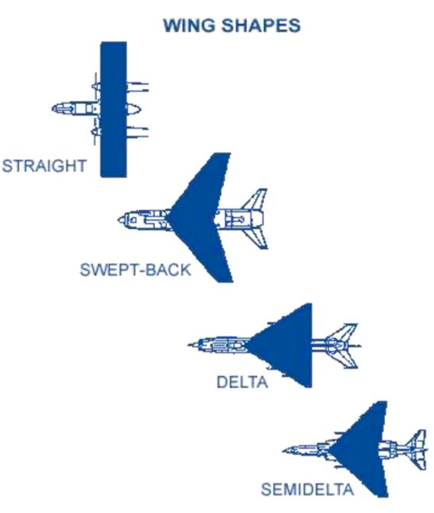
Enumerate the four common wing planform:
Type of wing position adapted by most cargo aircraft.
High Wing
Type of wing position which has the fuselage closer to the ground for easier loading and unloading.
High Wing

Type of wing position which makes sufficient ground clearance for engine nacelle or propeller.
High Wing

Type of wing position in which the wing tips will less likely strike the ground
High Wing

Type of wing position wherein the landing gear is installed to the fuelage so external blisters might be necessary and those adds weight and drag.
High Wing

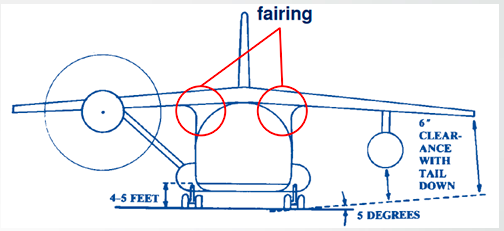
__ where wing connects to the circular fuselage to reduce interference drag.
Fairing
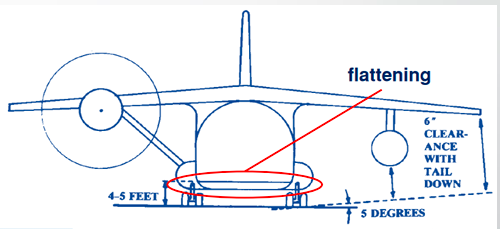
__ bottom will provide desired floor height but means more weight.
Flattened
Type of wing position with the least interference drag and has superior aerobatic maneuverability due to absence of dihedral which will act in the wrong direction in inverted flight. It also has ground clearance advantage of the high wing but the fuselage needs stiffening.
Mid Wing

Type of wing position that the landing gear can be installed to the wing so no stiffening required since the wings are already strong. It also allows for shorter landing gear strut which will lessen the weight.
Low Wing
In a low wing, given enough ground clearance, ___ can be reduced to decrease drag.
Aft Fuselage Upsweep

Type of wing position commonly adapted by large commercial transports which normally operate in well-equipped airfields.
Low Wing
In low wing configuration, ground clearance problems may be alleviated by ___, however too much can cause ___ tendencies.
Dihedral, Dutch Roll
Interference drag effect on high and low wing.
Low
Dihedral effect on high wing.
Negative
Dihedral effect on mid wing.
Neutral
Dihedral effect on low wing.
Positive
Loading and unloading for high and mid wing are ___ while, low wing need ___.
Easy, Stairs
Which is lighter, cantilevered or strutted?
Strutted wings

The vertical distance between the two wings.
Gap
The ratio between the shorter to the longer wing.
Span Ratio
The longitudinal offset of the two wings relative to each other. (Positive when upper wing is closer to the nose; negative, otherwise).
Stagger
Relative incidence between the two wings (positive, when upper wing has a larger incidence; negative, otherwise.)
Decalage
For a short field length and flight at high altitudes, a ___ wing is required.
Large
A low ___ translates to a high load factor and thus poor ride quality.
Wing Loading
High aspect ratio means reduced ___, and increased ___.
Induced Drag, (L/D)max
High aspect ratio means high ___, good ___, but bad ___ through turbulence.
Lift curve slope, approach attitude, ride
Higher thickness is equivalent to higher ___.
Profile drag
It delays drag divergence effects, used for balance and stability, better ride through turbulence.
Sweep Angle

Contributes to pitch up characteristics, performs less during takeoff and landing, reduces subsonic lift but all with a significant weight penalty.
Sweep Angle
A (large or small) loading and a (large or small) lift curve slope or wing sweep results in small changes in load factor, thus good ride through turbulence.
Large, small
(Forward sweep vs aft sweep) It is heavier and has superior stall characteristics and has outboard-mounted lateral controls to maintain effectiveness into a stall.
Forward sweep
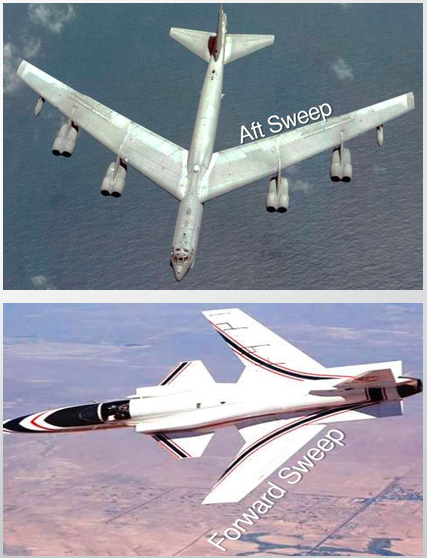

It is the solution to constant sweep and balance problems. However, it is more complex and have a weight penalty due to pivot mechanism.
Variable sweep


High taper ratio:
High
Good
Good
Greater cost
Lower taper ratio:
Opposite of everything else
Improved tip stall characteristics, cross sectional area distribution, and allows for smaller fuselage but has a weight penalty.
Reverse taper

Type of wing twist where one type of airfoil is used and its incidence is changing relative to root chord.
Geometric twist
Type of wing twist where the incidence is proportional to distrance from root airfoil.
Linear twist
Type of wing twist where the difference in the zero lift angles of the root and tip airfoil. It is the same as geometric twist if one type of airoil is used.
Aerodynamic twist
It is possible to have aerodynamic twist without geometric twist. This is by using differenet airoils.