Chemistry 1100 Keller Mizzou Exam 2
1/83
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
84 Terms
where is carbon found on our planet
reservoirs
- the atmosphere
- carbonate-containing rocks
- plants and animals (carbohydrates, proteins, lipids)
how does carbon "move"
carbon moves from reservoir to reservoir
- combustion
- photosynthesis
- sedimentation
why does where carbon ends up matter
today's carbon goes back into the atmosphere by burning fossil fuels matters because of future climate change
atomic mass
mass in grams of the same number of atoms that are found in a gram of atoms
avogadro's number
number of particles per mol substance
6.02x10^23
mol
containing avogadros number of objects
- 6.02x10^23
mole ratio
A mole ratio is the ratio between the amounts in moles of any two compounds involved in a chemical reaction
- can be determined by examining the coefficients in front of formulas in a balanced chemical equation
molar mass
mass of avogadro's number, or one mol, of whatever particles specified
global atmospheric lifetime
characterizes the time required for a gas added to the atmosphere to be removed aka "turnover time"
global warming potential (GWP)
a number that represents the relative contribution of a molecule of the atmospheric gas to global warming
anaerobic bacteria
bacterias that can function without the use of molecular oxygen
- many types produce methane, which then escapes into the atmosphere
sources of methane
- anaerobic bacteria
- termites
- agriculture
- landfills
- extraction of fossil fuels
sources of nitrus oxide "laughing gas"
- removal of nitrate ion (NO^3) from soils followed by the removal of oxygen
- automobile catalytic converters
- ammonia fertilizers
- biomass burning
- nitric acid and nylon production
radiative forcings
the factors (both natural and anthropogenic) that influence that the balance of Earth's incoming and outgoing radiation
albedo
the ratio of electromagnetic radiation reflected from a surface relative to the amount of radiation incident on it (measure of the reflectivity of a surface )
aerosols
a complex class of materials, that have a correspondingly complex effect on climate
- sources: dust storms, ocean spray, forest fires, volcanic eruptions, smoke, soot, sulfate aerosols from coal combustion
carbon footprint
an estimate of the amount of CO2 and other greenhouse gas emissions in a given time frame, usually a year
two things scientists need to consider when creating climate models
1) the rate of economic growth
2) the rate of development of "green" (less carbon-intensive) energy sources
weather
includes the daily high and low temperatures, the drizzles and down-pours, the blizzards and heat waves, and the fall breezes and hot summer winds, all of which have short durations
climate
regional temperatures, humidity, winds, rain, and snowfall over DECADES not DAYS
climate mitigation
is any action taken to permanently eliminate or reduce the long-term risk and hazards of climate change to human life, or the environment
carbon capture and storage (CCS)
involves separating CO2 from other combustion products and storing (sequestration) it in a variety of geological locations
climate adaptation
refers to the ability of a system to adjust to climate change (including climate variability and extremes) to moderate potential damage, to take advantage of opportunities, or to cope with the consequences
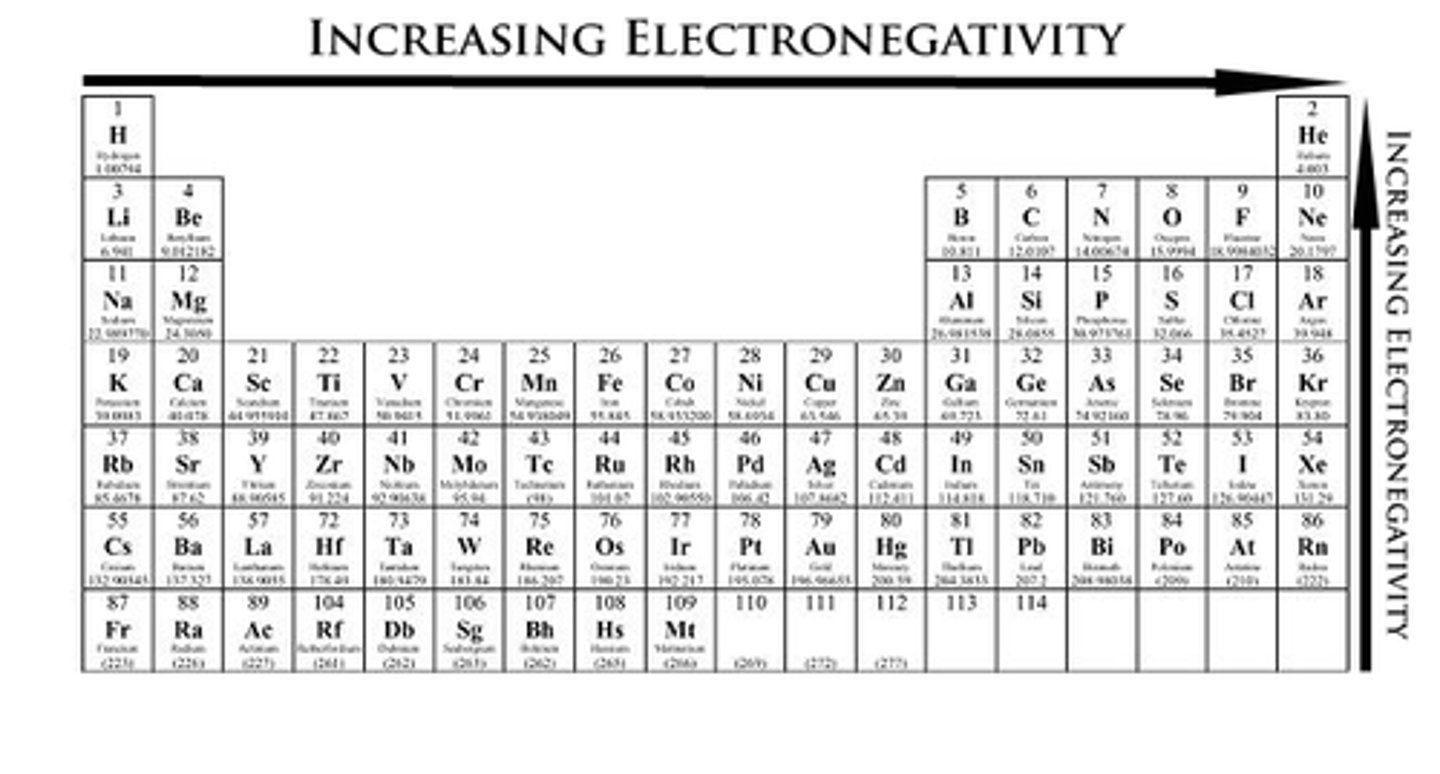
electronegativity
is a measure of the attraction of an atom for an electron in a chemical bond
- the greater the electronegativity the more an atom attracts the electrons a chemical bond toward itself
- the greater the difference in electronegativity between two bonded atoms, the more polar the bond is
polar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are not equally shared but rather are closer to the more electronegative atom
non polar covalent bond
a covalent bond in which the electrons are shared equally or nearly equally between atoms
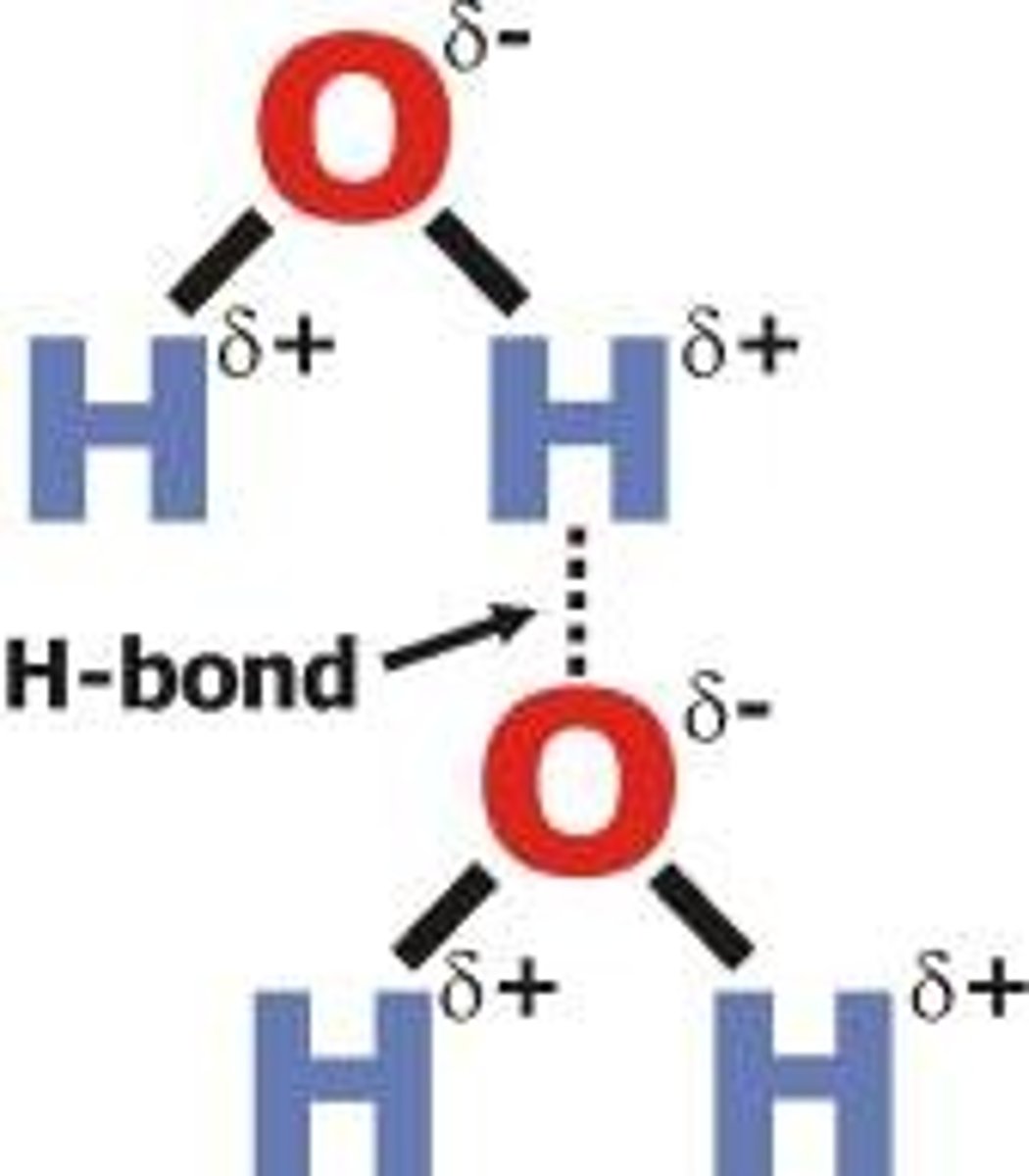
intermolecular force
a force that occurs between molecules
- example a H atom(+) on one of the water molecules is attracted to the O atom(-) on the neighboring molecule
hydrogen bond
is an electrostatic attraction between a H atom bonded to a highly electronegative atom (O, N, or F) and a neighboring O, N, or F atom, either in another molecule or in a different part of the same molecule
density
the mass per unit volume, of liquid water is greater than that of ice
specific heat
quantity of heat energy that must be absorbed to increase the temperature of 1 gram of a substance by 1 Celsius
potable water
water safe for drinking and cooking
surface water
the fresh water found in lakes, rivers, and streams
groundwater
fresh water found in underground reservoirs also known as aquifers
water footprints
estimates of the volume of fresh water used to produce particular goods or to provide services
solvent
a substance often a liquid capable of dissolving one or more pure substances
solute
the solid, liquid, or gas that dissolves in a solvent
solution
a homogeneous (of uniform consumption) mixture of a solvent and one or more solutes
aqueous solutions
solutions in which water is the solvent
concentration
the ratio of the amount of solute to the amount of solution is the same in each case
percent(%)
means parts per hundred
ppm
parts per million
ppb
parts per billion
volumetric flask
a type of glassware that contains a precise amount of solution when filled to the mark on its neck
non electrolyte
a solute that is nonconducting in an aqueous solution
electrolyte
a solute that conducts electricity in an aqueous solution
cation
a positively charged ion
anion
a negatively charged ion
ionic bond
the chemical bond formed when oppositely charged ions attract
ionic compound
composed of ions that are present in fixed proportions and arranged in a regular, geometric structure
polyatomic ion
two or more atoms covalently bonded together that have an overall positive or negative charge
general solubility rule
like dissolves like
surfactants
compounds that help polar and non polar compounds mix, sometimes called "wetting agents"
biomagnification
the increase in concentration of certain persistent chemicals in successively higher levels of a food chain
maximum contaminant level goal (MCLG)
the maximum level of a containment in drinking water which no known or anticipated adverse effect on human health would occur
maximum contaminant level (MCL)
the legal limit for concentration of a contaminant expressed inputs per million or parts per billion
residual chlorine
reers to chlorine containing chemicals that remain in the water after the chlorination step
trihalomethanes (THMs)
compounds such as chloroform, bromoform, bromodichloromethane, and dibromochloromethane that form from the reaction of chlorine or bromine with organic matter in drinking water
biological oxygen demand (BOD)
a measure of the amount of dissolved oxygen that microorganisms use up as they decompose organic wastes found in water
- a low BOD is one indicator of good water quality
desalination
any process that removes sodium chloride and other minerals from salt water thus producing potable water
distillation
a separation process in which a liquid solution is heated and the vapors are condensed and collected
osmosis
the passage of water through a semipermeable membrane from a solution that is less concentrated to a solution that is more concentrated
reverse osmosis
uses pressure to force the movement of water through a semipermeable membrane from a solution that is more concentrated to a solution that is less concentrated
true or false: global warming is the same everywhere
false: global warming is different everywhere
Ionian philosopher Theles
thought everything was made out of water
- required for all life
- could observe water in all 3 phases
property of water (1/3)
property: high boiling point (100C) and high freezing point (0C)
comparisons: higher than any other substance of similar molecular weight
importance: can observe all 3 phases
property of water (2/3)
property: "high" heat of vaporization (liquid to gas)
comparisons: higher than any other molecular substance
importance: condensation releases a lot of heat
property of water (3/3)
property: high heat capacity
comparisons: 2nd highest known heat capacity
importance: regulates body temperature and coastal temperatures
what makes water polar
it has a bent shape
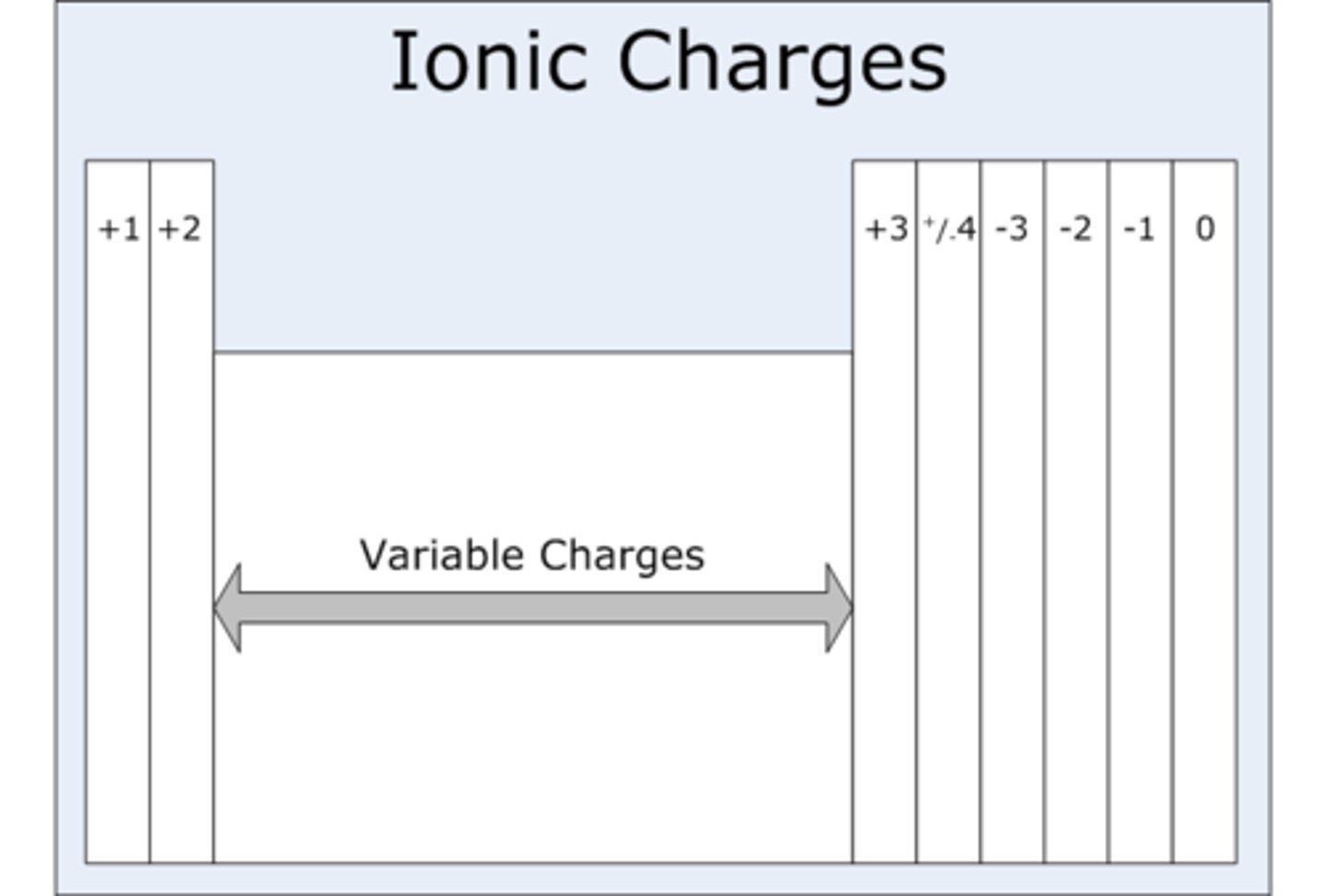
ionic charges
atoms can give up outer electrons only
- losing an electron gives an ion a positive charge
- gaining electrons gives an ion a negative charge
molarity
the number of moles of solute (the material dissolved) per liter of solution
- used to express the concentration of a solution
why is water a good solvent (3 step process)
1. break up the solvent (partially)
- need space to insert solute particles
- have to break hydrogen bonds (costs energy)
2. break up the solute
- ions are separated
- break apart anions(-) and cations(+) (costs energy)
3. combine them together
- putting solute into solvent (gives energy back)
true or false: forming H bonds between solute and solvent releases energy
true
why don't water and oil mix
hydrocarbon (C8H18) is non-polar because its electronegativity is about the same so nothing (no partial charges) on C8H18 to attract H2O
soap (polar or non-polar)
both polar and non-polar
- the non-polar part dissolves the non-polar grease
- the polar head forms a cap around the grease glob
- the grease glob is then removed into the water
water purification: what do we need to look for and control
viruses, bacteria, metals, particulate mater, chemicals, fluorine, etc.
who controls water regulations and what are the laws they have created
EPA
- Clean Water Act (1970)
- Safe Drinking Water (1974)
how does the EPA decide what to regulate and how much to regulate
- MCLG (goal)
- MCL (legal limit)
- all in ppm or ppb
how do we make sure water is pure
find a pure source so that less treatment would be required
aquifer
an underground geological formation of porous rocks
chlorine
a little bit stays in the water after leaving the water purification plant
chloramine
still disinfects water but doesn't produce any THM's like chlorine does
ozone as a method of disinfecting
advantage: reacts quickly with microorganisms
disadvantage: costs a lot, doesn't protect the water once it leaves the plant
UV light as a method of disinfecting
advantage: high energy light, very fast, no residue
disadvantage: high cost
ultrasound as a method of disinfecting
advantage: none
disadvantage: high cost