The Upper Respiratory Passageways - Nose, Nasal Vestibule and Nasal Cavity (Dog)
1/59
Earn XP
Description and Tags
M.9,W.1,L.1
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
60 Terms
what does the repiratory system consist of?
ancillary organs
the lungs
the diaphragm
plus muscles of the thoracic body wall
what are ancillary organs?
passageways leading to and from the lungs
list the ancillary organs
nose
nasal vestibule
nasal cavity
nasopharynx
larynx
trachea
what is within the lungs and where to they lead to?
passageways within each lung leading to exchange tissue
what is the main muscle of respiration?
diaphragm
what does the diaphragm form?
partition between thorax and abdominal cavities
Identify structures A-H.
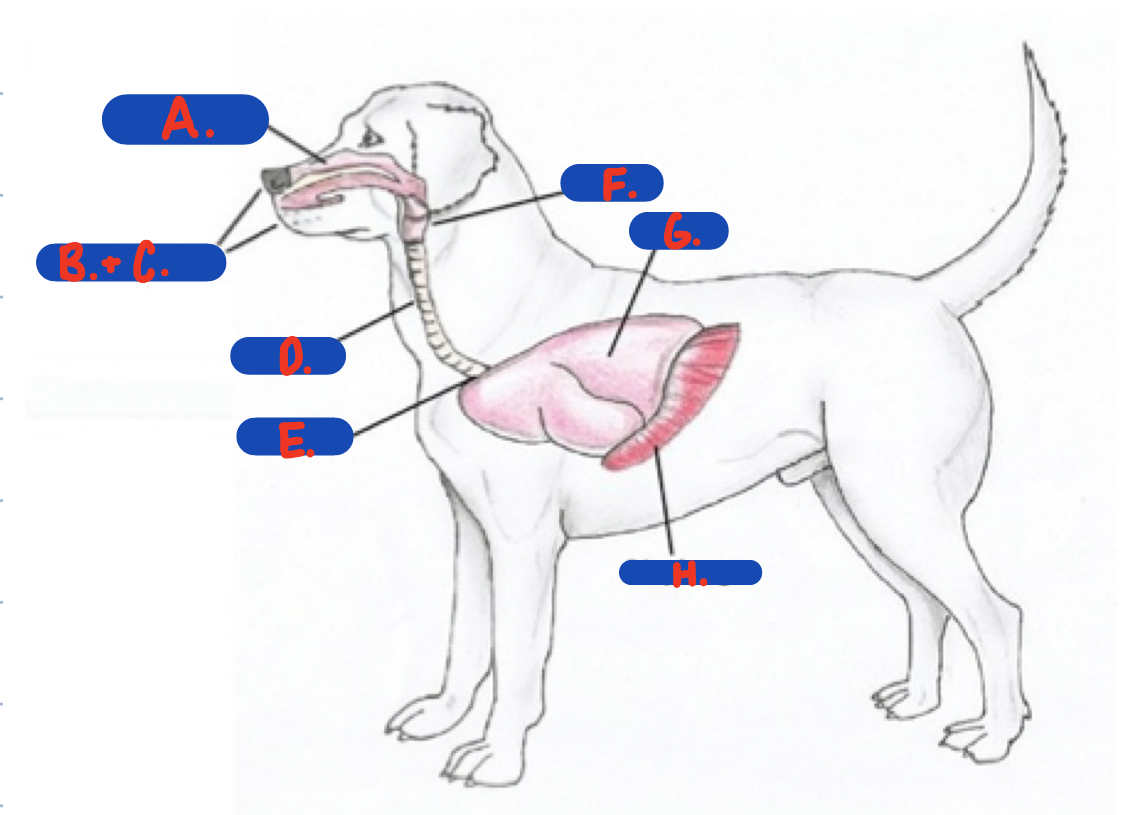
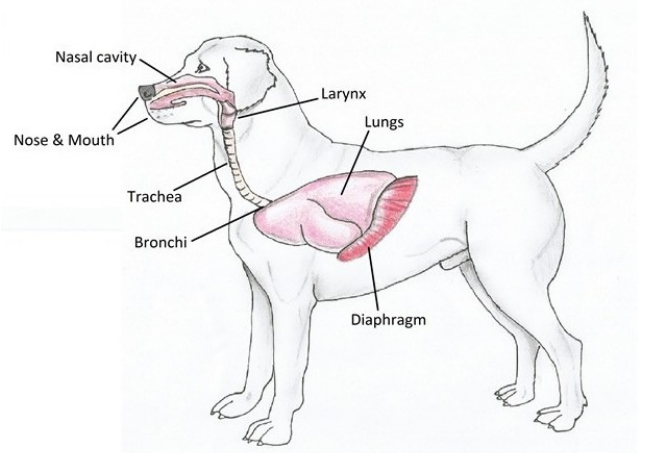
what are general functions of the respiratory system?
gaseous exchange
vocalization/phonation
olfaction
contributes to temp regulation and acid-base balance
what is the general function of ancillary organs in terms if gaseous exchange?
volume regulation and air conditioning
what is the general function of lung alveoli in terms of gaseous exchange?
blood gas barrier
Identify structures A-M.
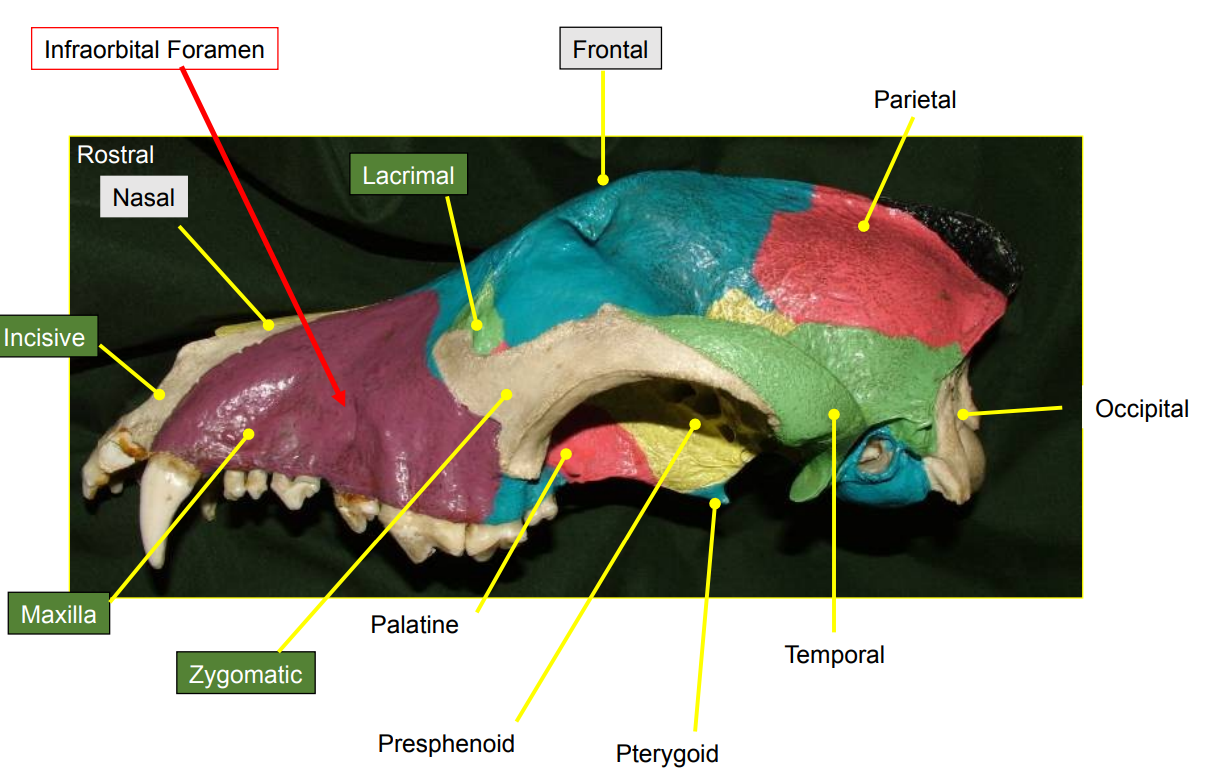
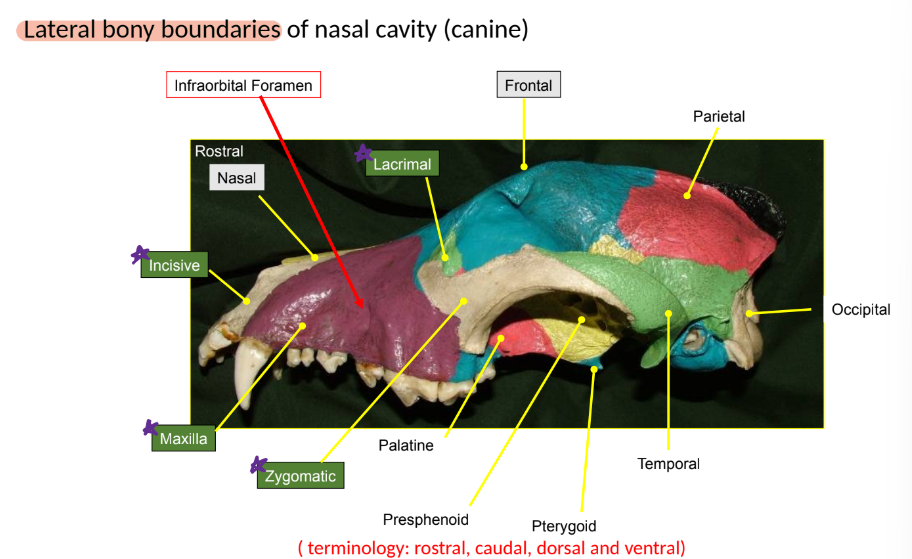
what are the lateral bony boundaries of the nasal cavity?
lacrimal
incisive
maxilla
zygomatic
what are the dorsal bony boundaries of the nasal cavity?
frontal
nasal
what are the rostral bony boundaries of the nasal cavity?
nasal
incisive
what is the caudal bony boundaries of the nasal cavity?
Cribriform plate of ethmoidal bone
what is the ventral bony boundary of the nasal cavity?
hard palate
what are nostrils?
external nares
what are nostrils divided by?
Philtrum
describe the skin of a nose
glandular, thick, hairless, pigmented and grooved
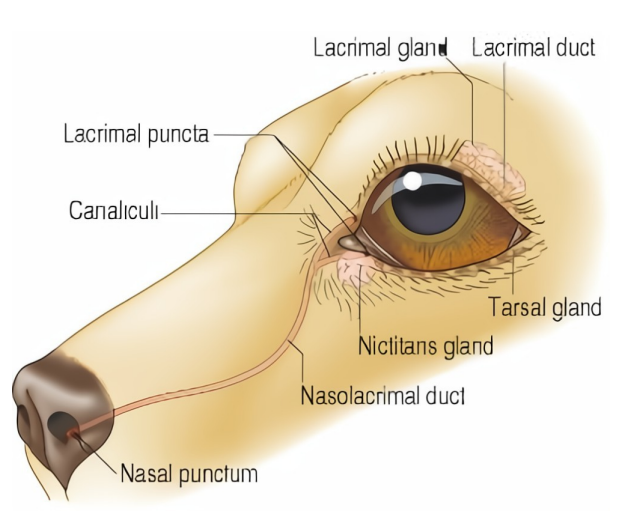
where do the secretions that moisten the nose come from?
lacrimal glands (via nasolacrimal duct)
lateral nasal glands (canine)
what provides blood supply to the nose/nasal plate area?
Sphenopalatine artery (br. maxillary artery)
Identify structures A-H.
what are facial expression muscles responsible for?
movement of muzzle region including nose
list the muscles involved in facial expression
a. Superficial M. - Levator nasolabialis
b. Deep M. - Levator labii maxillaris
c. M. - Caninus
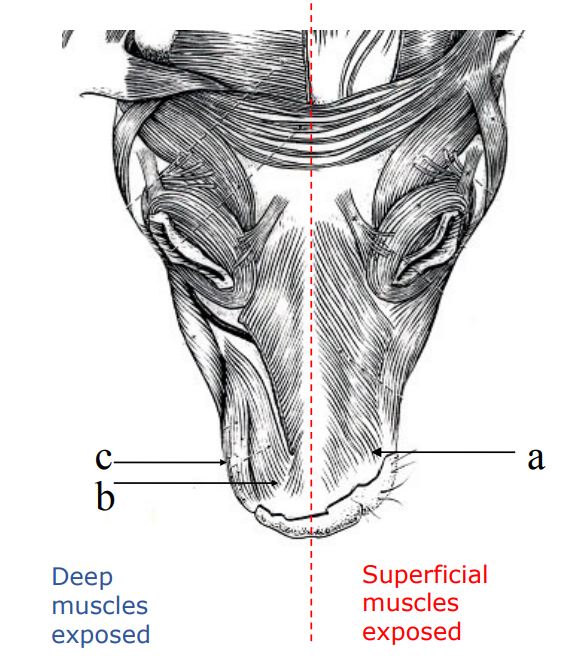
what is the motor supply for facial expression?
Facial Nerve (VII)
what is the sensory innervation of the nose?
infra-orbital nerve (br. Trigeminal (V))
what structure do the nostrils lead to?
nasal vestibule
what does the nasal vestibule extend beyond?
extends beyond the bony skull
what does the nasal septum divide?
divides the vestibule into two separate passageways that lead into nasal cavity which is also divided into right and left sides
describe the makeup of the nasal septum rostrally vs caudally
cartilage - rostrally
becomes bony at caudal attachment (ethmoid bone)
what supports the nasal septum ventrally?
the Vomer
what does the Vomer extend beyond and what does it attach to?
continues beyond caudal extent of hard palate
attaches to base of cranium
list the features of the nasal vestibule
3 mucosal folds in each vestibule
Nasolacrimal (NL) duct
Lateral nasal gland ducts
list the three mucosal folds found in each nasal vestibule and which is the largest?
Alar fold (largest)
Dorsal fold
Basal fold
what are dorsal and ventral conchae?
fragile, scrolled bony networks covered in very vascular mucosa
what is the function of dorsal and ventral conchae?
‘air conditioning’ (direct, slow, clean, warm & moisten)
what kind of epithelium does ethmoidal conchae have?
olfactory epithelium
what is the function of ethmoidal conchae and middle concha?
smell
after air enters the nasal cavity, what structure is it directed through?
Conchal labyrinth via a series of passageways called MEATUSES
what do the nasal cavities directly link with?
paranasal sinuses
what are paranasal sinuses?
air-filled spaces within skull bones that border each nasal cavity
what do the paranasal sinuses communicate with?
the nasal cavity
what kind of epithelium are the the paranasal sinuses lined with?
respiratory epithelium
list the functions of the paranasal sinuses?
lighten the head
protect the cranium
increase surface area for muscle attachment
contribute to resonance
how many compartments is the frontal sinus?
several compartments
why are the frontal sinuses clinically relevant in canines?
Infection (ex: Aspergillosis)
Is the maxillary recess (in carnivores) a true sinus?
NOT A TRUE SINUS
list two other features of the nasal cavities
Vomeronasal organ (VNO)
Incisive ducts
describe the VNO (what it is, location, mucosa, function)
tubular structure
lined with specialized olfactory mucosa
detects pheromones
located in ventral nasal meatus on either side of nasal septum
describe the incisive ducts (what they connect and function)
connect oral cavity (via incisive papilla) to vomeronasal organ
may allow tiny amounts of oral fluid to reach VNO (so it can chemically “evaluate” those substances)
list the boundaries of the Nasopharynx
Internal Nares (choana) - rostral
Soft Palate - ventral
Base of Cranium - dorsal
Palatopharyngeal arch - caudal
list the two features of the Nasopharynx
Openings of the Auditory tubes
The Pharyngeal tonsil
what does the opening of the auditory tube lead to?
tympanic bulla / middle ear
describe the auditory tubes (lined by and function)
lined by respiratory epithelium
equalization of pressure
what is the pharyngeal tonsil apart of?
part of retro-pharyngeal lymph center
Purpose of retro-pharyngeal lymph center?
immuno-surveillance (lymphatic tissue)
what is the role of the common pharynx / laryngopharynx?
passage for both breathing and swallowing
what forms the wall of the pharynx and what do they do?
pharyngeal muscles; constrict, dilate and shorten
what is the larynx supported by and which direction does it move during swallowing?
hyoid apparatus
moves rostrally
what is the Aditus?
entrance to larynx
laryngeal inlet
entrance point in which air will pass to the trachea