Ch 12-Limbic System + Language Disorders (Ch14)
1/79
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
80 Terms
Limbic System major functions:
emotions
memories
(mostly declarative memory formation, memory consolidation, emotion memory, conditioning)
arousal
behaviors we need for survival; feeding, reproduction and caring for our young, and fight or flight responses
Limbic system “surrounds”:
basal ganglia & thalamus
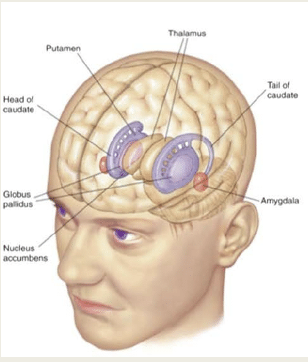
BG & Thalamus
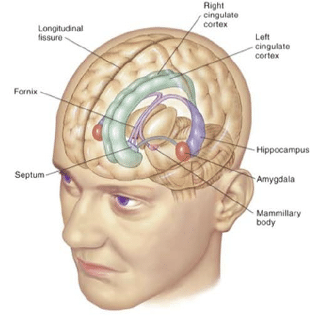
limbic system
Superior to corpus callosum
cingulate cortex
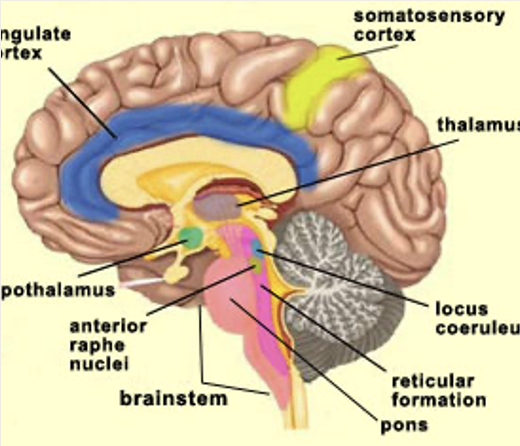
Cingulate Cortex
essential to emotional processing, learning, and memory
four parts of cingulate cortex
anterior cingulate cortex
midcingulate cortex
posterior cingulate cortex
retrosplenial cortex
part of temporal lobe
entorhinal cortex
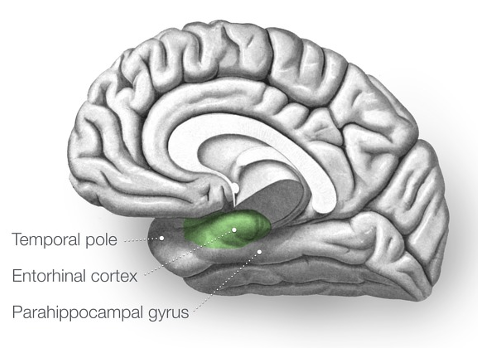
entorhinal cortex
essential for memory and spatial navigation
works with hippocampal and parahippocampal cortices; pathway for sensory information to travel from the cortex to the hippocampus
entorhinal cortex
Implicated in Alzheimer’s Disease
entorhinal cortex
located mostly in temporal lobe
hippocampus

looks like a seahorse
hippocampus
hippocampus afferent & efferent areas
afferents from cortex, olfactory areas, seuptum, hypothalamus
efferents to amygdala, septum, hypothalamus, thalamus
hippocampus function
memory, learning, spacial navigation, emotional processing
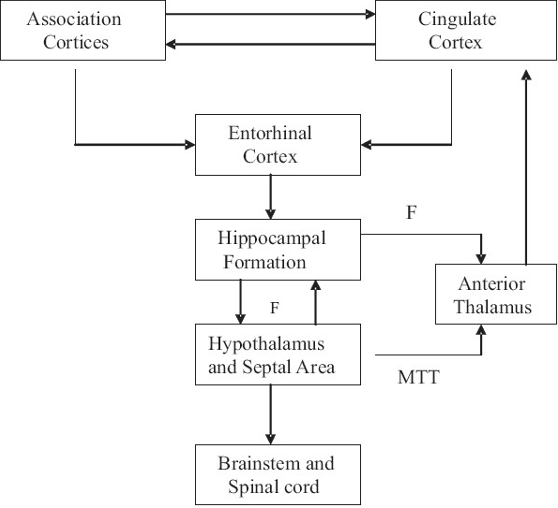
hippocampal connectivity
parahippocampal gyrus
grey matter region of the brain that surrounds the hippocampus
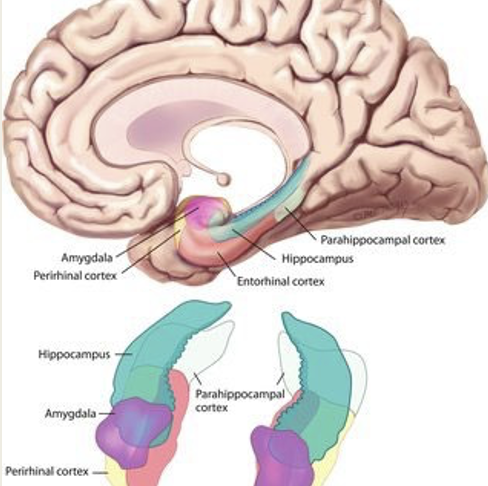
contains the entorhinal cortex, which provides most of the input to the hippocampus
parahippocampal gyrus
Damage to bilateral hippocampal areas cause severe ______ problems
memory
clinical issues in hippocampus:
alzheimer’s disease
frontotemporal lobar disease
related to recent memory and explicit memory
episodic memory
memory consolidation (encoding)
clinical issues to hippocampus
related to incoming words to stored semantic knowledge
hippocampus & language
hippocampal declarative memory system is long known to support ___________________.
relational binding and representational flexibility
recent findings demonstrate that these same functions are engaged during the real-time processes that support _______________.
behavior in-the-moment
hippocampus as a potentially key contributor to cognitive functions that require on-line integration of multiple sources of information, such as _______________________.
on-line language processing
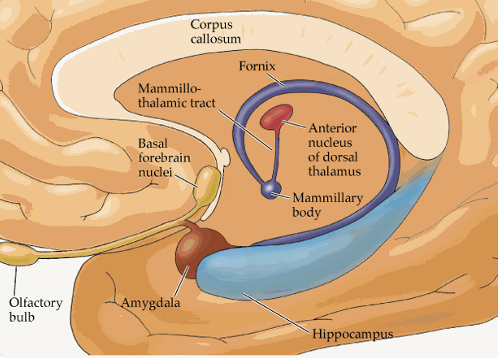
c-shaped fiber tract from hippocampus
myelinated afferent & efferent fibers
splits from hippocampus
continues to anterior commissure
fornix
fornix function
episodic memory
fornix clinical issues:
may relate to Alzheimer’s disease
hypothesized to degenerate and amount of degeneration may relate to severity of cognitive impairment

relates environmental stimuli to coordinated behavior for autonomic and endocrine responses
decision making
amygdala functions
amygdala responses include:
feeding
fighting
responses to stress
lesions=motivation problems
apathy
flat affect
inappropriate sexual behaviors and mouthing of objects
loss of normal fear and anger responses
clinical issues in amygdala
difficulty with discrimination of emotional faces
Kulver-Bucy syndrome
flat affect in amygdala

hypothalamus
central controller of homeostasis
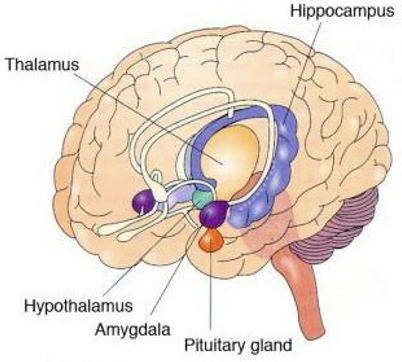
involved in autonomic control of endocrine system
involved in emotions & motivated behavior
hypothalamus
HPA axis
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis (what it is)
major neuroendocrine system (cortisol)
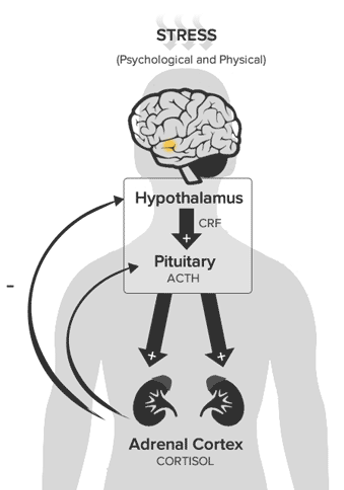
Hypothalamic-Pituitary-Adrenal Axis (what it does)
controls reactions to stress & regulates many body processes, including”
digestion
immune system
mood and emotions
sexuality
energy storage and expenditure
clinical issues in HPA axis:
depends on area disturbed (e.g., lateral portion)
reward & motivation
addiction
stress responses
anxiety disorders
feeding, reward
obesity
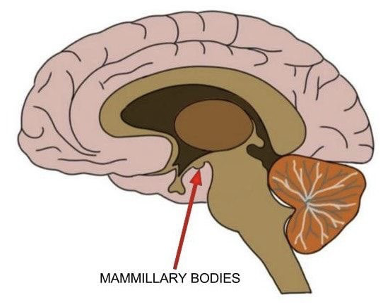
composed of medial and lateral nuclei
located at the ends of the anterior arches of the fornix
cells in mammillary bodies are projection neurons
mammillary bodies
mammillary bodies
thought to encode spatial memory through connections with anterior thalamus
clinical issues in mammillary bodies
amnesia
Wernicke-Korsakoff’s sydrome
mammillary body atrophy is observed; a disorder characterized by amnesia and usually linked to a thiamine deficiency
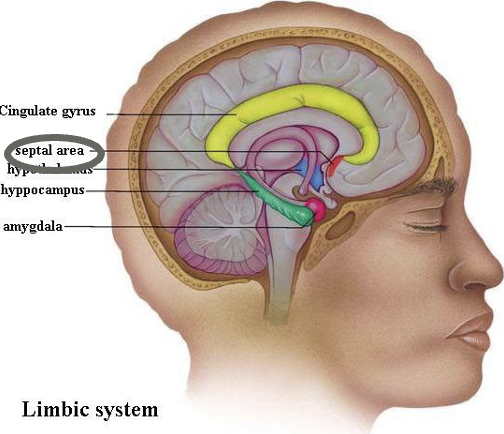
septal cortex
pleasure center
defensive reactions
inhibition of heart rate
limbic blood supply
originates from several sources
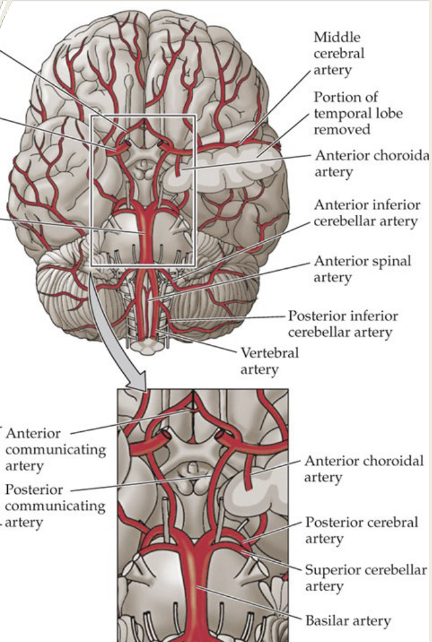
main vessels that serve much of the limbic system:
anterior cerebral artery (internal carotid)
posterior cerebral artery (basilar artery)
anterior choroidal artery (internal carotid)
branches arising from the circle of willis
amygdala, in conjunction with prefrontal cortex and medial temporal lobe, is involved in consolidation and retrieval of emotional memories. Amygdala, prefrontal cortex and hippocampus are also involved in the acquisition, extinction and recovery of fears to cues and contexts.
emotional memory
The components include the hippocampus and adjacent cortex, the parahippocampal regions (PHG), the entorhinal and perirhinal regions
Involved in the creation & storage of new memories (consolidation)
Memory is spatial and declarative
medial temporal lobe memory system
The diencephalic memory circuit consists of the hypothalamus, mammillary body and the dorsomedial nucleus of thalamus.
Important for the storage of recent memory
Dysfunction of this circuit results in Korsakoff's syndrome
diencephalic memory system
autonomic functions regulating heart rate and blood pressure as well as cognitive, attentional and emotional processing
cingulate gyrus
spacial memory
parahippocampal gyrus
long-term memory
hippocampus
anxiety, aggression, fear conditioning; emotional memory and social cognition
amygdala
regulates the autonomic nervous system via hormone production and release. Secondarily affects and regulates blood pressure, heart rate, hunger, thirst, sexual arousal and the circadian rhythm sleep/wake cycle
hypothalamus
memory
mammillary body
reward, addiction
nucleus accumbens
appetite, temperature and sleep disorders
hypothalamus
affected in several neurologic disorders and psychiatric disorders including Alzheimer’s, temporal lobe epilepsy (TLE), anxiety, and depression
symptoms manifest as impaired or unusual emotional behaviors in response to sensory stimuli, events, and memories (e.g. no threat response)
amygdala
Highly vulnerable area, so damaged in a variety of disorders (e.g., Alzheimer’s, TBI, epilepsy, etc) → it is so vulnerable because it is so plastic
Issues in learning and memory (especially declarative memory – making new memories or losing old memories), can also manifest as issues in emotional response, spatial orientation,
hippocampus
damage to limbic lobe connections:
Psychiatric disorders: depression, schizophrenia, anxiety
Addiction
Issues in motivation and reward
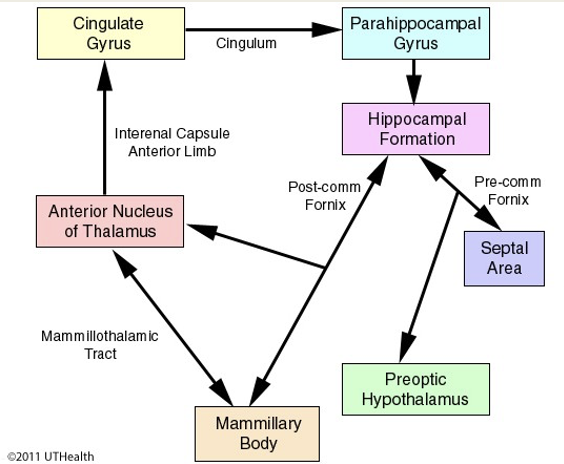
Major fiber tracts
Cingulum = projects from cingulate gyrus to entorhinal cortex
Mamillothalamic tract = fibers connect MB to cingulate through anterior thalamic nucleus
Fornix = connects hippocampus to septum, anterior thalamic nuclei, & mammillary body
neural tube →
prosencephalon
prosencephalon→
telencephalon & diencephalon
diencephalon→
thalamus, hypothalamus, retina
Diencephalon structures
thalamus
hypothalamus
optic tract
subthalamic nucleus
epithalamus
habenulus
pineal glad
stria medullaris
thalamus structure
bilateral structure
one in each hemisphere; separated by the third ventricle
connection between thalami is at thalamic adhesion
thalamus length
~3.5 cm long; size and shape of a walnut in its shell
thalamus is made up of groups of what?
subcortical nuclei (gray matter)
bidirectional pathways connect between many cortical and subcortical areas
involved in sensory, motor, limbic, reticular, conscious awareness, etc.
thalamus receives blood from where?
branches of the posterior cerebral artery
thalamus afferent pathway orientation
from contralateral side of body; sensory information cross over prior to thalamus
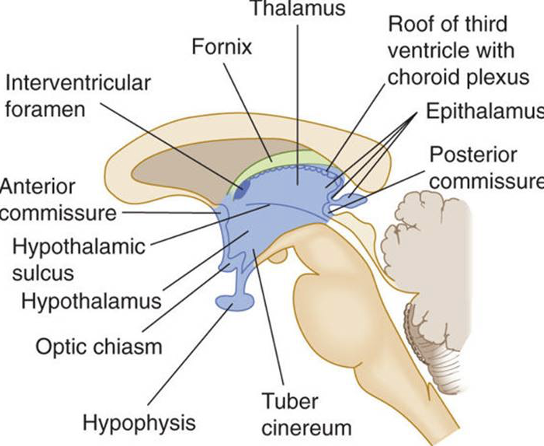
thalamus efferent pathway orientation
from ipsilateral side of brain; motor information cross over after to thalamus
most of the thalamic nuclei project to cerebral cortex
channels project sensation information (pain, taste, temperature, audition, and vision) to specific cortical areas
takes in sensorimotor and cognitive information & projects info to appropriate areas of cortex
behavior
memory
emotions
sleep-wake cycles
executive function
alertness
thalamus function
Mediodorsal TN primary functions
mood, emotion, cognition, personality
Mediodorsal TN connections
hippocampus, cortical association areas, prefrotal, oribitofrontal, limbic, hippocampus, hypothalamus