Equation recognition
1/94
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
95 Terms
True/False: Arbitrage is a very risky process of trading to take advantage of the same goods that have different prices in different competitive markets.
Robin is a private fisher. Each day he has a 1,000 kilos supply of fish. However, he does not like fish at all. The market price of fish is $30 per kilo. What is the value of 1,000 kilos supply of fish to Robin? 1. The value of fish to Robin is less than $30 per kilo because he does not like fish. 2. The value of fish to Robin is less than $30,000 per thousand kilos because fish is a perishable good. 3. The value of fish is more than $30 per kilo to Robin because he can wait for the market price to go up. 4. The value of fish to Robin is $30,000 per thousand kilos because it is the market price.
Robin’s friend Tom who runs a seafood business wants to offer shrimps in exchange for fish. He offers 400 kilos of shrimps in exchange for 1,000 kilos of fish. The market price of shrimp is $60 per kilo. Robin is so excited to hear this news because he likes shrimps so much. In the end, will Robin accept this offer? And why?
Ford Motor Company is considering installing new AI-assisted parking software on their SUVs and to make an emphasis on this feature in their marketing campaign. Incorporating this feature will reduce the profit margin from $12,000 to $10,000. At the same time, the marketing group estimates that it will increase the sales from 50,000 to 65,000 cars. If the change in sales is the only consequence of this decision, what are its benefits and costs? Is it a good idea?
Consider an investment project with an initial cost of $24 million and positive cash flow of $8 million at the end of year 1, $10 million at the end of year 2, and $15 million at the end of year 3. The discount rate for this kind of project is 12 percent.
a) How is the term Net Present Value (NPV) defined? Also, write it down in the form of a general equation. Calculate the NPV for this investment project.
Kevin Baker owns his own business and is considering an investment. If he undertakes the investment, it will pay $5,000 at the beginning of each of the next four years (t=1 to 4). The opportunity requires an initial investment of $7,000 plus an additional investment at the end of the third year of $13,000. What is the NPV of this opportunity if the interest rate is 4% per year? Should Kevin undertake it?
You are planning a trip around the world. You have calculated that to cover all expenses during the trip you will need €15,000, so you decide to put part of your salary, €2,000, to a savings account on a yearly basis. APR on this account is 6%. After how many years can you afford the trip? [Hint: remember your Mathematics course – you can take a natural logarithm of both sides if the unknown is in the exponent.]
You decide to refurbish your kitchen and buy a new kitchen set from IKEA for €6,700. IKEA offers you three payment schemes: 1. Pay €130 monthly for 5 years, or 2. Make 6 annual payments. The payment grows at 2% per year. The first payment is €1,270 and is due immediately, or 3. Pay €478.79 per year forever, the first payment starting exactly 4 years from now (so at the end of year 4).
Which payment scheme gives you the best deal if the discount rate is 6%?
When you purchased your house, you took out a 30-year annual-payment mortgage with an interest rate of 6% per year. The annual payment on the mortgage is $12,000. You have just made a payment and have now decided to pay the mortgage off by repaying the outstanding balance. What is the payoff amount if you have lived in the house for 12 years?
You borrow €3,565 from ING Bank. The interest rate on the loan is 7%, compounded daily. The EAR on the loan is closest to which of the following answers: a. 6.90%, b. 7.25%, c. 7.10%, d. 7.00%
Cambridge State Bank is paying 5% interest on its one-year certificate of deposit. If the inflation rate is 3%, which of the following is the best approximation for the real rate of interest that Cambridge State Bank is paying? a. 2.56%, b. 1.94%, c. 3%, d. 2%
Consider a zero-coupon government bond with a face value of €1,000 and with a remaining maturity of four years. Given the associated yield curve below, what is the current market value of this bond?
Imagine that instead you face a downward sloping yield curve. What are the expectations about the economy for the next few years? What is the intuition behind the curve shape?
The 5-year Treasury notes are issued at par with a coupon rate of 4.8%. The credit spread for 5-year maturity A-rated debt is 85 basis points. Your firm, with a credit ranking of A, issues 5-year debt with a coupon rate of 5% (with semi-annual payments). What does credit spread mean? What is the relation between its magnitude and the probability of default?
What is the price (expressed as percentage of the face value) of the bond? Does the bond trade at par, at a premium or at a discount?
Vertex Energy would like to raise $45,000,000 to finance a new production system. The company plans to issue five-year bonds with a face value of $1,000 and a coupon rate of 4.4% (with semi-annual payments). The following table summarizes the yield to maturity (YTM) for five-year coupon paying corporate bonds of various ratings… Assuming the bonds will be rated AA, what will be the price of bonds be?
Suppose JPMorgan issues a bond with ten years until maturity, a face value of $1,000, and a coupon rate of 4.05% (annual payment). JPMorgan’s bonds get a rating of A from Standard & Poor’s. The yield to maturity (YTM) on JPMorgan bonds is currently 4.20%. The YTM on 10-year US Treasury bonds is currently 3.12%. What is the price of the bond? Is this bond currently trading at a discount, at par, or at a premium? Explain.
Suppose JPMorgan issues a bond with ten years until maturity, a face value of $1,000, and a coupon rate of 4.05% (annual payment). The yield to maturity (YTM) on JPMorgan bonds is currently 4.20%. Assuming the yield to maturity remains constant, what is the (dirty) price of the bond immediately before it makes its first coupon payment?
Suppose JPMorgan issues a bond with ten years until maturity, a face value of $1,000, and a coupon rate of 4.05% (annual payment). The yield to maturity (YTM) on JPMorgan bonds is currently 4.20%. Assuming the yield to maturity remains constant, what is the price of the bond immediately after it makes its first coupon payment?
Suppose JPMorgan issues a bond with ten years until maturity, a face value of $1,000, and a coupon rate of 4.05% (annual payment). Because JPMorgan’s capacity to meet their financial commitment has improved, S&P is going to upgrade JPMorgan bonds to AA. Yields on 10-year AA bonds are currently 3.9%. Explain, without calculation, what will happen to the price of the bond if it is upgraded?
Suppose JPMorgan issues a bond with ten years until maturity, a face value of $1,000, and a coupon rate of 4.05% (annual payment). The YTM on 10-year US Treasury bonds is currently 3.12%. Yields on 10-year AA bonds are currently 3.9%. What is the default (or credit) spread of JPMorgan bonds if the bond is upgraded?
Assume it is the first of January 2023 and you just started working as a junior stock analyst specialized in the pharmaceutical industry. Your first assignment is to give a buy, hold, or sell recommendation for the stock of Laurel Inc. which currently sells for €12 at the NYSE-Euronext Exchange. Your boss provides you with the following tables and tells you that the P/E ratio of the pharmaceutical industry based on expected (=2023) earnings is 15. Assume that yesterday Laurel just paid out its dividend over 2022, that all cash flows (including earnings and dividends) occur at the end of each year, and that returns on new investments are identical to the ROE. | Data Sheet | | | Expected total earnings 2023 | €725,000,000 | Outstanding number of shares | 620,000,000 | Retention ratio | 40% | Return on book value of equity (ROE) | 10% | Required return of equity (Re; based on CAPM) | 12% | WACC | 9% | Total Cash holdings | €700,000,000 | Market value of debt | €8,000,000,000 |. Calculate a fair price for one share of Laurel stock for 2023 using the industry P/E multiple.
Assume it is the first of January 2023 and you just started working as a junior stock analyst specialized in the pharmaceutical industry. Your first assignment is to give a buy, hold, or sell recommendation for the stock of Laurel Inc. | Data Sheet | | | Expected total earnings 2023 | €725,000,000 | Outstanding number of shares | 620,000,000 | Retention ratio | 40% | Return on book value of equity (ROE) | 10% | Required return of equity (Re; based on CAPM) | 12% | WACC | 9% | Total Cash holdings | €700,000,000 | Market value of debt | €8,000,000,000 |. Calculate the expected dividend per share for 2017 for Laurel.
Assume it is the first of January 2023 and you just started working as a junior stock analyst specialized in the pharmaceutical industry. Your first assignment is to give a buy, hold, or sell recommendation for the stock of Laurel Inc. | Data Sheet | | | Expected total earnings 2023 | €725,000,000 | Outstanding number of shares | 620,000,000 | Retention ratio | 40% | Return on book value of equity (ROE) | 10% | Required return of equity (Re; based on CAPM) | 12% | WACC | 9% | Total Cash holdings | €700,000,000 | Market value of debt | €8,000,000,000 |. Calculate the dividend growth rate for Laurel.
Assume it is the first of January 2023 and you just started working as a junior stock analyst specialized in the pharmaceutical industry. Your first assignment is to give a buy, hold, or sell recommendation for the stock of Laurel Inc. | Data Sheet | | | Expected total earnings 2023 | €725,000,000 | Outstanding number of shares | 620,000,000 | Retention ratio | 40% | Return on book value of equity (ROE) | 10% | Required return of equity (Re; based on CAPM) | 12% | WACC | 9% | Total Cash holdings | €700,000,000 | Market value of debt | €8,000,000,000 |. Calculate a fair price for one share of Laurel stock using the Constant Dividend Growth Model (CDGM or DDM).
Assume it is the first of January 2023 and you just started working as a junior stock analyst specialized in the pharmaceutical industry. Your first assignment is to give a buy, hold, or sell recommendation for the stock of Laurel Inc. | Data Sheet | | | Expected total earnings 2023 | €725,000,000 | Outstanding number of shares | 620,000,000 | Retention ratio | 40% | Return on book value of equity (ROE) | 10% | Required return of equity (Re; based on CAPM) | 12% | WACC | 9% | Total Cash holdings | €700,000,000 | Market value of debt | €8,000,000,000 |. Using the above CDGM (or DDM), would you advise Laurel to change its pay-out ratio? Illustrate your answer with a clear example showing the eventual effect of a pay-out policy change (assume an increase from 60% to 80% pay-out) on the share price.
Assume it is the first of January 2023 and you just started working as a junior stock analyst specialized in the pharmaceutical industry. Your first assignment is to give a buy, hold, or sell recommendation for the stock of Laurel Inc. | Data Sheet | | | Expected total earnings 2023 | €725,000,000 | Outstanding number of shares | 620,000,000 | Retention ratio | 40% | Return on book value of equity (ROE) | 10% | Required return of equity (Re; based on CAPM) | 12% | WACC | 9% | Total Cash holdings | €700,000,000 | Market value of debt | €8,000,000,000 |. Free Cash Flows Forecast for MediQ: | Year 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026* | | FCF €850,000,000 | €867,500,000 | €876,550,000 | €880,700,500 | * from 2026 onwards free cash flows will grow at 2% annually forever. Calculate a fair price for the Laurel stock using the Discounted Free Cash Flow Model (DFCF). (Tip: first, calculate the Enterprise Value)
Assume it is the first of January 2023 and you just started working as a junior stock analyst specialized in the pharmaceutical industry. Your first assignment is to give a buy, hold, or sell recommendation for the stock of Laurel Inc. which currently sells for €12 at the NYSE-Euronext Exchange. Your boss provides you with the following tables and tells you that the P/E ratio of the pharmaceutical industry based on expected (=2023) earnings is 15. | Data Sheet | | | Expected total earnings 2023 | €725,000,000 | Outstanding number of shares | 620,000,000 | Retention ratio | 40% | Return on book value of equity (ROE) | 10% | Required return of equity (Re; based on CAPM) | 12% | WACC | 9% | Total Cash holdings | €700,000,000 | Market value of debt | €8,000,000,000 |. Free Cash Flows Forecast for MediQ: | Year 2023 | 2024 | 2025 | 2026* | | FCF €850,000,000 | €867,500,000 | €876,550,000 | €880,700,500 | * from 2026 onwards free cash flows will grow at 2% annually forever. Which recommendation (buy, hold, or sell) would you give for the Laurel stock given your outcome of the 3 valuation models above? What reservation (or nuance) might you have before you make your recommendation public?
On the stock exchange, the stock shares of Hitachi Ltd, United, and Sky Ltd are traded. Hitachi Ltd is as risky as United. However, Sky Ltd is a riskier investment. The next dividend of Hitachi Ltd, which will be paid tomorrow, is €2.05 per share and stays constant indefinitely. Hitachi Ltd is an all-equity firm. The expected return of United is 8% and Sky Ltd has an expected return of 12%. Calculate the current market price of the Hitachi Ltd stock.
On the stock exchange, the stock shares of Hitachi Ltd, United, and Sky Ltd are traded. Hitachi Ltd is as risky as United. The next dividend of Hitachi Ltd, which will be paid tomorrow, is €2.05 per share and stays constant indefinitely. The expected return of United is 8%. Calculate the expected market price of the Hitachi Ltd for next year, right after the dividend will be paid.
On the stock exchange, the stock shares of Hitachi Ltd, United, and Sky Ltd are traded. Hitachi Ltd is as risky as United. The next dividend of Hitachi Ltd, which will be paid tomorrow, is €2.05 per share and stays constant indefinitely. The expected return of United is 8%. The return on the book value of equity (ROE) of Hitachi Ltd is 11%. What would be today’s market price when the firm decides not to distribute all profits as dividends but retain 30% of it? Hitachi Ltd starts with this new policy including tomorrow’s dividend.
On the stock exchange, the stock shares of Hitachi Ltd, United, and Sky Ltd are traded. Hitachi Ltd is as risky as United. The next dividend of Hitachi Ltd, which will be paid tomorrow, is €2.05 per share and stays constant indefinitely. The expected return of United is 8%. The return on the book value of equity (ROE) of Hitachi Ltd is 11%. Give an economic interpretation of the difference between your answer on item 2.1 and 2.3.
Your company is considering an acquisition of another firm, Guerra Int, operating in the telecommunication industry. Before constructing an in-detail Discounted Cash Flow Model, you are instructed to value the target company using multiples. You find information about P/E and EV/EBITDA of several comparable companies, shown in the table below. You also mention that the comparable companies, although similar in future prospects, vary a lot in their capital structure. | | EV/EBITDA | P/E | | Comp 1 | 13.5 | 19 | | Comp 2 | 12 | 18 | | Comp 3 | 11 | 20 | | Comp 4 | 11.5 | 17 | | Median | 11.75 | 18.5 |. Guerra has Earnings of €212.5 million, EBITDA of €350 million, cash of €60 million, debt of €40 million, and 85 million shares outstanding. What is the range of share price that satisfies both multiples? Which method do you find more accurate?
Your company is considering an acquisition of another firm, Guerra Int, operating in the telecommunication industry. Before constructing an in-detail Discounted Cash Flow Model, you are instructed to value the target company using multiples. You find information about P/E and EV/EBITDA of several comparable companies, shown in the table below. | | EV/EBITDA | P/E | | Comp 1 | 13.5 | 19 | | Comp 2 | 12 | 18 | | Comp 3 | 11 | 20 | | Comp 4 | 11.5 | 17 | | Median | 11.75 | 18.5 |. Guerra has Earnings of €212.5 million, EBITDA of €350 million, cash of €60 million, debt of €40 million, and 85 million shares outstanding. Explain two limitations of using multiples.
A firm can increase its dividend by: a. Increasing its dividend pay-out rate. b. Decreasing its shares outstanding. c. Increasing its earnings (net income). d. All of the above.
The equity cost of capital is: a. Calculated as the capital gain rate minus the dividend yield. b. The same for all U.S. companies according to the efficient market hypothesis. c. Higher for firms paying out relatively high dividends. d. The expected return of other investments available in the market that have the same risk as the firm’s shares.
According to Efficient Market Hypothesis, an efficient market is one in which: a. There are no barriers to enter the market. b. New public information is gradually priced into the stock. c. All new information is immediately reflected in the stock price. d. There are no transaction costs.
Consider a capital market for which all assumptions of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) hold. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. In chapter 11 of BDH, two types of risk are distinguished. Define these types and relate them to the returns investors can expect on their investment. Additionally, define volatility and how diversification affects the volatility of an equally weighted portfolio.
Consider a capital market for which all assumptions of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) hold. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. Write down the equation of the security market line for this case. Define your symbols! Interpret the meaning behind the security market line.
The beta of the stock TripAdvisor is 1.7 and that of the stock Procter & Gamble (P&G) is 0.4. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. What do we usually call the stock with higher beta like TripAdvisor and lower beta like P&G? And explain its relationship with the economic situation.
The beta of the stock TripAdvisor is 1.7 and that of the stock Procter & Gamble (P&G) is 0.4. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. Calculate the expected return of a stock TripAdvisor and of a stock Procter & Gamble.
The beta of the stock TripAdvisor is 1.7. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. Suppose investors expect TripAdvisor stock to sell for $85.5 at year-end, while the current price is $77. Calculate the expected dividend of stock of TripAdvisor.
Consider a portfolio with weights of 50% in stock TripAdvisor, 30% in stock Procter & Gamble, and 20% US Treasury Bonds. The beta of the stock TripAdvisor is 1.7 and that of the stock Procter & Gamble (P&G) is 0.4. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. Calculate the beta and the expected return on this portfolio.
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. SD(R) is the standard deviation of return, Div is the dividend paid at t=1, and P₀ is the market price at t=0. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Write down the equation of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and use it to calculate expected returns of Google and Coca-Cola.
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Write down the Constant Dividend Growth Model (CDGM). If we assume that this model gives the same expected return as the CAPM, what are the implied growth rates of Google’s and Coca-Cola’s dividends? That is, calculate the growth rate according to the CDGM when the expected returns are given by the CAPM.
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Show how you can calculate the weights of Google and Coca-Cola in the market portfolio. Explain why they are 56% and 44%, respectively, and why the expected return of this portfolio is 8.50%.
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Write down the formula for the variance of a two-stock portfolio and calculate the standard deviation of a portfolio of Google and Coca-Cola when the correlation coefficient between the two stocks is -0.4. Explain whether investing in a portfolio of the two eliminates some volatility and if so, what causes the elimination of volatility?
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Calculate the beta of the portfolio of Google and Coca-Cola using two methods and explain its size.
Based on historical data, have higher volatility and higher average returns than , while have lower volatility and lower return than both of them. a. Large stocks; small stocks; bonds. b. Small stocks; large stocks; bonds. c. Bonds; large stocks; small stocks. d. Small stocks; bonds; large stocks.
Which of the following is a FALSE statement? a. Larger stocks tend to have less volatility than smaller stocks. b. Although there is no clear relationship between risk and return for individual stocks, there is a relationship between volatility and returns for portfolios of stocks. c. Individual stocks have higher risk than do large portfolios with comparable expected return. d. Holders of stock portfolios require a risk premium for independent risk because they diversify away systematic risk.
A firm has to decide on a new project proposal that requires a €600,000 investment in new machines. With these new machines, the firm will be able to launch a promising new product. Indicate whether the following is relevant for investment decision making and why: a. The part of the company’s building where the new machines will be installed could be rented out to another firm for €6,000 a month.
A firm has to decide on a new project proposal that requires a €600,000 investment in new machines. With these new machines, the firm will be able to launch a promising new product. Indicate whether the following is relevant for investment decision making and why: b. The internal technical support department of the company is costing €850,000 per year. The new project should carry 15% of these annual tech support costs (so €127,500).
A firm has to decide on a new project proposal that requires a €600,000 investment in new machines. With these new machines, the firm will be able to launch a promising new product. Indicate whether the following is relevant for investment decision making and why: c. In the past three years, the R&D department has spent €550,000 developing and testing the product prototypes.
A firm has to decide on a new project proposal that requires a €600,000 investment in new machines. With these new machines, the firm will be able to launch a promising new product. Indicate whether the following is relevant for investment decision making and why: d. To determine the attractiveness of the project, an external marketing research team evaluated the prospects of the new product for a €40,000 fee.
A firm has to decide on a new project proposal that requires a €600,000 investment in new machines. With these new machines, the firm will be able to launch a promising new product. Indicate whether the following is relevant for investment decision making and why: e. The yearly interest expense associated with this project is €60,000, because the firm finances it with a €600,000 loan at 10% interest rate.
Milton Shipment Company is investing in a new navigation system that will cost the company €5.15 million today. The network will increase cash flows by €1.2 million each year for the next five years when the system will become obsolete. Show that the IRR of this project equals 5.3%.
Ford Motor Company considers installing new 3D printers in their factories which will allow them to use recycled 3D material to print new spare car parts. They hired a third party in 2022 to find out the effect of the new printers on revenues and costs. From their research, which came at a cost of $15,000, they concluded that starting in 2023, the new printers would add to extra revenues of $35,000 per year, while it also reduces operating costs by $125,000 per year. The new navigation system is purchased at the end of 2022 (t=0) for $300,000, which will be linearly depreciated over 5 years to $50,000. At the end of 2022, they are also able to sell the old 3D printers for $45,000, which has a book value of $30,000. Since there is continuous innovation in 3D printers, the project lasts until the end of 2027. In that year, they expect to sell the navigation system for $75,000. To finance their investment, Ford issues a loan of $300,000, repayable at the end of 2021. The interest rate on the loan is 5%. Assume inflation is 0%, the tax rate is 25%, and all cash flows arrive at the end of the year. The discount rate is 12%. Indicate the free cash flow to Ford at the end of 2022.
Ford Motor Company considers installing new 3D printers in their factories which will allow them to use recycled 3D material to print new spare car parts. They hired a third party in 2022 to find out the effect of the new printers on revenues and costs. From their research, which came at a cost of $15,000, they concluded that starting in 2023, the new printers would add to extra revenues of $35,000 per year, while it also reduces operating costs by $125,000 per year. The new navigation system is purchased at the end of 2022 (t=0) for $300,000, which will be linearly depreciated over 5 years to $50,000. At the end of 2022, they are also able to sell the old 3D printers for $45,000, which has a book value of $30,000. Since there is continuous innovation in 3D printers, the project lasts until the end of 2027. In that year, they expect to sell the navigation system for $75,000. To finance their investment, Ford issues a loan of $300,000, repayable at the end of 2021. The interest rate on the loan is 5%. Assume inflation is 0%, the tax rate is 25%, and all cash flows arrive at the end of the year. The discount rate is 12%. Indicate the amount of yearly depreciation. Next, write down the full equation for calculating the free cash flows. Use it to indicate the free cash flow to Ford in 2023-2026.
Ford Motor Company considers installing new 3D printers in their factories which will allow them to use recycled 3D material to print new spare car parts. They hired a third party in 2022 to find out the effect of the new printers on revenues and costs. From their research, which came at a cost of $15,000, they concluded that starting in 2023, the new printers would add to extra revenues of $35,000 per year, while it also reduces operating costs by $125,000 per year. The new navigation system is purchased at the end of 2022 (t=0) for $300,000, which will be linearly depreciated over 5 years to $50,000. At the end of 2022, they are also able to sell the old 3D printers for $45,000, which has a book value of $30,000. Since there is continuous innovation in 3D printers, the project lasts until the end of 2027. In that year, they expect to sell the navigation system for $75,000. To finance their investment, Ford issues a loan of $300,000, repayable at the end of 2021. The interest rate on the loan is 5%. Assume inflation is 0%, the tax rate is 25%, and all cash flows arrive at the end of the year. The discount rate is 12%. Calculate the free cash flow to Ford in the final year (2027).
Ford Motor Company considers installing new 3D printers in their factories which will allow them to use recycled 3D material to print new spare car parts. They hired a third party in 2022 to find out the effect of the new printers on revenues and costs. From their research, which came at a cost of $15,000, they concluded that starting in 2023, the new printers would add to extra revenues of $35,000 per year, while it also reduces operating costs by $125,000 per year. The new navigation system is purchased at the end of 2022 (t=0) for $300,000, which will be linearly depreciated over 5 years to $50,000. At the end of 2022, they are also able to sell the old 3D printers for $45,000, which has a book value of $30,000. Since there is continuous innovation in 3D printers, the project lasts until the end of 2027. In that year, they expect to sell the navigation system for $75,000. To finance their investment, Ford issues a loan of $300,000, repayable at the end of 2021. The interest rate on the loan is 5%. Assume inflation is 0%, the tax rate is 25%, and all cash flows arrive at the end of the year. The discount rate is 12%. Draw a timeline for 2022-2027. Indicate the free cash flows at each point in time. Calculate the NPV of investing in a new navigation system.
Ford Motor Company considers installing new 3D printers in their factories which will allow them to use recycled 3D material to print new spare car parts. They hired a third party in 2022 to find out the effect of the new printers on revenues and costs. From their research, which came at a cost of $15,000, they concluded that starting in 2023, the new printers would add to extra revenues of $35,000 per year, while it also reduces operating costs by $125,000 per year. The new navigation system is purchased at the end of 2022 (t=0) for $300,000, which will be linearly depreciated over 5 years to $50,000. At the end of 2022, they are also able to sell the old 3D printers for $45,000, which has a book value of $30,000. Since there is continuous innovation in 3D printers, the project lasts until the end of 2027. In that year, they expect to sell the navigation system for $75,000. To finance their investment, Ford issues a loan of $300,000, repayable at the end of 2021. The interest rate on the loan is 5%. Assume inflation is 0%, the tax rate is 25%, and all cash flows arrive at the end of the year. The discount rate is 12%. Explain the NPV Decision Rule in your own words. How should companies apply this rule? Is investment in 4) a good idea?
Ford considers several smaller investment projects. They would like to replace parts of the conveyor belt (Project A), repair one of the factories damaged by storm (Project B), install new robotic assistants (Project C), invest in AI-assisted parking sensor development (Project D), and Others (Project E). Milton has $60,000 available for these 5 projects. | Project | Present value of operational cash flows (x 1,000) | Investment at t=0 (x 1,000) | | A | 44 | 35 | | B | 11 | 10 | | C | 36 | 30 | | D | 20 | 15 | | E | 59 | 50 |. Which project(s) (A, B, C, D, E) should Ford invest in and why?
Suppose Ford is confronted with 2 mutually exclusive investment projects. Project A has an IRR of 35% and an NPV of $75,000. Project B has an IRR of only 15%, but an NPV of $90,000. If Ford has to choose between project A and project B, which project should Ford choose based on this information? Shortly explain why.
Nestle is considering upgrading its warehouses and has estimated that this upgrade has a NPV of €550,000. Which of the following is the best way to interpret the NPV of this project? a. Taking the money that would be spent on the warehouse upgrade and investing it at the project’s IRR would result in a value of €550,000 at the end of the project. b. After the payback period, this project generates cash flows worth €550,000. c. Upgrading the warehouse is equivalent to receiving €550,000 today. d. This warehouse should be upgraded so long as the upgrade costs less than €550,000.
Your company has just been offered a contract worth €250,000 per year for five years. However, to take the contract, you will need to purchase some new equipment. If the discount rate for this project is 12%, what is the most you can pay for the equipment and still have a positive NPV for this project? Choose the closest value: a. €250,000, b. €900,000, c. €1,045,000, d. €550,000.
The owners of an office building in Scranton, USA, are deciding what types of businesses to place in the 500 square meter of empty office space. One of the businesses they are considering is a 240 square meter paper company Dunder Mifflin; they estimate the NPV of this company is $300,000. Another project they are considering is a 30 square meter paper company Michael Scott Paper Company with an estimated NPV of $50,000. Which of the following can you conclude from this information? a. The owners would need to know the IRR of the two projects to compare the projects. b. Dunder Mifflin’s profitability index is greater than Michael Scott Paper Company’s profitability index. c. The owners should choose Dunder Mifflin over Michael Scott Paper Company because it has a higher NPV. d. The Michael Scott Paper Company’s profitability index is greater than Dunder Mifflin’s stores profitability index.
We only want to consider incremental earnings in the capital budgeting process. Incremental earnings are the: a. Additional sales and costs associated with the project. b. Externalities generated from the projects. c. Capital expenditures minus the salvage values of the assets. d. Opportunity cost of the asset being used multiplied by the marginal tax rate.
Toyota is considering building an additional U.S. plant to produce hybrid cars. In considering this project, the interest expense associated with borrowing money to build the plant is: a. Captured in the cost of capital used to discount future cash flows. b. Considered a general and administrative expense. c. Considered a depreciable capital expenditure. d. Subtracted from incremental earnings when calculating free cash flows.
Ducky’s Submarine Hotdog Shop just signed a five-year lease contract for 600 square meters of space in the Outback Strip Center. Ducky will pay $750 a month for the lease. This contract states that Ducky also leases the adjacent 300 square meters of space at any time during the contract for $400 a month. Thus, Ducky has: a. A real option to expand. b. A real option to abandon. c. An opportunity cost of $400 a month. d. A sunk cost of $400 a month.
Problem 1.1) Assume AT&T has debt with a book value of $28 million, trading at 105% of par value. The firm has book equity of $24 million, and 1.5 million shares trading at $22 per share. What weights should JUP use in calculating its WACC? a) 53.85% for debt, 46.15% for equity b) 47.12% for debt, 52.88% for equity c) 55.06% for debt, 44.94% for equity d) 45.90% for debt, 54.10% for equity
HomeNet shares have a market capitalization of $60 billion. The company is expected to pay a dividend of $0.30 per share and each share trades for $40. The growth rate in dividends is expected to be 7% per year. Also, HomeNet has $20 billion of debt that trades with a yield to maturity of 8%. If the firm’s tax rate is 35%, compute the WACC? a) 6.05% b) 6.40% c) 6.76% d) 7.11%
Company FE is financed only by equity. The market value of equity is $20 mil, the cost of equity is 5% and the tax rate is 25%. Calculate the weighted average cost of capital. a) 4.375% b) 5% c) 5.75% d) None of the above.
In practice when raising external capital, issuing new shares or bonds, we the associated costs a) incorporate; into WACC. b) ignore; -. c) view; as cash outflows. d) none of the above.
We use in calculation of WACC because ? a) book values of debt and equity; they represent historical costs b) book values of debt and equity; it allows to keep debt-equity ratio constant c) market values of debt and equity; they represent current assessment of the firm’s performance d) None of the above
Firm X is a medium sized corporation headquartered in Groningen, The Netherlands. It operates in producing and selling exclusive sports cars. The firm is financed by common equity and fixed rate bonds. | DATA SHEET OF FIRM X AS OF JUNE 2016 | | | Book value of equity | €250 million | Current stock Price | €30.00 | Number of shares outstanding | 10 million | Face value of bonds outstanding | €520 million | Market value of bonds outstanding | €480 million | Return on book value of equity (ROE): | 17% | Required return on firm’s equity/ equity cost of capital (Re) | 15% | Equity risk premium | 6% | Yield to maturity (YTM) | 10% | Coupon rate of firm’s bonds | 6% | Risk free rate | 2% | Corporate tax rate | 25% |. Calculate the weighted average cost of capital (WACC) of Firm X.
Firm X is considering investing in a project that will enhance the efficiency of one of their facilities. The project requires €15 million in upfront investment and will generate additional net income of €1.5 million which will grow at 2% forever. | DATA SHEET OF FIRM X AS OF JUNE 2016 | | | Book value of equity | €250 million | Current stock Price | €30.00 | Number of shares outstanding | 10 million | Face value of bonds outstanding | €520 million | Market value of bonds outstanding | €480 million | Return on book value of equity (ROE): | 17% | Required return on firm’s equity/ equity cost of capital (Re) | 15% | Equity risk premium | 6% | Yield to maturity (YTM) | 10% | Coupon rate of firm’s bonds | 6% | Risk free rate | 2% | Corporate tax rate | 25% |. Under which conditions Firm X can use the firm’s overall business WACC to calculate NPV of the project? Is the project worth investing?
Consider the following information for the Tofutti Company specializing in vegan and vegetarian food products: | Equity | | | Book value of common equity | $750,000 | Retention rate | 30% | Debt | | | Face value of 10-year zero-coupon bonds | $1,250,000 | Other | | | Cash | $35,000 | Projected book value Return on Equity next year | 8% | Cost on Equity for a company with similar risk | 9% | Risk-free rate | 2% | Tax rate | 30% |. The average credit spread (in basis points) for bonds is given by: | Rating | Credit spread | | AAA | 160 bps | AA | 280 bps | A | 420 bps | BBB | 590 bps | BB | 690 bps | B | 790 bps | CCC | 870 bps |. Determine the cost of equity of Tofutti Company.
Consider the following information for the Tofutti Company specializing in vegan and vegetarian food products: | Equity | | | Book value of common equity | $750,000 | Retention rate | 30% | Debt | | | Face value of 10-year zero-coupon bonds | $1,250,000 | Other | | | Cash | $35,000 | Projected book value Return on Equity next year | 8% | Cost on Equity for a company with similar risk | 9% | Risk-free rate | 2% | Tax rate | 30% |. The average credit spread (in basis points) for bonds is given by: | Rating | Credit spread | | AAA | 160 bps | AA | 280 bps | A | 420 bps | BBB | 590 bps | BB | 690 bps | B | 790 bps | CCC | 870 bps |. Use a Constant Growth Dividend Discount Model to calculate the price-to-book ratio. Is the Tofutti Company over- or undervalued by the market?
Consider the following information for the Tofutti Company specializing in vegan and vegetarian food products: | Equity | | | Book value of common equity | $750,000 | Retention rate | 30% | Debt | | | Face value of 10-year zero-coupon bonds | $1,250,000 | Other | | | Cash | $35,000 | Projected book value Return on Equity next year | 8% | Cost on Equity for a company with similar risk | 9% | Risk-free rate | 2% | Tax rate | 30% |. The average credit spread (in basis points) for bonds is given by: | Rating | Credit spread | | AAA | 160 bps | AA | 280 bps | A | 420 bps | BBB | 590 bps | BB | 690 bps | B | 790 bps | CCC | 870 bps |. Tofutti Company has recently been rated an A. Calculate the Yield-to-Maturity and the market value of the zero-coupon bonds of Tofutti Company.
Consider the following information for the Tofutti Company specializing in vegan and vegetarian food products: | Equity | | | Book value of common equity | $750,000 | Retention rate | 30% | Debt | | | Face value of 10-year zero-coupon bonds | $1,250,000 | Other | | | Cash | $35,000 | Projected book value Return on Equity next year | 8% | Cost on Equity for a company with similar risk | 9% | Risk-free rate | 2% | Tax rate | 30% |. The average credit spread (in basis points) for bonds is given by: | Rating | Credit spread | | AAA | 160 bps | AA | 280 bps | A | 420 bps | BBB | 590 bps | BB | 690 bps | B | 790 bps | CCC | 870 bps |. Calculate the Weighted Average Cost of Capital based on your previous calculations.
Consider a capital market for which all assumptions of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) hold. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. In the text book, two types of risk are distinguished. Define these types and relate them to the returns investors can expect on their investment. Additionally, define volatility and how diversification affects the volatility of an equally weighted portfolio.
Consider a capital market for which all assumptions of the capital asset pricing model (CAPM) hold. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. Write down the equation of the security market line for this case. Define your symbols! Interpret the meaning behind the security market line.
10.11

The beta of the stock TripAdvisor is 1.7 and that of the stock Procter & Gamble (P&G) is 0.4. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. What do we usually call the stock with higher beta like TripAdvisor and lower beta like P&G? And explain its relationship with the economic situation.
The beta of the stock TripAdvisor is 1.7 and that of the stock Procter & Gamble (P&G) is 0.4. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. Calculate the expected return of a stock TripAdvisor and of a stock Procter & Gamble.
10.11

The beta of the stock TripAdvisor is 1.7. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. Suppose investors expect TripAdvisor stock to sell for $85.5 at year-end, while the current price is $77. Calculate the expected dividend of stock of TripAdvisor.
9.1 & 10.11

Consider a portfolio with weights of 50% in stock TripAdvisor, 30% in stock Procter & Gamble, and 20% US Treasury Bonds. The beta of the stock TripAdvisor is 1.7 and that of the stock Procter & Gamble (P&G) is 0.4. The risk-free interest rate for next year is 2% and the expected return of the market portfolio next year is 9.5%. Calculate the beta and the expected return on this portfolio.
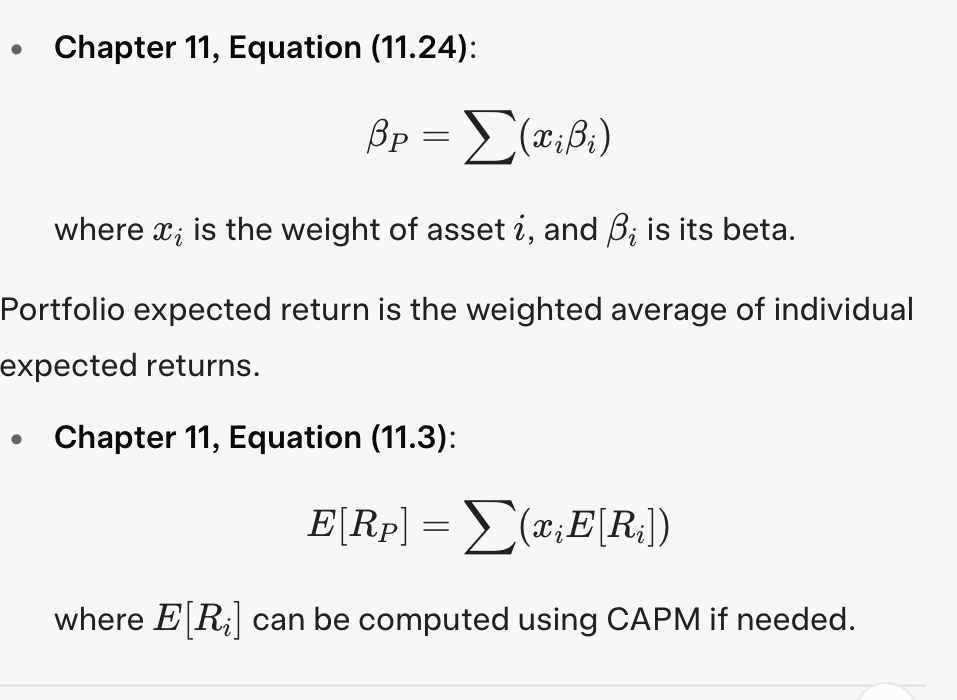
11.24 & 11.3
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. SD(R) is the standard deviation of return, Div₁ is the dividend paid at t=1, and P₀ is the market price at t=0. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Write down the equation of the Capital Asset Pricing Model (CAPM) and use it to calculate expected returns of Google and Coca-Cola.
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Write down the Constant Dividend Growth Model (CDGM). If we assume that this model gives the same expected return as the CAPM, what are the implied growth rates of Google’s and Coca-Cola’s dividends? That is, calculate the growth rate according to the CDGM when the expected returns are given by the CAPM.
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Show how you can calculate the weights of Google and Coca-Cola in the market portfolio. Explain why they are 56% and 44%, respectively, and why the expected return of this portfolio is 8.50%.
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Write down the formula for the variance of a two-stock portfolio and calculate the standard deviation of a portfolio of Google and Coca-Cola when the correlation coefficient between the two stocks is -0.4. Explain whether investing in a portfolio of the two eliminates some volatility and if so, what causes the elimination of volatility?
Consider a stock market in which only two stocks are traded, namely Google and The Coca-Cola Company. The market portfolio of these two stocks has an expected return of 8.5% and the risk-free rate is 2.5%. | | Google | Coca-Cola | | Beta | 1.30 | 0.62 | | SD(R) | 12% | 14% | | Div₁ | $9 | $6 | | P₀ | $150 | $120 | | Market value | $150 billion | $120 billion | | Book value of assets | $25 billion | $40 billion |. Both Google and Coca-Cola have 1 billion shares outstanding. Calculate the beta of the portfolio of Google and Coca-Cola using two methods and explain its size.
Based on historical data, have higher volatility and higher average returns than , while have lower volatility and lower return than both of them. a) Large stocks; small stocks; bonds. b) Small stocks; large stocks; bonds. c) Bonds; large stocks; small stocks. d) Small stocks; bonds; large stocks.
Which of the following is a FALSE statement? a) Larger stocks tend to have less volatility than smaller stocks. b) Although there is no clear relationship between risk and return for individual stocks, there is a relationship between volatility and returns for portfolios of stocks. c) Individual stocks have higher risk than do large portfolios with comparable expected return. d) Holders of stock portfolios require a risk premium for independent risk because they diversify away systematic risk.