Government Accounting
1/124
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
125 Terms
Operational accountability – financial.
The government demonstrates their operational accountability as a whole, they demonstrate that they can prepare timely, consistent, and comparable financial statements.
They demonstrate this by Government wide financial statements, full accrual.
Fiscal accountability.
Government shows that they use the money in the current period for the purpose that they were supposed to use the money for, and that the resources were not diverted to other needs. How do they show this by fund – based financial statements – modified accrual.
Why do governments need to report?
They need to report to demonstrate both fiscal and operational accountability.
The characteristics and financial reporting for government.
MNEMONIC: U R MICE
a. U Understandability.
b. R Reliability.
c. M Make a difference – relevance
d. I in timelines.
e. C Consistency year-over-year.
f. E Entity to entity comparability.

Recording the budget
A credit to budgetary control indicates an expectation that enough revenues will cover expenditures.
The close the budget at the end of the fiscal year, same amounts, same accounts, opposite balances. See picture below.


Closing the budget - continued

Debt service fund resources that are subject to the terms and conditions of a bond indenture would be classified within fund balances as:
Restricted
See picture below for example of committed funds.

Fiduciary funds
Full accrual bases of accounting
Excluded from government wide financial statements
The government safeguards assets that belong to a third-party.
The assets in a fiduciary fund will eventually be turned over to another party.
All net position is restricted for fiduciary funds

Statement of cash flows
Interest received is reported for GAAP in the operating section, but for enterprise funds, interest received is investing.
Interest paid for GAAP is operating, but for enterprise funds, interest paid as capital financing or non-capital financing.
Capital assets purchased are reported as investing for GAAP, financing for enterprise funds.


Government fund structure
See attached picture below
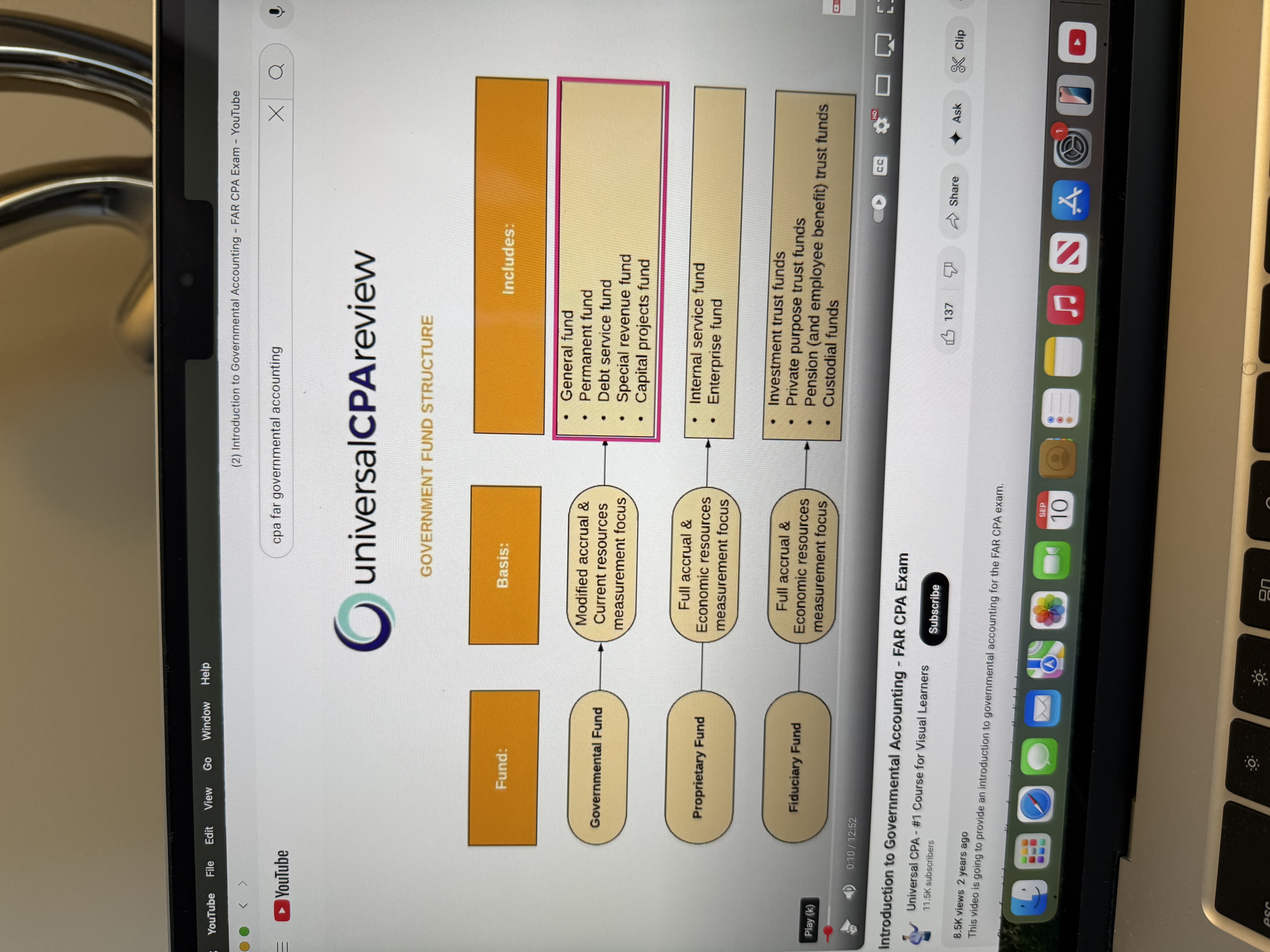

Basic governmental funds continued
Example of bond issuance:
Debit: Cash $xxx
Credit: Other Financing Sources $xxx


Example of bond issuance - Cont’d


Repayment of bond debt
Other financing sources and uses
Other financing sources: money is coming into the basic governmental fund, but it’s not revenue. Could be from a transfer, or could be borrowed money.
Other financing uses: money is leaving the basic governmental fund, but it’s not a payment for services, not an expenditure. Likely a transfer.

Encumbrance – fund based
Encumbrances are only recorded within the fund based financial statements for basic governmental funds such as the general fund.
Encumbrances are a reminder that a purchase has been made and a payment will need to be made soon.
Encumbrance order example: a commitment has been made so an encumbrance is recorded. General fund:(computer is ordered. Expected cost = $32k)
Debit: Encumbrance $32k
Credit: Budgetary Control $32k
The computer actual cost is $32.5k and arrives. The $32k encumbrance is removed and a $32.5k expenditure is recorded.
a. Debit: Budgetary Control $32k
Credit: Encumbrance $32k
(reverses the original entry)
b. Debit: Expenditure $32.5k
Credit: Vouchers Payable $32.5k
(Record the expenditure for the actual amount )
The payment for the computer is made.
a. Debit: Vouchers payable $32.5k
Credit: Cash $32.5k
Note: when determining amount available to be spent, do not include vouchers, payable, that amount has already been included in expenditures.


Encumbrances still outstanding at year end


Purchase vs Consumption Method
when a current asset is purchased, the governmental entity has the choice of either recording as a current asset immediately or recording as an expenditure immediately.
Purchase method – inventory at hand at year end
The answer in the picture above is “A”. At your end, the adjustment is an increase in supplies and a corresponding increase and non- spendable fund balance for $1000.

Purchase vs Consumption Method
Consumption method
Record expenditures as supplies are used, no adjusting entry needed at year-end. This method assumes a perpetual inventory is maintained.
At year-end no adjustment as needed because all year long you are debiting, expenditure, and crediting office applies as supplies are used.

Property taxes: Modified accrual accounting – revenue
DR: Real property taxes, receivable – current. $2mil.
CR: Revenues-Property Taxes $1.8mil
CR: allowance for uncollectible taxes – current $200k
Journal entry to record the collection: debit: cash $1.7 million credit: real property taxes receivable – current $1.7 million
Journal entry to record the classification of receivables to delinquent: debit: real property taxes receivable – delinquent $300,000 credit: real property taxes receivable - current $300,000
Journal entry to re-classify allowance to delinquent: debit: revenue $100,000 debit: allowance for uncollectible taxes – current $200,000 credit: allowance for uncollectible taxes – delinquent $300,000 (plug)


Test to determine “major fund”
General fund is automatically major fund.
The following funds can NOT be major funds: Fiduciary Funds, Pension Funds and Internal Service Funds
1st test: The 10% test: Fund assets are 10% of the total government fund assets.
2nd test: if a fund passes the first test, the 5% test is that fund assets must be 5% of the total governmental and enterprise fund assets.
The function of the GASB, the FASAB, the FASB, and AICPA?
GASB for state and local governments.
FASAB for the federal government.
FASB for non-governmental
not for profits is also governed by FASB.
SEA - service efforts and accomplishments?
In governmental accounting,
SEA stands for service Efforts and Accomplishments reporting, a voluntary method for governments to report on how efficiently and effectively they use resources to provide public services. It goes beyond traditional financial statements to include non-financial data, such as the number of services provided, the outcomes of those services, and the resources (inputs) used to deliver them. This type of reporting helps users, like taxpayers and budget analysts, assess a government's performance and accountability.
Interperiod Equity?
Financial reporting should provide information to determine whether current year revenue were sufficient to pay for current year services. It should show whether current year citizens shifted part of the cost of services they received to future year taxpayers.
Budgetary and fiscal compliance?
Financial reporting should demonstrate whether resources were obtained and used in accordance with the entities legally adopted budget; it should also demonstrate compliance with other finance related legal or contractual requirements.
Who are the users and what are the uses of financial reports for governments and not for profits?
Users include: governing boards, investors, and creditors, taxpayers and citizens and organizational members, donors and grantors, regulatory and oversight agencies, employees, and other constituents.
Financial statements are targeted mainly at parties external to the organization.
What is a fund?
Government and not for profit organizations established their accounting systems on a fund basis.
The crux of non-business accounting is fund accounting, and it forms the basic building block of governmental accounting, and financial reporting.
It is an accounting device that an entity uses to keep track of specific sources and uses of funds.
A fund is a fiscal and an accounting entity. Each fund has its own self, balancing set of account from which financial statements can be prepared.
Government Fund accounting uses the following equations
2 versions of the same:
Assets + deferred outflows = liabilities + deferred inflows + fund balance.
Assets + deferred outflows - liabilities - deferred inflows = fund balance.
Funds of Not-For-Profit use the equation:
Asset - Liabilities = Fund balance

Fund balance/net position
Government and not for profits do not have owners, so the term owners equity is replaced by the terms fund balance or net position.
GASB Statement No. 54?
This affects only the fund balance reported on the balance sheet of governmental type funds. It does not affect the reporting of net possession by proprietary or fiduciary funds. It also does not affect the reporting of net position of governmental activities in the government wide financial statements.
GASB Statement No. 54 Con’t.
Information is reported in five different classifications which provide a hierarchy, indicating the extent to which the government is bound to honor constraints on the specific purposes, for which amounts in the fund can be spent.
Nonspendable: fund balance includes amounts that are not expendable form or are legally or contractually required to be maintained intact.
Restricted: fund balance includes amount, constrained for specific purposes by external parties, through constitutional provisions, or by enabling legislation.
Committed: fund balance includes amount, constraint for specific purposes, determined and adopted by a formal action by the highest decision-making authority of the government itself.
Assigned: fund balance includes amounts a government, explicitly intends to use for specific purposes.
Unassigned: fund balance is the residual classification for the general fund and comprises all amounts not included in the other classifications.
Modified accrual basis, accounting?
Modified accrual basis accounting is a method used primarily by government entities that combines elements of both the cash and full accrual bases.
Revenues are recognized when they are both measurable and available to finance current expenditures,
while expenditures are recorded when the liability is incurred, not when it is paid.
This hybrid method allows governments to maintain budgetary control and accountability by focusing on short-term financial resources, making it different from the full accrual basis which recognizes revenues and expenses when earned and incurred, regardless of when cash is exchanged
GASB handling of Capital Assets and Long Term Liabilities?
Capital, assets and long-term liabilities are excluded from the balance sheet, and that changes in short term financial assets and liabilities are recognized as revenues or expenditures, as opposed to expenses.

Major vs. Nonmajor Funds?
The GASB distinguishes between major and non-major funds, and requires that major funds are displayed more prominently than non-major funds. Major funds are:
At least 10% of all funds of that category.
The 10% of the above are at least 5% of all gov’t and enterprise funds combined.
SEE Picture.

GASB Statement No. 34 2 sets of statements?
GASB statement number 34 mandates that governments prepare two separate, albeit related, sets of financial statements.
The first set, the government wide statements, concentrate on the government as a whole. It consolidate all of the governments operations and includes wooden. It’s measurement focus all of the government, economic resources, including capital assets.
The second set, the fund financial statements, views, the governmental entity as a collection of separate funds. Governmental_and business type funds are reported on separate schedules. The schedule that reports governmental funds includes one column for the general fund, one for each of the other major funds, and one that combines all the non-major funds.
FASB - NFP note.
FASB permits, not for profits to consolidate the assets and liabilities of funds into a single balance sheet. However, the net assets (assets, less liabilities) of the entity must be reported in two categories:
Net assets without donor restrictions.
Net assets with donor restrictions.
The same applies to the statement of activities. (Revenues must be separated).
Most general purpose, governments, and engages in three broad categories of activities. These activities are?
Governmental activities; are those finance predominantly through taxes and enter governmental grants.
Business type activities; are those finance predominantly through user charges.
Fiduciary activities; are those for which the government acts as a trustee or custodian for individuals, external organizations, or other governments.
Governmental type funds are maintained to account for government operating and financing activities. These are the five primary types of governmental funds:
See picture. GSDCP (go see dad cook pie)

Proprietary funds?
These are operated in a manner similar to private businesses; the government intent is to recover cost primarily through user charges. There are two types of proprietary funds.
Enterprise Fund: these funds are used to account for business type activities in which the government sells goods or services to the general public at large. (Users external to the governmental unit).
Internal Service Funds: these funds are used to account for business type activities in which the customers are other funds, departments, or agencies within the same governmental unit, or occasionally to other governmental units.
fiduciary funds?
these are used to account for resources held by the government in a capacity that are intended to benefit parties other than the government itself. These are on a full accrual basis. There are four types of fiduciary funds:
“CIPP”
See picture.

What is included in the government’s annual comprehensive financial report? (ACFR)
It includes statements that combine and report on the government activities from both a governmentwide and a fun perspective. It also includes the statements of individual funds and an array of statistical data on both the government itself and it’s jurisdiction. The AC FR is divided into three main sections:
Introductory section
Financial section
Statistical section

The Gov’t wide statement - note.
The government wide statements are on a full accrual basis. The fund statements are on the basis of accounting required for the specific category of fund – modified accrual basis for government funds and full accrual basis for proprietary funds.
Gov’t wide statement con’t
The objective of the governmentwide financial statements is to present a fairly broad and consolidated view of the financial position of the governmental entity. According to gap, they are just required financial statements:
Statement of net position (balance sheet)
Statement of activities (statement of revenues and expenses)
Fund Statements
See picture.

M2 what are Budgeted Revenues called?
What are Budgeted Expenditures called?
What are Budgeted other financial items (sources and uses) called?
Budgeted Revenue = Estimated Revenue
Budgeted Expenditure = Appropriations
Budgeted other financial items (sources and uses) are called Estimated Financing Sources and Uses.
What are the normal account balances for revenue (Budgeted Estimates) and expenditure (Appropriations)
Revenue (Budgeted Estimates) has a debit balance and Expenditures (Appropriations) has a credit balance.
What three types of events cause entries to budgetary accounts?
When the budget is approved.
When the budget is amended.
When the budget is closed at the end of the year.
never at any other time is an entry made to a budgetary account.
What are the key purposes of budgets?
Planning
Controlling and Administering
Reporting and Evaluating
Why is more than one type of budget necessary?
See picture below:
1. appropriation budgets.
2. Capital budgets
Flexible, budgets
In addition, many governments and not for profits prepare performance budgets

Flexible, budgets.
Government use flexible, budgets for enterprise funds.

How are expenditures and revenues classified?
See picture.

What are performance budgets?
Performance budget focus on measurable units of efforts, services, and accomplishments. They are formulated, so the dollar expenditures are directly associated with anticipated units of outputs or outcomes.
What are the key phases of the budget cycle?
Preparation
Legislative adoption and executive approval
Execution
Reporting and auditing
On what basis of accounting are budgets prepared
Budgetary principles are established either by individual government or organizations or body of governments or organizations that supervised them.
What are Encumbrances?
Encumbrances are commitments to purchase goods or services.
What cautions must be taken in budget to actual comparisons?
What are the differences in how actual results are determined?
Differences in basis of accounting
Differences in timing
Differences in perspective
Difference in the reporting entity
How do budgets enhance control?
These include preparing journal, entries both to record the budget and to give recognition to goods and services that have been ordered, but not yet received.
How does encumbrance accounting prevent overspending?
The entry to record an encumbrance is usually prepared when a purchase order is issued, a contract sign, or commitment is made.
Outstanding obligations at year end how are these reported?
These are to be reported on the entities fund balance sheet as a committed or assigned fund balance, and accordingly they reduced the unassigned portion of fund balance.
How to determine if governments complied with their budgets?
To demonstrate that they complied with their budgets, governments are required to include in their annual reports a budget to actual comparison on a budget basis, in other words, the same basis on which they prepare their budget, usually cash or near cash.
Governmental funds, the two types of financial statements.
1 governmental fund financial statements
1. Modified accrual basis.
2. Provides information relating to inter. Equity.
3. Presents, revenues, expenditures, other financing sources, and other financing uses.
2 government wide financial statements
1. Full accrual basis.
2. Presents revenues and expenses from the perspective of the entity as a hole and not of the individual
3. Follows GAAP.
Expenditures versus expenses.
See picture.
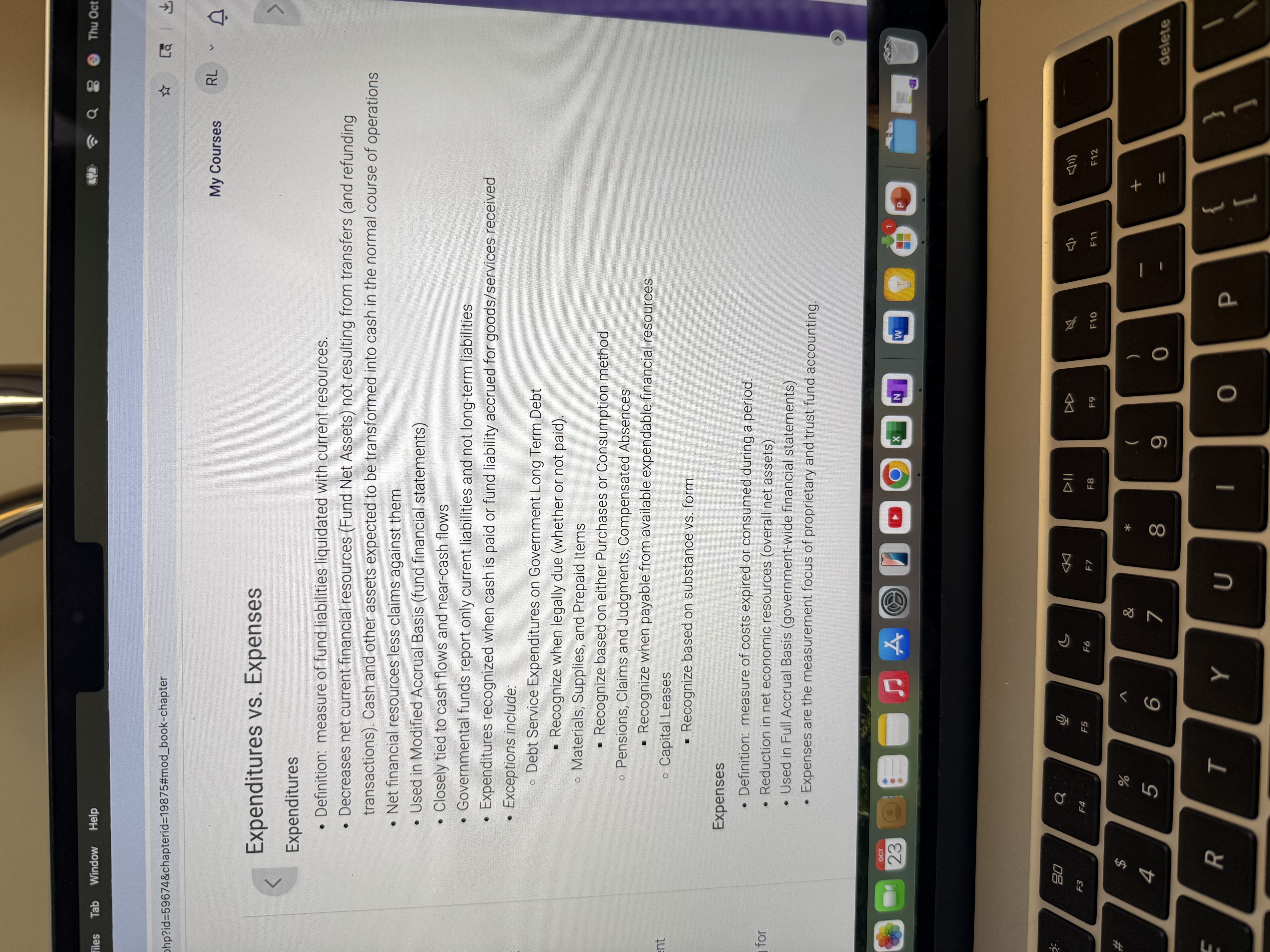
Expenditure vs Expenses note.
An expenditure is generally recognized when an asset is acquired, whereas an expense is generally recognized when an asset is consumed.
Salaries and wages
May be earned in one fiscal year, but paid in the next. Recognize the expenditure in a period in which it is earned by the employee.
Compensated absences and sick leave.
See picture
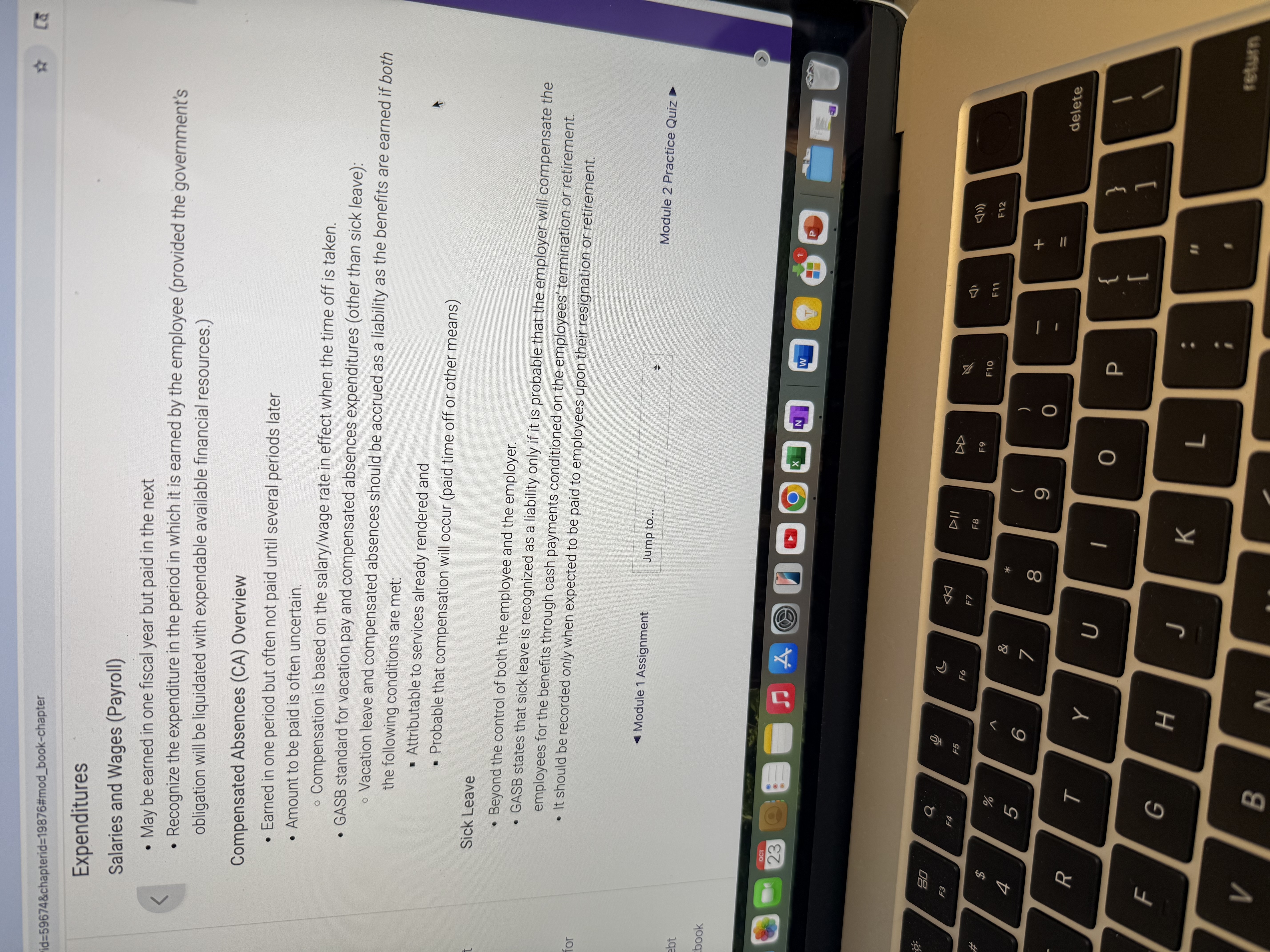
Consumption Method - Example
Example:
Supplies inventory $3.5
Accounts Payable $3.5
To record acquisition of supplies
Then, as it uses the inventory, it would record an expenditure, and reduce the balance in the inventory account:
Supplies expenditure $3.3
Supplies inventory $3.3
To record the consumption of inventory
The reported expenditure for the year would be $3.3 million, the amount of supplies consumed. At year end, the inventory balance would be $0.2 million, the amount of supplies on hand. Hence, a portion of fund balance equal to this amount would now have to be designated as nonspendable:
Fund balance – unassigned $0.2
Fund balance – nonspendable $0.2
To reclassify fund balance to reflect year-end inventory
Sabbatical Leave. How is it recorded?
It depends on the purpose of the leave.
Relief from normal duties to perform research or obtain additional training to enhance the reputation of the employer. ( Account for the Sabbatical in the period the leave is taken) No liability should be recorded in advance of the leave.
If the leave is for compensated unrestricted time off, then the government should accrue a liability during the period that the leave is earned.
note: only the portion expected to be liquidated with expendable available resources would be reported in a governmental fund. The balance of the liability would be recorded on the government wide statement of net position and in a schedule of long-term obligations.
The Purchase, and the Consumption Methods.
Purchase method: the government would record the purchase of the inventory as an expenditure when it is purchased.
Ex: Supplies expenditure $3.5
Accounts Payable $3.5
Consumption method: record it when it’s consumed. Using the consumption method, a government would account for inventory, the same, as would a business, with one additional feature, the designation of an amount equal to the inventory balance as non-expendable as opposed to spendable.
Ex: Supplies inventory $3.5
Accounts Payable $3.5
How should pre-payments be accounted for? On September 1 20X1, a town purchases a two year insurance policy for $60,000; a cost of $2500 per month.
The purchase method:
debit insurance expenditure $60,000
credit cash or accounts payable $60,000.
No additional entries would be required either in 20X1 or the subsequent two years.
The consumption method:
first entry upon purchasing the insurance policy:
Debit Prepaid insurance $60,000.
Credit cash or accounts payable $60,000.
Then each month of the next two years;
Debit insurance expenditure $2500 credit prepaid insurance $2500.
What is an appropriation?
In appropriation is legal authorization granted by the legislative body to incur liabilities for purposes specified in the appropriation act or ordinance.
What is the most commonly used budget?
The object classification budget.
It provides a budget by major spin categories, example salaries, and wages, travel, operating services, supplies, professional services, equipment.
Closing entries:
The first closing entry is to close the budget. The amount and the estimated revenue and appropriation accounts are respectively, credited, and debited. The residual is recorded to fund balance.
Encumbrances must also be closed at year end. The encumbrance account is closed to fund balance – unassigned. The reserve for encumbrance account need not be closed because it is a balance sheet account.
M3 - What are the criteria that an entity use to determines when to recognize revenues and expenditures?
Measurement focus – refers to what is being reported on; example to which assets, liabilities, and referrals are being measured.
Basis of accounting; refers to when transactions and other events are recognized.
What is the measurement focus of modified accrual basis?
The measurement focus is: current financial resources. Current financial resources means expendable financial resources – cash and other items that can be expected to be transformed into cash in a normal course of operations less current liabilities. The other items include investments and receivables, but not capital assets.
What are the main types of non-exchange revenues and limitations on how and when they can be used?
See picture.

Taxes stated due date versus substantive due date question
Stated due date: The date the amount is due.
The substantive due date is that date on which interest and penalties begin to accrue or imposed.
What are derived tax revenues?
Examples include sales taxes, and income taxes. They are derived from exchange transactions, such as the sale of goods or services, or other income – producing commercial transactions.
What are the three significant events in the earnings process?
The date of the sales transaction and the collection of the tax by the merchant
The date the merchant is required to file a tax return, and transmit the taxes (generally the same.)
The date, the merchant actually files the return and transmit the taxes
Additional notes on sales taxes, and other derived non-exchange revenues.
In the fund statements, the sales taxes must also satisfy the “available” test to be recognized as revenue. No official announcements provide guidance as to the length of the period after the close of the fiscal year in which resources must be received to be considered available.
Hence, governments must exercise their own judgment as to what constitutes “available.” at the very least, they must ensure consistency of practice from one year to the next.
Government should recognize assets from derived non-exchange transactions into the period in which the online transaction takes place.
Thus, a government should recognize an asset – sales taxes, receivables – on taxes to arrive from sales of the current year, even if the taxes will not be collected in time to be available to meet the current liabilities of that year.
Income Tax Note
In essence, GASB suggest that they recognize revenue on a cash basis.
See picture for example:

Tax Abatements Note
GASB mandate that governments make significant disclosures about the tax abatement. Do you include, but are not limited to:
A brief description of tax abatement programs
The specific taxes, being abated,
The gross amount of the taxes that were reduced during the reporting period,
The commitments made by recipient
The criteria that made the recipients eligible for the abatement
Provisions for recapturing taxes, if the recipient fails to meet its commitments.
Pass-through grants note.
GASB stated that, as a general rule, cash pass through grants should be recognized as revenue and expenditures or expenses in the funds of the primary government and in the government – wide financial statements.
Only in those and frequent cases in which the government serves as a cash conduit may pass through grants be reported in a custodial fund.
On-Behalf Payments
See picture.

Sales of Capital Assets example:
Debit: Cash
Credit: Other financing sources
Governments must maintain capital projects funds for resources that are legally restricted, and contractually required for the acquisition of capital assets. What is the primary purpose of the capital projects funds?
The primary purpose is to ensure and demonstrate the expenditure of the dedicated financial resource is both legally and contractually compliant
For the capital projects fund; GASB requires budgetary, accounting in circumstances in which control cannot readily be established by means other than a budget.
On the other hand, when a government can establish control by entering into a fixed-price contract with a single vendor or construction company, then budgetary entries are not necessary.

Recording, expenditures and infrastructure assets note.
See picture

Capital Projects Additional Notes
If the government intends to prepare report that indicate only cumulative amounts of revenues and expenditures over the life of the project, then there is no need to close the accounts. They can remain open until the project is completed.
Debt service fund note
Debt service funds do not account for the long-term that itself. The only circumstance in which the principle of debt is reported as an obligation is when it has matured, but actual payment has been delayed.
Until the period in which they must be paid, interest and principle are not considered current liabilities of the debt service funds.
Depth service fund note continued. How to account for “premium” from issuing a bond?
The premium is included in the debt service fund; or is transferred to the debt service fund.
Interest revenue note.
Interest revenue bonds held as investments is, in effect, accrued as earned, because investments must be stated at fair value, and interest earned, but not yet paid is incorporated into fair value.
Special assessment projects, and a related debt.
When the government levies special assessments, it should recognize them in a debt service fund. Special assessments are imposed non-exchange transactions. They should be recorded as assets in the period in which government has enforceable legal claim to the resources that it will receive.
In the debt service fund, they can be recorded as revenues only one available for expenditure. Therefore, when a government levies the special assessment, it should offset the assessments receivable with a deferred inflow of resources.

Arbitrage, as it applies to states and other municipalities, refers to the issuance of debt at relatively low, tax exempt rates of interest, and the investment of the proceeds in taxable securities, yielding a higher return.
See picture for federal regulations.
See picture for more details

M4 - accounting for works of art.
Works of art held, purely as an investment or acquired for an administrator’s office that is not accessible to the public or for research purposes must be capitalized.
Accounting for infrastructure.
in general, governments should account for infrastructure assets just as they do other capital assets. That is, they should report cost as expenditures in their fund statements. In their government wide statement, they should capitalize the cost and appreciate the assets over there. estimated useful lives.
See exceptions for Depreciation in Gov’t-wide statements in picture below.

Depreciation- modified approach
The initial cost of the asset is capitalized, but preservation cost (outlays that extend the useful life of an asset beyond The originally expected useful life) are expensed as incurred. No depreciation is charged on either the initial cost of acquiring the asset or the subsequent preservation costs.
If a government elects the modified approach, then it must disclose as required supplementary information.
Ex: the assessed condition of the assets and the basis on which it made that assessment. The basis would ordinarily be an engineering measurement scale, such as one that ranks pavements from zero unsafe to 100 perfect.
Depreciation- modified approach Con’t
Governments that do not depreciate their assets must demonstrate they are, in fact, maintaining their assets at, or above, a specified condition. In addition, they must disclose, for a five year period, the actual maintenance cost as compared to what would be necessary to maintain those assets at the specified condition.
A controversial pronouncement – statement number 34
Per GASB, if the government-wide statements are to provide a long-term measure of the cost of services, and thereby to be on a full accrual basis, then the statements cannot ignore the cost associated with the class of assets as significant as infrastructure
Accounting for impaired assets
See page 294 of text book for details.
Investments Reported at Fair Value with exceptions.
FASB and GASB required at all debt and equity securities held by not for profit, entities and government as investments be reported at fair value.
FASB exceptions for NFP. NFP are exempt from classifying securities into 3 sections. It should report all investments in debt and equity securities at fair value.
Investments in short term securities.
Governments are permitted to report short term investments, having a remaining maturity at time of purchase of one year or less at amortized cost rather than market value.