module 13: cytokines
1/52
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
53 Terms
cytokines
proteins that mediate the effector functions of the immune system. soluble proteins. low MW. secreted by large # of cell types. regulate many important processes. mediate cell-cell communication in immune response. regulate intensity & duration of response. NOT hormones

biological responses cytokines are involved in
inflammatory response. hematopoiesis. clonal expansion of T cells. proliferation & differentiation of B cells. activation of NK cells, cytotoxic T-cells, B-cells, neutrophils, eosinophils, mast cells
cytokines released by lymphocytes are called:
lymphokines (nomenclature)
cytokines released by monocytes & macrophages are called:
monokines (nomenclature)
cytokines released by leukocytes that act on other leukocytes are called:
interleukins (nomenclature)
cytokines with chemotactic activity are called:
chemokines (nomenclature)
properties of cytokines
work by binding receptors on membranes of target cells. target cells can be autocrine, paracrine, or endocrine (not hormones but do have endocrine action). pleiotropy, redundancy, synergy, antagonism. cascade induction
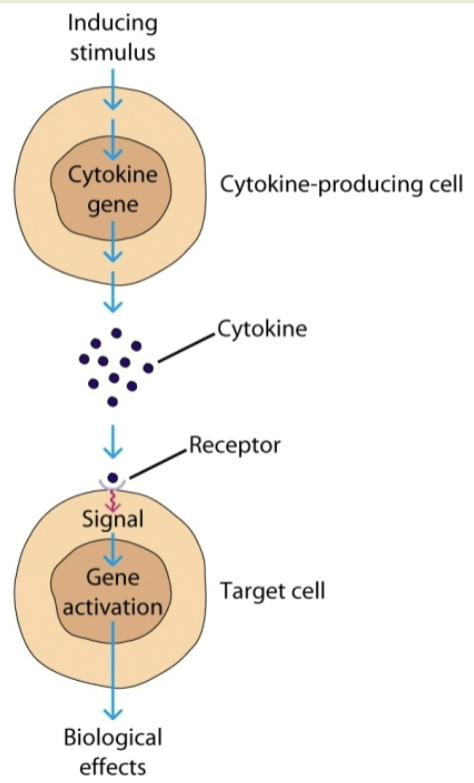
autocrine
target cell is the same cell
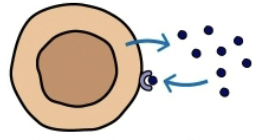
paracrine
target cell is in close proximity

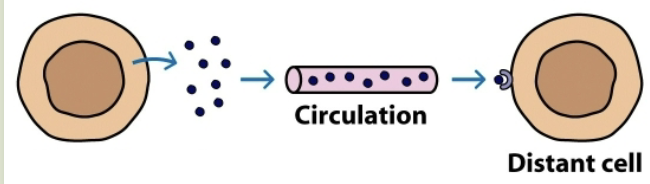
endocrine
target cell is in distant part of the body
pleiotropy
a given cytokine has different biological activities on different target cells
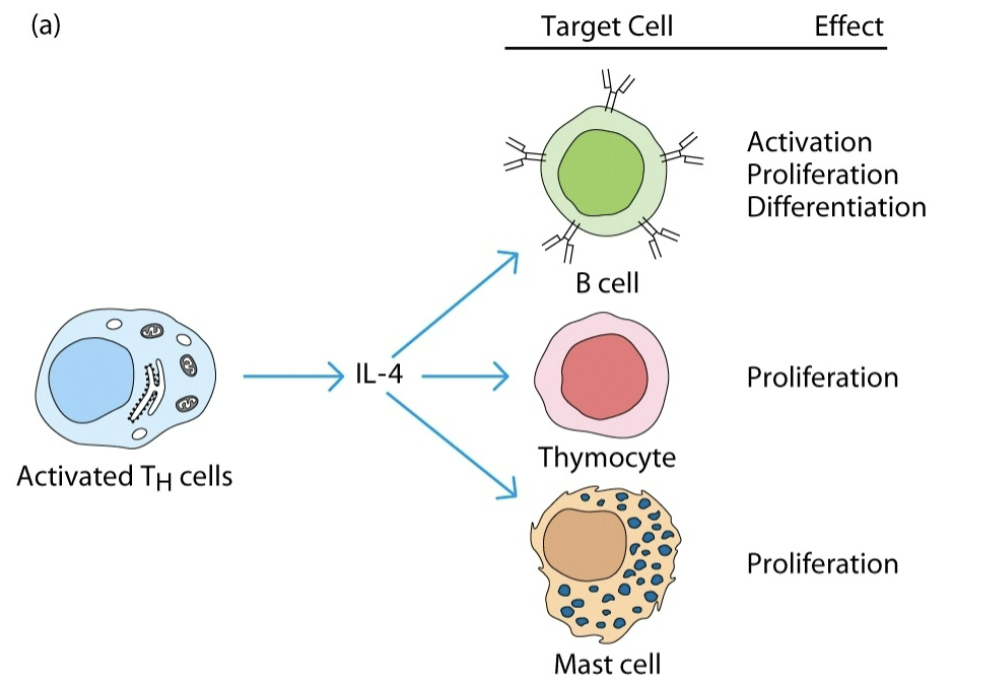
redundancy
2 or more cytokines mediate similar biological function
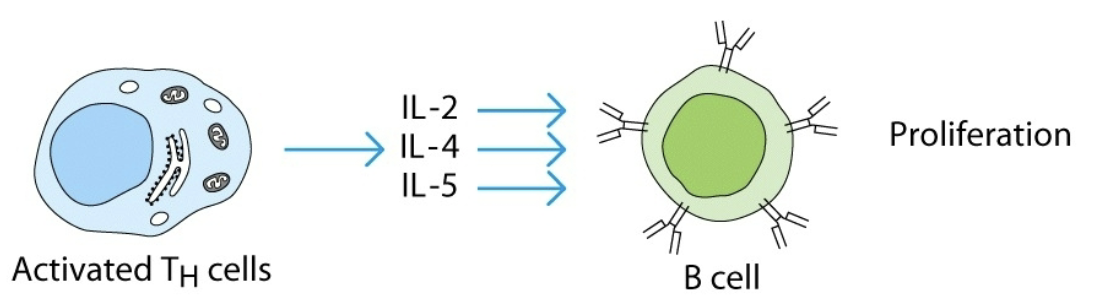
synergy
combined effect of 2 cytokines is greater than additive effects of individual cytokines

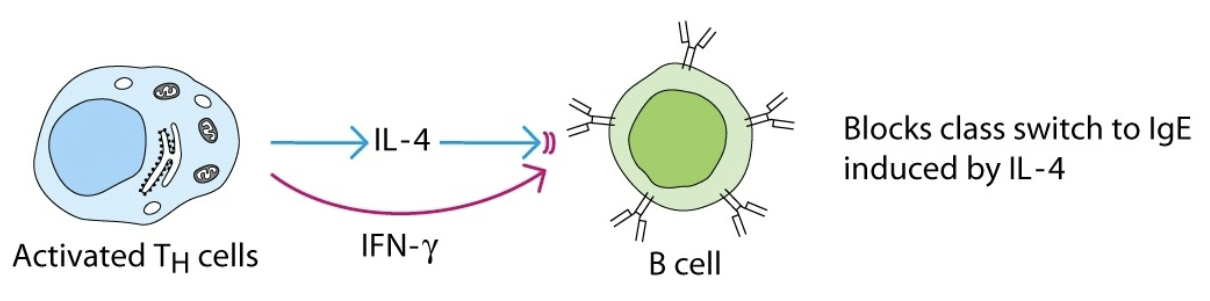
antagonism
effect of one cytokine inhibits or reduces the effect of another cytokine
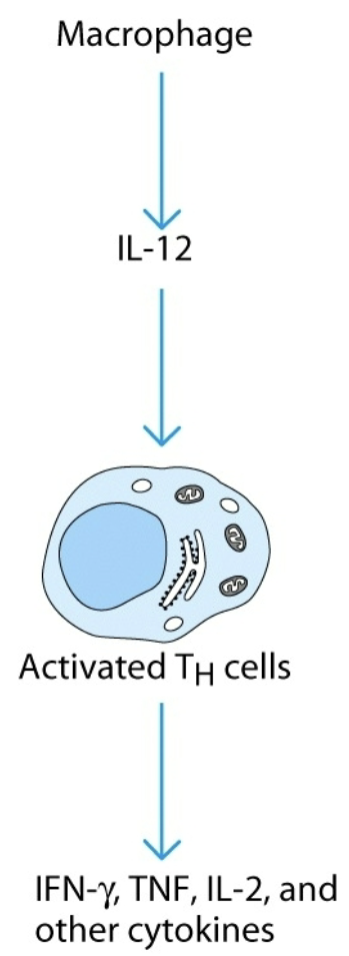
cascade induction
effect of one cytokine induces the target cell to produce a cytokine, which acts on other target cells to produce cytokines
what are the 2 major producers of cytokines?
macrophages & TH cells
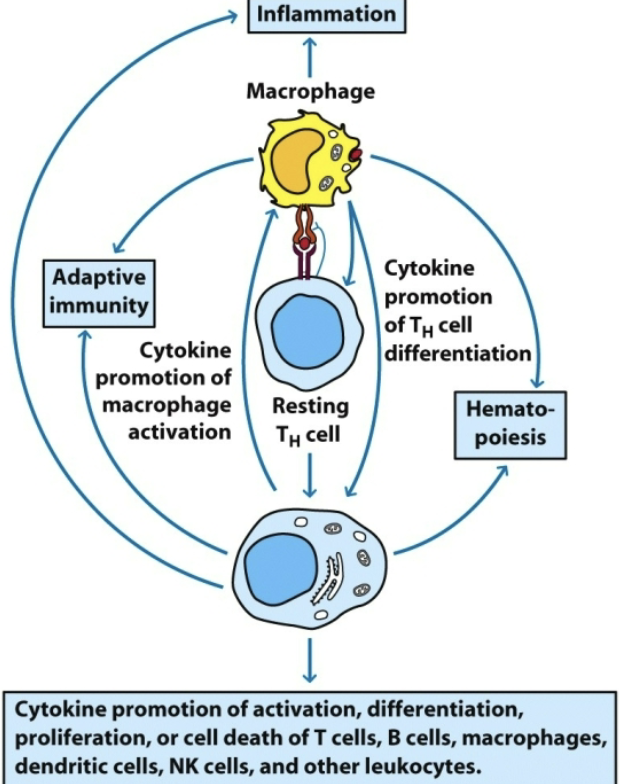
what prevents cytokines from activating cells in a nonspecific manner during an immune response?
expression of specific receptors by target cells. localized effective concentration. short half-life
what are the 6 families of cytokine receptors?
interleukin 1, class I (hematopoietin), class II (interferon), TNF receptor, chemokine receptor, interleukin 17. each distinguished by structure of ligand & receptor, nature of signaling pathways induced
interleukin 1 (IL-1) cytokines
promote inflammation (proinflammatory cytokines). stimulated by viral, parasitic, or bacterial antigens. secreted early in immune responses by monocytes, macrophages, dendritic cells. (ex: IL-18, IL-33)
action of IL-1 cytokines
acts locally on capillary permeability and makes leukocytes migrate to infected tissues. acts systemically to signal liver to produce acute phase proteins. can help to activate adaptive immune responses
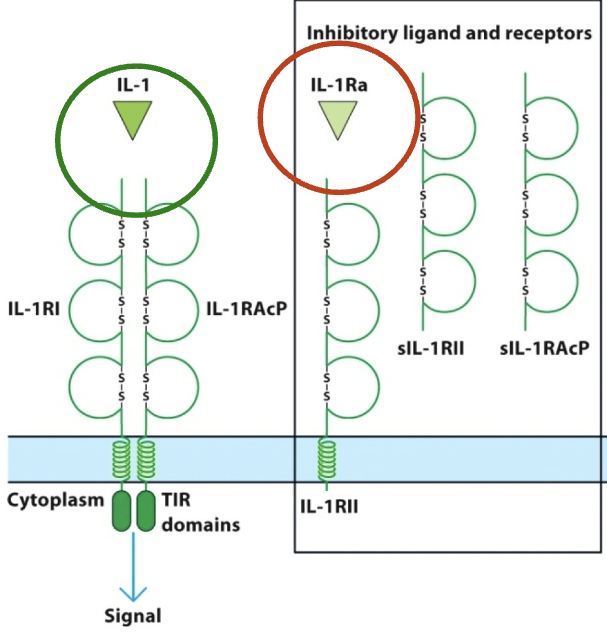
IL-1α & IL-1β
IL-1 cytokines that bind to IL-1RI & IL-1RAcP. IL-1 receptor antagonist (IL-1Ra) binds to IL-1RII, preventing it from binding w/ its functional partner IL-1RAcP
class 1 (hematopoietin) cytokines
multiple subunits: common subunits paired w/ distinct cytokine-binding subunit to form subfamilies of receptors. resting T-cells express β-chain & γ-chain: IL-R βγ. activated cells express α-chain. IL-R trimeric high affinity expressed only in activated CD4+ & CD8+ T-cells
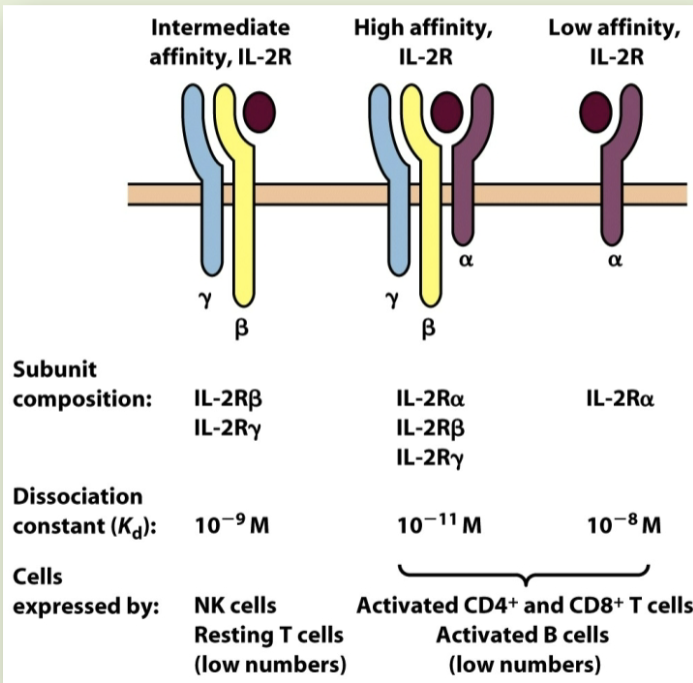
γ-chain (IL-2R) bearing subfamily
IL-2R is stereotypical member. exists in low, intermediate, & high-affinity forms. different forms marked by presence of accessory receptor chains. lymphocytes shift to expression of high-affinity form during activation events
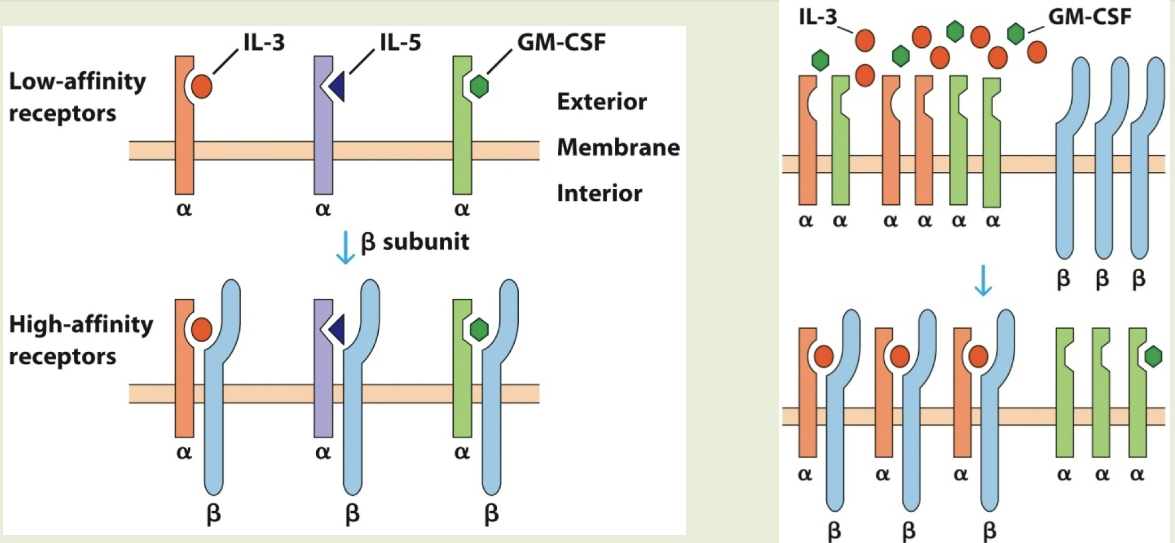
GM-CSF/β-chain bearing subfamily
includes receptors for IL-3, IL-5, & GM-CSF. each cytokine binds to unique α subunit. β subunit is a shared signal-transducing protein. these cytokines exhibit redundancy
IL-6/Gp130 receptor subfamily
includes IL-6 & IL-12 receptors. critically important: targeted disruption is lethal in embryonic mice. ligand-specific dimers/trimers are expressed w/ gp130 subunit. further subdivided into receptors for monomeric (IL-6) & dimeric (IL-12) cytokines
class II cytokines
include type I, type II (interferon γ), & type III interferons
type I interferons
18-20 kDa dimers w/ antiviral effects. secreted by activated macrophages & dendritic cells. interferon α (family of ~20 related proteins) & interferon β
type II interferons (aka interferon γ)
dimer produced by activated T/NK cells. potent modulator of adaptive immunity
type III interferons
newer: 3 current members. ex: interferon λ3 & interferon λ4. IFN λ secreted by plasmacytoid dendritic cells, controls viral infection. receptors for IFN λ4 is expressed by epithelial cells of GI, respiratory, & blood-brain barrier
examples of cytokine antagonists
IL-1Ra
enzymatic cleavage of cytokine receptor: IL-2 receptor → sIL-2R
virally produced cytokine mimic pox virus: IL-1 & TNF-binding proteins inhibit inflammation
epstein barr virus: IL-10 binding protein inhibits TH cells
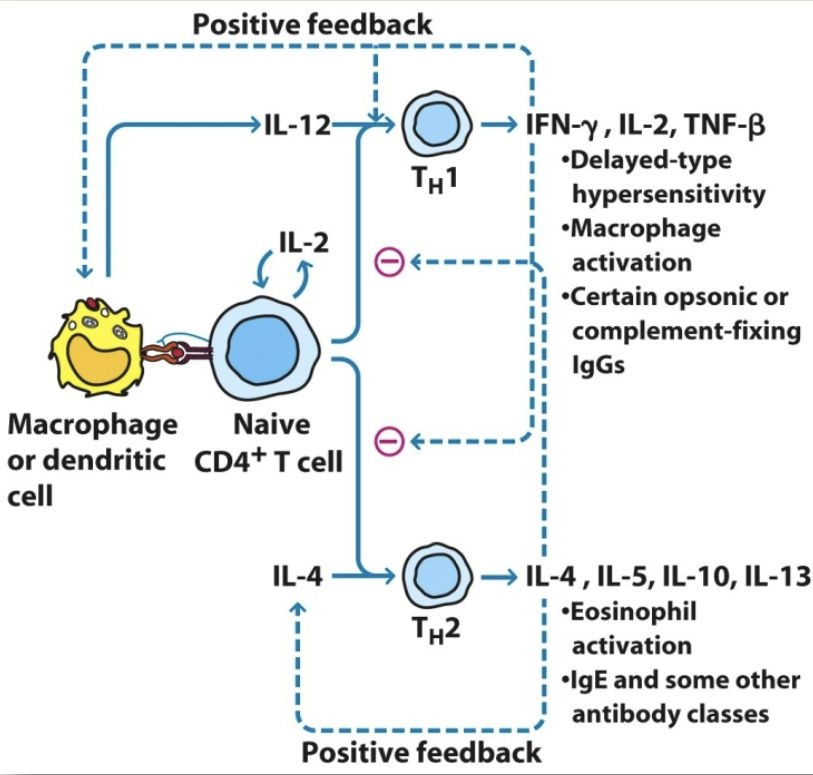
TH1 responses
delayed type hypersensitivity. macrophage activation. promotion of opsonin-complement fixing antibody
TH2 responses
eosinophil activation. help B cell function. IgM, IgE, and non-complement activating IgG isotypes
what cytokines do TH1 secrete?
IL-2, IFN-y, THF-β, GM-CSF, IL-3
what cytokines do TH2 secrete?
IL-3, IL-4, IL-5, IL-10, IL-13, GM-CSF
IFN-y functions
TH1: help for IgG2a production. macrophage activation. TC-cell activation
IL-2 functions
TH1: TC-cell activation
IL-4 + IL-5 functions
TH2: help for IgE production. eosinophil and mast-cell production
TH1 regulation
IFN-y positive feedback. IL-4 & IL-5 negative feedback
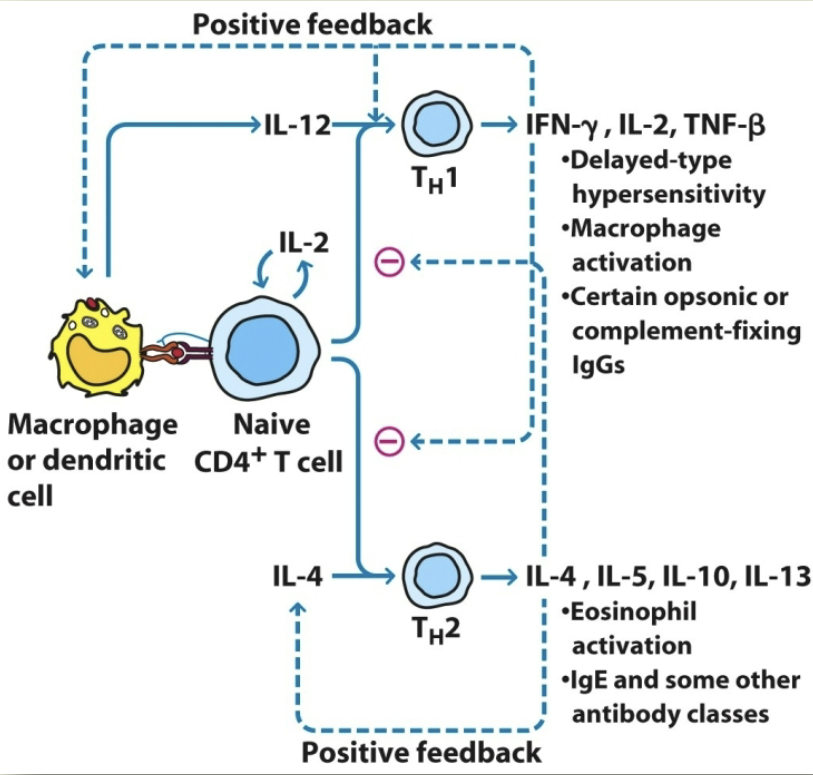
TH2 regulation
IFN-y negative feedback. IL-4 & IL-5 positive feedback
bacterial septic shock
endotoxin (LPS) in bacterial cell wall stimulates macrophages to overproduce IL-1 & TNF-α. symptoms: fever, drop in BP, diarrhea, widespread blood clotting in various organs (often fatal).
cytokine storm
release of a large amount of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-1, IL-6, TNF-α, and IFNs. caused by wide variety of infections & noninfectious diseases (and also some therapeutic approaches)
what happens during a local infection?
TNF-α induces endothelial cells to produce platelet activating factor (PAF). PAF triggers blood clotting, preventing pathogen from entering blood stream
what happens during a systemic infection?
TNF-α is released from the liver, spleen, etc. systemic release causes vasodilation, loss of plasma volume due to increased vascular permeability, and massive clotting in small blood vessels, frequently leading to organ failure
1st step of local infection w/ gram negative bacteria
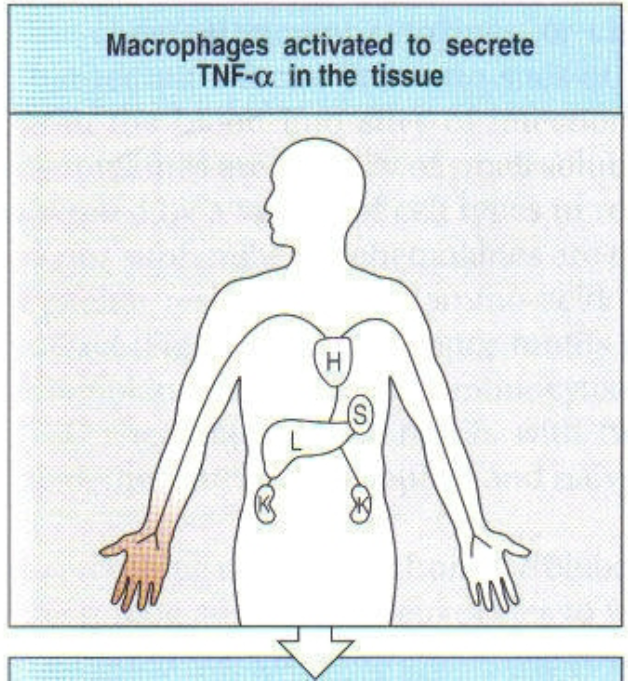
2nd step of local infection w/ gram negative bacteria
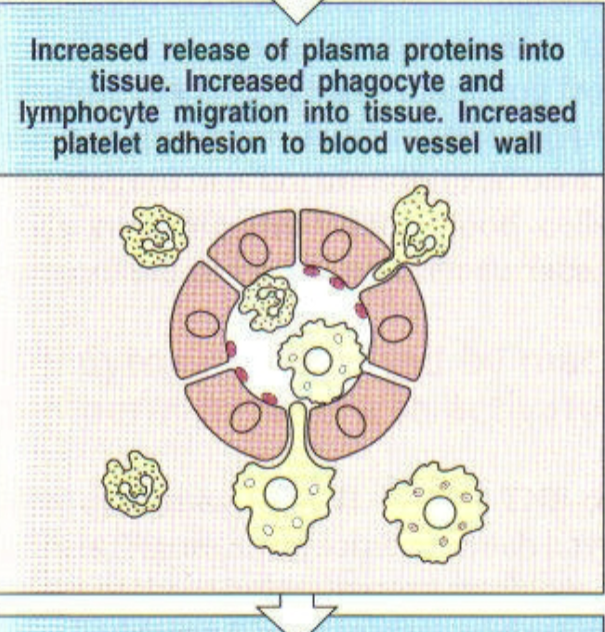
3rd step of local infection w/ gram negative bacteria
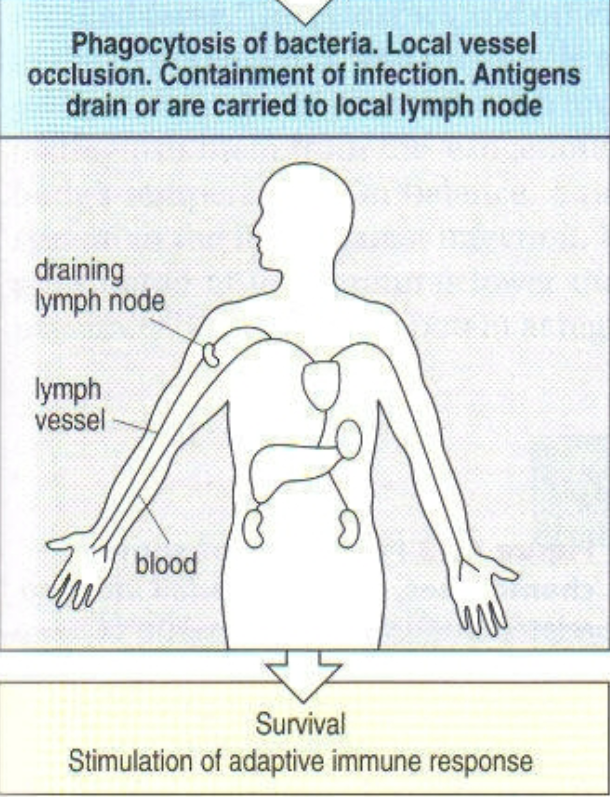
1st step of systemic infection with gram negative bacteria (sepsis)
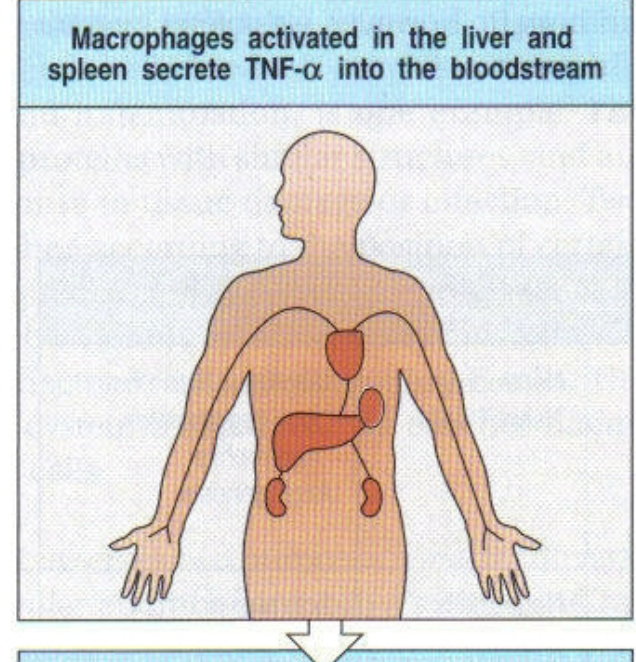
2nd step of systemic infection with gram negative bacteria (sepsis)
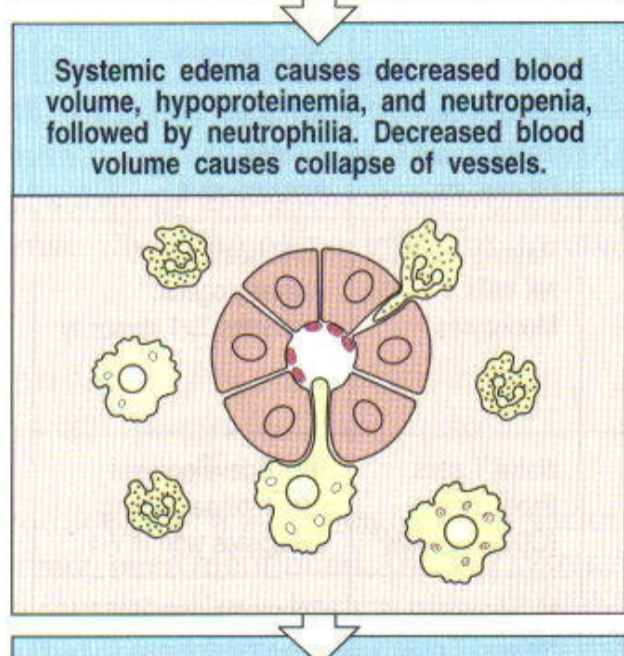
3rd step of systemic infection with gram negative bacteria (sepsis)
leprosy
infection with mycobacterium leprae. two polar forms: tuberculoid & lepromatous, but several intermediate forms also exist
tuberculoid leprosy
organisms present at low to undetectable levels. low infectivity. granulomas & local infection, peripheral nerve damage. normal serum immunoglobulin levels. normal T-cell responsiveness, specific response to M. leprae antigens
lepromatous leprosy
organisms show florid growth in macrophages. high infectivity. disseminated infection: bone, cartilage, & diffuse nerve damage. hypergammaglobulinemia. low or absent T-cell responsiveness, no response to M. leprae antigens
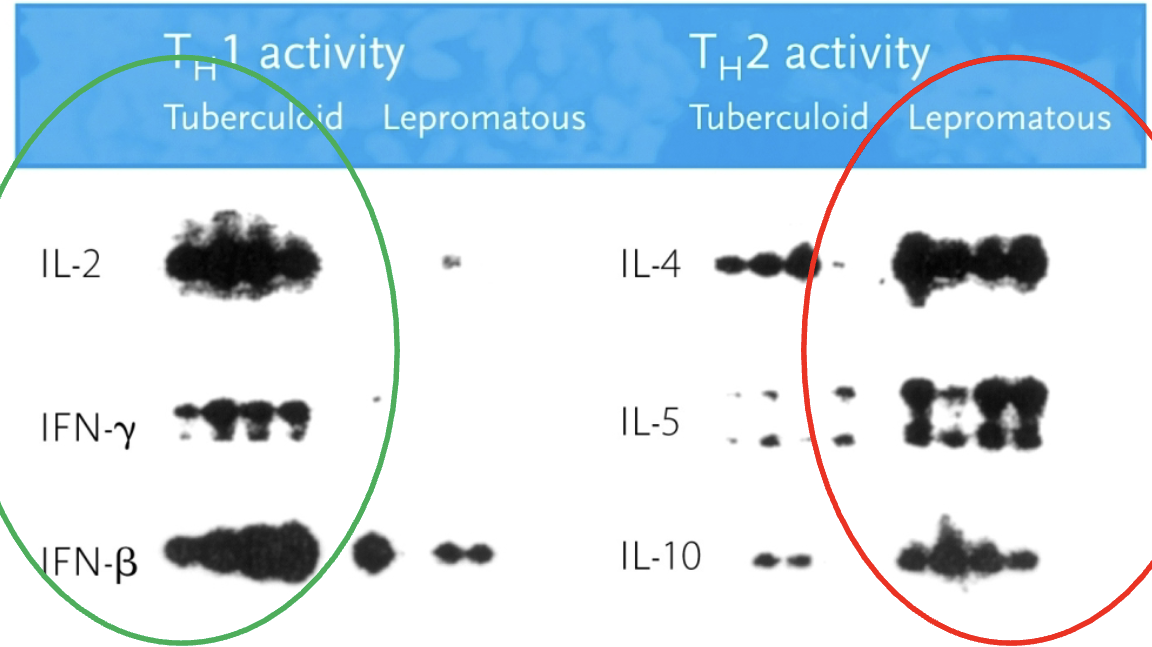
TH1 & 2 activity in leprosy
TH1 activity (IL-2, IFN-y, IFN-β) in tuberculoid leprosy. TH2 (IL-4, IL-5, IL-10) activity in lepromatous leprosy.