Exam 3: Endocrinology
1/143
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
144 Terms
which form of DM do mostly all dogs get? what is it characterized by?
Type 1, destruction of B-cells
which form of DM do mostly all cats get? what i it cahracterized by?
Type 2, insulin resistnace
Type of DM caused by diestrus, use of glucocorticoids, and pancreatitis, which may be reversible
Transient diabetes mellitus
What is the primary cause for DM in animals?
Immune-mediated destruction / resistance
Which dog breeds are predisposed to increased risk for DM?
Keeshond
terriers
schanuzers
poodles
beagles
What is the clinical triad for DM?
PU/PD
polyphagia
weight loss
What secondary findings can be seen with untreated DM in dogs?
cataracts
hepatomegaly
delayed wound healing
What diagnostic results should be seen with an animal with diabetes mellitus?
fasting hyperglycemia + glucosuria
Which diet is best used for managing a patient with diabetes mellitus
High fiber, complex carbohydrate, low fat
short acting insulin with a duration of 1-4 hours used in clinic patients can be given IV, IM, or SQ
Regular insulin (Humulin R)
FDA approved insulin which is a porcine insulin zinc suspension with a duration of 14 hours intermediate insulin
Vetsulin
Which insulin class is most often used in cats d/t thier inabilty to cope with human intervention
Long acting insulins
Glargine (Lantus)
Detemir (Levemir)
PZI (ProZinc)
Degludec and Glargine are known as _ and can be dosed once daily in cats
Basal insulin
veterinary products are _ whle human products are _
U40 and U100
Which of the following is an “intermediate-acting” insulin commonly used in dog species?
Vetsulin
Which insulin should be shaken and not rolled?
Vetsulin
which is more important tests glycemic testing with urine strips and glucosuria or physical clinical signs
physical clinical signs way more important
What is the term used for the period on a glucose curve which is half-way through the dosing interval?
Nadir
If nadir is too high on a glucose curve, what does this typically indicate?
patiet is under dosed
Term used to describe an overdose of insulin which may lead to insulin resistance and hyperglycemia
Somogyi
Which test should never call for adjustement of insulin dose without a proper glucose curve?
Spot checks
What flash glucose monitoring system can be used to make managing diabetic animals more straighforward?
FreStyle Libre
Compound which is a glycated protein that can indicate poor glycemic control with elevated levels
Fructosamine
What is fructosamine best used for?
Differentiating stress hyperglycemia and diabetes melliutus
Why is fructosamine often used in clinical settings?
can indicate longer periods of hyperglycemia up to 2 weeks prior
What is the leading cause for diabetes mellitus in felines?
Obesity
What secondary clinical sign can indicate DM in a feline patient?
Plantigrade stance
What diet is most effective when treating feline patients with DM?
High protein, low carbohydrate
type 2 DM in cats is reversible in some cases if caught early. What management should be provided to increase the likelihood of this?
treat underlying obesity
Which drug(s) are FDA approved for treating DM feline patients
Bexacat, Senvelgo (SGLT2 inhibitor)
How do SGLT2 inhibitors function?
Promote loss of glucose in the urine improving B cell function
In which circumstances are SGLT2is contraindicated?
Patient is/has receiving insulin or is clinically ill
What is the most severe side effect that can occur with cats on SGLT2is?
DKA
Insulin which are Q-12 hours in feline patients which are NOT peakless
Glargine, Detemir
Insulin which is FDA approved for cats which has Q12 hour dosing and has a more variable onset and DOA than glargine or detemir?
ProZinc
What is the ultimate goal of insulin therapy in cats?
Diabetic remission
A cat treated with SGLT2is is unknown if remission occurs
true
What diagnostic signs indicate DM in feline patients?
Hyperglycemia and glucosuria
Which of the following can cause insulin resistance?
Inflammatory cytokines in response to secondary diseases
Disease in cats which causes insulin resistance d/t a pituitary adenoma with clinical findings such as weight gain, broad face, widened interdental spaces, and respiratory stridor
Acromegaly
What is the treatment of choice for a cat surffering from acromegaly?
External beam radiation therapy
What is the treatment of choice for hyperlipidemia which can cause a secondary insulin resistance?
Low fat diet, bezafibrate r fenofibrate
Undiagnosed or poorly controlled DM may lead to what severe disease process?
Diabetic ketoacidosis
What process has to occur in order for ketones to built up in the body with a DKA patient?
Lipolysis
Ketone buildup can lead to osmotic diuresis and severe dehydration causing a build up of lactic acid. What process can excess lactic acid in the body cause?
Metabolic acidosis
What are some common clinical signs of a DKA patient?
GI (vomiting, diarrhea, anorexia), lethargy, wekaness, signs of DM
On physical examination of a patient, what finding often raises a red flag for potential DKA?
Smell of acetone breath
On urine dipstick analysis of DKA patient what will often come back positive?
Glucose and ketones
What is the FIRST treatment of choice for a patient with DKA?
fluid/electrolyte replacement
Which electrolyte must be provided for an animal with DKA? why are we providng it?
Phosphorus, blood levels will be decreased after IV fluids and insulin management
What are some clinical signs of a DKA patient being treated with fluids that may indicate hypophosphatemia?
Hemolysis, neuromuscular signs
When treating a DKA patient in clinica, what type of insulin should be provided and via what route of administration?
Regular insulin IM or CRI IV
Which species is most likely to have hypothyroidism?
canine -
what are some clinical signs of hypothyroidism
Lethargy, unwilling to exercise, mental dullness, weight gain, cold intolerant, repro issues
Bilateral truncal alopecia is most associated with which endocrine disorder?
Hypothyroidism
On physical exam, which clinical signs will you see that may indicate hypothyroidism
Hypothermia, bradycardia, myxedema
On blood work what CBC finding can be concurrent with hypothyroid animals
Decreased erythropoiesis (non-regenerative anemia)
Diagnosis of hypothyroidism must be based on _ as a low TT4 can be caused by any disease process.
clinical suspicion
A_____ TT4 rules out HypoT, but a _____ TT4 is not diagnostic alone for HypoT
Normal, low
Why may free T4 be better suited for helping diangose an animal with hypothyroidism?
less affected by sick euthyroid syndrome
This test can be used in conjunction with a TT4 to accurately diagnose hypothyroidism
TSH -
Which dog breed class normally has a lower FT4 and T4 which could be an inconsequential finding?
Sighthounds
What is the treatment of choice for hypothyroidism?
Levothyroxine
What is the earliest clinical sign that indicates a postive response to hypothyroid treatment
increased activity, 1-2 weeks
If treatment failure occurs for hypothyroidism, what other treatment option may need to be given?
T3 supplementation
Hyperthyroidism is mostly a primary disease caused by a ____ tuor
Benign
Most cats that present with hyperthyroidism are often ___ years of age
12-13 older cats
Which of the following clinical signs are mostly seen in cats with potential hyperthyroidism
Weight loss, polyphagia, hyperactivity, PU/PD
Term for animals with hyperthyroidism but present with anorexia and weight loss
Apathetic hyperthyroidism
A cat present with a poor BCS, unkempt hair coat, agitated, tachypneic, and a thyroid slip. what is tyour top differential?
Hyperthyroidism
What is the primary diagnosis which helps confirm hyperthyroidism in cats?
presenting clinical signs
A cat with a higher but still within RI thyroid level, is there need for futher evaluation?
yes further evaluation is needed
Which of the following substances is trapped and concentrated by the thyroid and can be used to diangose hyperthyroidism?
T3dhn35ium-99m
During a T3 suppression test the animal fails to suppress, is this a normal animal or not
Not a normal healhty animal
What drug is used to treat HyperT cats by inhibiting iodide incorporation?
Methimazole
How often should T4 levels in a HyperT cat be checked when recieving methimazole for signs of euthyroid?
2-3 weeks
HyperT treatent method which is trapped by the thyroid and destroys tissues within a certain distance. One time cure treatment, but expensive
Radioactive Iodine
Which type of diet can be used in cats that may help to some extent treat HyperT?
Iodine restricted diet
Majority of Cushings cases are ___ dependent
pituitary
Type of Cushings which is autonomous (non-responsive to ACTH), unilateral and episodic in nature
adrenal dependent
Overuse of glucocorticoids can cause ___ HyperA
Iatrogenic
What are some of the most common clinical signs seen with cushings patients?
Polyhagia, PU/PD, “Pot belly” appearane, symmetrical alopecia
Which of the following tests is NOT a confirmatory test for diagnosing Cushings?
Urine cortisol: creatinine
Due dogs with cushings tend to feel generally well or bad
they feel well
This rule out test is used in animals with suspected Cushings and uses a urine sample usually first of the morning
Urine cortisol: creatinine
Test which uses Cortrosyn after an initial baseline cortisol and rechecks in one hour for results
ACTH stimulation test
which of the following ACTH stimulation results indicates a response that is consistent with Cushings?
increases significantly
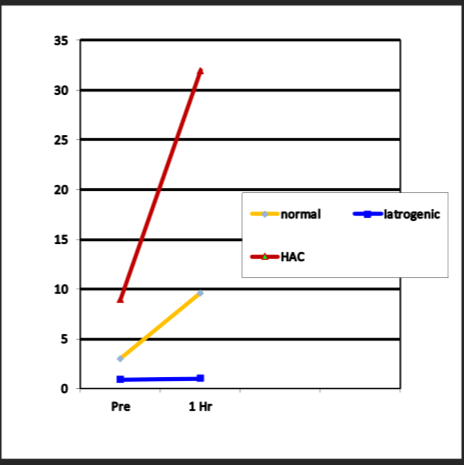
Which of the following ACTH stimulation results indicates a response that is consistent with Iatrogenic Cushings?
no change at all
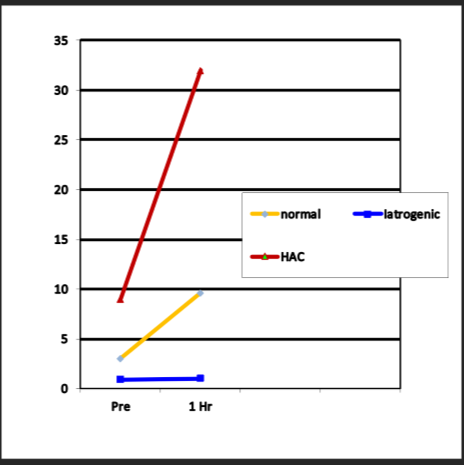
Which of the following ACTH stimulaiton results indicates a response that is consistent with a normal healhty animal?
increases a little
60% of PDH patients will ____ a LDDST
suppress
When should cortisol levels be taken after administrating dexamethasone for a LDDST?
4 and 8 hours
Which of the following is consistent with a normal healthy response to LDDST?
light blue
starts high slowly decreases
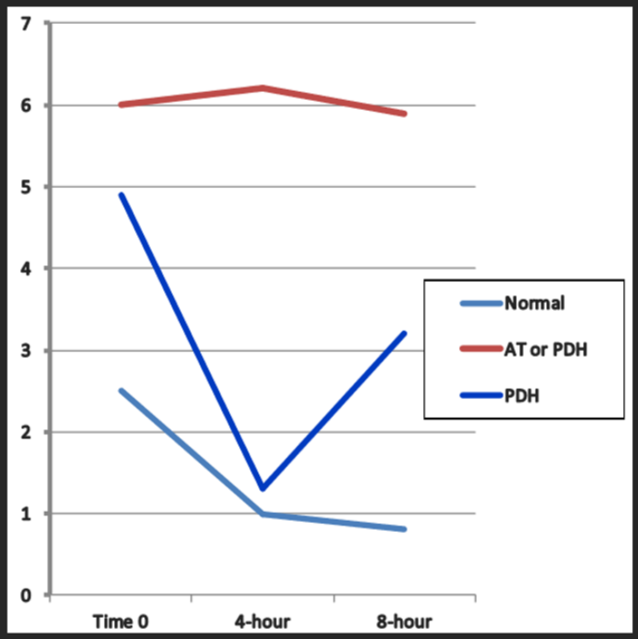
Which of the following is consistent with a PDH repsonse to LDDST?
Dark blue / red
starts high decreases fast and goes back up again fast
or atypical red
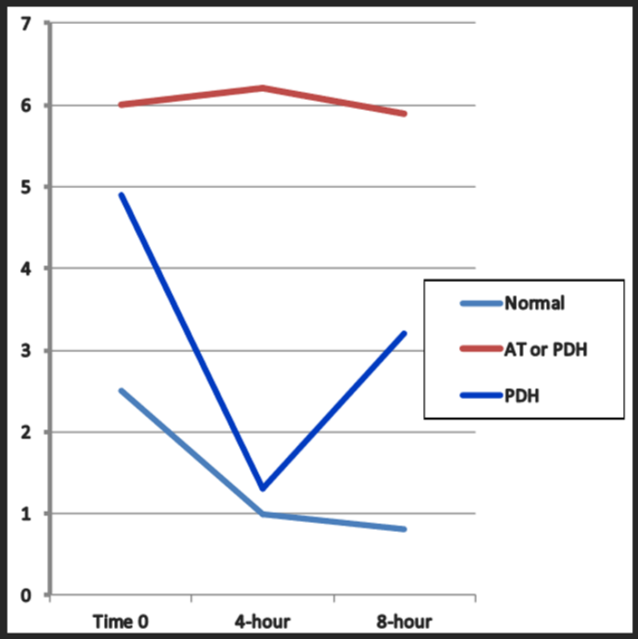
Which of the following is consistent with a AT or PDH response to LDDST?
red
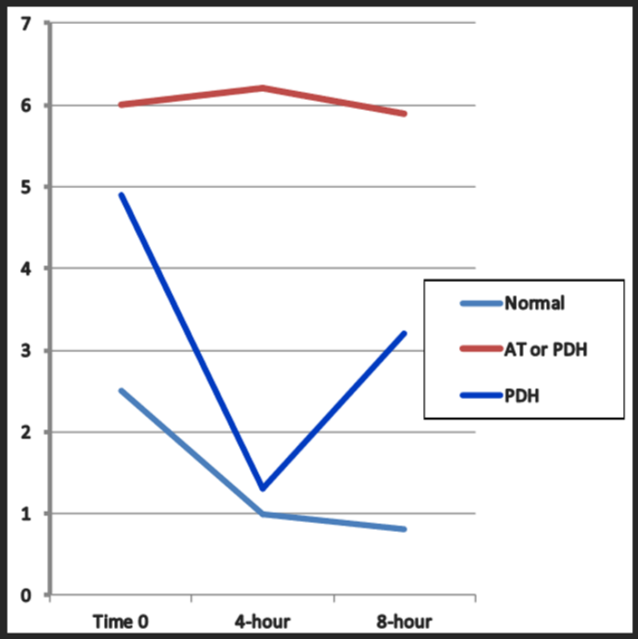
On a LDDST, an animal which suppresses, then escapes is ALWAYS ____
PDH
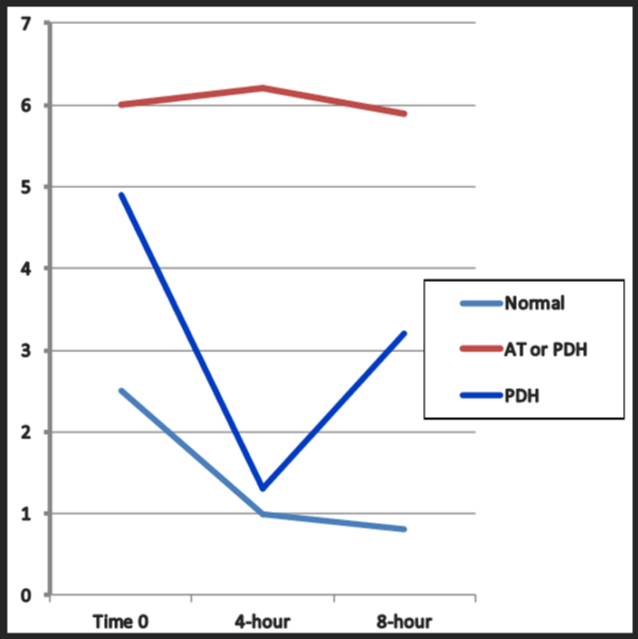
When ultrasounding an adrenal gland, which of the following is most associated with a functional adrenal tumor (FAT)?
one large and irregular adrenal gland, contralateral gland atrophy
When ultrasounding an adrenal gland, which of the following is most associated with PDH?
Bilaterally symmetric normal or enlarged glands
When ultrasounding an adrneal gland, which of the following is most associated with Iatrogenic hyperadrenocorticism? (IH)
Bilaterally small adrenal glands
Which of the following treatments can be used for PDH patients which can inhibit the synthesis of cortisol?
Trilostane, Ketoconazole
FDA approved PDH/FAT medication for dogs suffering from Cushings which comeptitively inhibits 3-b-hydroxysteroid dehydroganse
Trilostane