3.6- Social-Emotional Development Across the Lifespan
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
Ecological Systems Theory
Views the person as developing within a complex system of relationships affected by multiple levels of the surrounding environment
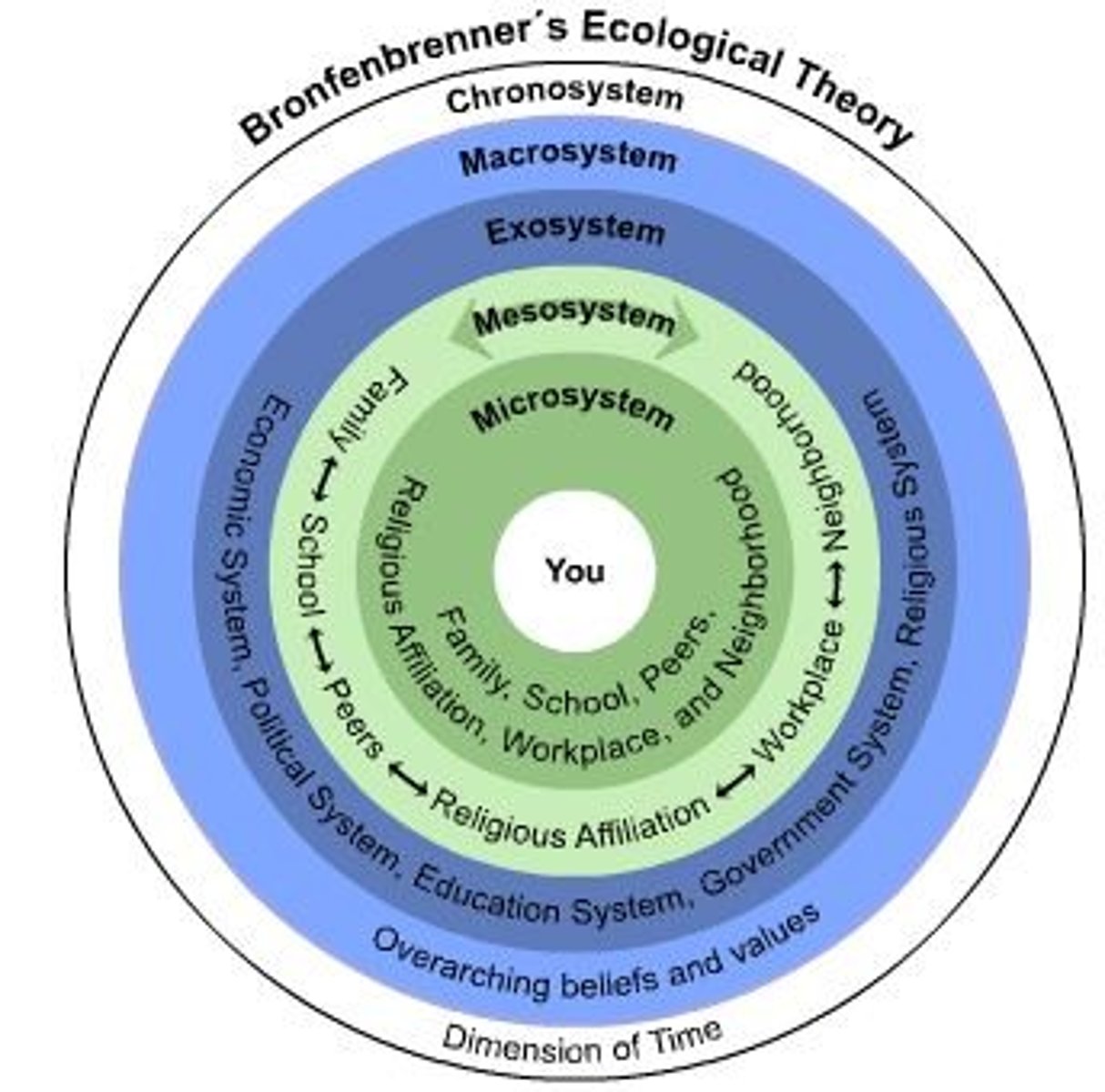
Microsystem
The people and objects in an individual's immediate environment
Mesosystem
Provides connections across microsystems
Exosystem
Social settings that a person may not experience firsthand but that still influence development
Macrosystem
Consists of cultural values, laws, customs, and resources
Chronosystem
Time
Authoritarian Parenting Style
Parents place a high value on conformity and obedience, are often rigid, and express little warmth to the child
Authoritative Parent Style
Parenting style in which parents set clear standards for their children's behavior but are also responsive to their children's needs and wishes
Permissive Parenting Style
A parenting style that allows freedom, lax parenting that doesn't set limits or enforce rules constantly
Attatchement
The positive emotional bond that develops between a child and a particular individual
Temperament
Aa person's characteristic emotional reactivity and intensity
Secure Attachment
A relationship in which an infant obtains both comfort and confidence from the presence of his or her caregiver
Avoidant Attachment
Infants who seem unresponsive to the parent when they are present, are usually not distressed when she leaves, and avoid the parent when they return
Anxious Attachment
Demonstrated by babies who seem constantly afraid of potential separation from the caregiver; they cling to caregivers in strange settings and display intense distress upon separation
Disorganized Attachment
A type of attachment that is marked by an infant's inconsistent reactions to the caregiver's departure and return
Separation Anxiety
Emotional distress seen in many infants when they are separated from people with whom they have formed an attachment
Monkey Attachment Experiment
The monkey prefered the contact comfort from the cloth mother rather than the food from the wired mother
Parallel Play
Activity in which children play side by side without interacting
Imaginary Audience
Adolescents' belief that they are the focus of everyone else's attention and concern
Personal Fable
Type of thought common to adolescents in which young people believe themselves to be unique and protected from harm
Adult Relationships
Support & care
Social Clock
The culturally preferred timing of social events such as marriage, parenthood, and retirement
Emerging Adulthood
For some people in modern cultures, a period from the late teens to mid-twenties, bridging the gap between adolescent dependence and full independence and responsible adulthood
Trust vs Mistrust
Erikson's first stage during the first year of life, infants learn to trust when they are cared for in a consistent warm manner
Autonomy vs Shame and Doubt
Erikson's second stage in which a toddler learns to exercise will and to do things independently; failure to do so causes shame and doubt
Initiative vs Guilt
Erikson's third stage in which the child finds independence in planning, playing and other activities
Industry vs Inferiority
Erikson's fourth stage between 6 and 11 years, when the child learns to be productive
Identity vs Role Confusion
Erikson's fifth stage during which teenagers and young adults search for and become their true selves
Intimacy vs Isolation
Erikson's sixth stage in which individuals form deeply personal relationships, marry, begin families
Generativity vs Stagnation
Erikson's seventh stage of social development in which middle-aged people begin to devote themselves more to fulfilling one's potential and doing public service
Integrity vs Despair
Erikson's eighth stage in which those near the end of life look back and evaluate their lives
Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACEs)
Stressful or traumatic experiences, including abuse, neglect, and a range of household dysfunction, such as witnessing domestic violence or growing up with substance abuse, mental disorders, parental discord, or crime in the home
Identity Diffusion
An apathetic state characterized by lack of both exploration and commitment
Identity Foreclosure
Commitment in the absence of exploration
Identity Moratorium
Exploration without having reached commitment
Identity Acheivement
Commitment to values, beliefs, and goals following a period of exploration
Possible Self
Person's conceptions of the self as it potentially may be; may include both an ideal self and a feared self