MLSP 112 FINALS
1/372
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
373 Terms
it the transporting fluid of the body
blood
percentage of plasma in blood composition
55%
percentage of formed elements in blood composition
45%
examples of granulocytes
basophils
eosinophils
neutrophils
examples of agranulocytes
monocytes
lymphocytes
how thick is blood compared to water?
about five times thicker
what is the taste of bood?
salty
what is the pH level of blood?
7.4 slightly alkaline
blood volume of average adult weighing 70 kg
5 liters
it is a clear, pale-yellow liquid
plasma
composition of plasma
90% water, 10% solutes
gases of plasma
O2
CO2
N
minerals of plasma
Na
K
Ca
Mg
nutrients of plasma
carbohydrates
lipids
proteins of plasma
albumin
fibrinogen
antibodies
waste products of plasma
BUN
uric acid
creatinine
normal quantity of Erythrocytes in male
4.5 - 6.2 million/mm³
normal quantity of Erythrocytes in female
4.2 - 5.4 million/mm³
normal quantity of Leukocytes
5,000-10,000/mm³
normal quantity for Thrombocytes
150,000-450,000/mm³
average of MOST NUMEROUS CELLS in the blood
4.5 - 5 million/mm³
appearance of a shape of a doughnut without a hole is referred to as
bioncave
size of bioncave
7-8 microns
life span of erythrocyte
120 days
Ability to transport oxygen and carbon dioxide occurs as a result of a very important molecule, called
hemoglobin
Hemoglobin is made up of a protein molecule called
globin
an iron compound called
heme
when large amounts of oxygen attached to the hemoglobin in the RBC
bright red color (oxygenated)
when large amounts of carbon dioxide are attached to hemoglobin in the RBC
dark bluish red (deoxygenated)
what is the Hemoglobin Reference Values of an adult male
14-18 g/dl
what is the Hemoglobin Reference Values of an adult female
12-16 g/dl
primarily responsible for destroying foreign substances
leukocytes
WBC can pass through the thin walls of capillaries to enter the tissues
diapedesis
WBCs engulf or “eat” foreign substances and/or cellular debris
phagocytosis
how much of WBC does an average adult have?
5,000-10,000/mm³
granules are present in the cytoplasm
granulocytes
no granules are present
agranulocytes
it is the first to repond to bacteria or a virus
neutrophils
fight infection by producing antibodies
lymphocytes
it is known for their role in allergy symptoms
eosinophils
it clean up dead cells
monocytes
it is known for their roles in asthma
basophils
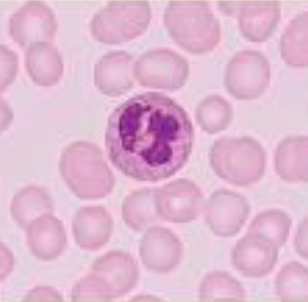
it has distinct nuclei with many lobes
neutrophils
Cytoplasm stains pale pink and contains fine granules, which are difficult to see; deep purple nucleus consist of three to seven lobes connected by thin strands of nucleoplasm
neutrophils
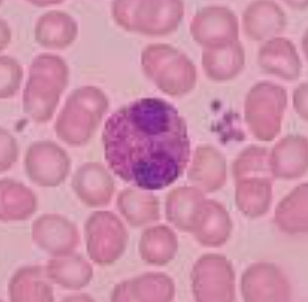
have cytoplasmic granules that stain red
eosinophils
assist in inflammatory responses; it secrete chemicals that destroy parasites; levels inscrease with allergies and parasitic infection (stain red-orange)
eosinophils
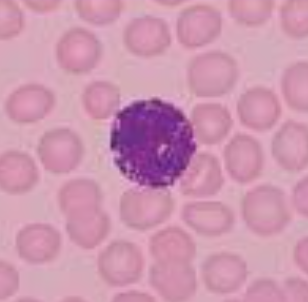
have cytoplasmic granules that stain deep blue
basophils
assist with inflammatory response by releasing histamine and heparin; it produces vasodilator (stain dark blue or blue-black)
basophils
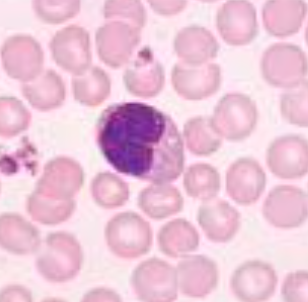
kidney shaped nuclei
monocyte
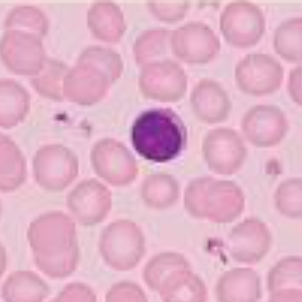
it has a large round nuclei
lymphocyte
it produces antibodies
lymphocytes
smallest in size of all the cellular components
platelets
life span of platelets
9-12 days
bleeding is diminished or halted as a result of platelets sticking to the site of injury
platelet plug
causes the blood vessels to spasm or narrow and decrease blood loss until the clot forms
serotonin
hemostasis stage
vasoconstriction
platelet plug
coagulation
fibrinolysis
it means blood
hemo
it means stopping
stasis
the study of the formed (cellular) elements of the blood
hematology
blood is analyzed in the form of
whole blood, plasma, serum
the most common body fluid analyzed in the hematology section is
whole blood
whole blood specimen is obtained by using
EDTA and Citrate
method for hemoglobin estimation
cyanmethemoglobin
is the volume of packed RBCs that occupies a given volume of whole blood
hematocrit
Correlation checks between the Hgb and Hct are a significant part of quality assurance for the CBC and are known as the
rule of three
unit of Mean Corpuscular Volume
femtoliters
unit of Mean Cell Hemoglobin
picograms
is the average volume of the RBC
Mean Corpuscular Volume
is the average weight of hemoglobin in an RBC
Mean Cell Homoglobin
is the average concentration of hemoglobin in each individual erythrocyte
Mean Cell Hemoglobin Concentration
is used to assess the erythropoietic activity of the bone marrow
reticulocyte count
in reticulocyte count, whole blood, anticoagulated with EDTA, is stained with a
supravital stain
it measures how quickly erythrocytes settle at the bottom of a test tube
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
useful for monitoring the course of an existing inflammatory disease or for differentiating between similar diseases
ESR
use blood collected in EDTA and dilute at four parts blood to one part
modified westergren method
the phlebotomist used a lancet to make a small, controlled puncture wound and recorded the duration of bleeding
bleeding time
reference interval of bleeding time
2-9 minutes
bleeding time test was first described by
Duke 1912
modified bleeding time
Ivy 1941
attempted to standardize the bleeding time by specifying a lancet that used a template to establish incision depth
Mielke 1969
a calibrated spring-loaded lancet was developed
1976
The device was triggered on the volar surface of the forearm a few inches distal to the antecubital crease, and the resulting wound was blotted every 30 seconds with filter paper until bleeding stopped
Surgicutt Bleeding Time Device
it was the first in vitro clot procedure that employed the principle that the time interval from the initiation of clotting to visible clot formation
Lee-White whole blood coagulation time
a prolonged clotting time indicates a
coagulopathy
modification of ACT
1953
uses a particulate clot activator in the test tube, which speeds the clotting process
Activated Clotting Time
PT reagent
thromboplastin
typical PT reference interval is
12.6 - 14.6 seconds
is prolonged in multiple factor deficiency disorders that include deficiencies of factors VII and X
prothrombin time
The tissue factor-phospholipid-calcium chloride reagent is warmed to
37 C
volume for PPP in PT
50-100 mL
is employed to monitor the effects of UFH (Unfractionated Heparin) and to detect LAC (Lupus Anticoagulant)
partial thromboplastin time
PTT reagent
phospolipid
PTT reference interval
26-38 seconds
a bank of blood and their components, gathered as a result of blood donation
blood bank
a least 70% of cells that have been transfused should remain viable for
24 hours
blood is stored in the liquid state in what temperature
1℃ and 6℃
ACD and its shelf life
acid citrate dextrose 21 days
CPD and its shelf life
citrate phosphate dextrose 21 days
CP2D and its shelf life
citrate phosphate double dextrose 21 days