PSY 200 EXAM 1
5.0(1)
Card Sorting
1/99
Earn XP
Last updated 1:20 AM on 2/7/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
100 Terms
1
New cards
What is the method of introspection?
participants report their own mental processes
2
New cards
What are weaknesses of the introspection method?
results vary from person to person, difficult to verify
3
New cards
What is behaviorism?
studies observable behaviors (stimulus-->response)
4
New cards
What are some critiques of behaviorism?
doesn't account for generative learning, genetic influences, critical periods, or cognitive strategies
5
New cards
What is generative learning?
when learners construct meaning actively while integrating new ideas into their knowledge base (eg. children constructing new sentences while learning to speak)
6
New cards
What is a critical period?
a period during someone's development in which a particular skill or characteristic is believed to be most readily acquired.
7
New cards
What are the three assumptions of an information processing model?
Humans process information, processes act on representations of objects and events, and cognition involves sequential steps
8
New cards
What did Descartes believe about the pineal gland?
It was the seat of the soul (ventricles controlled brain function)
9
New cards
What is phrenology?
Pseudoscience that claimed that bumps on the skull corresponded with different traits or mental abilities, though no one agreed on the number of mental organs. Used in social Darwinism to justify slavery.
10
New cards
Define localization of function
different parts of the brain contribute to different kinds of information processing
11
New cards
What is a homonculus?
"tiny man" model mapping the body according to the sensory space each part takes up in the cerebral cortex
12
New cards
what is specificity coding?
a single cell codes for a single stimulus
13
New cards
what is distributive coding?
multiple cells fire for a stimulus, and the pattern of firing differs with each stimulus
14
New cards
What are the advantages of distributive coding?
many stimuli can be represented by only a few cells (more efficient use of the brain's resources)
15
New cards
what is hierarchical processing?
the brain processes visual stimuli starting with low level features and moving up in complexity
16
New cards
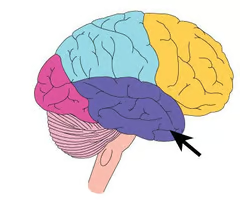
Where is the temporal lobe located? What are its functions?
functions: hearing, learning, feelings
17
New cards
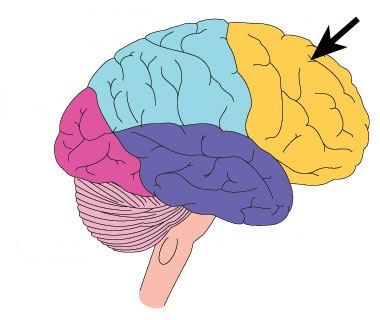
Where is the frontal lobe located? What are its functions?
functions: thinking, memory, behavior, and movement
18
New cards
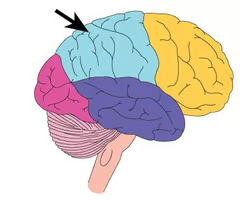
Where is the parietal lobe located? What are its functions?
functions: language and touch
19
New cards
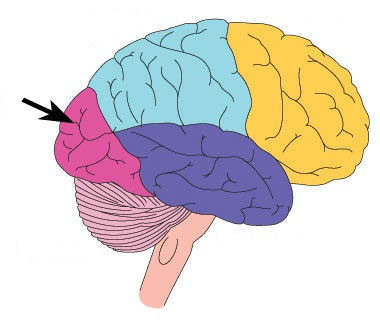
Where is the occipital lobe located? What are its functions?
function: vision
20
New cards
Where is the cerebellum located and what are its function?
functions: balance and coordination
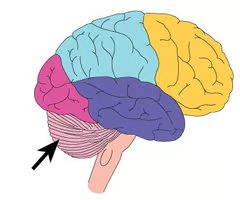
21
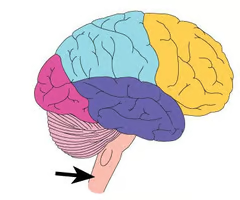
New cards
where is the brain stem located and what are its functions?
functions: breathing, heart rate, temperature
22
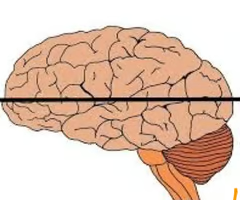
New cards
what does the horizontal view of the brain look like?
23
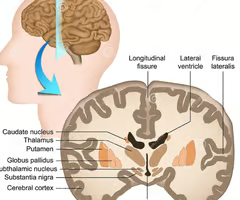
New cards
what does the coronal view of the brain look like?
24
New cards
what does the sagittal view of the brain look like?
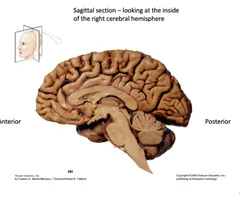
25
New cards
what is an example of a double dissociation?
people with Wernicke's aphasia can't understand words due to damage to the Wernicke's area, meanwhile people with Broca's aphasia can't produce words due to damage to the Broca area. different lesions, opposite effects.
26
New cards
what are three limitations of lesion studies?
small samples, no comparative data from before the injury, confounds due to source of damage
27
New cards
What is TMS?
transcranial magnetic stimulation \n creates temporary lesions through sending magnetic stimulation to the scalp
28
New cards
Pros of TMS
simulates lesions and allows for causal inferences \n noninvasive
29
New cards
What is EEG?
electroencephalography \n measures event related potentials at the scalp
30
New cards
Cons of TMS
Can only target superficial cortical areas \n \n Stimulates regions other than target \n \n Uncomfortable
31
New cards
Pros of EEG
good temporal resolution \n inexpensive
32
New cards
What is fMRI?
functional magnetic resonance imaging \n scanner measures blood oxygen level-dependent (BOLD) signals
33
New cards
Cons of EEG
coarse spatial resolution \n caps not always inclusive for all hair types
34
New cards
Pros of fMRI
great spatial resolution \n can identify networks of regions associated with a task
35
New cards
Cons of fMRI
low temporal resolution \n indirect measure of neuronal activity
36
New cards
How is behavior research overlooked?
Because neuroscience has more quantitative and technology driven findings, it is often invested in more than behavioral research, even though we have learned more about the brain through behavioral studies than from neuro research.
37
New cards
sensation vs perception
Sensation is arrival of info to brain, perception is interpretation of info in the brain
38
New cards
What is sensory adaptation?
diminished sensitivity as a consequence of constant stimulation
39
New cards
Define synesthesia
a condition where people experience involuntary perceptions that cross over sensory modalities.
40
New cards
list three challenges of visual perception
visual ambiguity \n inverse projection problem \n invariance
41
New cards
What is visual ambiguity?
one object could be perceived as multiple different objects

42
New cards
What is the inverse projection problem?
an image on the retina can be caused by an infinite number of objects
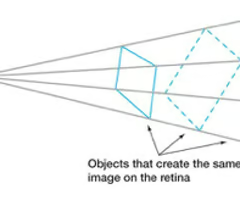
43
New cards
What is invariance?
the same object looks different from every angle

44
New cards
What is the blind spot?
the point at which the optic nerve leaves the eye, creating a "blind" spot because no receptor cells are located there
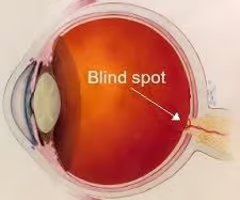
45
New cards
What are the 5 Gestalt Principles?
proximity, similarity, closure, continuity, simplicity
46
New cards
Define the gestalt principle of proximity
things that are close to one another seem to belong together
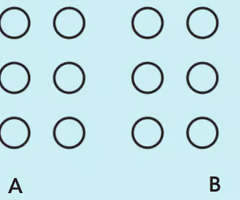
47
New cards
define the gestalt principle of similarity
people tend to group stimuli that are similar

48
New cards
define the gestalt principle of closure
People will group elements to create a sense of closure or completeness

49
New cards
define the gestalt principle of continuity
objects with smooth edges are seen as continuous
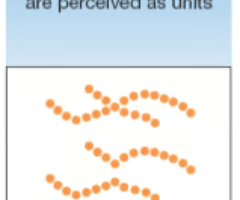
50
New cards
define the gestalt principle of simplicity
people assume the simplest objects possible

51
New cards
What are the cultural differences in the Muller-Lyer illusion?
the illusion is more pronounced in western cultures, possibly due to living in a "carpentered world"
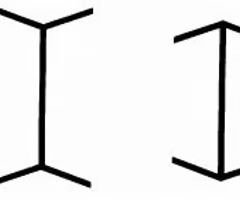
52
New cards
What is bottom-up processing?
stimulus affects our perception, data driven (content)
53
New cards
What is top-down processing?
Experience influencing the perception of stimuli (context)
54
New cards
Define reconstual
our perception of an image can change based on suggestion
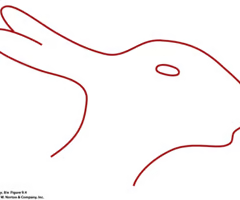
55
New cards
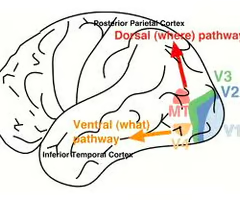
what is the ventral visual stream?
moves to the temporal lobe, tells us what it is
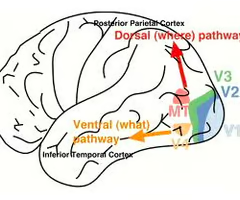
56
New cards
what is the dorsal visual stream?
moves to the parietal lobe, tells us where it is
57
New cards
What is the fusiform face area?
The FFA is the location that is activated when we see faces.
58
New cards
What is the other-race effect?
poorer recognition of other-race than own-race faces \n exposure to other races before age 12 can mitigate this (critical period)
59
New cards
What is the expertise hypothesis?
faces aren't particularly special, the FFA responds to anything greatly familiar to a person, including faces. (eg. a car expert when they see a car)
60
New cards
What is the Parahippacampal place area
The PPA is the location of the brain activated when we see places.
61
New cards
What is wishful seeing?
people subconsciously alter their perception toward their preferences
62
New cards
How does meaning of our work affect our attention?
The more meaningful we find a task, the easier we can pay attention
63
New cards
How does difficulty affect our attention?
If a task is too hard or too easy it gets harder to pay attention, the difficulty level has to be "just right"
64
New cards
What is attention?
a concentration or focusing of mental activity and resources
65
New cards
How does attention relate to consciousness?
Attention refers to the mental processes that set priorities for mental functioning, it determines the content of consciousness
66
New cards
What is the filter theory of attention?
our brains filter through sensory information so only one information source at a time is given awareness and transferred to working memory
67
New cards
What is change blindness?
failing to notice changes in the environment
68
New cards
What is inattentional blindness?
failing to see visible objects when our attention is directed elsewhere
69
New cards
What is an attentional blink?
Second of two stimuli cannot be identified when it closely follows (100-500ms) the first
70
New cards
disjunctive vs conjunctive search
disjunctive search is looking for what "pops out," so you look through everything in parallel \n conjunctive search takes more time because the items are similar at first glance, serial search
71
New cards
What is feature integration theory?
Suggests that there are two stages when perceiving objects: the pre-attentive stage (low level features) and the focused attention stage (conjunctive)
72
New cards
exogenous vs endogenous attention
exogenous: controlled by lower brain functions (automatic) \n endogenous: controlled by executive systems and the frontal lobe (voluntary)
73
New cards
location vs object theories of attention
whether attention is directed to a point in space or to objects that occupy various locations
74
New cards
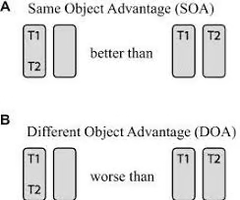
What is same-object advantage?
focusing on two different features on the same object is easier than when they are points on different objects. This is eliminated when spatial cues are given in advance
75
New cards
What is Chun and Potter's Two Stage Theory?
First stage: individual item is presented and recognized \n Second stage: 2nd item presented and only basically recognized, not remembered
76
New cards
Is there one kind of attention, or does attention do different things in different situations?
Attention does different things in different situations
77
New cards
What is the purpose of attention? How does it help us to deal with the outside world?
attention lets us filter through the stimuli of the outside world and sort it into levels of focus
78
New cards
Does attention change over space and time, or does it follow where we're looking and our current level of alertness?
Our attention follows where we guide it and is dependent upon our alertness/ investment in a task
79
New cards
What is language?
system of communication using sounds or symbols that enables us to express our feelings, thoughts, ideas, and experiences
80
New cards
What are the key attributes of language?
arbitrary, structured, generative, dynamic
81
New cards
what are phonemes?
smallest unit of sound
82
New cards
what are morphemes?
smallest unit of meaning
83
New cards
what is semantic ambiguity?
expressions have multiple meanings out of context \n Either lexical or syntactic
84
New cards
give an example of lexical ambiguity
I saw her duck
85
New cards
give an example of syntactic ambiguity
The chicken is ready to eat
86
New cards
garden path sentences
sentences that begin by appearing to mean one thing, but then end up meaning something else
87
New cards
What is coarticulation?
The influence of preceding and following sounds on how speech sounds are produced
88
New cards
What are disfluencies?
Pauses , repeats, filler words, corrections
89
New cards
What is the good-enough approach to language?
we don't deeply process every single part of language, and we often skip over details
90
New cards
What is the Moses illusion?
an example of good-enough language processing (you don't notice that notice that Moses is mentioned instead of Noah)
91
New cards
What is the McGurk effect?
visual input can conflict and misrepresent what we are hearing
92
New cards
What is the phonemic restoration effect?
"fill in" missing phonemes based on context of sentence and portion of word presented
93
New cards
What is categorical perception?
Perceived sound changes from one category to another at one point, rather than gradually
94
New cards
What is speech segmentation?
the ability to tell when one word ends and another begins even without pauses--- infants can do this
95
New cards
What is the word frequency effect?
we respond more rapidly to high-frequency words than to low-frequency words
96
New cards
What is meaning dominance?
some meanings of words occur more frequently than others, and we are more likely to perceive that meaning first
97
New cards
What is the Sapir-Whorf hypothesis?
language shapes how people experience their world
98
New cards
What aspects of language can primates understand?
displaced reference, lexigrams, individual signs
99
New cards
What are limitations of teaching primates language?
extensive training, inflexible vocal anatomy, can only respond to questions, lack of recursive grammar
100
New cards
what are the benefits of bilingualism?
does not cause delays in language learning \n requires more executive control than being monolingual, \n protects older adults from declines, \n facilitates perspective taking