Supporting Connective Tissues and Bone Structure
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
A collection of vocabulary flashcards based on the supporting connective tissues and bone structure concepts outlined in the lecture notes.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Supporting Connective Tissues: Cartilage
Specialized, resilient, and smooth, connective tissue that supports body structures, provides flexibility, and reduces friction in joints. Compose of chondrocytes within a firm gel matrix it acts as a shock absorber.
Hyaline Cartilage
A type of cartilage characterized by a translucent matrix, providing stiff but flexible support, found in various locations such as between ribs and sternum.
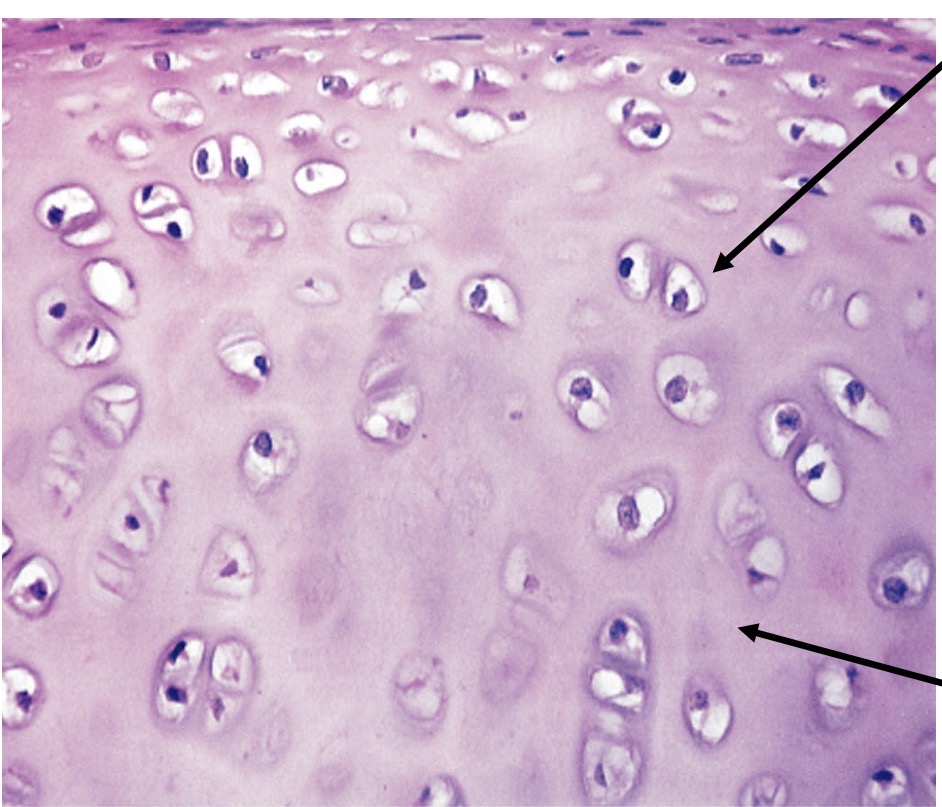
Articular Cartlidge
Type of hyaline Cartlidge (no perichondrium)
Lacunae
Small chambers in which chondrocytes or osteocytes are located within cartilage or bone tissue.
Cartlidge Matrix
Firm gel containing chondrin. Physical properties depend on protein, fibers in matrix, matrix prevents cellular movement.
Chondrocytes (mature Cartlidge) and chondroblasts (immature cartilage)
Cells in the cartilage matrix found in small chambers called lucunae
Perichondrium
A layer of dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds some types of cartilage, providing mechanical support and protection.
Perichondrium outer fibrous layer
Dense irregular connective tissue, mechanical support, protection, and attachment
Perichondrium Inner cellular layer (chrondrogenic layer)
Where Cartlidge grows (during development) and is maintained
Avascular
Referring to tissues that lack blood vessels, such as cartilage, which limits their ability to regenerate.
Appositional Growth
A type of cartilage growth where new layers of matrix are added to the surface by new chondroblasts from the perichondrium. Causes Cartlidge to expand and widen (becomes thicker) helps to maintain the weight of an individual
Interstitial Growth
Growth of cartilage that occurs when chondrocytes divide and secrete more matrix from within. Growth and length. Mainly occurs during childhood and adolescence.
Three types of cartilage
Hyaline, elastic, and fibrous
Fibrous cartilage
The strongest type of cartilage, rich in collagen fibers, providing tensile strength. Prevents bone to bone contact, limits relative movement, resistance compression, and located in structures like intervertebral discs, pads within knee joint, between pubic bones of pelvis
Elastic Cartilage
A type of cartilage containing thread, like network elastic fibers, allowing it to maintain shape while being flexible. Found in the epiglottis and supports the external ear
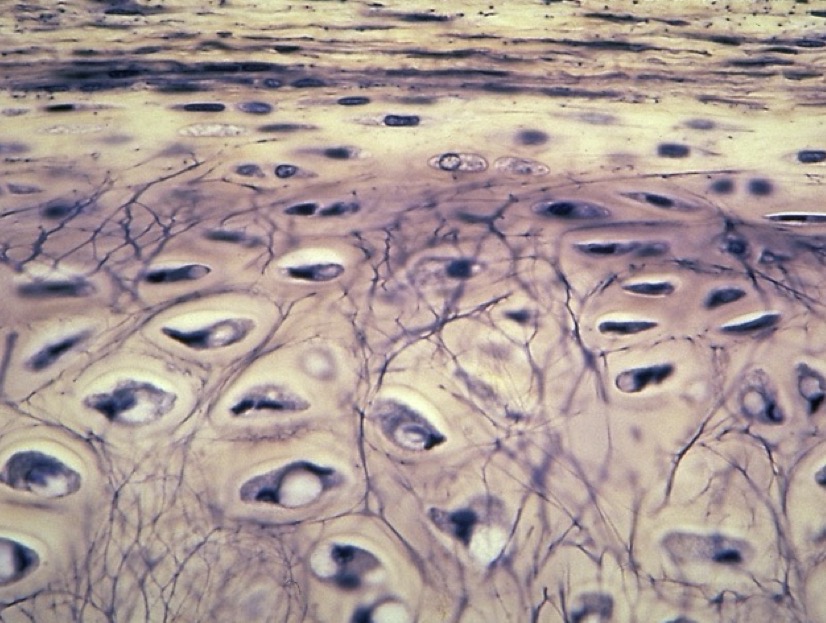
The four types of specialized cells in bones
Osteocyte, osteoblast, osteogenic cell, and osteoclast
Functions of skeletal system (bone)
Support, protection, movement (with muscular system), stores minerals (calcium, phosphate), blood cell production (marrow)
Structure of bone: two types of osseous tissue
Compact bone (dense bone) and spongy bone (trabecular bone)
Compact bone (dense bone)
Dense and solid, forms the walls of bone outlining the medullary cavity, medullary cavity consist of bone marrow. Made of stacks of osteons.
Spongy bone (trabecular bone)
Open network of plates. No central canal, blood vessels weave through the trabeculae, cells receive nutrients from the canaliculi, bone marrow is present, and no osteons
Diaphysis
Shaft of a bone
Epiphysis
End of a bone
Metaphysis
Middle of shaft and end a bone
Blood vessels bone
Well vascularized, a large blood supply
Medullary cavity
Hollow cavity inside bone, filled with marrow
Ossification
Bone development and growth. Intramembranous and endochondral
Endochondral Ossification
A process of bone development where cartilage is replaced by bone tissue, typically in weight-bearing bones. Replacement of existing chondrocytes by osteoblast. Occurs in all other bones that bear weight.
Intramembranous Ossification
The process of bone formation where mesenchyme transforms directly into bone, typical for certain flat bones. Replacement of mesenchyme by osteoblasts. Forms the clavicle, mandible, flat bones of face, and skull
Osteoblasts
Immature bone cells that secrete organic components of the bone matrix.
Osteoclasts
Large multinucleated cells responsible for the resorption of bone tissue.
Osteocytes
Mature bone cells that maintain the bone matrix and reside in lacunae.
Bone remodeling stage one
Hematoma formation, a mass of clotted blood forms at the fracture site
Bone remodeling stage two
Break a splintered by a fibrocartilage callus, mass of connective repair tissue
Bone remodeling stage three
Bony callus formation (spongy bone)
Bone remodeling stage four
Healed fracture
Rickets
Vitamin D, calcium, or phosphate deficiency. Soft., weak bones occurs in children.
Osteogenesis imperfecta
Brittle bone disease. Caused by abnormal type one collagen synthesis. Resulting in bone, fragility and susceptibility to fractures.
Achondroplasia (dwarfism)
Bones do not grow, genetic reduction of growth hormone
Gigantism
Excess growth hormone before the epiphyseal plates
Epiphyseal Plate
A layer of hyaline cartilage that allows for growth in the length of long bones during childhood and adolescence.