Davidson Unit 10 Digestive System
5.0(2)Studied by 42 people
Card Sorting
1/86
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:00 AM on 4/27/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
87 Terms
1
New cards
functions of digestive system
1. ingestion (taking in food)
2. propulsion (movement of food)
3. digestion + absorption (breaking down food & taking in nutrients)
4. egestion (elimination of waste)
2. propulsion (movement of food)
3. digestion + absorption (breaking down food & taking in nutrients)
4. egestion (elimination of waste)
2
New cards
2 sections of digestive system:
alimentary canal (GI tract) & accessory organs
3
New cards
alimentary canal--
mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine
4
New cards
accessory organs--
teeth, tongue, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, pancreas
5
New cards
layers of alimentary canal (superficial to deep)
serosa, muscularis, submucosa, mucosa
6
New cards
serosa--
(visceral peritoneum) membrane that secretes slippery watery fluid; reduces friction as organs contract + move
7
New cards
muscularis-
layer of muscle extending in 2 directions: circular & longitudinal layer
8
New cards
submucosa-
contains glands, nerve fibers, & blood vessels
9
New cards
mucosa-
1. secreting mucus, digestive enzymes, & hormones
2. absorption of nutrients
3. protection from pathogens (lymphatic tissue)
2. absorption of nutrients
3. protection from pathogens (lymphatic tissue)
10
New cards
teeth:
accessory digestive organs, responsible for beginning the mechanical digestion process
11
New cards
types of teeth
incisors (cutting), canines (cuspids; tear & pierce), premolars (bicuspids; crushing), molars (tricuspids; grinding)
12
New cards
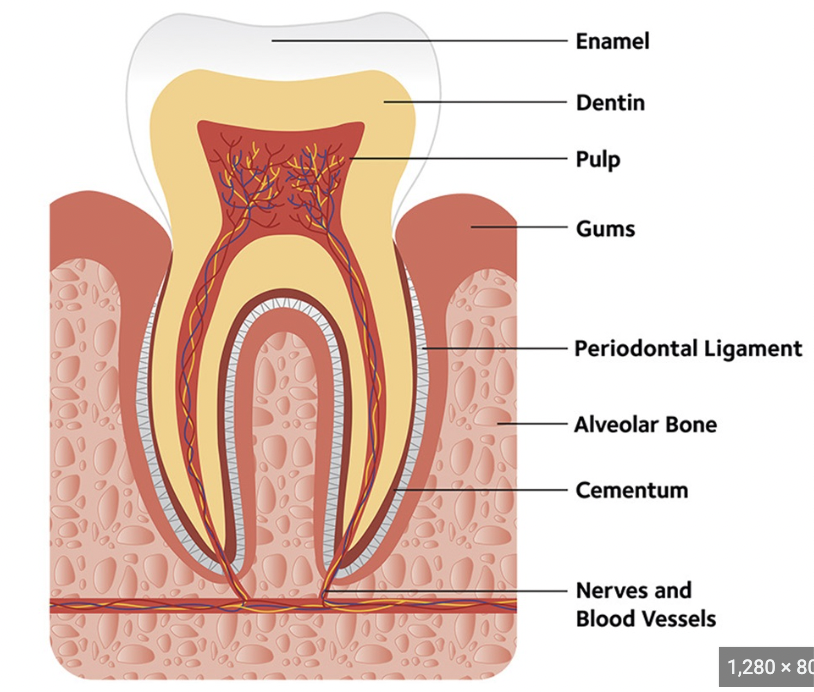
anatomy of a tooth:
enamel (hard, protects tooth), dentin (calcified connective tissue), pulp cavity (has blood vessels + nerves), gingivae/gum (seal arnd tooth), cementum (covers dentin in root)
13
New cards
child vs adult teeth
20 teeth @ toddler, adult has 32; incisors come in first (6-8 months) then canines and molars (teens/early twenties)
14
New cards
saliva
99% water, mucus (lubricates food for swallowing), analyse (breaks down starch), lysozymes (kill bacteria), antibodies (mark foreign invaders)
15
New cards
structures in the mouth:
hard palate (bony roof of mouth), soft palate, uvula (prevents swallowed food from entering nasal cavity), & tongue (helps push food towards esophagus)
16
New cards
deglutition
swallowing; has 2 major phases: buccal and pharyngeal-esophageal phase
17
New cards
buccal phase--
after mastication (chewing) + mixed w/ saliva, food lump \= bolus, forced into pharynx by tongue; consciously-controlled process
18
New cards
pharyngeal-esophageal phase--
epiglottis (thin flap of skin) blocks larynx, and uvula blocks nasal cavity, this causes food to go to esophagus instead of into respiratory system, bolus is propelled down by peristalsis
19
New cards
peristalsis:
waves of muscle contractions; involuntary, caused by parasympathetic nervous system rather than gravity
20
New cards
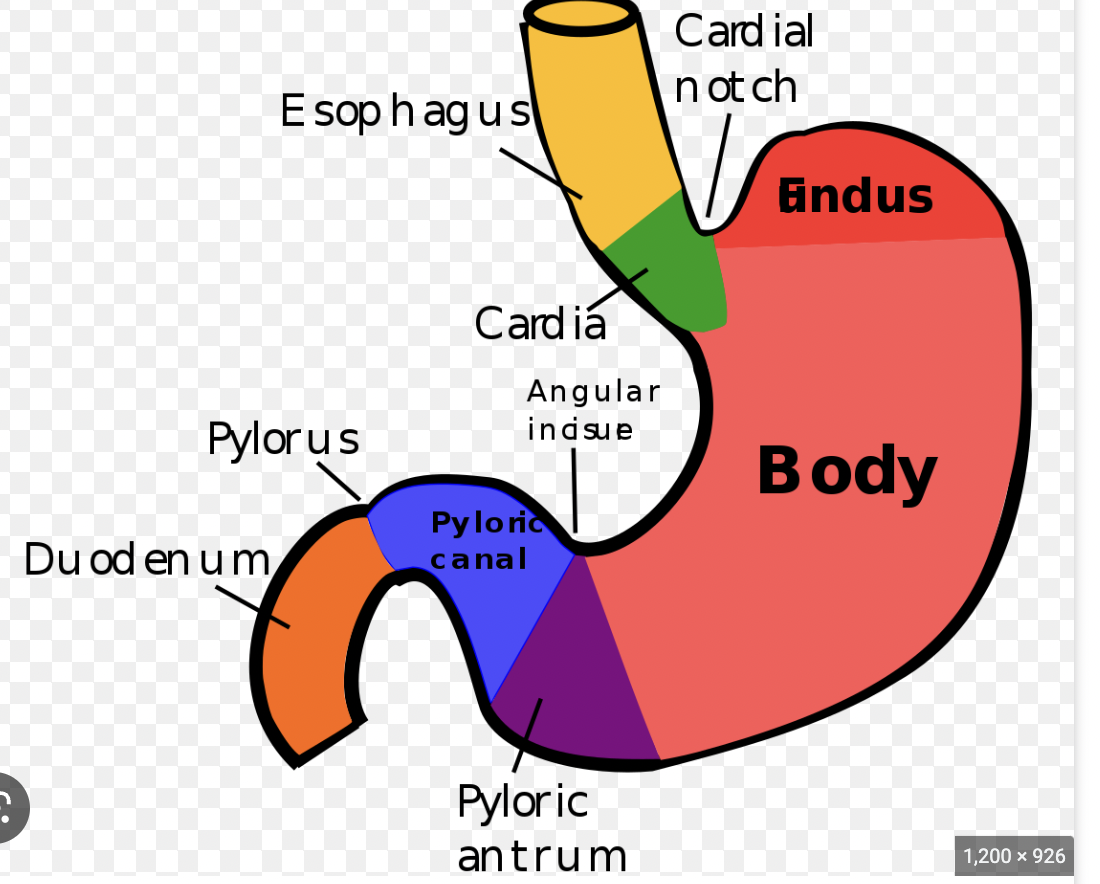
stomach:
muscular sac w/ thick walls, continues process of mechanical + chemical digestion
21
New cards
sphincters:
thick rings of muscle; serve as gatekeepers to allow food to enter & leave at appropriate time
22
New cards
2 sphincters of stomach:
enter cardiac (separates esophagus from stomach) & leave thru pyloric (separates stomach from small intestine)
23
New cards
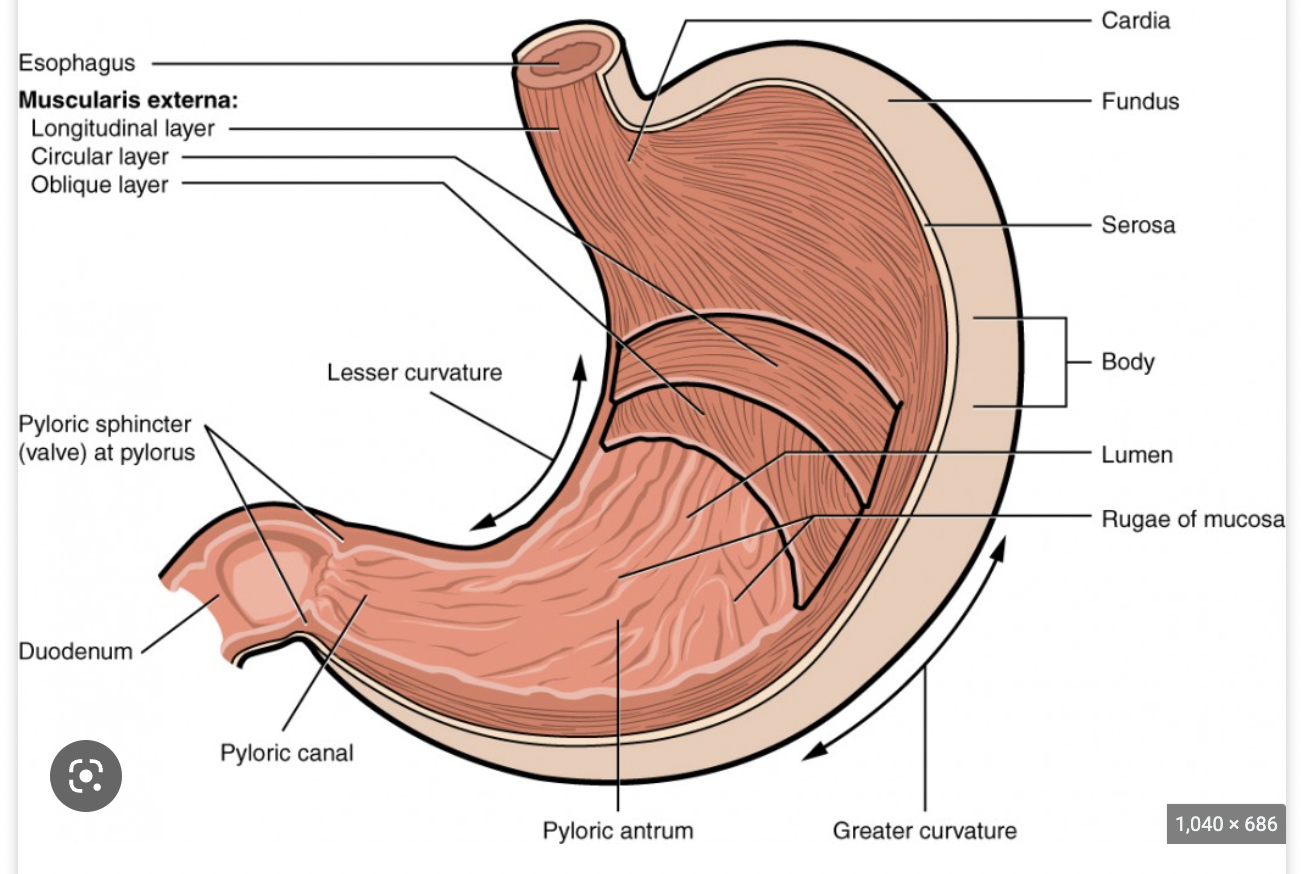
3 layers that follow outer layer of serosa:
longitudinal muscularis, circular muscularis, and oblique muscularis; help churn food (maceration) + propel to small intestine
24
New cards
rugae:
folds/"wrinkles" of mucosa that stretch when stomach is full
25
New cards
specialized gastric and gland cells in mucosa layer:
mucous, chief, and parietal cells (all make up gastric juices)
26
New cards
mucous cells-
secrete mucus to protect stomach lining
27
New cards
chief cells-
secrete pepsinogen (inactive enzyme)
28
New cards
parietal cells-
secrete HCl to kill microbes in food & convert pepsinogen --\> pepsin (digestive enzyme) which breaks down food proteins
29
New cards
chyme:
soupy mixture from squeezing stomach + gastric juices
30
New cards
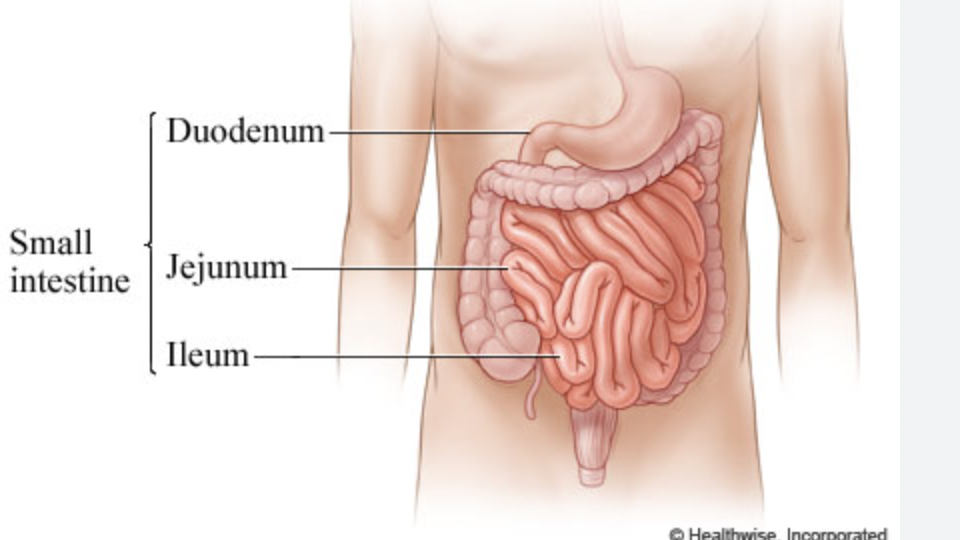
small intestine-
location of most digestion + nutrient absorption, 10ft long in adult, 3 sections \= duodenum, jejunum, ileum (joins intestine at ileocecal sphincter)
31
New cards
villi:
tiny finger-like projections in lining of intestine filled w/ blood vessels; help absorb nutrients efficiently
32
New cards
glands in small intestine
many line the small intestine + secrete digestive hormones
33
New cards
mucus-
alkaline mucus from glands & duodenal glands protects from pathogens
34
New cards
secretin-
inhibits release of gastric juices when chyme is very acidic
35
New cards
colecystokinin (CCK)-
cause gall bladder to release bile
36
New cards
maltase, sucrase, lactase-
breakdown enzymes
37
New cards
peptidase & enterokinase-
break down proteiens
38
New cards
in small intestine, chyme must be
slowed down b/c small int needs time to absorb
39
New cards
circular muscles in the intestinal wall cause
segmentation of the chyme
40
New cards
longitudinal muscles in the intestinal wall cause
peristaltic contractions
41
New cards
large intestine-
food from small int --\> large int, 3 major sections \= cecum, colon (ascending, transverse, descending), & rectum
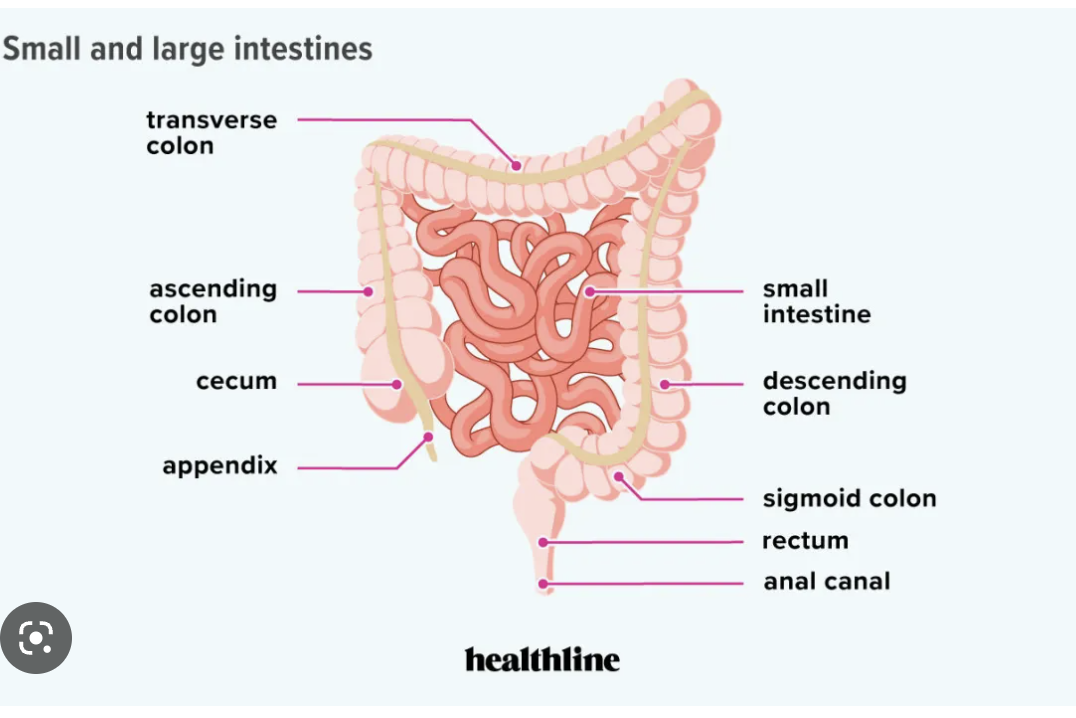
42
New cards
2 major functions of large intestine:
absorption of water back into the body ; removal of waste (feces) thru rectum and anus
43
New cards
bacteria in large int
large amt (abt 3lbs) located here that help produce vitamins B and K (strong doses of antibiotics can disrupt these bacteria & cause vitamin deficiencies)
44
New cards
haustra:
small pouches that give the large intestine its lumpy appearance
45
New cards
haustral contractions:
slow, segmenting movements, last abt 30 min after food moves into large itn
46
New cards
mass movements:
slower & more powerful movements that push waste towards rectum 3-4x a day
47
New cards
rectum collects and stores
undigested waste + bacteria, as it fells pressure is placed on internal anal sphincter causing it to relax, the external anal sphincter needs to be voluntarily relaxed to release built-up feces thru anus
48
New cards
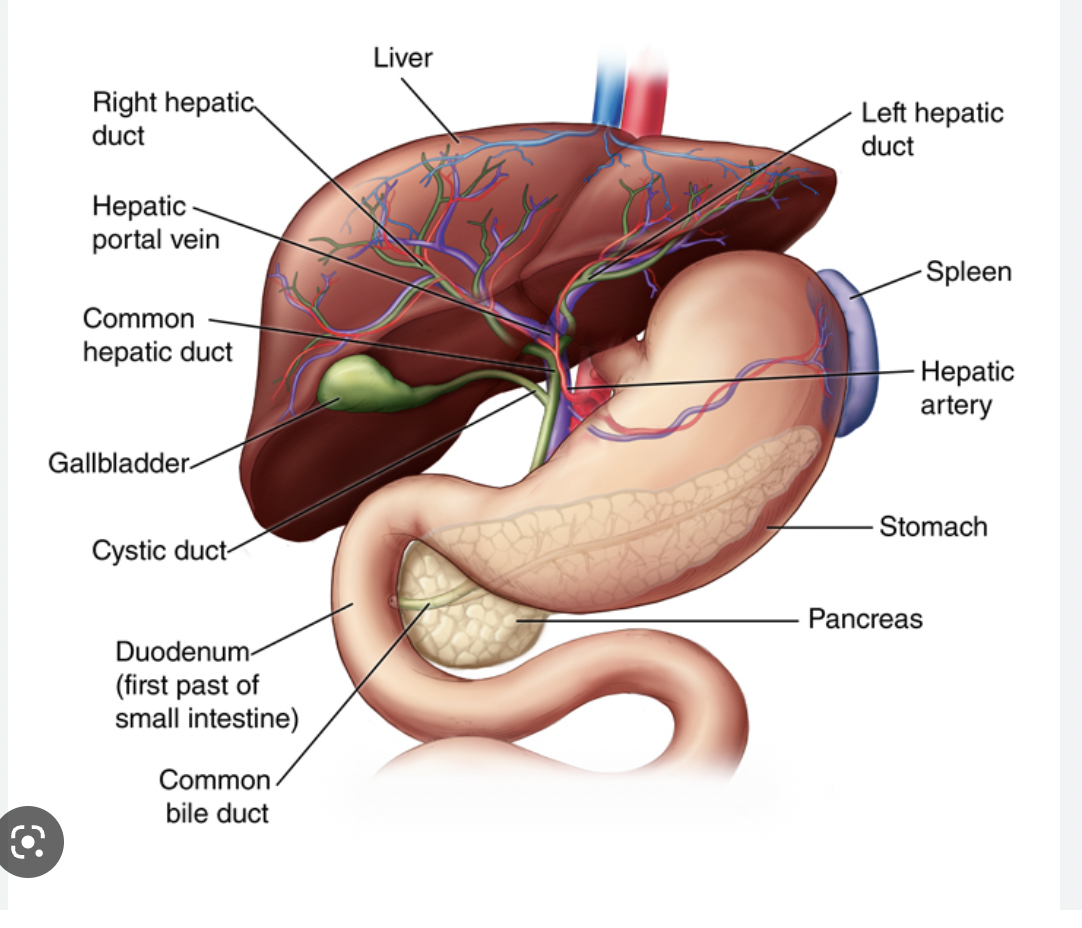
liver-
largest internal organ, 2 major lobes \= L & R, contains hepatic sinusoids (full of blood)
49
New cards
functions of liver cells:
removing bacteria and old RBCs, detoxifying blood from drugs and poisons, storing glycogen and producing fats, manufacturing proteins, storing iron and copper
50
New cards
bile:
greenish fluid responsible for breaking down fat, secreted by liver
51
New cards
gallbladder-
small, green sac attached to liver by bile duct; stores bile b4 sending it to small int to digest fats
52
New cards
gall bladder concentrates bile by
removing water; if too much is removed, gallstones (made of cholesterol crystals) may form [gallbladder may be removed if stones too large/painful]
53
New cards
pancreas-
long, thin gland behind stomach
54
New cards
pancreas functions:
1. secreting digestive enzymes & sodium bicarbonate- a base that neutralizes stomach acid so digestive enzymes are not affected by the lowered pH
2. secreting hormones that regulate blood sugar levels
2. secreting hormones that regulate blood sugar levels
55
New cards
metabolism:
life-sustaining chemical rxns of body; 2 types \= catabolism & anabolism
56
New cards
catabolism:
breaking down of complex molecules while releasing energy/ATP
57
New cards
anabolism:
formation of complex molecules while using energy
58
New cards
nutrients:
substances that provide the body w energy & can be used for growth
59
New cards
4 macronutrients required by body:
carbs, lipids, protiens, water
60
New cards
2 micronutrients:
vitamins & minerals
61
New cards
carbohydrates-
- sugars/glucose; main source of eneergy
- broken down by: salivary amylase; pancreatic amylase; brush border enzyme (epithelial enzymes of small int)
- broken down in: mouth; small int
- process: cellular respiration (glycolysis, citric acid, ETC); excess sugar \= stored as fat or glycogen
- broken down by: salivary amylase; pancreatic amylase; brush border enzyme (epithelial enzymes of small int)
- broken down in: mouth; small int
- process: cellular respiration (glycolysis, citric acid, ETC); excess sugar \= stored as fat or glycogen
62
New cards
lipids-
- fats; secondary source of energy
- broken down by: bile salts; pancreatic lipase
- broken down in: liver; small int
- process: are insoluble so must be emulsified first; broken into acetic acid --\> metabolized into ATP or stored for later use
- broken down by: bile salts; pancreatic lipase
- broken down in: liver; small int
- process: are insoluble so must be emulsified first; broken into acetic acid --\> metabolized into ATP or stored for later use
63
New cards
proteins-
- make up majority of cellular structures; some used as enzymes
- broken down by: pepsin, pancreatic enzymes, brush border enzymes
- broken down in: stomach (in presence of HCl), small int
- process: polypeptide chains broken into individual amino acids, which r actively pumped into cell
- broken down by: pepsin, pancreatic enzymes, brush border enzymes
- broken down in: stomach (in presence of HCl), small int
- process: polypeptide chains broken into individual amino acids, which r actively pumped into cell
64
New cards
water used for:
chemical rxns, dissolving food for digestion, maintaining blood pH lvls, regulating body temp thru sweat
65
New cards
vitamins:
organic molecules needed in small quantities; can be broken down by heat, acid, or air
66
New cards
minerals:
inorganic molecules needed in small quantities (ex. calcium, chlorine, fluorine, iodine, iron, magnesium, phosphorous, potassium, zinc)
67
New cards
order of anatomical structures involved in the process of digestion from ingestion to excretion of waste
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, rectum and anus & sections within
68
New cards
peptic ulcer
sore that develops on lining of esophagus, stomach, or small intestine
69
New cards
constipation
condition where stools are hard, dry, or lumpy, stools are difficult/painful to pass, or feeling that not all stool has passed
70
New cards
dumping syndrome
group of symptoms, like diarrhea, nausea, light-headed/tired after meals caused by rapid gastric emptying
71
New cards
appendicitis
condition where appendix is inflamed and filled with pus causing pain
72
New cards
Cholecystectomy
surgical removal of gallbladder due to gall stones
73
New cards
Cirrhosis
chronic inflammation where liver is severely damaged, becomes hard + fibrous
74
New cards
Indigestion
Group of symptoms like bloating, pain, burning, feeling full after eating + discomfort
75
New cards
Gastroenteritis
vomiting, diarrhea, fever, headaches, gut infection caused by bacterium/virus
76
New cards
Helicobacter pylori
bacterium associated with development of stomach ulcers
77
New cards
Ulcerative colitis
chronic, inflammatory bowel disease where open sores form in colon, colon is inflamed, small intestine rarely affected
78
New cards
Gastroparesis
affects stomach muscles, prevents proper stomach emptying
79
New cards
diarrhea
loose, watery stools
80
New cards
Crohn’s disease
chronic, inflammatory bowel disease of unknown origin, causing diarrhea, severe abdominal pain, fever, chills, nausea, weight loss
81
New cards
Pancreatitis
serious inflammation of the pancreas because of activation of pancreatic enzymes in pancreatic duct, digests pancreatic tissue and the duct
82
New cards
hiatal hernia
structural abnormality in which superior part of stomach protrudes slightly over diaphragm
83
New cards
Celiac Disease
serious sensitivity to gluten, protein in wheat, causes immune system to attack
84
New cards
hemorrhoids
condition of inflammation and enlargement of the rectal veins
85
New cards
cystic fibrosis
inherited disorder causes damage to lungs, digestive system, and other organs in body, affects cells producing mucus, sweat, digestive juices
86
New cards
gastroesophageal reflux disorder
cardioesophageal sphincter fails to close tightly and gastric juice backs up into esophagus, which has little mucus protection.
87
New cards
irritable bowel disease
disorder affecting colon + rectum, causing bouts of constipation and diarrhea, cramping, bloating, excessive gas