Unit 4 - equilibroum
1/187
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
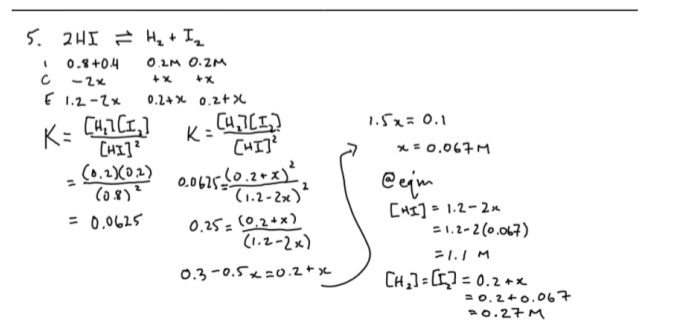
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
188 Terms
What is the difference between static equilibrium and dynamic equilibrium
static equilibrium
Static equilibrium occurs when all forces are balanced and the system is at rest
dynamic equilibrium
Dynamic equilibrium occurs when a system is in motion but the opposing forces are balanced, resulting in constant velocity or continuous but equal rates of forward and reverse reactions
What is chemical equilibrium
the state of a reaction in which all reactants and products have reached constant concentrations in a closed system
WHat are the 3 characteristics of equilibrium
Observable properties do not change with time; constant macroscopic properties
the system is closed and temperature and pressure and kept constant
opposing internal processes proceed at equal rates (the reaction is reversible)
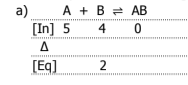



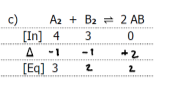
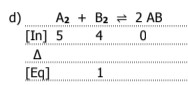


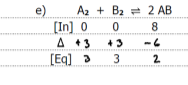

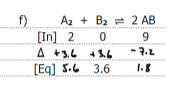
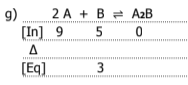
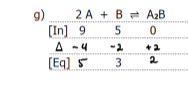
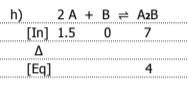
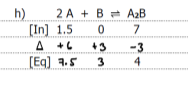
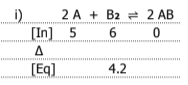
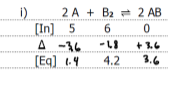



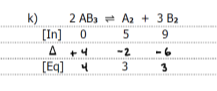





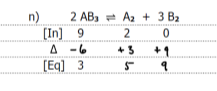

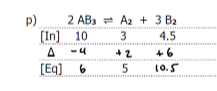
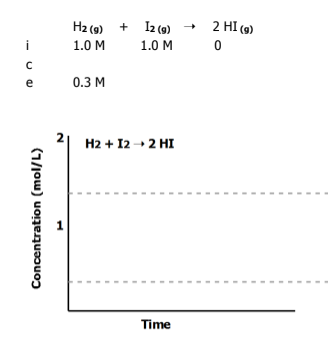
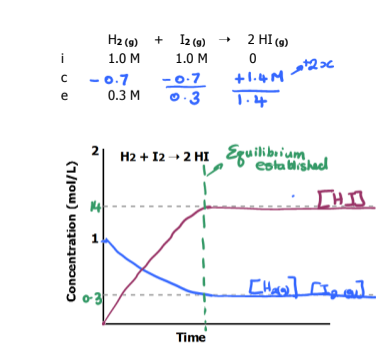
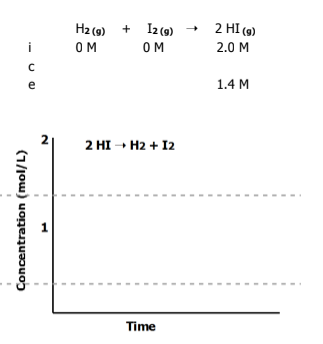
Graph the equilibrium
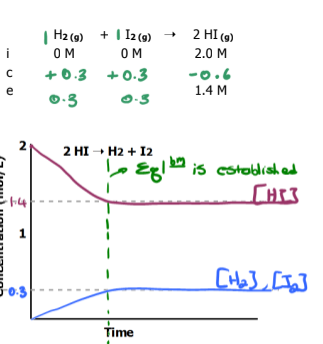
WHat happens if the equilibrium constant, Keq is large? WHat happens if its small?
if Keq is large
ratio of product/reactant is large
the reaction happens to a large extent (more products than reactants at equilibrium)
If Keq is small
ratio of products/reactant is small
the reaction happens to a small extent and there are more reactants than product at equilibrium
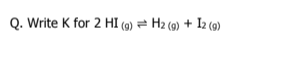
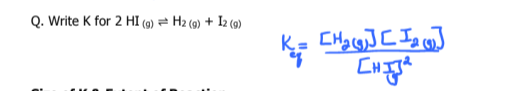
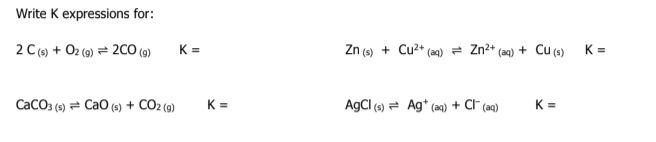
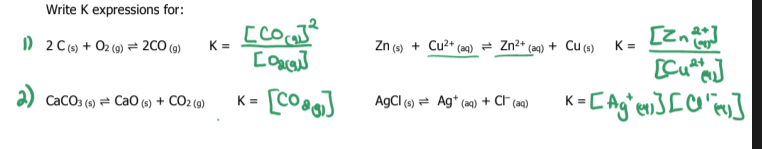


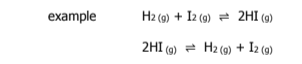
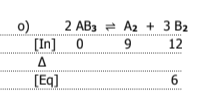
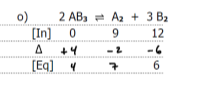
write k and k1 for the following

What does Le Chatelier’s Principle state
when a change is imposed on a system in equilibrium, the system will shift in the direction which counteracts the imposed change





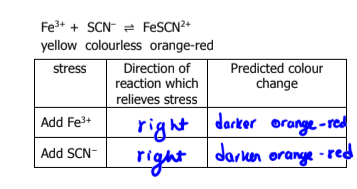
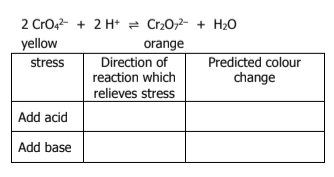
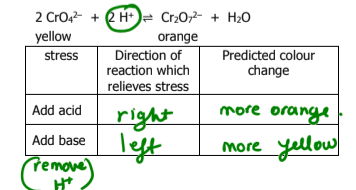
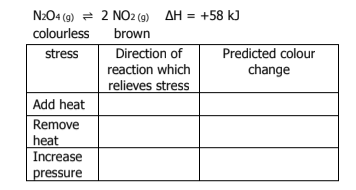
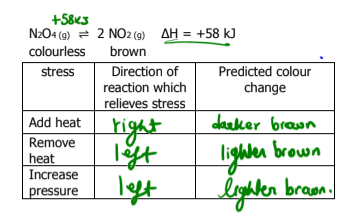
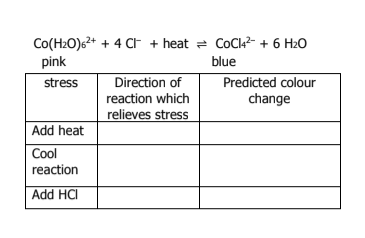
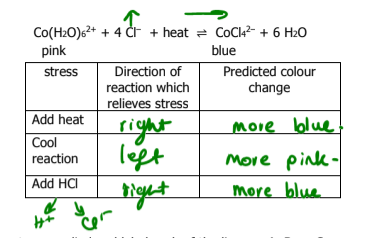
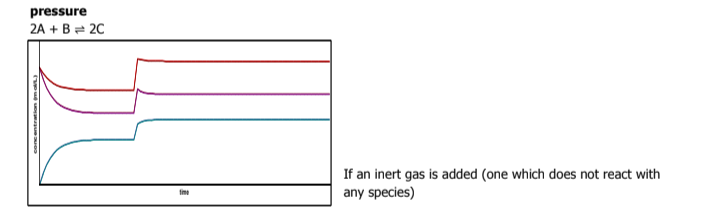
What happens if an inert gas is added to a reaction? What way does the direction go toward
nothing
if an inert gas is added, it does not react with anything
What happens when a catalyst is added
nothing happens it just speeds up the reaction on both sides
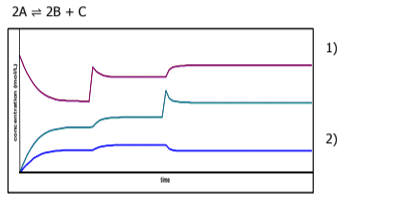
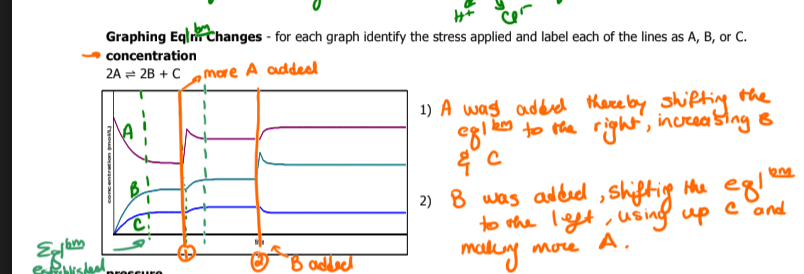
Identify A B and C and describe what's happening in the graph
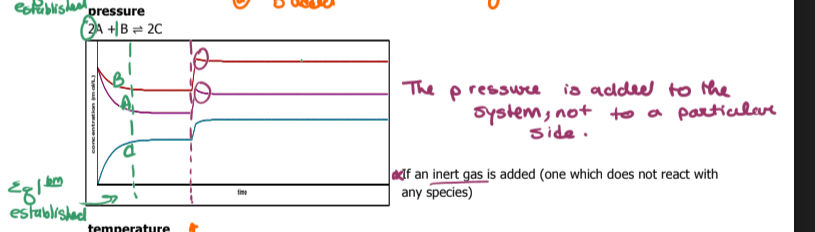
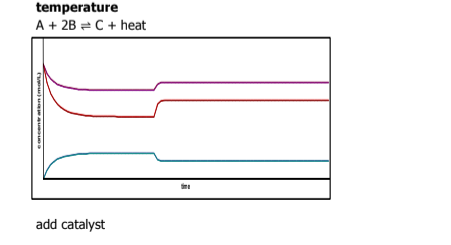
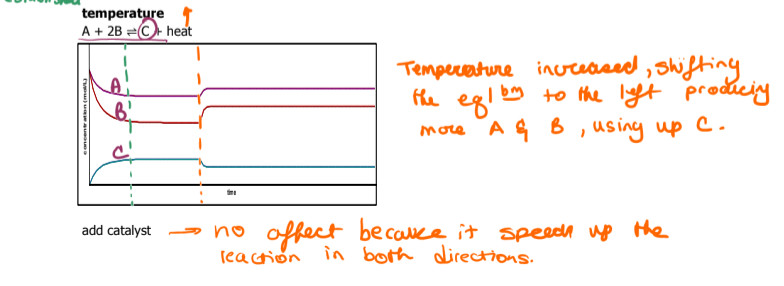


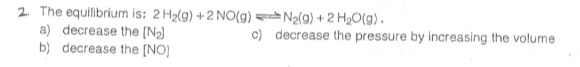
Use le chatlier principle to describe what's appening
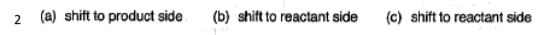
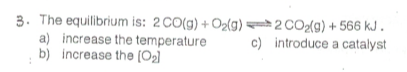
Use le chatlier principle to describe what's appening


Use le chatlier principle to describe what's appening



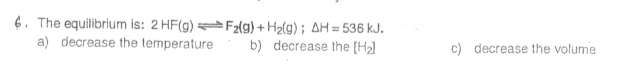
describe the effect on the concentration of the bold substance by the following changes. Write INC for increase, DEC for decrease, and NC for no change


describe the effect on the concentration of the bold substance by the following changes. Write INC for increase, DEC for decrease, and NC for no change
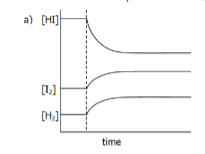
Interpret the following graph in terms of the changes which musth ave been imposed on the equilibrium
The equilibrium us:
H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g) + 52 kJ

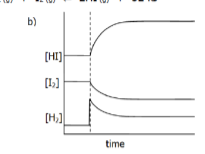
Interpret the following graph in terms of the changes which musth ave been imposed on the equilibrium
The equilibrium us:
H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g) + 52 kJ

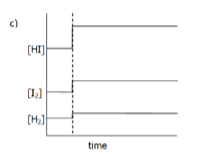
Interpret the following graph in terms of the changes which musth ave been imposed on the equilibrium
The equilibrium us:
H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g) + 52 kJ

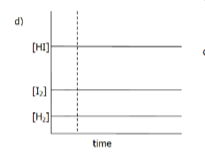
Interpret the following graph in terms of the changes which musth ave been imposed on the equilibrium
The equilibrium us:
H2(g) + I2(g) → 2HI(g) + 52 kJ





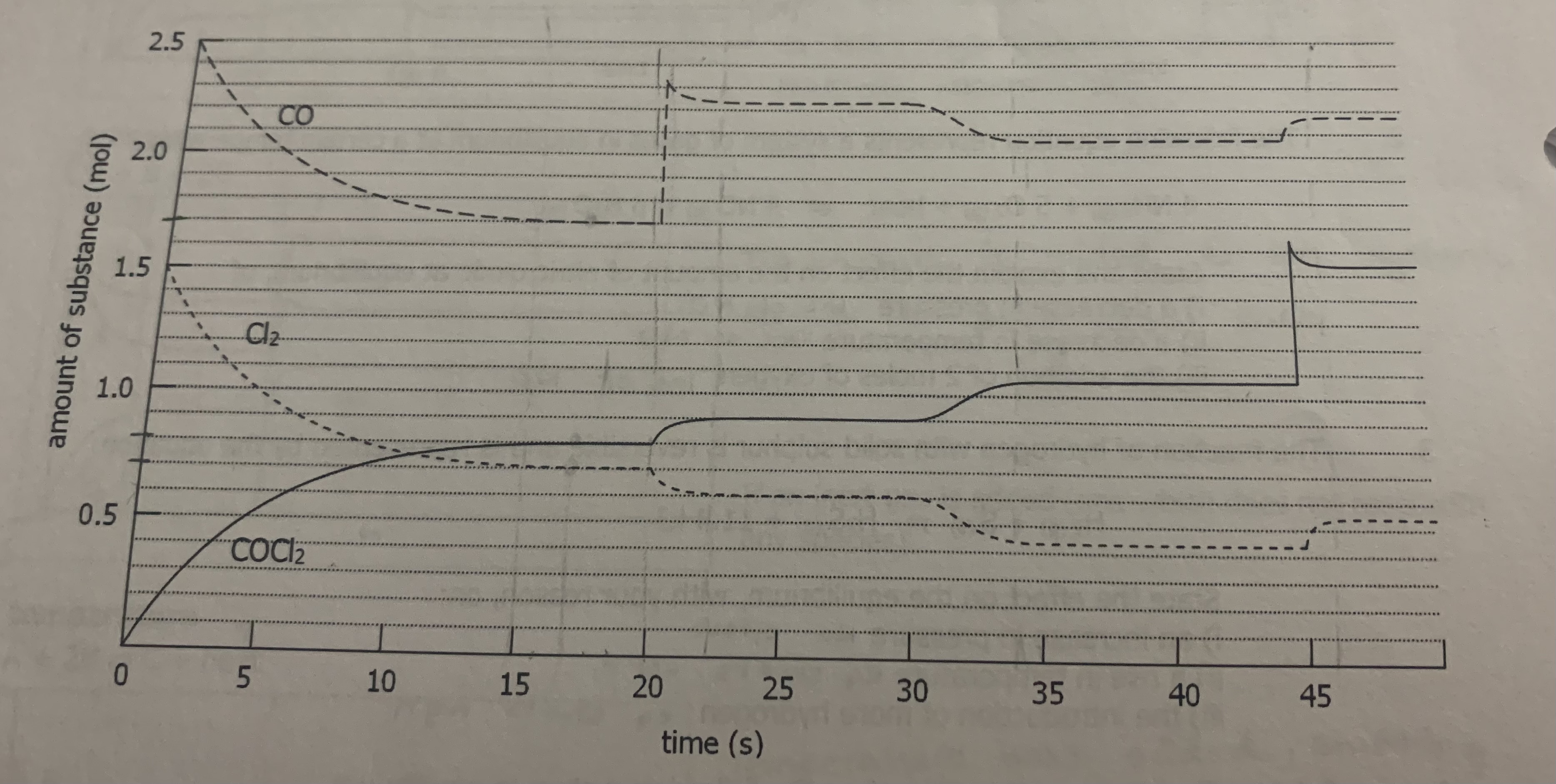
The graph below shows the number of moles of all three species of the system plotted against time under a given set of conditions
CO(g) + Cl2(g) → COCl2(g)
a) How much time was required for the system to reach equilibrium
b) Approximate the value of K using the concentration at t = 17s
c) Explain the changes 20 seconds after the initiation of the reaction
d) What change in conditions might have been imposed on the system 30 seconds after the initiation of the reaction?
e) are any events taking place between the interval of 15s and 20s? Explain.
f) what changes may have taken place at t = 45s
g) What differences would you have noted if a catalyst had been present during the entire course of this reaction?
h) List the changes you might impose on this system if you wanted to produce a maximum amount of COCl2?
i) How could you account for the differences in the value of K at different points on the graph?
h) increase the concentration of reactants (Co and Cl2)
increase the pressure
i) change in temperature
The equation represents a gaseous system at equilibrium
2SO2(g) + O2(g) → 2SO3(g) + heat
Indicate the direction in which the equilibrium shifts when these changes are made. Briefly justify your answer
a) The concentration of SO2 is increased
b) The partial pressure of SO3 is decreased
c) The temperature of the system is decreased
d) The volume of the container is increased
e) Helium gas is added at constant volume so that the total pressure is increased
f) Helium gas is added. but the total pressure is kept constant
g) a catalyst is added
a) right
b) right
c) right
d) left
e) no shift
f) left (inert gas at constant pressure affects equilibrium while intert gas at constant volume doesn't)
increases volume
decreases pressure
g) no shift
The equation represents a gaseous system at equilibrium
heat + 2H2O(g) → 2H2(g) + O2(g)
Indicate the direction in which the equilibrium shifts when these changes are made. Briefly justify your answer
a) The concentration of H2 is increased
b) The partial pressure H2O is increased
c) The concentration of O2 is decreased
d) The temperature is increased
e) The volume of the container is decreased
f) Helium gas is added at constant volume so that the total pressure is increased
g) Helium gas is added, but the total pressure is kept constant
h) A catalyst is added



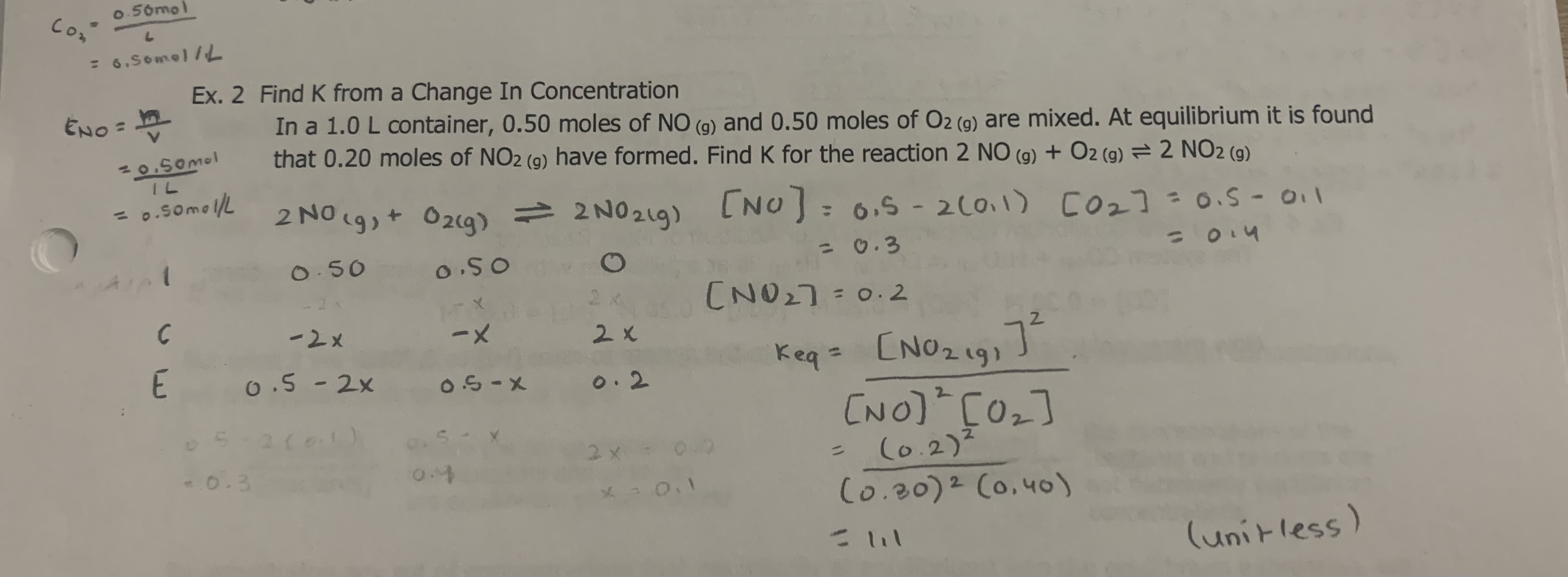





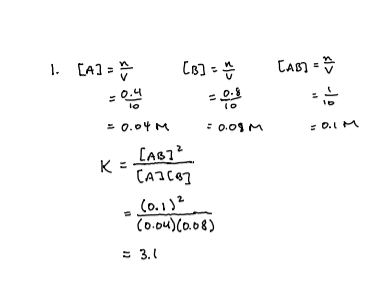

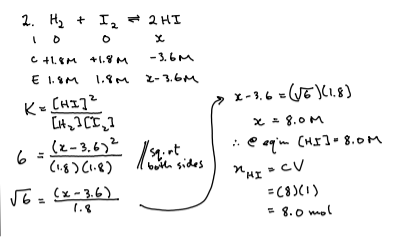

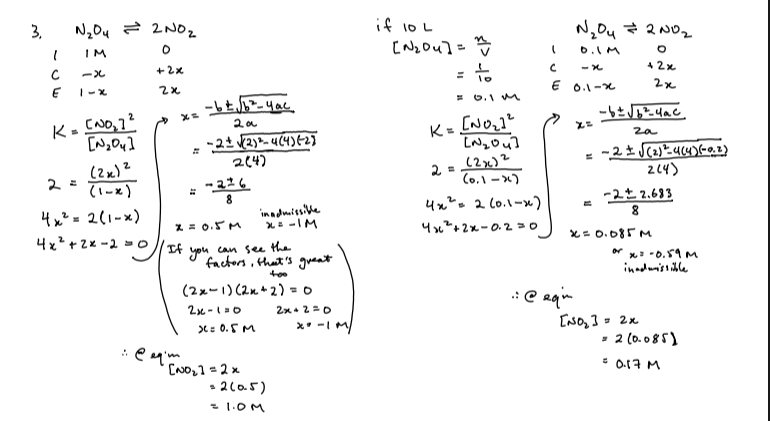



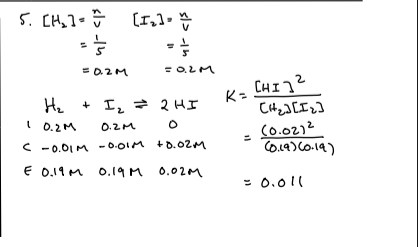



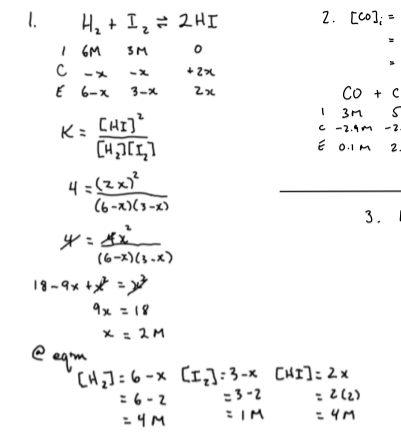
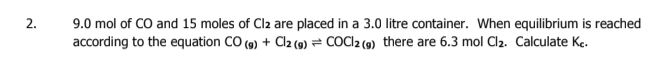
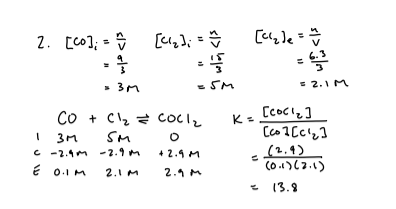
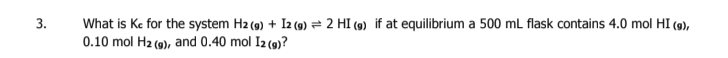
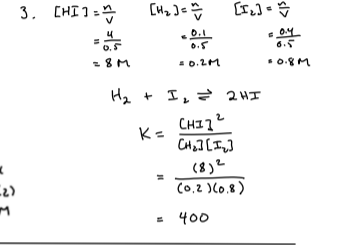

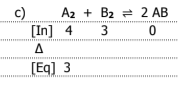
3

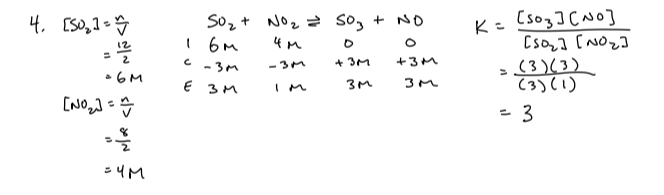
















A2 = 1..0M
B2 = 4.0M
AB = 2.8 × 10-3 M










Who made the equilibrium law
Guldberg and Wage
Norwegian chemists
What is the difference between the Arrhenius acid-base theory and the bronsted-lowry acid-base theory
The Arrhenius acid-base theory states that an acid is a substance which produced H+ when dissolved in water and a base is a substance that produces OH- when dissolved in water
The bronsted-lowry acid-base theory states that acids are hydrogen ion (proton) donors and bases are hydrogen ion (proton) acceptors
B-L is more accurate
Give a definition of Amphiprotic. Give a common example
amphiprotic is a substance that can act as a substance or a base
an example is water
what is a conjugate base and conjugate acid
A conjugate base is a B-L acid that loses a proton
A conjugate acid is a B-L base that gains a proton
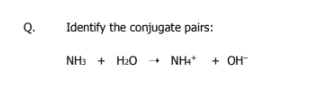
NH3 base → NH4+ conjugate acid
H2O acid → OH- conjugate base

NH3
HPO4(2-)
CO3(2-)
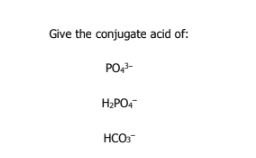
HPO4(2-)
H3PO4
H2CO3
What are strong acids and weak acids
Whats the difference between them
strong acids react with water and ionize to produce a high concentration of hydronium (H3O+)
weak acids react with water and ionize to produce a low concentration of hydronium ions
all organic acids are weak acids
While strong acids ionize to a large extent, with equilibrium favouring the product side, weak acids ionize to a small extent, favouring the reactant side
What are strong bases and weak bases
What is the difference between them
strong bases dissociate in water to produce a high concentration of hydroxide ions
weak bases- dissociate in water to produce a low concentration of hydroxide ions
While strong bases dissociate completely, weak bases- ionize to a small extent, with equilibrium favouring the reactant side
What side does the equilibirum favor when it comes to weak acids and weak bases. Why?
the reactant side, as weak acids and bases only ionize to a small extent to produce little products and keep more reactants
What side does equilibrium favor when it comes to strong acids and strong bases. Why?
equilibrium favors the product side as strong acids and bases ionizes to a large extent so that more product is produced while little reactants remain
What is the general rule to tell if a base or an acid is strong or weak
if k is »» 1, the acid or base is strong
if k is ««« 1, the acid or base is weak
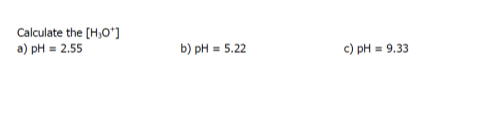
a) 2.8 × 10-3M
b) 6.0 × 10-6M
c) 4.7 × 10-10M


do h
d) 0.60
e) 2.00
f) 1.08
g) 12.11
h) 12.04
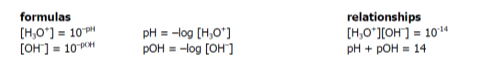
What is Kw of water
10-14
What is the conjugate relationship
Kw = Ka x Kb
What is wrong with the Arrhenius theory
only considered aqueous systems
could not explain why some molecular substances that lacked a hydroxide ion were basic
also the theory suggested some ionic compounds (salts) that were made from neutralization reactions were neutral but they aren't